Response Mechanism of Fuse with Different Structures under Thermal Stimulation
-
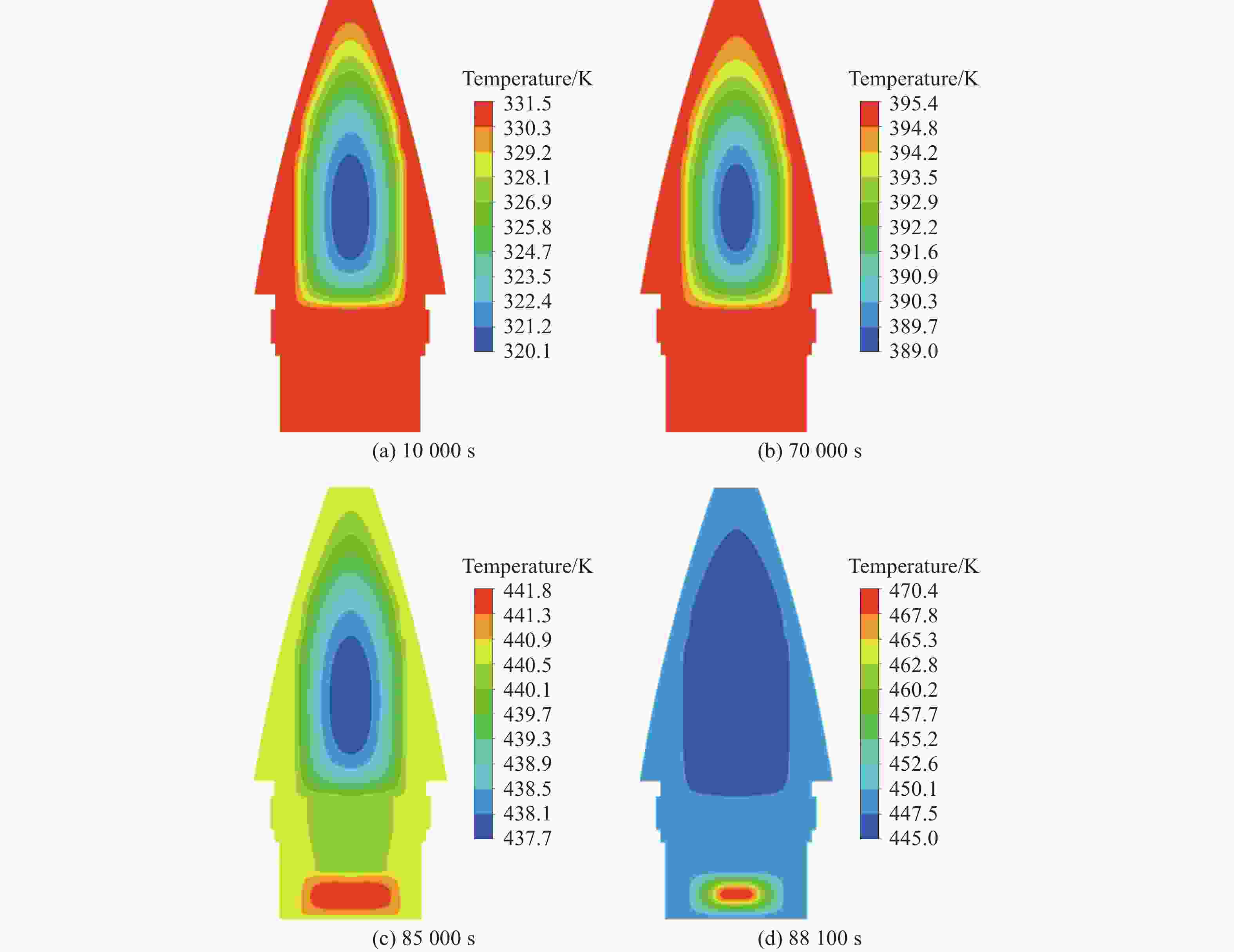
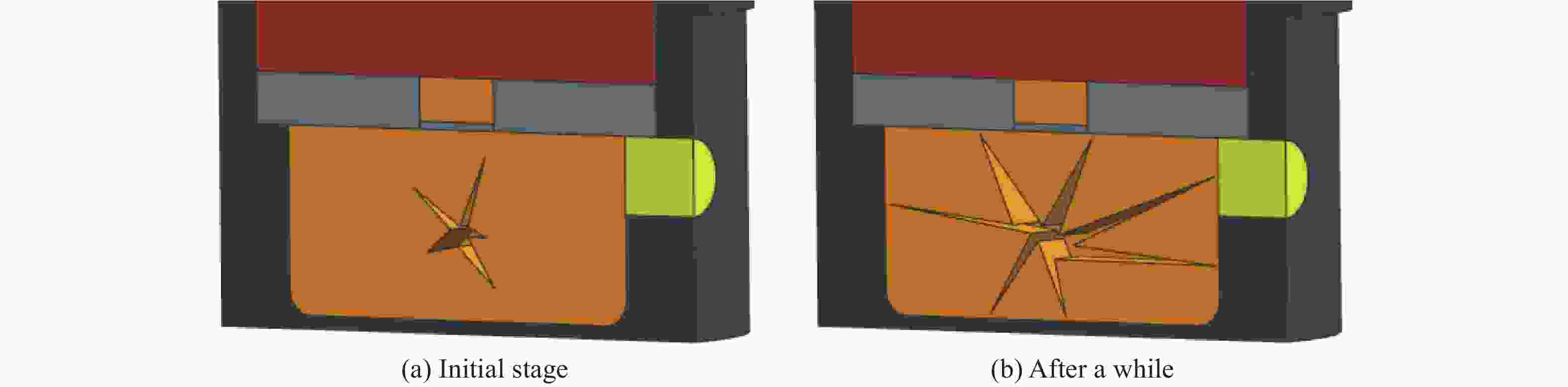
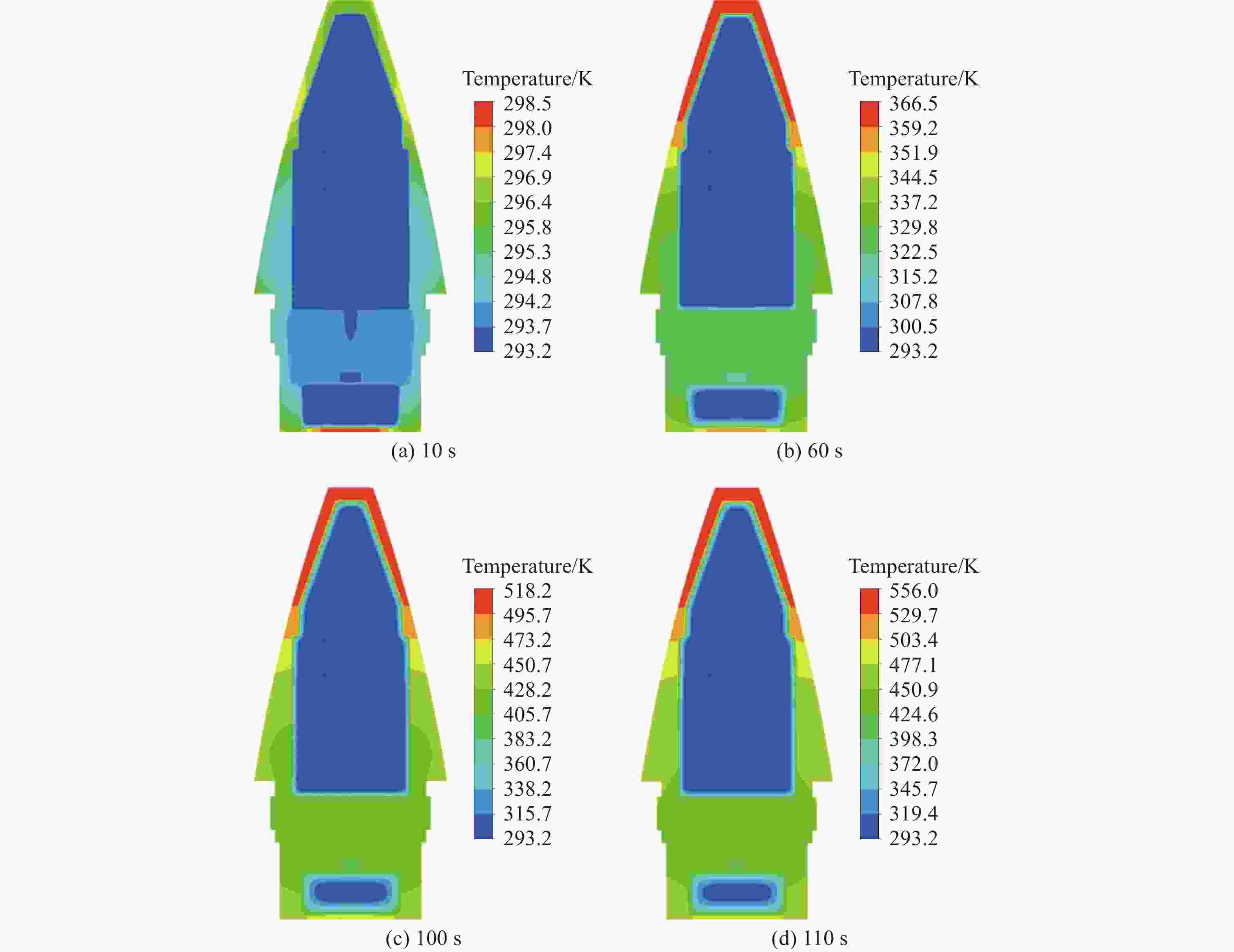
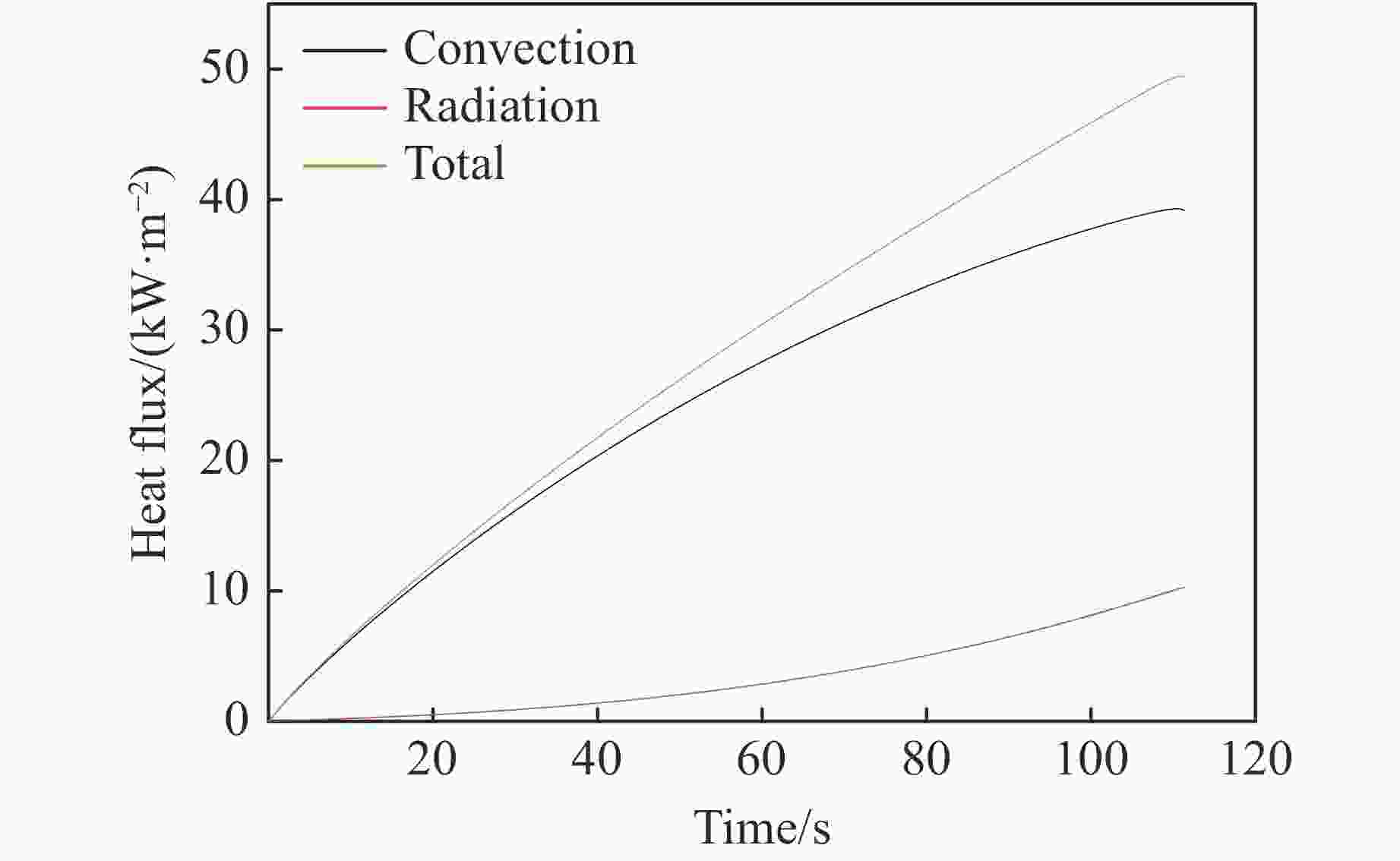
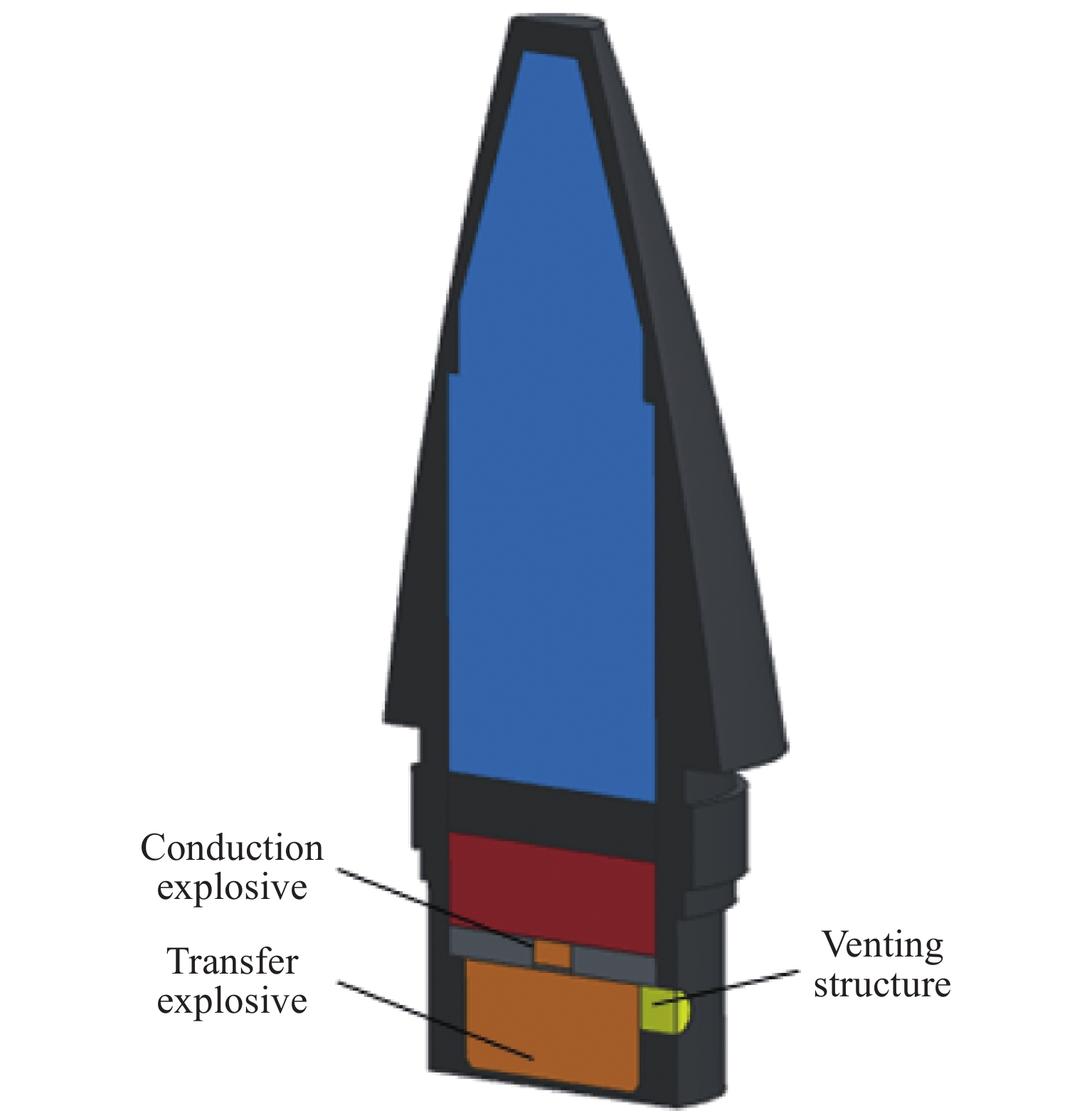
摘要: 为了掌握引信在泄压结构作用下的响应特性,通过自行设计的引信泄压装置,开展了烤燃条件下泄压装置对引信响应剧烈程度的影响研究。试验结果表明,慢速烤燃和快速烤燃条件下,泄压结构均可以有效降低引信响应时刻的内部压力,降低引信在烤燃条件下的响应烈度,但是引信在慢速烤燃和快速烤燃条件下的响应情况存在一定差异。通过数值模拟对引信的响应情况进一步分析,结果表明:慢速烤燃条件下,引信点火点位于传爆药柱中心;快速烤燃条件下,引信点火点位于传爆药底部。点火位置不同使得传爆药的压力释放过程不同,慢速烤燃通过中心点火形成从中心至泄压孔的排气通道来释放内部压力,快速烤燃泄压孔释放部分压力后,剩余压力导致底部端盖被冲破。Abstract: To study the response characteristics of the fuse with venting structure, the self-designed fuse venting device is used to study the effect of venting device on the reaction violence of the fuse under cook-off. The results show that under slow cook-off, the reaction violence of fuse is deflagration without venting structure, and the fuse structure is destroyed. The reaction violence with the venting structure is combustion. Under fast cook-off, the reaction violence fuse is deflagration when there is no venting structure, the bottom end cover of the fuse is damaged, and the reaction violence is burning with the venting structure. The temperature inside the explosive is obtained through numerical simulation. The ignition point of slow cook-off is located at the center of the booster, and the ignition point of fast cook-off is at the bottom of the booster. Different ignition positions make the pressure release process of the booster different. Slow cook-off uses the pressure of the center ignition to form an exhaust channel from the center to the venting structure to release the internal pressure. In the fast cook-off test, after the venting structure releases part of the pressure, the remaining pressure causes the bottom end cover to burst.
-
Key words:
- thermal stimulation /
- fuse /
- venting structure /
- ignition /
- cook-off test
-
表 1 炸药在不同温度下点火所需泄压孔的尺寸
Table 1. Size of venting structure required for explosive ignition at different temperatures
Temperature/K AV/SB Temperature/K AV/SB 443 0.0065 473 0.0078 453 0.0069 483 0.0083 463 0.0073 495 0.0091 表 2 不同引信慢速烤燃试验结果
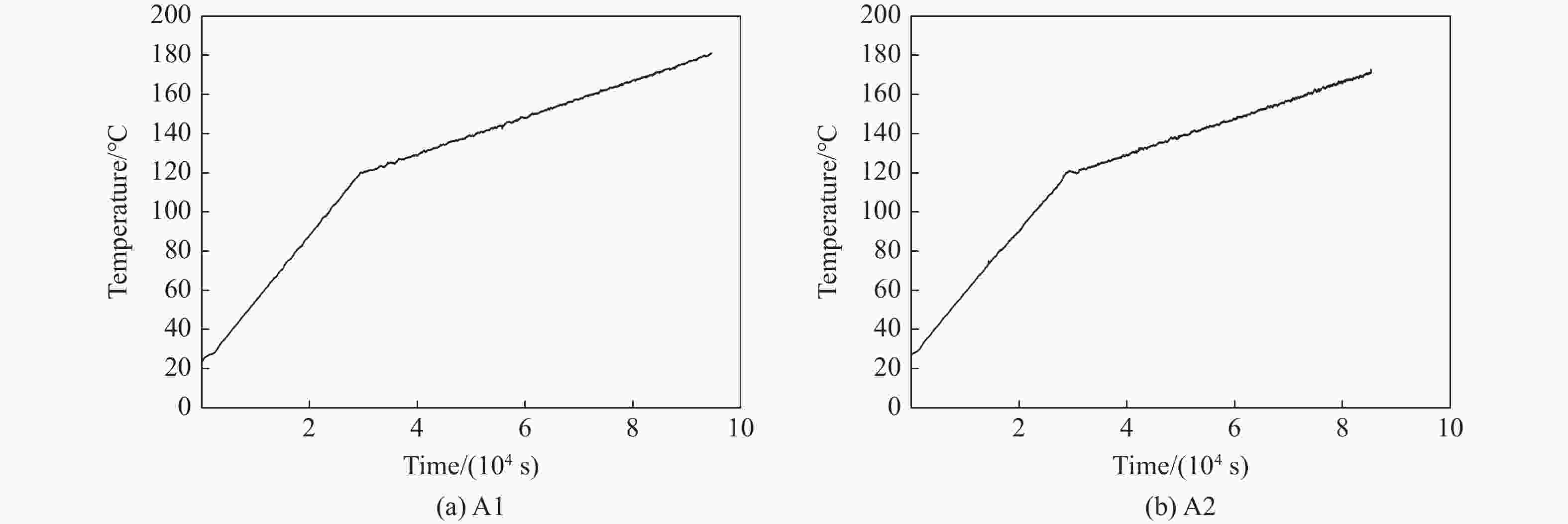
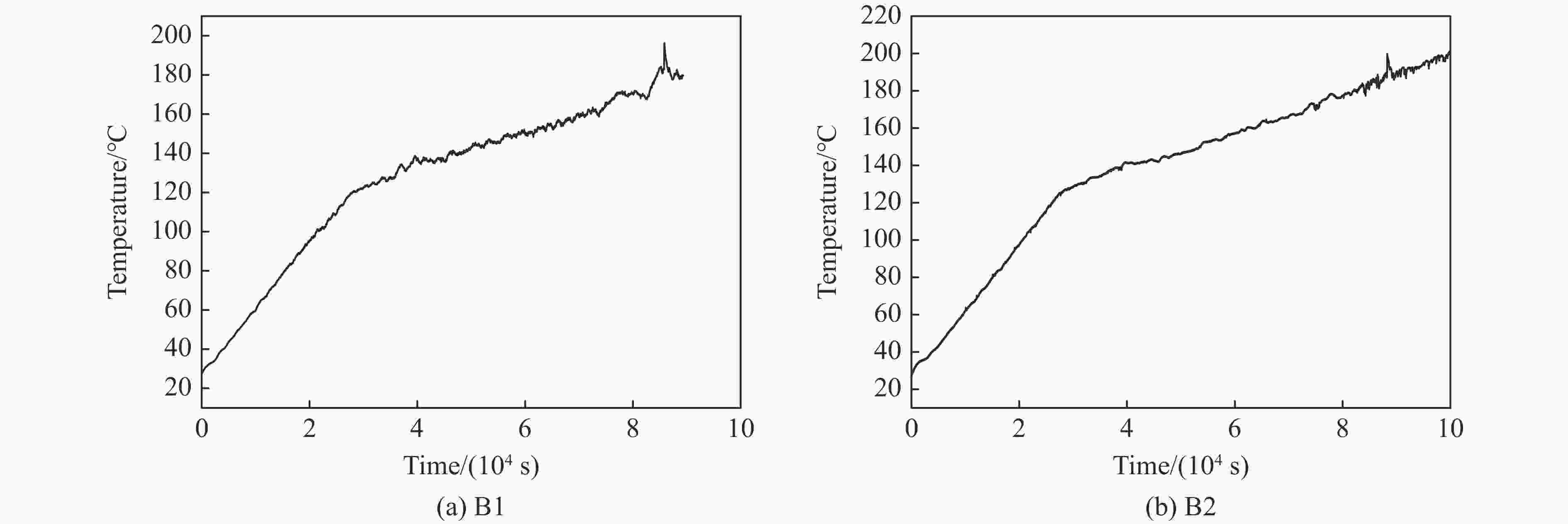
Table 2. Results of slow cook-off test of different fuses
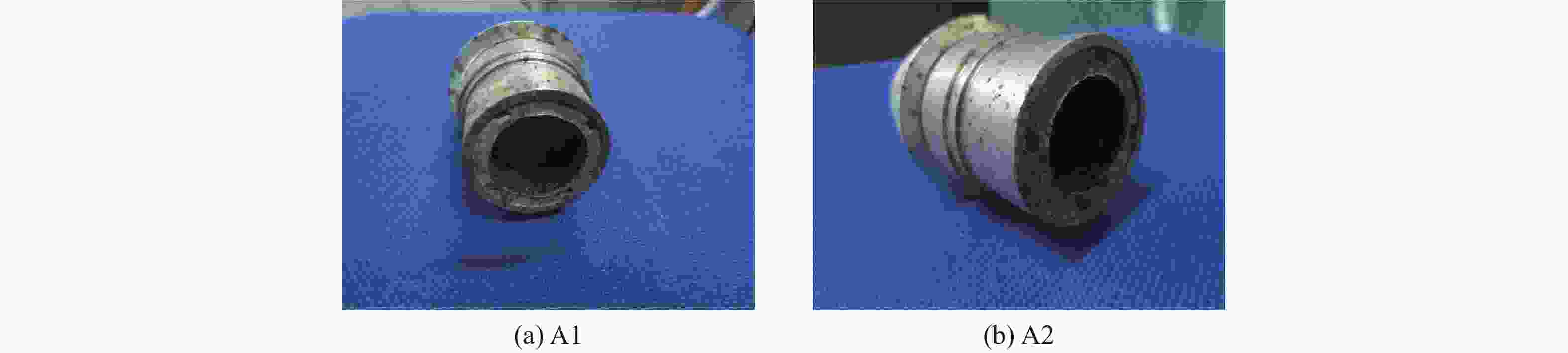
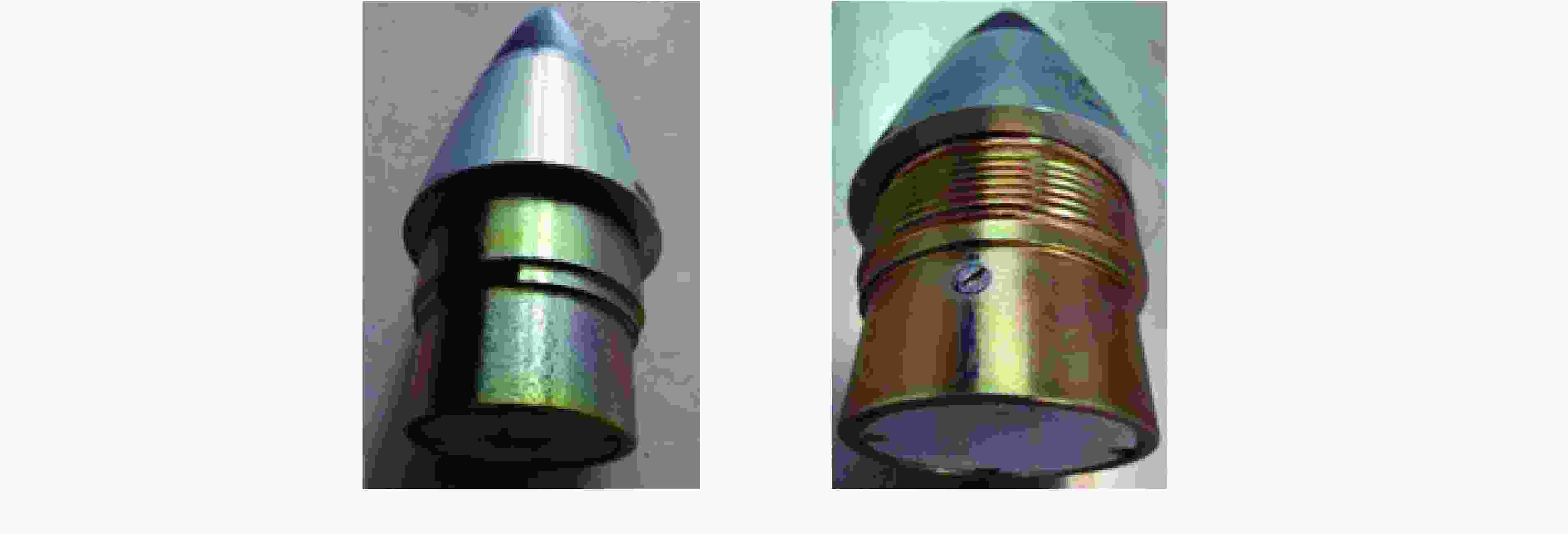
Test No. Venting structure Response time/min Response temperature/℃ Reaction violence A1 None 1566.4 180.9 Combustion A2 None 1422.7 171.0 Combustion B1 6.00 mm 1442.3 179.7 Under the combustion B2 6.00 mm 1556.8 187.7 Under the combustion 表 3 装填FOX-7炸药引信的快烤试验结果
Table 3. Fast cook-off test results of fuses with FOX-7 explosive
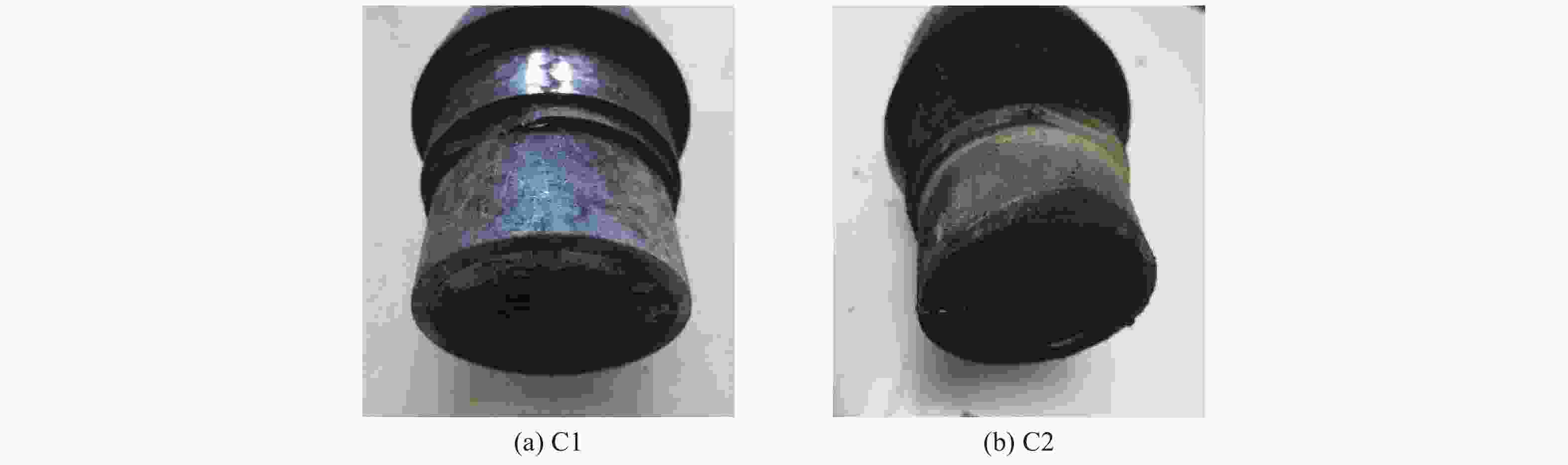
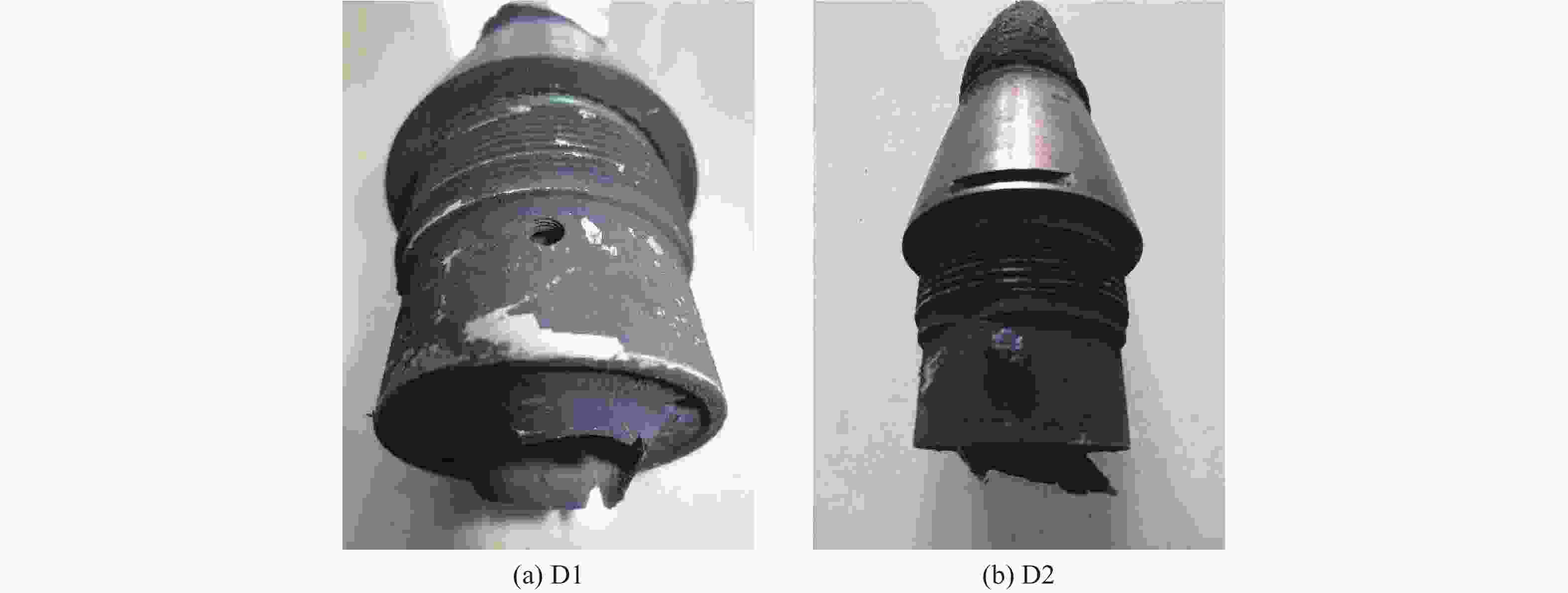
Test No. Response time/s Average temperature after flame stabilization/℃ Venting structure Reaction violence C1 108 576.0 None Combustion C2 113 576.0 None Combustion D1 59 688.5 6.00 mm Combustion D2 62 688.5 6.00 mm Combustion 表 4 FOX-7炸药的物性参数与化学反应动力学参数
Table 4. Property parameters and chemical reaction kinetic parameters of FOX-7 explosive
Material $\,\rho/({\rm {kg}}\cdot {\mathrm{m} }{^{-3} }$) ${c}{{_V}}/(\rm{J}\cdot {\rm{k}\rm{g} }{^{-1} } \cdot {\rm{K} }{^ {-1} } )$ $\lambda/(\mathrm{J}\cdot {\mathrm{m} }{^{-1}} \cdot {\mathrm{K} }{^{-1}} \cdot {\mathrm{s} }{^{-1}} )$ $Q/(\mathrm{MJ}\cdot {\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g} }{^{-1}} )$ $Z/{\mathrm{s} }{^{-1} }$ $E/(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{J}\cdot {\mathrm{m}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{l} }{^{-1}} )$ FOX-7 1600 1423.87 0.25 9.293 4.5×1026 275.97 Steel 7850 480 43 -
[1] KELLEY S, CENTER A A, DIRECTORATE A. Venting techniques for penetrator warheads [C]//Insensitive Munitions & Energetic Materials Technology Symposium. Munich, Germany, 2010. [2] MADSEN T, DEFISHER S, BAKER E L, et al. Explosive venting technology for cook-off response mitigation: ARMET-TR-10003 [R]. Picatinny Arsenal, NJ: Munitions Engineering Technology Center, 2010. [3] 陈科全, 黄亨建, 路中华, 等. 一种弹体排气缓释结构设计方法与试验研究 [J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2015, 35(4): 15–18. doi: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2015.04.004CHEN K Q, HUANG H J, LU Z H, et al. Structural design and experimental study on venting of projectile body [J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2015, 35(4): 15–18. doi: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2015.04.004 [4] 沈飞, 王胜强, 王辉. HMX基含铝炸药装药慢烤缓释结构设计及验证 [J]. 含能材料, 2019, 27(10): 861–866. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2018273SHEN F, WANG S Q, WANG H. Slow release structure design and verification of HMX-based aluminized explosive charge under slow cook-off condition [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2019, 27(10): 861–866. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2018273 [5] GRAHAM K J. Mitigation of fuel fire threat to large rocket motors by venting [C]//Insensitive Munitions & Energetic Materials Symposium. Munich, Germany, 2010. [6] KINNEY G F, SEWELL R G S. Venting of explosions: NWC TM 2448 [R]. China Lake: Naval Weapons Center, 1974. [7] SINDITSKII V P, LEVSHENKOV A I, EGORSHEV V Y, et al. Study on combustion and thermal decomposition of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene (FOX-7) [C]//Proceedings of the International Pyrotechnics Seminar. California, 2006. [8] 胡荣祖, 赵凤起, 高红旭, 等. 用C-H-N-O炸药的M、ρ、ΔfH mθ、C p、Tigorb和爆轰产物的ΔfH mθ估算炸药的爆轰性能 [J]. 火炸药学报, 2013, 36(2): 20–23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2013.02.005HU R Z, ZHAO F Q, GAO H X, et al. Estimation of detonation performances of explosives using M, ρ, ΔfHmθ, C p, Tigorb of C-H-O-N explosives and ΔfHmθ of detonation products [J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2013, 36(2): 20–23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2013.02.005 [9] 薛超阳, 智小琦, 王帅, 等. 某引信及其等效构件的慢速烤燃研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2019, 40(5): 962–967. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.05.008XUE C Y, ZHI X Q, WANG S, et al. Study of cook-off of a fuze and its equivalent components [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2019, 40(5): 962–967. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.05.008 [10] BOBELEV V K, MARGOLIN A D, CHUIKO S V. The mechanism by which combustion products penetrate into the pores of a charge explosive material [J]. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences, 1965. [11] 杨世铭. 传热学[M]. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1987: 330−333.YANG S M. Heat transfer [M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1987: 330−333. [12] 吴松, 李明海, 张中礼. 火灾环境下含炸药结构传热问题的数值模拟 [J]. 含能材料, 2014, 22(5): 617–623. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2014.05.008WU S, LI M H, ZHANG Z L. Numerical simulation of heat transfer problems in structure with explosive under fire [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2014, 22(5): 617–623. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2014.05.008 [13] CONOLLY R, DAVIES R M. A study of convective heat transfer from flames [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1972, 15(11): 2155–2172. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(72)90039-7 -







 下载:
下载: