Numerical Simulation Study of Dynamic Response of Salt Cavern Gas Storage under High-Velocity Penetration
-
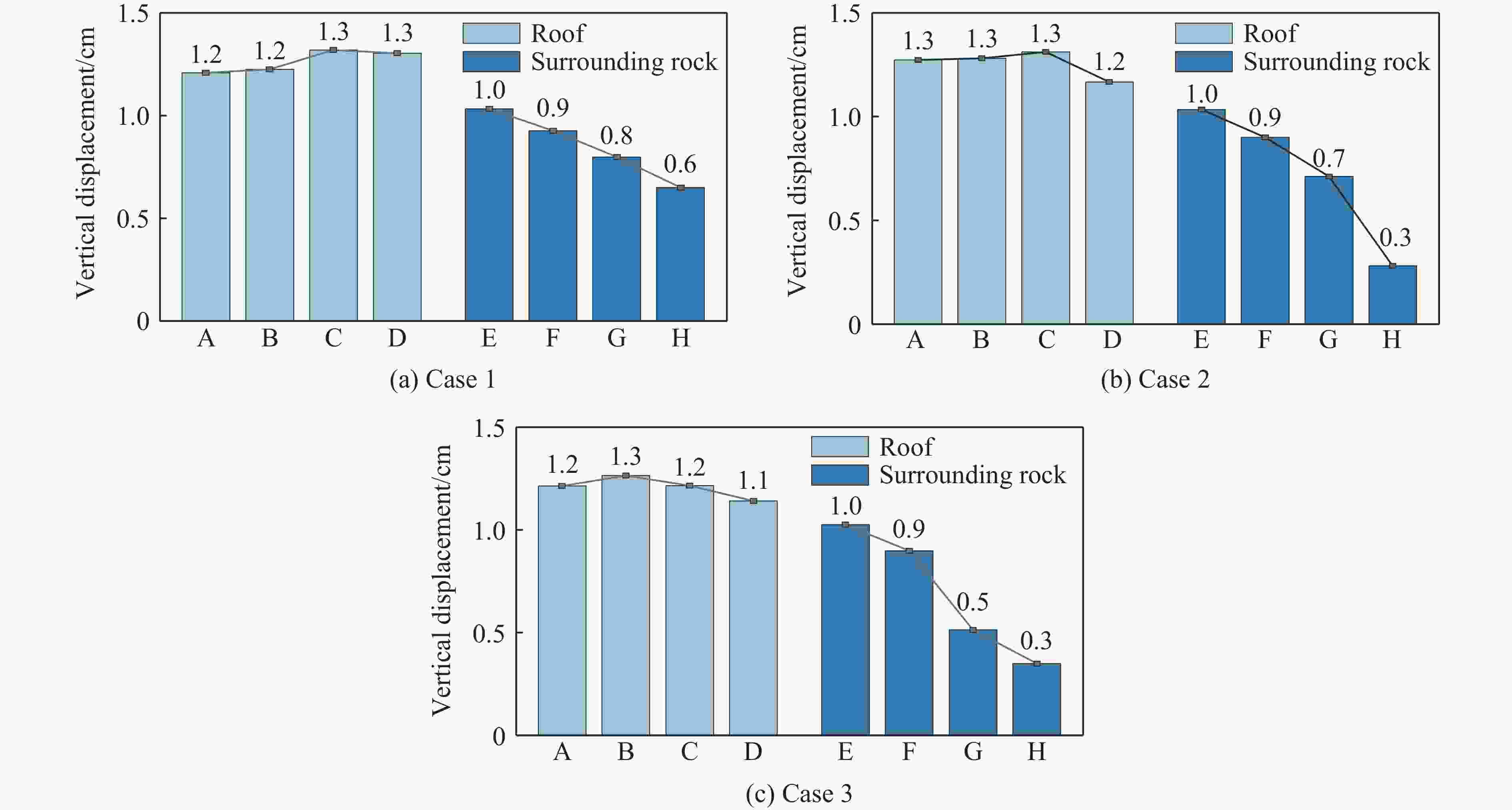
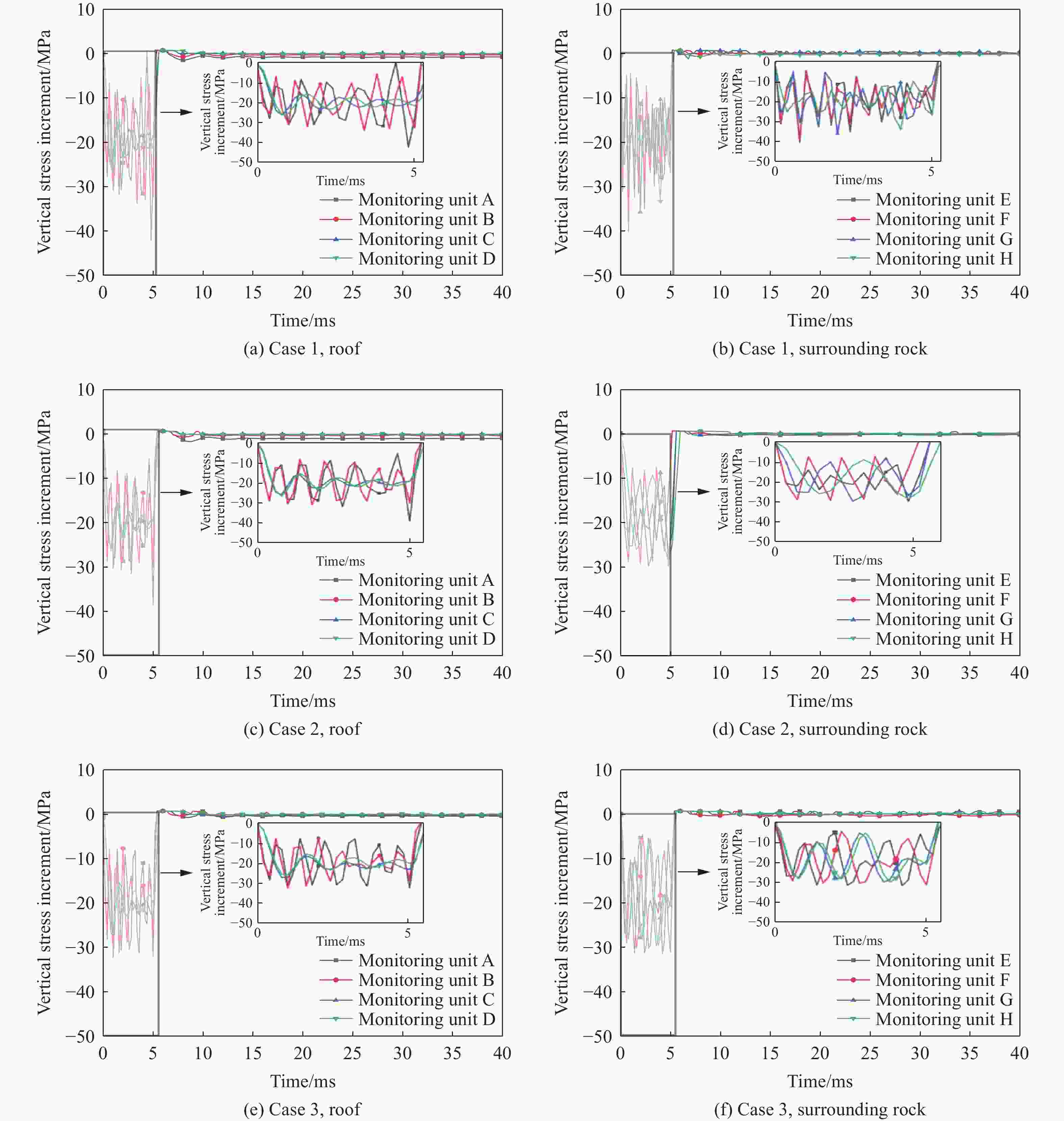
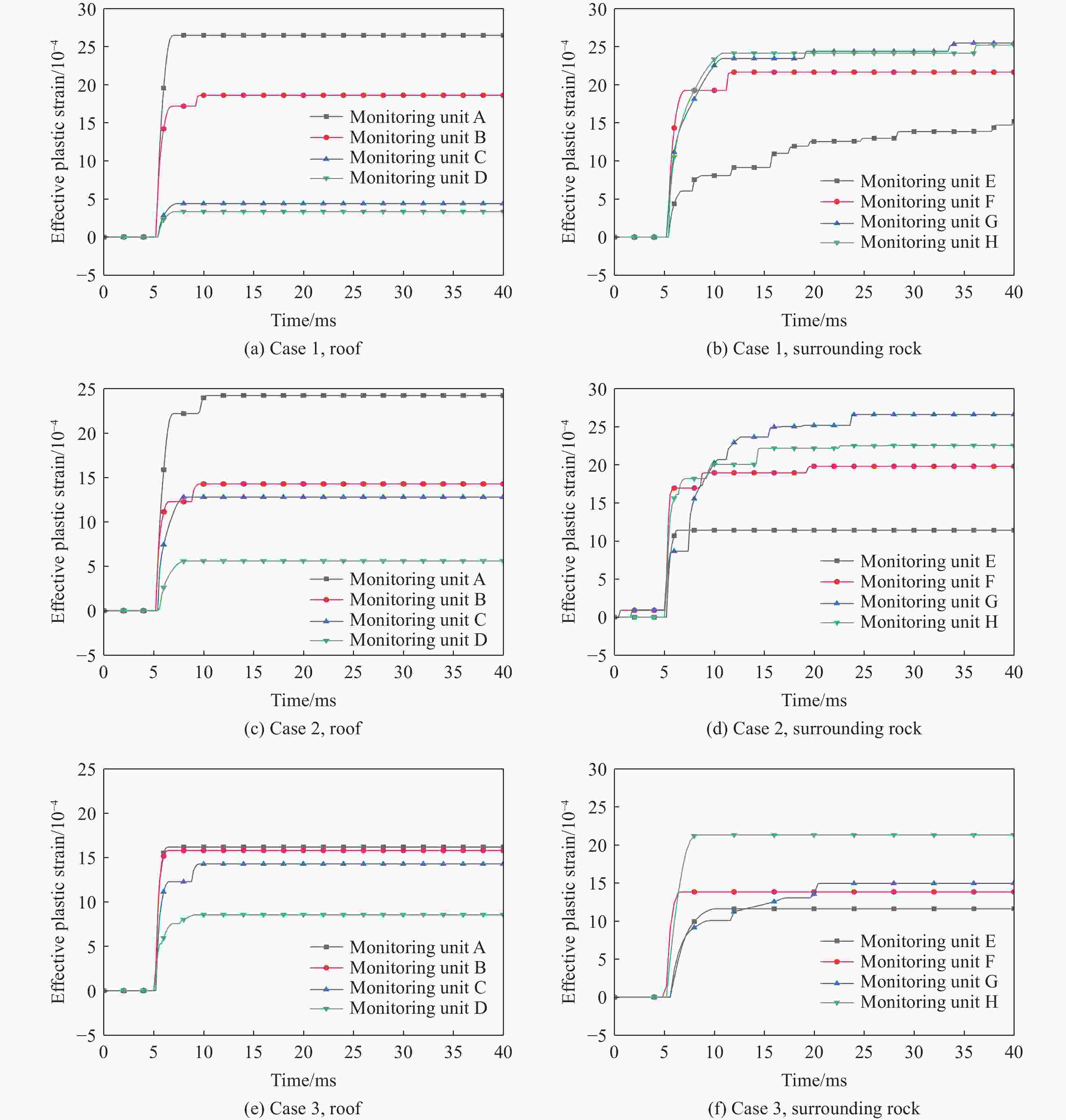
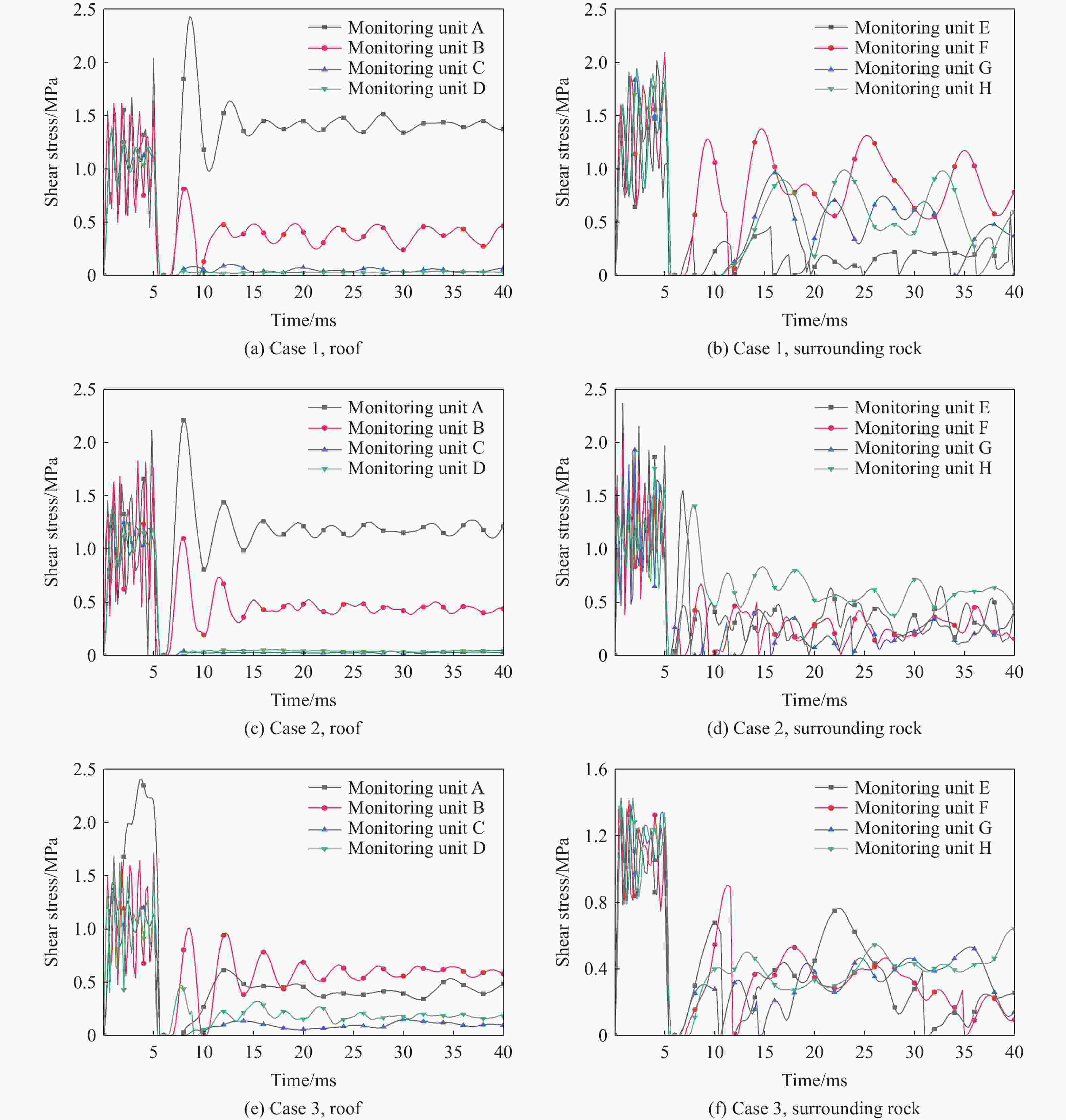
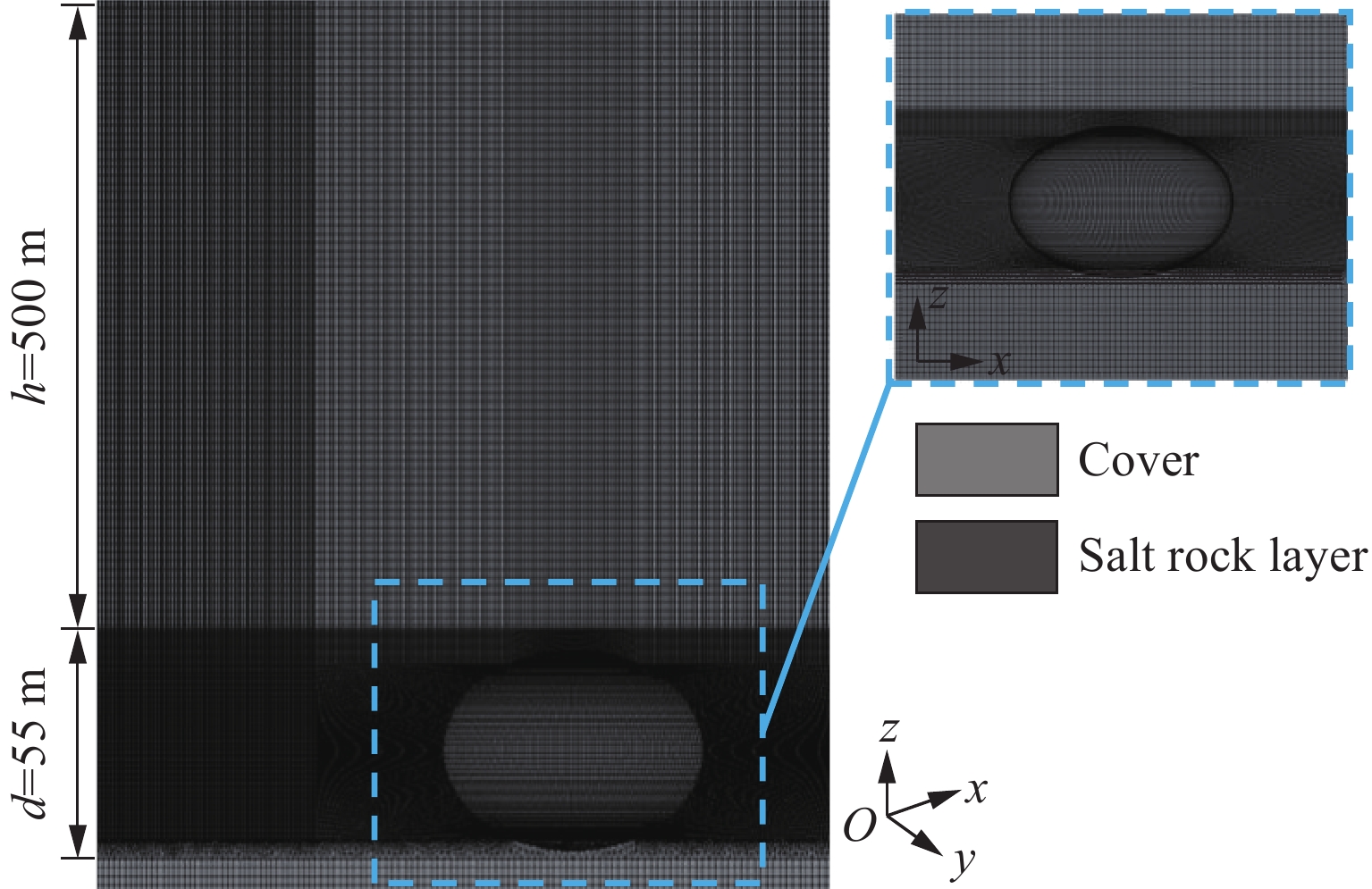
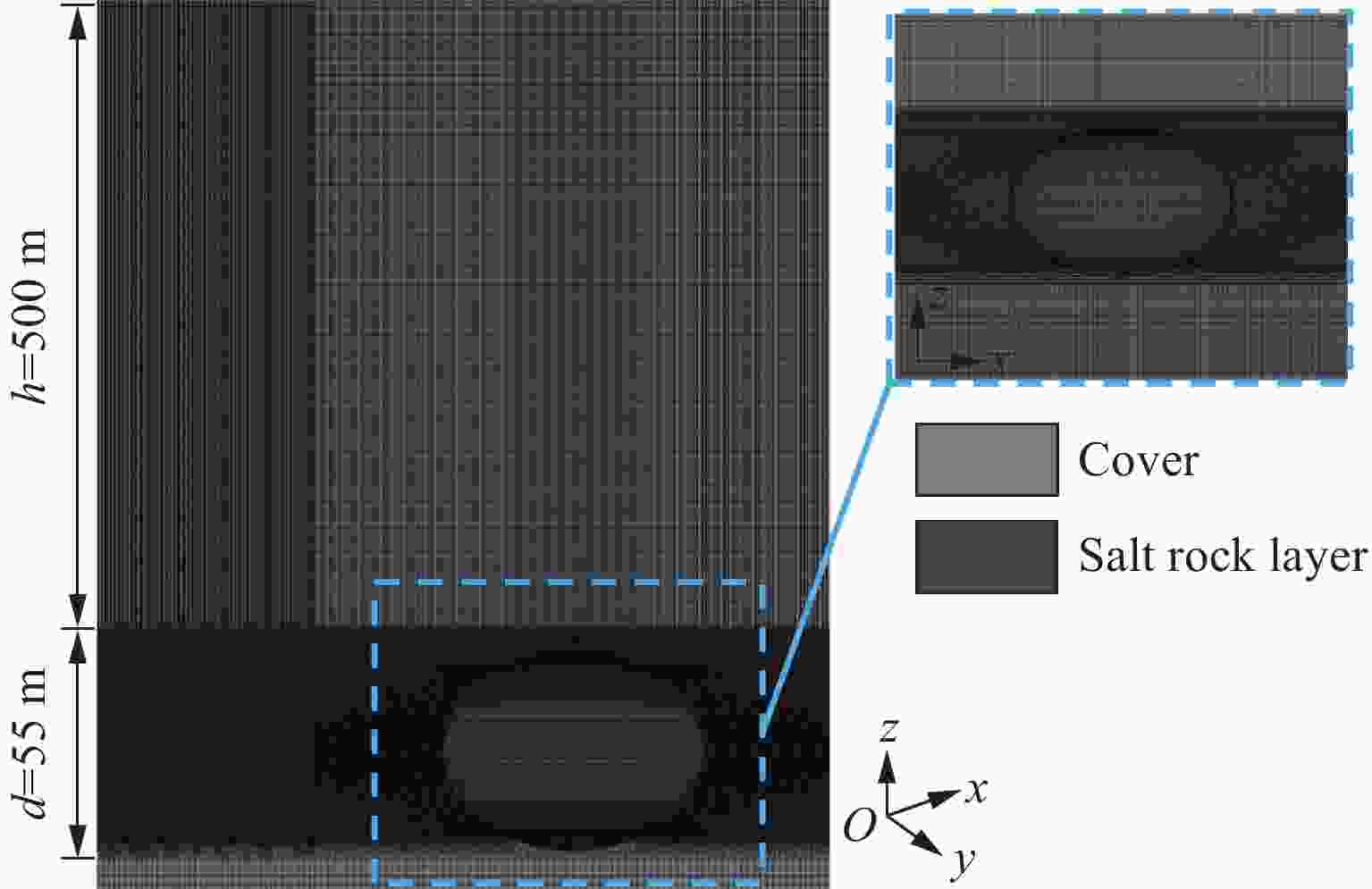
摘要: 地下盐穴储气库是重要的能源基础设施,一旦发生冲击破坏,将造成不可挽回的损失,因此,确定评估盐穴在极端冲击载荷下安全性的关键动态稳定性指标具有重要意义。为探究高速侵彻下盐穴储气库的动力学响应,基于Riedel-Hiermaier-Thoma本构模型对盐岩材料进行定义,采用ANSYS/LS-DYNA软件构建了储气库的有限元模型,分析某种武器对盐穴结构的损伤效应,在此基础上,开展了3种不同盖层厚度工况的数值模拟,考虑垂直位移、竖向应力、有效塑性应变、剪切应力4个参数,揭示了动态冲击下盐穴溶腔顶板和围岩结构的破坏机制,以及形成关键稳定性指标的变化规律。数值模拟结果表明:减小盖层厚度会导致围岩动态响应加剧,塑性变形区域扩大;顶板和围岩的位移呈先上升后下降趋势;低竖向应力区的盐岩会受到较大的剪切应力,更容易发生破坏;围岩积累更大的塑性应变,其塑性变化受侵彻扰动更敏感。Abstract: Underground salt cavern gas storage serves as a critical piece of energy infrastructure. Damage from impact events can cause irreparable losses, making it essential to establish key dynamic stability indicators for evaluating salt cavern safety under extreme impact loads. To investigate the dynamic response of salt cavern gas storage under high-velocity penetration, the salt rock material was modeled using the Riedel-Hiermaier-Thoma (RHT) constitutive model, and a finite element model of the gas storage structure was developed in ANSYS/LS-DYNA software to analyze the damage effects of a weapon on the salt cavern structure. Numerical simulations were conducted for three scenarios with different overburden thicknesses, monitoring four key parameters: vertical displacement, vertical stress, effective plastic strain, and shear stress. These simulations revealed the failure mechanisms of the cavern roof and surrounding rock under dynamic impact, as well as the variation patterns of the key stability indicators. The results demonstrate that reducing the overburden thickness intensifies the dynamic response of the surrounding rock and expands plastic deformation zones. Displacements of the roof and surrounding rock exhibited a trend of initial increase followed by a decrease. Salt rock in regions of low vertical stress experienced higher shear stresses, increasing its susceptibility to failure. Furthermore, the surrounding rock accumulated greater plastic strain, indicating heightened sensitivity to penetration-induced disturbances.
-
Key words:
- penetration effect /
- dynamic response /
- salt cavern gas storage /
- stability
-
$ \rho $/(g·cm−3) G/GPa fc/MPa $ f_{\rm{t}}^{*} $ $ f_{\rm{s}}^{*} $ A 2.30 0.96 34.69 0.033 0.28 2.55 N Q B $ {\beta }_{\rm{c}} $ $ {\beta }_{\rm{t}} $ 0.63 0.68 0.01 0.03 0.04 表 2 盖层泥岩的HJC材料模型参数
Table 2. Model parameters of HJC material of cover layer mudstone
$ \rho $/(g·cm−3) G/GPa fc/MPa T/MPa D1 D2 2.60 0.20 27.15 1.75 0.04 1.00 -
[1] 刘烨, 何刚, 杨莉娜, 等. “十四五”期间我国储气库建设面临的挑战及对策建议 [J]. 石油规划设计, 2020, 31(6): 9–13, 62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2970.2020.06.003LIU Y, HE G, YANG L N, et al. Challenges and suggestions to gas storage development during the 14th Five-Year Plan period [J]. Petroleum Planning & Engineering, 2020, 31(6): 9–13, 62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2970.2020.06.003 [2] LU L, SHI Y, WANG M M, et al. Seismic performance of salt cavern gas storage subjected to moderate earthquake loads in compressed CO2 energy storage scenario [J]. Energy Reports, 2025, 13: 2366–2383. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2025.01.043 [3] 宫丹妮, 李景翠, 万继方, 等. 多场作用下盐穴储气库腔体稳定性的数值模拟研究 [J]. 石油科学通报, 2023, 8(6): 787–796. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1693.2023.06.072GONG D N, LI J C, WAN J F, et al. The numerical simulation of the stability of salt cavern gas storage considering multiple fields [J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2023, 8(6): 787–796. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1693.2023.06.072 [4] 武志德, 刘冰冰, 冉莉娜, 等. 盐穴储气库运行参数设计及稳定性评价研究 [J]. 盐科学与化工, 2024, 53(12): 1–5, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3408.2024.12.001WU Z D, LIU B B, RAN L N, et al. Research on the operation parameters and stability analysis of salt cavern gas storage [J]. Journal of Salt Science and Chemical Industry, 2024, 53(12): 1–5, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3408.2024.12.001 [5] 张雪岩, 孙凯, 李元龙, 等. 基于Ottosen屈服条件的不同强度混凝土空腔膨胀模型及侵彻机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(9): 091403. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0511ZHANG X Y, SUN K, LI Y L, et al. Cavity expansion model and penetration mechanism of concrete with different strengths based on the Ottosen yield condition [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(9): 091403. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0511 [6] 李国辉, 刘基程, 耿汉生, 等. 岩石高速-超高速侵彻效应研究进展 [J]. 防护工程, 2023, 45(5): 67–78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1854.2023.05.012LI G H, LIU J C, GENG H S, et al. Progress of research on high and ultra-high speed rock penetration effects [J]. Protective Engineering, 2023, 45(5): 67–78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1854.2023.05.012 [7] LI J, WANG M Y, CHENG Y H, et al. Analytical model of hypervelocity penetration into rock [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 122: 384–394. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.08.008 [8] 邓国强, 杨秀敏. 超高速武器对地打击效应数值仿真 [J]. 科技导报, 2015, 33(16): 65–71. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2015.16.010DENG G Q, YANG X M. Numerical simulation of damage effect of hyper velocity weapon on ground target [J]. Science & Technology Review, 2015, 33(16): 65–71. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2015.16.010 [9] WANG Z L, WANG H C, WANG J G, et al. Finite element analyses of constitutive models performance in the simulation of blast-induced rock cracks [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2021, 135: 104172. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104172 [10] TIAN H F, BAO T, LI Z, et al. Determination of constitutive parameters of crystalline limestone based on improved RHT model [J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2021, 2022: 3794898. doi: 10.1155/2022/3794898 [11] 靳绍虎, 刘科伟, 黄进, 等. 基于Lagrange及SPH算法的花岗岩侵彻数值模拟 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2021, 35(5): 055103. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200665JIN S H, LIU K W, HUANG J, et al. Numerical simulation of granite penetration based on Lagrange and SPH algorithm [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2021, 35(5): 055103. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200665 [12] 邱薛, 刘晓辉, 胡安奎, 等. 煤岩动态RHT本构模型数值模拟研究 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2024, 49(Suppl 1): 261–273. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.0540QIU X, LIU X H, HU A K, et al. Research on numerical simulation of coal dynamic RHT constitutive model [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2024, 49(Suppl 1): 261–273. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.0540 [13] 刘晓辉, 薛洋, 郑钰, 等. 冲击荷载下煤岩破碎过程能量释放研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(Suppl 2): 3201–3211. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0214LIU X H, XUE Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Research on energy release in coal rock fragmentation process under impact load [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(Suppl 2): 3201–3211. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0214 [14] 侯秉仁, 宋鹤, 牛耀辉, 等. 超深盐穴储气库力学特性与稳定性分析 [J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2024, 20(Suppl 2): 646–653. doi: 10.20174/j.JUSE.2024.S2.16HOU B R, SONG H, NIU Y H, et al. Mechanical properties and stability analysis of ultra-deep salt cavern gas storage [J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2024, 20(Suppl 2): 646–653. doi: 10.20174/j.JUSE.2024.S2.16 [15] 王贵君, 李东, 刘存宽, 等. 含泥岩夹层盐穴储气库的爆炸动力响应数值模拟 [J]. 油气储运, 2019, 38(7): 764–771. doi: 10.6047/j.issn.1000-8241.2019.07.007WANG G J, LI D, LIU C K, et al. Numerical simulation on dynamic response of salt-cavern gas storages with mudstone interbeds to the explosion [J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2019, 38(7): 764–771. doi: 10.6047/j.issn.1000-8241.2019.07.007 [16] 陈盛威. 基于RHT本构的盐岩动载损伤模型与地下畸形溶腔爆破整形研究 [D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2024.CHEN S W. Study on dynamic load damage model of salt rock based on RHT constitutive model and shaping of underground abnormal cavity blasting [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2024. [17] 娄乾星, 陶铁军, 田兴朝, 等. 基于HJC本构模型的石灰岩冲击破坏形态数值模拟方法研究 [J]. 爆破, 2022, 39(4): 71–79. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2022.04.009LOU Q X, TAO T J, TIAN X C, et al. Research on numerical simulation method of limestone impact failure based on HJC constitutive model [J]. Blasting, 2022, 39(4): 71–79. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2022.04.009 [18] 王海洋, 冯晋昊, 周宴民, 等. 不同围压和倾角砂泥岩互层岩样力学特性研究 [J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2023, 19(6): 1809–1817, 1840. doi: 10.20174/j.juse.2023.06.007WANG H Y, FENG J H, ZHOU Y M, et al. Study on mechanical properties of sand-mudstone interbedded rock samples with different confining pressures and dip angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2023, 19(6): 1809–1817, 1840. doi: 10.20174/j.juse.2023.06.007 [19] 李振. 基于HCJ本构模型下岩石破坏过程的数值模拟研究 [J]. 中国水运 (下半月), 2021, 21(8): 49–51. [20] 梁五星, 唐璐宣, 李新奇, 等. 盐穴压气蓄能储库近场围岩稳定性分析 [J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2023, 19(Suppl 2): 698–706. doi: 10.20174/j.juse.2023.s2.024LIANG W X, TANG L X, LI X Q, et al. Stability analysis of near field surrounding rock of salt cavern compressed air energy storage [J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2023, 19(Suppl 2): 698–706. doi: 10.20174/j.juse.2023.s2.024 [21] 张桂民, 王贞硕, 刘俣轩, 等. 水平盐穴中压气蓄能储库关键顶板稳定性研究 [J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(3): 800–812. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0903ZHANG G M, WANG Z S, LIU Y X, et al. Research on stability of the key roof above horizontal salt cavern for compressed air energy storage [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(3): 800–812. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0903 [22] 韩明海, 刘闯, 李鹏程, 等. 弹体高速侵彻花岗岩靶体的结构响应特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2025, 45(1): 013302. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0145HAN M H, LIU C, LI P C, et al. A study on structural response characteristics of projectile penetrating on granite target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2025, 45(1): 013302. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0145 [23] 王明洋, 李杰, 李海波, 等. 岩石的动态压缩行为与超高速动能弹毁伤效应计算 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(6): 1200–1217. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0173WANG M Y, LI J, LI H B, et al. Dynamic compression behavior of rock and simulation of damage effects of hypervelocity kinetic energy bomb [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(6): 1200–1217. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0173 [24] WANG T T, YANG C H, CHEN J S, et al. Geomechanical investigation of roof failure of China’s first gas storage salt cavern [J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 243: 59–69. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.06.013 [25] 陈加松, 李建君, 井岗, 等. 金坛盐穴储气库地质力学评价体系研究进展 [J]. 油气储运, 2018, 37(10): 1088–1096. doi: 10.6047/j.issn.1000-8241.2018.10.002CHEN J S, LI J J, JING G, et al. Research progress of geomechanical evaluation system used for Jintan salt cavern gas storage [J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2018, 37(10): 1088–1096. doi: 10.6047/j.issn.1000-8241.2018.10.002 -






 下载:
下载: