Structural Optimization and Energy Absorption Characteristics of Double-Layer Variable-Diameter Energy-Absorbing Components for Anti-Impact Brackets
-
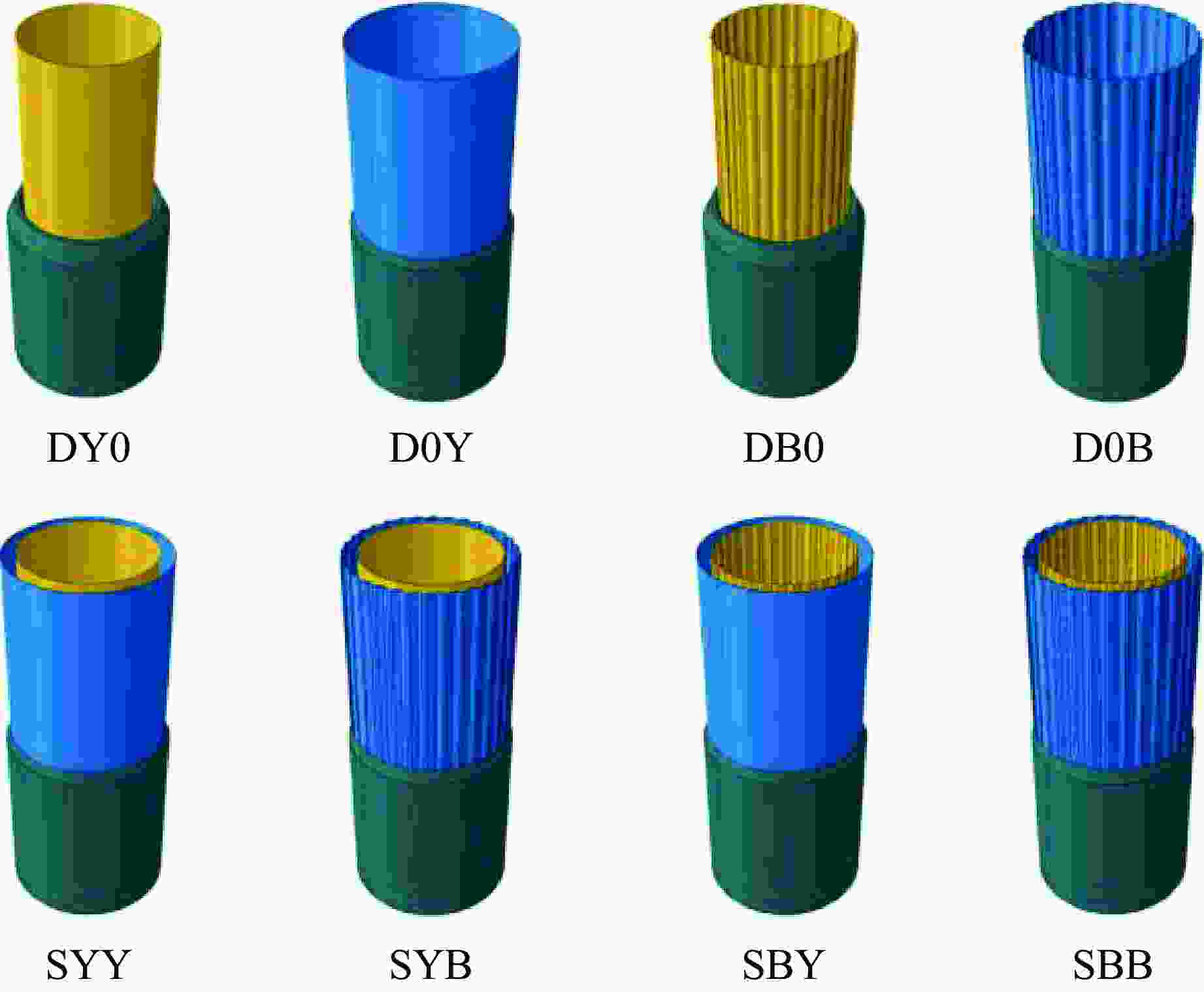
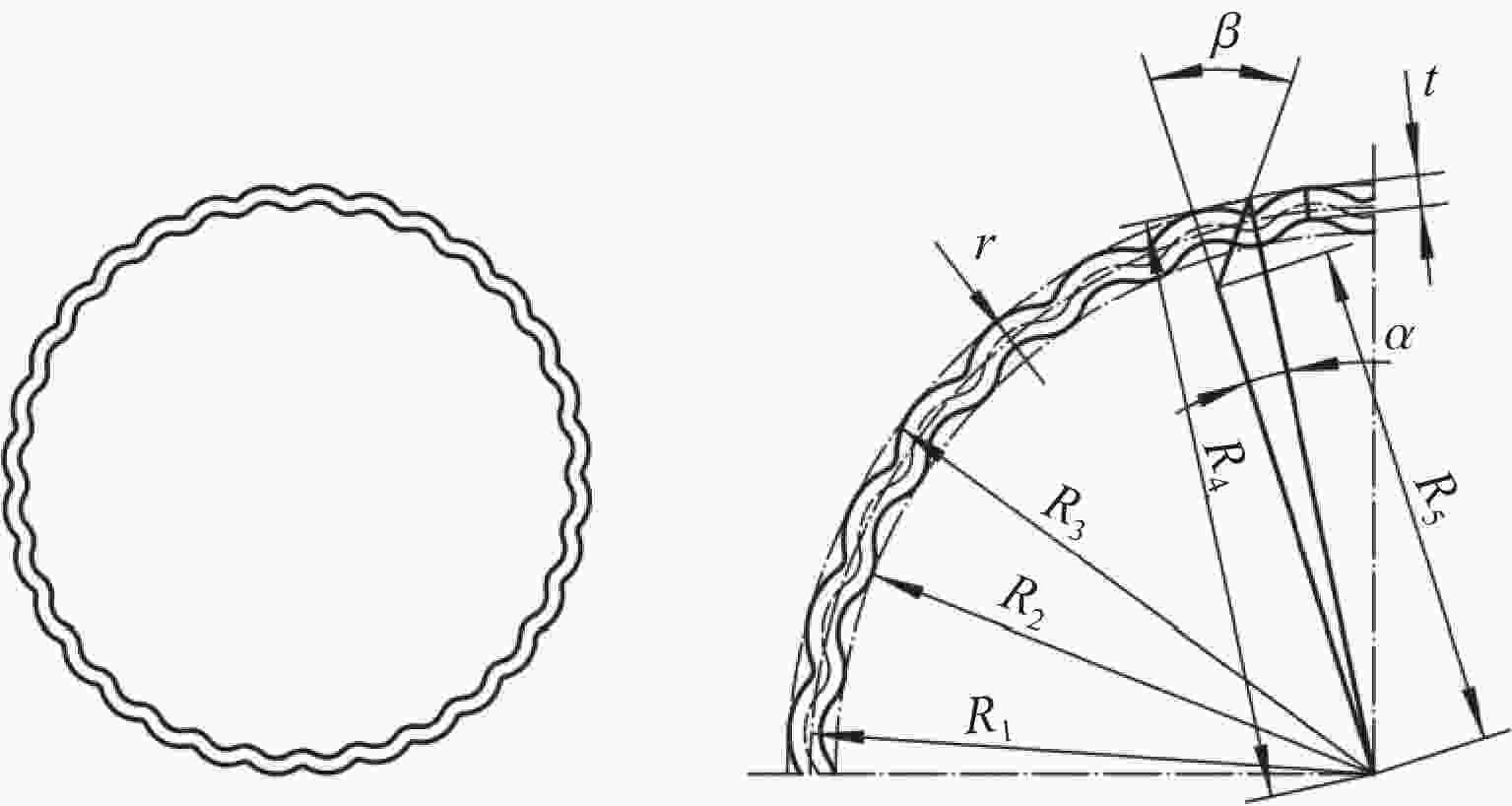
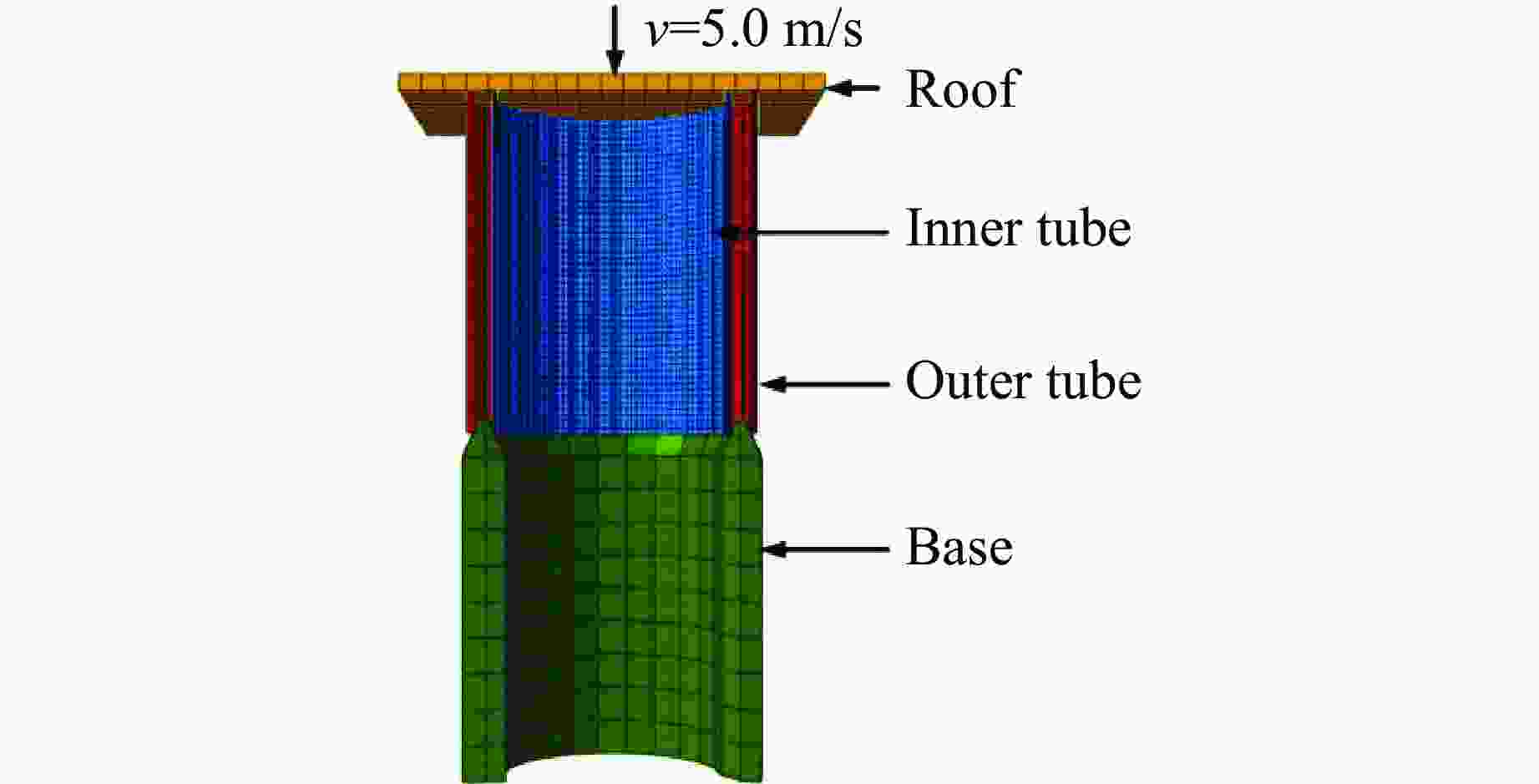
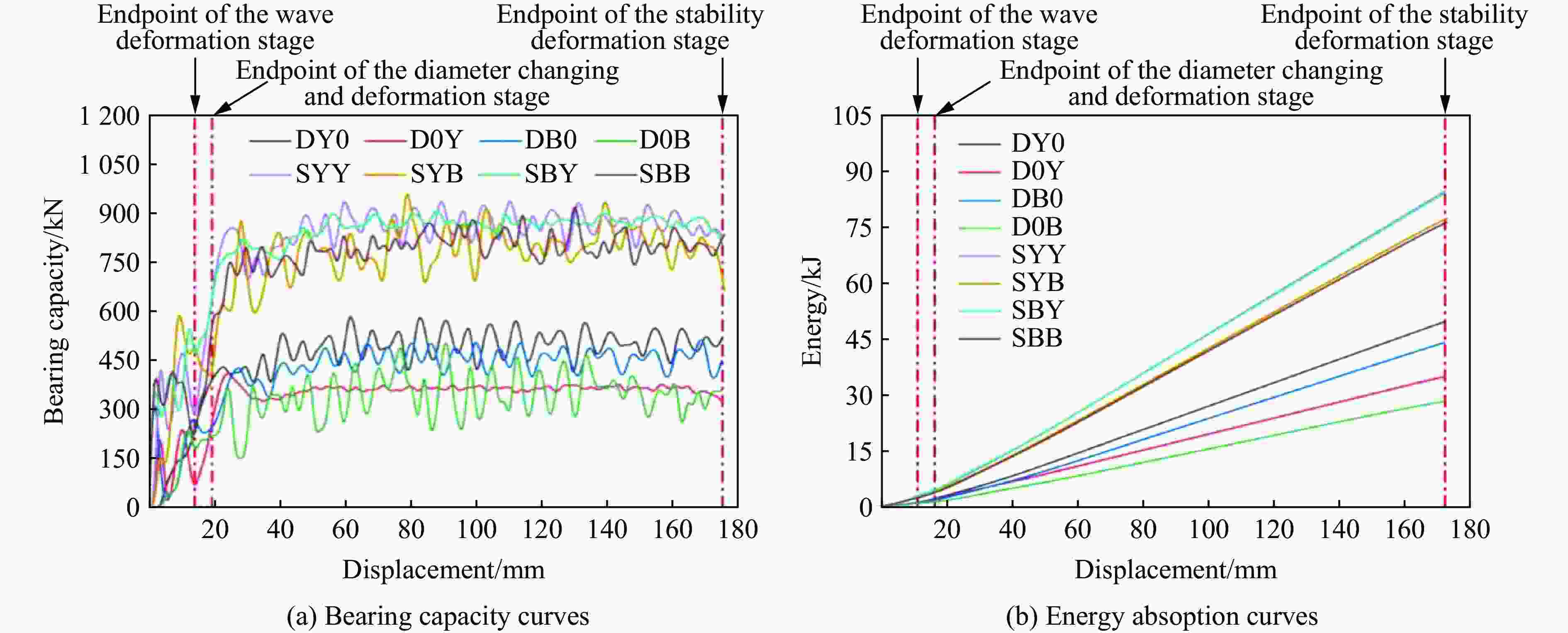
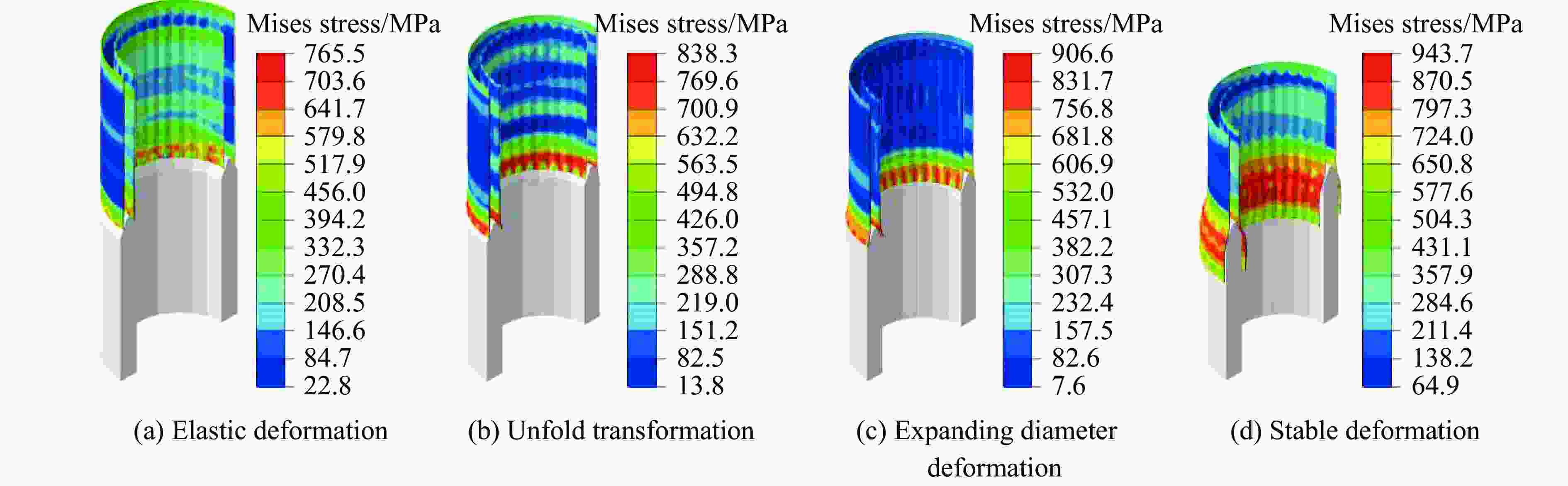
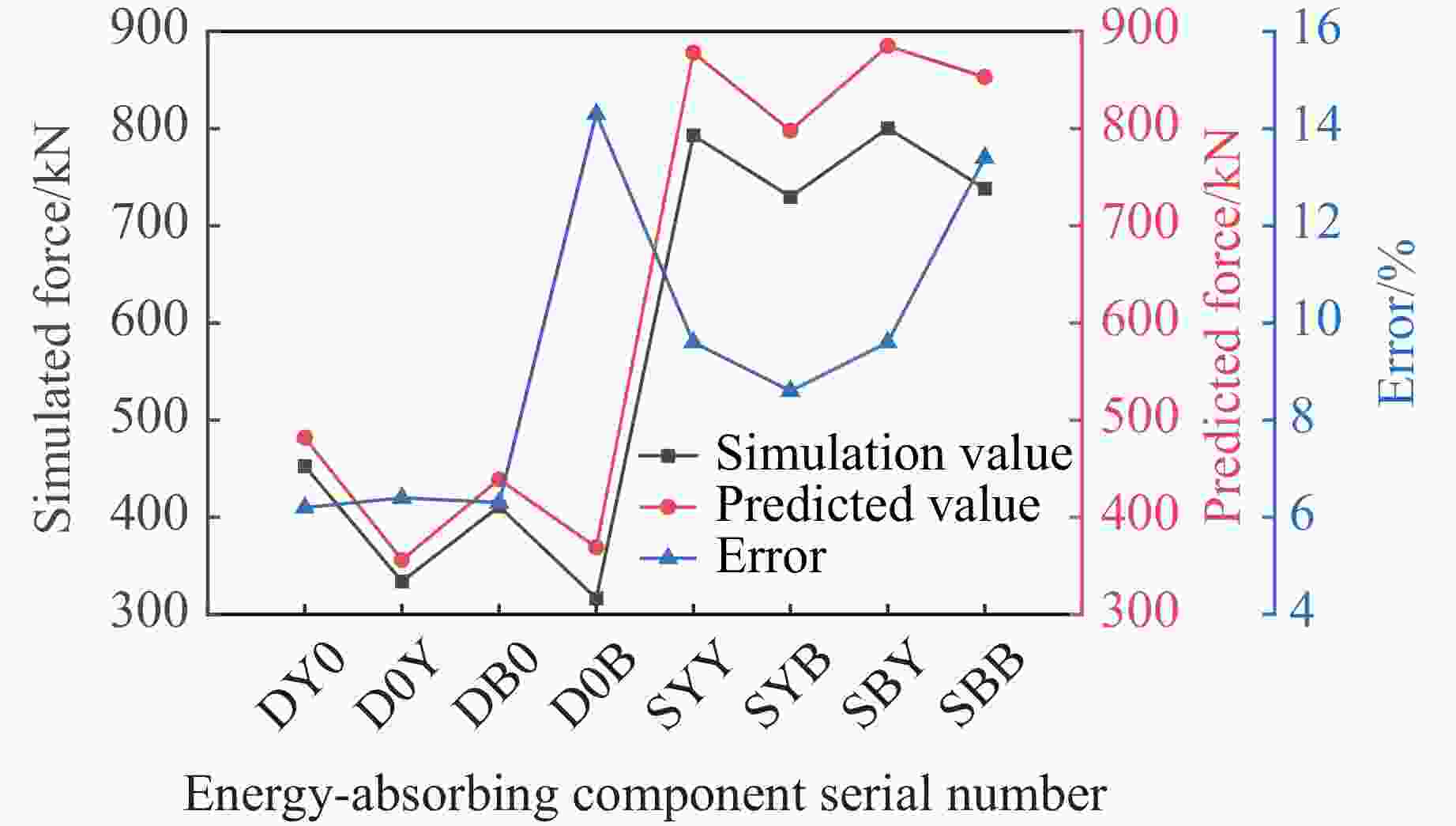
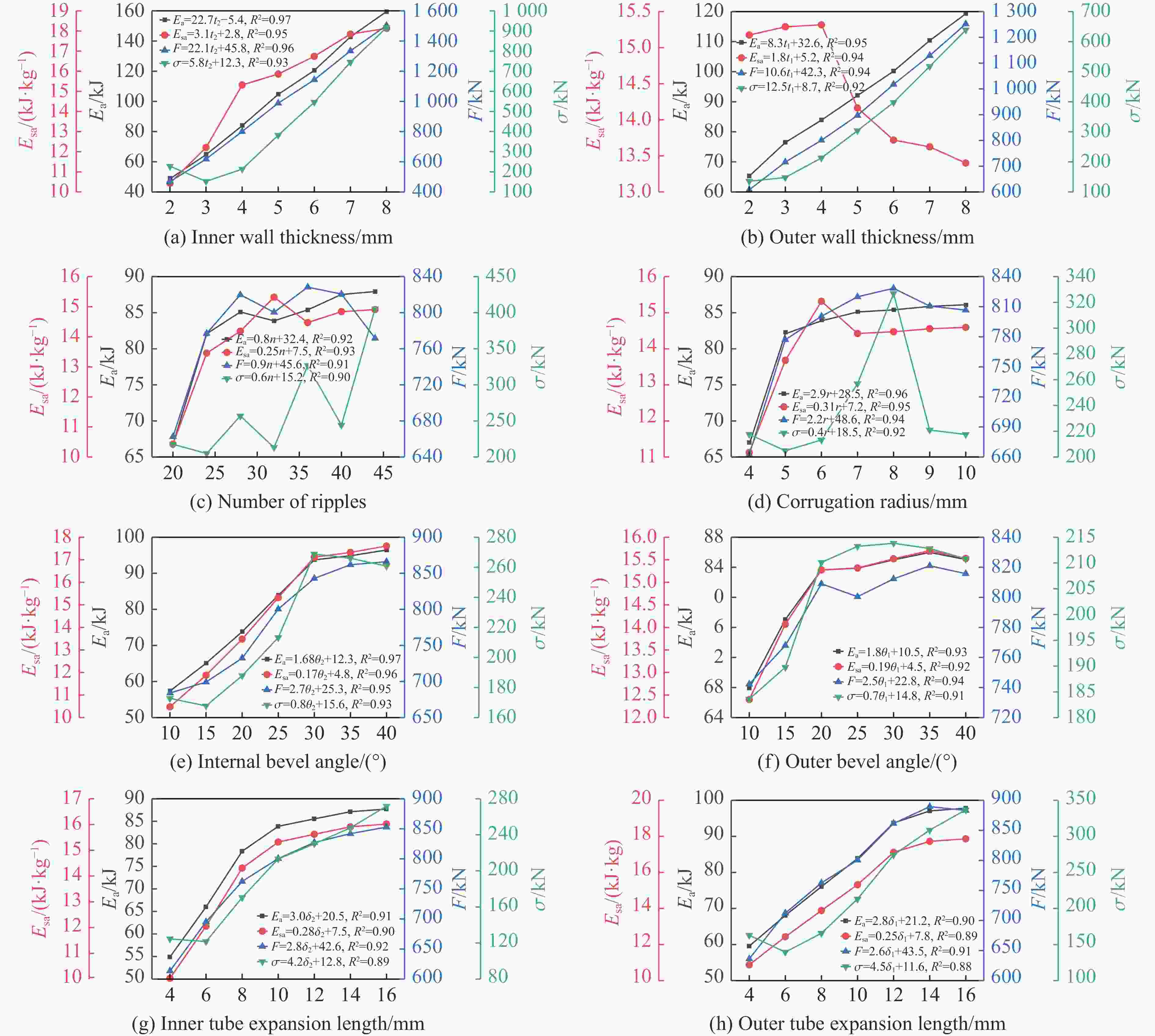
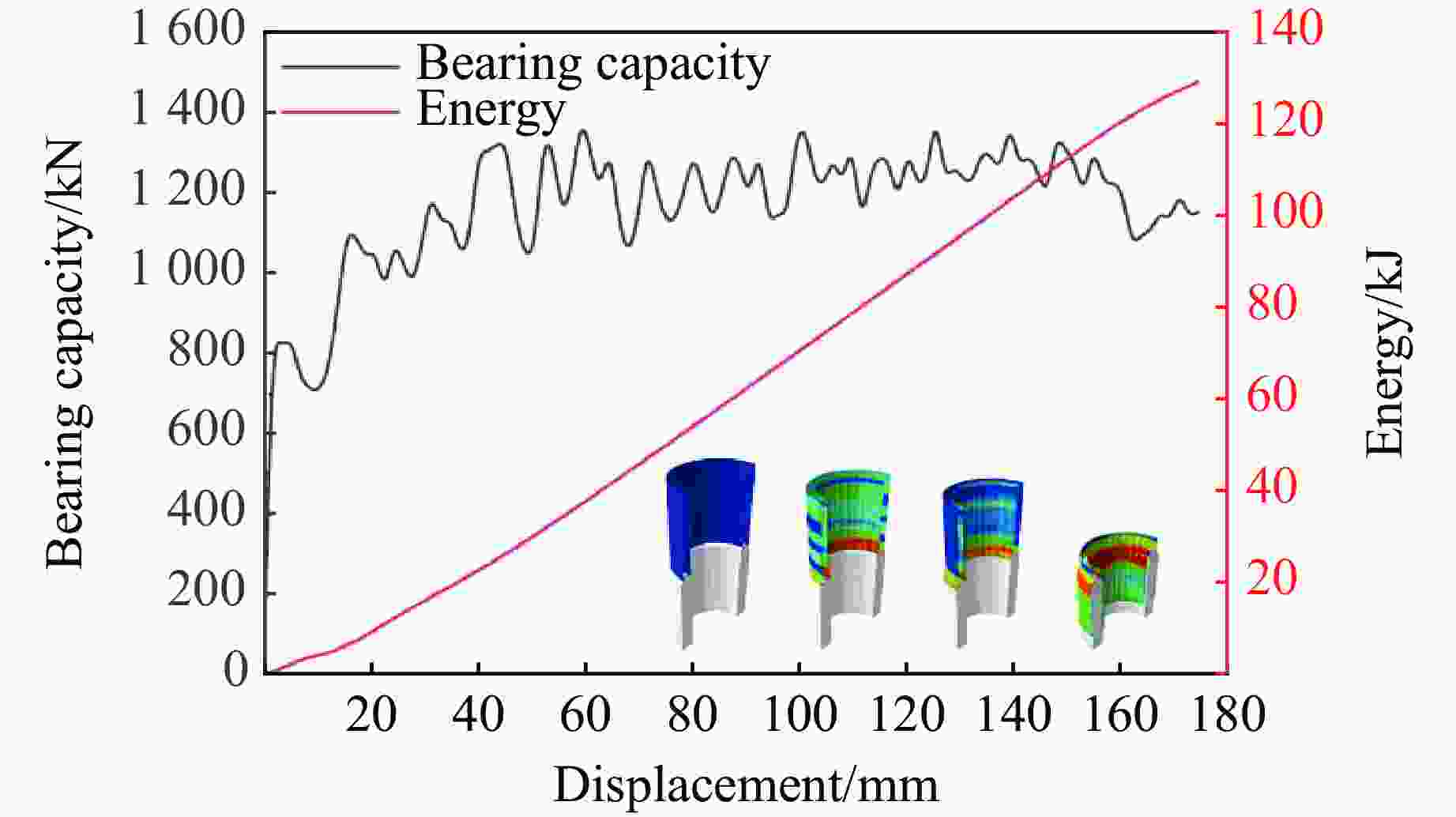
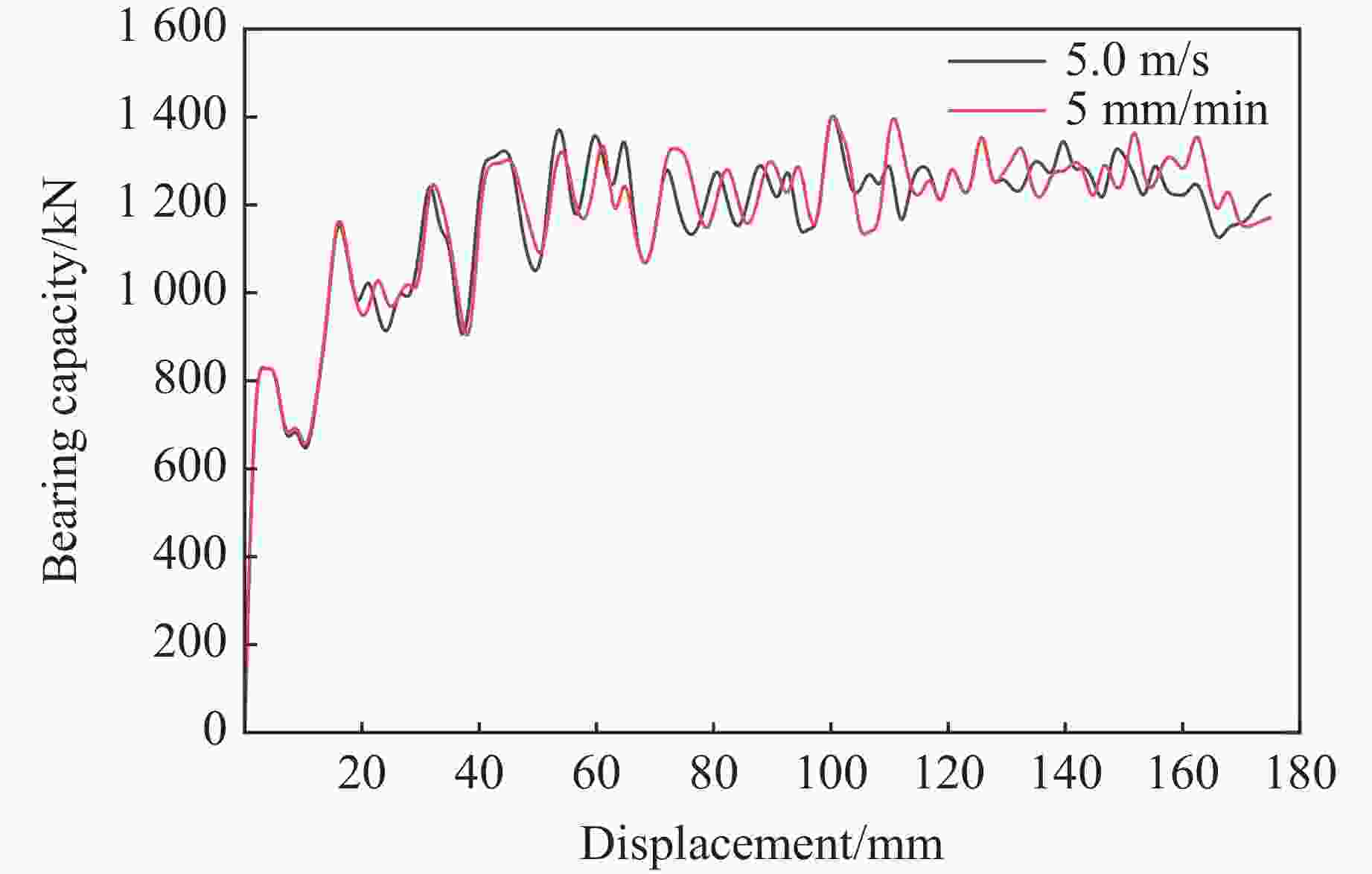
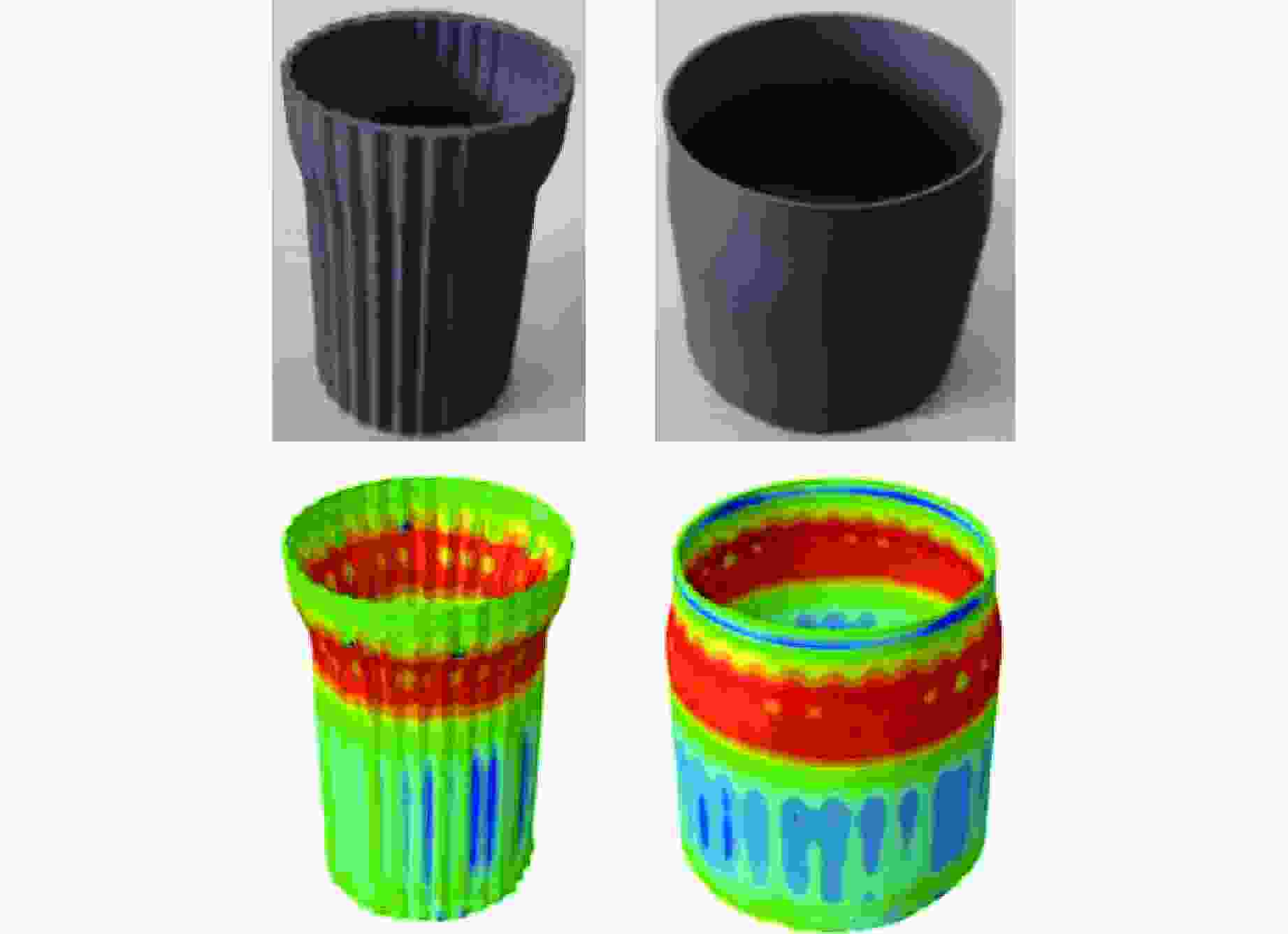
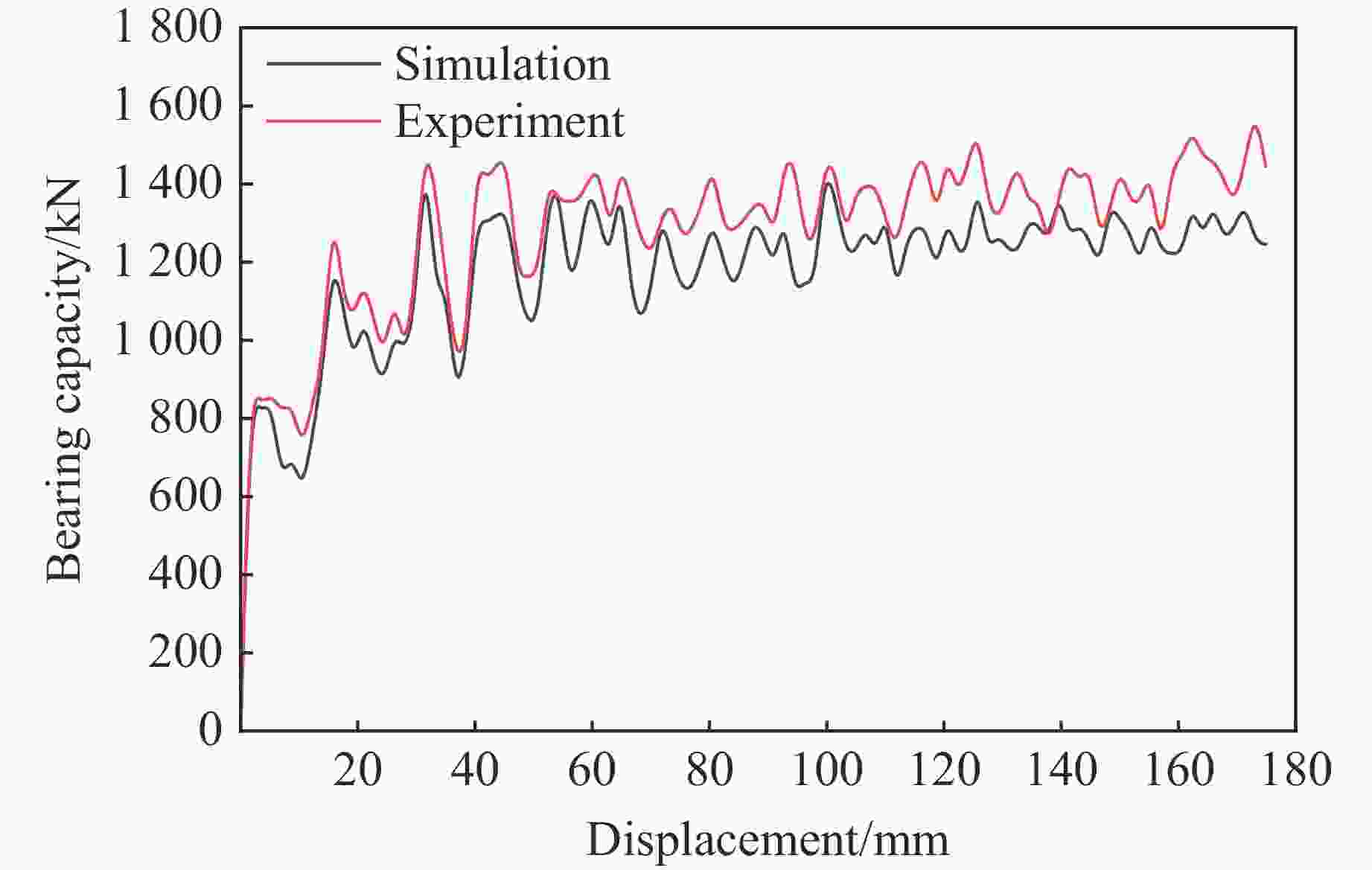
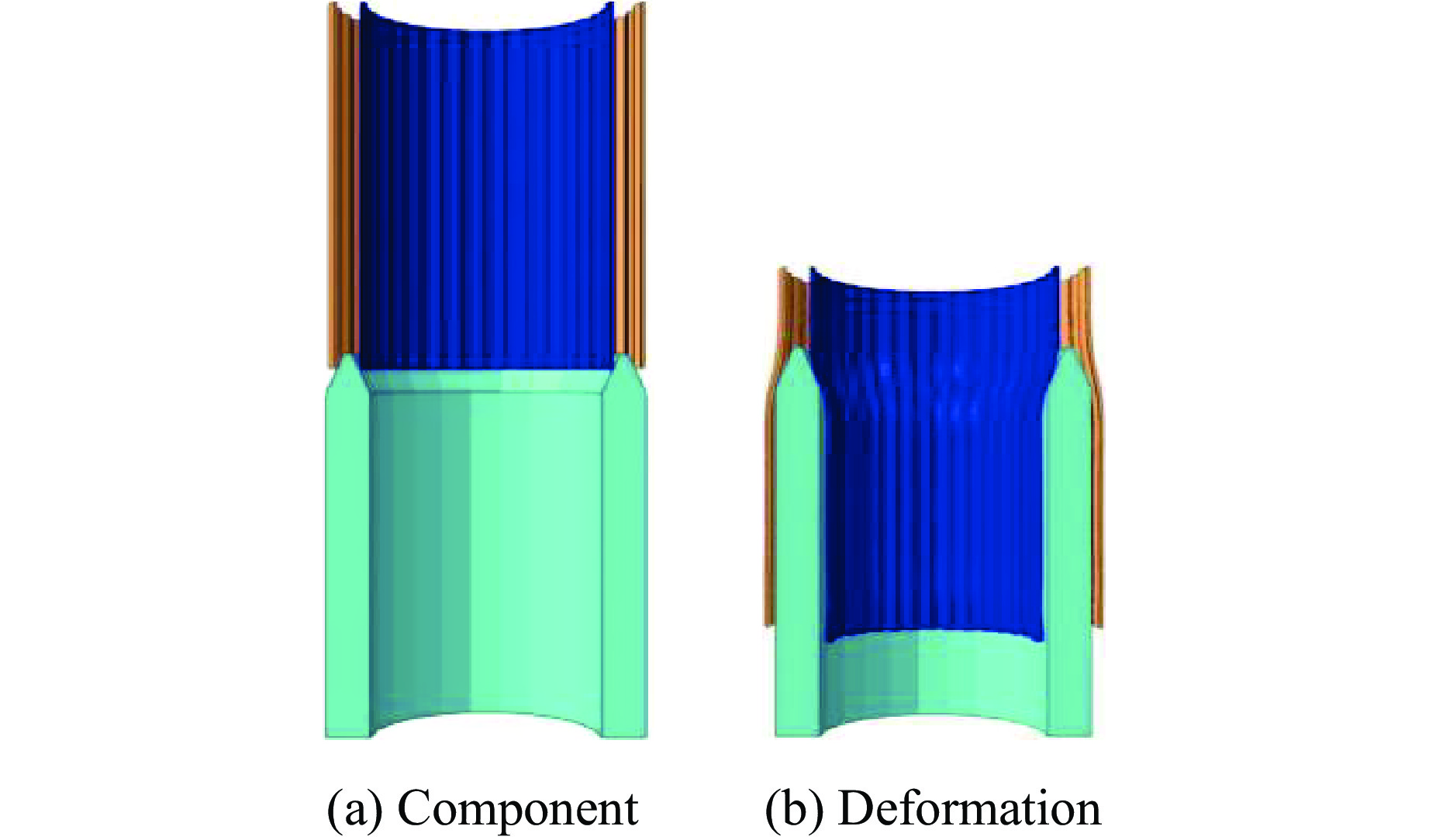
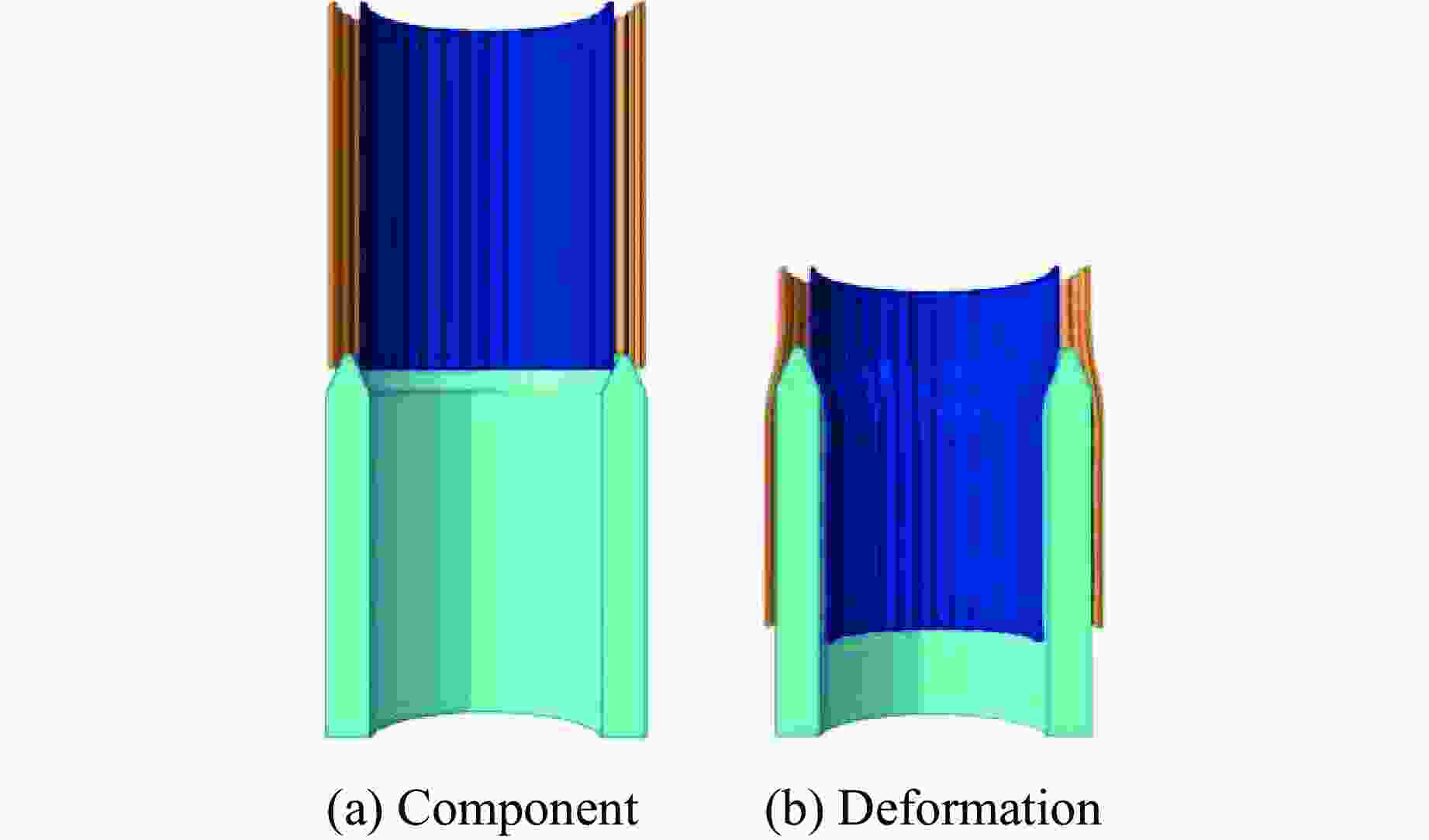
摘要: 为有效缓解冲击地压对液压支架的破坏作用,基于单层变径式吸能构件研究基础,提出了一种具有更高吸能量的双层变径式吸能构件。基于能量法剖析了不同截面管件扩径与缩径变形的能量耗散理论,推导了波纹管与圆管不同组合形式下构件稳定变径过程的承载力计算公式;通过数值模拟得到了8种不同类型吸能构件的吸能量曲线、承载力曲线及变形规律,对比发现,内层波纹管、外层圆管的双层变径式吸能构件结构(SBY类型)具备较优的吸能性能;探究了不同结构参数对吸能效果的影响规律,其中,内管壁厚、外管壁厚、波纹半径和底座内倒角4种结构参数对吸能特性参数影响显著。根据拉丁超立方取样方法设计试验方案,利用Kriging代理模型,结合多目标粒子群优化算法对结构参数进行优化,最终选择优化后的结构参数组合为内管壁厚6.0 mm、外管壁厚2.9 mm、波纹半径6.9 mm、底座内倒角40°。据此,制作了吸能构件并进行了轴向准静态加压实验,验证了数值模拟分析及优化结果的准确性和有效性。结果表明:经参数优化后的双层变径式吸能构件的总吸能提高了54.2%,比吸能提高了55.6%,平均承载力提高了43.2%,载荷标准差提高了59.5%。所设计的构件具有更好的吸能性能,让位防冲过程更加可靠。本研究可为深部巷道支护液压支架的吸能构件设计提供理论依据和参考。Abstract: In order to effectively mitigate the destructive effects of impact ground pressure on hydraulic supports, a double-layer variable-diameter energy-absorbing component with enhanced energy absorption was proposed based on previous research on single-layer variable-diameter structures. Using the energy method, the energy dissipation theory of the expansion and reduction deformation of tubular components with different cross-sections was analyzed, and the bearing capacity formulas for stable diameter reduction processes under various combinations of corrugated and circular tubes were derived. Through numerical simulations, the energy absorption curves, bearing capacity curves, and deformation patterns of eight types of energy-absorbing components were obtained. Comparative analysis revealed that the double-layer variable-diameter energy-absorbing component structure (SBY-type), consisting of an inner corrugated tube and an outer circular tube, exhibited superior energy absorption performance. The influence of key structural parameters on the energy absorption characteristics was further investigated. Among these, inner tube thickness, outer tube thickness, corrugation radius, and inner chamfer angle of the base were found to have the most significant effects. A Latin hypercube sampling scheme was designed, and the parameters were optimized using a Kriging surrogate model coupled with a multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm. The optimal parameter combination was determined as follows: inner tube thickness of 6.0 mm, outer tube thickness of 2.9 mm, corrugation radius of 6.9 mm, and base chamfer angle of 40°. Subsequently, axial quasi-static compression tests were conducted to verify the accuracy and effectiveness of the numerical and optimization results. The results indicate that, the total energy absorption of the double-layer variable-diameter energy-absorbing component increased by 54.2%, the specific energy absorption increased by 55.6%, the average bearing capacity increased by 43.2%, and the load standard deviation increased by 59.5%. These enhancements demonstrate that the optimized component exhibits superior and more stable energy absorption performance, thereby improving the reliability of the yielding anti-impact process. This study provides an important theoretical basis and design reference for developing energy-absorbing components in hydraulic supports for deep roadway reinforcement.
-
表 1 构件结构尺寸
Table 1. Structural dimensions of components
No. H/mm Di,t/mm Do,t/mm t/mm Rp/mm Np θb/(º) Lr/mm Di,b/mm Do,b/mm h/mm DY0 200 140 4 25 10 130 180 210 D0Y 200 170 4 25 10 130 180 210 DB0 200 140 4 6 32 25 10 130 180 210 D0B 200 170 4 6 32 25 10 130 180 210 SYY 200 140 170 4 25 10 130 180 210 SYB 200 140 170 4 6 32 25 10 130 180 210 SBY 200 140 170 4 6 32 25 10 130 180 210 SBB 200 140 170 4 6 32 25 10 130 180 210 ρ/(kg·m−3) E/GPa $\nu $ A0/MPa B0/MPa C n m $ \dot{{\varepsilon }}_{0}$/s−1 7 800 210 0.3 507 320 0.064 0.28 1.06 1 表 3 吸能构件结构参数设置
Table 3. Structural parameters of energy-absorbing components
Wall thickness/mm Number of ripples Corrugation radius/mm Bevel angle/(°) Tube expansion length/mm Inner Outer Internal Outer Inner Outer 2 2 20 4 10 10 4 4 3 3 24 5 15 15 6 6 4 4 28 6 20 20 8 8 5 5 32 7 25 25 10 10 6 6 36 8 30 30 12 12 7 7 40 9 35 35 14 14 8 8 44 10 40 40 16 16 表 4 设计变量名称、范围及符号
Table 4. Design variable names, ranges and symbols
Variable Range Variable symbols Inner wall thickness 2–6 t2 Outer wall thickness 2–6 t1 Corrugation radius 4–10 r Internal bevel angle 10–40 θ2 表 5 设计方案与模拟试验结果
Table 5. Design scheme and simulation test results
Test No. t2/mm t1/mm r/mm θ2/(°) Ea/kJ Esa/(kJ·kg−1) F/kN σ/kN 1 4.8 2.6 9.9 14 61.590 11.664 677.867 185.433 2 2.7 6.0 4.9 28 72.514 11.810 745.688 202.799 3 5.0 3.3 5.4 37 100.795 23.495 904.223 349.058 4 2.5 3.8 6.4 23 52.702 12.199 522.087 168.616 5 2.6 5.7 4.1 30 64.758 11.481 691.203 157.264 6 4.5 4.5 8.2 13 70.050 11.101 793.841 271.380 7 3.4 5.6 6.8 40 111.602 17.742 1 037.534 442.364 8 4.7 4.2 9.8 24 98.743 14.961 930.947 338.425 9 5.4 3.8 6.6 29 113.710 20.525 1 064.797 455.378 10 4.3 2.1 7.9 11 44.258 11.232 538.184 234.592 11 5.3 5.2 4.7 33 132.156 21.629 1 254.845 658.498 12 3.1 4.4 6.4 31 78.067 15.397 721.831 185.786 13 5.2 4.5 4.8 13 75.830 13.638 860.273 310.182 14 5.9 4.9 8.9 23 121.447 15.917 1 180.091 595.308 15 5.8 2.2 9.4 18 79.435 14.903 814.922 263.393 16 2.0 4.0 6.1 25 49.217 11.553 472.824 221.050 17 3.5 5.6 8.4 19 83.458 12.364 792.687 594.416 18 3.6 5.3 5.6 20 82.925 14.055 806.865 608.462 19 4.9 2.7 7.5 15 64.683 13.940 717.075 303.754 20 4.3 2.8 9.3 16 62.186 12.639 646.060 168.125 21 5.7 2.3 7.8 10 58.318 12.200 766.204 306.045 22 3.6 2.0 6.0 38 70.521 23.046 609.296 134.071 23 3.0 4.2 5.8 27 66.230 13.913 666.416 234.210 24 2.1 5.1 7.2 39 65.104 12.078 675.041 196.751 25 5.5 5.5 6.9 14 91.176 12.663 1 012.650 446.851 26 2.9 4.6 6.2 37 77.353 14.990 717.828 156.515 27 3.7 2.5 7.7 33 69.498 17.683 645.452 465.485 28 4.2 5.0 8.7 26 100.172 14.973 944.222 351.379 29 3.0 2.7 6.9 21 50.876 14.093 490.494 198.120 30 4.6 2.9 7.0 17 68.829 15.160 696.020 184.417 31 4.0 2.4 4.6 31 68.630 21.380 608.745 217.909 32 2.8 3.0 4.1 16 42.011 12.769 425.738 253.344 33 5.5 3.1 5.5 12 64.491 14.111 749.341 328.338 34 2.3 3.4 5.9 32 49.498 13.129 458.532 541.357 35 3.3 4.1 8.0 28 77.916 14.841 745.422 240.880 36 3.1 4.0 9.7 30 76.593 14.183 692.087 163.685 37 4.1 3.6 9.6 27 89.081 15.738 805.697 235.588 38 2.2 3.7 7.3 21 47.653 11.212 462.985 243.584 39 3.8 5.8 5.3 19 81.746 12.893 847.130 307.000 40 2.4 5.3 9.2 35 76.494 12.706 741.704 179.399 41 2.5 4.7 9.0 17 56.703 10.253 583.673 171.673 42 5.7 3.2 8.5 34 120.616 20.512 1 104.944 492.756 43 3.2 3.5 8.7 33 79.353 16.395 697.082 165.946 44 4.5 2.2 4.4 35 71.710 22.479 682.375 199.250 45 5.9 5.9 8.1 23 129.615 15.749 1 326.121 801.735 46 3.8 5.4 7.4 26 93.217 14.341 946.522 398.420 47 5.0 4.8 5.2 39 110.336 18.860 1 066.671 467.711 48 5.4 3.9 4.3 22 94.149 19.253 938.998 345.628 49 4.0 3.1 9.2 12 54.494 10.877 614.714 169.374 50 4.7 4.9 5.0 36 104.431 17.943 995.080 382.310 表 6 代理模型评估指标
Table 6. Evaluation indicators of agent model
Parameter R2 Ea 0.9513 Esa 0.9425 F 0.9535 σ 0.9616 表 7 吸能构件缩放前后尺寸
Table 7. Dimensions of energy-absorbing components before and after scaling
Scaling H/mm Di,t/mm Do,t/mm Inner wall
thickness/mmOuter wall
thickness/mmCorrugation
radius/mmNp h/mm Before 200 140 170.0 6.0 2.9 6.9 32 210.0 After 50 35 42.5 2.4 1.2 1.7 32 52.5 Scaling Inner tube
expansion
length/mmOuter tube
expansion
length/mmBase inner
diameter/mmBase outer
diameter/mmInternal bevel
angle/(°)Outer bevel
angle/(°)v/(m·s−1) Before 10.0 10.0 130.0 180.0 40 25 5.0 After 2.5 2.5 32.5 45.0 40 25 8.1 -
[1] 郭涛, 吴文禄, 黎振华, 等. 防冲击地压薄壁吸能构件的压溃吸能机理分析 [J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2024, 20(1): 276–286. doi: 10.20174/j.juse.2024.01.029GUO T, WU W L, LI Z H, et al. Numerical analysis of energy-absorption characteristics of energy absorbing components for anti-impact hydraulic support [J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2024, 20(1): 276–286. doi: 10.20174/j.juse.2024.01.029 [2] 顾敏康, 雷君相, 王陶, 等. 变径管吸能元件的成形工艺和翻转吸能性能研究 [J]. 塑性工程学报, 2018, 25(6): 85–92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2018.06.013GU M K, LEI J X, WANG T, et al. Study on forming process and inversion energy absorption performance of energy absorbing components of variable diameter tube [J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2018, 25(6): 85–92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2018.06.013 [3] 曹自幸. 耦合缩径-膨胀-撕裂变形模式的圆管耐撞性研究 [D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2023.CAO Z X. Study on the crashworthiness of circular tube with coupled shrinking-expanding-splitting deformation mode [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2023. [4] XIAO Y, LIU Y, WU Q W, et al. Structure optimization design for pre-folded external double-layer biomimetic multi-cell thin-walled tubes [J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2024, 38(7): 3465–3475. doi: 10.1007/s12206-024-0621-z [5] XIE S C, CAO Z X, YANG G H, et al. The energy absorption of a shrinking-expanding circular tube: an experimental and numerical investigation [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 184: 110509. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2022.110509 [6] PANG T, KANG H H, YAN X L, et al. Crashworthiness design of functionally graded structures with variable diameters [J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2017, 22(2): 148–162. doi: 10.1080/13588265.2016.1242548 [7] 张建卓, 潘强, 王洁, 等. 直纹管扩径式吸能构件设计与吸能特性 [J]. 机械设计与研究, 2022, 38(1): 180–185, 190. doi: 10.13952/j.cnki.jofmdr.2022.0070ZHANG J Z, PAN Q, WANG J, et al. Design and energy absorbing properties research on diameter expanding energy absorbing components of straight corrugated tube [J]. Machine Design and Research, 2022, 38(1): 180–185, 190. doi: 10.13952/j.cnki.jofmdr.2022.0070 [8] XIANG Y F, WANG M, YU T X, et al. Key performance indicators of tubes and foam-filled tubes used as energy absorbers [J]. International Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2015, 7(4): 1550060. doi: 10.1142/S175882511550060X [9] 王爱文, 范德威, 潘一山, 等. 扩胀-摩擦式吸能防冲锚索及其力学特性 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(2): 695–710. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.xr21.1728WANG A W, FAN D W, PAN Y S, et al. Expansion-friction energy-absorption anti-impact cable and its mechanical characteristics [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(2): 695–710. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.xr21.1728 [10] 吴明泽, 张晓伟, 张庆明. 材料和内边界约束对薄壁圆管轴向压缩吸能特性的影响研究 [J]. 应用力学学报, 2020, 37(4): 1415–1421. doi: 10.11776/cjam.37.04.D037WU M Z, ZHANG X W, ZHANG Q M. Effects of material properties and inner-constraints on the energy absorption of thin-walled circular tube under axial compression [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2020, 37(4): 1415–1421. doi: 10.11776/cjam.37.04.D037 [11] 张金鹏, 张玮炜, 齐瑾, 等. 与45钢对摩材料干摩擦条件下的摩擦学性能 [J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2024, 40(2): 115–123. doi: 10.16865/j.cnki.1000-7555.2024.0029ZHANG J P, ZHANG W W, QI J, et al. Tribological properties of friction material with 45 steel under dry friction condition [J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 2024, 40(2): 115–123. doi: 10.16865/j.cnki.1000-7555.2024.0029 [12] 田立勇, 于晓涵, 周禹鹏, 等. 液压支架立柱防冲吸能构件优化仿真及压溃实验研究 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2024, 49(6): 2924–2936. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.0676TIAN L Y, YU X H, ZHOU Y P, et al. Optimization simulation and crushing experiment of anti-impact energy absorption component of hydraulic support column [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2024, 49(6): 2924–2936. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.0676 [13] 潘一山, 肖永惠, 李国臻. 巷道防冲液压支架研究及应用 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(1): 90–99. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.YG19.1762PAN Y S, XIAO Y H, LI G Z. Roadway hydraulic support for rockburst prevention in coal mine and its application [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(1): 90–99. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.YG19.1762 [14] 田立勇, 董成, 于宁, 等. 含泡沫铝填充多胞圆管吸能立柱的防冲特性 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2025, 39(7): 074205. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240938TIAN L Y, DONG C, YU N, et al. Anti-scour characteristics of multi-cell tube energy-absorbing column filled with aluminum foam [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2025, 39(7): 074205. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240938 [15] 王鸿鼎, 秦甘霖, 刘洪, 等. 加强筋对薄壁结构件耐冲撞性能的影响 [J]. 锻压技术, 2021, 46(11): 176–182. doi: 10.13330/j.issn.1000-3940.2021.11.025WANG H D, QIN G L, LIU H, et al. Influence of reinforcing ribs on impact resistance for thin-walled structural parts [J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2021, 46(11): 176–182. doi: 10.13330/j.issn.1000-3940.2021.11.025 [16] 田立勇, 王泽, 于宁, 等. 多胞体汽车后防撞吸能器耗能机制研究与结构优化设计 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2024, 43(17): 91–99, 122. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2024.17.011TIAN L Y, WANG Z, YU N, et al. Energy dissipation mechanism study and structural optimization design of car rear anti-collision multi-cellular energy absorber [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2024, 43(17): 91–99, 122. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2024.17.011 [17] 潘怡, 王萌, 周阳, 等. 新型负刚度超材料吸能结构的设计与优化 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2023, 42(6): 180–187. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.06.022PAN Y, WANG M, ZHOU Y, et al. Design and optimization of a new energy absorbing structure with negative stiffness metamaterial [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2023, 42(6): 180–187. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.06.022 [18] 赵洪林, 姜金花, 赵永顺, 等. 基于熵权TOPSIS决策的汽车吸能盒冲压成形质量多目标优化 [J]. 锻压技术, 2023, 48(10): 67–74. doi: 10.13330/j.issn.1000-3940.2023.10.010ZHAO H L, JIANG J H, ZHAO Y S, et al. Multi-objective optimization on stamping quality for automotive energy absorption box based on entropy weight TOPSIS decision-making [J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2023, 48(10): 67–74. doi: 10.13330/j.issn.1000-3940.2023.10.010 [19] 刘刚, 孙佳琦, 董伟星. 改进粒子群优化算法在建筑能耗优化中的参数设置 [J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 2021, 54(1): 82–90. doi: 10.11784/tdxbz201911030LIU G, SUN J Q, DONG W X. Parameter settings of improved particle swarm optimization algorithm in building energy consumption optimization [J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2021, 54(1): 82–90. doi: 10.11784/tdxbz201911030 [20] 常新哲, 徐绯, 杨磊峰, 等. 薄壁方管轴向压溃的相似性研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2023, 42(11): 284–294. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.11.034CHANG X Z, XU F, YANG L F, et al. Study on the similarity of axial crushing of thin-walled square tubes [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2023, 42(11): 284–294. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.11.034 [21] MOU H L, ZOU T T, FENG Z Y, et al. Crashworthiness analysis and evaluation of fuselage section with sub-floor composite sinusoidal specimens [J]. Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures, 2016, 13(6): 1186–1202. doi: 10.1590/1679-78252446 [22] LI W W, LUO Y H, LI M, et al. A more weight-efficient hierarchical hexagonal multi-cell tubular absorber [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2018, 140: 241–249. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.03.006 -






 下载:
下载: