Structural Properties and Phase Transition of Pyroxene Polymorphs from First-Principles
-
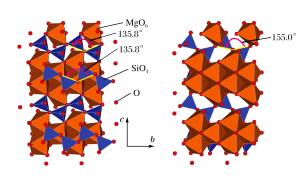
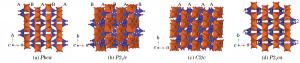
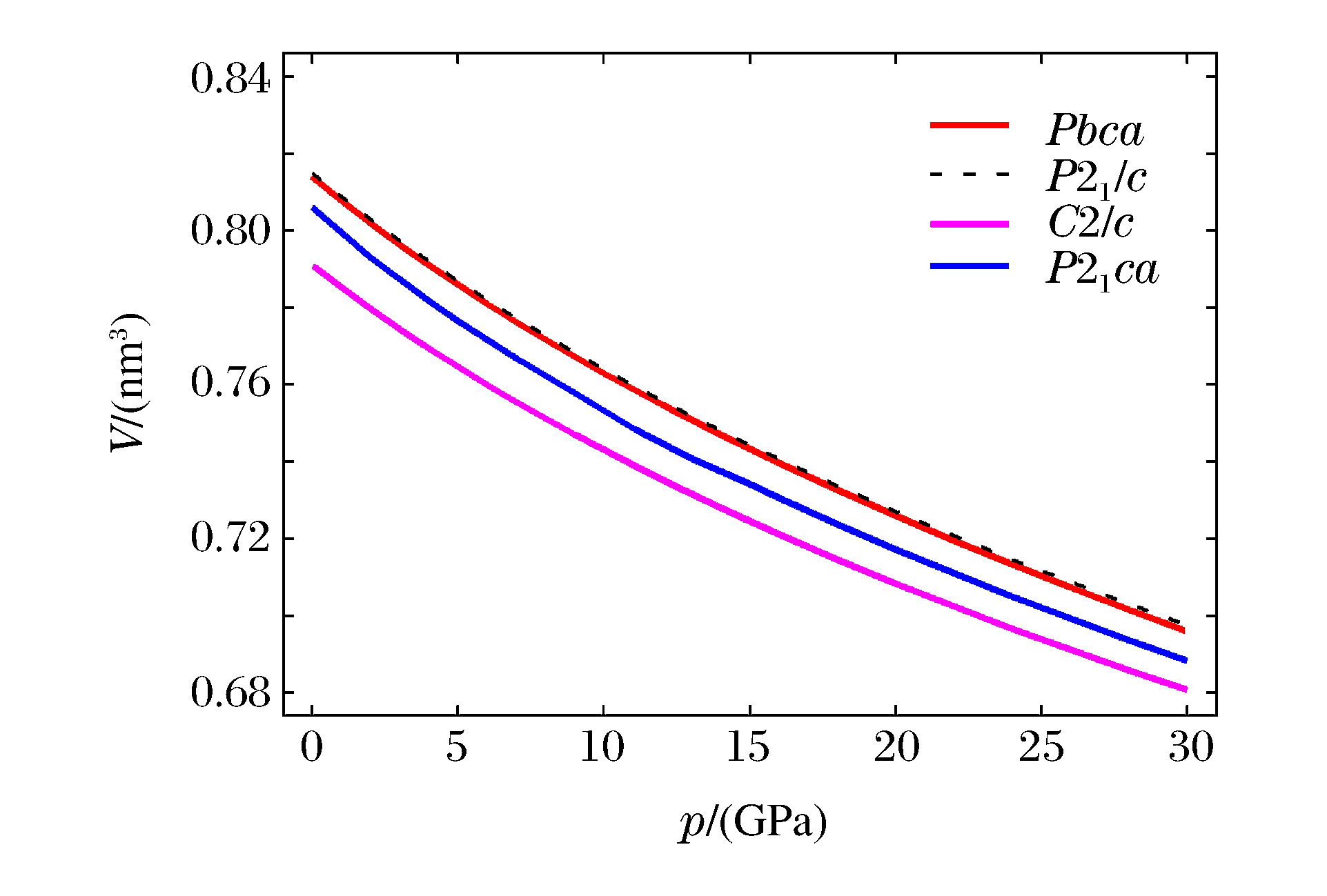
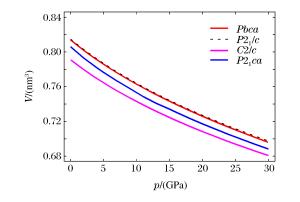
摘要: 利用第一性原理方法研究了Mg端员辉石(MgSiO3)低压相(Pbca、P21/c)和高压相(C2/c、P21ca)在不同压力下(0~30 GPa)的结构。首先计算得到了不同压力下各相的晶胞体积,并由状态方程拟合得到了体积模量,结果显示在零温零压条件下Pbca和P21/c(低压单斜相)的体积模量相近,C2/c的体积模量最大(比Pbca的大3%),而P21ca作为高压相其体积模量却比Pbca小很多。其次分析了Mg端员辉石3个轴向的压缩性,发现C2/c相的c轴比a轴难压缩,与前人研究的透辉石(MgCaSi2O6)的表现相反。P21/c、C2/c、P21ca的链角随着压力的增大而减小;Pbca其中一种链角的变化趋势和其他3个相一样,而另一种链角先随着压力的增大而减小,在达到7 GPa后开始增大,可能表示相的不稳定或开始相变。最后通过研究不同相之间的焓值差,讨论了Mg端员辉石在低温高压下可能存在的相变情况。Abstract: In order to evaluate the structures of magnesium end-member pyroxene polymorphs (MgSiO3) under different pressures, first-principles theoretical calculation on low- and high-pressure phases, with space group Pbca, P21/c, C2/c, P21ca respectively, was conducted under pressures up to 30 GPa.The bulk moduli of polymorphs were obtained from fitting the third-order Birch-Murnaghan equation with calculated pressure-volume data.The C2/c phase had the largest modulus (an increase of 3% compared to Pbca) under zero-temperature and zero-pressure, whereas little difference was observed between moduli of Pbca and P21/c, and the high-pressure phase P21ca showed a smaller value than Pbca.Moreover, the results of axial compression showed that the c-axis was harder to compress than a-axis in C2/c, which was opposite to the previous first-principle results on diopside (MgCaSi2O6).The angels of SiO4 tetrahedral chains in P21/c, C2/c, and P21ca decreased monotonically as a function of pressure while in Pbca, which had two kinds of angles, one showed the same trend as the aforementioned three polymorphs and the other increased monotonically above 7 GPa, implying an unstable structure or the onset of a new phase transition.The static enthalpy differences among the four polymorphs indicated the possible phase transitions of the pyroxene under low-temperature and high-pressure.
-
Key words:
- first-principles /
- pyroxene /
- phase transition /
- bulk modulus /
- axial compression
-
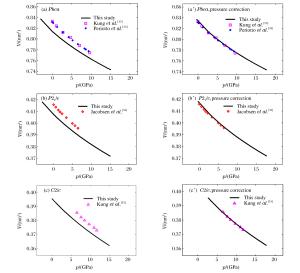
图 2 不同压力下,Pbca、P21/c以及C2/c的晶胞体积计算结果和实验结果的比较(左图和右图分别为加压力校正前和加压力校正后;为了方便与实验数据对比,对于Pbca和P21/c,计算的压力范围为-3~15 GPa)
Figure 2. Comparisons of unit cell volumes of Pbca, P21/c and C2/c under different pressures from first-principles and experiments (The pressure ranged from -3 GPa to 15 GPa and a pressure correction of 2.7 GPa was applied to all first-principles results in right figures)
表 1 Mg端员辉石晶胞体积、体积模量的计算结果(0 K)和实验结果(室温)
Table 1. Unit cell volumes and elastic moduli of Mg end-member pyroxene polymorphs from first-principles results (at 0 K) and experiments (at room temperature)
Space group V/(nm3) K/(GPa) K′ Reference Pbca 0.813 8 130.8(0.6) 5.2 This study (LDA) 0.812 239(90) 129 Kung et al., 2004 (2.7 GPa)[15] 0.812 5(1) Periotto et al., 2012 (2.69 GPa)[33] 0.832 918(114) 108(1) 7.2(7) Kung et al., 2004 (Ambient condition)[15] P21/c 0.407 4 131.0(0.4) 5.2 This study (LDA) 0.409 Yu et al., 2010 (LDA)[29] 0.397 Jahn, 2008 (LDA)[17] 0.407 Jacobsen et al., 2010 (2.58 GPa)[34] 0.415 78 113(2) 6.6(9) Jacobsen et al., 2010 (Ambient condition)[34] 0.416 7 Kung et al., 2004 (Ambient condition)[15] C2/c 0.395 4 134.7(0.5) 5.5 This study (LDA) 0.382 3 This study (LDA; 4.98 GPa) 0.375 6 This study (LDA; 8.0 GPa) 0.379 1 Yu et al., 2010 (LDA; 7.9 GPa)[29] 0.382 317(57) 163 Kung et al., 2004 (Room temperature, 7.6 GPa)[15] P21ca 0.805 8 121.7(2.5) 5.7 This study (LDA) 0.753 6 This study (LDA; 10 GPa) 0.733 9 Jahn, 2008 (LDA; 10 GPa)[17] 表 2 辉石的轴向体积模量以及轴向压缩性比值
Table 2. Axial moduli and compressibility ratios of pyroxenes
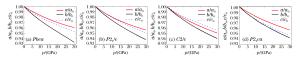
Space group Ka 0/(GPa) Kb 0/(GPa) Kc 0/(GPa) βa:βb:βc Pbca 160.7 106.1 135.1 0.66:1.00:0.79 P21/c 132.6 106.7 138.9 0.80:1.00:0.77 C2/c 124.2 111.9 150.5 0.90:1.00:0.74 P21ca 152.3 110.4 102.1 0.72:1.00:1.08 -
[1] ANDERSON D L.New theory of the earth[M].New York:Cambridge University Press, 2007:30-32. [2] 佐尔泰T, 斯托特J H.矿物学原理[M].施倪承, 马喆生, 译.北京: 地质出版社, 1992: 353-355.ZOLTAI T, STOUT J H.Mineralogy: concepts and principles[M].Translated by SHI N C, MA Z S.Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1992: 353-355. [3] DUFFY T S, VAUGHAN M T.Elasticity of enstatite and its relationship to crystal structure[J].J Geophys Res, 1988, 93(B1):383-391. doi: 10.1029/JB093iB01p00383 [4] MORIMOTO N, KOTO K.The crystal structure of orthoenstatite[J].Z Kristallogr, 1969, 129(1-6):65-83. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=432200f92f81f62696700f8f6cc3f1ae&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] MORIMOTO N, APPLEMAN D E, EVANS H T Jr.The crystal structures of clinoenstatite and pigeonite[J].Z Kristallogr, 1960, 114(1-6):120-147. doi: 10.1524/zkri.1960.114.1-6.120 [6] ANGEL R J, CHOPELAS A, ROSS N L.Stability of high-density clinoenstatite at upper-mantle pressures[J].Nature, 1992, 358(6384):322-324. doi: 10.1038/358322a0 [7] ZHANG J S, DERA P, BASS J D.A new high-pressure phase transition in natural Fe-bearing orthoenstatite[J].Am Mineral, 2012, 97(7):1070-1074. doi: 10.2138/am.2012.4072 [8] ZHANG J S, REYNARD B, MONTAGNAC G, et al.Pressure-induced Pbca-P21/c phase transition of natural orthoenstatite:compositional effect and its geophysical implications[J].Am Mineral, 2013, 98(5/6):986-992. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031920113001428 [9] ZHANG J S, REYNARD B, MONTAGNAC G, et al.Pressure-induced Pbca-P21/c phase transition of natural orthoenstatite:the effect of high temperature and its geophysical implications[J].Phys Earth Planet Inter, 2014, 228:150-159. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2013.09.008 [10] YANG H, FINGER L W, CONRAD P G, et al.A new pyroxene structure at high pressure:single-crystal X-ray and Raman study of the Pbcn-P21cn phase transition in protopyroxene[J].Am Mineral, 1999, 84(3):245-256. doi: 10.2138/am-1999-0305 [11] JACKSON J M, SINOGEIKIN S V, CARPENTER M A, et al.Novel phase transition in orthoenstatite[J].Am Mineral, 2004, 89(1):239-244. doi: 10.2138/am-2004-0128 [12] MATSUI M, PRICE G D.Computer simulation of the MgSiO3 polymorphs[J].Phys Chem Miner, 1992, 18(6):365-372. doi: 10.1007/BF00199417 [13] YANG H, PREWITT C T.Chain and layer silicates at high temperatures and pressures[J].Rev Mineral Geochem, 2000, 41(1):211-255. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2000RvMG...41..211Y [14] LIN C C.Pressure-induced metastable phase transition in orthoenstatite (MgSiO3) at room temperature:a Raman spectroscopic study[J].J Solid State Chem, 2003, 174(2):403-411. doi: 10.1016/S0022-4596(03)00278-0 [15] KUNG J, LI B, UCHIDA T, et al.In situ measurements of sound velocities and densities across the orthopyroxene→high-pressure clinopyroxene transition in MgSiO3 at high pressure[J].Phys Earth Planet Inter, 2004, 147(1):27-44. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2004.05.008 [16] LIN C M, CHAO J L, LIN C C.Metastable phase transition of orthoenstatite (MgSiO3) under high pressure[J].Solid State Sci, 2005, 7(3):293-297. doi: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2004.10.005 [17] JAHN S.High-pressure phase transitions in MgSiO3 orthoenstatite studied by atomistic computer simulation[J].Am Mineral, 2008, 93(4):528-532. doi: 10.2138/am.2008.2710 [18] JAHN S.Integral modeling approach to study the phase behavior of complex solids:application to phase transitions in MgSiO3 pyroxenes[J].Acta Crystallogr Sect A, 2010, 66(5):535-541. doi: 10.1107/S0108767310026449 [19] WOODLAND A B.The orthorhombic to high-p monoclinic phase transition in Mg-Fe pyroxenes:can it produce a seismic discontinuity?[J].Geophys Res Lett, 1998, 25(8):1241-1244. doi: 10.1029/98GL00857 [20] LI B, KUNG J, LIU W, et al.Phase transition and elasticity of enstatite under pressure from experiments and first-principles studies[J].Phys Earth Planet Inter, 2014, 228:63-74. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2013.11.009 [21] GIANNOZZI P, BARONI S, BONINI N, et al.QUANTUM ESPRESSO:a modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials[J].J Phys:Condens Matter, 2009, 21(39):1-19. doi: 10.1088-0953-8984-21-39-395502/ [22] CEPERLEY D M, ALDER B J.Ground state of the electron gas by a stochastic method[J].Phys Rev Lett, 1980, 45(7):566-569. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.45.566 [23] PERDEW J P, ZUNGER A.Self-interaction correction to density-functional approximations for many-electron systems[J].Phys Rev B, 1981, 23(10):5048-5079. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.23.5048 [24] DAL CORSO A, BARONI S, RESTA R, et al.Ab initio calculation of phonon dispersions in Ⅱ-Ⅵ semiconductors[J].Phys Rev B, 1993, 47(7):3588-3592. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.47.3588 [25] VANDERBILT D.Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism[J].Phys Rev B, 1990, 41(11):7892-7895. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.41.7892 [26] MONKHORST H J, PACK J D.Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations[J].Phys Rev B, 1976, 13(12):5188-5192. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.13.5188 [27] MOLIN G M.Crystal-chemical study of cation disordering in Al-rich and Al-poor orthopyroxenes from spinel lherzolite xenoliths[J].Am Mineral, 1989, 74:593-598. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=03954abf3a5446155db74c4928b8ac22&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [28] THOMPSON R M, DOWNS R T.Model pyroxenes Ⅰ:ideal pyroxene topologies[J].Am Mineral, 2003, 88(4):653-666. doi: 10.2138/am-2003-0419 [29] YU Y G, WENTZCOVITCH R M, ANGEL R J.First principles study of thermodynamics and phase transition in low-pressure (P21/c) and high-pressure (C2/c) clinoenstatite MgSiO3[J].J Geophys Res:Solid Earth, 2010, 115(B2):1-10. doi: 10.1029/2009JB006329/full [30] HERNÁNDEZ E R, BRODHOLT J, ALFÈ D.Structural, vibrational and thermodynamic properties of Mg2SiO4 and MgSiO3 minerals from first-principles simulations[J].Phys Earth Planet Inter, 2015, 240:1-24. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2014.10.007 [31] JACKSON J M, PALKO J W, ANDRAULT D, et al.Thermal expansion of natural orthoenstatite to 1 473 K[J].Eur J Mineral, 2003, 15(3):469-473. doi: 10.1127/0935-1221/2003/0015-0469 [32] HUGH-JONES D.Thermal expansion of MgSiO3 and FeSiO3 ortho-and clinopyroxenes[J].Am Mineral, 1997, 82(7/8):689-696. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1997AmMin..82..689H [33] PERIOTTO B, BALIC-ŽUNIC T, NESTOLA F, et al.Re-investigation of the crystal structure of enstatite under high-pressure conditions[J].Am Mineral, 2012, 97(10):1741-1748. doi: 10.2138/am.2012.4157 [34] JACOBSEN S D, LIU Z, BALLARAN T B, et al.Effect of H2O on upper mantle phase transitions in MgSiO3:is the depth of the seismic X-discontinuity an indicator of mantle water content?[J].Phys Earth Planet Inter, 2010, 183(1):234-244. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031920110001354 [35] WALKER A M, TYER R P, BRUIN R P, et al.The compressibility and high pressure structure of diopside from first principles simulation[J].Phys Chem Miner, 2008, 35(7):359-366. doi: 10.1007/s00269-008-0229-3 [36] ANGEL R J, HUGH-JONES D A.Equations of state and thermodynamic properties of enstatite pyroxenes[J].J Geophys Res, 1994, 99(B10):19777-19783. doi: 10.1029/94JB01750 [37] HATTORI T, NAGAI T, YAMANAKA T, et al.Single-crystal X-ray diffraction study of FeGeO3 high-p clinopyroxene (C2/c) up to 8.2 GPa[J].Am Mineral, 2000, 85(10):1485-1491. doi: 10.2138/am-2000-1018 [38] PACAL R E G, GASPARIK T.Reversals of the orthoenstatite-clinoenstatite transition at high pressures and high temperatures[J].J Geophys Res:Solid Earth, 1990, 95(B10):15853-15858. doi: 10.1029/JB095iB10p15853 -






 下载:
下载: