Progress on Compounds of Inert Element Helium under High Pressure
-
摘要: 氦(He)是元素周期表第2号元素,也是宇宙中除氢以外含量最丰富的元素,广泛存在于恒星和气态巨行星(gas giant planets)的内部高压强(高压)极端环境中。氦因其满壳层的电子结构具有极强的化学惰性,极难与其他元素结合形成化合物。近年来,多项研究工作表明,惰性氦在极端高压条件下具有“不简单”的物理行为,如通过计算“预言”了在高压下稳定的铁氧氦化合物FeO2He和具有反常原子传播的水氦化合物He-H2O等。这些研究工作不仅有助于发现新的化学成键范式,也有力推动了高压物理、地学和行星科学等相关领域的研究进展。本文重点介绍了高压下氦化合物的相关研究进展,聚焦讨论氦化合物在高压下稳定的物理机制,并对未来在高压下设计和制备新型氦化合物的相关研究进行展望。Abstract: Helium (He), the second element in the periodic table, is the most abundant element in the universe apart from hydrogen. It is widely accepted that He exists in the interiors of gas giant planets which holds the high-pressure conditions. Helium is extremely difficult to react with other elements to form compounds owing to its strong chemical inertness determined by the full-shell electronic structure. However, in recent years, several studies have shown that physical behavior of helium is not that simple under extremely high pressure, such as the predicted stable helium compound FeO2He and the predicted water helium compound He-H2O with anomalous atomic diffusion under high pressure. These results not only play a leading role in the discovery of new paradigm on chemical bonding, but also make a substantial step for the relevant researches in the fields of high-pressure physics, geoscience, and planetary science. This paper mainly introduces the progress on helium compounds at high pressure, focuses on discussing the physical mechanism of their stability, and provides prospects for future research on the design and discovery of new helium compounds under high pressure.
-
Key words:
- crystal structure prediction /
- high pressure /
- inert helium compounds
-
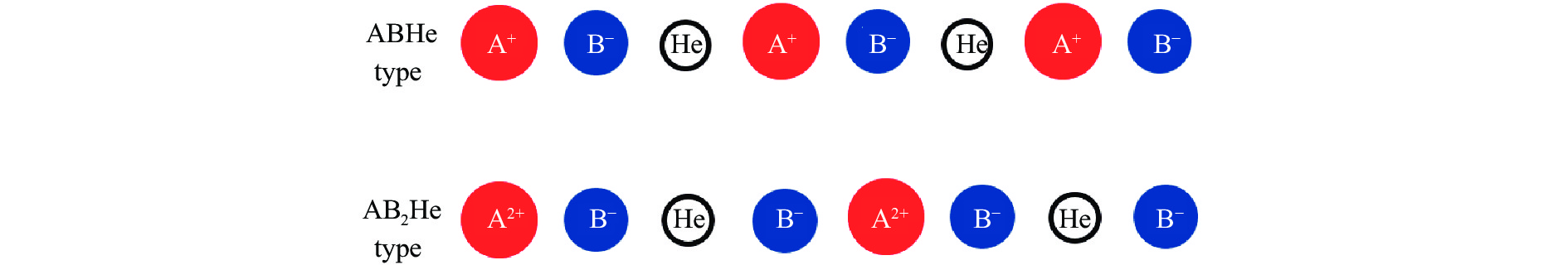
图 1 He原子插入AB和AB2型离子化合物的一维示意图(红色大圆圈代表带有1或2个正电荷的离子,蓝色小圆圈代表带有1个负电荷的离子,白色圆圈代表氦原子)
Figure 1. One-dimensional schematic diagrams of He atom insertion in AB and AB2 ionic compounds (The large andred filled circles represent the ions with +1 or +2 charges, the small and blue filled circles representthe ions with –1 charge, the white circles represent the neutral helium atoms.)
-
[1] BARTLETT N. Xenon hexafluoroplatinate (V) Xe+ [PtF6]– [J]. Proceedings of the Chemical Society London, 1962(6): 197–236. [2] ZHANG L J, WANG Y C, LV J, et al. Materials discovery at high pressures [J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2(4): 17005. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2017.5 [3] MIAO M S. Noble gases in solid compounds show a rich display of chemistry with enough pressure [J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2020, 8: 570492. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.570492 [4] MIAO M S, SUN Y H, ZUREK E, et al. Chemistry under high pressure [J]. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2020, 4(10): 508–527. doi: 10.1038/s41570-020-0213-0 [5] WANG Y C, LV J, ZHU L, et al. CALYPSO: a method for crystal structure prediction [J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2012, 183(10): 2063–2070. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2012.05.008 [6] WANG Y C, LV J, ZHU L, et al. Crystal structure prediction via particle-swarm optimization [J]. Physical Review B, 2010, 82(9): 094116. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.82.094116 [7] SHAO X C, LV J, LIU P, et al. A symmetry-orientated divide-and-conquer method for crystal structure prediction [J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2022, 156(1): 014105. doi: 10.1063/5.0074677 [8] XIA K, GAO H, LIU C, et al. A novel superhard tungsten nitride predicted by machine-learning accelerated crystal structure search [J]. Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(13): 817–824. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.05.027 [9] ZHU L, LIU H Y, PICKARD C J, et al. Reactions of xenon with iron and nickel are predicted in the Earth’s inner core [J]. Nature Chemistry, 2014, 6(7): 644–648. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1925 [10] ZHANG J R, LV J, LI H F, et al. Rare helium-bearing compound FeO2He stabilized at deep-Earth conditions [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 121(25): 255703. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.255703 [11] STAVROU E, YAO Y S, GONCHAROV A F, et al. Synthesis of xenon and iron-nickel intermetallic compounds at Earth’s core thermodynamic conditions [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(9): 096001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.096001 [12] LIU C, GAO H, WANG Y, et al. Multiple superionic states in helium-water compounds [J]. Nature Physics, 2019, 15(10): 1065–1070. doi: 10.1038/s41567-019-0568-7 [13] LOUBEYRE P, JEAN-LOUIS M, LETOULLEC R, et al. High pressure measurements of the He-Ne binary phase diagram at 296 K: evidence for the stability of a stoichiometric Ne(He)2 solid [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1993, 70(2): 178–181. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.178 [14] DONG X, OGANOV A R, GONCHAROV A F, et al. A stable compound of helium and sodium at high pressure [J]. Nature Chemistry, 2017, 9(5): 440–445. doi: 10.1038/nchem.2716 [15] LIU Z, BOTANA J, HERMANN A, et al. Reactivity of He with ionic compounds under high pressure [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 951. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03284-y [16] XIONG Z H, TSUCHIYA T, VAN ORMAN J A. Helium and argon partitioning between liquid iron and silicate melt at high pressure [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(3): e2020GL090769. doi: 10.1029/2020GL090769 [17] RIZO H, WALKER R J, CARLSON R W, et al. Preservation of Earth-forming events in the tungsten isotopic composition of modern flood basalts [J]. Science, 2016, 352(6287): 809–812. doi: 10.1126/science.aad8563 [18] JACKSON M G, CARLSON R W, KURZ M D, et al. Evidence for the survival of the oldest terrestrial mantle reservoir [J]. Nature, 2010, 466(7308): 853–856. doi: 10.1038/nature09287 [19] HU Q Y, KIM D Y, YANG W G, et al. FeO2 and FeOOH under deep lower-mantle conditions and Earth’s oxygen-hydrogen cycles [J]. Nature, 2016, 534(7606): 241–244. doi: 10.1038/nature18018 [20] NISHI M, KUWAYAMA Y, TSUCHIYA J, et al. The pyrite-type high-pressure form of FeOOH [J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7662): 205–208. doi: 10.1038/nature22823 [21] LIU J, HU Q Y, KIM D Y, et al. Hydrogen-bearing iron peroxide and the origin of ultralow-velocity zones [J]. Nature, 2017, 551(7681): 494–497. doi: 10.1038/nature24461 [22] ZHANG J R, LIU H Y, MA Y M, et al. Direct H-He chemical association in superionic FeO2H2He at deep-Earth conditions [J]. National Science Review, 2022, 9(7): nwab168. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwab168 [23] CAVAZZONI C, CHIAROTTI G L, SCANDOLO S, et al. Superionic and metallic states of water and ammonia at giant planet conditions [J]. Science, 1999, 283(5398): 44–46. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5398.44 [24] LIU H Y, YAO Y S, KLUG D D. Stable structures of He and H2O at high pressure [J]. Physical Review B, 2015, 91(1): 014102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.91.014102 [25] TEERATCHANAN P, HERMANN A. Computational phase diagrams of noble gas hydrates under pressure [J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2015, 143(15): 154507. doi: 10.1063/1.4933371 [26] SHI J M, CUI W W, HAO J, et al. Formation of ammonia-helium compounds at high pressure [J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3164. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16835-z [27] LIU C, GAO H, HERMANN A, et al. Plastic and superionic helium ammonia compounds under high pressure and high temperature [J]. Physical Review X, 2020, 10(2): 021007. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.10.021007 [28] GAO H, LIU C, HERMANN A, et al. Coexistence of plastic and partially diffusive phases in a helium-methane compound [J]. National Science Review, 2020, 7(10): 1540–1547. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa064 [29] SHEN G Y, MEI Q, PRAKAPENKA V B, et al. Effect of helium on structure and compression behavior of SiO2 glass [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(15): 6004–6007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102361108 [30] SATO T, FUNAMORI N, YAGI T. Helium penetrates into silica glass and reduces its compressibility [J]. Nature Communications, 2011, 2: 345. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1343 [31] LI D, LIU Y, TIAN F B, et al. High-pressure structures of helium and carbon dioxide from first-principles calculations [J]. Solid State Communications, 2018, 283: 9–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ssc.2018.06.012 [32] MONSERRAT B, MARTINEZ-CANALES M, NEEDS R J, et al. Helium-iron compounds at terapascal pressures [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 121(1): 015301. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.015301 [33] DING S C, ZHANG P, YANG K, et al. Formation of solid SiO2He compound at high pressure and high temperature [J]. Physical Review B, 2022, 106(2): 024102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.106.024102 [34] EREMETS M I, GAVRILIUK A G, TROJAN I A, et al. Single-bonded cubic form of nitrogen [J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3(8): 558–563. doi: 10.1038/nmat1146 [35] HOU J Y, WENG X J, OGANOV A R, et al. Helium-nitrogen mixtures at high pressure [J]. Physical Review B, 2021, 103(6): L060102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.103.L060102 [36] LI Y W, FENG X L, LIU H Y, et al. Route to high-energy density polymeric nitrogen t-N via He−N compounds [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 722. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03200-4 [37] DING S C, SHI J M, XIE J H, et al. Helium incorporation induced direct-gap silicides [J]. npj Computational Materials, 2021, 7(1): 89. doi: 10.1038/s41524-021-00558-w [38] PENG F, SONG X Q, LIU C, et al. Xenon iron oxides predicted as potential Xe hosts in Earth’s lower mantle [J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5227. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19107-y -







 下载:
下载: