A-Site Ordered Quadruple Perovskite Oxides: Structures, Properties and Prospects
-
摘要: A位有序四重钙钛矿氧化物
$\rm AA'_3 B^{\;}_4 O^{\;}_{12} $ 具有丰富的物理性质和优异的材料性能,是当今凝聚态物理和材料科学的重要研究对象。相较于简单的ABO3型钙钛矿,在A位有序四重钙钛矿氧化物中,3/4的A位离子被过渡金属离子A′所取代,形成了1∶3的A/A′有序结构。因此,A位有序四重钙钛矿氧化物中的磁-电相互作用不再局限于B位子晶格内部,新颖的A′-A′、A′-B等磁-电相互作用也随之产生,从而展现出许多新现象和新物理机制,并为未来的实际应用提供了材料基础。围绕几种具有代表性的A位有序四重钙钛矿氧化物,回顾其研究脉络,对其晶体结构、物理性质和内在机理进行简单介绍,并对这类材料体系的研究方向和应用前景做出一些展望。Abstract: A-site ordered quadruple perovskite oxides with a formula as$\rm AA'_3 B^{\;}_4 O^{\;}_{12}$ exhibit multiple physical properties and superior performances, thus act as important subjects of current condensed matter physics and material science. Compared to the simple ABO3 perovskite, in the A-site ordered quadruple perovskite three quarters of the A atoms are replaced by transition metal Aʹ, forming ordered A/Aʹ occupancy with a 1∶3 ratio. As a result, the electric and magnetic interactions such as Aʹ-Aʹ and Aʹ-B can occur, leading to novel phenomena and new physics. Here we focus on several representative A-site ordered quadruple perovskites, recall their researches, briefly introduce their structures, physical properties and inner mechanisms, and discuss the opportunities for both fundamental studies and potential applications.-
Key words:
- high-pressure synthesis /
- perovskite oxide /
- dielectricity /
- charge order /
- multiferroics /
- half metal
-
图 1 (a)
$\rm ABO^{\;}_3 $ 型钙钛矿、(b) A位有序四重钙钛矿$\rm AA'_3 B^{\;}_4 O^{\;}_{12} $ 和(c) A位有序四重钙钛矿$\rm AA'_3 B^{\;}_2 B'_2 O^{\;}_{12} $ 的结构示意图Figure 1. Schematic crystal structures of (a)
$\rm ABO^{\;}_3 $ perovskite, A-site ordered perovskites (b)$\rm AA'_3 B^{\;}_4 O^{\;}_{12} $ and (c)$\rm AA'_3 B^{\;}_2 B'_2 O^{\;}_{12} $ 图 2 (a) Aʹ的氧配位示意图(黄色表示Aʹ离子,红色表示O离子,颜色由深至浅表示Aʹ―O键长由短至长),(b) AʹO4平面四边形晶体场示意图(10Dq为d轨道(t2g、eg)的劈裂,Δt2g、Δeg分别为t2g(xy、xz、yz)和eg(x2–y2、z2–r2)轨道的劈裂),(c) BO6八面体的倾斜(蓝色表示B离子,红色表示O离子)
Figure 2. (a) Coordination of the Aʹ site, the Aʹ ion is displayed in yellow, the O anions are displayed in red, and the different colors of O indicate the different Aʹ―O bond lengths; (b) crystal field of AʹO4 square planar, the 10Dq represents the split of the d orbit (t2g, eg), the Δt2g and Δeg represent the split of the t2g (xy, xz, yz) and eg (x2–y2, z2–r2) orbits, respectively; (c) tilt of the BO6 octahedra, the B ions are displayed in blue, and the O anions are displayed in red
图 3 (a) CaCu3Ti4O12的εʹ和tan δ随温度的变化关系(2条曲线分别为2个样品的测试数据)[27];(b) 不同频率下εʹ、tan δ和ω0随温度的变化关系[27];(c) εʹ随频率的变化关系;(d) 弛豫时间(τ)随温度的变化关系(10 K的τ为预测值)[29]
Figure 3. (a) Temperature-dependent εʹ and tan δ of two CaCu3Ti4O12 samples[27]; (b) temperature-dependent εʹ, tan δ and ω0 at selected frequencies[27]; (c) frequency-dependent εʹ of CaCu3Ti4O12 and (d) the relaxation time (τ) as a function of 1/T, the legend also gives the estimated τ at 10 K[29]
图 6 LaCu3Fe4O12在TN=393 K的多种转变:(a) Cu―O键、Fe―O键的键长随温度的变化关系;(b) 体积随温度的变化关系;(c) 穆斯堡尔(Mössbauer)谱的光吸收随运动速度的变化关系;(d) 磁化率(χ)和电阻率(ρ)随温度的变化曲线(插图为磁矩M随温度的变化曲线)[7]
Figure 6. Multiple transitions of LaCu3Fe4O12 at TN=393 K: (a) temperature-dependent Cu―O and Fe―O bond lengths; (b) temperature-dependent negative thermal expansion; (c) Mössbauer spectra, the velocity-dependent absorption; (d) temperature-dependent magnetic susceptibility (χ) and resistivity (ρ), the inset displays the temperature-dependent magnetization (M)[7]
图 7 (a) LnCu3Fe4O12的电荷有序形式总览;(b) LnCu3Fe4O12在相变温度附近的体积随温度的变化曲线;(c) Ln和Fe的键合状态(d为价键求和(bond valence sum,BVS)计算得到的价态与自由离子价态之差,d < 0表示欠键合,d > 0表示过键合)[61]
Figure 7. (a) An overview of charge order of LnCu3Fe4O12; (b) temperature-dependent volume of LnCu3Fe4O12; (c) correlation between dLn and dFe (d is the difference between bond valence sum (BVS) and ionic valence state. d < 0 indicates underbonding and d > 0 indicates overbonding.)[61]
图 8 (a) ACu3Fe4O12体系电荷有序能级示意图[62];(b) 当体积为原体积的102%、100%、96%、90%、88%、80%、78%时的电荷分布(不同颜色表示不同位置电荷相对密度差异Δn(r))[63]
Figure 8. (a) Schematic diagram of charge order in the ACu3Fe4O12 compounds[62]; (b) computed charge densities for volumes of 102%, 100%, 96%, 90%, 88%, 80% and 78%, the colors represent the charge density differences Δn(r)[63]
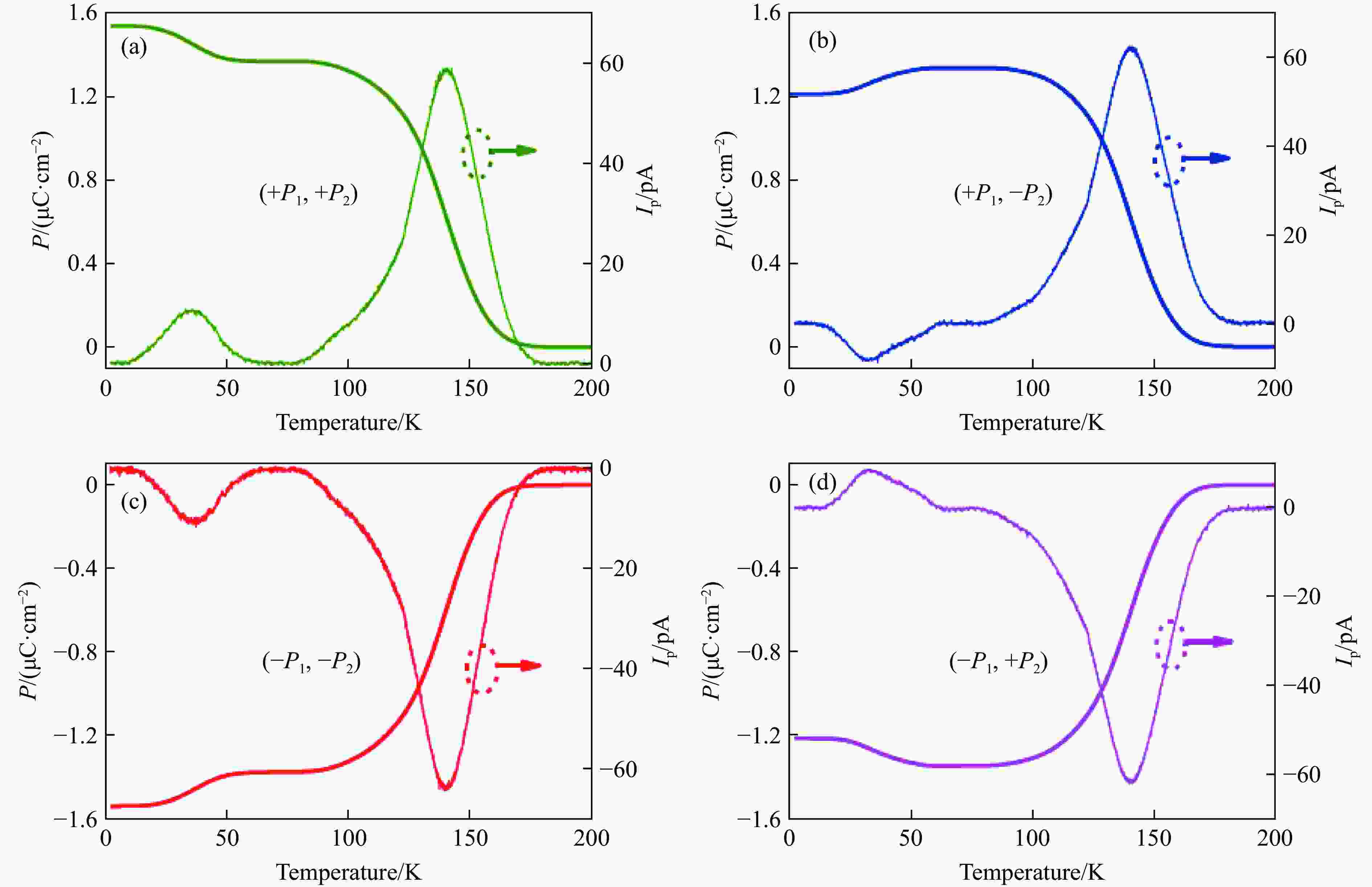
图 19 LaCu3Fe2Re2O12的 (a) 磁化率随温度的变化曲线、(b) 磁化强度随磁场的变化曲线、(c) 能带计算结果以及 (d) 半金属综合性能指标η与其他半金属氧化物的比较[101]
Figure 19. (a) Temperature-dependent magnetic susceptibility, (b) field-dependent magnetization, (c) calculated band structure from first principles and (d) overall performance factor η of LaCu3Fe2Re2O12 (The η values of some selected half-metallic oxides are displayed for comparison.)[101]
-
[1] CARPENTER M A, HOWARD C J. Symmetry rules and strain/order-parameter relationships for coupling between octahedral tilting and cooperative Jahn-Teller transitions in ABX3 perovskites. Ⅰ. theory [J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B, 2009, 65(Pt 2): 134−146. [2] CARPENTER M A, HOWARD C J. Symmetry rules and strain/order-parameter relationships for coupling between octahedral tilting and cooperative Jahn-Teller transitions in ABX3 perovskites. Ⅱ. application [J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B, 2009, 65(Pt 2): 147−159. [3] VASALA S, KARPPINEN M. A2BʹBʹʹO6 perovskite: a review [J]. Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2015, 43(1/2): 1–36. [4] ANDERSON P W. More is different: broken symmetry and the nature of the hierarchical structure of science [J]. Science, 1972, 177(4047): 393–396. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4047.393 [5] DESCHANVRES A, RAVEAU B, TOLLEMER F. Substitution of copper for a divalent metal in perovskite-type titanates [J]. Bulletin de la Société Chimique de France, 1967, 11: 4077–4078. [6] SUBRAMANIAN M A, LI D, DUAN N, et al. High dielectric constant in ACu3Ti4O12 and ACu3Ti3FeO12 phases [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2000, 151(2): 323–325. doi: 10.1006/jssc.2000.8703 [7] LONG Y W, HAYASHI N, SAITO T, et al. Temperature-induced A-B intersite charge transfer in an A-site-ordered LaCu3Fe4O12 perovskite [J]. Nature, 2009, 458(7234): 60–63. doi: 10.1038/nature07816 [8] ZHAO J F, GAO J C, LI W M, et al. A combinatory ferroelectric compound bridging simple ABO3 and A-site-ordered quadruple perovskite [J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 747. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20833-6 [9] WANG X, CHAI Y S, ZHOU L, et al. Observation of magnetoelectric multiferroicity in a cubic perovskite system: LaMn3Cr4O12 [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2015, 115(8): 087601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.087601 [10] DENG H S, LIU M, DAI J H, et al. Strong enhancement of spin ordering by A-site magnetic ions in the ferrimagnet CaCu3Fe2Os2O12 [J]. Physical Review B, 2016, 94(2): 024414. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.94.024414 [11] ZENG Z, GREENBLATT M, SUBRAMANIAN M A, et al. Large low-field magnetoresistance in perovskite-type CaCu3Mn4O12 without double exchange [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1999, 82(15): 3164–3167. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.82.3164 [12] CHEN W T, MIZUMAKI M, SEKI H, et al. A half-metallic A- and B-site-ordered quadruple perovskite oxide CaCu3Fe2Re2O12 with large magnetization and a high transition temperature [J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 3909. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4909 [13] YAGI S, YAMADA I, TSUKASAKI H, et al. Covalency-reinforced oxygen evolution reaction catalyst [J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 8249. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9249 [14] OVSYANNIKOV S V, ZAINULIN Y G, KADYROVA N I, et al. New antiferromagnetic perovskite CaCo3V4O12 prepared at high-pressure and high-temperature conditions [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2013, 52(20): 11703–11710. doi: 10.1021/ic400649h [15] PATINO M A, ROMERO F D, GOTO M, et al. Multi- k spin ordering in CaFe3Ti4O12 stabilized by spin-orbit coupling and further-neighbor exchange [J]. Physical Review Research, 2021, 3(4): 043208. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevResearch.3.043208 [16] BOCHU B, DESCHIZEAUX M N, JOUBERT J C, et al. Synthèse et caractérisation d'une série de titanates pérowskites isotypes de [CaCu3](Mn4)O12 [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1979, 29(2): 291–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-4596(79)90235-4 [17] MAREZIO M, DERNIER P D, CHENAVAS J, et al. High pressure synthesis and crystal structure of NaMn7O12 [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1973, 6(1): 16–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-4596(73)90200-4 [18] BOCHU B, CHENAVAS J, JOUBERT J C, et al. High pressure synthesis and crystal structure of a new series of perovskite-like compounds CM7O12 (C=Na, Ca, Cd, Sr, La, Nd) [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1974, 11(2): 88–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-4596(74)90102-9 [19] CHENAVAS J, JOUBERT J C, MAREZIO M, et al. The synthesis and crystal structure of CaCu3Mn4O12: a new ferromagnetic-perovskite-like compound [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1975, 14(1): 25–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-4596(75)90358-8 [20] OZAKI Y, GHEDIRA M, CHENAVAS J, et al. High-pressure synthesis and bond lengths of calcium copper germanium oxide [CaCu3](Ge4)O12 [J]. Acta Crystallographica, 1977, B33: 3615–3617. [21] MEYER C, GROS Y, BOCHU B, et al. Synthesis, crystal structure, and Mössbauer study of a series of perovskite-like compounds [ACu3](M, Fe)4O12 [J]. Physica Status Solidi (A), 1978, 48(2): 581–586. doi: 10.1002/pssa.2210480239 [22] BOCHU B, JOUBERT J C, COLLOMB A, et al. Ferromagnetic oxides [Ln3+/Cu3]Mn4O12 (Ln=La to Lu and Y) [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 1980, 15: 1319–1321. [23] BRYNTSE I, WERNER P E. Synthesis and structure of a perovskite related oxide, Bi2/3Cu3Ti4O12 [J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 1990, 25(4): 477–483. doi: 10.1016/0025-5408(90)90183-3 [24] LEINENWEBER K, LINTON J, NAVROTSKY A, et al. High-pressure perovskites on the joint CaTiO3-FeTiO3 [J]. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 1995, 22(4): 251–258. [25] TROYANCHUK I O, LOBANOVSKY L S, KASPER N V, et al. Magnetotransport phenomena in A(Mn3− x Cu x )Mn4O12 (A=Ca, Tb, Tm) perovskites [J]. Physical Review B, 1998, 58(22): 14903–14907. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.58.14903 [26] ZENG Z, GREENBLATT M, SUNSTROM J E, et al. Giant magnetoresistance in CaCu3Mn4O12-based oxides with perovskite-type structure [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1999, 147(1): 185–198. doi: 10.1006/jssc.1999.8212 [27] RAMIREZ A P, SUBRAMANIAN M A, GARDEL M, et al. Giant dielectric constant response in a copper-titanate [J]. Solid State Communications, 2000, 115(5): 217–220. doi: 10.1016/S0038-1098(00)00182-4 [28] CHOUDHARY R N P, BHUNIA U. Structural, dielectric and electrical properties of ACu3Ti4O12 (A=Ca, Sr, and Ba) [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2002, 37(24): 5177–5182. doi: 10.1023/A:1021019412533 [29] HOMES C C, VOGT T, SHAPIRO S M, et al. Optical response of high-dielectric-constant perovskite-related oxide [J]. Science, 2000, 293(5530): 673–676. [30] HE L X, NEATON J B, COHEN M H, et al. First-principles study of the structure and lattice dielectric response of CaCu3Ti4O12 [J]. Physical Review B, 2002, 65(21): 214112. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.65.214112 [31] COLLOMB A, SAMARAS D, BOCHU B, et al. Propriétés et structure magnétiques de CaCu3Ti4O12 à structure perovskite [J]. Physica Status Solidi A, 1977, 41(2): 459–463. doi: 10.1002/pssa.2210410215 [32] KOITZSCH A, BLUMBERG G, GOZAR A, et al. Antiferromagnetism in CaCu3Ti4O12 studied by magnetic Raman spectroscopy [J]. Physical Review B, 2002, 65(5): 052406. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.65.052406 [33] LUNKENHEIMER P, BOBNAR V, PRONIN A V, et al. Origin of apparent colossal dielectric constants [J]. Physical Review B, 2002, 66(5): 052105. [34] MAXWELL J C. A Treatise on electricity and magnetism [M]. 3rd ed. New York: Dover, 1954. [35] WAGNER K W. Zur theorie der unvollkommenen dielektrika [J]. Annalen der Physik, 1913, 345(5): 817–855. doi: 10.1002/andp.19133450502 [36] LARSEN P K, METSELAAR R. Electric and dielectric properties of polycrystalline yttrium iron garnet: space-charge-limited currents in an inhomogeneous solid [J]. Physical Review B, 1973, 8(5): 2016–2025. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.8.2016 [37] TSELEV A, BROOKS C M, ANLAGE S M et al. Evidence for power-law frequency dependence of intrinsic dielectric response in the CaCu3Ti4O12 [J]. Physical Review B, 2004, 70(14): 144101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.70.144101 [38] LIU J J, DUAN C G, YIN W G, et al. Large dielectric constant and Maxwell-Wagner relaxation in Bi2/3Cu3Ti4O12 [J]. Physical Review B, 2004, 70(14): 144106. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.70.144106 [39] LIU J J, DUAN C G, MEI W N. Dielectric properties and Maxwell-Wagner relaxation of compounds ACu3Ti4O12 (A=Ca, Bi2/3, Y2/3, La2/3) [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 98(9): 093703. doi: 10.1063/1.2125117 [40] SHAO S F, ZHANG J L, ZHENG P, et al. Microstructure and electrical properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2006, 99(8): 084106. doi: 10.1063/1.2191447 [41] FU D S, TANIGUCHI H, TANIYAMA T, et al. Origin of giant dielectric response in nonferroelectric CaCu3Ti4O12: inhomogeneous conduction nature probed by atomic force microscopy [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(5): 1694–1698. doi: 10.1021/cm0710507 [42] CHUNG S Y, KIM I D, KANG S J L. Strong nonlinear current-voltage behaviour in perovskite-derivative calcium copper titanate [J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3(11): 774–778. doi: 10.1038/nmat1238 [43] CLARKE D R. Varistor ceramics [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1999, 82(3): 485–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1999.tb01793.x [44] FALCÓN H, ALONSO J A, SÁNCHEZ-BENÍTEZ J, et al. Crystal structure, magnetic and electrical properties of CaCu3Mn4− x Ti x O12 (0.3≤ x≤ 3.0) perovskites [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2006, 18(29): 6841–6852. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/18/29/021 [45] DENG G C, XANTHOPOULOS N, MURALT P. Chemical nature of colossal dielectric constant of CaCu3Ti4O12 thin film by pulsed laser deposition [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(17): 172909. doi: 10.1063/1.2919076 [46] JACOB K T, SHEKHAR C, LI X G, et al. Gibbs energy of formation of CaCu3Ti4O12 and phase relations in the system CaO-CuO/Cu2O-TiO2 [J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56(17): 4798–4803. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2008.05.038 [47] AMARAL F, RUBINGER C P L, VALENTE M A, et al. Enhanced dielectric response of GeO2-doped CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 105(3): 034109. doi: 10.1063/1.3075909 [48] CHOI S Y, CHUNG S Y, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Direct determination of dopant site selectivity in ordered perovskite CaCu3Ti4O12 polycrystals by aberration-corrected STEM [J]. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(8): 885–889. doi: 10.1002/adma.200802728 [49] DENG G C, MURALT P. Annealing effects on electrical properties and defects of CaCu3Ti4O12 thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition [J]. Physical Review B, 2010, 81(22): 224111. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.81.224111 [50] YAMADA I, TAKATA K, HAYASHI N, et al. A perovskite containing quadrivalent iron as a charge-disproportionated ferrimagnet [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47(37): 7032–7035. doi: 10.1002/anie.200801482 [51] XIANG H P, LIU X J, ZHAO E J, et al. Ferrimagnetic and half-metallic CaCu3Fe4O12: prediction from first principles investigation [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 91(1): 011903. doi: 10.1063/1.2753734 [52] MIZUMAKI M, CHEN W T, SAITO T, et al. Direct observation of the ferrimagnetic coupling of A-site Cu and B-site Fe spins in charge-disproportionated CaCu3Fe4O12 [J]. Physical Review B, 2011, 84(9): 094418. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.84.094418 [53] LONG Y W. A-site ordered quadruple perovskite oxides AAʹ3B4O12 [J]. Chinese Physics B, 2016, 25(7): 078108. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/25/7/078108 [54] YAMADA I, TSUCHIDA K, OHGUSHI K, et al. Giant negative thermal expansion in the iron perovskite SrCu3Fe4O12 [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(29): 6579–6582. doi: 10.1002/anie.201102228 [55] TAKENAKA K, TAKAGI H. Giant negative thermal expansion in Ge-doped anti-perovskite manganese nitrides [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 87(26): 261902. doi: 10.1063/1.2147726 [56] HAO X F, XU Y H, GAO F M, et al. Charge disproportionation in CaCu3Fe4O12 [J]. Physical Review B, 2009, 79(11): 113101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.79.113101 [57] LI H P, LV S H, WANG Z C, et al. Mechanism of A-B intersite charge transfer and negative thermal expansion in A-site-ordered perovskite LaCu3Fe4O12 [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 111(10): 103718. doi: 10.1063/1.4721408 [58] CHEN W T, SAITO T, HAYASHI N, et al. Ligand-hole localization in oxides with unusual valence Fe [J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2: 449. doi: 10.1038/srep00449 [59] ALLUB R, ALASCIO B. A thermodynamic model for the simultaneous charge/spin order transition in LaCu3Fe4O12 [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2012, 24(49): 495601. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/24/49/495601 [60] ETANI H, YAMADA I, OHGUSHI K, et al. Suppression of intersite charge transfer in charge-disproportionated perovskite YCu3Fe4O12 [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 135(16): 6100–6106. [61] YAMADA I, ETANI H, TSUCHIDA K, et al. Control of bond-strain-induced electronic phase transitions in iron perovskites [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2013, 52(23): 13751–13761. doi: 10.1021/ic402344m [62] REZAEI N, HANSMANN P, BAHRAMY M S, et al. Mechanism of charge transfer/disproportionation in LnCu3Fe4O12 (Ln=lanthanides) [J]. Physical Review B, 2014, 89(12): 125125. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.89.125125 [63] MENG J L, ZHANG L F, YAO F, et al. Theoretical study on the negative thermal expansion perovskite LaCu3Fe4O12: pressure-triggered transition of magnetism, charge, and spin state [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2017, 56(11): 6371–6379. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b00458 [64] YAMADA I, MARUKAWA S, MURAKAMI M, et al. “True” negative thermal expansion in Mn-doped LaCu3Fe4O12 perovskite oxides [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105(23): 231906. doi: 10.1063/1.4903890 [65] SAKAI Y, YANG J Y, YU R Z, et al. A-site and B-site charge orderings in an s- d level controlled perovskite oxide PbCoO3 [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(12): 4574–4581. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b01851 [66] LIU Z H, SAKAI Y, YANG J Y, et al. Sequential spin state transition and intermetallic charge transfer in PbCoO3 [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(12): 5731–5741. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b13508 [67] OVSYANNIKOV S V, ABAKUMOV A M, TSIRLIN A A, et al. Perovskite-like Mn2O3: a path to new manganites [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(5): 1494–1498. doi: 10.1002/anie.201208553 [68] BYKOVA E, DUBROVINSKY L, DUBROVINSKAIA N, et al. Structural complexity of simple Fe2O3 at high pressures and temperatures [J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 10661. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10661 [69] SMOLENSKII G A, BOKOV V A. Coexistence of magnetic and electric ordering in crystals [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1964, 35(3): 915–918. doi: 10.1063/1.1713535 [70] KIMURA T, GOTO T, SHINTANI H, et al. Magnetic control of ferroelectric polarization [J]. Nature, 2003, 426(6962): 55–58. doi: 10.1038/nature02018 [71] WANG J, NEATON J B, ZHENG H, et al. Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures [J]. Science, 2003, 299(5613): 1719–1722. doi: 10.1126/science.1080615 [72] KHOMSKII D I. Multiferroics: different ways to combine magnetism and ferroelectricity [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2006, 306(1): 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.01.238 [73] DONG S, LIU J M, CHEONG S W, et al. Multiferroic materials and magnetoelectric physics: symmetry, entanglement, excitation, and topology [J]. Advances in Physics, 2015, 64(5/6): 519–626. [74] POPOV Y F, KADOMTSEVA A M, KROTOV S S, et al. Features of the magnetoelectric properties of BiFeO3 in high magnetic fields [J]. Low Temperature Physics, 2001, 27(6): 478–479. doi: 10.1063/1.1382990 [75] TOKURA Y, SEKI S, NAGAOSA N. Multiferroics of spin origin [J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2014, 77(7): 076501. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/77/7/076501 [76] GAJEK M, BIBES M, FUSIL S, et al. Tunnel junctions with multiferroic barriers [J]. Nature Materials, 2007, 6(4): 296–302. doi: 10.1038/nmat1860 [77] CHU Y H, MARTIN L W, HOLCOMB M B, et al. Electric-field control of local ferromagnetism using a magnetoelectric multiferroic [J]. Nature Materials, 2008, 7(6): 478–482. doi: 10.1038/nmat2184 [78] SHEVLIN S. Multiferroics and the path to the market [J]. Nature Materials, 2019, 18(3): 191–192. doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0295-6 [79] NAN T X, LIN H, GAO Y, et al. Acoustically actuated ultra-compact NEMS magnetoelectric antennas [J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 296. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00343-8 [80] LONG Y W, SAITO T, MIZUMAKI M, et al. Various valence states of square-coordinated Mn in A-site-ordered perovskites [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(44): 16244–16247. doi: 10.1021/ja906668c [81] LV S H, LI H P, LIU X J, et al. Mn-Cr intersite independent magnetic behavior and electronic structures of LaMn3Cr4O12: study from first-principles [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 110(2): 023711. doi: 10.1063/1.3610504 [82] 殷云宇, 王潇, 邓宏芟, 等. 多种有序钙钛矿结构的高压制备与特殊物性 [J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(3): 030201. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.030201YIN Y Y, WANG X, DENG H S, et al. High-pressure synthesis and special physical properties of several ordered perovskite structures [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(3): 030201. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.030201 [83] SCHIRBER M. Multiferroic surprise [J]. Physics, 2015, 8: s95. doi: 10.1103/Physics.8.s95 [84] FENG J S, XIANG H J. Anisotropic symmetric exchange as a new mechanism for multiferroicity [J]. Physical Review B, 2016, 93(17): 174416. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.93.174416 [85] HUR N, PARK S, SHARMA P A, et al. Electric polarization reversal and memory in a multiferroic material induced by magnetic fields [J]. Nature, 2004, 429(6990): 392–395. doi: 10.1038/nature02572 [86] ZHOU L, DAI J H, CHAI Y S, et al. Realization of large electric polarization and strong magnetoelectric coupling in BiMn3Cr4O12 [J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(44): 1703435. doi: 10.1002/adma.201703435 [87] 周龙, 王潇, 张慧敏, 等. 多阶有序钙钛矿多铁性材料的高压制备与物性 [J]. 物理学报, 2018, 67(15): 157505. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20180878ZHOU L, WANG X, ZHANG H M, et al. High pressure synthesis and physical properties of multiferroic materials with multiply-ordered perovskite structure [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(15): 157505. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20180878 [88] LIU G X, LIU Z H, CHAI Y S, et al. Magnetic and electric field dependent anisotropic magnetoelectric multiferroicity in SmMn3Cr4O12 [J]. Physical Review B, 2021, 104(5): 054407. [89] TANDA S, TSUNETA T, OKAJIMA Y, et al. A Möbius strip of single crystals [J]. Nature, 2002, 417(6887): 397–398. doi: 10.1038/417397a [90] HAN D R, PAL S, LIU Y, et al. Folding and cutting DNA into reconfigurable topological nanostructures [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2010, 5(10): 712–717. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2010.193 [91] GRAY A. Modern differential geometry of curves and surfaces with mathematica [M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1997. [92] LIU G X, PI M C, ZHOU L, et al. Physical realization of topological Roman surface by spin-induced ferroelectric polarization in cubic lattice [J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 2373. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29764-w [93] WANG Z W, CHAI Y S, DONG S. First-principles demonstration of Roman-surface topological multiferroicity [J]. Physical Review B, 2023, 108(6): L060407. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.108.L060407 [94] BAIBICH M N, BROTO J M, FERT A, et al. Giant magnetoresistance of (001)Fe/(001)Cr magnetic superlattices [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1988, 61(21): 2472–2475. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.61.2472 [95] MOTT N F. The electrical conductivity of transition metals [J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1936, 153(880): 699-717. [96] PICKETT W E, MOODERA J S. Half metallic magnets [J]. Physics Today, 2001, 54(5): 39–44. doi: 10.1063/1.1381101 [97] PARK J H, VESCOVO E, KIM H J, et al. Direct evidence for a half-metallic ferromagnet [J]. Nature, 1998, 392(6678): 794–796. doi: 10.1038/33883 [98] HWANG H Y, CHEONG S W, ONG N P, et al. Spin-polarized intergrain tunneling in La2/3Sr1/3MnO3 [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(10): 2041–2044. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.2041 [99] KOBAYASHI K I, KIMURA T, SAWADA H, et al. Room-temperature magnetoresistance in an oxide material with an ordered double-perovskite structure [J]. Nature, 1998, 395(6703): 677–680. doi: 10.1038/27167 [100] KOBAYASHI K I, KIMURA T, TOMIOKA Y, et al. Intergrain tunneling magnetoresistance in polycrystals of the ordered double perovskite Sr2FeReO6 [J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59(17): 11159–11162. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.59.11159 [101] LIU Z H, ZHANG S K, WANG X, et al. Realization of a half metal with a record-high Curie temperature in perovskite oxides [J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(17): 2200626. doi: 10.1002/adma.202200626 [102] WANG X, LIU Z H, DENG H S, et al. Comparative study on the magnetic and transport properties of B-site ordered and disordered CaCu3Fe2Os2O12 [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2022, 61(42): 16929–16935. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c03030 [103] EL GANICH H, EL RHAZOUANI O, AHMED Y A, et al. Computation of the exchange interactions in CaCu3Fe2Os2O12 quadruple perovskite: Monte Carlo simulation [J]. Physica E: Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2023, 150: 115696. doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2023.115696 [104] MEHMOOD S, ALI Z, ALHARBI Y T, et al. Structural and magneto-elastic properties of the quadruple perovskites CaCu3B2Os2O12 (B=Mn–Ni): the Heisenberg model and DFT study [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2023, 52(9): 5872–5883. doi: 10.1007/s11664-023-10555-y [105] LIU Z H, SUN Q, YE X B, et al. Quadruple perovskite oxide LaCu3Co2Re2O12: a ferrimagnetic half metal with nearly 100% B-site degree of order [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2020, 117(15): 152402. doi: 10.1063/5.0025704 [106] WANG X, LIU M, SHEN X D, et al. High-temperature ferrimagnetic half metallicity with wide spin-up energy gap in NaCu3Fe2Os2O12 [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2019, 58(1): 320–326. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b02404 [107] WANG X, LIU Z H, YE X B, et al. Os doping suppressed Cu-Fe charge transfer and induced structural and magnetic phase transitions in LaCu3Fe4− x Os x O12 ( x = 1 and 2) [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2021, 60(9): 6298–6305. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c00009 [108] YE X B, WANG X, LIU Z H, et al. Emergent physical properties of perovskite-type oxides prepared under high pressure [J]. Dalton Transactions, 2022, 51(5): 1745–1753. doi: 10.1039/D1DT03551G [109] LI X X, WU X J, LI Z Y, et al. Bipolar magnetic semiconductors: a new class of spintronics materials [J]. Nanoscale, 2012, 4(18): 5680–5685. doi: 10.1039/c2nr31743e [110] KATSNELSON M I, IRKHIN V Y, CHIONCEL L, et al. Half-metallic ferromagnets: from band structure to many-body effects [J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2008, 80(2): 315–378. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.80.315 [111] YAMADA I, FUJII H, TAKAMATSU A, et al. Bifunctional oxygen reaction catalysis of quadruple manganese perovskites [J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(4): 1603004. doi: 10.1002/adma.201603004 [112] YE X B, SONG S Z, LI L L, et al. Aʹ-B intersite cooperation-enhanced water splitting in quadruple perovskite oxide CaCu3Ir4O12 [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2021, 33(23): 9295–9305. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.1c03015 [113] AKIZUKI Y, YAMADA I, FUJITA K, et al. A-site-ordered perovskite MnCu3V4O12 with a 12-coordinated manganese (Ⅱ) [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2013, 52(19): 11538–11543. doi: 10.1021/ic401855j [114] AKIZUKI Y, YAMADA I, FUJITA K, et al. Rattling in the quadruple perovskite CuCu3V4O12 [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(37): 10870–10874. doi: 10.1002/anie.201504784 [115] CONG J Z, ZHAI K, CHAI Y S, et al. Spin-induced multiferroicity in the binary perovskite manganite Mn2O3 [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 2996. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05296-0 [116] BARTEL C J, SUTTON C, GOLDSMITH B R, et al. New tolerance factor to predict the stability of perovskite oxides and halides [J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(2): eaav0693. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav0693 [117] ALBRECHT E K, KARTTUNEN A J. Investigation on the predictive power of tolerance factor τ for A-site double perovskite oxides [J]. Dalton Transactions, 2023, 52(35): 12461–12469. doi: 10.1039/D3DT01990J [118] STRELTSOV S V, KHOMSKII D I. Jahn-Teller distortion and charge, orbital, and magnetic order in NaMn7O12 [J]. Physical Review B, 2014, 89(20): 201115(R). [119] JOHNSON R D, KHALYAVIN D D, MANUEL P, et al. Magneto-orbital ordering in the divalent A-site quadruple perovskite manganites AMn7O12 (A=Sr, Cd, and Pb) [J]. Physical Review B, 2017, 96(5): 054448. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.96.054448 [120] BELIK A A, JOHNSON R D, KHALYAVIN D D. The rich physics of A-site-ordered quadruple perovskite manganites AMn7O12 [J]. Dalton Transactions, 2021, 50(43): 15458–15472. doi: 10.1039/D1DT02992D -















 下载:
下载: