Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure Treatments on Chlorophyll and Protein Spectra Characteristic of Spinach Thylakoid Membranes
-
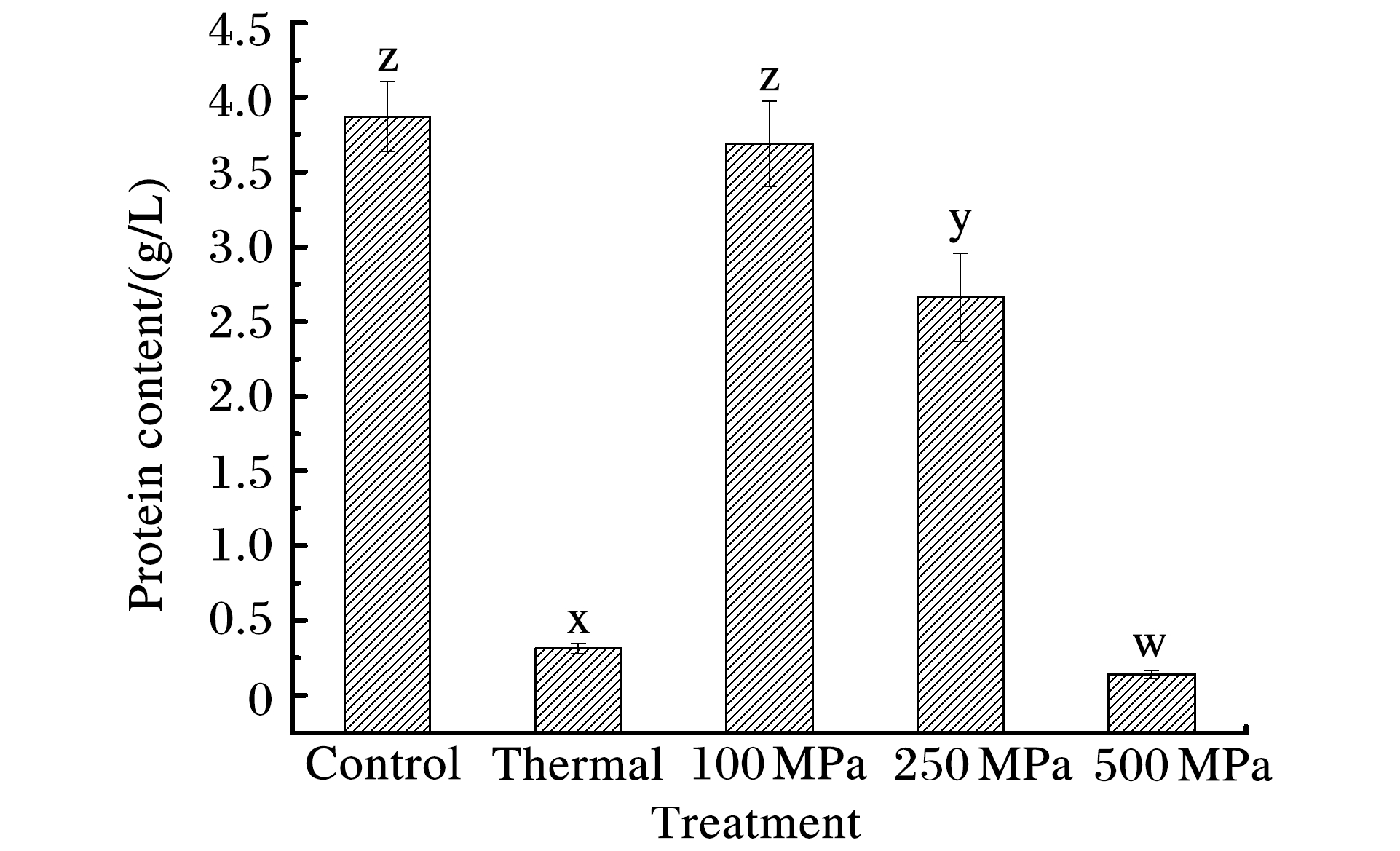
摘要: 研究了100、250和500 MPa高静压(High Hydrostatic Pressure, HHP)处理对菠菜类囊体膜叶绿素浓度、可溶性蛋白浓度、叶绿素室温吸收光谱、叶绿素发射和激发荧光光谱、蛋白荧光光谱的影响。结果表明,同热处理的菠菜相比,HHP处理的菠菜类囊体膜能保持较高的叶绿素和可溶性蛋白浓度,较高的叶绿素室温吸收光谱、叶绿素发射和激发荧光光谱、蛋白荧光光谱能力,并且在100和250 MPa时效果更加显著。另外,HHP处理后的菠菜类囊体膜仍能保持光系统Ⅱ捕光和被激发的能力,同时蛋白荧光光谱的变化也反应出HHP处理后类囊体膜蛋白组分的变化。由此推断,HHP保持绿色蔬菜的颜色品质可能与类囊体膜功能特性的维持有关。Abstract: The effects of 100, 200 and 500 MPa high hydrostatic pressure (HHP) treatments on spinach thylakoid membrane chlorophyll content, soluble protein content, chlorophyll absorption spectra, chlorophyll emission and excitation fluorescence spectra, protein fluorescence spectra were assessed in this study.The results show that the HHP-treated samples have higher chlorophyll content and soluble protein content, higher absorption spectra capacity, higher chlorophyll emission and excitation fluorescence spectra capacity than those of the thermal-treated.This is especially obvious for the samples that have received 100 and 250 MPa HHP treatments, for they maintain functional activity of harvesting light and have high excitability.Meanwhile, protein composition of thylakoid membrane undergoes some change after HHP treatment, suggested by great difference in protein fluorescence spectra.It is speculated the preservation of thylakoid membrane function plays a positive role for better green color retention in HHP-treated vegetables.
-
Key words:
- high hydrostatic pressure /
- spinach /
- thylakoid membrane /
- chlorophyll /
- protein /
- spectra characteristic
-
表 1 高静压对菠菜类囊体膜叶绿素浓度的影响
Table 1. Effects of HHP on thylakoid membrane chlorophyll contents of spinach
Method Ca/(g/L) Cb/(g/L) Control 0.244±0.001d 0.148±0.003g Thermal 0.037±0.004a 0.011±0.003h 100 MPa 0.232±0.003c 0.142±0.001g 250 MPa 0.253±0.002e 0.152±0.003gk 500 MPa 0.096±0.002b 0.075±0.002i Note:(1) Data are expressed in mean±standard deviation (n=3).
(2) Values with different letters are significantly different (P≤0.05). -
[1] Steet J A, Tong C H. Degradation kinetics of green color and chlorophylls in peas by colorimetry and HPLC[J]. J Food Sci, 1996, 61(5): 924-927. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1996.tb10903.x [2] Heaton J W, Marangoni A G. Chlorophyll degradation in processed foods and senescent plant tissues[J]. Trends Food Sci Tech, 1996, 7(1): 8-15. doi: 10.1016/0924-2244(96)81352-5 [3] Monreal M, de Ancos B, Cano M P. Influence of critical storage temperatures on degradative pathways of pigments in green beans[J]. J Agr Food Chem, 1999, 47(1): 19-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=45879cea8db8d390f021c52704b0a476 [4] Butz P E, Denharder R, García A F, et al. Changes in functional properties of vegetables induced by high pressure treatment[J]. Food Res Int, 2002, 35(2): 295-300. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=81be8dc82bf5577e007d02d5db83493e [5] Norton T, Sun D W. Recent advances in the use of high pressure as an effective processing technique in the food industry[J]. Food Bioprocess Tech, 2008, 1(1): 2-34. doi: 10.1007/s11947-007-0007-0 [6] Krebbers B, Matser A M, Koets M, et al. Quality and storage-stability of high-pressure preserved green beans[J]. J Food Eng, 2002, 54(1): 27-33. http://europepmc.org/abstract/AGR/IND43617616 [7] van Buggenhout S, Messagie I, van der Plancken I, et al. Influence of high-pressure-low-temperature treatments on fruit and vegetable quality related enzymes[J]. Eur Food Res Technol, 2006, 223(4): 475-485. doi: 10.1007/s00217-005-0227-3 [8] López-Malo A, Palou Z, Barbosa-Cánovas G V, et al. Polyphenoloxidase activity and color changes during storage of high hydrostatic pressure treated avocado puree[J]. Food Res Int, 1998, 31(8): 549-556. doi: 10.1016/S0963-9969(99)00028-9 [9] Wang R R, Wang T T, Zheng Q, et al. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on color of spinach puree and related properties[J]. J Sci Food Agr, 2012, 92(7): 1417-1423. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4719 [10] Wang R R, Xu Q, Yao J, et al. Post-effects of high hydrostatic pressure on green color retention and related properties of spinach puree during storage[J]. Innov Food Sci Emerg, 2013, 17: 63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2012.11.007 [11] Schlüter O, Foerster J, Geyer M, et al. Characterization of high-hydrostatic-pressure effects on fresh produce using chlorophyll fluorescence image analysis[J]. Food Bioprocess Tech, 2009, 2(3): 291-299. doi: 10.1007/s11947-008-0143-1 [12] Eggleston V, Tanner D J. Are carrots under pressure still alive?The effect of high pressure processing on respiration rate of carrots[J]. Acta Horticulture, 2005, 687: 371-374. http://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201301037976 [13] Oku T, Tomita G. Photoactivation of oxygen-evolving system in dark-grown spruce seedlings[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 1976, 38(3): 181-185. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1976.tb03987.x [14] Wittig I, Braun H P, Schägger H. Blue native PAGE[J]. Nat Protoc, 2006, 1: 418-428. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.62 [15] Arnon D I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris[J]. Plant Physiol, 1949, 24(1): 1-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=PubMed000001994638 [16] Lowry O, Rosebrough A, Farr A, et al. Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent[J]. J Biol Chem, 1951, 193: 680-685. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1177/004051754001000501 [17] Herendeen S L, Vanbogelen R A, Neidhardt F C. Levels of major proteins of Escherichia coli during growth at different temperatures[J]. J Bacteriol, 1979, 139(1): 185-194. doi: 10.1128/JB.139.1.185-194.1979 [18] Havaux M. Stress tolerance of photosystem Ⅱ in vivo. Antagonistic effects of water, heat, and photoinhibition stresses[J]. Plant Physiol, 1992, 100(1): 424-422. http://jxb.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/ijlink?linkType=ABST&journalCode=plantphysiol&resid=100/1/424 [19] Wei H M, Chen Y W, Zhang N H, et al. Study on the spectra properties of cotyledon thylakoid membranes in chlorophyll-reduced rapeseed mutant Cr3529 and its wild type[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinia, 2005, 25(2): 250-255. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbzwxb200502007 [20] Naus J, Dvorak L, Kuropatwa R, et al. Transition in the thylakoid membranes of barley leaves studied by chlorophyll fluorescence temperature curve[J]. Photosynthetica, 1992, 27(4): 563-570. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284877359_Transitions_in_the_thylakoid_membranes_of_barley_leaves_studied_by_chlorophyll_fluorescence_temperature_curve [21] Tang Y L, Wen X G, Lu Q T, et al. Heat stress induces an aggregation of the light-harvesting complex of photosystem Ⅱin spinach plants[J]. Plant Physiol, 2007, 143(2): 629-638. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.090712 -







 下载:
下载: