Numerical Investigation on Penetration Performance of Segmented Rods
doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2015.06.002
-
摘要: 为研究分段杆弹的侵彻效率, 对不同结构的钨合金分段及连续杆弹侵彻半无限厚4340钢靶进行了数值模拟, 撞击速度范围为1 500~3 500 m/s。数值模拟的侵彻深度及弹坑形状与冲击实验一致, 验证了数值模拟的有效性。基于AUTODYN软件的数值模拟结果表明, 在一定条件下, 分段杆弹的侵彻效率高于连续杆弹, 这是因为分段杆弹的侵彻效率取决于s/d(分弹体的间隔与直径之比)和撞击速度。分段杆弹的最佳s/d由弹体结构和撞击速度决定。计算结果揭示了分段、连续杆弹以及分段杆弹高速、低速侵彻靶体得到的弹坑的差异。Abstract: To investigate the penetration performance of segmented rods against targets, a series of numerical simulations were conducted to research the penetration performance of tungsten alloy segmented rods with various configurations and their corresponding continuous rods into semi-infinite thick 4340 steel targets at velocities ranging from 1 500 to 3 500 m/s by using the SPH (Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics) hydro code of AUTODYN.The shape of the crater and the depth of penetration were in good agreement with the results obtained from experiments.The numerical results indicate that the penetration performance of segmented rods is significantly improved compared with that of continuous rods under some conditions.The penetration efficiency of segmented rods depends on the s/d value (where s is the segment spacing and d is the rod diameter) and the impact velocity.Moreover, there is an optimum s/d for the segmented rods which depends on the impact velocity and configuration of projectiles.The calculations show that there are significant differences in the crater profile of targets between continuous and segmented rods, and also those of segmented rods at high and low velocities are different.
-
Key words:
- impact /
- segmented rod /
- target /
- penetration /
- numerical simulation
-
Figure 2. Comparison of results between calculations and experiments by Holland[2]
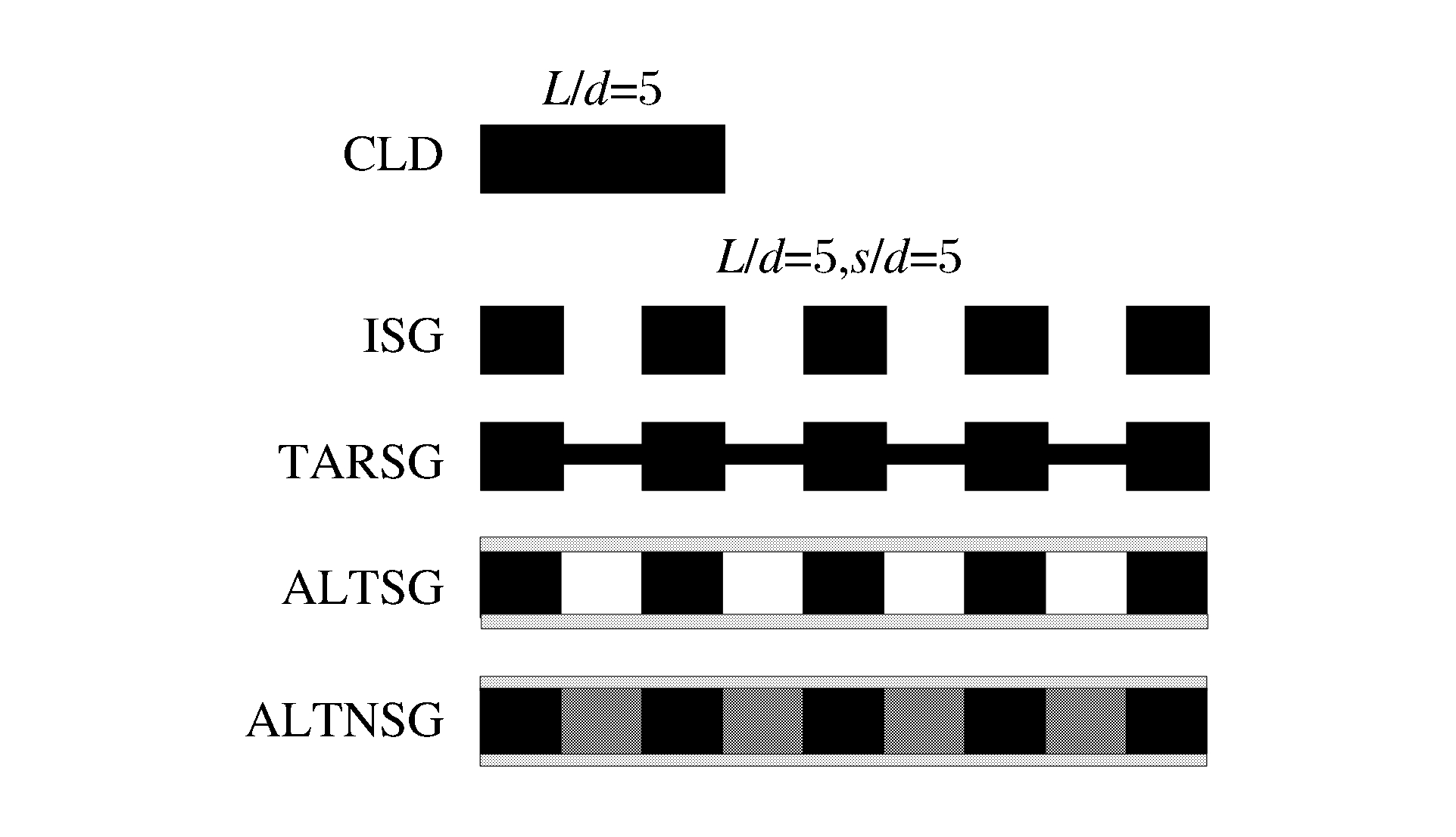
Table 1. Parameters of the projectiles
Projectile
types/d L/
(mm)ms/
(g)ξm Projectile
types/d L/
(mm)ms/
(g)ξm ISG 1 49.85 11.35 1 ALTSG 1 49.86 14.14 1.25 ISG 2 72.02 11.35 1 ALTSG 2 72.02 15.39 1.36 ISG 3 94.18 11.35 1 ALTSG 3 94.18 16.63 1.46 ISG 4 116.34 11.35 1 ALTSG 4 116.34 17.87 1.57 ISG 5 138.50 11.35 1 ALTSG 5 138.50 19.11 1.68 TARSG 1 49.86 12.20 1.08 ALTNSG 1 49.86 14.75 1.29 TARSG 2 72.02 13.06 1.15 ALTNSG 2 72.02 16.60 1.46 TARSG 3 94.18 13.91 1.23 ALTNSG 3 94.18 18.45 1.63 TARSG 4 116.34 14.77 1.30 ALTNSG 4 116.34 20.30 1.79 TARSG 5 138.50 15.62 1.38 ALTNSG 5 138.50 22.15 1.95 CLD 0 27.70 11.35 1 Table 2. Material constants of the projectiles and targets
Material Density/
(g/cm3)Tensile
limit/(GPa)Bulk modulus/
(GPa)Shear
modulus/(GPa)Yield stress/
(GPa)W-10 tungsten 17.0 -2 311.3 160.514 0.646 7 4340 steel 7.84 -2.5 183 75.864 1.0 Material Density/
(g/cm3)Tensile
limit/(GPa)Shear modulus/
(GPa)Yield
stress/(GPa)Grüneisen
coef.C1/
(km/s)S1 Nylon 1.14 -0.999 999 9 3.68 0.05 0.87 2.29 1.63 Material Density/
(g/cm3)Tensile
limit/(GPa)Shear modulus/
(GPa)Yield
stress/(GPa)A1/
(GPa)A2/
(GPa)A3/
(GPa)Al6061-T6 2.704 -0.999 999 9 27.5 0.27 77.389 99 105.99 153.78 Material Grüneisen
coef.Expansion
coef.Sublimation
Energy/(MJ/kg)Reference
temperature/(T)Specific heat/
(J/(kg·K))Al6061-T6 2.0 0.67 3.14 300 884.999 939 Note: (1) C1, S1 are coefficients of the shock velocity-particle velocity curve;
(2) A1, A2 and A3 are the parameters of puff equation of state. -
[1] Charters A C. The penetration of rolled homogeneous armor by continuous and segmented rods at high velocity: Theory and experiments, CR-86-1031[R]. USA: General Research Corporation, 1986. [2] Holland P M, Gordon J T, Menna T L, et al. Hydrocode results for the penetration of continuous, segmented and hybrid rods compared with experiments[J]. Int J Impact Engng, 1990, 10: 241-250. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(90)90062-Z [3] Charters A C, Menna T L, Piekutowski A J. Penetration dynamics of rods from direct ballistic tests of advance armor components at 2-3 km/s[J]. Int J Impact Engng, 1990, 10: 93-106. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(90)90051-V [4] Tate A. Engineering modelling of some aspects of segmented rod penetration[J]. Int J Impact Engng, 1990, 9: 327-341. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(90)90006-H [5] Scheffier D R, Zukas J A. Numerical simulation of segmented penetrator impact[J]. Int J Impact Engng, 1990, 10: 487-497. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(90)90082-7 [6] Lee M. A numerical comparison of the ballistic peneformance of unitary rod and segmented rods against stationary and moving oblique plates[J]. Int J Impact Engng, 2001, 26: 399-407. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(01)00090-2 [7] Littlefield D L. Effect of aligenment on penetration of segmented rods[J]. Int J Impact Engng, 2001, 26: 421-431. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(01)00092-6 [8] Orphal D L, Franzen R R. Penetration mechanics and performance of segmented rods against metal targets[J]. Int J Impact Engng, 1990, 10: 427-438. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(90)90077-9 [9] Anderson C E. Penetration mechanics of seg-tel penetrators[J]. Int J Impact Engng, 1997, 20: 13-26. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(97)87477-5 [10] Naz P, Lehr H F. The crater formation due to segmented rod penentrators[J]. Int J Impact Engng, 1990, 10: 413-425. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(90)90076-8 [11] Century Dynamics Inc. AUTODYN Theory Manual Revision 4.3[M]. USA: Century Dynamics Inc, 2005. [12] Rohr I, Nahme H, Thoma K, et al. Material characterisation and constitutive modelling of a tungsten-sintered alloy for a wide range of strain rates[J]. Int J Impact Engng, 2008, 35: 811-819. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.12.006 [13] Wang X M, Zhao G Z, Shen P H, et al. High velocity impact of segmented rods with an aluminum carrier tube[J]. Int J Impact Engng, 1995, 17: 915-923. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)99910-J [14] Aly S Y, Li Q M. Numerical investigation of penetration performance of non-ideal segmented-rod projectiles[J]. Trans Tianjin Univ, 2008, 14: 391-395. doi: 10.1007/s12209-008-0067-x [15] 邓云飞, 张伟, 曹宗胜, 等.分段弹侵彻效率的数值模拟研究[J].高压物理学报, 2011, 25(3): 251-261. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gywlxb201103011Deng Y F, Zhang W, Cao Z S. Numerical investigation of penetration performance of segmented rods penetration into steel target[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2011, 25(3): 251-261. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gywlxb201103011 -







 下载:
下载: