 PDF(9)
PDF(9)
 PDF(8)
PDF(8)
The deep interior of the Earth is under extreme high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. Its material composition, phase transition behavior, and physical properties are crucial for understanding the Earth’s internal structure, dynamic processes, and evolution. Traditional experimental methods face challenges in maintaining thermodynamic states and diagnosing physical quantities under such extreme conditions. While first-principles calculations offer quantum-level precision, their computational efficiency limits their direct application to simulating deep-Earth minerals across large spatiotemporal scales. Machine learning methods present new opportunities. By constructing high-precision, efficient machine learning potentials based on first-principles datasets, machine learning methods significantly extend the spatiotemporal scale of first-principles simulations, which provide revolutionary tools for studying the physical states, phase transitions, elasticity, and transport properties of deep-Earth minerals. This paper systematically reviews the progress of machine learning applications in studying major deep-Earth minerals, including those in the upper mantle, transition zone, lower mantle, subduction zone components, and core materials, and summarizes the representative achievements of machine learning methods in revealing phase transitions, thermal conductivity, diffusion, melting, and elastic properties, while also discussing current limitations and future research directions.
With the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies and hardware capabilities, AI has gradually become a revolutionary tool driving transformative changes across multiple scientific research domains. In the field of materials science, machine learning methods are significant in high-throughput materials design and property prediction. Over the past decade, machine learning-based approaches for constructing interatomic potentials have been widely applied in the study of material properties, and are providing crucial support for the theoretical design of novel materials and in-depth understanding of their underlying microscopic mechanisms. This article reviews the development of machine learning potentials, and introduces their fundamental workflows. The principles of mainstream methods and their applications in materials property research are outlined. Moreover, recent progress in emerging universal potential models is briefly discussed, then concludes with an analysis of current challenges and future research directions.
This study systematically investigates the structural phase transition mechanisms of silicon dioxide under high pressure by using the high-dimensional neural network potential model combined with the stochastic surface walking algorithm. First, a global potential energy surface of quartz, coesite, stishovite, and amorphous states was constructed, and the thermodynamic phase diagram reveals the thermodynamic stability advantage of stishovite in high-pressure regions. Further analysis demonstrated that the energy barrier for the quartz-to-stishovite transition path shows a significant decrease under high pressure, which exhibits strong kinetic feasibility; while for the coesite-to-stishovite pathway, it follows a single transition state mechanism and the energy barrier displays a slightly increase under high pressure. Regarding the amorphization transition, the low symmetry structure group plays a key role in the high-pressure amorphization of quartz based on sampling and identification, and the “short-range order−middle range-disorder−topological order” structure was unveiled as a defining characteristic of the amorphous state. Notably, we did not observe effective quartz-coesite transition path during the study and further confirmed that the advantage of kinetic dynamics in the amorphization transition inhibits this transformation pathway, revealing the origin of the absence of the quartz-coesite transition. This work systematically explores the mechanisms of crystalline and amorphous phase transitions in silicon dioxide under high pressure and provides theoretical foundations and methodological paradigms for high-pressure simulation studies of complex oxides.
The ubiquitous presence of water, from Earth and planetary bodies to interstellar space, renders its phase behavior across an extensive thermodynamic range fundamental to understanding key scientific phenomena such as biochemical reactions, climate dynamics, and planetary evolution. Nevertheless, although liquid water exhibits distinct anomalous behaviors under extreme pressure, research has been hampered by experimental limitations and computational complexity, resulting in scarce atomic-scale data and hindered understanding of its microscopic mechanisms. To address this, our study employed a deep learning interaction model trained on high-precision
The density of the Earth’s inner core is lower than that of pure iron, indicating the presence of light elements. Among the candidate elements, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and silicon are considered the most likely. Viscosity is a key physical property controlling the dynamics and evolutionary history of the inner core, and it has significant implications for the origin of seismic anisotropy. Previous studies have investigated the viscosity of pure iron in its hexagonal close-packed (HCP) and body-centered cubic (BCC) phases under inner-core conditions through computational simulations. However, the influence of light elements on the viscosity of the inner core remains insufficiently constrained. In this study, we constructed a neural network potential (NNP) for Fe-S alloy under inner-core conditions and employed it to perform large-scale molecular dynamics simulations. We systematically examined the impact of vacancy concentrations as low as 0.01% on the ionic transport properties of Fe-S alloy. Based on the self-diffusion coefficients of Fe in the lattice, we further explored the creep mechanisms and viscosity of Fe-S alloy under core conditions. Our results indicate that dislocation creep dominates the rheological behavior, yielding viscosities of 1×1014–2×1016 Pa·s, consistent with constraints from free-core nutation and seismic observations.
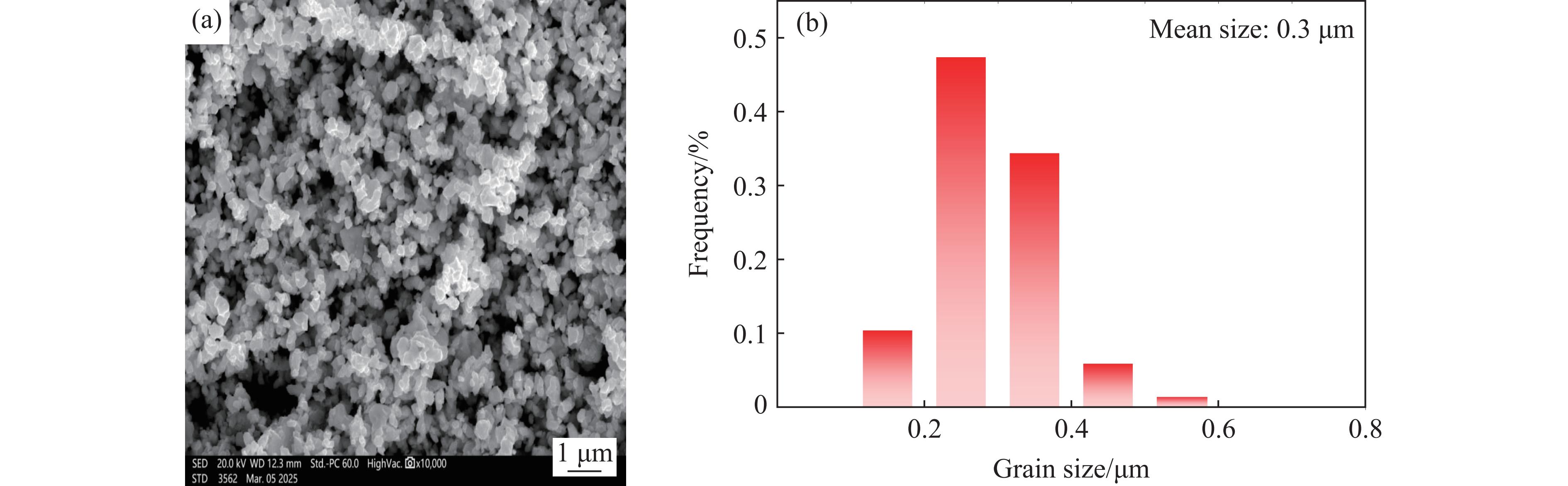
Lead is a low-melting-point metal with a complex temperature-pressure phase diagram. Alloying with tin further reduces its melting temperature, making lead-tin alloys an important model material for studying dynamic mechanical responses and failure behavior. However, experimental characterization of atomic-scale dynamic failure mechanisms in PbSn alloys remains challenging due to current technical limitations. Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics (NEMD) simulations can track atom trajectories and reveal key dynamic processes under dynamic loading-unloading. It thus serves as a critical alternative tool. Yet, the reliability of molecular dynamics relies on the accuracy of interatomic potentials, and currently, no high-accuracy potential exists for PbSn alloys under dynamic conditions. In this work, we develop a machine-learning interatomic potential (DP-PbSn) for PbSn alloys using a concurrent learning scheme. This potential achieves first-principles accuracy across a wide thermodynamic range (0–100 GPa, 0–
Metallic tin is a focal point in high-pressure physics research and a critical material of strategic importance in defense-related technologies. Due to the rich physical phases of tin, it is crucial to study the multiphase equation of state and phase boundaries of tin, whether in basic research or industrial applications. This work systematically investigates the high-temperature and high-pressure multiphase equation of state (EOS), phase boundaries, elastic modulus, sound velocities, and Hugoniot curves of tin using density functional theory (DFT) combined with the mean-field potential (MFP) method. The results not only provide the multiphase EOS of tin under extreme conditions but also demonstrate good agreement with experimental data for the
By employing the first-principles calculations and the structure prediction method, which are based on density functional theory and particle swarm optimization algorithm respectively, this work conducted a structural search of SrB2C2 in the pressure range of 0−350 GPa, and successfully determined the structure of tetragonal phase tI20-SrB2C2 at ambient pressure and orthorhombic phase oF40-SrB2C2 at high pressures. Based on the enthalpy difference curve of SrB2C2, the phase transition pressure was determined to be 44.7 GPa. Moreover, the stability and the possibility of experimental synthesis of tI20-SrB2C2 and oF40-SrB2C2 at the corresponding pressure were verified by calculating the phonon spectrum, elastic constants and formation enthalpy. In addition, the tI20-SrB2C2 has higher degree of mechanical anisotropy than oF40-SrB2C2, which can be seen from the Young’s modulus and shear modulus as a function of orientations. It can be ascribed to the fact that the sp2-hybridized boron-carbon bonds form the layered structure of tI20-SrB2C2, while the boron-carbon bonds of oF40-SrB2C2 are mainly sp3-hybridized covalent bonds, forming a more stable three-dimensional tetrahedral network structure. The electronic structure calculations show that SrB2C2 is an indirect band gap semiconductor, and the calculated electronic localization function reveals that the boron-carbon bonds in tI20-SrB2C2 and oF40-SrB2C2 are sp2 and sp3 covalent bonds, respectively.
Accurate pressure measurement in static high-pressure experiments relies on the equation of state (EOS) of standard materials, where uncertainties in EOS parameters can significantly affect the accuracy of pressure predictions. This study focuses on magnesium oxide (MgO, B1 phase) and rhenium (Re, hexagonal close packed phase), employing Bayesian statistical methods and Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation techniques to systematically quantify the uncertainty in pressure prediction during diamond anvil cell (DAC) experiments. By constructing a Bayesian framework with uniform prior distributions and normal likelihood functions, and integrating multiple sets of experimental data for parameter calibration, the results demonstrate that the Bayesian statistical approach successfully quantifies the posterior distribution of EOS parameters, revealing strong correlations between them, e.g., a negative correlation between Grüneisen parameter and initial volume for MgO, and a positive correlation between bulk modulus and Grüneisen parameter for Re. The uncertainty in pressure predictions for both MgO and Re increases significantly at higher pressures; for Re, this uncertainty also rises markedly with increasing temperature, whereas no clear trend is observed for MgO. This study provides pressure benchmarks with quantified uncertainties, contributing to improved accuracy in high-pressure experimental measurements. It holds significant reference value for ensuring the reliability of experimental data in materials science and geophysical research.
Login in
NewsMore
- 2025 Symposium on Engineering Structure Safety and Protection (First Announcement)
- The 22nd Chinese Conference on High Pressure Science (Third Announcement)
- Notification for the Selection of the Fifth High-Pressure Science Outstanding Young Scholars
- Results of the 2024 Excellent Reviewer Selection for the Journal of High Pressure Physics
- Call for Papers for the Special Issue on Machine Learning and High-Throughput Research of Material Properties under Dynamic Loading
- Notice for the 2024 Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Large Pressure Machine Experimental Technology Training Course
- Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics will change from a bimonthly journal to a monthly journal starting in January 2025









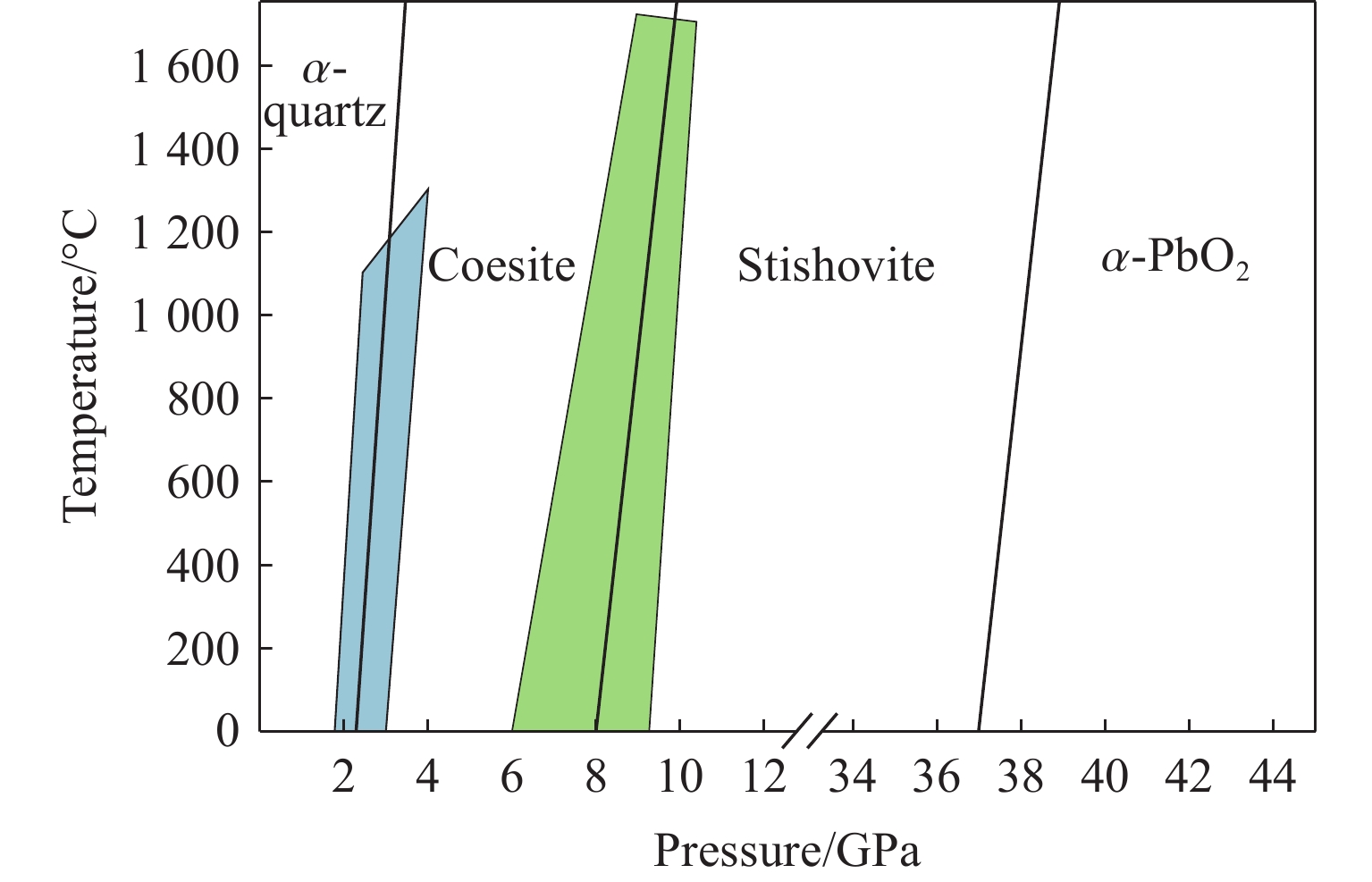
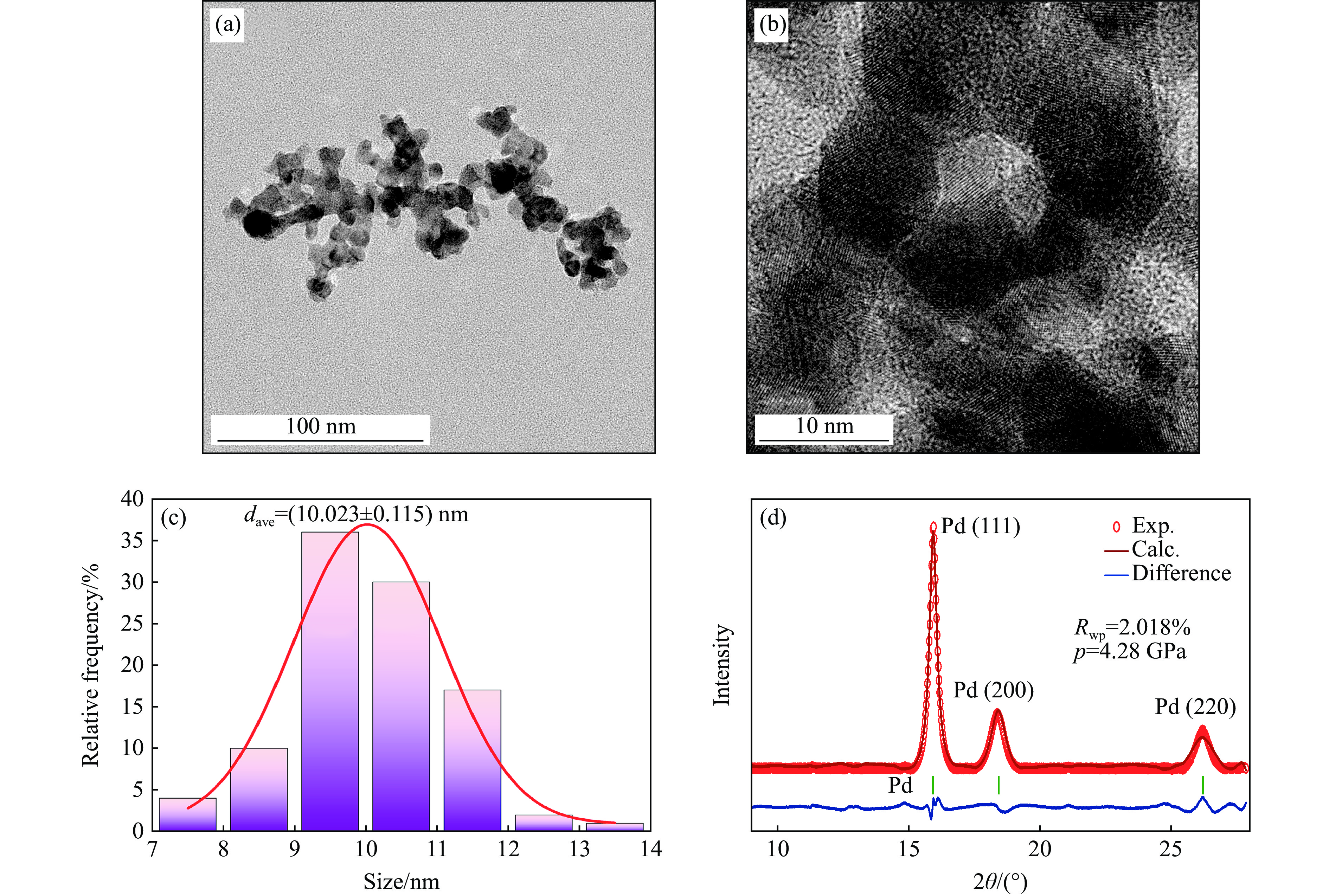
 HTML
HTML









