Strain Response and Analysis of Pressure Vessels with Small Delamination Defects
-
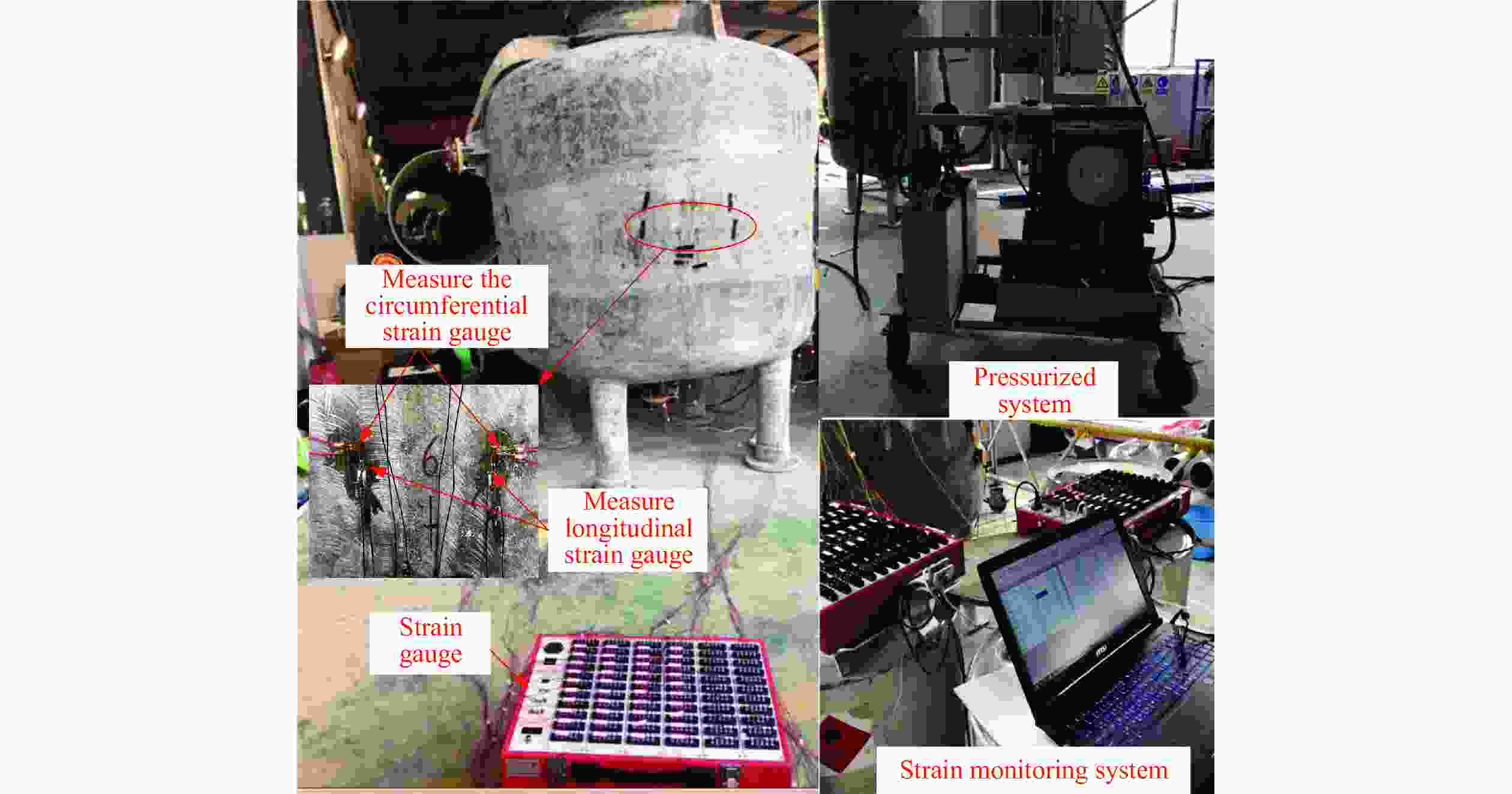
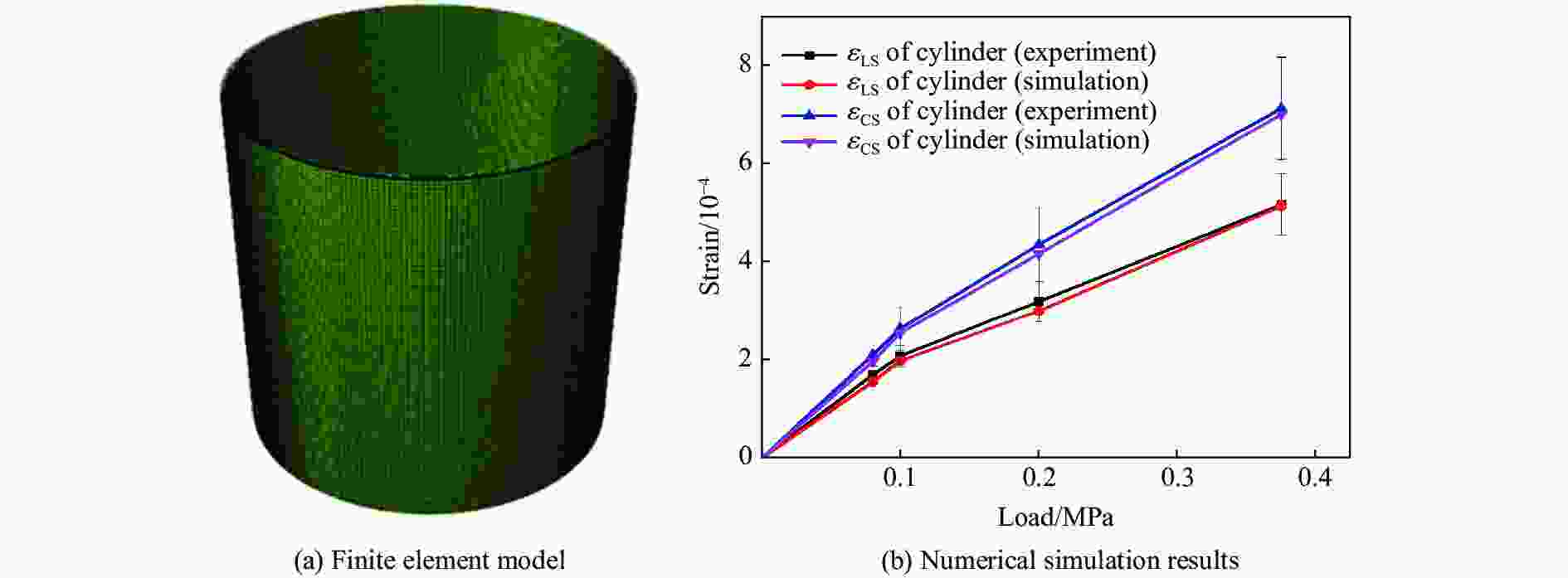
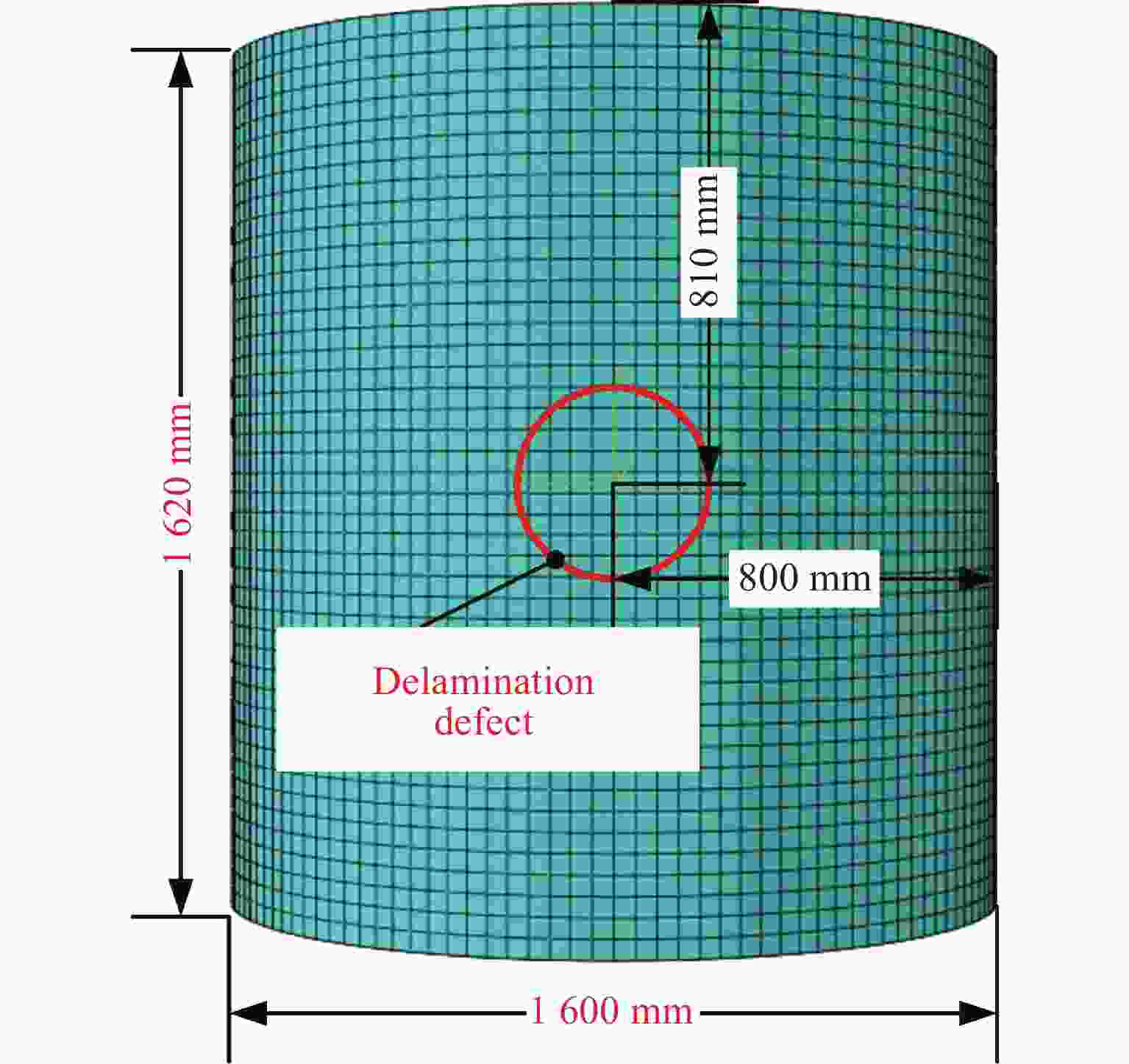
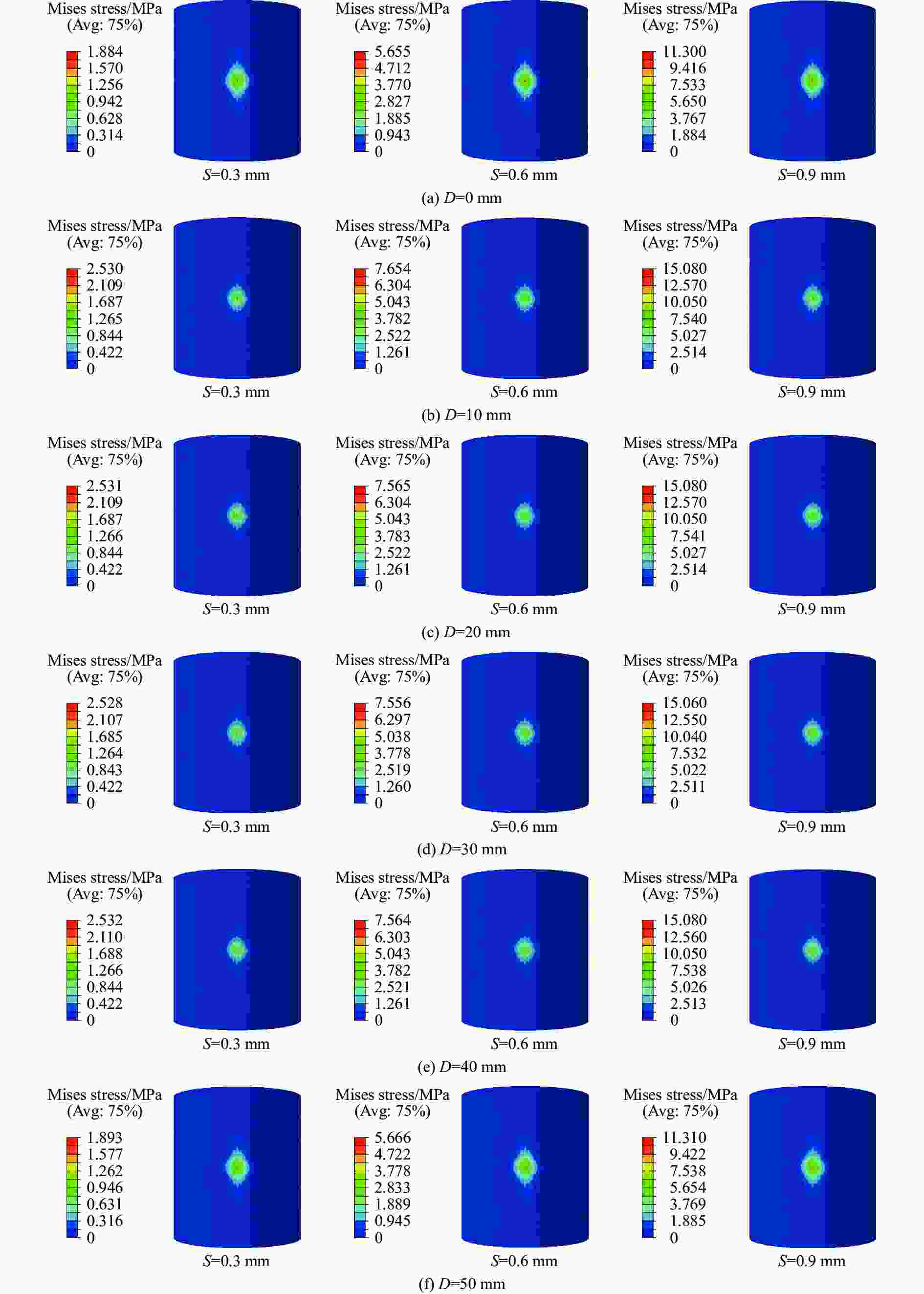
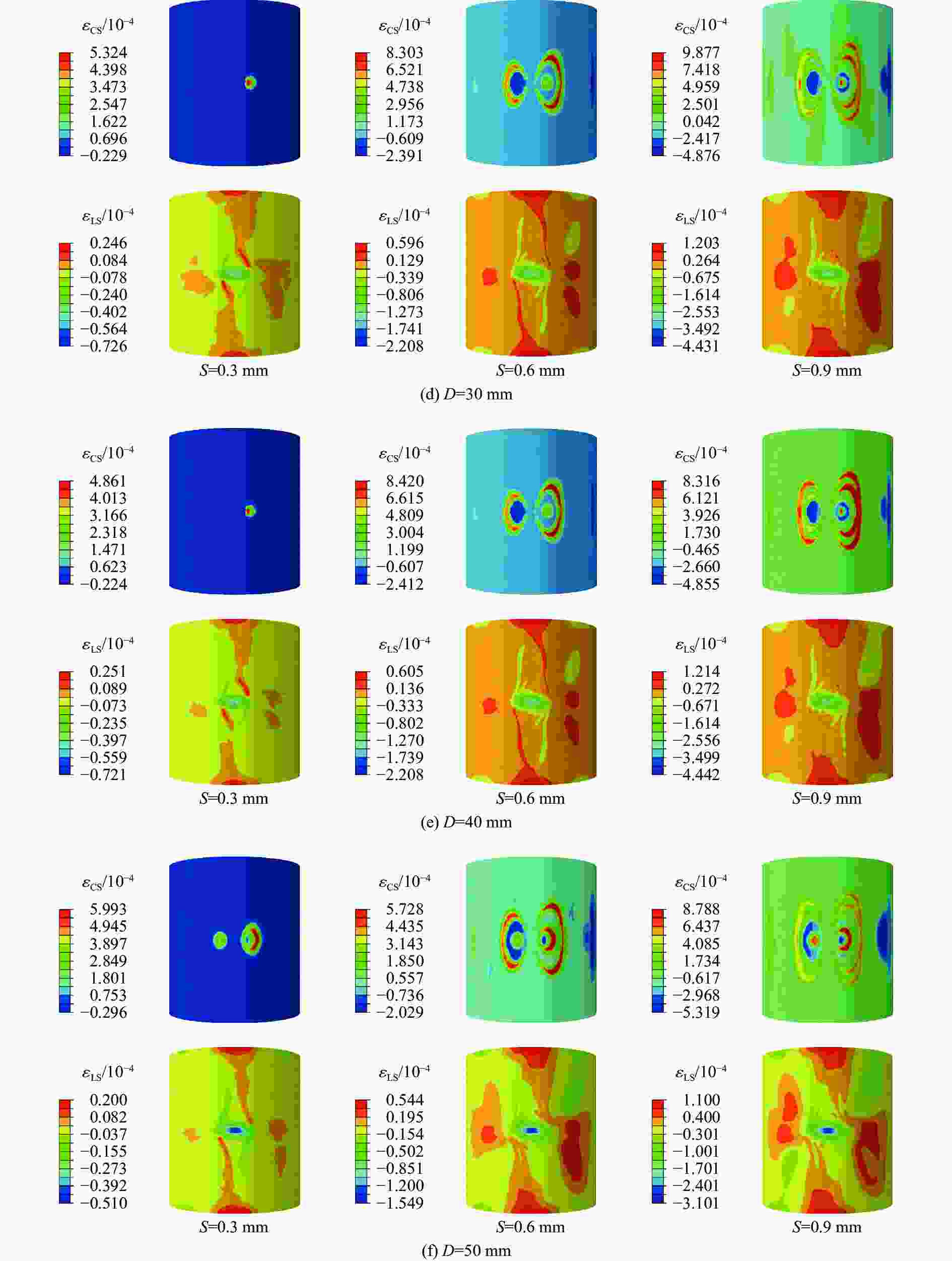
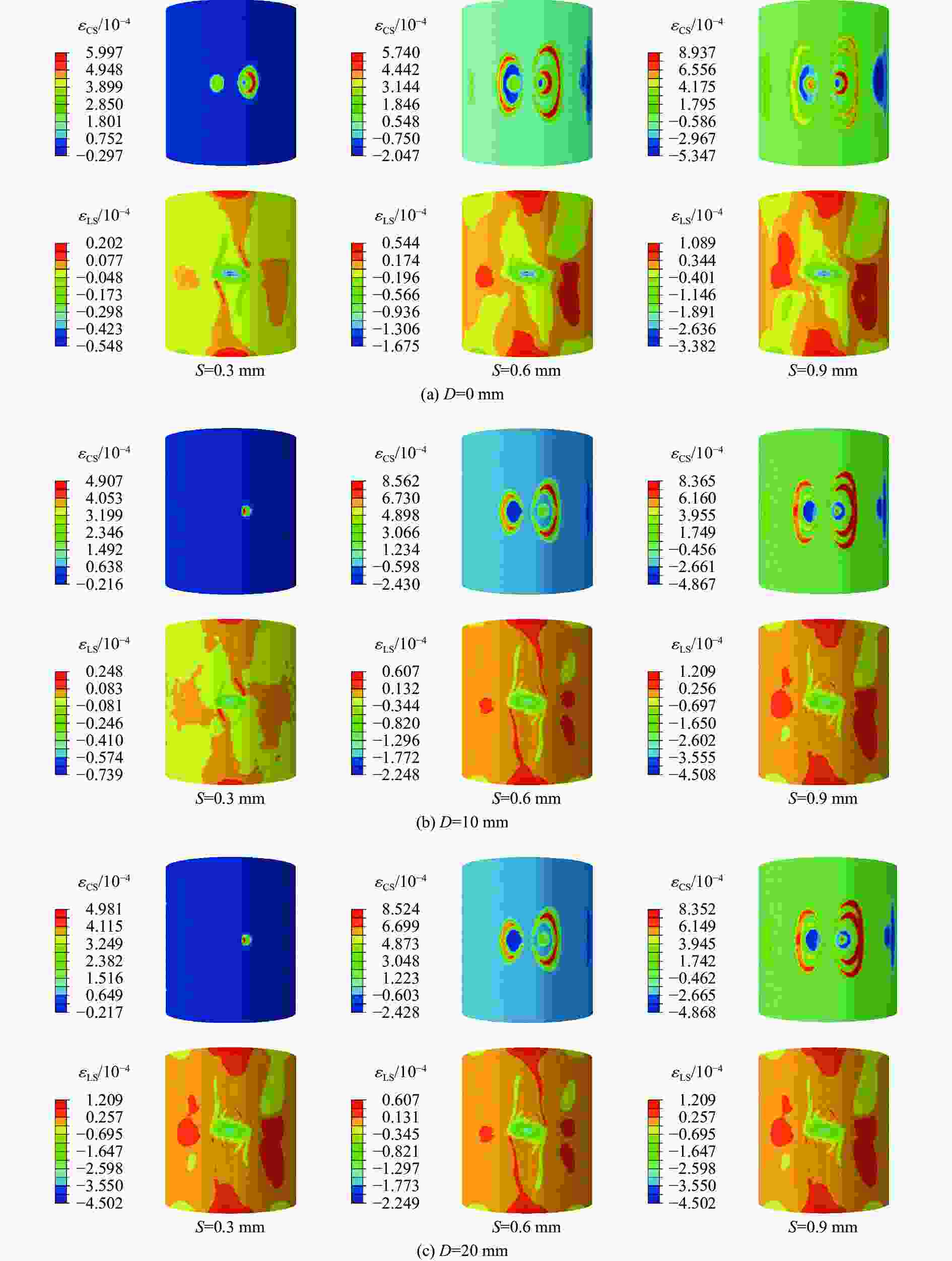
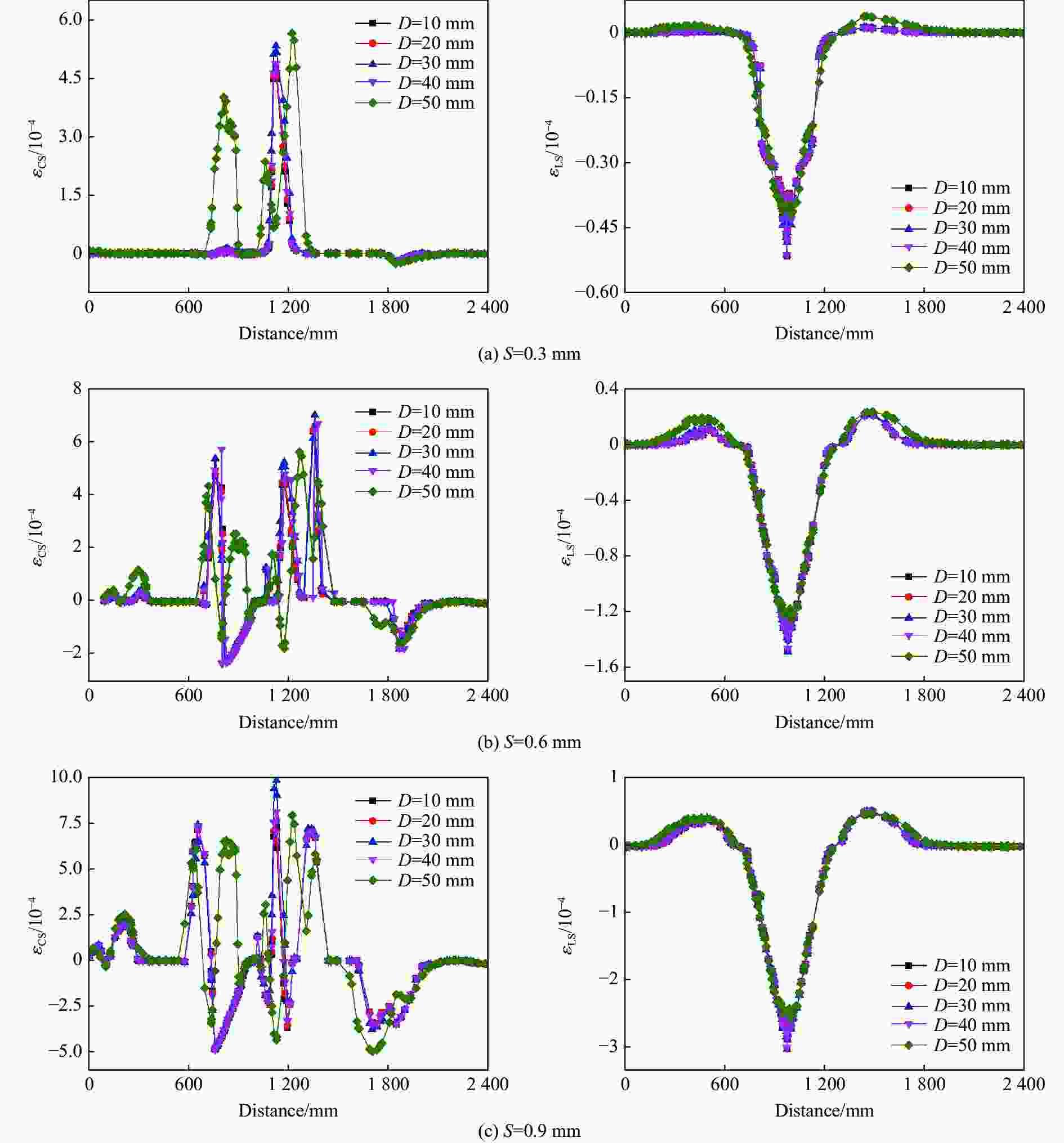
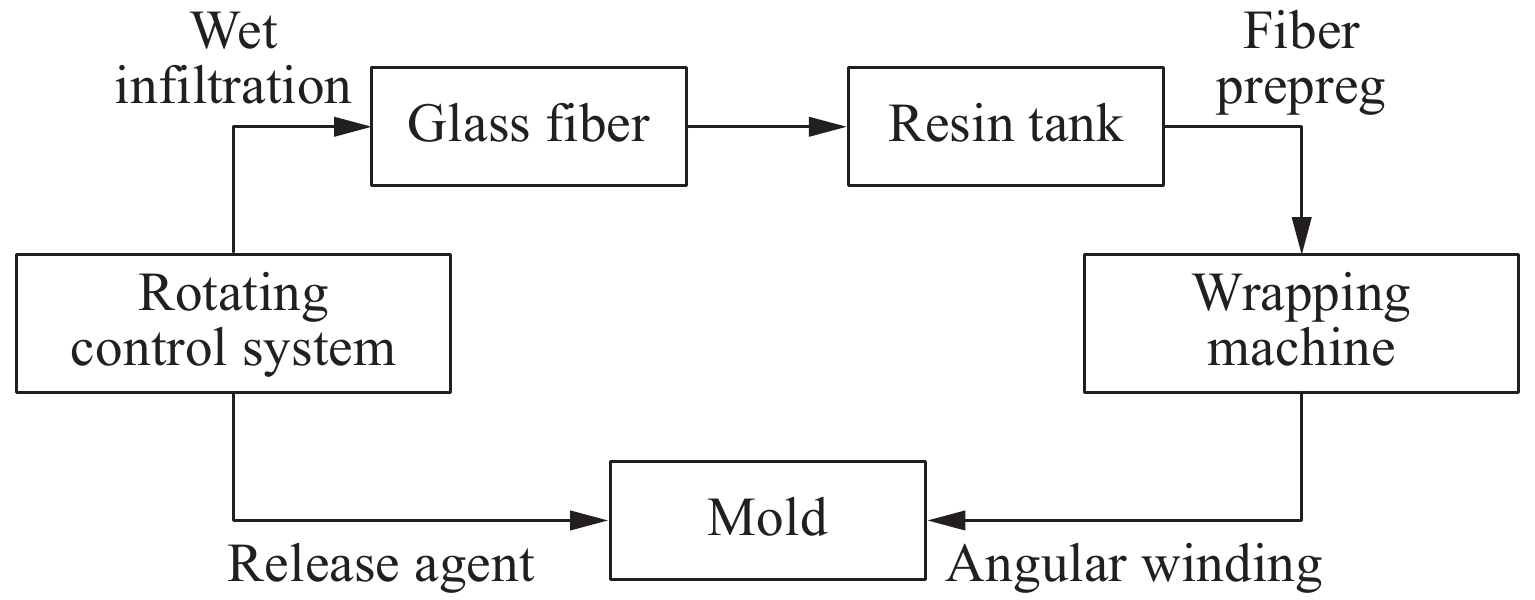
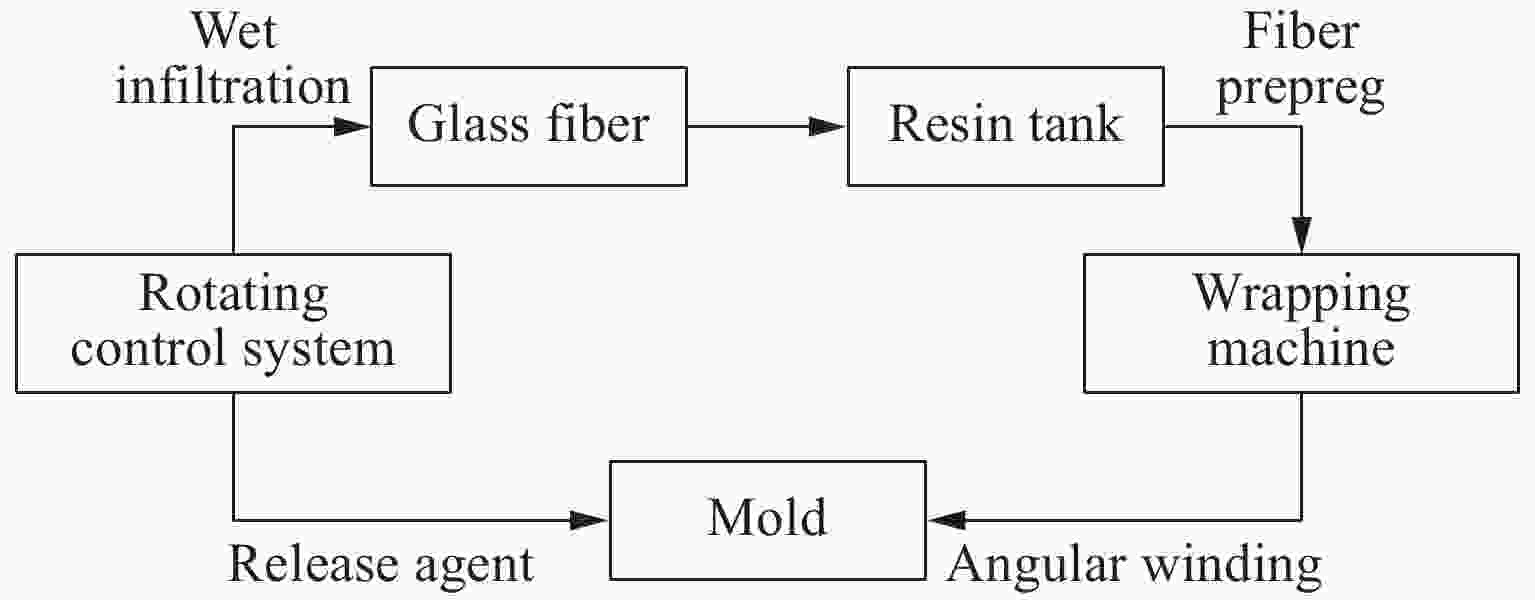
摘要: 采用乙烯基酯树脂预浸料,利用缠绕法制造了ECR耐腐蚀玻璃纤维增强环氧树脂基复合材料压力容器,在水压试验过程中基于电测法测量压力容器筒体的应变变化情况,结合Abaqus/Explicit有限元模拟重点预测了含有内部分层缺陷的压力容器在外载荷作用下的应变响应。试验和模拟结果表明:该有限元模型的结果与实验结果的相对误差小于12%;当含有内部分层缺陷(缺陷直径分别为10、20、30、40和50 mm)的复合材料压力容器受到位移载荷时,周向应变是主要应变,最大纵向应变和Mises应力位置与加载位置重合,且最大Mises应力随分层面积的增加而增大。Abstract: Using vinyl ester resin prepreg and winding method, a ECR corrosion resistant glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin matrix composite pressure vessel was manufactured. The strain variation of the pressure cylinder was measured in the hydraulic test using the electrical method.And the strain response of the pressure vessel with internal delamination defects under external loadings was predicted by Abaqus/Explicit finite element simulation. The experimental and simulation results show that the error between the results of the finite element model and the experimental results is less than 12%. When the composite pressure vessel containing internal delamination defects (defect diameter 10, 20, 30, 40 and50 mm) is subjected to displacement load, the circumferential strain is the main strain, the maximum longitudinal strain and Mises stress position coincide with the loading position, and the maximum Mises stress increases with the increasing delamination area.
-
Key words:
- composite material /
- pressure vessel /
- defect /
- strain /
- delamination
-
表 1 玻璃纤维/环氧树脂复合材料板的刚度参数[18-19]
Table 1. Stiffness parameters of glass fiber/epoxy resin composite plate[18-19]
E1/GPa E2/GPa E3/GPa G12/GPa G13/GPa G23/GPa v12 v13 v23 39.39 ± 0.36 18.10 ± 0.24 18.10 ± 0.24 6.31 ± 0.38 6.00 ± 0.27 6.00 ± 0.27 0.270 ± 0.012 0.350 ± 0.015 0.350 ± 0.015 表 2 玻璃纤维/环氧树脂复合材料板的强度参数[18-19]
Table 2. Strength parameters of glass fiber/epoxy rsesin composite plate[18-19]
MPa XT XC YT YC ZT ZC S12 S13 S23 222.7 ± 18.0 200 ± 22 136 ± 22 100 ± 4 50 ± 2 100 ± 4 90.5 ± 4.2 50.00 ± 3.12 50.00 ± 3.12 表 3 玻璃纤维压力容器的材料刚度递减规则
Table 3. Decreasing rules of material stiffness for glass fiber pressure vessels
Failure mode Rules for decreasing stiffness of materials Tensile damage of longitudinal fiber E11 = 0.07E11, G12 = 0.07G12, G13 = 0.07G13, v12 = 0.07v12, v13 = 0.07v13 Compression damage of transverse E11 = 0.14E11, G12 = 0.14G12, G13 = 0.14G13, v12 = 0.14v12, v13 = 0.14v13 Radial fiber tensile damage E22 = 0.2E22, G12 = 0.2G12, G23 = 0.2G23, v12 = 0.2v12, v23 = 0.2v23 Radial fiber compression damage E22 = 0.4E22, G12 = 0.4G12, G23 = 0.4G23, v12 = 0.4v12, v23 = 0.4v23 Z-direction fiber tensile damage E33 = 0.2E33, G13 = 0.2G13, G23 = 0.2G23, v13 = 0.2v13, v23 = 0.2v23 Z-direction fiber compression damage E33 = 0.2 E33, G13 = 0.2G13, G23 = 0.2G23, v13 = 0.2v13, v23 = 0.2v23 -
[1] HAN M G, CHANG S H. Failure analysis of a Type Ⅲ hydrogen pressure vessel under impact loading induced by free fall [J]. Composite Structures, 2015, 127: 288–297. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.03.027 [2] PERILLO G, GRYTTEN F, SØRBØ S, et al. Numerical/experimental impact events on filament wound composite pressure vessel [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2015, 69: 406–417. [3] 杨留鑫. 低速冲击载荷下复合材料缠绕压力容器的损伤分析 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2012.YANG L X. Damage analysis of composite overwrapped pressure vessel under low velocity impact [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2012. [4] HER S C, LIANG Y C. The finite element analysis of composite laminates and shell structures subjected to low velocity impact [J]. Composite Structures, 2004, 66(1/2/3/4): 277–285. [5] SHI Y, SWAIT T, SOUTIS C. Modelling damage evolution in composite laminates subjected to low velocity impact [J]. Composite Structures, 2012, 94(9): 2902–2913. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.03.039 [6] 王晓宏, 张博明, 刘长喜, 等. 纤维缠绕复合材料压力容器渐进损伤分析 [J]. 计算力学学报, 2009, 26(3): 446–452.WANG X H, ZHANG B M, LIU C X, et al. Progressive failure analysis of composite overwrapped pressure vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2009, 26(3): 446–452. [7] OKABE Y, TSUJI R, TAKEDA N. Application of chirped fiber Bragg grating sensors for identification of crack locations in composites [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2004, 35(1): 59–65. [8] 何录菊, 马李. 复合材料压力容器输进损伤的模拟研究 [J]. 台州学院学报, 2011, 33(6): 36–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3708.2011.06.008HE L J, MA L. Study on simulation progressive damage of composite pressure vessel [J]. Journal of Taizhou University, 2011, 33(6): 36–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3708.2011.06.008 [9] 饶辉, 许希武, 朱炜垚, 等. 复合材料加筋板低速冲击损伤的数值模拟 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(4): 211–218.RAO H, XU X W, ZHU W Y, et al. Numerical simulation of low velocity impact damage on stiffened composite panels [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2013, 30(4): 211–218. [10] SHIVAKUMAR K N, ELBER W, ILLG W. Prediction of impact force and duration due to low-velocity impact on circular composite laminates [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1985, 52(3): 674–680. doi: 10.1115/1.3169120 [11] ZU L, XU H, ZHANG B, et al. Design and production of filament-wound composite square tubes [J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 191: 202–208. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.02.069 [12] ZU L, WANG J H, LI S X. Influence of fiber slippage coefficient distributions on the geometry and performance of composite pressure vessels [J]. Polymer Composites, 2016, 37: 315–321. doi: 10.1002/pc.23183 [13] ZHANG B, XU H, ZU L, et al. Design of filament-wound composite elbows based on non-geodesic trajectories [J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 189: 635–640. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.02.008 [14] HAO J C, LENG J S, WEI Z. Non-destructive evaluation of composite pressure vessel by using FBG sensors [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2007, 20(2): 120–123. [15] LIU P F, ZHENG J Y. Progressive failure analysis of carbon fiber/epoxy composite laminates using continuum damage mechanics [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 48(1/2): 5711–5717. [16] 王莉, 刘国强, 肖迎春. 基于代理模型的复合材料加筋壁板分层损伤定量监测方法 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(2): 302–308.WANG L, LIU G Q, XIAO Y C. Quantitative monitoring method for delamination damage of stiffened composite panel based on surrogate model [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(2): 302–308. [17] KHECHAI A, TATI A, GUERIRA B, et al. Strength degradation and stress analysis of composite plates with circular, square and rectangular notches using digital image correlation [J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 185: 699–715. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.11.060 [18] ALSHAHRANI R F, MERAH N, KHAN A M A, et al. On the impact-induced damage in glass fiber reinforced epoxy pipes [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 97: 57–65. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.06.002 [19] YANG B, HE L, GAO Y. Simulation on impact response of FMLs: effect of fiber stacking sequence, thickness, and incident angle [J]. Science and Engineering of Composite Materials, 2018, 25(3): 621–631. doi: 10.1515/secm-2016-0226 -






 下载:
下载: