Dynamic Failure of Foam-Reinforce Composite Lattice Sandwich Beam to Local Impulsive Load
-
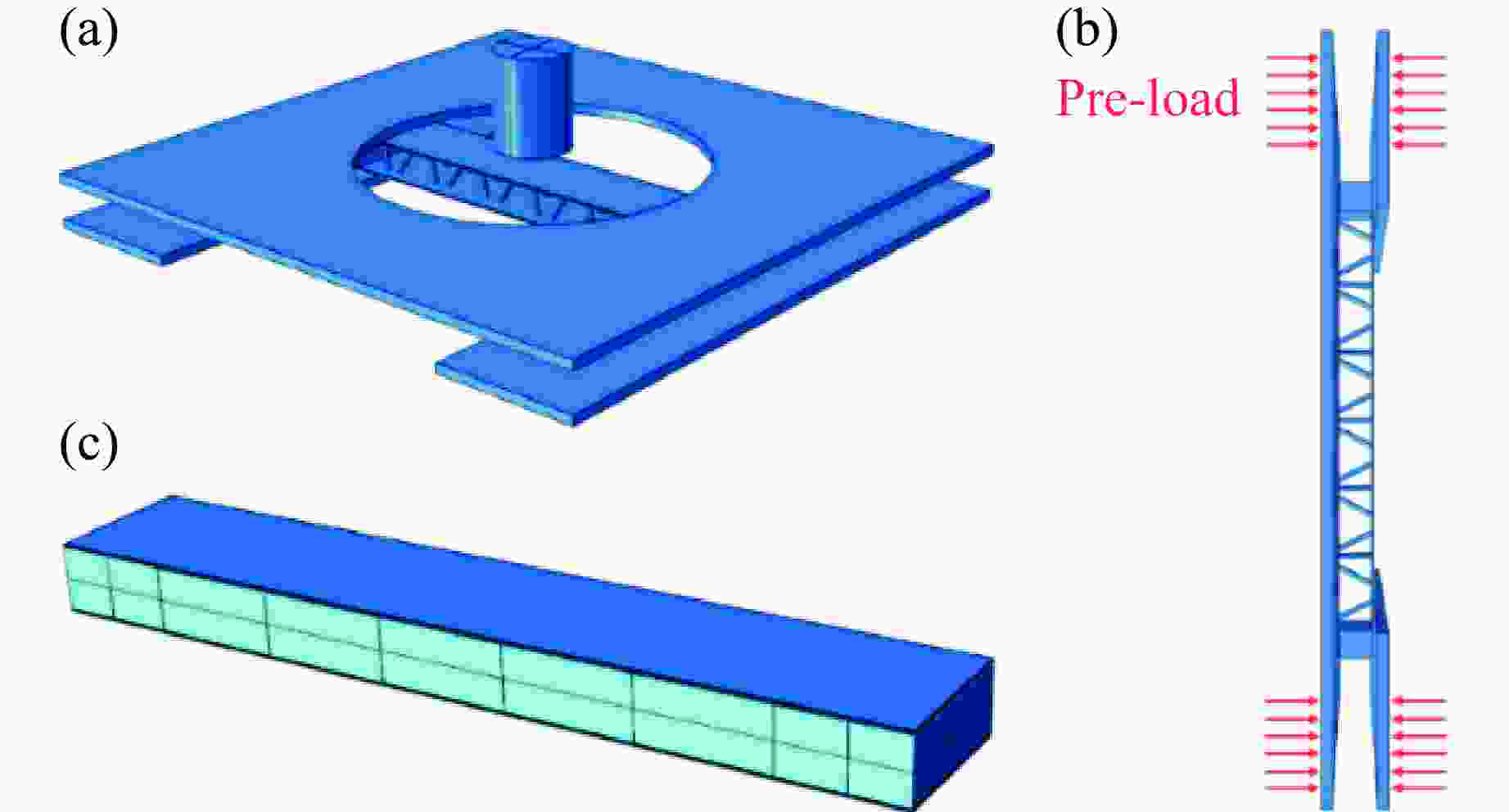
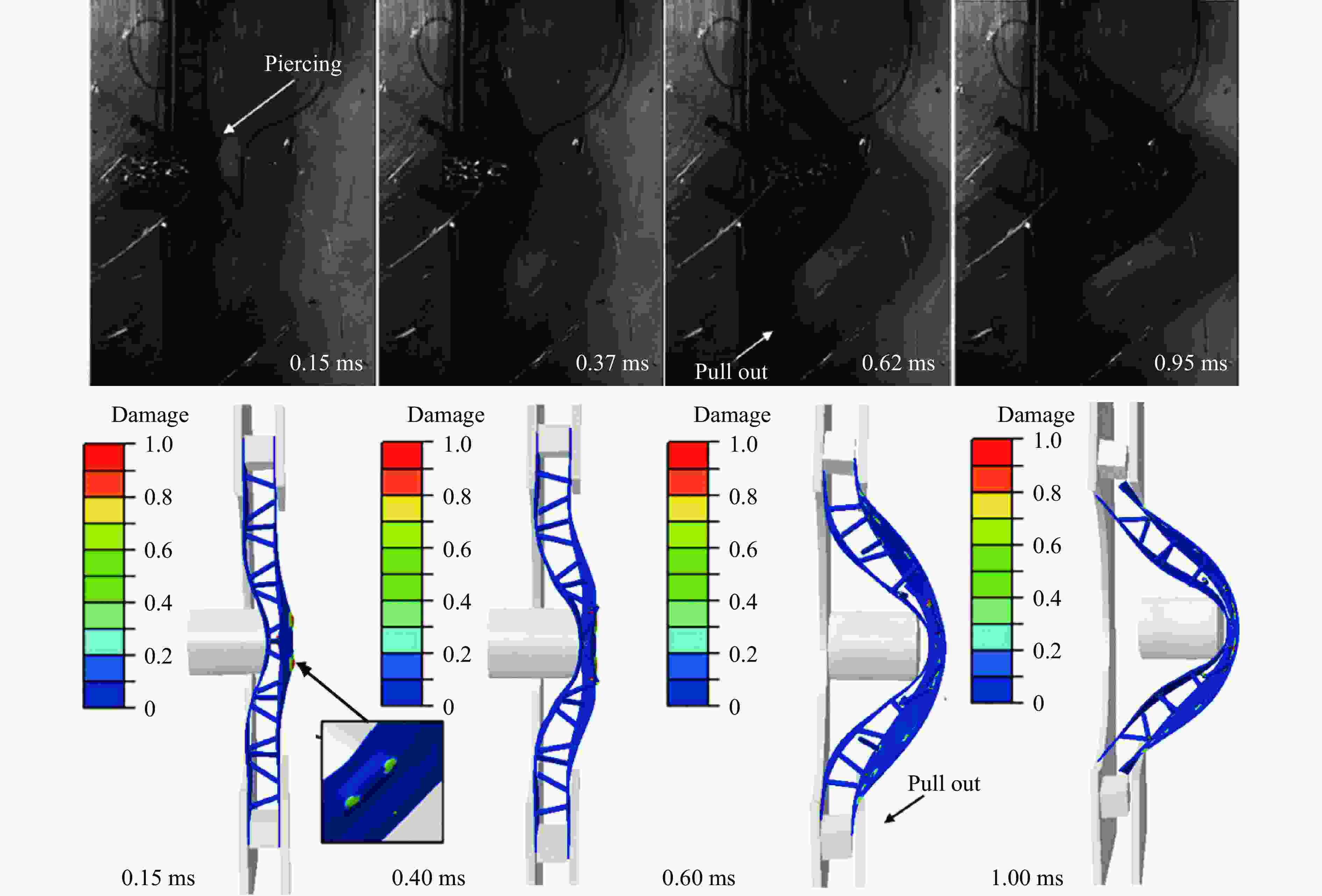
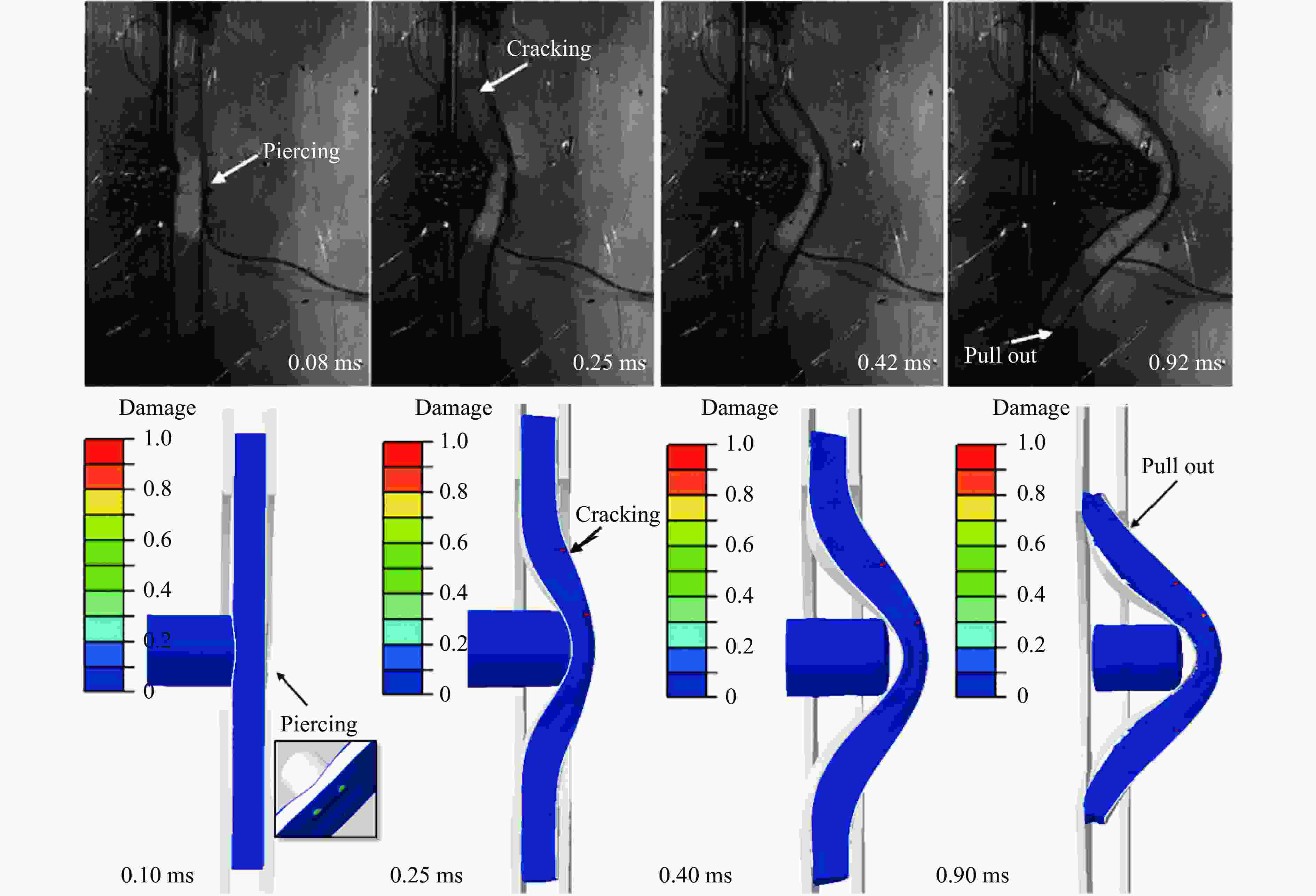
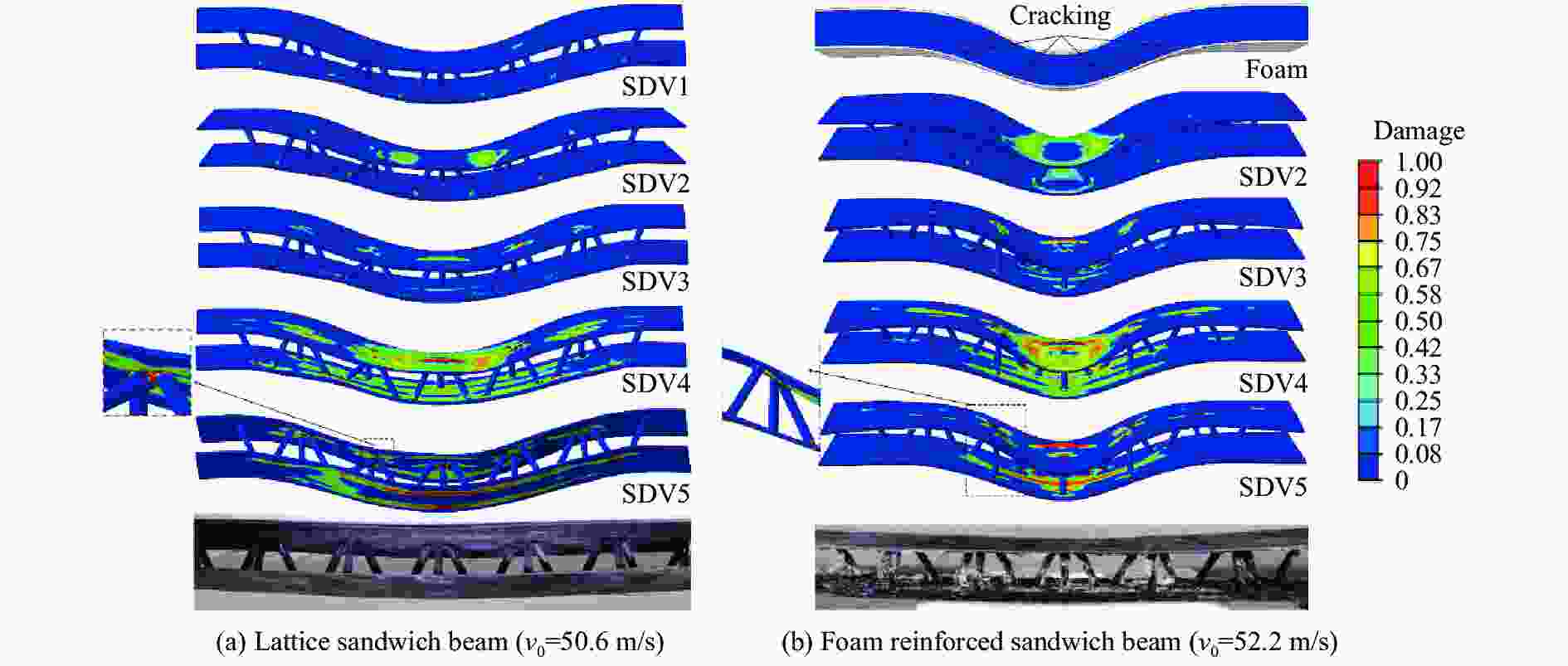
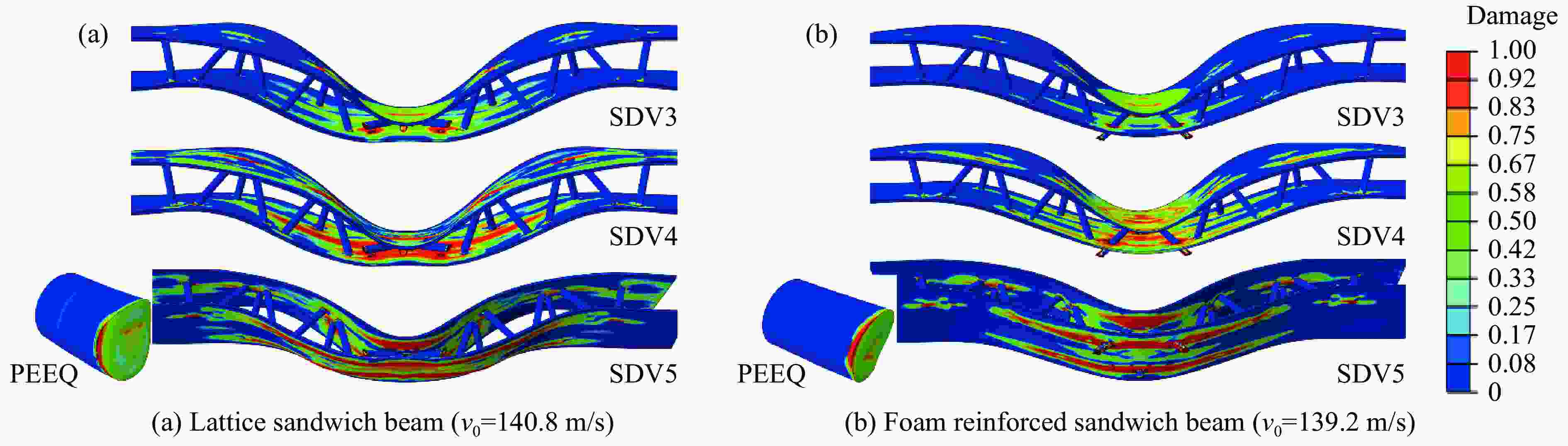
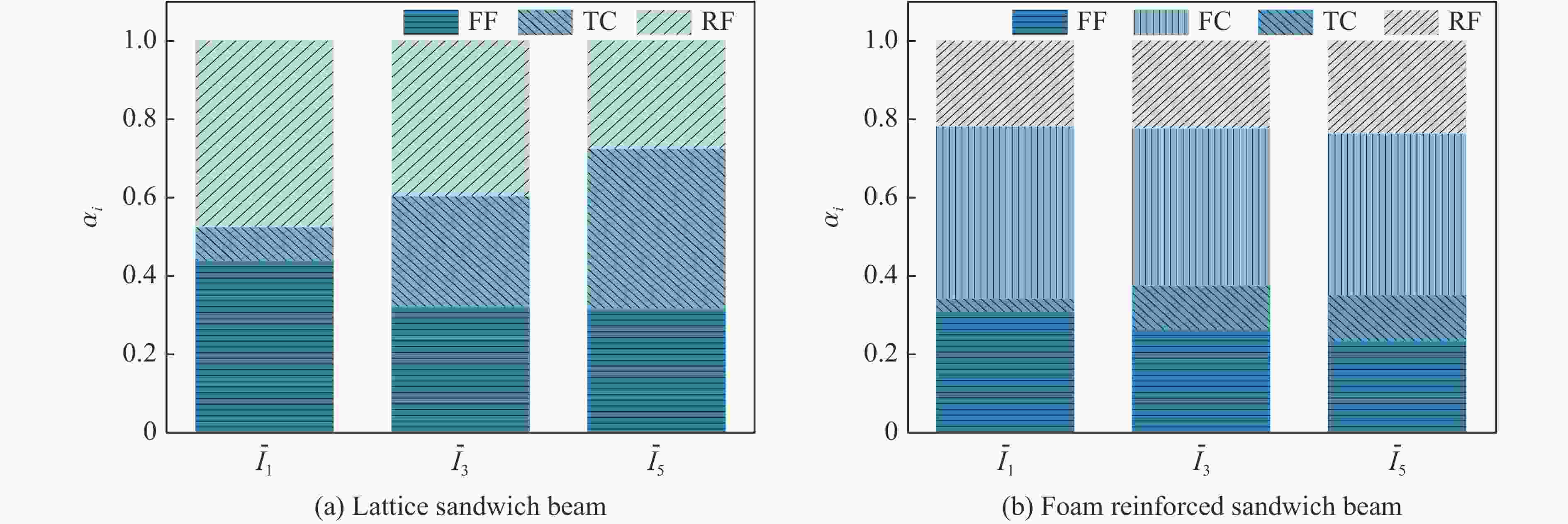
摘要: 基于考虑分层失效和渐进损伤的三维Hashin失效准则,对复合材料点阵夹芯梁结构及其泡沫增强夹芯结构开展了局部冲击加载下的数值模拟分析,研究了冲击强度及泡沫增强效应对复合材料点阵夹芯梁结构抗冲击性能的影响。通过与实验的对比分析,验证了数值模型的有效性。结果显示,冲击强度的变化对结构的动态响应、失效模式及能量耗散形式都有明显的影响。泡沫增强效应使结构的横向变形响应速度降低,并且随着冲击强度的增加尤为敏感。泡沫芯材的压缩和开裂失效使得结构保持良好的完整性和更低的损伤程度,有效地降低了其他组分的能量吸收比,表明泡沫填充有效地提升了复合材料点阵梁结构在局部冲击载荷作用下的防护效能。Abstract: Based on the Hashin 3D failure criteria, both stiffness degradation and interface delamination are adopted to model the damage evolution of the composites, a numerical study on the composite lattice sandwich and its foam-reinforce sandwich beams subjected to local impulsive load is performed to identify the effects of impulsive intensity and foam reinforcement on the dynamic response, failure modes, and energy absorption mechanisms. The numerical result is confirmed to have a great agreement with the previously experimental results. The results show the impact strength has a significant influence on the dynamic response, failure mode, and energy dissipation mechanisms of the beams. With the reinforcement of the foam, the composite sandwich beam undergoes a slower deformed response than the lattice sandwich beam, especially for the intensive loads. The compression and cracking of the foam core reduces the degree of failure and keeps the structural integrity, and at the same time effectively decreases the energy absorption ratio of other components, indicating a noticeable improvement of impact resistance of the foam-reinforce composite lattice sandwich beam to concentrated impact load.
-
Key words:
- composite material /
- lattice sandwich beam /
- impulsive resistance
-
表 1 T700碳纤维/环氧单向预浸料的材料属性
Table 1. Material properties of T700 carbon/epoxy prepregs
E11/MPa E22/MPa E33/MPa ν12 ν13 ν23 G12/MPa 100 8 8 0.21 0.21 0.30 4 G13/MPa G23/MPa Xt/MPa Xc/MPa Yt/MPa Yc/MPa Zt/MPa 4 3 2100 700 42 160 42 Zc/MPa S12/MPa S13/MPa S23/MPa $\,\rho $/(kg·m–3) 160 104 104 86 1500 表 2 撞击初始条件及无量纲冲击强度
Table 2. Initial conditions and non-dimensional impulse of the impacts
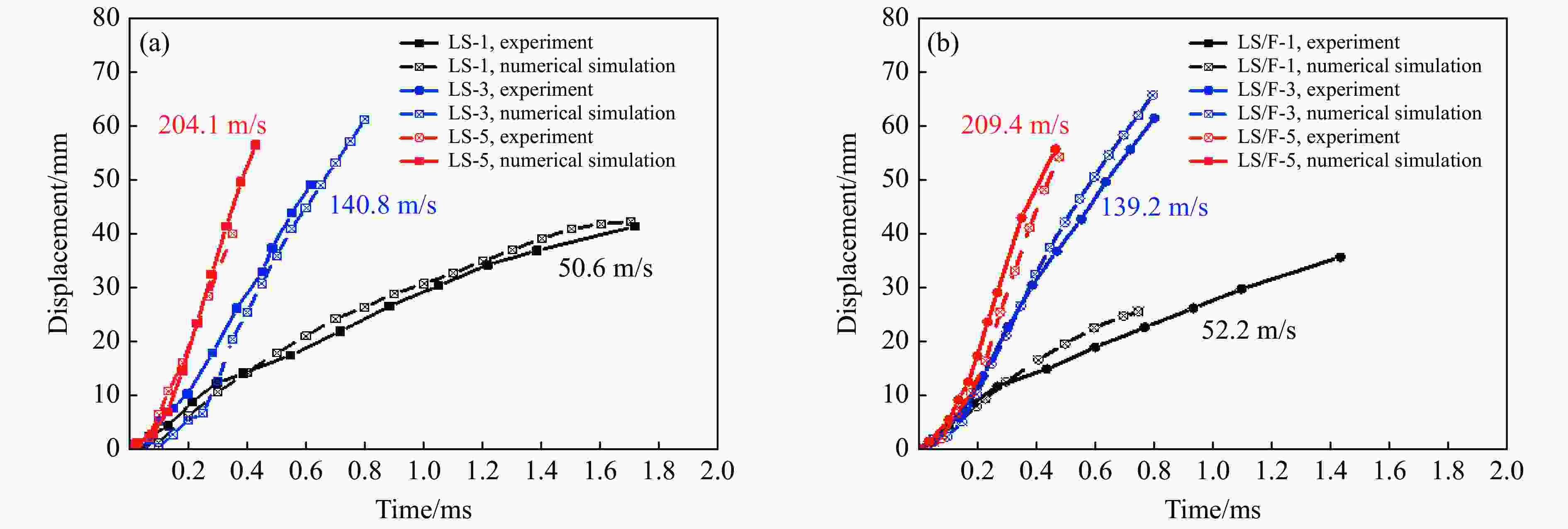
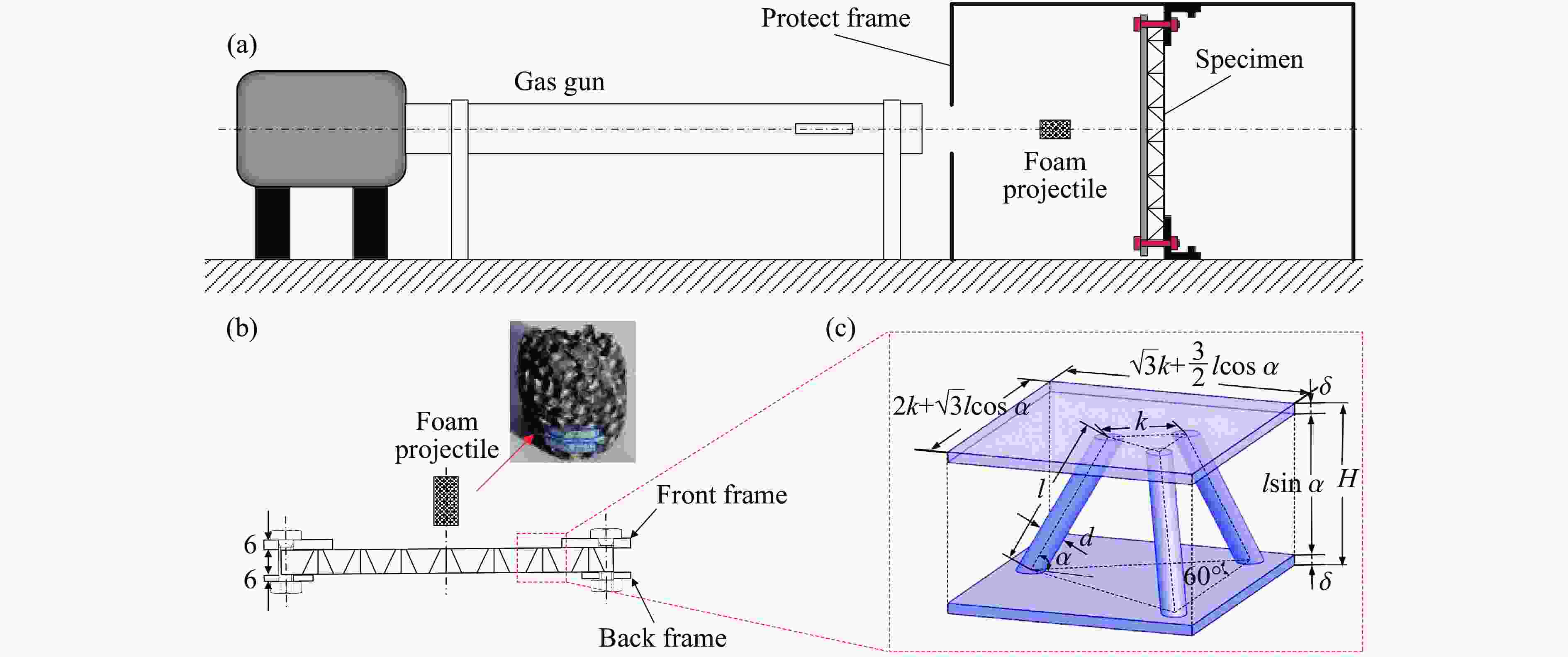
Sample Exp. No. mp/g v0/(m·s–1) $ \overline I $ Sample Exp. No. mp/g v0/(m·s–1) $ \overline I $ Lattice
sandwichLS-1 29.8 50.6 0.25 Lattice/foam
sandwichLS/F-1 30.3 52.2 0.26 LS-2 28.8 77.5 0.36 LS/F-2 29.1 80.5 0.38 LS-3 29.7 140.8 0.68 LS/F-3 29.2 139.2 0.66 LS-4 27.9 175.4 0.80 LS/F-4 30.6 167.6 0.83 LS-5 29.9 204.1 0.99 LS/F-5 28.9 209.4 0.99 -
[1] 熊健, 杜昀桐, 杨雯, 等. 轻质复合材料夹芯结构设计及力学性能最新进展 [J]. 宇航学报, 2020, 41(6): 749–760.XIONG J, DU Y T, YANG W, et al. Research progress on design and mechanical properties of lightweight composite sandwich structures [J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2020, 41(6): 749–760. [2] FLECK N A, DESHPANDE V S. The resistance of clamped sandwich beams to shock loading [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2004, 71(3): 386–401. doi: 10.1115/1.1629109 [3] FLECK N A, DESHPANDE V S, ASHBY M F. Micro-architectured materials: past, present and future [J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2020, 466(2121): 2495–2516. [4] YANG J S, MA L, CHAVES-VARGAS M, et al. Influence of manufacturing defects on modal properties of composite pyramidal truss-like core sandwich cylindrical panels [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2017, 147(28): 89–99. [5] XIONG J, MA L, VAZIRI A, et al. Mechanical behavior of carbon fiber composite lattice core sandwich panels fabricated by laser cutting [J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(13/14): 5322–5334. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2012.06.004 [6] MEI J, LIU J, LIU J. A novel fabrication method and mechanical behavior of all-composite tetrahedral truss core sandwich panel [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2017, 102: 28–39. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.07.020 [7] MEI J, TAN P J, LIU J, et al. Moisture absorption characteristics and mechanical degradation of composite lattice truss core sandwich panel in a hygrothermal environment [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2019, 127: 105647. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105647 [8] XU G D, ZHAI J J, TA Z, et al. Response of composite sandwich beams with graded lattice core [J]. Composite Structures, 2015, 119: 666–676. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2014.09.042 [9] ZHANG J, YE Y, QIN Q, et al. Low-velocity impact of sandwich beams with fibre-metal laminate face-sheets [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2018, 168(10): 152–159. [10] ZHANG J, QIN Q, XIANG C, et al. A theoretical study of low-velocity impact of geometrically asymmetric sandwich beams [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 96: 35–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.05.011 [11] ZHANG J, QIN Q, XIANG C, et al. Dynamic response of slender multilayer sandwich beams with metal foam cores subjected to low-velocity impact [J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 153: 614–623. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.06.059 [12] ZHANG G, MA L, WANG B, et al. Mechanical behaviour of CFRP sandwich structures with tetrahedral lattice truss cores [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2012, 43(2): 471–476. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.11.017 [13] ZHANG G, WANG B, MA L, et al. Energy absorption and low velocity impact response of polyurethane foam filled pyramidal lattice core sandwich panels [J]. Composite Structures, 2014, 108: 304–310. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.09.040 [14] HUANG W, FAN Z, ZHANG W, et al. Impulsive response of composite sandwich structure with tetrahedral truss core [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2019, 176: 17–28. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.03.020 [15] HUANG C, LEE Y. Quasi-static simulation of composite-laminated shells subjected to low-velocity impact [J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 2005, 24(7): 763–774. doi: 10.1177/0731684405046613 [16] XIAO J R, GAAM B A, GILLESPIE J W. Progressive damage and delamination in plain weave S-2 glass/SC-15 composites under quasi-static punch-shear loading [J]. Composite Structures, 2007, 78(2): 182–196. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2005.09.001 [17] DESHPANDE V S, FLECK N A. Isotropic constitutive models for metallic foams [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2000, 48(6/7): 1253–1283. -






 下载:
下载: