Experimental Study of Wide Strain Rates and Constitutive Model Based on Damage of 5083 Aluminum Alloy
-
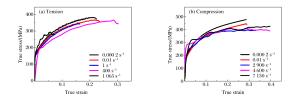
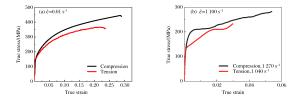
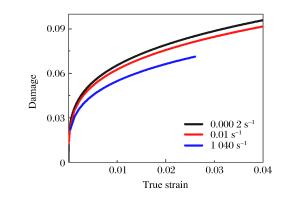
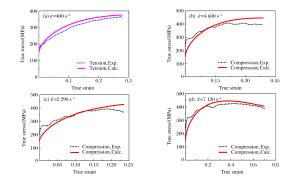
摘要: 5083铝合金材料在工程领域应用广泛,会受到包括冲击和碰撞等多种不同情况的强动加载,亟需对其宽应变率加载下的力学性能及其本构模型开展研究。首先,对5083铝合金进行了系统的准静态实验及中、高应变率加载下的拉伸和压缩实验,得到了宽应变率加载下的应力-应变曲线。实验结果表明,该材料在同一实验条件下所得到的应力-应变曲线,其强化阶段的拉伸曲线总是低于压缩曲线,并从微观机制上对这一现象进行了合理解释。然后,通过引入损伤,考虑了损伤对该材料拉伸加载情况下的力学性能影响。基于连续介质力学及其实验结果,获得了损伤演化方程。最后,借助改进的Johnson-Cook (JC)本构模型,并基于已确定的损伤演化方程,得到了考虑损伤的5083铝合金本构模型。通过实验曲线与所得模型曲线的对比,吻合良好,表明该模拟具有很好的适用性,能够对该材料的工程应用提供有效的科学依据、分析模型和必要的参考。
-
关键词:
- 5083铝合金 /
- 冲击 /
- 损伤 /
- Johnson-Cook模型 /
- 本构关系
Abstract: The 5083 aluminum alloy is widely used in engineering, and is inevitably subjected to a variety of different loadings, including strong dynamic loading such as impact and collision.Therefore it is necessary to study its mechanical properties under loading of a wide range of strain rates as well as its constitutive model.With this in view, firstly, an experimental study of the 5083 aluminum alloy was carried out at quasi-static, middle and high strain rates of tension and compression loading and the stress-strain curves of the wide strain rate were obtained.The experimental results show that in the strengthening stage, the tensile stress-strain curves are always lower than the compression stress-strain curves when the experimental condition is kept constant, so the phenomenon is explained by microscopic mechanism.Then, by introducing damage into our study, the effects of damage on the material's mechanical properties were considered under impact tensile loading.Based on the continuum mechanics and experimental results, the damage evolution equation was obtained.Finally, by improving the Johnson-Cook (JC) constitutive model and the existing damage evolution equation, the dynamic constitutive model considering the damage of the 5083 aluminum alloy was established.By comparing the experimental curves with the model curves, it was found that their fitting is good, showing that the proposed model has good applicability.Our research can serve as an effective scientific basis, an analytical model and necessary reference for the engineering application of the 5083 aluminum alloy.-
Key words:
- 5083 aluminum alloy /
- impact /
- damage /
- Johnson-Cook model /
- constitutive relation
-
表 1 5083铝合金化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of 5083 aluminum alloy
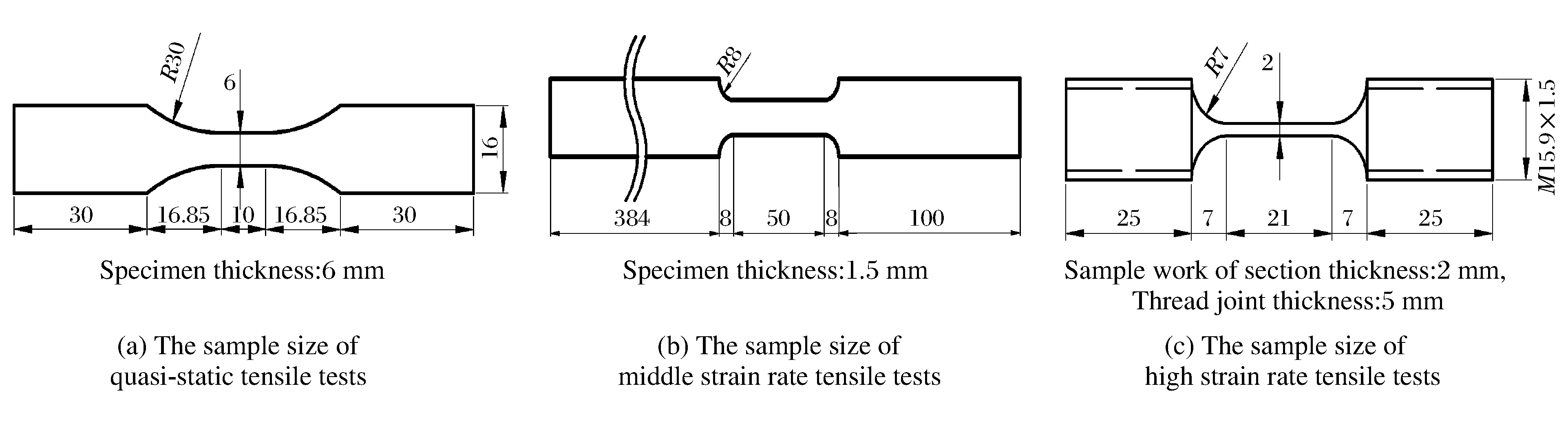
(%) Mg Mn Si Zn Ti Cu Cr Fe 4.0-4.9 0.40-1.00 ≤0.40 ≤0.25 ≤0.15 ≤0.10 0.05-0.25 0.0-0.4 表 2 压缩实验试样尺寸
Table 2. Sample specifications in compression tests
$ \dot \varepsilon $/(s-1) d/(mm) h/(mm) 0.000 2, 1 270-2 700 10 8 0.001, 2 700-3 800 10 6 0.01, 2 100-7 130 6 4 表 3 屈服应力随应变率的变化关系
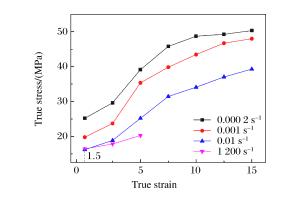
Table 3. Variation of yield stress with strain rates
$ \dot \varepsilon $/(s-1) σs/(MPa) 0.000 2 152.21 0.010 0 151.21 1 150.54 10 149.31 100 166.11 400 177.66 表 4 应变率敏感系数
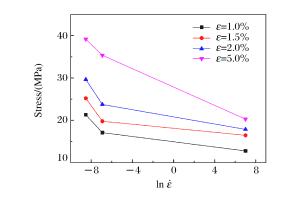
Table 4. Strain rate sensitivity coefficient
λ Sensitivity coefficient Tension Compression λ1 -3.698 61 -4.440 0 λ2 8.660 89 5.809 4 表 5 5083铝合金的JC模型参数
Table 5. JC model parameters of 5083 aluminum alloy
A n C1 C2 Dk e f p q εth 149.3 0.626 6 -0.002 97 0.018 01 0.110 7 -0.004 75 0.149 4 6.824 6 -1.447 5 0.002 42 -
[1] BENALLAL A, BERSTAD T, BØRVIK T, et al.An experimental and numerical investigation of the behaviour of AA5083 aluminium alloy in presence of the Portevin-Le Chatelier effect [J].Int J Plant Sci, 2008, 24:1916-1945. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0749641908000570 [2] CLAUSEN A H, BØRVIK T, HOPPERSTAD O S, et al.Flow and fracture characteristics of aluminium alloy AA5083-H116 as function of strain rate, temperature and triaxiality [J].Mat Sci Eng R, 2004, A364:260-272. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921509303007032 [3] 苗建芸.5083铝合金的超塑性研究[D].南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2008. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D052398MIAO J Y.Research on the superplasticity of aluminium alloy 5083 [D].Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D052398 [4] 徐雪峰.5083铝合金力学性能及超塑性成形数值模拟与实验研究[D].南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2009. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1855055XU X F.Research on mechanical behavior and simulation and experiment of superplastic forming of 5083 aluminum alloy [D].Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1855055 [5] 徐清波, 陶友瑞, 米芳.5083铝合金高温流变本构关系研究[J].矿冶工程, 2013, 33(5):124-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2013.05.031XU Q B, TAO Y R, MI F.Constitutive equation of rheological properties for 5083 aluminum alloy at elevated temperature [J].Min Metal Eng, 2013, 33(5):124-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2013.05.031 [6] 晏宁, 康国政, 朱志武.5083H111铝合金宽应变率拉伸动态本构模型[J].固体力学学报, 2014, 35(3):259-265. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10613-1014254635.htmYAN N, KANG G Z, ZHU Z W.Tensile dynamic constitutive model of 5083H111 aluminum alloy at a wide range of strain rates [J].Acta Mech Solid Sin, 2014, 35(3):259-265. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10613-1014254635.htm [7] KACHANOV L M.On the time to failure under creep condition [J].Izvestia Academii Nauk Sssr Otdelenie Tekhnicheskich Nauk, 1958, 8:26-31. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201801007 [8] LEMAITRE J.A contiuous damage mechanics model for ductile fracture [J].Eng Mater Tech, 1985, 107(1):83-89. doi: 10.1115/1.3225775 [9] CHABOCHE J L.Continuum damage mechanics:present state and future trend [J].Nucl Eng Des, 1987, 105(1):19-33. doi: 10.1016/0029-5493(87)90225-1 [10] GURSON A L.Plastic flow and fracture behavior of ductile materials incorporating void nucleation, growth and interaction [D].Providence, RI: Brown University, 1975. [11] GURSON A L.Continuum theory of ductile rupture by viod nucleation and growth [J].Eng Mater Tech, 1977, 99(2):2-15. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0c51c627757e6c5eb365384bd6b3a7a9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [12] WU S C, LIANG H.A kinetice quation for ductile damage at large plastic strain [J].J Mater Process Manu, 1992, 21(3):295- 302. [13] 高玉华.铝合金LC4和LC12CZ在高应变率拉伸和压缩下的本构关系[J].材料科学与工艺, 1994, 2(2):24-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CLKG402.005.htmGAO Y H.Dynamic compression and tensile properties of Al alloys LC4 and LY12CZ at high strain rate [J].Mater Sci Technol, 1994, 2(2):24-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CLKG402.005.htm [14] 孙瑞雪, 徐磊, 赵文博.不同应变速率下5083铝合金的拉伸性能及断口形貌[J].轻金属, 2012(8):59-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1752.2012.08.016SUN R X, XU L, ZHAO W B.The tensile properties and fracture morphologies of 5083 aluminum alloy under different strain rates [J].Light Metals, 2012(8):59-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1752.2012.08.016 [15] 李玉兰.真应力-应变的定义及其力学特征[J].重庆大学学报, 2001, 24(3):58-60. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cqdxxb200103016LI Y L.Definition and mechanical characteristics of true stress-strain [J].Journal of Chongqing University, 2001, 24(3):58-60. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cqdxxb200103016 [16] 郭伟国.4种新型舰艇钢的塑性流变应力及其本构模型[J].金属学报, 2006, 42(5):463-468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2006.05.004GUO W G.Plastic flow stresses and constitutive models of four newer naval vessel steels [J].Acta Metall, 2006, 42(5):463-468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2006.05.004 [17] 陈增涛, 王铎.高应变率下金属塑性损伤的形核机理[J].材料料学与工程, 1995, 13(1):51-55. doi: 10.4161-cc.9.8.11487/CHEN Z T, WANG D.Nucleation mechanism of plastic damage in metals under high strain rate [J].Materials Science and Engineering, 1995, 13(1):51-55. doi: 10.4161-cc.9.8.11487/ [18] 刘旭红, 黄西成, 陈裕泽, 等.强动载荷下金属材料塑性变形本构模型评述[J].力学进展, 2007, 37(3):362-363. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lxjz200703004LIU X H, HUANG X C, CHEN Y Z, et al.A review on constitutive models for plastic deformation of metal materials under dynamic loading [J].Advances in Mechanics, 2007, 37(3):362-363. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lxjz200703004 [19] 贺红亮.延性金属动态拉伸断裂的损伤演化[C]//中国力学学会学术大会.郑州, 2009: 29-30. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-AGLU200908008069.htmHE H L.Damage evolution for dynamic tensile fracture of ductile metal [C]//Chinese Conference of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics.Zhengzhou, 2009: 29-30. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-AGLU200908008069.htm [20] 王礼立, 董新龙, 孙紫建.高应变率下计及损伤演化的材料动态本构行为[J].爆炸与冲击, 2006, 26(3):193-198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2006.03.001WANG L L, DONG X L, SUN Z J.Dynamic constitutive behavior of materials at high strain rate taking account of damage evolution [J].Explosion and Shock Waves, 2006, 26(3):193-198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2006.03.001 [21] JOHNSON G R, COOK W H.A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures [C]//7th International Symposium on Ballistics.The Hague, Netherlands, 1983: 541-547. [22] 尚福林, 王子昆.塑性力学基础[M].西安:西安交通大学出版社, 2011:3.SHANG F L, WANG Z K.Plastic mechanics basis [M].Xi'an:Xi'an Jiaotong University Press, 2011:3. [23] 王礼立, 胡时胜.铝合金LF6R和纯铝L4R在高应变率下的动态应力应变关系[J].固体力学学报, 1986(2):163-166. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=GTLX198602010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQWANG L L, HU S S.Dynamic stress-stain relations of Al alloy LF6R and Al L4R under high strain rates [J].Acta Mech Solid Sin, 1986(2):163-166. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=GTLX198602010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [24] 宋玉泉, 程永春, 刘颍.拉伸变形应变硬化指数的力学涵义及其规范测量[J].中国科学, 2000, 30(3):200-207. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-ce200003002SONG Y Q, CHENG Y C, LIU Y.Mechanical meaning and metrical standardization of strain hardening index in tensile deformation [J].Science in China, 2000, 30(3):200-207. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-ce200003002 [25] 林木森, 庞宝君, 张伟, 等.5A06铝合金的动态本构关系实验[J].爆炸与冲击, 2009, 29(3):306-311. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2009.03.014LIN M S, PANG B J, ZHANG W, et al.Experimental investigation on a dynamic constitutive relationship of 5A06 Al alloy [J].Explosion and Shock Waves, 2009, 29(3):306-311. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2009.03.014 -






 下载:
下载: