Hybrid Design of Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Structure and Its Mechanical Behavior under Impact Loading
-
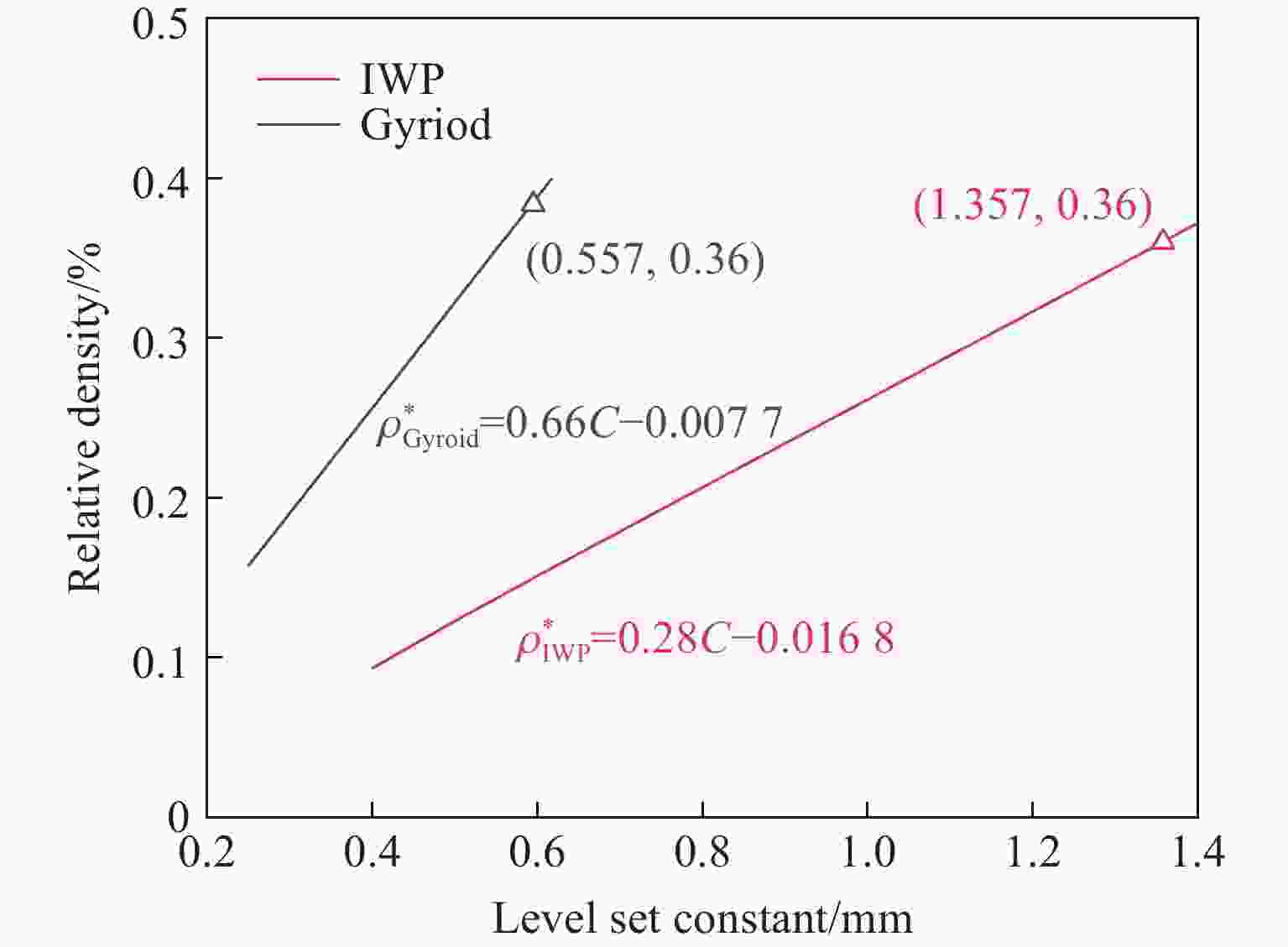
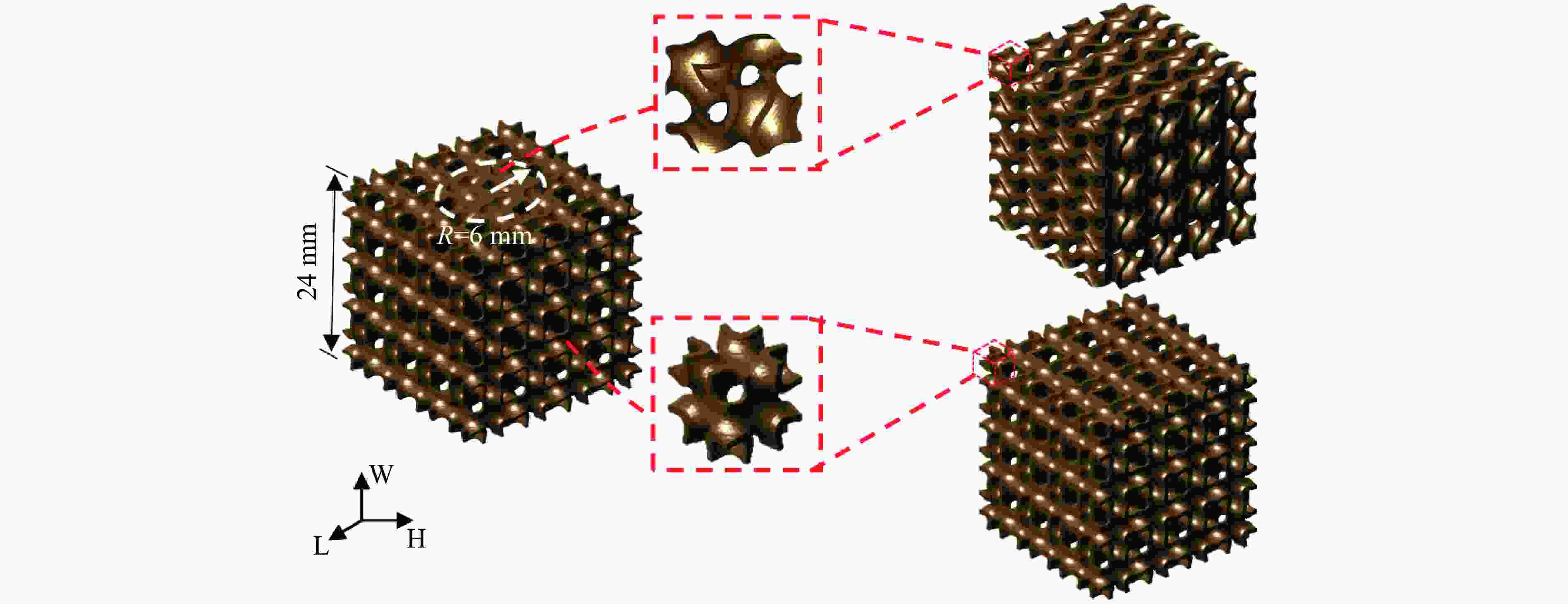
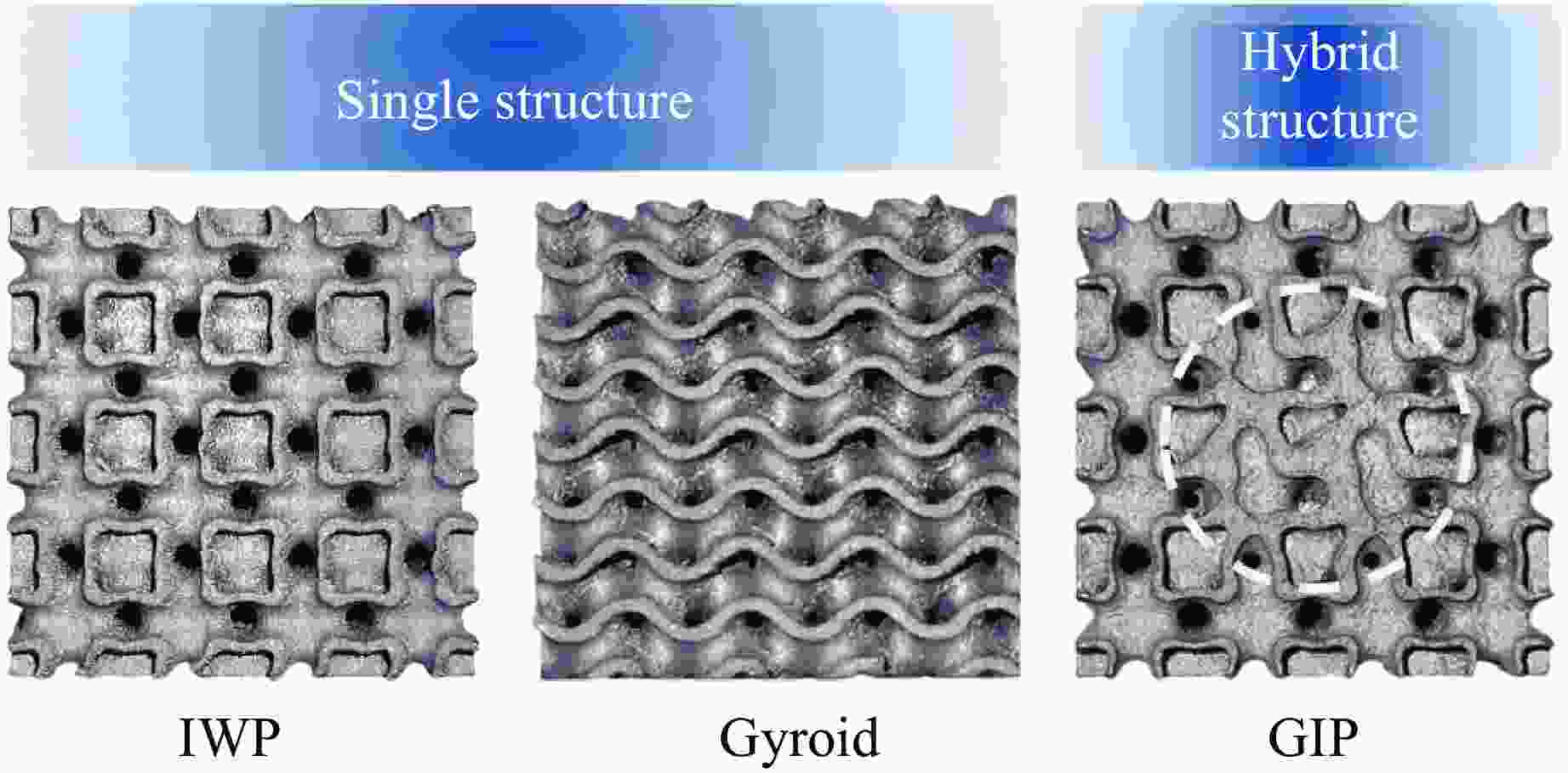
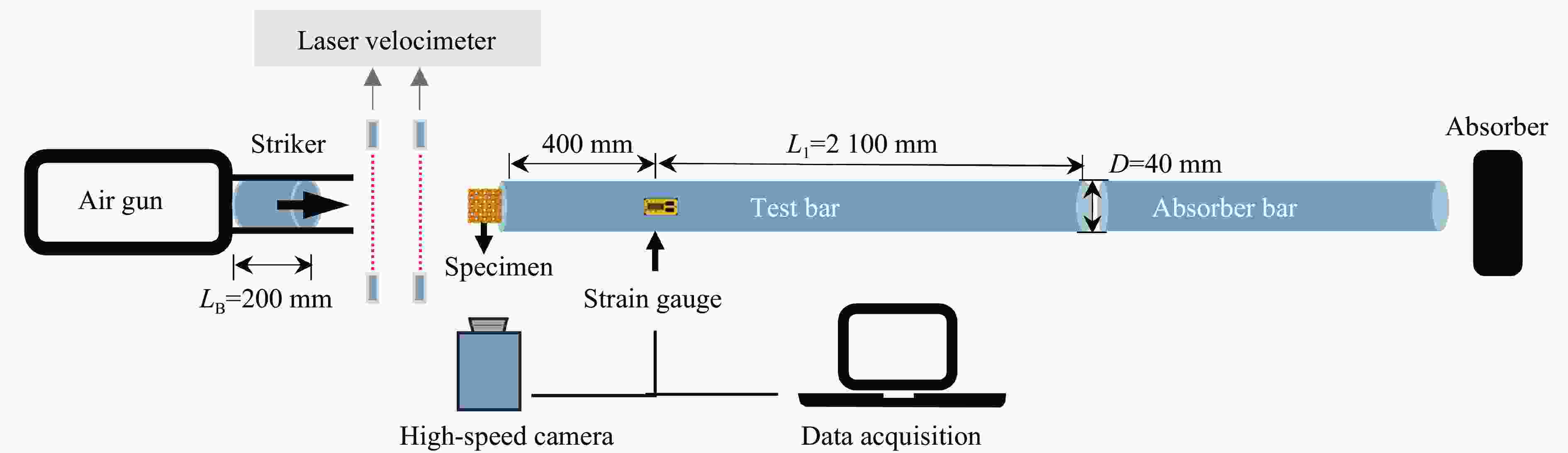
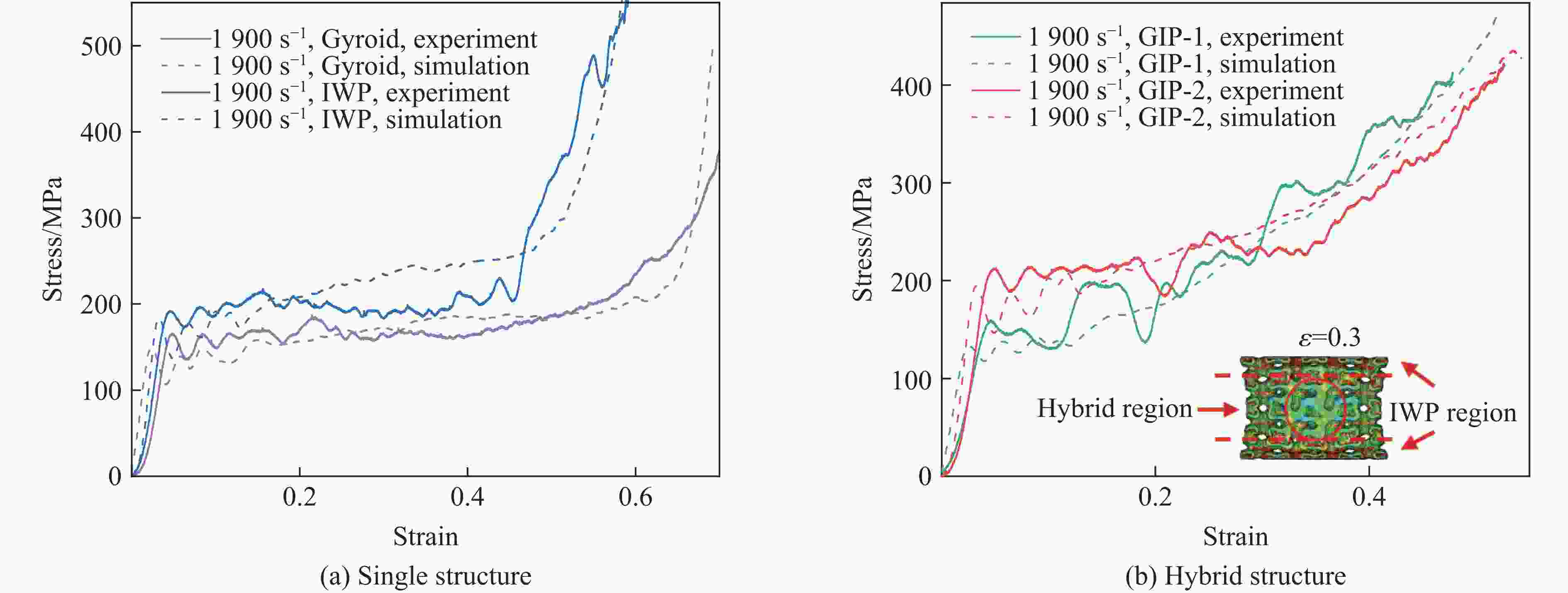
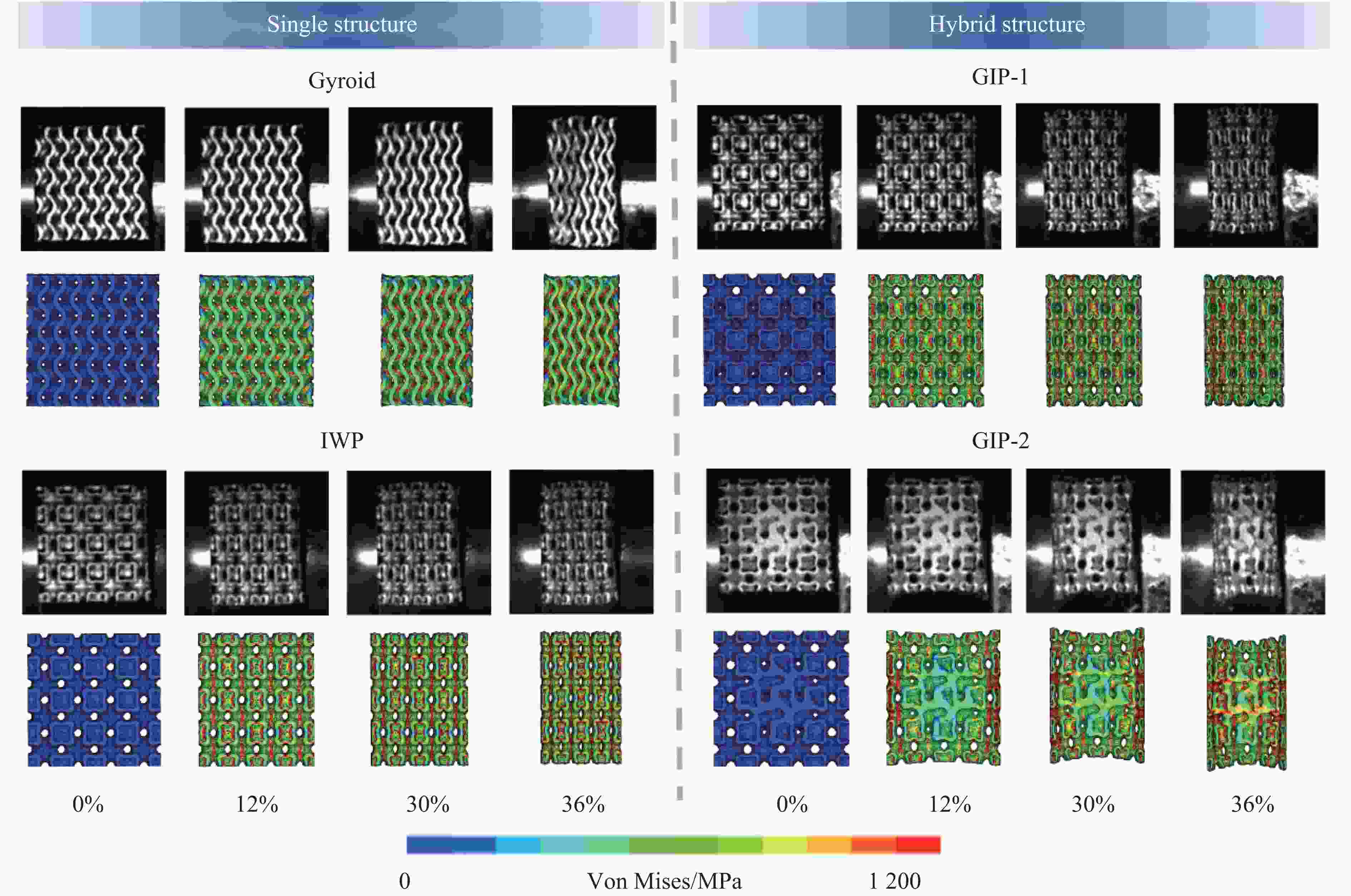
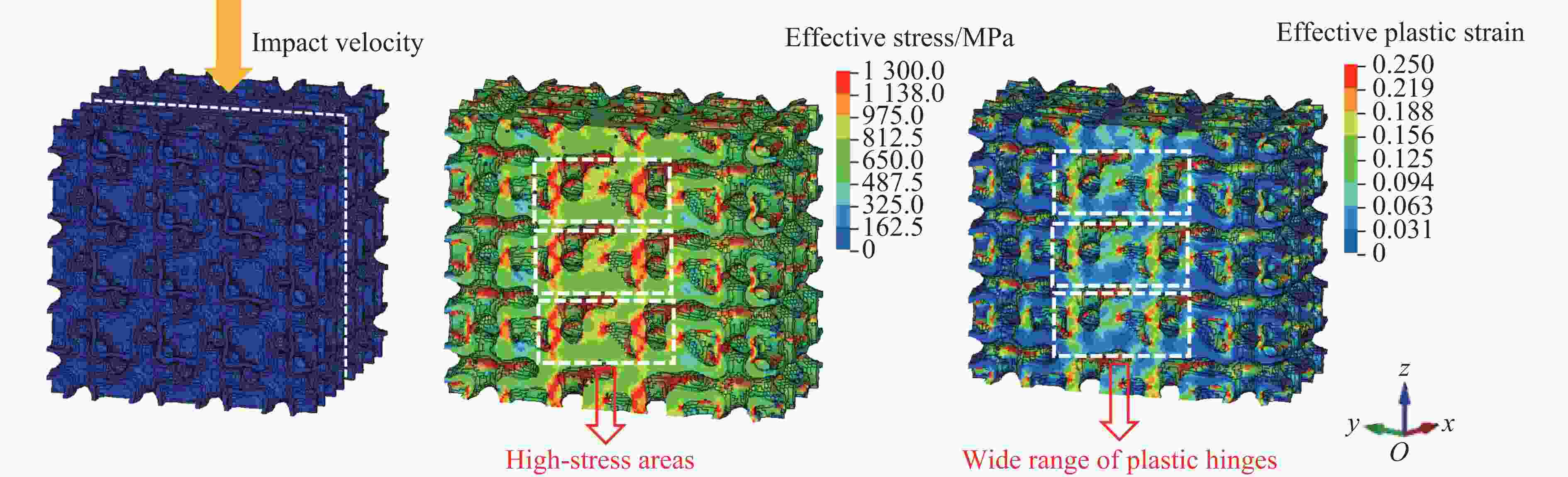
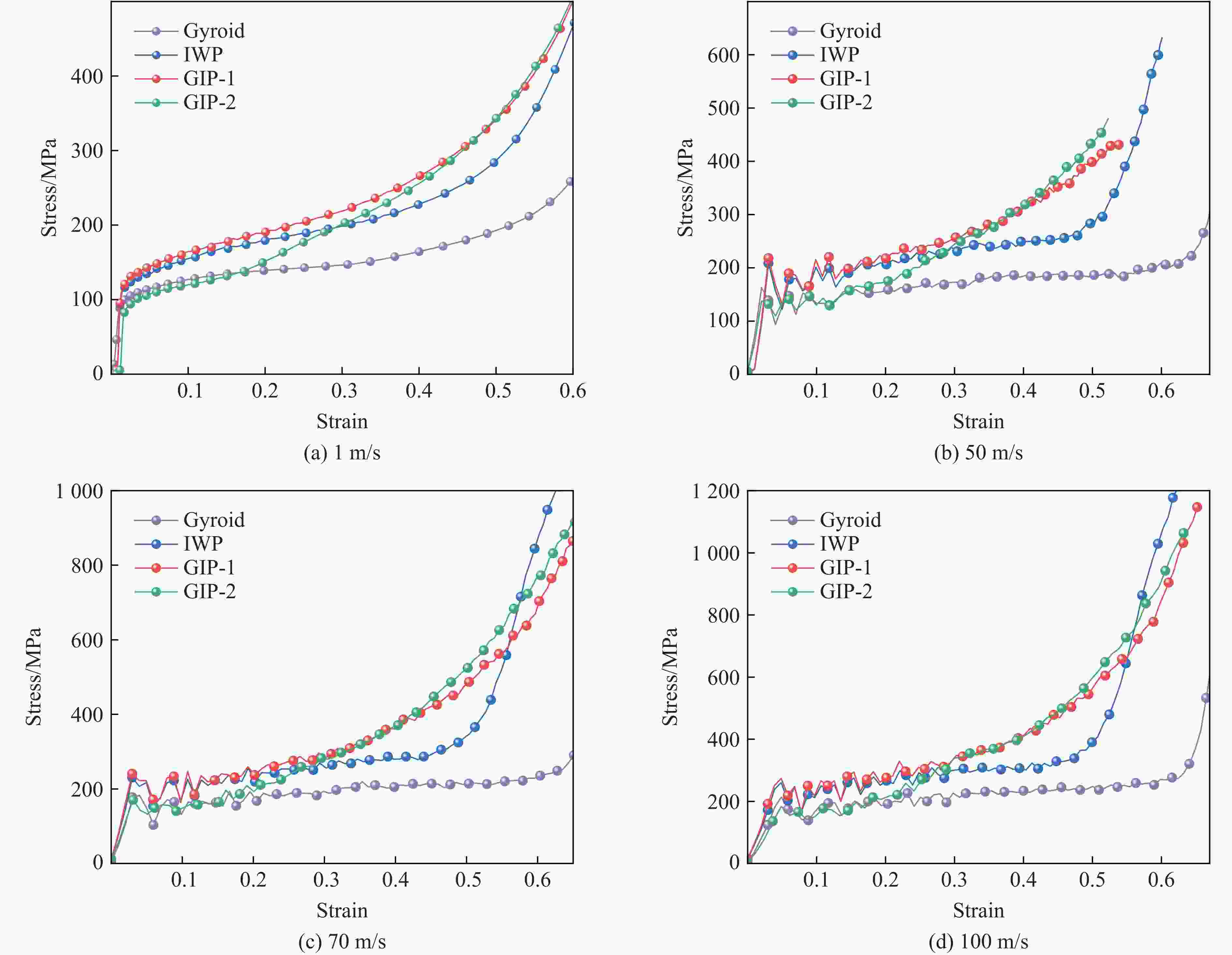
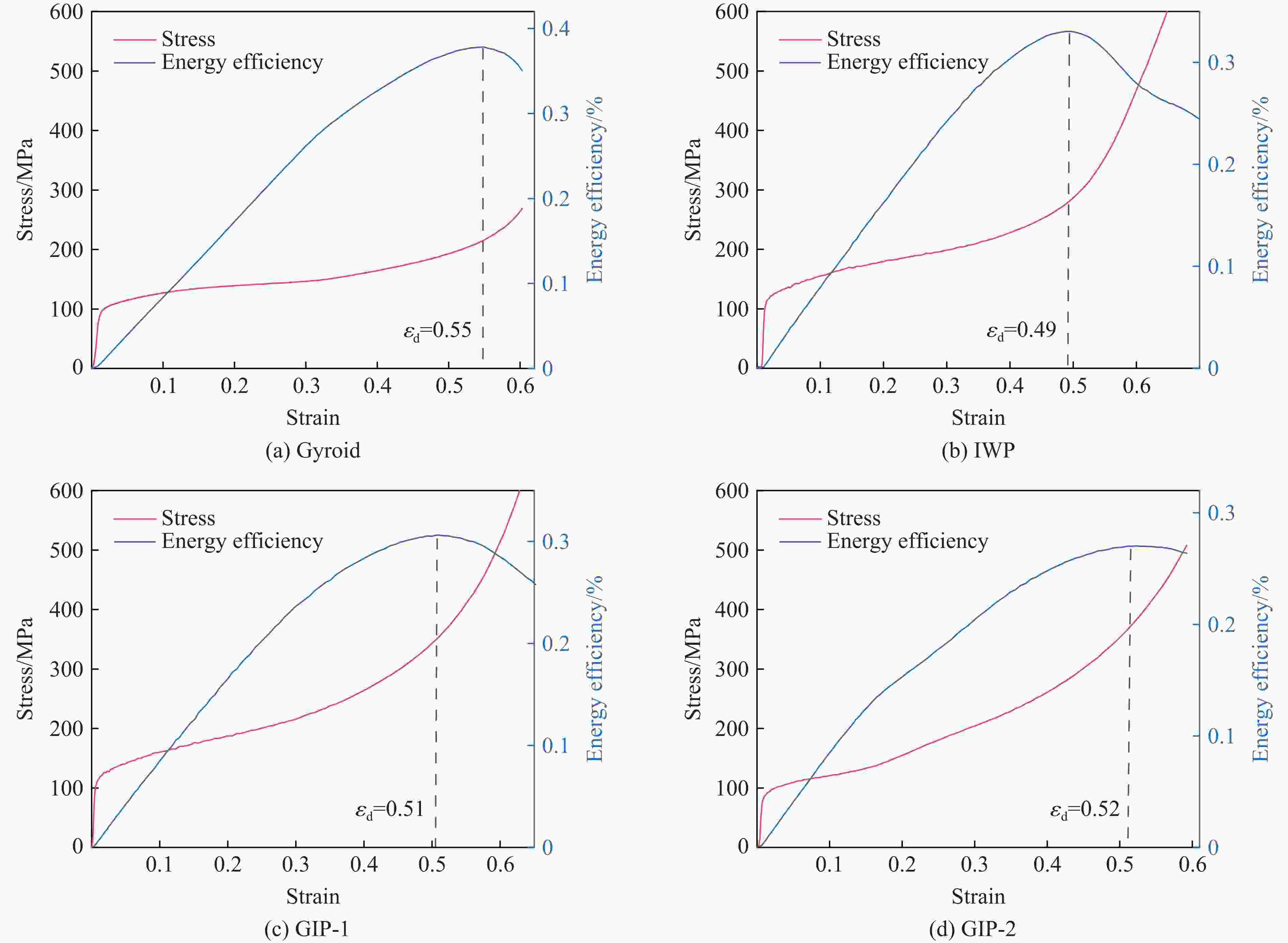
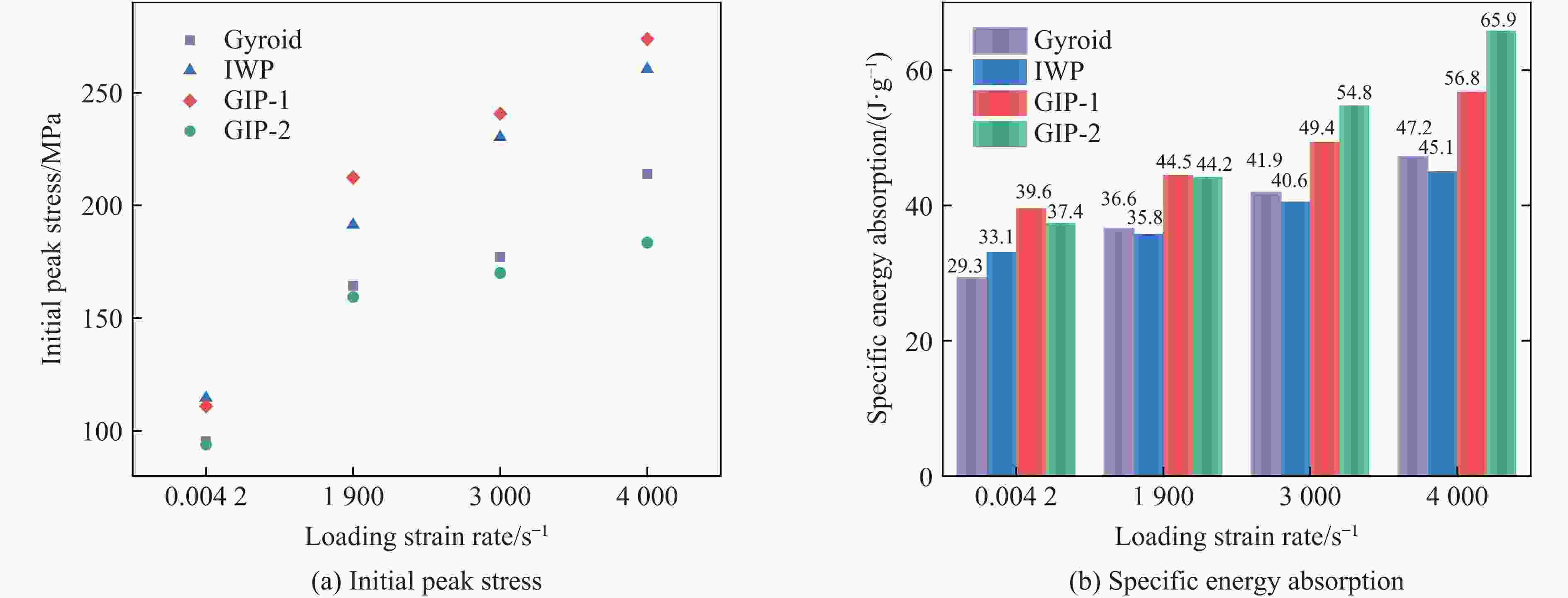
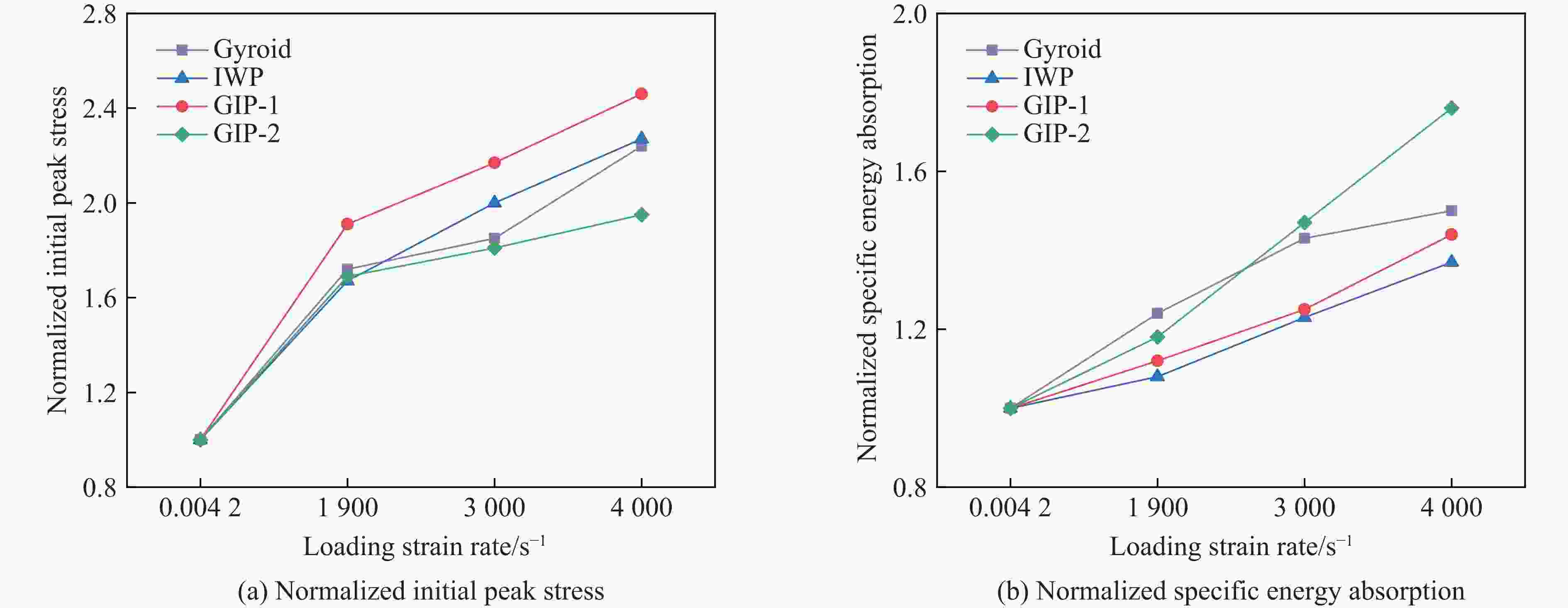
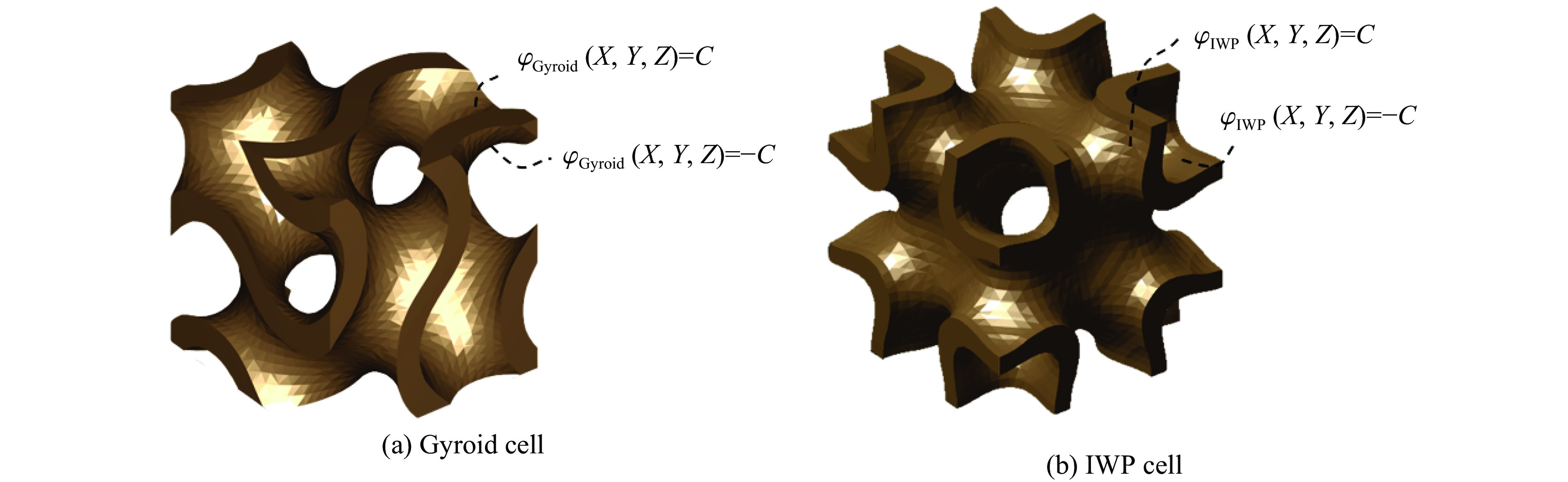
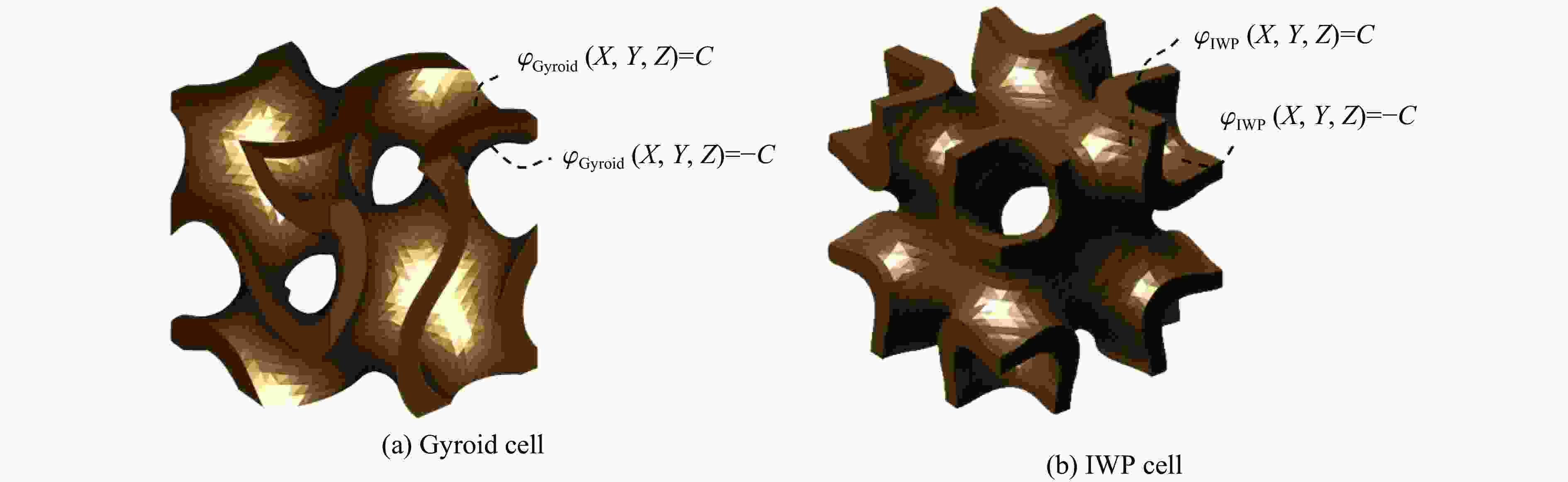
摘要: 三周期极小曲面(triply periodic minimal surface,TPMS)结构材料作为一种高孔隙率和高能量吸收效率的多孔介质,在许多领域得到广泛应用。以Gyroid和IWP结构作为设计基元,利用Sigmoid函数构建圆柱形过渡层,将外层IWP结构与内层Gyroid结构连接,设计了内外嵌套的GIP混合胞元结构。通过选择性激光熔融技术打印了Gyroid结构、IWP结构和GIP混合结构试样,并利用直撞式霍普金森杆对其进行了实验研究。结合LS-DYNA软件进行了更大冲击速度范围的数值模拟,分析了试件的变形演化过程和动态应力-应变关系。结果表明:结构的初始峰值应力和比吸能表现出不同程度的应变率敏感性。与Gyroid和IWP结构相比,GIP混合结构材料的应力-应变曲线表现出更明显的应变硬化趋势和更强的能量吸收能力。相较于GIP-1结构(冲击方向与圆柱形过渡层轴线方向相同),随着冲击速度的提高,GIP-2结构(冲击方向与圆柱形过渡层轴线方向垂直)具有更低的初始峰值应力和更大的比吸能,因而具有更优异的抗冲击性能。Abstract: Triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) structural material is widely used in many fields as a porous medium with high porosity and high energy absorption efficiency. In this paper, the Gyroid and IWP structures were used as the design elements, and the Sigmoid function was used to construct the cylindrical transition layer. The outer IWP structure was connected with the inner Gyroid structure, hence the inner and outer nested GIP hybrid cellular structure was designed. Gyroid structure, IWP structure and GIP hybrid structure samples were printed by selective laser melting technology, and the experimental study was performed by direct impact Hopkinson bar. Combined with LS-DYNA software, the numerical simulation of larger impact velocity range was carried out, and the deformation evolution process as well as dynamic stress-strain relationship of the specimen were analyzed. The results show that the initial peak stress and specific energy absorption of the structure present different strain rate sensitivity. Compared with Gyroid and IWP structures, the stress-strain curves of GIP hybrid structural materials exhibit more obvious strain hardening trend and stronger energy absorption capacity. With the increase in impact velocity, the GIP-2 structure (the impact direction is perpendicular to the axis direction of the cylindrical transition layer) presents lower initial peak stress and larger specific energy absorption than the GIP-1 structure (the impact direction is the same as the axis direction of the cylindrical transition layer), which demonstrates its better impact resistance.
-
Key words:
- TPMS hybrid structure /
- 3D printing /
- dynamic loading /
- energy absorption
-
表 1 测试试样的质量
Table 1. Masses of test specimens
Specimen Designed
mass/gSpecimen
mass/gMass
deviation/%Designed relative
density/%Relative density
of specimen/%Relative density
deviation/%Gyroid-1 38.96 40.52 4.00 36 37.43 3.97 Gyroid-2 38.96 40.35 3.56 36 37.27 3.52 IWP-1 38.96 40.21 3.20 36 37.14 3.16 IWP-2 38.96 40.12 2.97 36 37.06 2.94 GIP-1 38.96 40.65 4.33 36 37.55 4.30 GIP-2 38.96 40.37 3.61 36 37.29 3.58 -
[1] ZHANG J W, ZHAO J X, RONG Q G, et al. Machine learning guided prediction of mechanical properties of TPMS structures based on finite element simulation for biomedical titanium [J]. Materials Technology, 2022, 37(1): 1–8. [2] CHATZIGEORGIOU C, PIOTROWSKI B, CHEMISKY Y, et al. Numerical investigation of the effective mechanical properties and local stress distributions of TPMS-based and strut-based lattices for biomedical applications [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2022, 126: 105025. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2021.105025 [3] ZHANG S N, DA D, WANG Y J. TPMS-infill MMC-based topology optimization considering overlapped component property [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2022, 235: 107713. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107713 [4] SANTIAGO R, RAMOS H, ALMAHRI S, et al. Modelling and optimisation of TPMS-based lattices subjected to high strain-rate impact loadings [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 177: 104592. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104592 [5] 冯根柱, 于博丽, 李世强, 等. 多层级夹芯结构的变形与能量吸收 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2019, 33(5): 055902.FENG G Z, YU B L, LI S Q, et al. Deformation and energy absorption of multi-hierarchical sandwich structures [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2019, 33(5): 055902. [6] FENG J W, FU J Z, SHANG C, et al. Porous scaffold design by solid T-splines and triply periodic minimal surfaces [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 336: 333–352. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2018.03.007 [7] LIU B, LIU M Y, CHENG H Q, et al. A new stress-driven composite porous structure design method based on triply periodic minimal surfaces [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2022, 181: 109974. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2022.109974 [8] FENG J W, LIU B, LIN Z W, et al. Isotropic porous structure design methods based on triply periodic minimal surfaces [J]. Materials & Design, 2021, 210: 110050. [9] WANG H, TAN D W, LIU Z P, et al. On crashworthiness of novel porous structure based on composite TPMS structures [J]. Engineering Structures, 2022, 252: 113640. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.113640 [10] ZHANG L, FEIH S, DAYNES S, et al. Energy absorption characteristics of metallic triply periodic minimal surface sheet structures under compressive loading [J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 23: 505–515. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2018.08.007 [11] AL-KETAN O, ROWSHAN R, ABU AL-RUB R K. Topology-mechanical property relationship of 3D printed strut, skeletal, and sheet based periodic metallic cellular materials [J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 19: 167–183. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2017.12.006 [12] LI X, XIAO L J, SONG W D. Compressive behavior of selective laser melting printed gyroid structures under dynamic loading [J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 46: 102054. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2021.102054 [13] NAZIR A, HUSSAIN S, ALI H M, et al. Design and mechanical performance of nature-inspired novel hybrid triply periodic minimal surface lattice structures fabricated using material extrusion [J]. Materials Today Communications, 2024, 38: 108349. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2024.108349 [14] LI S, ZHU H, FENG G, et al. Influence mechanism of cell-arrangement strategy on energy absorption of dual-phase hybrid lattice structure [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 175: 104528. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104528 [15] YU G J, XIAO L J, SONG W D. Deep learning-based heterogeneous strategy for customizing responses of lattice structures [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2022, 229: 107531. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107531 [16] ZHANG J, XIE S, LI T, et al. A study of multi-stage energy absorption characteristics of hybrid sheet TPMS lattices [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 190: 110989. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.110989 [17] SREEDHAR N, THOMAS N, AL-KETAN O, et al. Mass transfer analysis of ultrafiltration using spacers based on triply periodic minimal surfaces: effects of spacer design, directionality and voidage [J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 561: 89–98. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2018.05.028 [18] AL-KETAN O, ABU AL-RUB R K. MSLattice: a free software for generating uniform and graded lattices based on triply periodic minimal surfaces [J]. Material Design & Processing Communications, 2021, 3(6): e205. [19] MASKERY I, STURM L, AREMU A O, et al. Insights into the mechanical properties of several triply periodic minimal surface lattice structures made by polymer additive manufacturing [J]. Polymer, 2018, 152: 62–71. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2017.11.049 [20] YIN H F, ZHENG X J, WEN G L, et al. Design optimization of a novel bio-inspired 3D porous structure for crashworthiness [J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 255: 112897. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112897 [21] NOVAK N, TANAKA S, HOKAMOTO K, et al. High strain rate mechanical behaviour of uniform and hybrid metallic TPMS cellular structures [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 191: 111109. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.111109 [22] 厉雪, 肖李军, 宋卫东. 3D打印梯度Gyroid结构的动态冲击响应 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2021, 35(3): 034201.LI X, XIAO L J, SONG W D. Dynamic behavior of 3D printed graded gyroid structures under impact loading [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2021, 35(3): 034201. [23] 李吉祥. 基于三周期极小曲面的三维点阵结构的防护性能研究 [D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2023.LI J X. Study on protective performance of three-dimensional lattice structures based on triply periodic minimal surfaces [D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2023. [24] DUAN Y, DU B, SHI X P, et al. Quasi-static and dynamic compressive properties and deformation mechanisms of 3D printed polymeric cellular structures with Kelvin cells [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 132: 103303. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.05.017 [25] XI H, ZHOU Z, ZHANG H, et al. Multi-morphology TPMS structures with multi-stage yield stress platform and multi-level energy absorption: design, manufacturing, and mechanical properties [J]. Engineering Structures, 2023, 294: 116733. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2023.116733 -






 下载:
下载: