Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Energetic Materials
-
摘要: 理解含能材料的物理化学性质、爆轰性能及分解机制,对于含能材料的分子设计、安全性评估及实际应用有着重要的指导意义。第一性原理分子动力学不但可以研究含能材料的物理化学性质,还可以用于研究含能材料的分解反应过程。本文综述了当前第一性原理分子动力学模拟含能材料的理论研究进展。首先讨论了含能材料的晶体结构和基本性质,如热学、力学、电学性质和结构的温度、压力效应。随后讨论了含能材料常压下单分子分解行为,侧重讨论了常压下含能材料的热解产物、热解机制及热解反应的动力学性质,其中含能材料的热解起始反应机制主要包括质子转移、C—N键断裂和N—NO2键断裂3种方式。同时,还对静水压、冲击波等加载条件对含能材料热解反应的影响进行了讨论,尤其是冲击波加载可能带来新的反应机制,如C—H键的断裂。Abstract: Understanding the physical and chemical properties, detonation properties and decomposition mechanism is very important for molecular design, safety assessment and practical utilization of energetic materials.Ab initio molecular dynamics can be used to not only study the physical and chemical properties, but also understand the decomposition mechanism of energetic materials.The theoretical studies on energetic materials using ab initio molecular dynamics have been reviewed in this paper.Firstly the current progress on crystal structure and basic properties, such as thermal, mechanical and electronic properties, the effect of pressure and temperature on crystal structure of energetic materials are summarized.Then unimolecular decomposition of energetic materials are discussed, especially the products, mechanism and dynamics properties.The main initial reactions of thermal decomposition include proton transfer, C—N bond fission and N—NO2 bond cleavage.The effects of hydrostatic pressure, shock wave and other loading conditions on thermal decomposition are also discussed.In particular, shock wave loading may lead up to new reaction mechanism, for example, C—N bond fission.
-
表 1 基于从头算分子动力学模拟凝聚态含能材料热解的总结
Table 1. thermal decomposition of condensed energetic materials using ab initio molecular dynamics
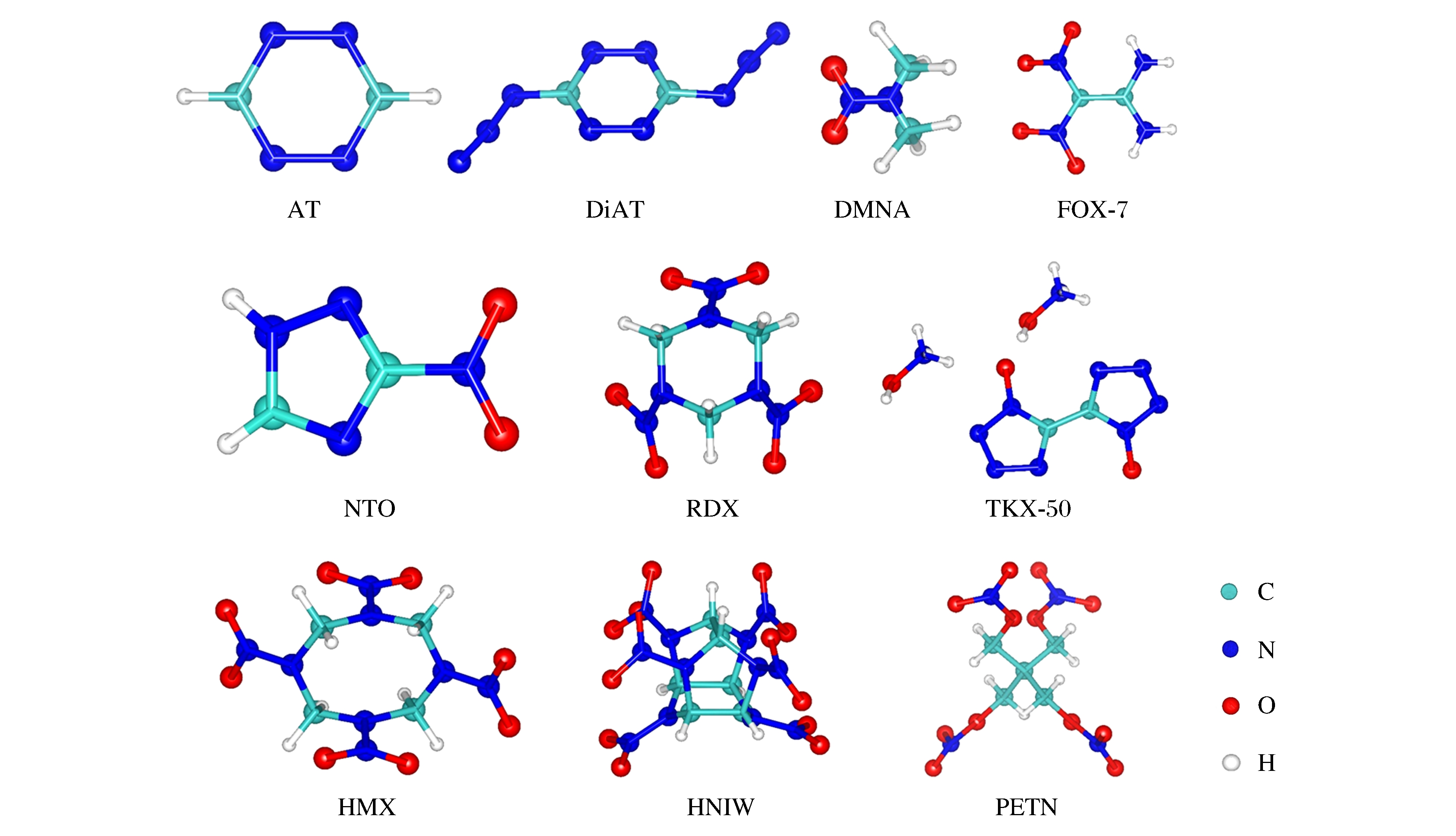
Materials Status Method Condition Initial mechanism Products Ref. HMX Crystal SCC-DFTB 3 500 K N—NO2 cleavage H2O,N2,CO2,CO [121] HMX Crystal SCC-DFTB 300 K
shock waveN—NO2 cleavage (below 11 km/s)
C—N bond fission (above 11 km/s)NO2, NO, N2, N2O,
H2O, CO, CO2[135-137] BCHMX Crystal AIMD 20-3 000 K and
hydrostatic pressureProton transfer (non-compress)
proton and NO2 releasing(compress)H2O,N2 [133] RDX Crystal AIMD 3 000 K N—NO2 cleavage N2,H2O,NO2 and
carbon clusters[123] RDX Molten
crystalDFT-MD 1 500 K and
hydrostatic pressureN—N bond and
C—N bond fission- [138] NM Crystal AIMD 3 000 K Proton transfer and C—NO2 cleavage H2O [127] NM Crystal CPMD 2 200 K Proton transfer and C—N bond fission H2O, CO2, N2, CNCNC [128] NM Crystal CPMD Heating rate and
fast annealingProton transfer (high temperature)
C—N bond fission (low temperature)H2O [139] NM Liquid AIMD 3 000 K and
hydrostatic pressureProton transfer and
C—NO2 cleavageH2O, CO, CO2 [131] NM Liquid CPMD Shock wave C—NO2 cleavage (above 11-12 km/s) - [134] NM Liquid AIMD Functional graphene sheets
and 300-2 400 KDefects improve decomposition H2O, N2, CO2 [140] FOX-7 Crystal AIMD 3 000 K and
hydrostatic pressureC—NO2 cleavage N2, H2O, CO2, NH3
and carbon clusters[132] FOX-7 Crystal CPMD 2 500-4 000 K C—NO2 cleavage and proton transfer H2O, CO2, N2 [130] HNIW Crystal CPMD 300-3 000 K N—NO2 cleavage NO2, NO, N2O, N2 [115] TKX-50 Crystal SCC-DFTB 300-3 000 K Proton transfer N2 [122] DiAT Crystal AIMD 3 000 K N—N bond and C—N bond fission N2 [120] -
[1] 王文俊.新型含能材料及其推进剂的研究进展[J].推进技术, 2001, 22(4): 269-275. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tjjs200104002Wang W J. Advance on new energetic materials and its application to solid propellants[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2001, 22(4): 269-275. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tjjs200104002 [2] Suceskac M, Rajic M, Zeman S, et al. 1, 3, 3-trinitroazetidine(TNAZ). Study of thermal behaviour. Part Ⅱ[J]. J Energ Mater, 2001, 19(2/3): 241-254. doi: 10.1080/07370650108216128 [3] Lee J S, Hsu C K, Chang C L. A study on the thermal decomposition behaviors of PETN, RDX, HNS and HMX[J]. Thermochim Acta, 2002, 392-393: 173-176. doi: 10.1016/S0040-6031(02)00099-0 [4] Turcotte R, Vachon M, Kwok Q S M, et al. Thermal study of HNIW(CL-20)[J]. Thermochim Acta, 2005, 433(1/2): 105-115. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040603105001322 [5] Pourmortazavi S, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M, Kohsari I, et al. Non-isothermal kinetic studies on thermal decomposition of energetic materials[J]. J Therm Anal Calorim, 2012, 110(2): 857-863. doi: 10.1007/s10973-011-1845-6 [6] Henson B F, Asay B W, Sander R K, et al. Dynamic measurement of the HMX β-δ phase transition by second harmonic generation[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 82(6): 1213-1216. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.82.1213 [7] Brill T B, Karpowicz R J. Solid phase transition kinetics. The role of intermolecular forces in the condensed-phase decomposition of octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine[J]. J Phys Chem, 1982, 86(21): 4260-4265. doi: 10.1021/j100218a033 [8] Cardão P A, Gois J C, Campos J A. Thermal decomposition of energetic materials[J]. AIP Conf Proc, 2000, 505(1): 853-856. [9] Czerski H, Greenaway M W, Proud W G, et al. Links between the morphology of RDX crystals and their shock sensitivity[J]. AIP Conf Proc, 2006, 845(1): 1053-1056. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC026526418 [10] Bolotina N B, Hardie M J, Speer R L, et al. Energetic materials: Variable-temperature crystal structures of γ-and ε-HNIW polymorphs[J]. J Appl Crystallogr, 2004, 37(5): 808-814. doi: 10.1107/S0021889804017832 [11] Naya T, Kohga M. Thermal decomposition behaviors and burning characteristics of AN/nitramine-based composite propellant[J]. J Energ Mater, 2015, 33(2): 73-90. doi: 10.1080/07370652.2014.902406 [12] Oyumi Y, Brill T B. Thermal decomposition of energetic materials 5. High-rate, in situ, thermolysis of two nitrosamine derivatives of RDX by FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Combust Flame, 1985, 62(3): 233-241. doi: 10.1016/0010-2180(85)90149-X [13] Zhao X, Hintsa E J, Lee Y T. Infrared multiphoton dissociation of RDX in a molecular beam[J]. J Chem Phys, 1988, 88(2): 801-810. doi: 10.1063/1.454158 [14] Huwei L, Rionong F. Investigation of thermal decomposition of HMX and RDX by pyrolysis-gas chromatography[J]. Thermochim Acta, 1989, 138(1): 167-171. doi: 10.1016/0040-6031(89)87251-X [15] Botcher T R, Wight C A. Explosive thermal decomposition mechanism of RDX[J]. J Phys Chem, 1994, 98(21): 5441-5444. doi: 10.1021/j100072a009 [16] Kim E S, Lee H S, Mallery C F, et al. Thermal decomposition studies of energetic materials using confined rapid thermolysis/FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Combust Flame, 1997, 110(1/2): 239-255. [17] Löbbecke S, Keicher T, Krause H, et al. The new energetic material ammonium dinitramide and its thermal decomposition[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1997, 101-103(Part 2): 945-951. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167273897002154 [18] Glarborg P, Bendtsen A B, Miller J A. Nitromethane dissociation: Implications for the CH3+NO2 reaction[J]. Int J Chem Kinet, 1999, 31(9): 591-602. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4601(1999)31:9<591::AID-KIN1>3.0.CO;2-E [19] Oxley J C, Smith J L, Rogers E, et al. Gas production from thermal decomposition of explosives: Assessing the thermal stabilities of energetic materials from gas production data[J]. J Energ Mater, 2000, 18(2/3): 97-121. doi: 10.1080/07370650008216115 [20] Maharrey S, Behrens R. Thermal decomposition of energetic materials. 5. reaction processes of 1, 3, 5-trinitrohexahydro-s-triazine below its melting point[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2005, 109(49): 11236-11249. doi: 10.1021/jp054188q [21] Paletsky A A, Budachev N V, Korobeinichev O P. Mechanism and kinetics of the thermal decomposition of 5-aminotetrazole[J]. Kinet Catal, 2009, 50(5): 627-635. doi: 10.1134/S0023158409050036 [22] Behrens R. Thermal decomposition of energetic materials: Temporal behaviors of the rates of formation of the gaseous pyrolysis products from condensed-phase decomposition of octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine[J]. J Phys Chem, 1990, 94(17): 6706-6718. doi: 10.1021/j100380a034 [23] Brill T B, Gongwer P E, Williams G K. Thermal decomposition of energetic materials. 66. Kinetic compensation effects in HMX, RDX, and NTO[J]. J Phys Chem, 1994, 98(47): 12242-12247. doi: 10.1021/j100098a020 [24] Oyumi Y, Brill T B. Thermal decomposition of energetic materials 3. A high-rate, in situ, FTIR study of the thermolysis of RDX and HMX with pressure and heating rate as variables[J]. Combust Flame, 1985, 62(3): 213-224. doi: 10.1016/0010-2180(85)90147-6 [25] Glascoe E A, Zaug J M, Burnham A K. Pressure-dependent decomposition kinetics of the energetic material HMX up to 3.6 GPa[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2009, 113(48): 13548-13555. doi: 10.1021/jp905276k [26] Piermarini G J, Block S, Miller P J. Effects of pressure on the thermal decomposition rates, chemical reactivity and phase behavior of HMX, RDX and nitromethane[J]. Chem Phys Energ Mater(NATO ASI Series), 1990, 309: 391-412. doi: 10.1007/978-94-009-2035-4_17 [27] Piermarini G J, Block S, Miller P J. Effects of pressure and temperature on the thermal decomposition rate and reaction mechanism of beta-octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine[J]. J Phys Chem, 1987, 91(14): 3872-3878. doi: 10.1021/j100298a028 [28] Pinheiro G F M, Lourenço V L, Iha K. Influence of the heating rate in the thermal decomposition of HMX[J]. J Therm Anal Calorim, 2002, 67(2): 445-452. doi: 10.1023/A:1013984813195 [29] Zhang Y X, Bauer S H. Modeling the decomposition of nitromethane, induced by shock heating[J]. J Phys Chem B, 1997, 101(43): 8717-8726. doi: 10.1021/jp970716p [30] Patterson J E, Dreger Z A, Miao M, et al. Shock wave induced decomposition of RDX: Time-resolved spectroscopy[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2008, 112(32): 7374-7382. doi: 10.1021/jp800827b [31] Im H S, Bernstein E R. On the initial steps in the decomposition of energetic materials from excited electronic states[J]. J Chem Phys, 2000, 113(18): 7911-7918. doi: 10.1063/1.1315609 [32] Guo Y Q, Greenfield M, Bernstein E R. Decomposition of nitramine energetic materials in excited electronic states: RDX and HMX[J]. J Chem Phys, 2005, 122(24): 244310. doi: 10.1063/1.1929741 [33] Yu Z, Bernstein E R. Decomposition of pentaerythritol tetranitrate[C(CH2ONO2)4]following electronic excitation[J]. J Chem Phys, 2011, 135(15): 154305. doi: 10.1063/1.3652893 [34] Yuan B, Yu Z, Bernstein E R. Initial decomposition mechanism for the energy release from electronically excited energetic materials: FOX-7(1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethene, C2H4N4O4)[J]. J Chem Phys, 2014, 140(7): 074708. doi: 10.1063/1.4865266 [35] Mozgina O, Koutsospyros A, Gershman S, et al. Decomposition of energetic materials by pulsed electrical discharges in gas-bubbled aqueous solutions[J]. Plasma Science, IEEE Transactions on, 2009, 37(6): 905-910. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2009.2016970 [36] Oxley J C, Hiskey M, Naud D, et al. Thermal decomposition of nitramines: Dimethylnitramine, diisopropylnitramine, and N-nitropiperidine[J]. J Phys Chem, 1992, 96(6): 2505-2509. doi: 10.1021/j100185a023 [37] Giefers H, Pravica M. Radiation-induced decomposition of PETN and TATB under extreme conditions[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2008, 112(15): 3352-3359. doi: 10.1021/jp710512b [38] Shackelford S, Coolidge M, Goshgarian B, et al. Deuterium isotope effects in condensed-phase thermochemical decomposition reactions of octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine[J]. J Phys Chem, 1985, 89(14): 3118-3126. doi: 10.1021/j100260a034 [39] Lee J S, Jaw K S. Thermal decomposition properties and compatibility of CL-20, NTO with silicone rubber[J]. J Therm Anal Calorim, 2006, 85(2): 463-467. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a253a19b9077282ee4c59ae5ae06effe [40] Tarver C M, Koerner J G. Effects of endothermic binders on times to explosion of HMX-and TATB-based plastic bonded explosives[J]. J Energ Mater, 2007, 26(1): 1-28. doi: 10.1080/07370650701719170 [41] Tarver C M, Tran T D. Thermal decomposition models for HMX-based plastic bonded explosives[J]. Combust Flame, 2004, 137(1/2): 50-62. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=05dc31b67b9e0367564de77ad0e839fd [42] Chaturvedi S, Dave P N. Review on thermal decomposition of ammonium nitrate[J]. J Energ Mater, 2012, 31(1): 1-26. doi: 10.1080/07370652.2011.573523 [43] Urtiew P A, Tarver C M. Shock initiation of energetic materials at different initial temperatures(Review)[J]. Combust, Explos, Shock Waves, 2005, 41(6): 766-776. doi: 10.1007/s10573-005-0085-0 [44] Walley S M, Field J E, Greenaway M W. Crystal sensitivities of energetic materials[J]. Mater Sci Tech, 2006, 22(4): 402-413. doi: 10.1179/174328406X91122 [45] Davies A G, Burnett A D, Fan W, et al. Terahertz spectroscopy of explosives and drugs[J]. Mater Today, 2008, 11(3): 18-26. doi: 10.1016/S1369-7021(08)70016-6 [46] Sorescu D C, Rice B M, Thompson D L. A transferable intermolecular potential for nitramine crystals[J]. J Phys Chem A, 1998, 102(43): 8386-8392. doi: 10.1021/jp9820525 [47] Sorescu D C, Rice B M, Thompson D L. Theoretical studies of solid nitromethane[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2000, 104(35): 8406-8419. doi: 10.1021/jp000942q [48] 赵纪军, 刘红, 龚自正, 等.有机分子晶体的从头算研究[J].含能材料, 2004, z2: 497-504. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hncl2004z2040Zhao J J, Liu H, Gong Z Z, et al. Ab initio studies of organic molecular crystals: A literature review[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2004, z2: 497-504. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hncl2004z2040 [49] Manaa M R, Fried L, Reed E. Explosive chemistry: Simulating the chemistry of energetic materials at extreme conditions[J]. J Comput-Aided Mater Design, 2003, 10(2): 75-97. doi: 10.1023/B:JCAD.0000036812.64349.15 [50] 肖鹤鸣, 朱卫华, 肖继军, 等.含能材料感度判别理论研究——从分子、晶体到复合材料[J].含能材料2012, 20(5): 514-527.Xiao H M, Zhu W H, Xiao J J, et al. Theoretical studies on sensitivity criterion of energetic materials-From molecules, crystals, to composite materials[J]. Chinese Journary of Energetic Materials, 2012, 20(5): 514-527. (in Chinese) [51] Chakraborty D, Muller R P, Dasgupta S, et al. The mechanism for unimolecular decomposition of RDX(1, 3, 5-trinitro-1, 3, 5-triazine), an ab initio study[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2000, 104(11): 2261-2272. doi: 10.1021/jp9936953 [52] Chakraborty D, Muller R P, Dasgupta S, et al. Mechanism for unimolecular decomposition of HMX(1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine), an ab initio study[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2001, 105(8): 1302-1314. doi: 10.1021/jp0026181 [53] Chakraborty D, Muller R, Dasgupta S, et al. A detailed model for the decomposition of nitramines: RDX and HMX[J]. J Comput-Aided Mater Design, 2001, 8(2/3): 203-212. doi: 10.1023/A:1020074113000 [54] Hablot O, Soulard L. Shock decomposition of nitromethane[J]. AIP Conf Proc, 2000, 505(1): 857-860. [55] Booth R S, Butler L J. Thermal decomposition pathways for 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethene(FOX-7)[J]. J Chem Phys, 2014, 141(13): 134315. doi: 10.1063/1.4896165 [56] Irikura K K. Aminoxyl(Nitroxyl)radicals in the early decomposition of the nitramine RDX[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2013, 117(10): 2233-2241. doi: 10.1021/jp310247z [57] Sharia O, Kuklja M M. Modeling thermal decomposition mechanisms in gaseous and crystalline molecular materials: Application to β-HMX[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2011, 115(44): 12677-12686. doi: 10.1021/jp202733d [58] Sharia O, Kuklja M M. Comparative analysis of decomposition reactions in gaseous and crystalline β-HMX[J]. AIP Conf Proc, 2012, 1426(1): 1223-1226. [59] Xiao H M, Ju X H, Xu L N, et al. A density-functional theory investigation of 3-nitro-1, 2, 4-triazole-5-one dimers and crystal[J]. J Chem Phys, 2004, 121(24): 12523-12531. doi: 10.1063/1.1812258 [60] Qiu L, Gong X D, Xiao H M. Theoretical studies on thermolysis mechanism and stability of trans-1, 4, 5, 8-tetranitro-1, 4, 5, 8-tetraazadecalin isomers[J]. Chin J Chem, 2008, 26(12): 2165-2172. doi: 10.1002/cjoc.200890386 [61] Zhang S, Truong T N. Branching ratio and pressure dependent rate constants of multichannel unimolecular decomposition of gas-phase α-HMX: An ab initio dynamics study[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2001, 105(11): 2427-2434. doi: 10.1021/jp0043064 [62] Kuklja M M, Rashkeev S N, Zerilli F J. Shear-strain induced decomposition of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89(7): 071904. doi: 10.1063/1.2335680 [63] Kuklja M M, Rashkeev S N. Shear-strain-induced structural and electronic modifications of the molecular crystal 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene: Slip-plane flow and band gap relaxation[J]. Phys Rev B, 2007, 75(10): 104111. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.75.104111 [64] Zhang C. Stress-induced activation of decomposition of organic explosives: A simple way to understand[J]. J Mol Model, 2013, 19(1): 477-483. doi: 10.1007/s00894-012-1575-0 [65] Tsyshevsky R V, Sharia O, Kuklja M M. Thermal decomposition mechanisms of nitroesters: Ab initio modeling of pentaerythritol tetranitrate[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2013, 117(35): 18144-18153. doi: 10.1021/jp407754q [66] Melius C. Molecular decomposition mechanisms of energetic materials[J]. J Phys Colloques, 1987, 48(C4): 341-352. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/45573685_MOLECULAR_DECOMPOSITION_MECHANISMS_OF_ENERGETIC_MATERIALS [67] Melius C F, Binkley J S. Thermochemistry of the decomposition of nitramines in the gas phase[J]. Sympos(Int)Combus, 1988, 21(1): 1953-1963. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0082078488804326 [68] Kuklja M M. Thermal decomposition of solid cyclotrimethylene trinitramine[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2001, 105(42): 10159-10162. doi: 10.1021/jp011563f [69] Kuklja M M, Tsyshevsky R V, Sharia O. Effect of polar surfaces on decomposition of molecular materials[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2014, 136(38): 13289-13302. doi: 10.1021/ja506297e [70] Kimmel A V, Sushko P V, Kuklja M M. The structure and decomposition chemistry of isomer defects in a crystalline DADNE[J]. J Energ Mater, 2010, 28(sup1): 128-139. doi: 10.1080/07370651003639389 [71] Sharia O, Kuklja M M. Surface-enhanced decomposition kinetics of molecular materials illustrated with cyclotetramethylene-tetranitramine[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2012, 116(20): 11077-11081. doi: 10.1021/jp301723j [72] Sharia O, Tsyshevsky R, Kuklja M M. Surface-accelerated decomposition of δ-HMX[J]. J Phys Chem Lett, 2013, 4(5): 730-734. doi: 10.1021/jz302166p [73] Zhang C, Li Y, Xiong Y, et al. Acid and alkali effects on the decomposition of HMX molecule: A computational study[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2011, 115(43): 11971-11978. doi: 10.1021/jp204698b [74] Wang L, Tuo X, Yi C, et al. Ab initio calculations of the effects of H+ and NH4+ on the initial decomposition of HMX[J]. J Mol Graphics Modell, 2008, 27(3): 388-393. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2008.06.007 [75] Sharia O, Kuklja M M. Ab initio kinetics of gas phase decomposition reactions[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2010, 114(48): 12656-12661. doi: 10.1021/jp108065c [76] He W, Zhou G, Li J, et al. Molecular design of analogues of 2, 6-diamino-3, 5-dinitropyrazine-1-oxide[J]. J Molec Struc: Theochem, 2004, 668(2/3): 201-208. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b3064c54ae292ea0c9d83b2bb61d7ed4 [77] Mota O U O, Çan T. Anisotropic behavior of energetic materials at elevated pressure and temperature[J]. J Loss Prevent Proc, 2011, 24(6): 805-813. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950423011000878 [78] Liu H, Zhao J, Ji G, et al. Compressibility of liquid nitromethane in the high-pressure regime[J]. Physica B, 2006, 382(1/2): 334-339. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=aa0466c1f2aeb3c2647bca85d003d62c [79] Chambers C C, Thompson D L. Further studies of the classical dynamics of the unimolecular dissociation of RDX[J]. J Phys Chem, 1995, 99(43): 15881-15889. doi: 10.1021/j100043a029 [80] Guo Y, Thompson D L. Theoretical studies of the decomposition of RDX in liquid xenon[J]. J Phys Chem B, 1999, 103(48): 10599-10603. doi: 10.1021/jp992096t [81] Kohno Y, Ueda K, Imamura A. Molecular dynamics simulations of initial decomposition process on the unique N—N bond in nitramines in the crystalline state[J]. J Phys Chem, 1996, 100(12): 4701-4712. doi: 10.1021/jp9503223 [82] Losada M, Chaudhuri S. Transport in aluminized RDX under shock compression explored using molecular dynamics simulations[J]. J Phys Conf Ser, 2014, 500(16): 162002. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/500/16/162002 [83] Zhu W, Huang H, Huang H, et al. Initial chemical events in shocked octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine: A new initiation decomposition mechanism[J]. J Chem Phys, 2012, 136(4): 044516. doi: 10.1063/1.3679384 [84] Boyd S, Murray J S, Politzer P. Molecular dynamics characterization of void defects in crystalline(1, 3, 5-trinitro-1, 3, 5-triazacyclohexane)[J]. J Chem Phys, 2009, 131(20): 204903. doi: 10.1063/1.3265986 [85] Duan X, Li W, Pei C, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of void defects in the energetic material HMX[J]. J Mol Model, 2013, 19(9): 3893. doi: 10.1007/s00894-013-1924-7 [86] Qiu L, Zhu W H, Xiao J J, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of trans-1, 4, 5, 8-tetranitro-1, 4, 5, 8-tetraazadecalin-based polymer-bonded explosives[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2007, 111(7): 1559-1566. doi: 10.1021/jp065430b [87] Qiu L, Xiao H. Molecular dynamics study of binding energies, mechanical properties, and detonation performances of bicyclo-HMX-based PBXs[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2009, 164(1): 329-336. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.08.030 [88] Xu X, Xiao J, Huang H, et al. Molecular dynamic simulations on the structures and properties of ε-CL-20(001)/F2314 PBX[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2010, 175(1/3): 423-428. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19954888 [89] Li M, Li F, Shen R, et al. Molecular dynamics study of the structures and properties of RDX/GAP propellant[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2011, 186(2/3): 2031-2036. http://www.europepmc.org/abstract/MED/21237558 [90] van Duin A C T, Dasgupta S, Lorant F, et al. ReaxFF: A reactive force field for hydrocarbons[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2001, 105(41): 9396-9409. doi: 10.1021/jp004368u [91] Strachan A, Kober E M, van Duin A C T, et al. Thermal decomposition of RDX from reactive molecular dynamics[J]. J Chem Phys, 2005, 122(5): 054502. doi: 10.1063/1.1831277 [92] Zhang L, Zybin S V, van Duin A C T, et al. Carbon cluster formation during thermal decomposition of octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine and 1, 3, 5-triamino-2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzene high explosives from ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics simulations[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2009, 113(40): 10619-10640. doi: 10.1021/jp901353a [93] Han S P, van Duin A C T, Goddard W A, et al. Thermal decomposition of condensed-phase nitromethane from molecular dynamics from ReaxFF reactive dynamics[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2011, 115(20): 6534-6540. doi: 10.1021/jp1104054 [94] Rom N, Zybin S V, van Duin A C T, et al. Density-dependent liquid nitromethane decomposition: Molecular dynamics simulations based on ReaxFF[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2011, 115(36): 10181-10202. doi: 10.1021/jp202059v [95] 刘海, 李启楷, 何远航. CL20-TNT共晶高温热解的ReaxFF/lg反应力场分子动力学模拟[J].物理学报, 2013, 62(20): 208202. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wlxb201320067Liu H, Li Q K, He Y H. Pyrolysis of CL20-TNT cocrystal from ReaxFF/lg reactive molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2013, 62(20): 208202. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wlxb201320067 [96] 刘海, 董晓, 何远航. TNT高温热解及含碳团簇形成的反应分子动力学模拟[J].物理化学学报, 2014, 30(2): 232-240. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wlhxxb201402005Liu H, Dong X, He Y H. Reactive molecular dynamics simulations of carbon-containing clusters formation during pyrolysis of Tnt[J]. Acta Phys-Chim Sin, 2014, 30(2): 232-240. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wlhxxb201402005 [97] Furman D, Kosloff R, Dubnikova F, et al. Decomposition of condensed phase energetic materials: Interplay between uni-and bimolecular mechanisms[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2014, 136(11): 4192-4200. doi: 10.1021/ja410020f [98] Zhou T T, Huang F L. Effects of defects on thermal decomposition of HMX via ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulations[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2011, 115(2): 278-287. doi: 10.1021/jp105805w [99] Zhou T, Song H, Liu Y, et al. Shock initiated thermal and chemical responses of HMX crystal from ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2014, 16(27): 13914-13931. doi: 10.1039/c4cp00890a [100] 张力, 陈朗.高压下固相硝基甲烷分解的分子动力学计算[J].物理学报, 2013, 62(13): 138201. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wlxb201313069Zhang L, Chen L. The effect of pressure on thermal decomposition of solid nitromethane via MD simulation[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2013, 62(13): 138201. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wlxb201313069 [101] Strachan A, van Duin A C T, Chakraborty D, et al. Shock waves in high-energy materials: The initial chemical events in nitramine RDX[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2003, 91(9): 098301. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.098301 [102] Zhou T, Zybin S V, Liu Y, et al. Anisotropic shock sensitivity forβ-octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine energetic material under compressive-shear loading from ReaxFF-lg reactive dynamics simulations[J]. J Appl Phys, 2012, 111(12): 124904. doi: 10.1063/1.4729114 [103] Shan T R, van Duin A C T, Thompson A P. Development of a ReaxFF reactive force field for ammonium nitrate and application to shock compression and thermal decomposition[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2014, 118(8): 1469-1478. doi: 10.1021/jp408397n [104] Guo F, Cheng X L, Zhang H. Reactive molecular dynamics simulation of solid nitromethane impact on(010)surfaces induced and nonimpact thermal decomposition[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2012, 116(14): 3514-3520. doi: 10.1021/jp211914e [105] 张力, 陈朗, 王晨, 等.水分子对α相CL-20热分解机理影响的分子动力学研究[J].物理化学学报2013, 29(6): 1145-1153.Zhang L, Chen L, Wang C, et al. Molecular dynamics study of the effect of H2O on the thermal decomposition of α phase CL-20[J]. Acta Phys-Chim Sin, 2013, 29(6): 1145-1153. (in Chinese) [106] Wood M A, van Duin A C, Strachan A. Coupled thermal and electromagnetic induced decomposition in the molecular explosive αHMX; a reactive molecular dynamics study[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2014, 118(5): 885-895. doi: 10.1021/jp406248m [107] Zhang L. Thermal decomposition of plastic bonded explosives by molecular dynamic simulations with the ReaxFF force field[C]//APS March Meeting. Los Angeles, 2005. [108] Zhang L, Zybin S V, van Duin A C T, et al. Thermal decomposition of energetic materials by ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics[J]. AIP Conf Proc, 2006, 845(1): 589-592. http://meetings.aps.org/link/BAPS.2005.SHOCK.E5.4 [109] Politzer P, Boyd S. Molecular dynamics simulations of energetic solids[J]. Struct Chem, 2002, 13(2): 105-113. doi: 10.1023/A:1015748330357 [110] Tuckerman M E, Klein M L. Ab initio molecular dynamics study of solid nitromethane[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 1998, 283(3/4): 147-151. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009261497013638 [111] Zhu W, Xiao H. Ab initio molecular dynamics study of temperature effects on the structure and stability of energetic solid silver azide[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2011, 115(42): 20782-20787. doi: 10.1021/jp206290k [112] Wu Q, Zhu W, Xiao H. Comparative DFT-and DFT-D-based molecular dynamics studies of pressure effects in crystalline 1, 3, 5-triamino-2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzene at room temperature[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(95): 53149-53156. doi: 10.1039/C4RA09123J [113] Manaa M R, Kuo I F W, Fried L E. First-principles high-pressure unreacted equation of state and heat of formation of crystal 2, 6-diamino-3, 5-dinitropyrazine-1-oxide(LLM-105)[J]. J Chem Phys, 2014, 141(6): 064702. doi: 10.1063/1.4891933 [114] Yim W L, Liu Z f. Application of ab initio molecular dynamics for a priori elucidation of the mechanism in unimolecular decomposition: The case of 5-nitro-2, 4-dihydro-3h-1, 2, 4-triazol-3-one(NTO)[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2001, 123(10): 2243-2250. doi: 10.1021/ja0019023 [115] Isayev O, Gorb L, Qasim M, et al. Ab initio molecular dynamics study on the initial chemical events in nitramines: Thermal decomposition of CL-20[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2008, 112(35): 11005-11013. doi: 10.1021/jp804765m [116] Wang H, Stalnaker J, Chevreau H, et al. Potential of mean force calculations using ab initio tight-binding molecular dynamics: Application to N-NO2 bond dissociation in DMNA and HMX[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 2008, 457(1/3): 26-30. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009261408004284 [117] Schweigert I V, Dunlap B I. Electronic structure and molecular dynamics of breaking the RO—NO2 bond[J]. J Chem Phys, 2009, 130(24): 244110. doi: 10.1063/1.3155081 [118] 熊鹰, 舒远杰, 周歌, 等.均四嗪热分解机理的从头算分子动力学模拟及密度泛涵理论研究[J].含能材料, 2006, 14(6): 421-424. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hncl200606005Xiong Y, Shu Y J, Zhou G, et al. Thermal decomposition mechanism of s-tetrazine by ab initio molecular dynamics and density functional theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2006, 14(6): 421-424. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hncl200606005 [119] 熊鹰, 舒远杰, 王新锋, 等.四嗪类高氮化合物结构对热分解机理影响的理论研究[J].火炸药学报, 2008, 31(1): 1-5. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hzyxb200801001Xiong Y, Shu Y J, Wang X F, et al. Theoretical study on effect of tetrazine structures on their thermal decomposition mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives and Propellants, 2008, 31(1): 1-5. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hzyxb200801001 [120] Wu Q, Zhu W, Xiao H. An ab initio molecular dynamics study of thermal decomposition of 3, 6-Di(azido)-1, 2, 4, 5-tetrazine[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2014, 16(39): 21620-21628. doi: 10.1039/C4CP02579B [121] Manaa M R, Fried L E, Melius C F, et al. Decomposition of HMX at extreme conditions: A molecular dynamics simulation[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2002, 106(39): 9024-9029. doi: 10.1021/jp025668+ [122] An Q, Liu W G, Goddard W A, et al. Initial steps of thermal decomposition of dihydroxylammonium 5, 5′-bistetrazole-1, 1′-diolate crystals from quantum mechanics[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2014, 118(46): 27175-27181. doi: 10.1021/jp509582x [123] Xu J, Zhao J, Sun L. Thermal decomposition behaviour of RDX by first-principles molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Mol Simulat, 2008, 34: 961-965. doi: 10.1080/08927020802162892 [124] Wight C A, Botcher T R. Thermal decomposition of solid RDX begins with nitrogen-nitrogen bond scission[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1992, 114(21): 8303-8304. doi: 10.1021/ja00047a059 [125] Wu C J, Fried L E. Ab initio study of RDX decomposition mechanisms[J]. J Phys Chem A, 1997, 101(46): 8675-8679. doi: 10.1021/jp970678+ [126] Zhao J, Winey J M, Gupta Y M, et al. First-principles studies of RDX crystals under compression[J]. AIP Conf Proc, 2006, 845(1): 555-558. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC026526808 [127] Manaa M R, Reed E J, Fried L E, et al. Early chemistry in hot and dense nitromethane: Molecular dynamics simulations[J]. J Chem Phys, 2004, 120(21): 10146-10153. doi: 10.1063/1.1724820 [128] Chang J, Lian P, Wei D Q, et al. Thermal decomposition of the solid phase of nitromethane: Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2010, 105(18): 188302. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.188302 [129] Damianos K, Frank I. Car-parrinello molecular dynamics study of the thermal decomposition of sodium fulminate[J]. Chem-Eur J, 2010, 16(27): 8041-8046. doi: 10.1002/chem.200903076 [130] Liu Y, Li F, Sun H. Thermal decomposition of FOX-7 studied by ab initio molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Theor Chem Acc, 2014, 133(10): 1-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b9b6a81738306e920b89e48bb453d9e6 [131] 徐京城, 赵纪军.液态硝基甲烷热分解行为及压力效应的第一性原理研究[J].物理学报, 2009, 58(6): 4144-4149. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wlxb200906083Xu J C, Zhao J J. First-principles study of thermal decomposition of liquid nitromethane and its compressive effect[J]. Acta Physica Sinca, 2009, 58(6): 4144-4149. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wlxb200906083 [132] Zheng Z Y, Xu J C, Zhao J J. First-principles studies on the thermal decomposition behavior of FOX-7[J]. High Pressure Res, 2010, 30(2): 301-309. doi: 10.1080/08957959.2010.485390 [133] Ye C C, An Q, Goddard W A, et al. Initial decomposition reactions of bicyclo-HMX[BCHMX or cis-1, 3, 4, 6-tetranitrooctahydroimidazo-[4, 5-D]Imidazole]from quantum molecular dynamics simulations[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2015, 119(5): 2290-2296. doi: 10.1021/jp510328d [134] Decker S A, Chau D, Woo T K, et al. Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations of nitromethane under shock initiation conditions[C]//Jiang Z. Shock Waves. Berlin: Springer, 2005: 1193-1198. [135] Ge N N, Wei Y K, Ji G F, et al. Initial decomposition of the condensed-phase β-HMX under shock waves: Molecular dynamics simulations[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2012, 116(46): 13696-13704. doi: 10.1021/jp309120t [136] Ge N N, Wei Y K, Song Z F, et al. Anisotropic responses and initial decomposition of condensed-phase β-HMX under shock loadings via molecular dynamics simulations in conjunction with multiscale shock technique[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2014, 118(29): 8691-8699. doi: 10.1021/jp502432g [137] Ge N N, Wei Y K, Zhao F, et al. Pressure-induced metallization of condensed phase β-HMX under Shock loadings via molecular dynamics simulations in conjunction with multi-scale shock technique[J]. J Mol Model, 2014, 20(7): 2350. doi: 10.1007/s00894-014-2350-1 [138] Igor V S. Quantum mechanical simulations of condensed-phase decomposition dynamics in molten RDX[J]. J Phys: Conf Ser, 2014, 500(5): 052039. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/500/5/052039 [139] Xu K, Wei D Q, Chen X R, et al. Thermal decomposition of solid phase nitromethane under various heating rates and target temperatures based on ab initio molecular dynamics simulations[J]. J Mol Model, 2014, 20(10): 2438. doi: 10.1007/s00894-014-2438-7 [140] Liu L M, Car R, Selloni A, et al. Enhanced thermal decomposition of nitromethane on functionalized graphene sheets: Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134(46): 19011-19016. doi: 10.1021/ja3058277 -







 下载:
下载: