Study on the Blast-Resistant Performance and Influence Factors of High-Toughness Steel Subjected to Close-Range Air-Blasts
-
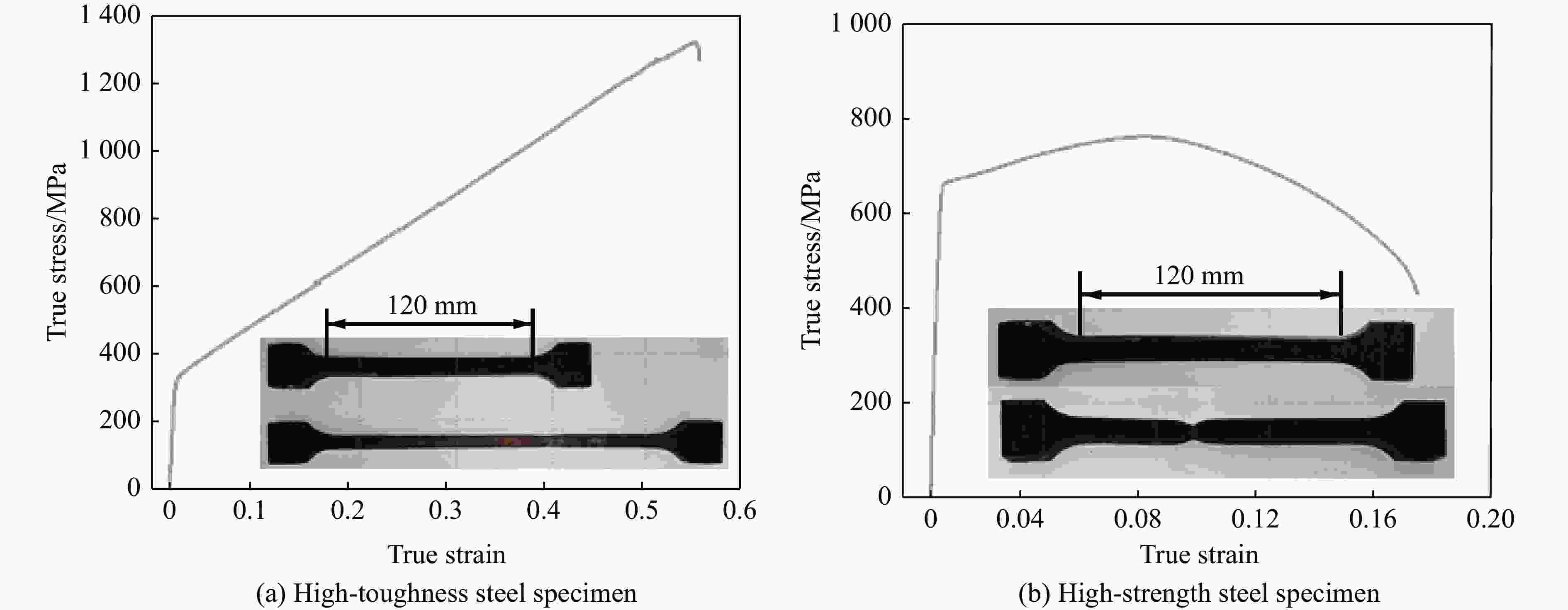
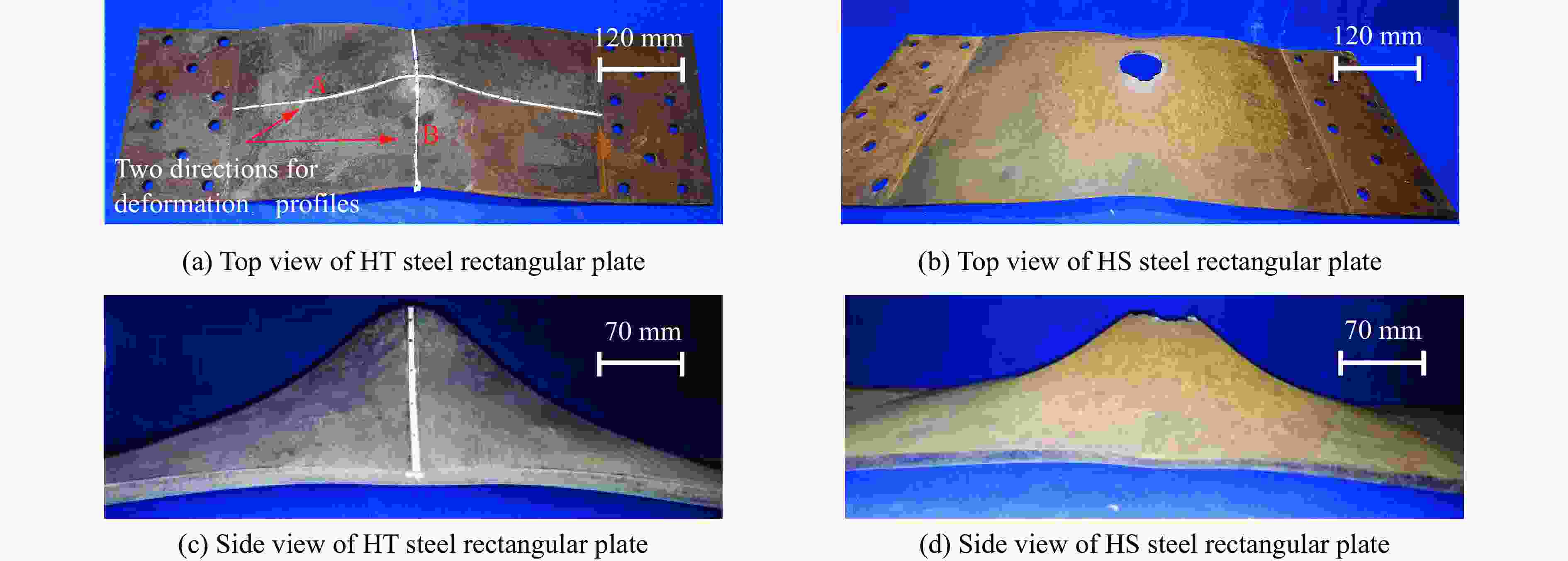
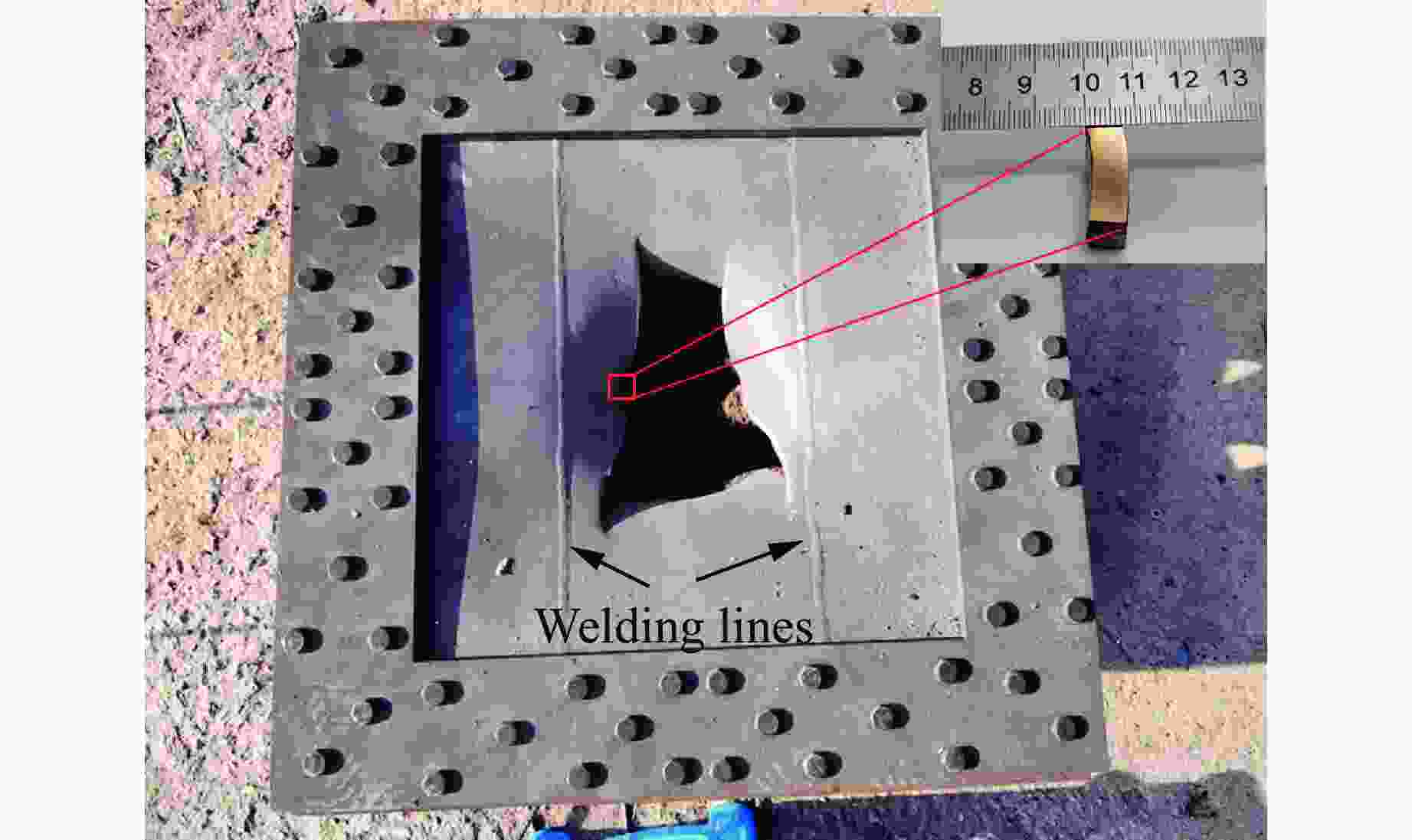
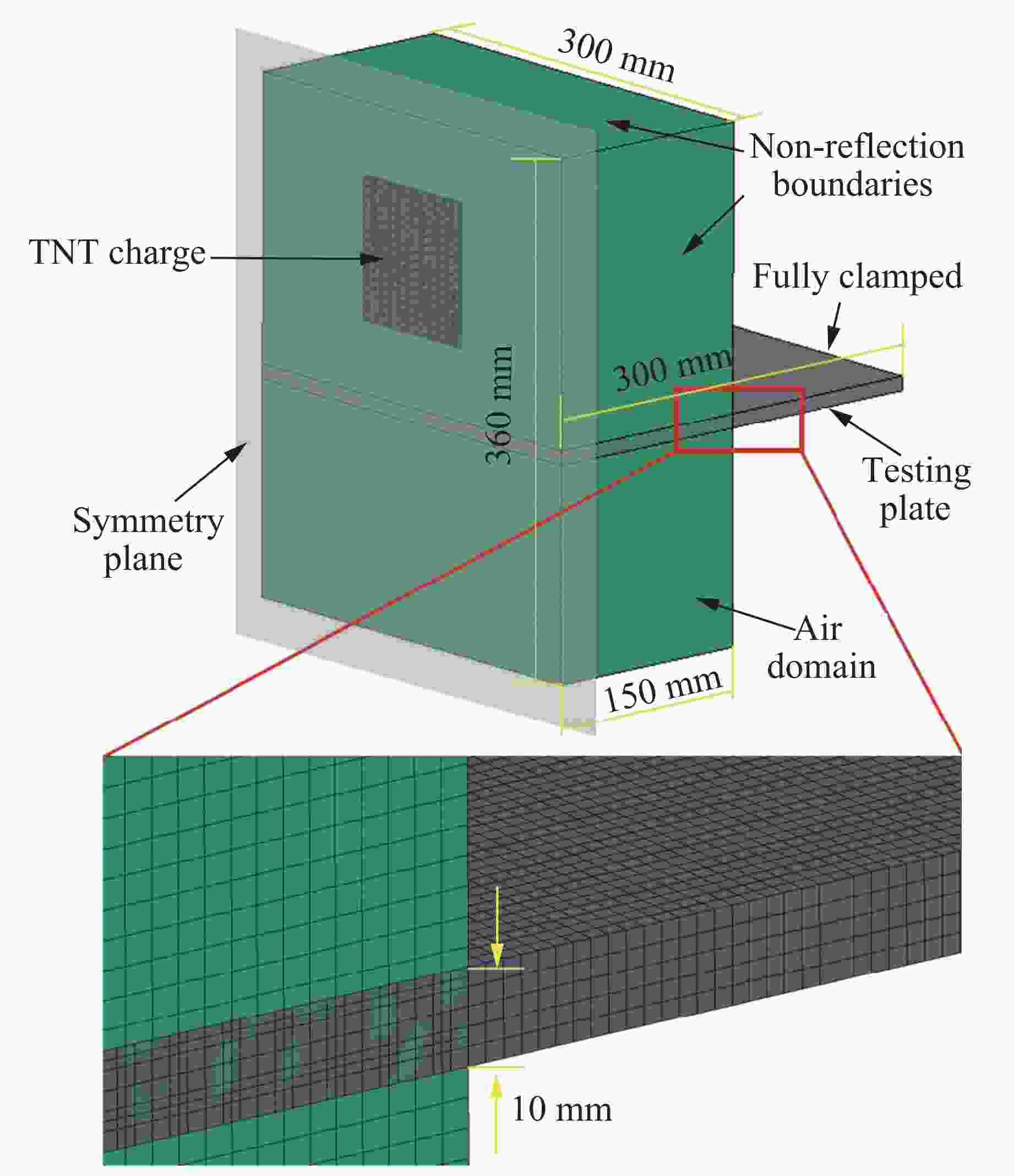
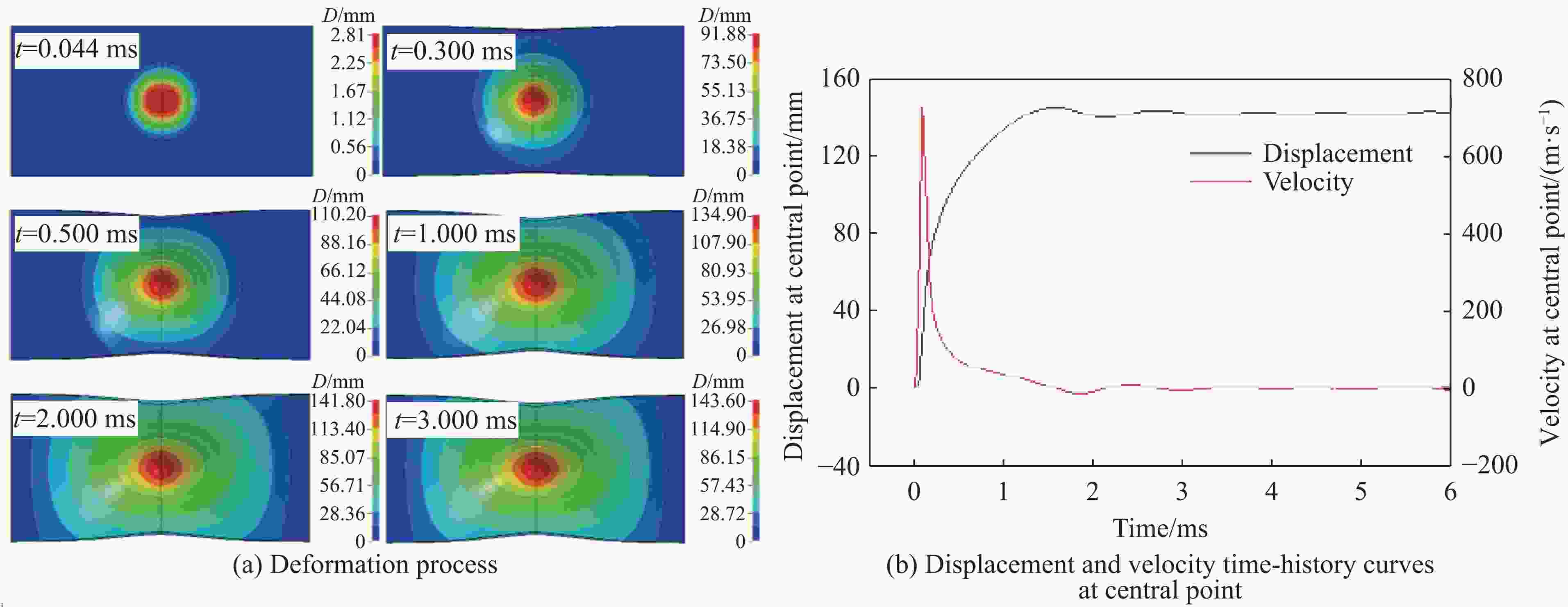
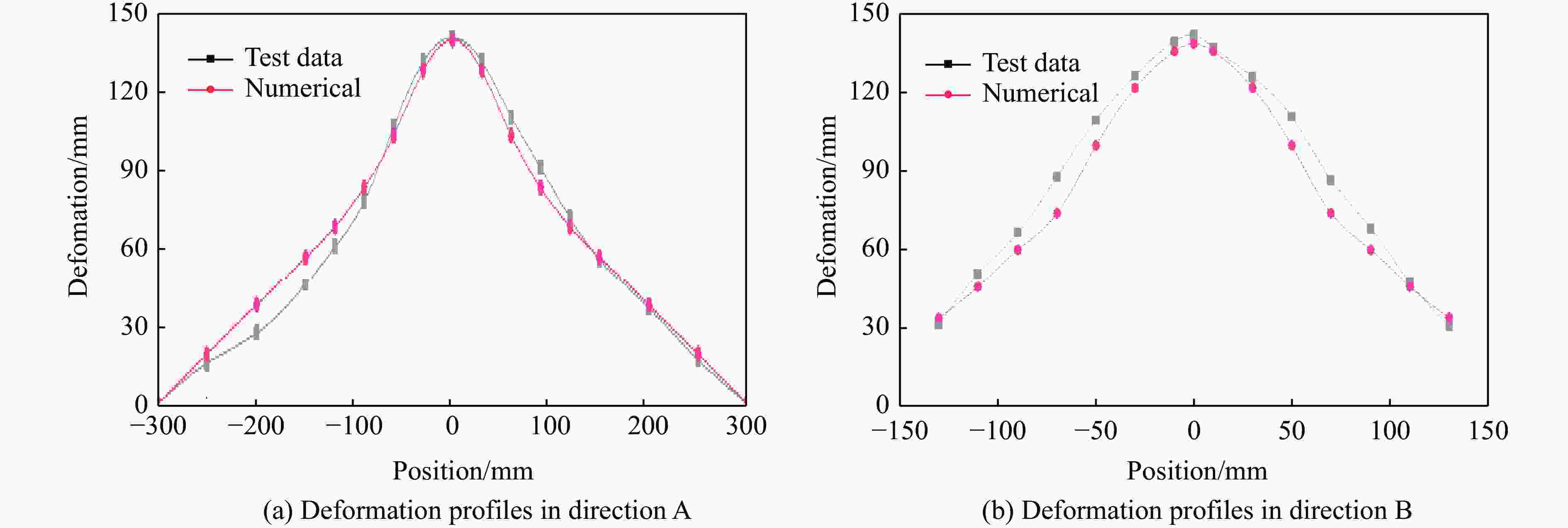
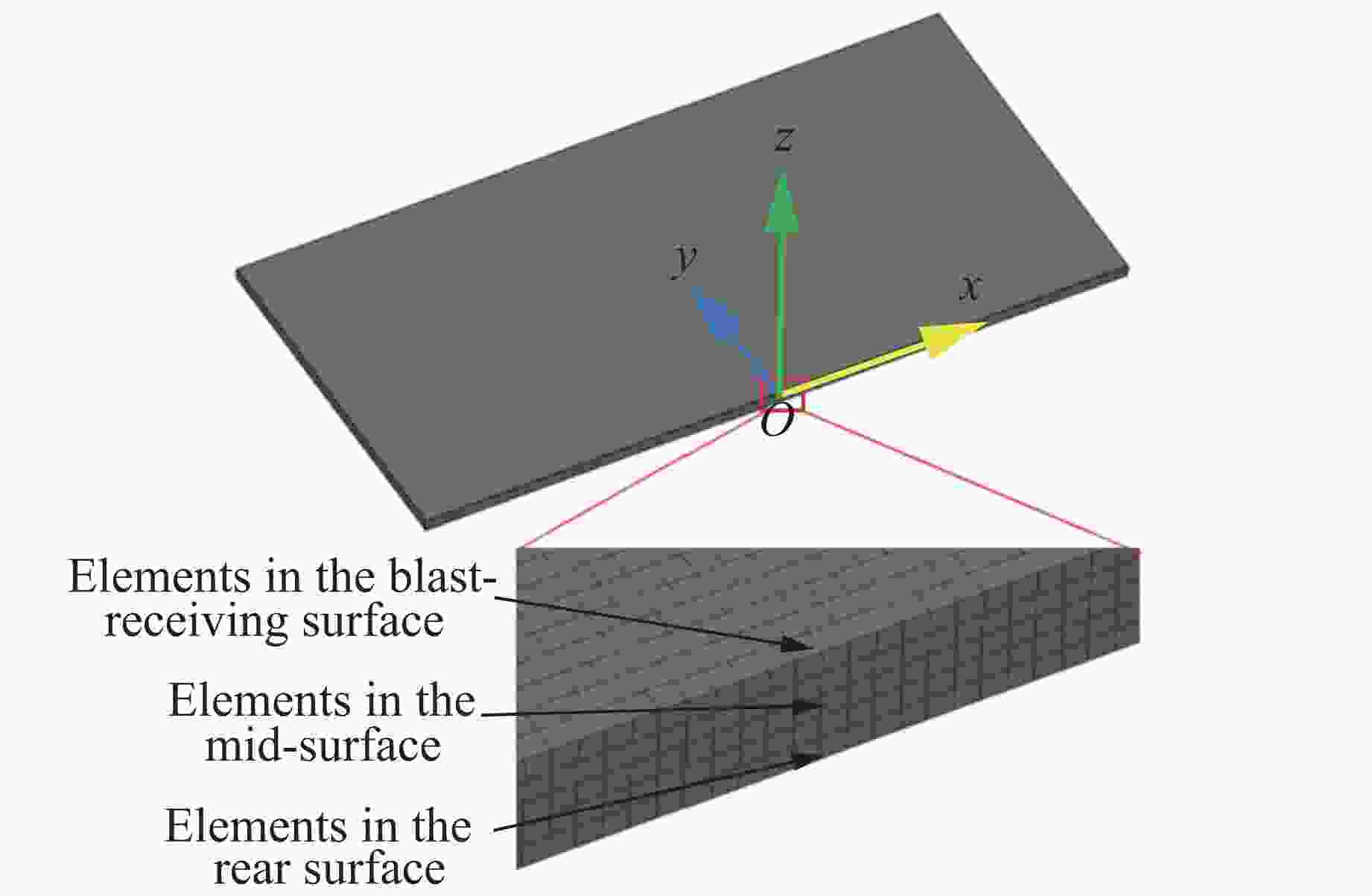
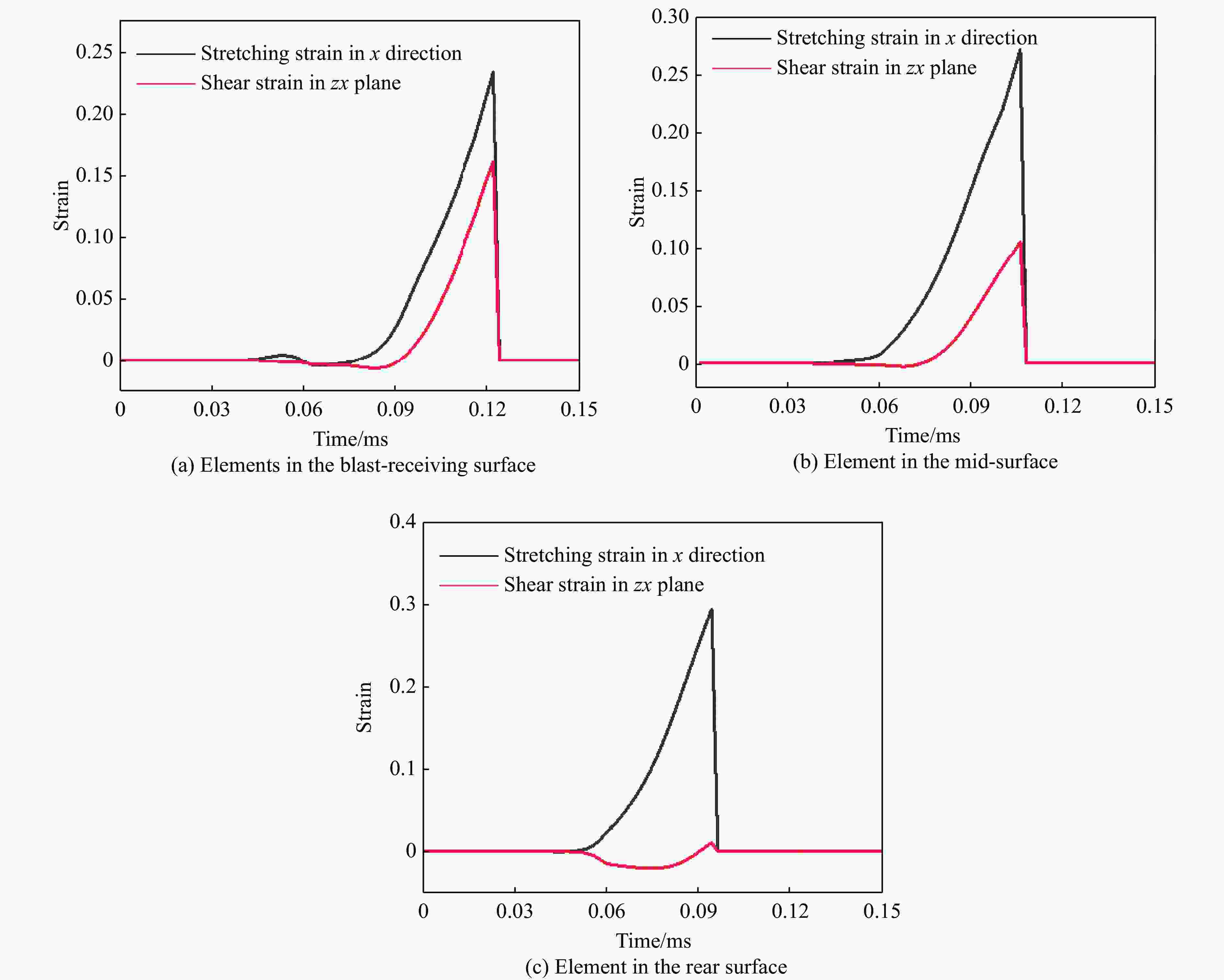
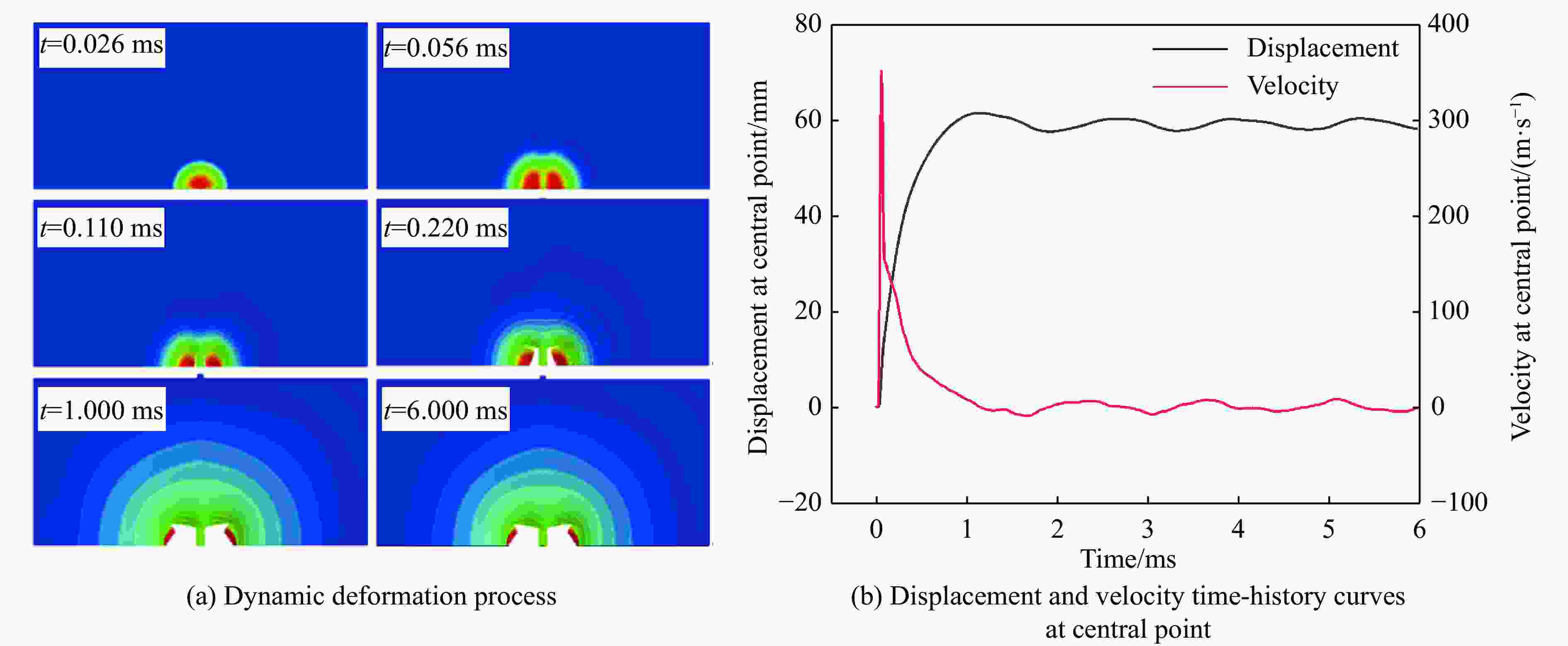
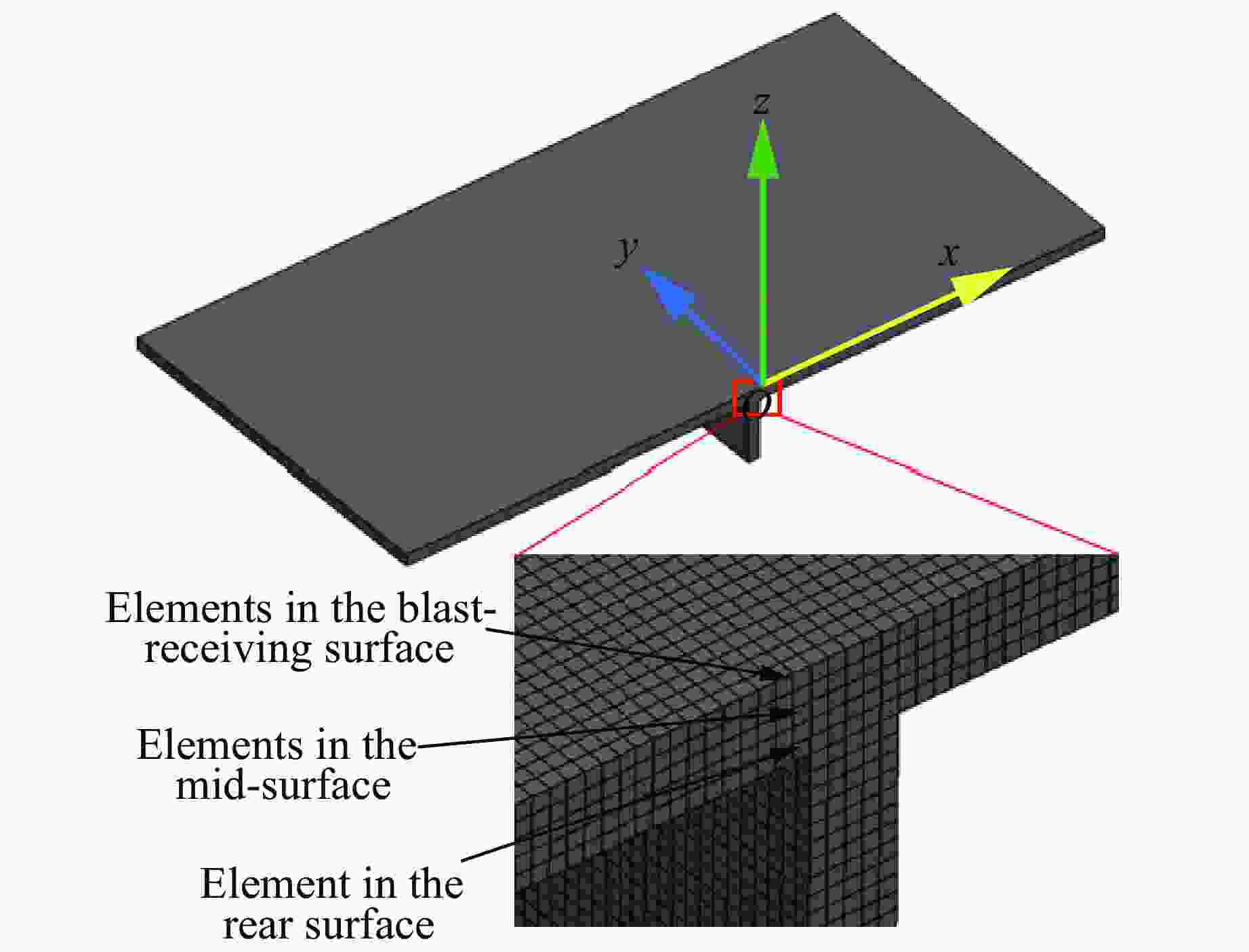
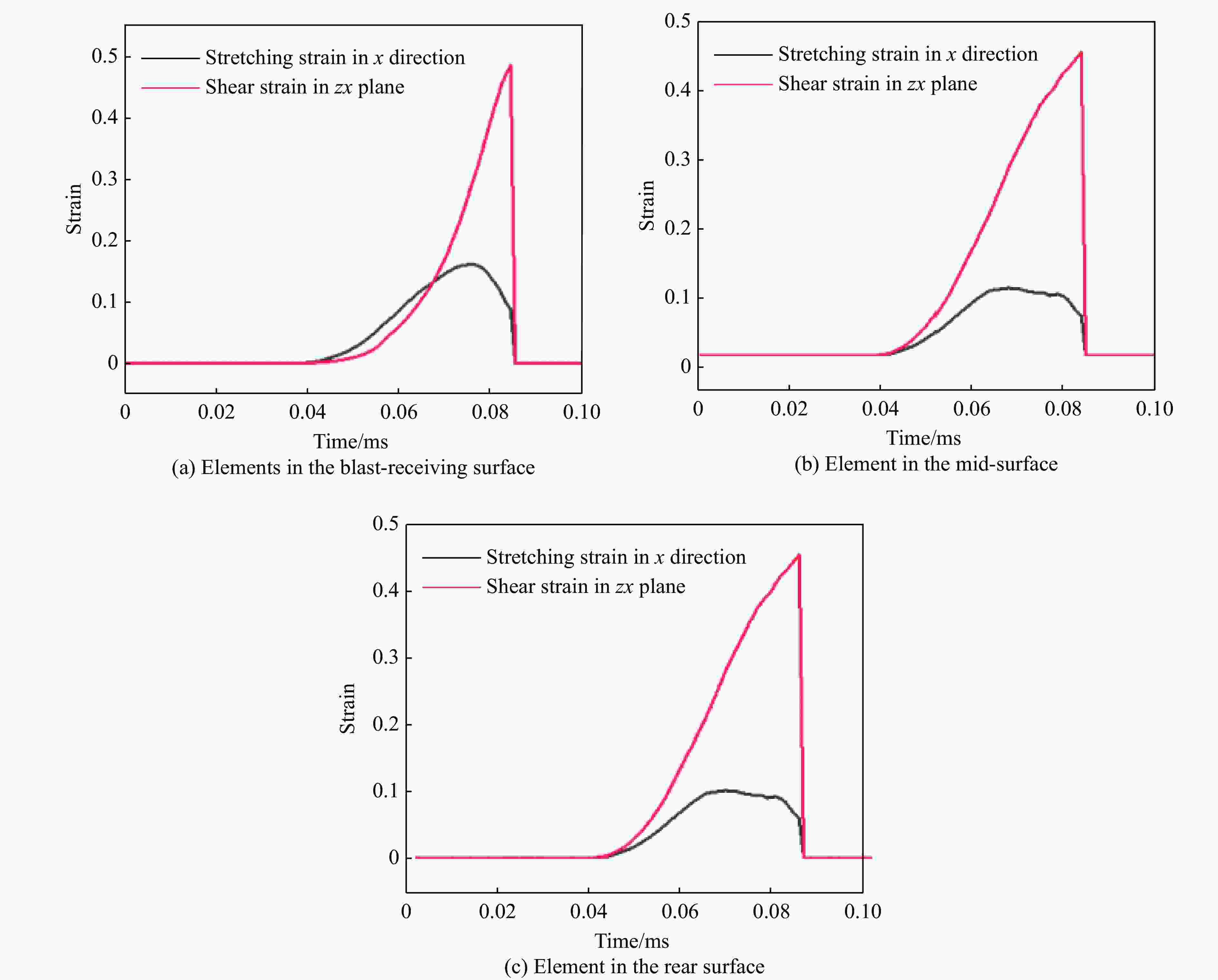
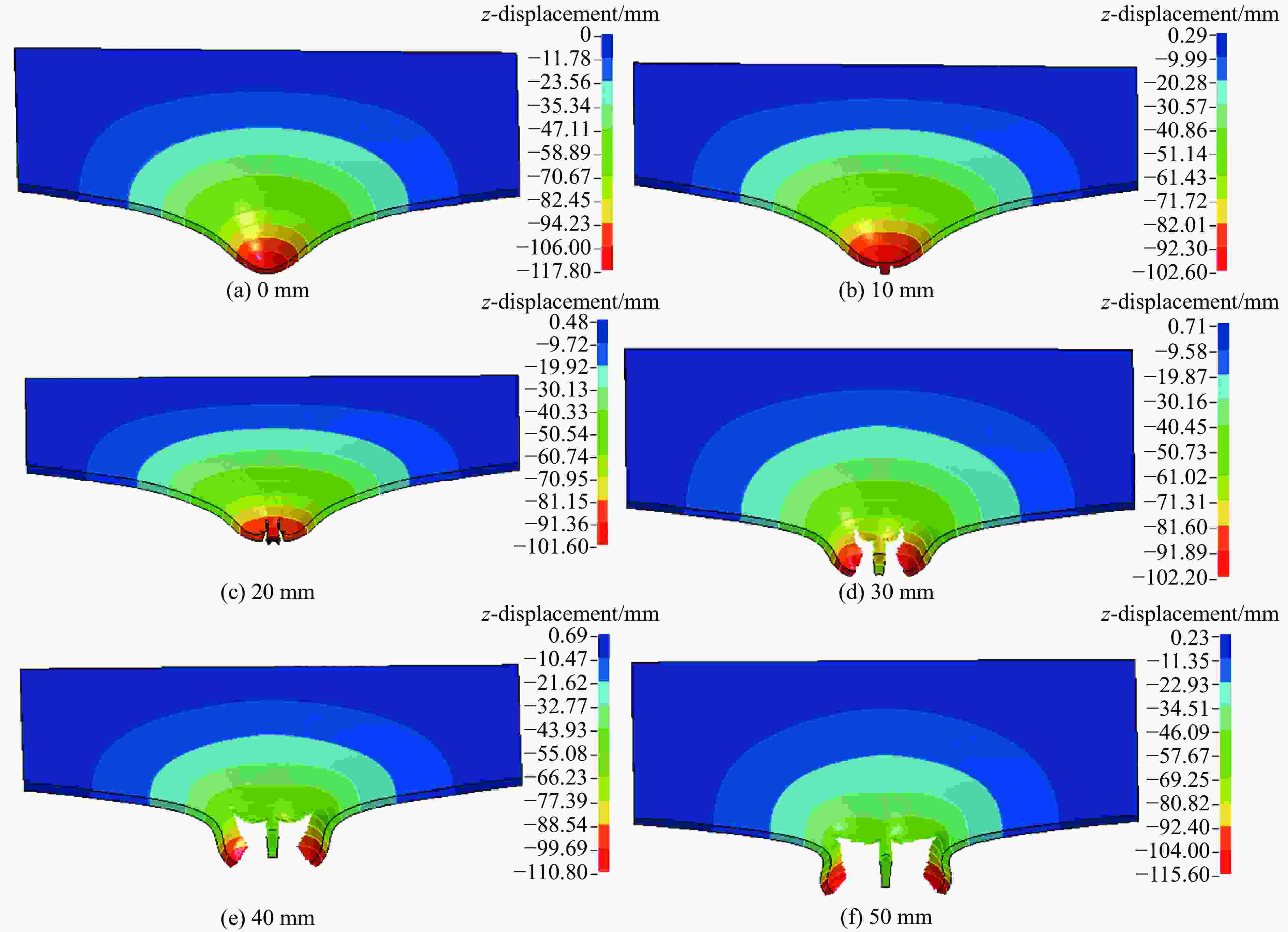
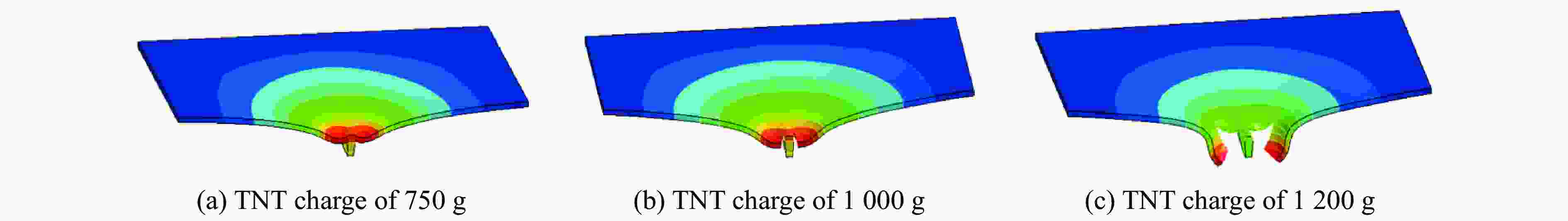
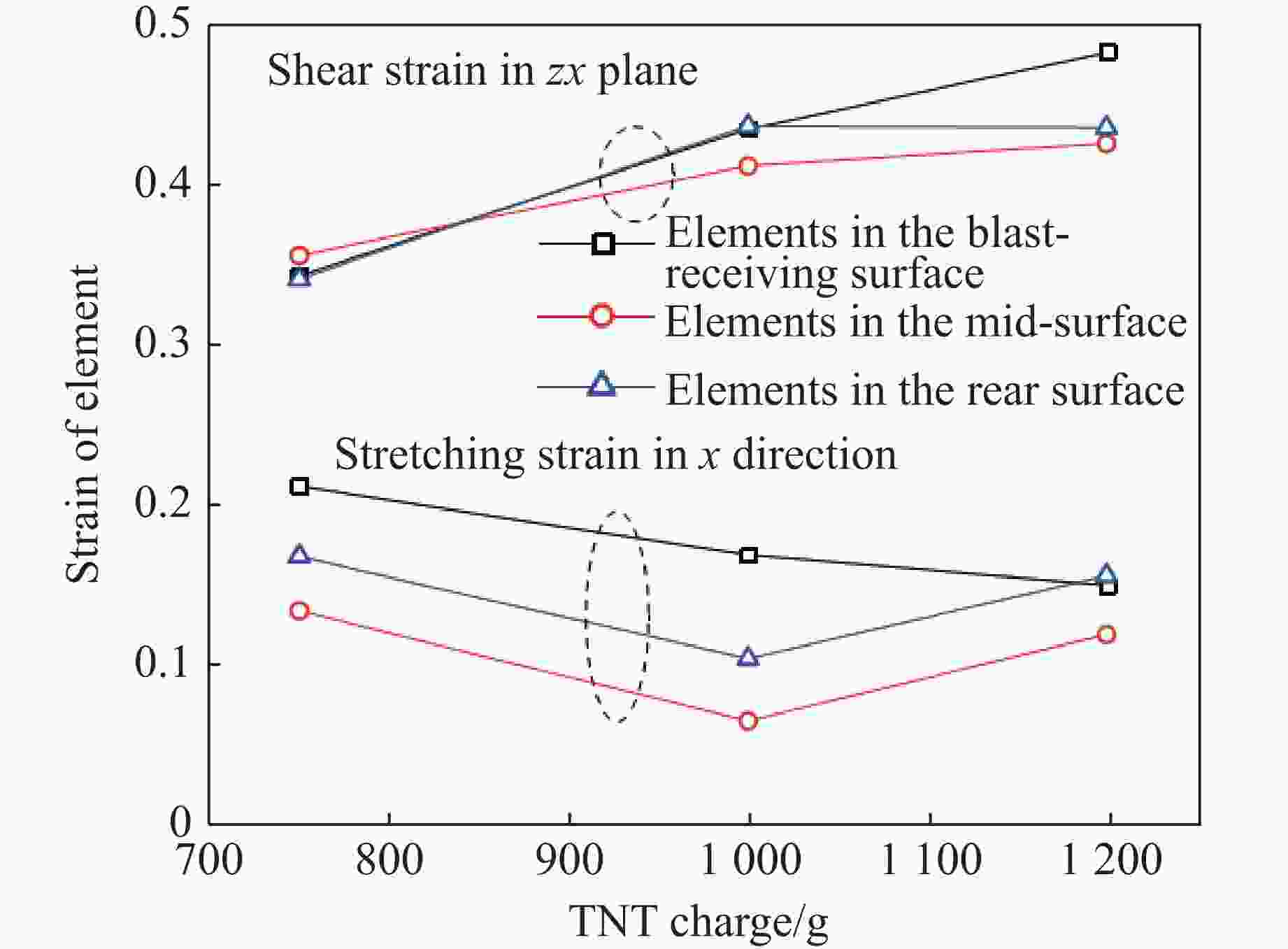
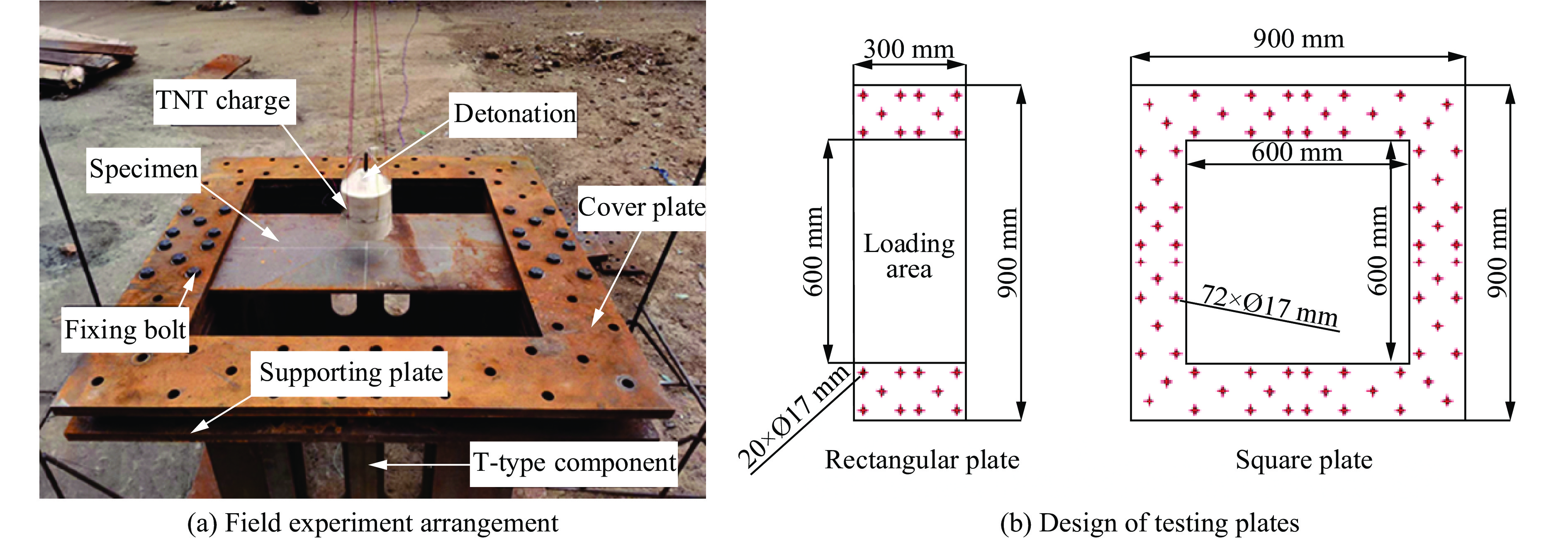
摘要: 为探讨高韧钢的抗爆性能及其影响因素,结合空爆试验,对高韧钢平板和加筋板的动响应过程进行了数值模拟,并与相同厚度的高强钢进行了对比。首先,开展了高韧钢和高强钢平板的空爆试验,对比分析了2种材料平板的变形和破坏试验结果。随后,采用LS-DYNA非线性有限元程序对高韧钢平板在近距空爆载荷作用下的变形/失效过程进行了数值模拟,并与试验结果进行了对比,验证了数值模拟方法的合理性。在此基础上,通过数值模拟进一步分析了高韧钢平板和加筋板结构的动态响应过程和失效机理。研究结果表明,在TNT药量为1 200 g、爆距为100 mm的近距空爆载荷作用下,10 mm厚的高韧钢平板仅发生拉伸大变形,而10 mm厚的高强钢平板中部出现大破口。高韧钢平板的抗爆性能明显优于同等厚度下的高强钢平板。近距离空爆载荷作用下,高韧钢平板的主要变形模式为整体拉伸变形,而高韧钢加筋板结构的主要破坏模式为沿加筋部位的剪切破坏。随着载荷强度的增大,高韧钢加筋板结构呈现出3种不同的失效破坏模式;随着加筋高度的增大,面板沿加筋的局部剪切应力更大,高韧钢加筋板的抗爆性能反而会劣化。研究结果展示了高韧钢的抗爆优势,可为高韧钢在舰船防护结构中的潜在应用提供技术支撑。Abstract: To study the blast-resistant performance and influence factors of high-toughness steel, dynamic response processes of high-toughness (HT) steel flat and stiffened plates were analyzed by numerical simulations and air-blast experiments. Firstly, air-blast experiments for both HT steel and high-strength (HS) steel flat plates were carried out. Comparisons of deformation and damage between HT and HS flat plates for experimental results were performed. Subsequently, deformation and failure processes of HT steel flat plates under close-range air-blast loading were analyzed by nonlinear finite element code LS-DYNA. The validity of numerical simulation method was verified by experimental results. On the basis of verification, the dynamic responses and failure mechanisms of HT steel flat and stiffened plates were further investigated by numerical simulations. Results show that under the close-range air blast of 1 200 g TNT charge and 100 mm stand-off distance, the HT steel flat plate of 10 mm thickness only produces large stretching deformation, whereas the HS steel flat plate of the same thickness appears a big crevasse at its central region. To the same thickness, HT steel flat plates behave obvious superior blast-resistant performance. Under close-range air-blast loading, HT steel flat plates mainly exhibit overall stretching deformation, whereas HT steel stiffened plates produce shear damage along stiffeners. As load intensity increases, three different failure modes occur for HT steel stiffened plates. The local shear stresses in the panel of the HT steel stiffened plate increase with the increase of stiffener’s height. This instead deteriorates the blast-resistant performance of HT steel stiffened plates. This study demonstrates the blast resistance superiority of HT steel, and can provide a technical support for the potential application of HT steel in warship protective structures.
-
Key words:
- ship structure /
- high-toughness steel /
- close-range air-blast load /
- dynamic response /
- failure mode
-
表 1 高韧钢和高强钢材料的基本力学参数
Table 1. Basic mechanical parameters of high-toughness (HT) and high-strength (HS) steels
Material ρ/(kg∙m−3) E/GPa ν σs/MPa εf HS steel 7 830 210 0.30 660 0.18 HT steel 7 650 190 0.26 330 0.58 表 2 数值模拟采用的高韧钢材料参数
Table 2. Material parameters used in numerical simulation for high-toughness steel
ρ/(kg∙m−3) E/GPa ν G/GPa A/MPa B/MPa n c m Tm/K Tr/K 7650 190 0.26 75.4 330 1 502 0.79 0.001 0 1 765 300 -
[1] 辛春亮, 王俊林, 薛再清, 等. 反舰导弹战斗部现状及发展趋势 [J]. 战术导弹技术, 2016(6): 105–110.XIN C L, WANG J L, XUE Z Q, et al. Review on status and development of antiship missile warhead [J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2016(6): 105–110. [2] 李营, 张磊, 赵鹏铎, 等. 舰船抗反舰导弹技术研究进展与发展路径 [J]. 中国造船, 2016, 57(4): 186–196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2016.04.021LI Y, ZHANG L, ZHAO P D, et al. A review on research progress and developing routes of warship anti-explosion under anti-ship missile explosion [J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2016, 57(4): 186–196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2016.04.021 [3] 陈长海, 朱锡, 侯海量, 等. 近距空爆载荷作用下固支方板的变形及破坏模式 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2012, 32(4): 368–375. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1455.2012.04.005CHEN C H, ZHU X, HOU H L, et al. Deformation and failure modes of clamped square plates under close-range air blast loads [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2012, 32(4): 368–375. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1455.2012.04.005 [4] WIERZBICKI T, NURICK G N. Large deformation of thin plates under localised impulsive loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(7): 899–918. [5] JACOB N, NURICK G N, LANGDON G S. The effect of stand-off distance on the failure of fully clamped circular mild steel plates subjected to blast loads [J]. Engineering Structures, 2007, 29(10): 2723–2736. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2007.01.021 [6] 白志海, 蒋志刚, 严波, 等. 金属加筋板局部爆炸冲击荷载研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2011, 30(12): 93–97, 194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.12.019BAI Z H, JIANG Z G, YAN B, et al. Localized blast loading of a stiffned metal plate [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30(12): 93–97, 194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.12.019 [7] CHUNG K Y S, NURICK G N. Experimental and numerical studies on the response of quadrangular stiffened plates. part Ⅰ: subjected to uniform blast load [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 31(1): 55–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2003.09.048 [8] LANGDON G S, YUEN S C K, NURICK G N. Experimental and numerical studies on the response of quadrangular stiffened plates. part Ⅱ: localised blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 31(1): 85–111. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2003.09.050 [9] LANGDON G S, LEE W C, LOUCA L A. The influence of material type on the response of plates to air-blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 78: 150–160. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.12.008 [10] 邵军. 舰船用钢研究现状与发展 [J]. 鞍钢技术, 2013(4): 1–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4613.2013.04.001SHAO J. Present status on researching shipbuilding steel and its development [J]. Angang Technology, 2013(4): 1–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4613.2013.04.001 [11] 刘振宇, 陈俊, 唐帅, 等. 新一代舰船用钢制备技术的现状与发展展望 [J]. 中国材料进展, 2014, 33(9/10): 595–602, 629. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2014.09.08LIU Z Y, CHEN J, TANG S, et al. State of the art development of the manufacturing technologies of new generation war ship steels [J]. Materials China, 2014, 33(9/10): 595–602, 629. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2014.09.08 [12] NURICK G N, MARTIN J B. Deformation of thin plates subjected to impulsive loading—a review: part Ⅰ: theoretical considerations [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1989, 8(2): 159–170. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(89)90014-6 [13] NURICK G N, MARTIN J B. Deformation of thin plates subjected to impulsive loading—a review: part Ⅱ: experimental studies [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1989, 8(2): 171–186. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(89)90015-8 [14] CHUNG KIM YUEN S, NURICK G N, LANGDON G S, et al. Deformation of thin plates subjected to impulsive load: part Ⅲ — an update 25 years on [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 107: 108–117. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.06.010 [15] 李营, 张磊, 杜志鹏, 等. 反舰导弹舱内爆炸作用下舰船结构毁伤机理研究进展 [J]. 中国造船, 2018, 59(3): 185–202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2018.03.020LI Y, ZHANG L, DU Z P, et al. Research advance of damage mechanism of cabins under warhead internal blast [J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2018, 59(3): 185–202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2018.03.020 [16] GU T, JIA L J, CHEN B, et al. Unified full-range plasticity till fracture of meta steel and structural steels [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2021, 253: 107869. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2021.107869 [17] JIA L J, ZHANG R, ZHOU C F, et al. In-situ three-dimensional X-ray investigation on micro ductile fracture mechanism of a high-Mn steel with delayed necking effect [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 24: 1076–1087. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.03.062 -






 下载:
下载: