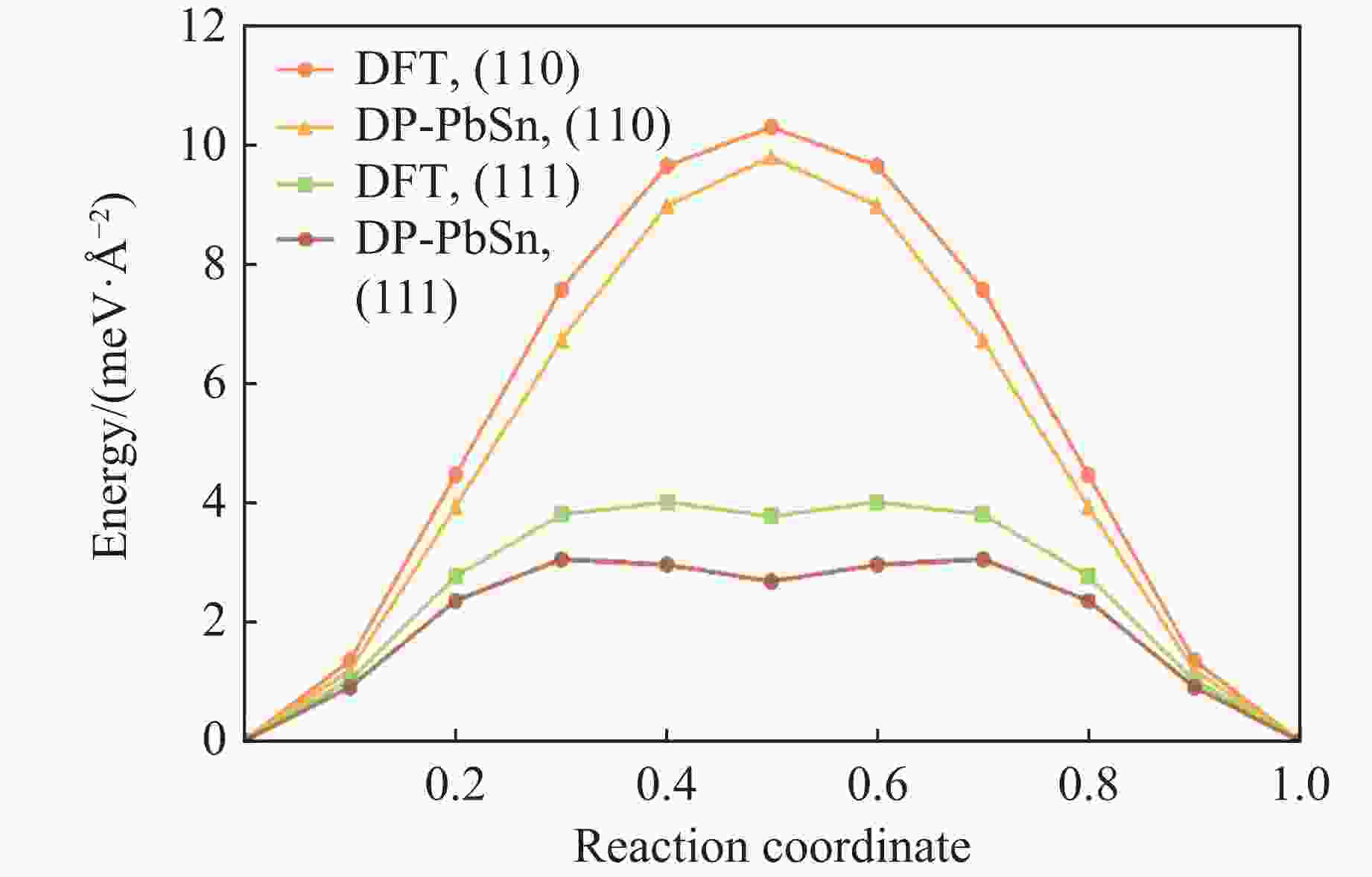
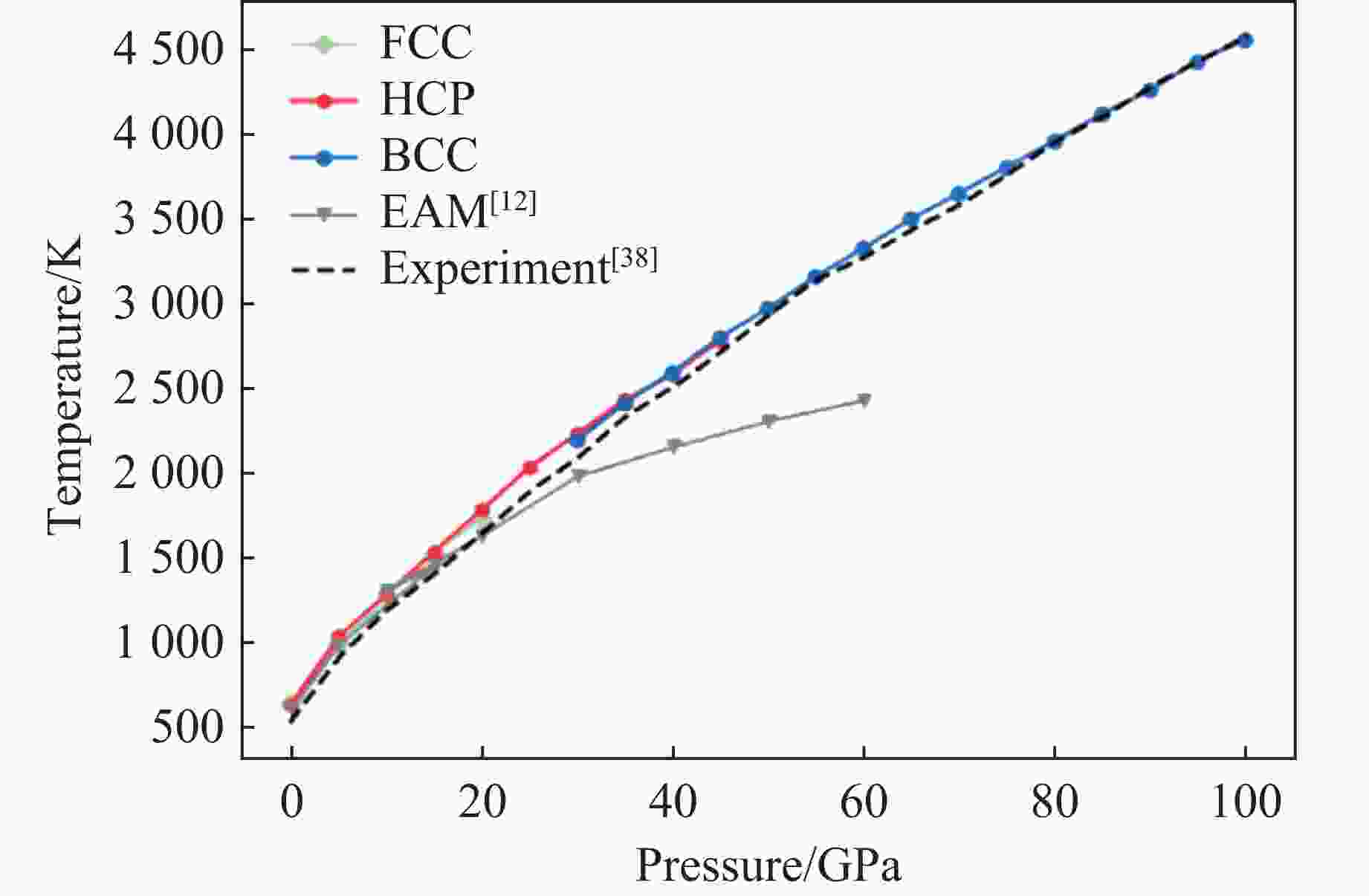
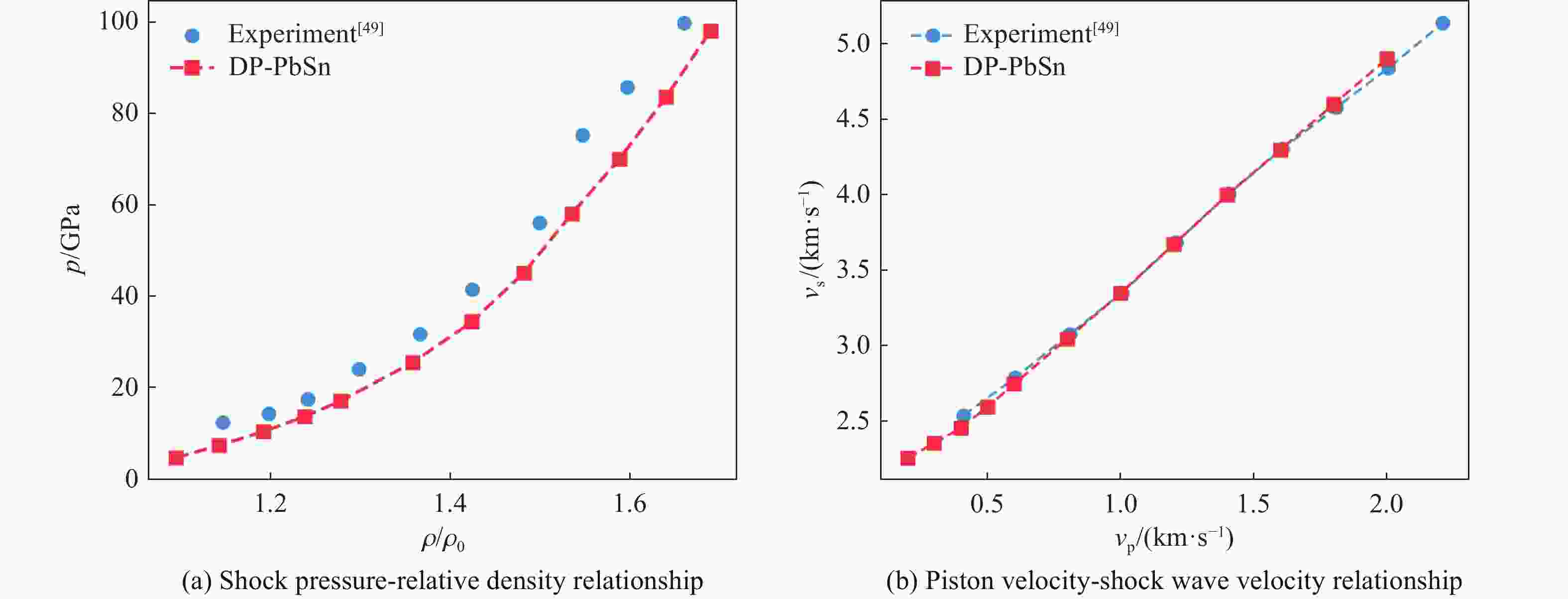
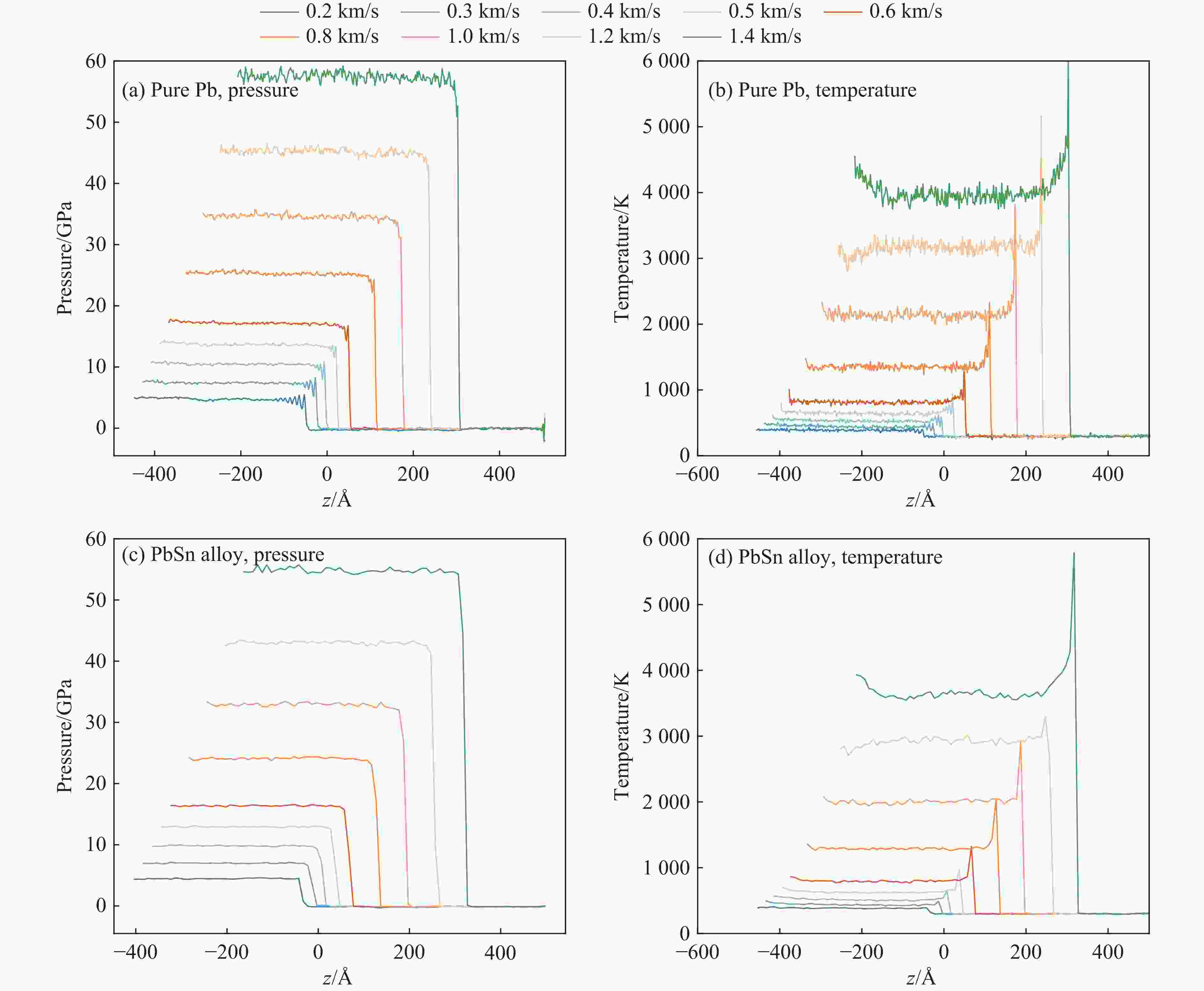
A Machine Learning Potential Model for Simulating Dynamic Mechanical Response of Pb-Sn Alloy
-
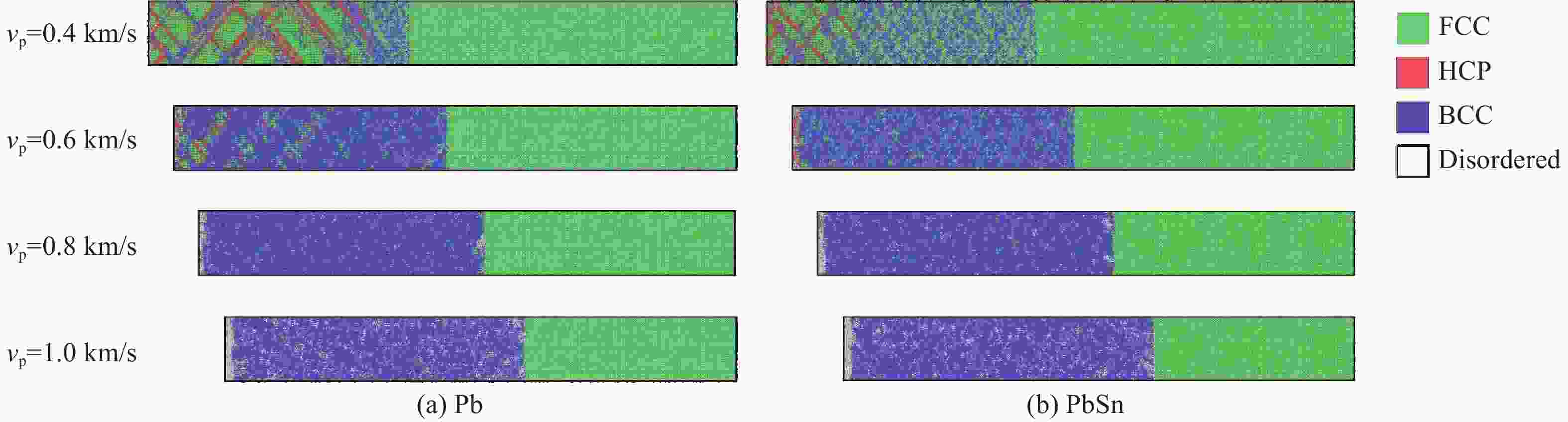
摘要: 铅是一种低熔点且具有复杂温度-压力相图的金属材料,经过与锡的合金化,能够进一步降低其熔点,使得铅锡合金成为研究材料动态力学响应及动态破坏行为的重要模型材料。目前,受表征手段的限制,通过实验方法揭示铅锡合金在原子尺度上的动态破坏行为和机理仍存在巨大挑战。非平衡分子动力学是一种重要的理论研究手段,可以模拟动态过程中的原子运动轨迹,从而揭示动态加载-卸载及破坏行为中的关键原子尺度过程。然而,分子动力学方法的可靠性依赖其所采用的原子间相互作用势函数的精度,目前并没有适用于铅锡合金的动态响应研究的高精度势函数,因此,制约了铅锡合金的动态模拟研究。通过同步学习策略,构建了压力为0~100 GPa、温度为0~5 000 K下具有第一性原理精度的铅锡合金机器学习势函数模型DP-PbSn。该势函数能够以第一性原理的精度预测铅锡合金的点阵常数和弹性常数等基本性质,以及表面能、层错能、空位形成能等缺陷性质,还能够准确地预测其熔化线和冲击Hugoniot曲线,展现了其在动态响应模拟过程中的适用性。利用该势函数对铅和铅锡合金的动态力学响应行为进行了初步的模拟研究,揭示了锡对动态加载过程中相变及塑性行为的影响。该势函数作为重要的理论工具,能够实现高精度的非平衡分子动力学模拟,从而为铅锡合金动态力学损伤行为的实验研究提供关键理论依据。Abstract: Lead is a low-melting-point metal with a complex temperature-pressure phase diagram. Alloying with tin further reduces its melting temperature, making lead-tin alloys an important model material for studying dynamic mechanical responses and failure behavior. However, experimental characterization of atomic-scale dynamic failure mechanisms in PbSn alloys remains challenging due to current technical limitations. Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics (NEMD) simulations can track atom trajectories and reveal key dynamic processes under dynamic loading-unloading. It thus serves as a critical alternative tool. Yet, the reliability of molecular dynamics relies on the accuracy of interatomic potentials, and currently, no high-accuracy potential exists for PbSn alloys under dynamic conditions. In this work, we develop a machine-learning interatomic potential (DP-PbSn) for PbSn alloys using a concurrent learning scheme. This potential achieves first-principles accuracy across a wide thermodynamic range (0–100 GPa, 0–
5000 K), reliably predicting fundamental properties (e.g., lattice constants, elastic constants), defect energetics (e.g., surface energy, stacking fault energy, vacancy formation energy), as well as melting curves and shock Hugoniot curves, demonstrating its suitability for dynamic simulations. Leveraging this potential, we conduct preliminary NEMD simulations to investigate the dynamic mechanical responses of pure Pb and PbSn alloys, elucidating the influence of Sn on phase transitions and plastic deformation under dynamic loading. The DP-PbSn serves as a robust theoretical tool for high-accuracy non-equilibrium molecular dynamics, providing essential insights for experimental studies on the dynamic damage behavior of PbSn alloys.-
Key words:
- lead-tin alloy /
- dynamic mechanical responses /
- machine learning /
- interatomic potential
-
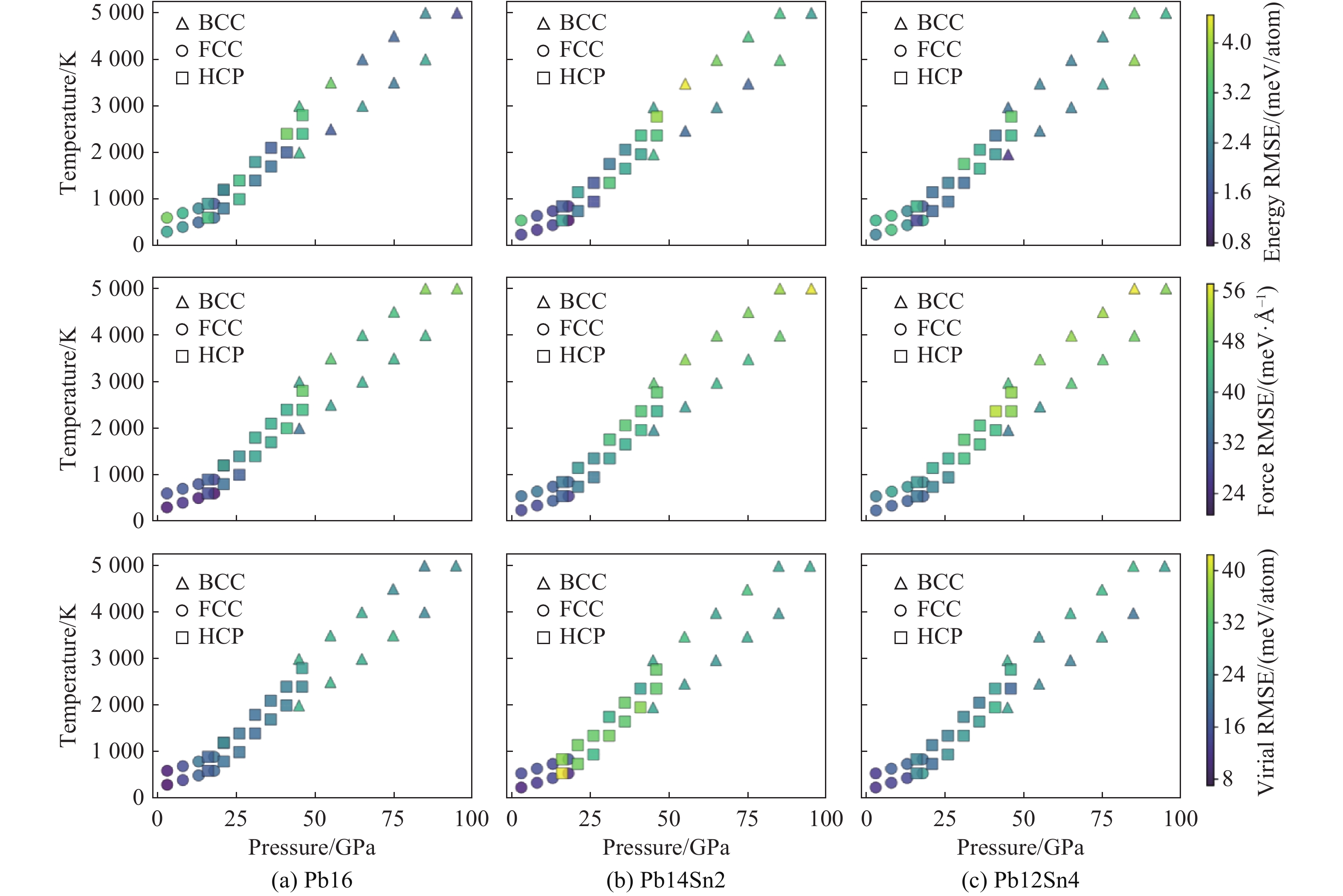
表 1 DP-PbSn的训练误差与测试误差
Table 1. Training and testing error of DP-PbSn
Dataset RMSE Energy/(meV/atom) Force/(meV·Å–1) Virial stress/(meV/atom) Training 4.76 61.98 32.54 Testing 2.88 31.39 25.73 表 2 利用DP-PbSn预测的纯Pb的基本性质
Table 2. Basic properties of pure Pb predicted by DP-PbSn
Phase Model a/Å Ecoh/eV C11/GPa C12/GPa C44/GPa Esurf/(meV·Å–2) Evac/eV (100) (110) (111) FCC DP-PbSn 5.037 –3.243 45.75 39.14 14.64 18.87 20.82 17.68 0.485 DFT 5.039 –3.247 51.80 34.52 16.79 18.78 22.48 17.26 0.490 Phase Model a/Å c/Å c/a Ecoh/eV C11/GPa C12/GPa C44/GPa Evac/eV HCP DP-PbSn 3.539 5.892 1.665 –3.238 58.032 38.603 5.162 0.530 DFT 3.542 5.863 1.655 –3.234 51.840 35.560 6.950 0.520 表 3 利用DP-PbSn预测的不同组分PbSn合金的基本性质
Table 3. Basic properties of PbSn alloys with different compositions predicted by DP-PbSn
Phase aSn/% Model a/Å C11/GPa C12/GPa C44/GPa Esol/
(meV/atom)Esurf/(meV·Å–2) (100) (110) (111) FCC 9 DP-PbSn 5.031 44.78 38.79 13.81 88.57 18.92 20.22 17.53 DFT 5.021 51.28 35.19 14.25 127.09 20.10 22.40 19.20 25 DP-PbSn 5.001 45.45 38.93 13.01 72.97 19.42 20.82 18.45 DFT 4.991 51.21 36.28 12.53 95.39 22.60 24.60 23.90 Phase aSn/% Model a/Å c/Å c/a C11/GPa C12/GPa C44/GPa Esol/
(meV/atom)HCP 9 DP-PbSn 3.541 5.862 1.656 55.73 36.98 5.40 133.90 DFT 3.541 5.846 1.651 55.26 40.71 11.29 252.10 25 DP-PbSn 3.519 5.824 1.655 54.29 38.33 3.97 96.08 DFT 3.465 5.885 1.698 55.71 40.34 5.16 157.06 -
[1] DEWAELE A, MEZOUAR M, GUIGNOT N, et al. Melting of lead under high pressure studied using second-scale time-resolved X-ray diffraction [J]. Physical Review B, 2007, 76(14): 144106. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.76.144106 [2] KUZNETSOV A, DMITRIEV V, DUBROVINSKY L, et al. FCC-HCP phase boundary in lead [J]. Solid State Communications, 2002, 122(3/4): 125–127. doi: 10.1016/S0038-1098(02)00112-6 [3] TAKAHASHI T, MAO H K, BASSETT W A. Lead: X-ray diffraction study of a high-pressure polymorph [J]. Science, 1969, 165(3900): 1352–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3900.1352 [4] VANDERBORGH C A, VOHRA Y K, XIA H, et al. BCC lead at 109 GPa: diffraction studies to 208 GPa [J]. Physical Review B, 1990, 41(10): 7338–7340. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.41.7338 [5] DAI C D, TAN H, GENG H Y. Model for assessing the melting on Hugoniots of metals: Al, Pb, Cu, Mo, Fe, and U [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 92(9): 5019–5026. doi: 10.1063/1.1510561 [6] KARAKAYA I, THOMPSON W T. The Pb-Sn (lead-tin) system [J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria, 1988, 9(2): 144–152. doi: 10.1007/BF02890552 [7] CHEN Y, REN G, TANG T, et al. Experimental study of micro-spalling fragmentation from melted lead [J]. Shock Waves, 2016, 26(2): 221–225. doi: 10.1007/s00193-015-0601-4 [8] ANTIPOV M V, ARININ V A, GEORGIEVSKAYA A B, et al. Experimental and computational damage and ejecta studies of Pb explosively shock loaded to pSL≈32 to 40 GPa [J]. Journal of Dynamic Behavior of Materials, 2017, 3(2): 300–315. doi: 10.1007/s40870-017-0113-7 [9] XIANG M Z, HU H B, CHEN J. Spalling and melting in nanocrystalline Pb under shock loading: molecular dynamics studies [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113(14): 144312. doi: 10.1063/1.4799388 [10] WANG K, ZHANG F G, HE A M, et al. An atomic view on spall responses of release melted lead induced by decaying shock loading [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 125(15): 155107. doi: 10.1063/1.5081920 [11] MAYER A E, MAYER P N. Strain rate dependence of spall strength for solid and molten lead and tin [J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2020, 222(1/2): 171–195. doi: 10.1007/s10704-020-00440-8 [12] LI G M, WANG Y B, WANG K, et al. Shock induced plasticity and phase transition in single crystal lead by molecular dynamics simulations [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 126(7): 075902. doi: 10.1063/1.5097621 [13] DAW M S, BASKES M I. Embedded-atom method: derivation and application to impurities, surfaces, and other defects in metals [J]. Physical Review B, 1984, 29(12): 6443–6453. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.29.6443 [14] BASKES M I. Modified embedded-atom potentials for cubic materials and impurities [J]. Physical Review B, 1992, 46(5): 2727–2742. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.46.2727 [15] HORSFIELD A P, BRATKOVSKY A M, FEARN M, et al. Bond-order potentials: theory and implementation [J]. Physical Review B, 1996, 53(19): 12694–12712. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.53.12694 [16] WANG X Y, WANG Z Y, GAO P Y, et al. Data-driven prediction of complex crystal structures of dense lithium [J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 2924. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38650-y [17] WANG K, ZHU W J, XIANG M Z, et al. Improved embedded-atom model potentials of Pb at high pressure: application to investigations of plasticity and phase transition under extreme conditions [J]. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, 27(1): 015001. doi: 10.1088/1361-651X/aaea55 [18] LIU A Y, GARCA A, COHEN M L, et al. Theory of high-pressure phases of Pb [J]. Physical Review B, 1991, 43(2): 1795–1798. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.43.1795 [19] CUI S X, CAI L C, FENG W X, et al. First-principles study of phase transition of tin and lead under high pressure [J]. Physica Status Solidi (B), 2008, 245(1): 53–57. doi: 10.1002/pssb.200743240 [20] CRICCHIO F, BELONOSHKO A B, BURAKOVSKY L, et al. High-pressure melting of lead [J]. Physical Review B, 2006, 73(14): 140103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.73.140103 [21] VOHRA Y K, RUOFF A L. Static compression of metals Mo, Pb, and Pt to 272 GPa: comparison with shock data [J]. Physical Review B, 1990, 42(13): 8651–8654. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.42.8651 [22] YU D K, SCHEFFLER M. First-principles study of low-index surfaces of lead [J]. Physical Review B, 2004, 70(15): 155417. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.70.155417 [23] BOMBIS C, EMUNDTS A, NOWICKI M, et al. Absolute surface free energies of Pb [J]. Surface Science, 2002, 511(1/2/3): 83–96. doi: 10.1016/S0039-6028(02)01554-6 [24] BARTÓK A P, PAYNE M C, KONDOR R, et al. Gaussian approximation potentials: the accuracy of quantum mechanics, without the electrons [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104(13): 136403. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.136403 [25] SHAPEEV A V. Moment tensor potentials: a class of systematically improvable interatomic potentials [J]. Multiscale Modeling & Simulation, 2016, 14(3): 1153–1173. doi: 10.1137/15M1054183 [26] THOMPSON A P, SWILER L P, TROTT C R, et al. Spectral neighbor analysis method for automated generation of quantum-accurate interatomic potentials [J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2015, 285: 316–330. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2014.12.018 [27] ZHANG L F, HAN J Q, WANG H, et al. End-to-end symmetry preserving inter-atomic potential energy model for finite and extended systems [C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal: Curran Associates Inc., 2018: 4441–4451. [28] 高天雨, 曾启昱, 陈博, 等. 超快激光诱导Cu薄膜熔化的神经网络分子动力学研究 [J]. 金属学报, 2024, 60(10): 1439–1450. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2024.00143GAO T Y, ZENG Q Y, CHEN B, et al. Neural network molecular dynamics study of ultrafast laser-induced melting of copper nanofilms [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2024, 60(10): 1439–1450. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2024.00143 [29] 曾启昱, 陈博, 康冬冬, 等. 大规模、量子精度的分子动力学模拟: 以极端条件液态铁为例 [J]. 物理学报, 2023, 72(18): 187102. doi: 10.7498/aps.72.20231258ZENG Q Y, CHEN B, KANG D D, et al. Large scale and quantum accurate molecular dynamics simulation: liquid iron under extreme condition [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2023, 72(18): 187102. doi: 10.7498/aps.72.20231258 [30] D’SOUZA J X, HU S X, MIHAYLOV D I, et al. Designing a quantum-accurate machine-learning potential to enable large-scale simulations of deuterium under shock [J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2025, 32(4): 042701. doi: 10.1063/5.0254638 [31] PAN S N, SHI J Y, LIANG Z X, et al. Shock compression pathways to pyrite silica from machine learning simulations [J]. Physical Review B, 2024, 110(22): 224101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.110.224101 [32] ZENG Q Y, CHEN B, ZHANG S, et al. Full-scale ab initio simulations of laser-driven atomistic dynamics [J]. NPJ Computational Materials, 2023, 9(1): 213. doi: 10.1038/s41524-023-01168-4 [33] ZHANG Y Z, WANG H D, CHEN W J, et al. DP-GEN: a concurrent learning platform for the generation of reliable deep learning based potential energy models [J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2020, 253: 107206. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2020.107206 [34] WANG H, ZHANG L F, HAN J Q, et al. DeePMD-kit: a deep learning package for many-body potential energy representation and molecular dynamics [J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2018, 228: 178–184. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2018.03.016 [35] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization [C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). San Diego: ICLR, 2015. [36] NOSÉ S. A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods [J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1984, 81(1): 511–519. doi: 10.1063/1.447334 [37] HOOVER W G. Canonical dynamics: equilibrium phase-space distributions [J]. Physical Review A, 1985, 31(3): 1695–1697. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.31.1695 [38] KRYGIER A, POWELL P D, MCNANEY J M, et al. Extreme hardening of Pb at high pressure and strain rate [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 123(20): 205701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.205701 [39] ERNZERHOF M, SCUSERIA G E. Assessment of the Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof exchange-correlation functional [J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1999, 110(11): 5029–5036. doi: 10.1063/1.478401 [40] SCHLIPF M, GYGI F. Optimization algorithm for the generation of ONCV pseudopotentials [J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2015, 196: 36–44. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2015.05.011 [41] ZHOU W Q, ZHENG D Y, LIU Q R, et al. ABACUS: an electronic structure analysis package for the AI era [EB/OL]. arXiv: 2501.08697, 2025 (2025-10-22)[2025-08-06]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.08697. [42] CHEN T, YUAN F B, LIU J C, et al. Modeling the high-pressure solid and liquid phases of tin from deep potentials with ab initio accuracy [J]. Physical Review Materials, 2023, 7(5): 053603. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.7.053603 [43] LI W, LU S, HU Q M, et al. Generalized stacking fault energies of alloys [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2014, 26(26): 265005. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/26/26/265005 [44] 余永宁, 杨平, 强文江, 等. 材料科学基础 [M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006.YU Y N, YANG P, QIANG W J, et al. Fundamentals of materials science [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. [45] MO P H, LI C, ZHAO D, et al. Accurate and efficient molecular dynamics based on machine learning and non von Neumann architecture [J]. NPJ Computational Materials, 2022, 8(1): 107. doi: 10.1038/s41524-022-00773-z [46] Sandia National Laboratories. LAMMPS [CP/OL]. [2025-10-02]. https://lammps. sandia. gov. [47] LI W H, HAHN E N, YAO X H, et al. Shock induced damage and fracture in SiC at elevated temperature and high strain rate [J]. Acta Materialia, 2019, 167: 51–70. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.12.035 [48] STUKOWSKI A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO—the open visualization tool [J]. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 2010, 18(1): 015012. doi: 10.1088/0965-0393/18/1/015012 [49] MARSH S P. LASL shock Hugoniot data [M]. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1980. [50] ALIPPI P, MARCUS P M, SCHEFFLER M. Strained tetragonal states and Bain paths in metals [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1997, 78(20): 3892–3895. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.3892 -






 下载:
下载: