Research on Electromagnetic Radiation Generated During Explosion Based on Wavelet Transform
-
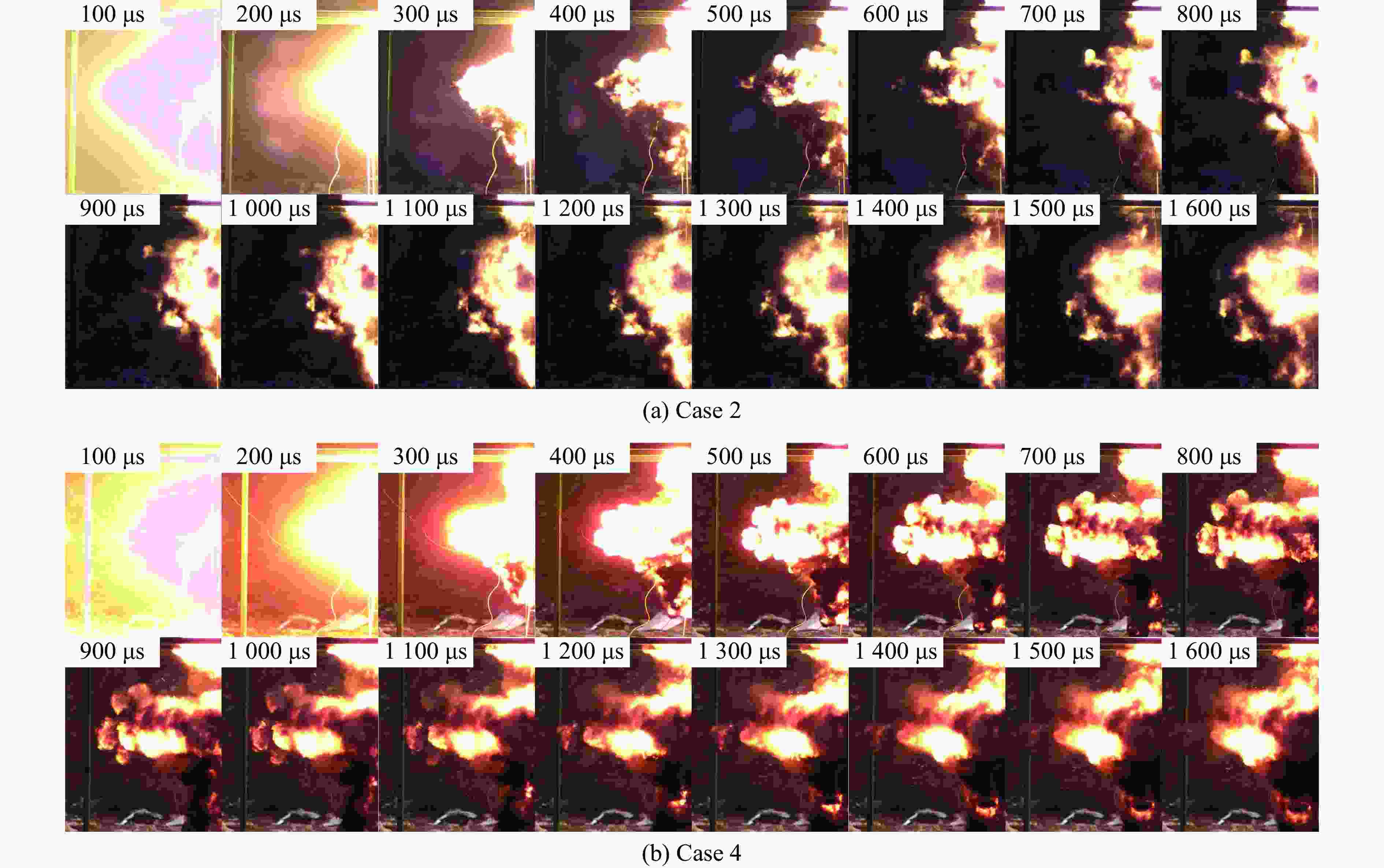
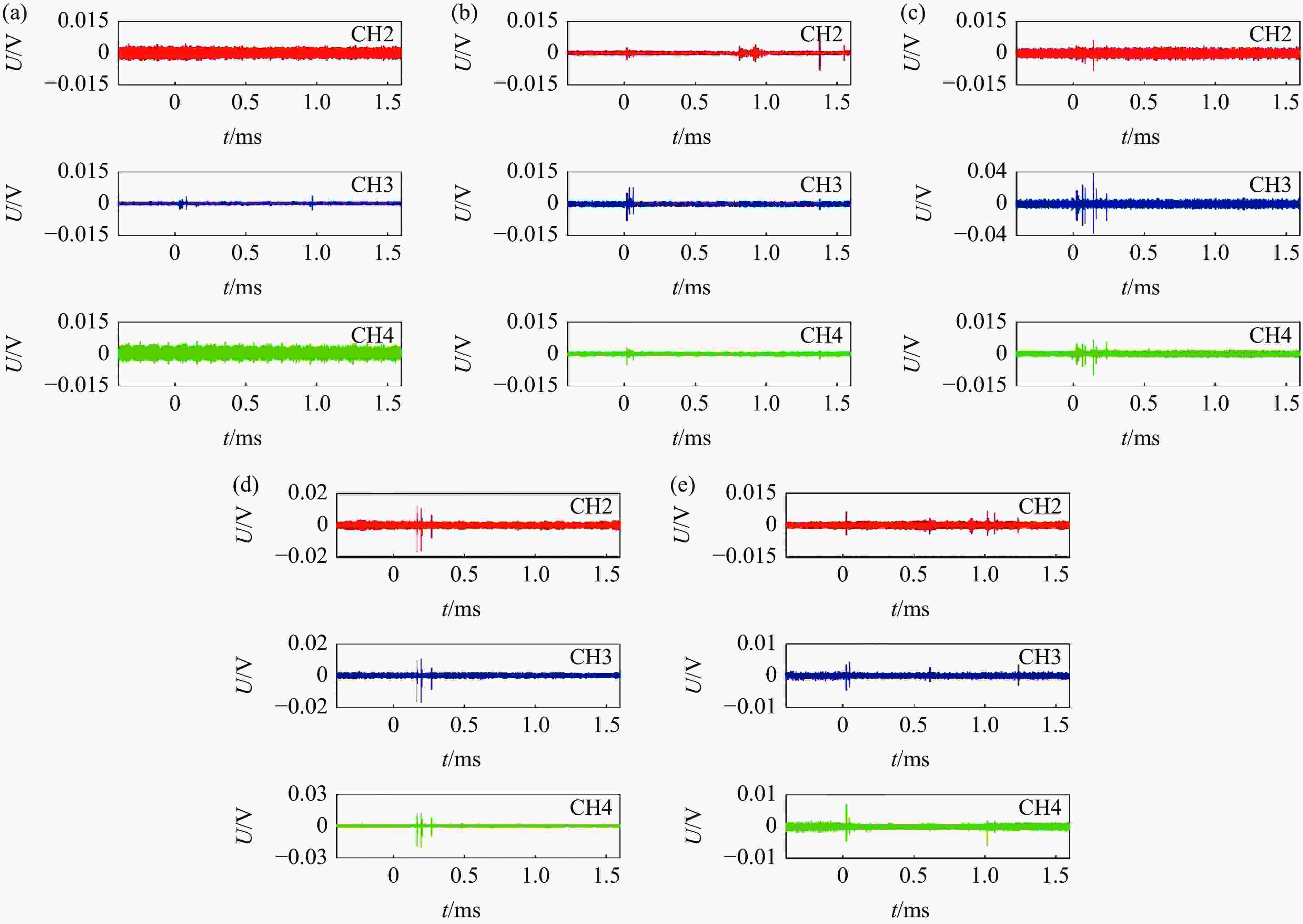
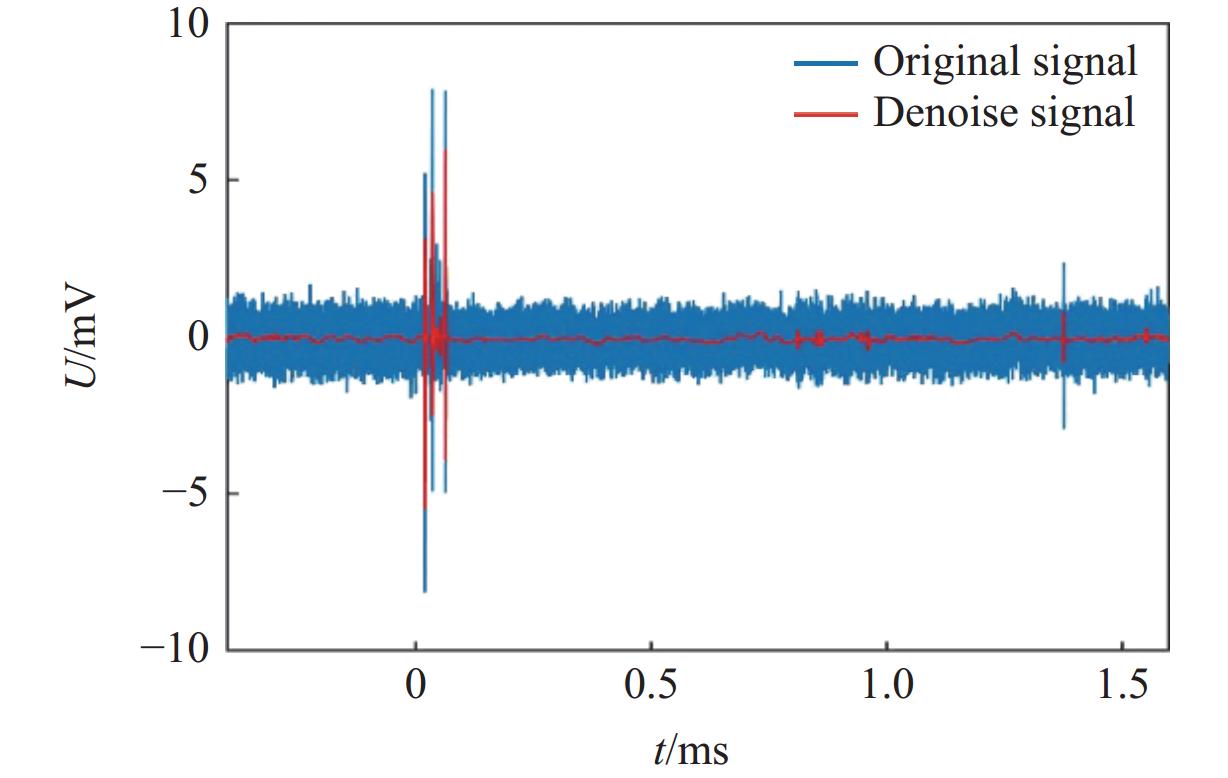
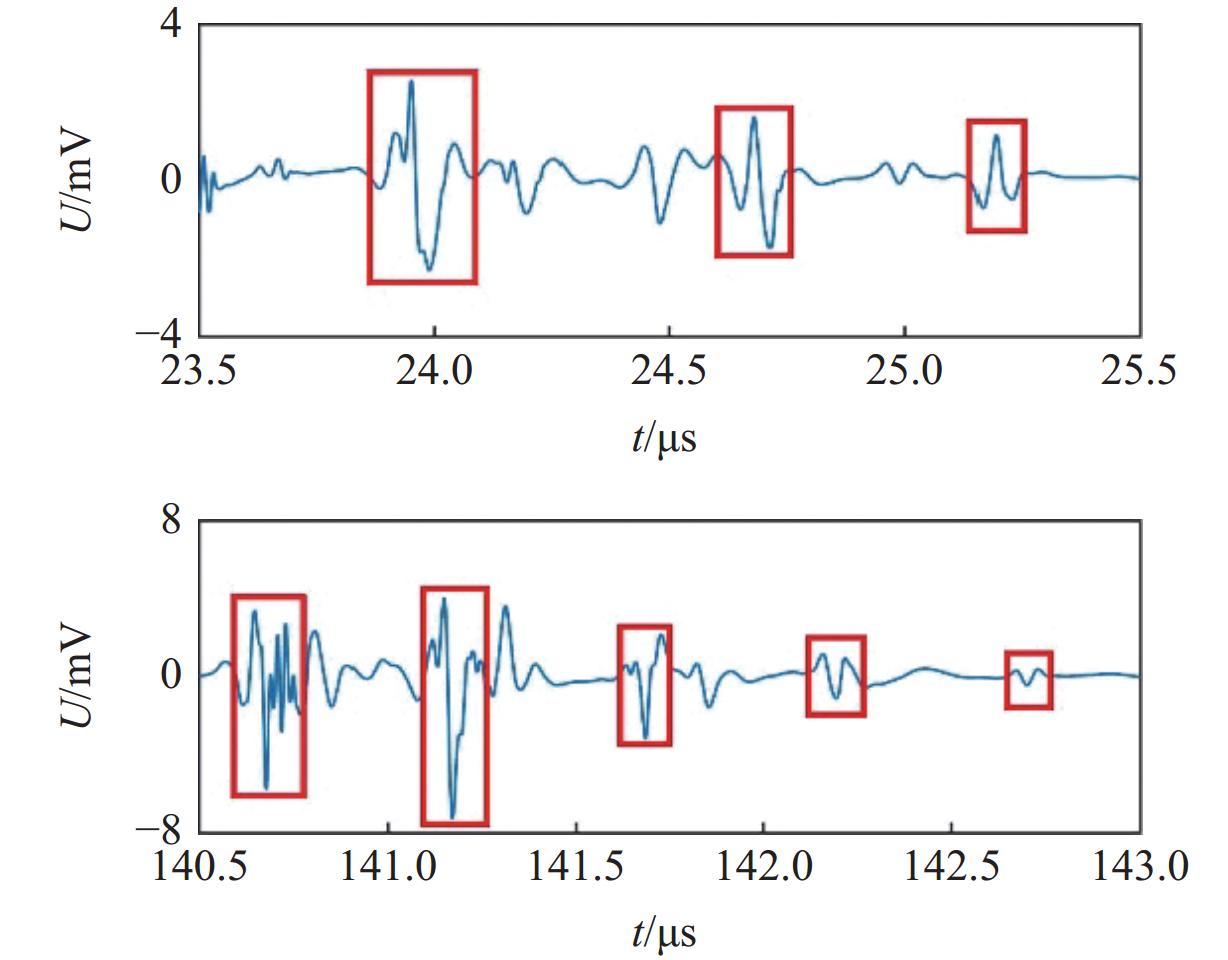
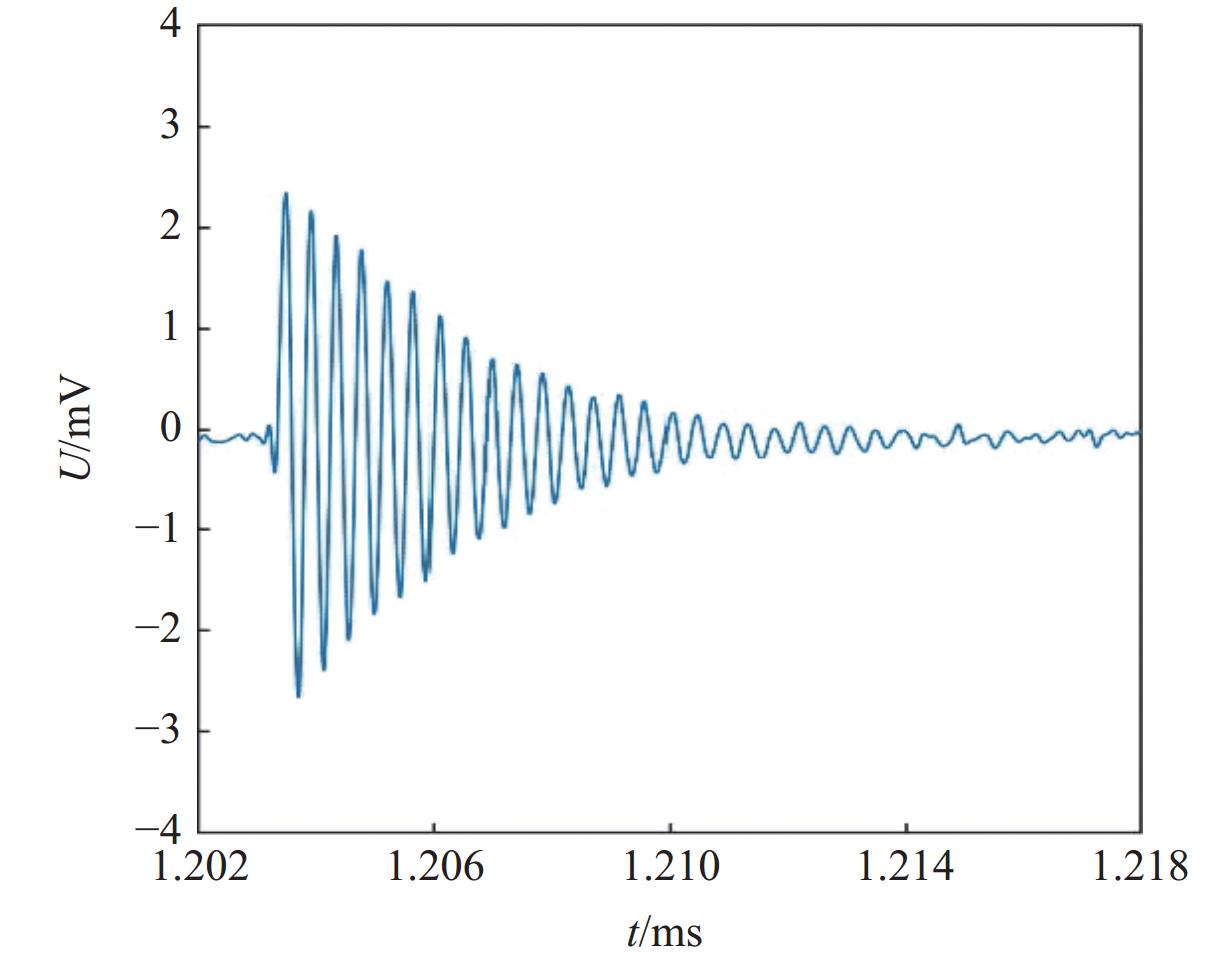
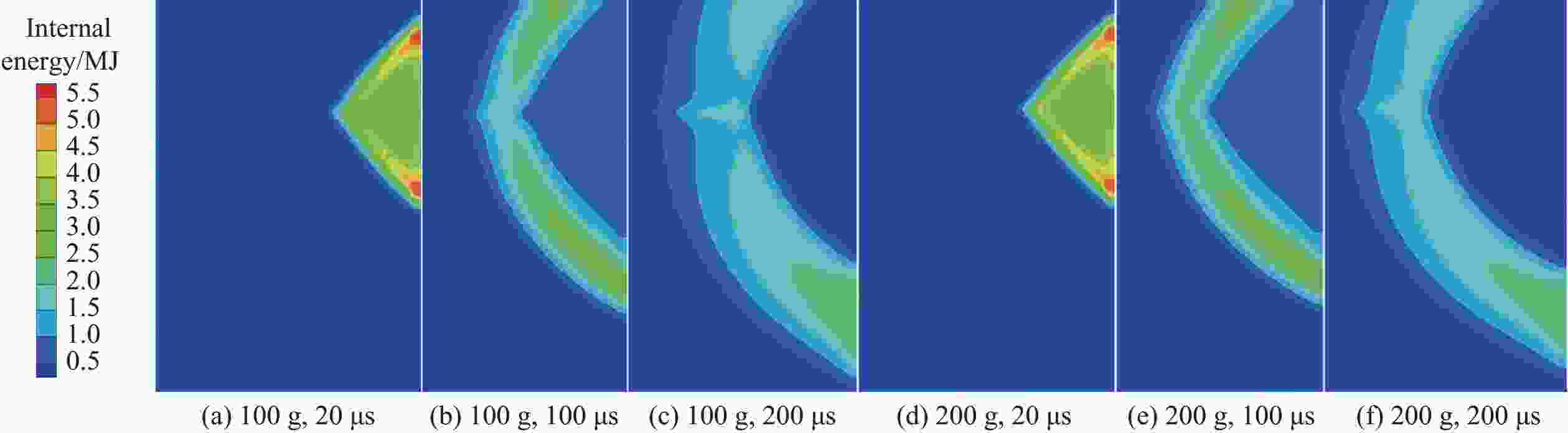
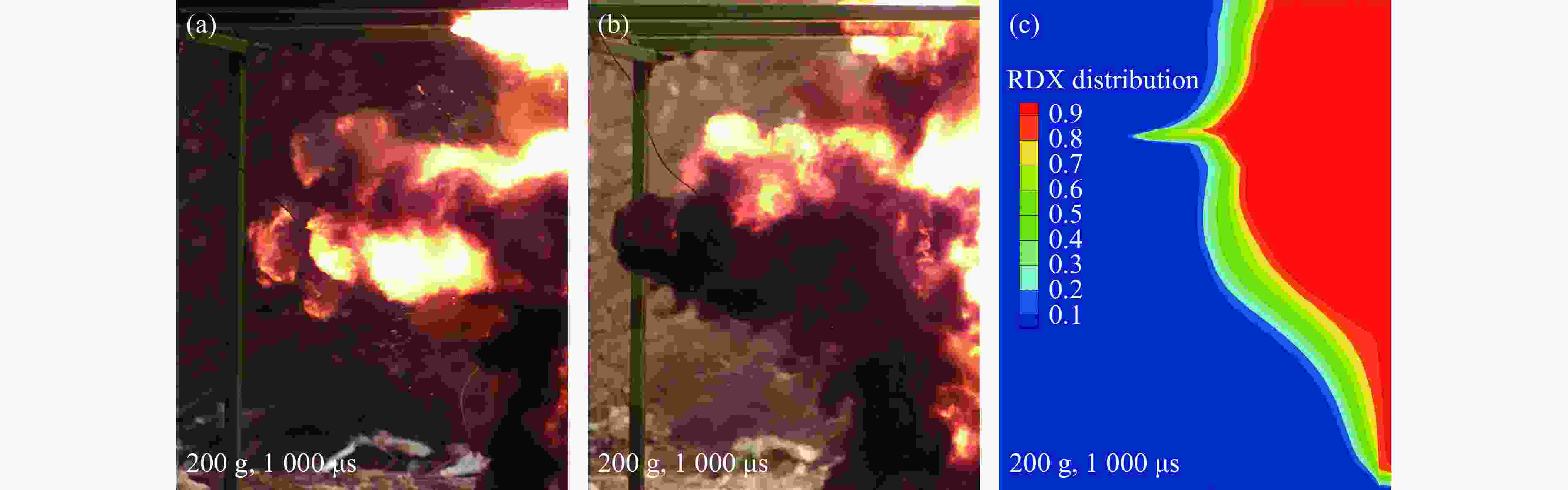
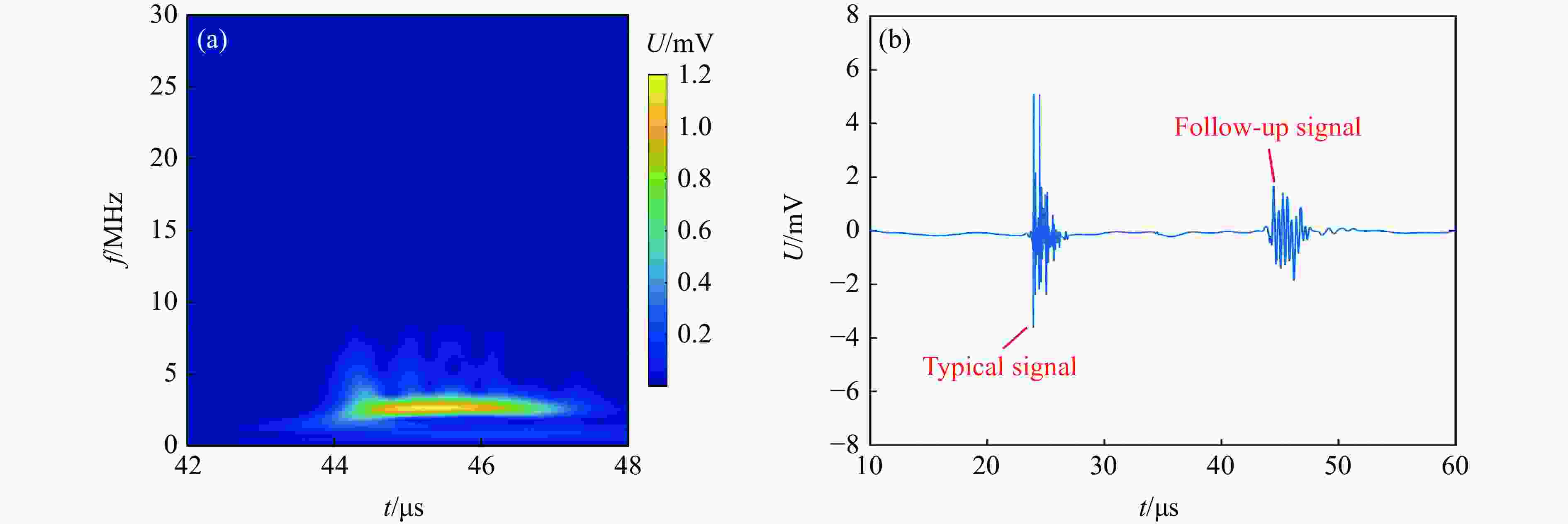
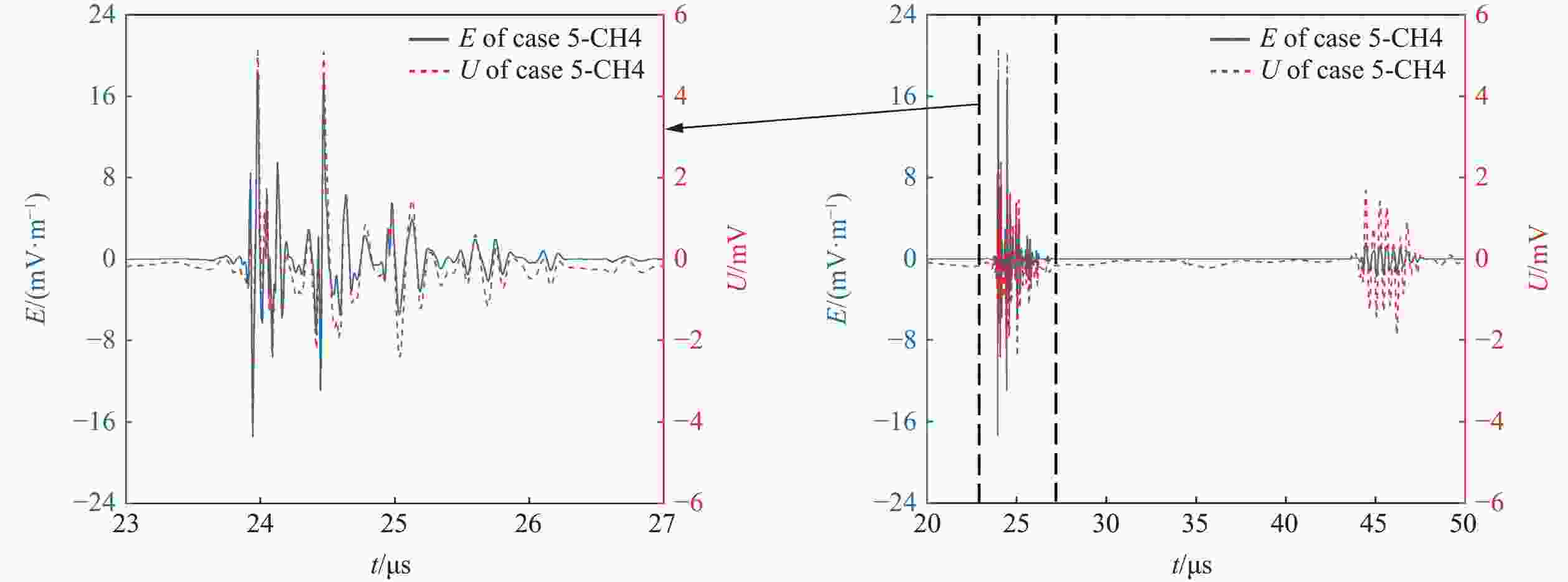
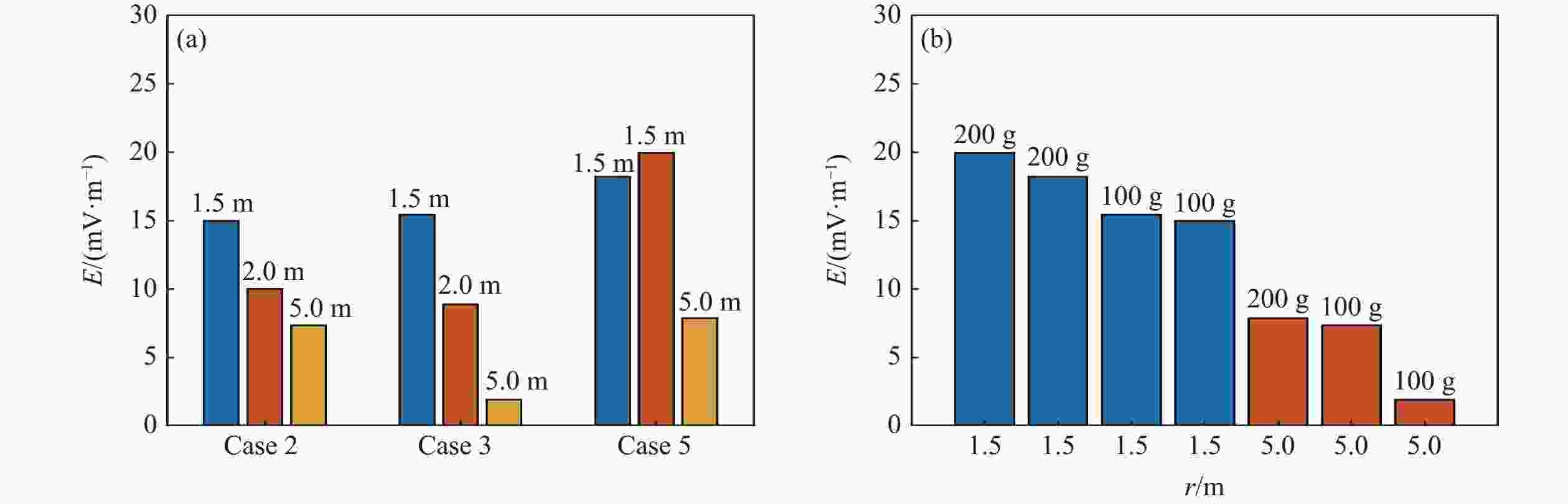
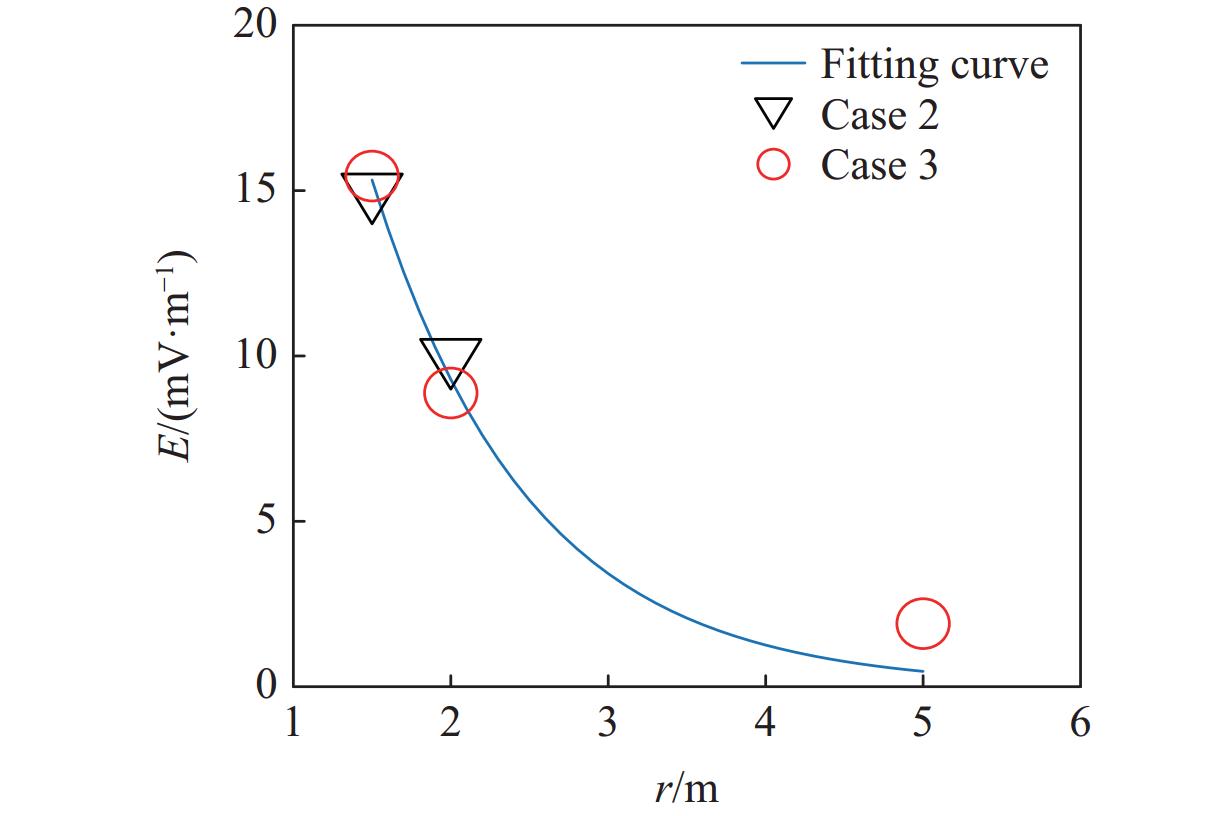
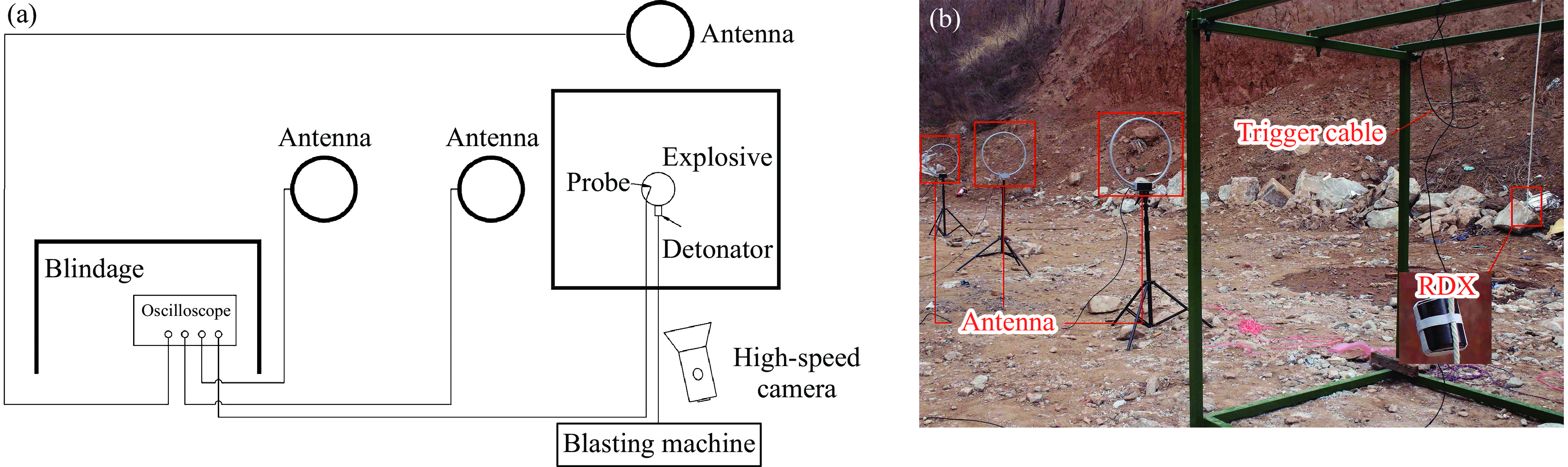
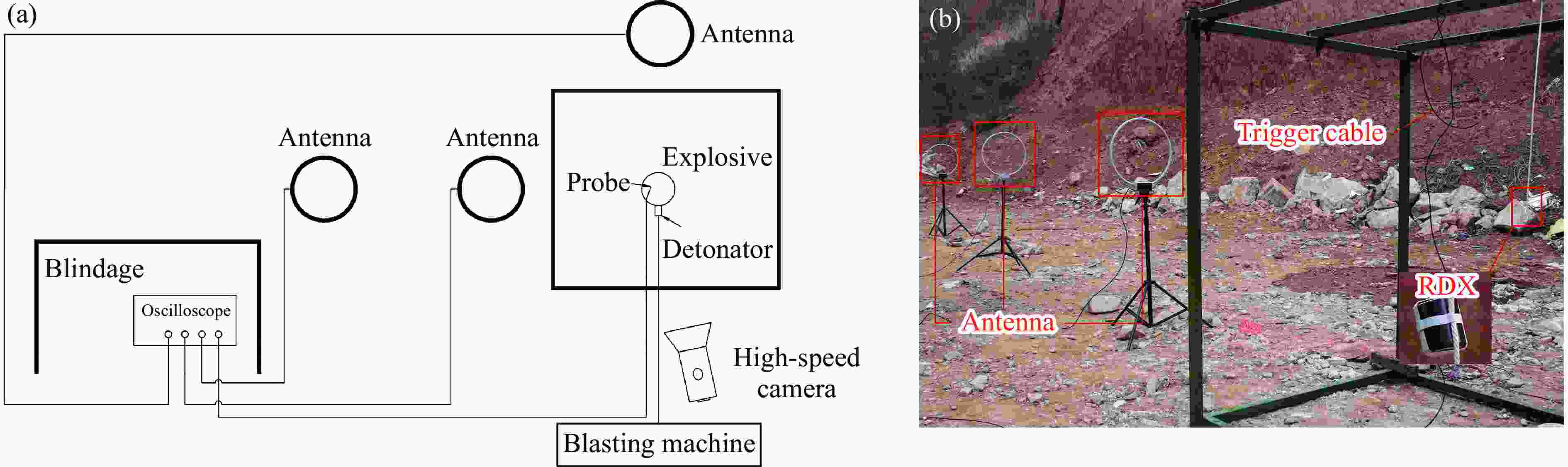
摘要: 常规爆炸伴随着显著的电磁效应,能够对爆炸测试产生干扰,也可以作为一种无接触手段测试爆炸冲击场。研究爆炸电磁效应具有重要的工程应用价值。采用示波器、天线、高速摄像机组成的测量系统对100、200 g药量RDX爆炸电磁辐射进行了5组不同距离测量实验,记录2 ms的电磁辐射信号并对RDX爆炸产生的电磁辐射进行分析。结果表明,RDX爆炸电磁辐射信号主要分为3种时段:重复性强的30 μs附近典型特征峰;同组重复性强、不同组重复性一般的30~200 μs后续特征峰;200 μs后无明显重复性的脉冲信号。结合爆炸高速影像发现,爆炸电磁辐射信号与爆轰产物状态有较强关联,典型特征峰以及后续特征峰主要是爆轰前期剧烈反应使爆轰产物电离产生的信号。利用天线系数反演电场强度曲线,分析药量、距离与电场强度之间的关系,发现对于典型特征峰:同药量下,电场强度随着距离成指数下降;同距离下,200 g药量比100 g药量爆炸产生的电场强度大。Abstract: Conventional explosions are accompanied by significant electromagnetic effects, which can interfere with explosion testing and also serve as a non-contact means of testing explosion shock waves. The study of explosive electromagnetic effects has important engineering application value. A measurement system composed of an oscilloscope, antennas, and a high-speed camera was used to conduct 5 sets of electromagnetic radiation measurement experiments, whose testing object is 100 or 200 g RDX. The experiment recorded electromagnetic radiation signals with 2 ms, and analyzed the electromagnetic radiation generated by RDX explosion. The experimental results showed that the RDX explosive electromagnetic radiation signal mainly consists of three periods: a typical peak at 30 μs with strong repeatability, subsequent peaks with strong repeatability in the same group but poor repeatability in different groups during 30−200 μs, and a pulse signal without obvious repeatability after 200 μs. Combined with high-speed imaging of the explosion, it’s found that there has been a strong correlation between the explosive electromagnetic radiation and the state of detonation products. The typical peak and subsequent peaks are mainly signals generated by the ionization of the explosive products during the violent reaction in the pre-explosion stage. By using the antenna factor to invert the electric field strength curve, the relationship between the explosive equivalent, distance, and electric field strength was analyzed. It’s found that at the same explosive equivalent, the electric field intensity of typical peak decreases exponentially with distance. At the same distance, the electric field intensity of typical peak generated by a 200 g explosion is greater than that of a 100 g explosion.
-
表 1 实验条件
Table 1. Experimental condition
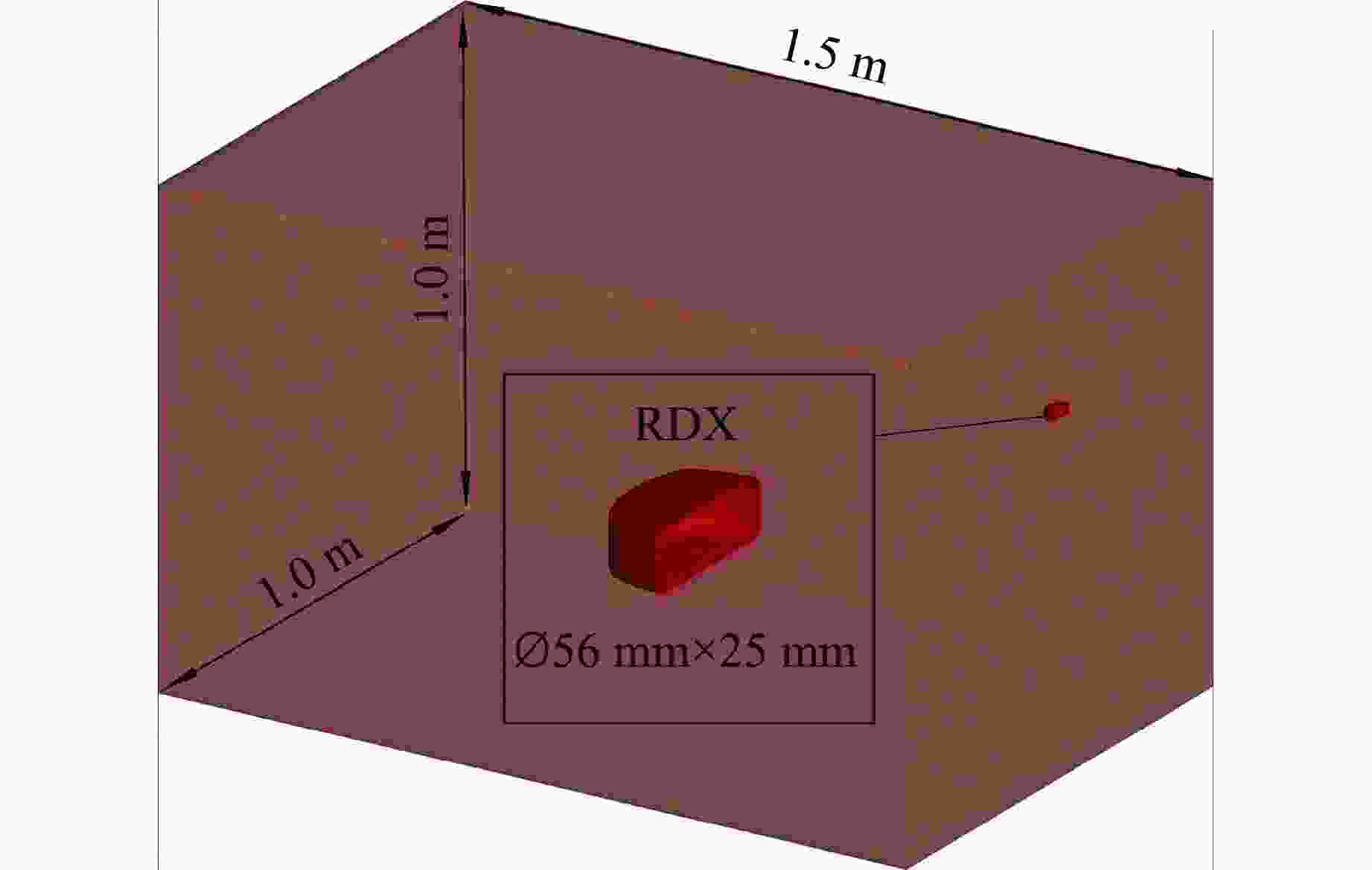
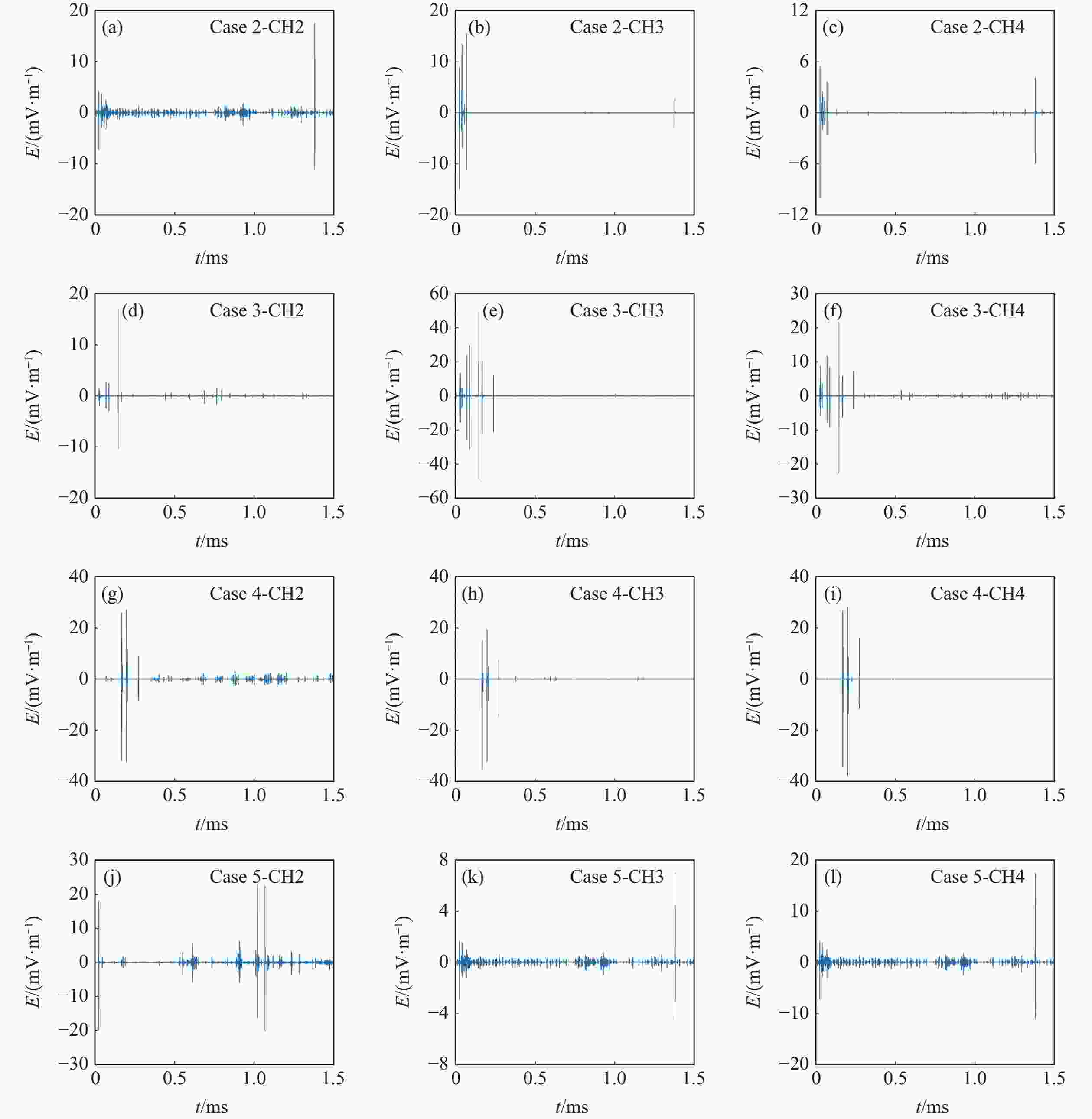
Case Charge/g Channel Distance/m 1 100 CH2 3.4 CH3 2.1 CH4 5.2 2 100 CH2 5.0 CH3 1.5 CH4 2.0 3 100 CH2 5.0 CH3 1.5 CH4 2.0 4 200 CH2 1.5 CH3 5.0 CH4 1.5 5 200 CH2 1.5 CH3 5.0 CH4 1.5 表 2 RDX和空气的模拟参数
Table 2. Simulation parameters of RDX and air
ρ0,RDX/(kg·m−3) pCJ/GPa DCJ/(m·s−1) e0,RDX/(MJ·m−3) ρ0,Air/(kg·m−3) γ e0,Air/(MJ·m−3) 1650 32 8250 9.2 1.26 1.4 0.196 2 表 3 典型特征峰和后续特征峰的时间参数及幅值
Table 3. Time parameters & amplitudes of typical peak and follow-up peak
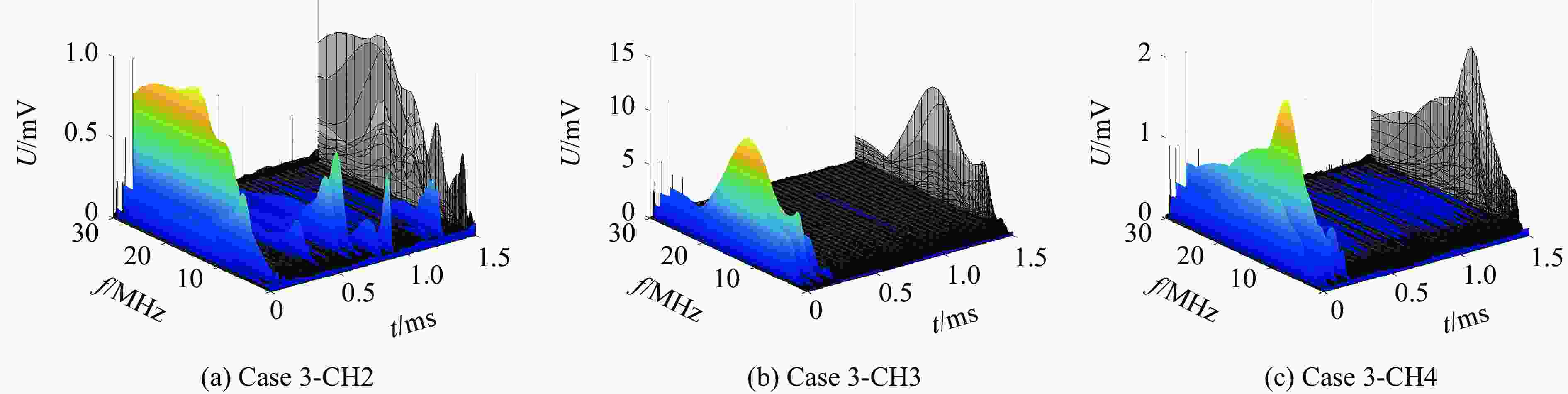
Case Channel Typical peak Follow-up peak t/μs U/V t/μs U/V 2 CH2 23.62 −0.0023 39.89 0.0012 CH3 23.61 −0.0055 39.53 0.0046 CH4 23.77 −0.0032 39.84 −0.0009 3 CH2 28.12 −0.0007 140.70 0.0047 CH3 28.45 −0.0044 140.60 0.0294 CH4 28.35 −0.0025 141.20 −0.0073 4 CH2 167.50 −0.0123 198.00 −0.0127 CH3 167.40 −0.0124 197.90 −0.0118 CH4 168.00 −0.0145 198.10 −0.0153 5 CH2 23.82 0.0037 44.96 −0.0010 CH3 23.84 0.0024 44.74 0.0033 CH4 23.98 0.0051 44.46 0.0017 表 4 典型特征峰和后续特征峰的频域特性
Table 4. Frequency domain characteristics of typical peak and follow-up peak
Case Channel Typical peak Follow-up peak t/μs f/MHz t/μs f/MHz
2CH2 24.0 15 41.1 15 CH3 24.0 18 41.1 18 CH4 23.7 14 40.2 22 3 CH2 28.5 15 145.3 17 CH3 27.9 8 145.5 10 CH4 28.2 9 145.4 11 4 CH2 167.9 12 198.0 17 CH3 167.4 17 198.0 7 CH4 168.1 12 198.5 11 5 CH2 24.0 12 45.0 2 CH3 23.9 7 45.0 2 CH4 24.5 7 45.2 2 表 5 特征峰的电场强度
Table 5. Electric field intensity of characteristic peak
Case Channel Typical peak Follow-up peak t/μs E/(V·m−1) t/μs E/(V·m−1) 2 CH2 23.6 −0.0073 39.8 0.0028 CH3 23.8 −0.0150 39.8 0.0130 CH4 23.8 −0.0100 40.3 0.0025 3 CH2 27.9 −0.0019 144.9 0.0170 CH3 27.6 −0.0154 144.8 0.0504 CH4 28.2 0.0088 145.4 −0.0229 4 CH2 167.5 −0.0318 198.0 −0.0326 CH3 167.9 −0.0354 198.4 −0.0325 CH4 168.0 −0.0343 198.5 −0.0379 5 CH2 23.9 −0.0199 44.8 −0.0016 CH3 23.9 −0.0079 45.0 0.0018 CH4 24.0 0.0182 45.5 −0.0016 -
[1] 舒志强. 核电磁脉冲孔耦合及防护研究 [D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2009: 1−2.SHU Z Q. Analysis of NEMP aperture coupling and protection [D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2009: 1−2. [2] 李顺. 强电磁脉冲下的冲击波超压测试系统设计 [D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2022: 1−3.LI S. Design of shock wave overpressure test system under strong EMP [D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2022: 1−3. [3] YAO W B, ZHOU H B, HAN R Y, et al. An empirical approach for parameters estimation of underwater electrical wire explosion [J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2019, 9(26): 093502. doi: 10.1063/1.5111518 [4] 曹景阳, 谢树果, 苏东林. 航天火工品爆炸引起的电磁干扰测量 [J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2011, 37(11): 1384–1387, 1394. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2011.11.015CAO J Y, XIE S G, SU D L. Electromagnetic interference caused by aerospace explosives [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011, 37(11): 1384–1387, 1394. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2011.11.015 [5] CHEN C, GAO R K, GUO K, et al. Thermoelectric behavior of Al/PTFE reactive materials induced by temperature gradient [J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 123: 105203. doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105203 [6] KOLSKY H. Electromagnetic waves emitted on detonation of explosives [J]. Nature, 1954, 173(4393): 77. doi: 10.1038/173077a0 [7] COOK M A. The science of high explosives [M]. New York: Reinhold, 1958. [8] BORONIN A P, KAPINOS V N, KRENEV S A, et al. Physical mechanism of electromagnetic field generation during the explosion of condensed explosive charges. Survey of literature [J]. Combustion, Explosion and Shock Waves, 1990, 26(5): 597–602. doi: 10.1007/BF00843137 [9] VAN L V. Electromagnetic emission from chemical explosions [J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1982, 29(6): 1843–1849. doi: 10.1109/TNS.1982.4336458 [10] 陈生玉, 孙新利, 钱世平, 等. 化爆引起的电磁辐射 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1997, 17(4): 363–368.CHEN S Y, SUN X L, QIAN S P, et al. Electromagnetic radiation caused by chemical explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1997, 17(4): 363–368. [11] HARLIN J, NEMZEK R. Physical properties of conventional explosives deduced from radio frequency emissions [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2009, 34(6): 544–550. doi: 10.1002/prep.200800076 [12] NEMZEK R J, ARROWSMITH S, LAYNE J P. Ten trials at lower slobbovia: searching for repetitive electromagnetic and seismoacoustic signatures in explosions: LA-UR-13-22138 [R]. Los Alamos: Los Alamos National Laboratory, 2013. [13] 栗建桥, 马天宝, 宁建国. 爆炸对自然磁场干扰机理 [J]. 力学学报, 2018, 50(5): 1206–1218. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-18-081LI J Q, MA T B, NING J G. Mechanism of explosion-induced disturbance in natural magnetic field [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2018, 50(5): 1206–1218. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-18-081 [14] REN H L, CHU Z X, LI J Q. Study on electromagnetic radiation generated during detonation [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2019, 44(12): 1541–1553. doi: 10.1002/prep.201900118 [15] 崔元博, 商飞, 孔德仁, 等. 爆炸场电磁辐射特性测试技术研究 [J]. 火工品, 2019(5): 1–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2019.05.001CUI Y B, SHANG F, KONG D R, et al. Research on testing technology of electromagnetic radiation characteristics in explosive field [J]. Initiators & Pyrotechnics, 2019(5): 1–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2019.05.001 [16] 崔元博, 孔德仁, 张学辉, 等. TNT爆炸电磁辐射信号测量及分析 [J]. 含能材料, 2021, 29(3): 241–250. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2020181CUI Y B, KONG D R, ZHANG X H, et al. Measurement and analysis of electromagnetic radiation signals of TNT explosives [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2021, 29(3): 241–250. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2020181 [17] 崔元博, 孔德仁, 张学辉, 等. 典型炸药爆炸过程中电磁辐射特性分析 [J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2022, 44(6): 70–80. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202206009CUI Y B, KONG D R, ZHANG X H, et al. Analysis of electromagnetic radiation characteristics during typical explosives explosion [J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2022, 44(6): 70–80. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202206009 [18] 张斯薇. 基于小波变换的探地雷达数据去噪方法研究 [D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2022: 1−3.ZHANG S W. Research on denoising method of ground penetrating radar data based on wavelet transform [D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science & Technology, 2022: 1−3. -






 下载:
下载: