Theoretical Study on the Reaction of Chlorine Trifluoride Oxidewith Propylene Oxide by Density Functional Theory
doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2015.03.011
-
摘要: 应用密度泛函理论对ClF3O和环氧丙烷的反应机理进行了研究。在B3PW91/6-31++G(d, p)水平上优化了各驻点(反应物、中间体、过渡态和产物)的几何构型,并计算了它们的振动频率和零点振动能。采用CCSD(T)/6-31++G(d, p)//B3PW91/6-3l++G(d, p)单点能计算方法求得各物质的能量,并做零点能校正。计算结果表明,ClF3O与C3H6O可经过不同的反应路径,引发C3H5O自由基和ClOF2自由基生成环氧丙醇和三氟化氯, 其中, 位于ClF3O周向位置的F原子与C3H6O的C(7)上与CH3异侧的H(9)原子结合的活化能最低, 仅15.63 kJ/mo1;ClF3O与C3H6O反应生成的C3H5O自由基和ClOF2自由基继续反应,经过不同反应路径生成C3H4O、ClOF和HF, 其中, ClOF2中的F原子和C3H5O中的H(2)或H(4)原子结合是无能垒的过程。整个反应的主要路径为C3H6O+ClF3O→TS12→P4 (C3H5O+HF+ClOF2)→P12 (CH2CHCHO+2HF+ClOF)。Abstract: Using density functional theory (DFT), the reaction of chlorine trifluoride oxide (ClF3O) with propylene oxide (C3H6O) was studied.At the B3PW91/6-31++G(d, p) level, geometries of all species (reactants, transition states and products) were optimized, and the vibrational frequencies and zero point vibrational energies (ZPVE) were calculated.The energies of all species were refined with CCSD(T)/6-31++G(d, p)//B3PW91/6-31++G(d, p) method and ZPVE correction.The calculated results suggest that the initial reaction has various pathways to yield the main products of C3H5O and ClOF2 radicals, and C3H6O2 and ClF3 molecules.The reactions of C3H5O and ClOF2 radicals have different pathways to yield the main products of C3H4O, ClOF and HF molecules.The main reaction channel is C3H6O+ClF3O→TS12→P4 (C3H5O+HF+ClOF2)→P12 (CH2CHCHO+2HF+ClOF).P4 is produced by C3H6O and ClF3O via TS12 with a low barrier of 15.63 kJ/mol, and P12 can be formed from P4 through a barrierless process.
-
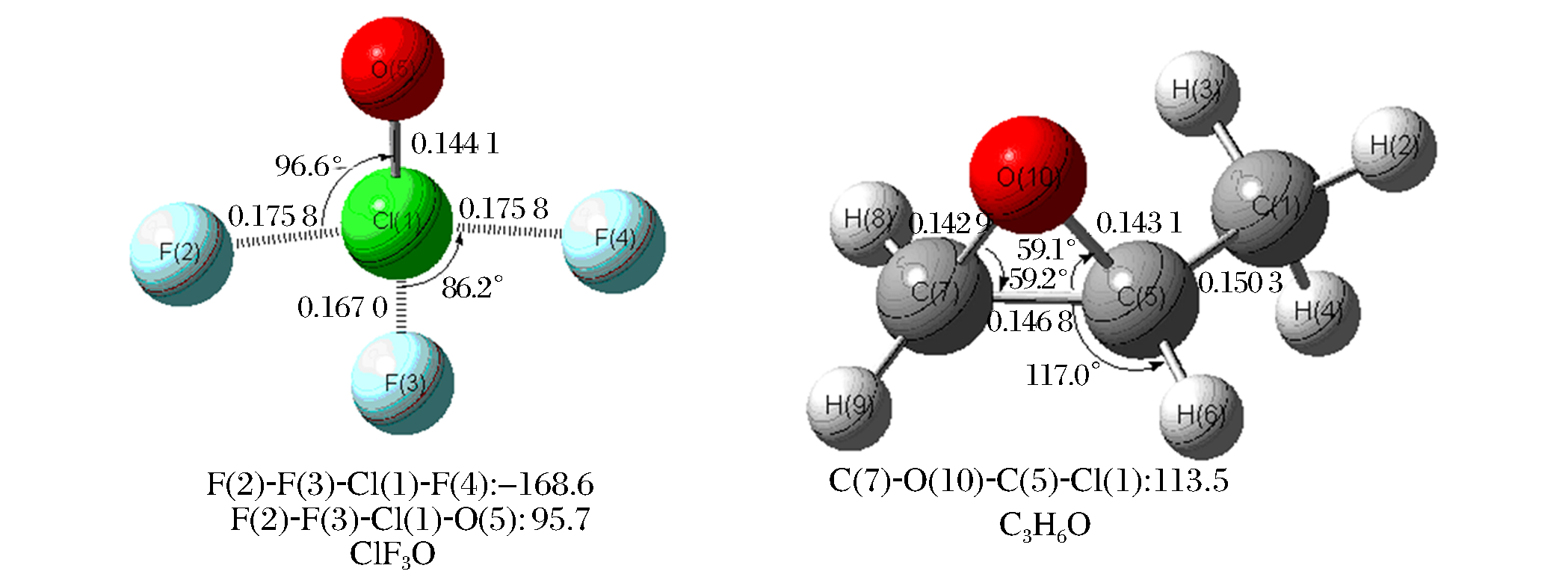
Table 1. Calculated Mulliken atomic charges of ClF3O and C3H6
Species Muliken atomic charges ClF3O Cl O(5) F(2) F(3) F(4) 1.498 e -0.377 e -0.412 e -0.297 e -0.412 e C3H6O C(1) C(5) C(7) O(10) H(2) H(3) H(4) H(6) H(8) H(9) -0.589 e 0.154 e -0.195 e -0.312 e 0.176 e 0.166 e 0.144 e 0.172 e 0.145 e 0.139 e Table 2. Theoretically predicted total energies and ZPVE of the reactants, products, intermediates andtransition states of the initial reaction of ClF3O with C3H6
Species Theoretically predicted total energy/(Eh) ZPVE/(Eh) B3PW91/6-31++G(d, p) CCSD(T)/6-31++G(d, p) R -1 027.394 86 -1 025.794 45 0.096 70 HF -100.405 44 -100.221 69 0.009 37 ClF3 -759.334 92 -758.257 61 0.006 83 ClOF2 -734.690 69 -733.648 15 0.006 85 m1 -192.314 18 -191.929 13 0.071 08 m2 -192.311 31 -191.926 34 0.072 49 m3 -192.308 17 -191.924 18 0.072 32 m4 -192.308 07 -191.923 93 0.072 33 m5 -192.317 63 -191.933 14 0.070 34 m6 -268.114 73 -267.606 26 0.090 87 m7 -268.150 09 -267.634 78 0.091 28 m8 -268.146 94 -267.631 29 0.090 92 m9 -268.167 10 -267.650 67 0.089 91 m10 -268.164 82 -267.647 49 0.090 32 m11 -268.165 91 -267.648 25 0.090 24 TS1 -1 027.342 31 -1 025.753 62 0.088 97 TS2 -1 027.342 95 -1 025.751 83 0.088 74 TS3 -1 027.342 98 -1 025.750 91 0.088 69 TS4 -1 027.350 54 -1 025.749 54 0.089 33 TS5 -1 027.346 43 -1 025.747 74 0.089 01 TS6 -1 027.346 48 -1 025.753 75 0.088 93 TS7 -1 027.375 16 -1 025.778 08 0.089 66 TS8 -1 027.375 98 -1 025.772 56 0.089 69 TS9 -1 027.375 88 -1 025.772 91 0.089 62 TS10 -1 027.384 15 -1 025.776 72 0.090 79 TS11 -1 027.380 53 -1 025.780 98 0.089 91 TS12 -1 027.380 94 -1 025.781 61 0.089 82 TS13 -1 027.350 89 -1 025.737 00 0.090 18 TS14 -1 027.352 74 -1 025.741 21 0.090 20 TS15 -1 027.352 66 -1 025.741 63 0.090 09 TS16 -1 027.363 19 -1 025.752 76 0.091 12 TS17 -1 027.357 43 -1 025.744 04 0.090 47 TS18 -1 027.358 81 -1 025.747 13 0.090 53 P1 -1 027.410 31 -1 025.798 97 0.087 30 P2 -1 027.407 44 -1 025.796 18 0.088 71 P3 -1 027.404 31 -1 025.794 02 0.088 54 P4 -1 027.404 20 -1 025.793 77 0.088 55 P5 -1 027.413 76 -1 025.802 98 0.086 56 P6 -1 027.482 23 -1 025.863 87 0.097 70 P7 -1 027.485 01 -1 025.892 38 0.098 11 P8 -1 027.481 86 -1 025.888 89 0.097 75 P9 -1 027.502 02 -1 025.908 28 0.096 74 P10 -1 027.499 74 -1 025.905 10 0.097 15 P11 -1 027.500 83 -1 025.905 85 0.097 07 *R refers to the reactants, i.e., ClF3O+C3H6O. Table 3. Theoretically predicted energy barriers (Ea) and reaction enthalpies (ΔH)for various pathways of ClFO3 reacting with C3H6
Path Reactionposition Transitionstates Product Ea/(kJ/mol) ΔH/(kJ/mol) 1 F(2)-H(2) TS1 P1 86.88 -36.55 2 F(2)-H(3) TS2 P1 90.99 -36.55 3 F(2)-H(4) TS3 P1 93.28 -36.55 4 F(2)-H(6) TS4 P2 98.55 -25.54 5 F(2)-H(8) TS5 P3 102.41 -20.31 6 F(2)-H(9) TS6 P4 86.44 -19.63 7 F(3)-H(2) TS7 P1 24.47 -36.55 8 F(3)-H(3) TS8 P1 39.07 -36.55 9 F(3)-H(4) TS9 P5 37.93 -49.05 10 F(3)-H(6) TS10 P2 31.02 -25.54 11 F(3)-H(8) TS11 P3 17.53 -20.31 12 F(3)-H(9) TS12 P4 15.63 -19.63 13 O-H(2) TS13 P6 133.70 -179.65 14 O-H(3) TS14 P7 122.71 -253.43 15 O-H(4) TS15 P8 121.32 -245.22 16 O-H(6) TS16 P9 94.77 -298.77 17 O-H(8) TS17 P10 115.98 -289.34 18 O-H(9) TS18 P11 108.02 -291.53 Table 4. Theoretical predicted total energies and ZPVE of the intermediates, transition states andproducts for the reaction of ClOF2 with C3H5
Species Theoretical predicted total energy/(Eh) ZPVE/(Eh) B3PW91/6-31++G(d, p) CCSD(T)/6-31++G(d, p) M1 -927.136 18 -925.730 57 0.083 21 IM2 -927.158 76 -925.759 06 0.082 38 IM3 -927.074 46 -925.669 47 0.078 47 TS19 -927.080 68 -925.672 53 0.080 66 TS20 -927.049 69 -925.631 00 0.073 00 TS21 -927.068 35 -925.653 06 0.077 01 ClOF -634.947 28 -634.100 93 0.024 43 CH2CHCHO -191.784 92 -191.406 14 0.061 46 a-CH3CHCO -191.789 66 -191.403 24 0.061 10 b-CH3CHCO -191.700 30 -191.320 40 0.060 60 P12 -927.137 64 -925.728 76 0.075 26 P13 -927.142 38 -925.725 86 0.074 90 P14 -927.053 02 -925.643 02 0.074 40 Table 5. Theoretical predicted energy barriers (Ea) andreaction enthalpies (ΔH) for various pathways of ClOF2 reacting with C3H5
Path Reaction position Transition states Product Ea/(kJ/mol) ΔH/(kJ/mol) 19 F(11)-H(2) - P12 - -374.92 20 F(11)-H(3) TS19 P12 139.02 -374.92 21 F(11)-H(4) - P12 - -374.92 22 F(11)-H(6) TS20 P13 261.73 -388.31 23 F(11)-H(8) TS21 P14 12.21 -155.01 -
[1] Bauer H F, Pilipovich D, Wilson R D.Oxychlorine trifluoride and alkali fluoride-Cl2O complex: US, 3733392[P].1972. [2] Pilipovich D, Lindahl C B, Schack C J, et al.Chlorine trifluoride oxide.Ⅰ.Preparation and properties[J].Inorg Chem, 1972, 11(9):2189-2192. doi: 10.1021/ic50115a040 [3] Pilipovich D, Rogers H H, Wilson R D.Chlorine trifluoride oxide.Ⅱ.Photochemical synthesis[J].Inorg Chem, 1972, 11(9):2192-2195. doi: 10.1021/ic50115a041 [4] Christe K O, Curtis E C.Chlorine trifluoride oxide.Ⅲ.Vibrational spectrum, force constants, and thermodynamic properties[J].Inorg Chem, 1972, 11(9):2196-2201. doi: 10.1021/ic50115a042 [5] Schack C J, Lindahl C B, Pilipovich D, et al.Chlorine trifluoride oxide.Ⅵ.Reaction chemistry[J].Inorg Chem, 1972, 11(9):2201-2205. doi: 10.1021/ic50115a043 [6] Christe K O, Schack C J, Pilipovich D.Chlorine trifluoride oxide.Ⅴ.Complex formation with lewis acids and bases[J].Inorg Chem, 1972, 11(9):2205-2208. doi: 10.1021/ic50115a044 [7] Christe K O, Curtis E C.Chlorine trifluoride oxide.Ⅵ.Tetrafluorooxychlorate (V) anion, ClF4O- vibrational spectra and force constants[J].Inorg Chem, 1972, 11(9):2209-2211. doi: 10.1021/ic50115a045 [8] Christe K O, Curtis E C, Schack C J.Chlorine trifluoride oxide.Ⅶ.Difluorooxychloronium (V) cation, ClF2O+ vibrational spectrum and force constants[J].Inorg Chem, 1972, 11(9):2212-2215. doi: 10.1021/ic50115a046 [9] Oberhammer H, Christe K O.Gas-phase structure of chlorine trifluoride oxide ClF3O[J].Inorg Chem, 1982, 21:273-275. doi: 10.1021/ic00131a050 [10] 钟亮.丙烯部分氧化合成环氧丙烷表面反应规律的研究[D].天津: 天津大学, 2004.Zhong L.Study on the surface reaction behaviors of propylene partial oxidation to propylene oxide[D].Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2004.(in Chinese) [11] 胡栋, 袁长迎, 李萍, 等.环氧丙烷点火的光谱研究.高压物理学报[J], 2003, 17(3):70-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gywlxb200303002Hu D, Yuan C Y, Li P, et al.Spectroscopic studies of epoxy propane ignition[J].Chinese Journal of High Press Physics, 2003, 17(3):70-72.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gywlxb200303002 [12] Brower K R.Explosive reactions of liquid mixtures of chlorine trifluoride with hydrocarbons and halocarbons[J].J Fluo Chem, 1986, 31(3):333-349. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1139(00)81435-9 [13] von Elbe G, McHale E T.Chemical Initiation of FAE Clouds[M].Washington:Atlantic Research Corporation, 1980:1-21. [14] Brower K R.Fluorination of alkanes by chlorine trifluoride hydride abstraction mechanism[J].J Org Chem, 1987, 52:798-802. doi: 10.1021/jo00381a017 [15] Baddiel C B, Cullis C F.The explosive reaction of chlorine trifluoride with paraffin hydrocarbons[C]//Eighth Symposium (International) on Combustion.California: California Institute of Technology, 1991, 8(1): 1089-1095. [16] 许学忠, 裴明敬, 李明, 等.碳氢燃料与卤素氟化物的爆炸反应特性[J].火炸药学报, 1999, 22(3):36-37 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hzyxb199903011Xu X Z, Pei M J, Li M, et al.Explosive reaction characteristics on hydrocarbon and fluorine agent[J].Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 1999, 22(3):36-37.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hzyxb199903011 [17] 闫华, 贡雪东, 罗永锋, 等.三氟化氯和环氧丙烷反应的理论研究[J].化学学报, 2009, 24:2845-2850. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxxb200924015Yan H, Gong X D, Luo Y F, et al.Theoretical study on the reaction of chlorine trifluoride with propylene oxide by density functional theory[J].Acta Chimica Sinica, 2009, 24:2845-2850.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxxb200924015 [18] Elbe G V, Mchale E T.Chemical Initlation of FAE Clouds[M].Washington D C:Atlantic Research Corporation, 1979, 11:2-18. [19] Smirnov N N, Nikitin V F.Ignition of combustion of turbulized dust-air mixture[J].Combust Flame, 2000, 123(1):46-47. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ccf44044a26d6a777e2b1098f4e35040 [20] Gonthier K A, Powers J M.A high-resolution numerical method for a two-phase model of deflagration to detonation transition[J].J Com Phys, 2000, 163(2):376-433. doi: 10.1006/jcph.2000.6569 [21] Politzer P, Lane P.Energetics of ammonium perchlorate decomposition steps[J].J Mol Struct (Theochem), 1998, 454(2):229-235. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1872d16000f8193fbcbc272ede0ac23f [22] Christe K O, Schack C J.Chlorine oxyfluorides[J].Adv Inorg Chem Radiochem, 1976, 18:319-398. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2792(08)60033-3 -







 下载:
下载: