Prediction Model and Application of Rock Burst Tendency in Deep High Stress Areas
-
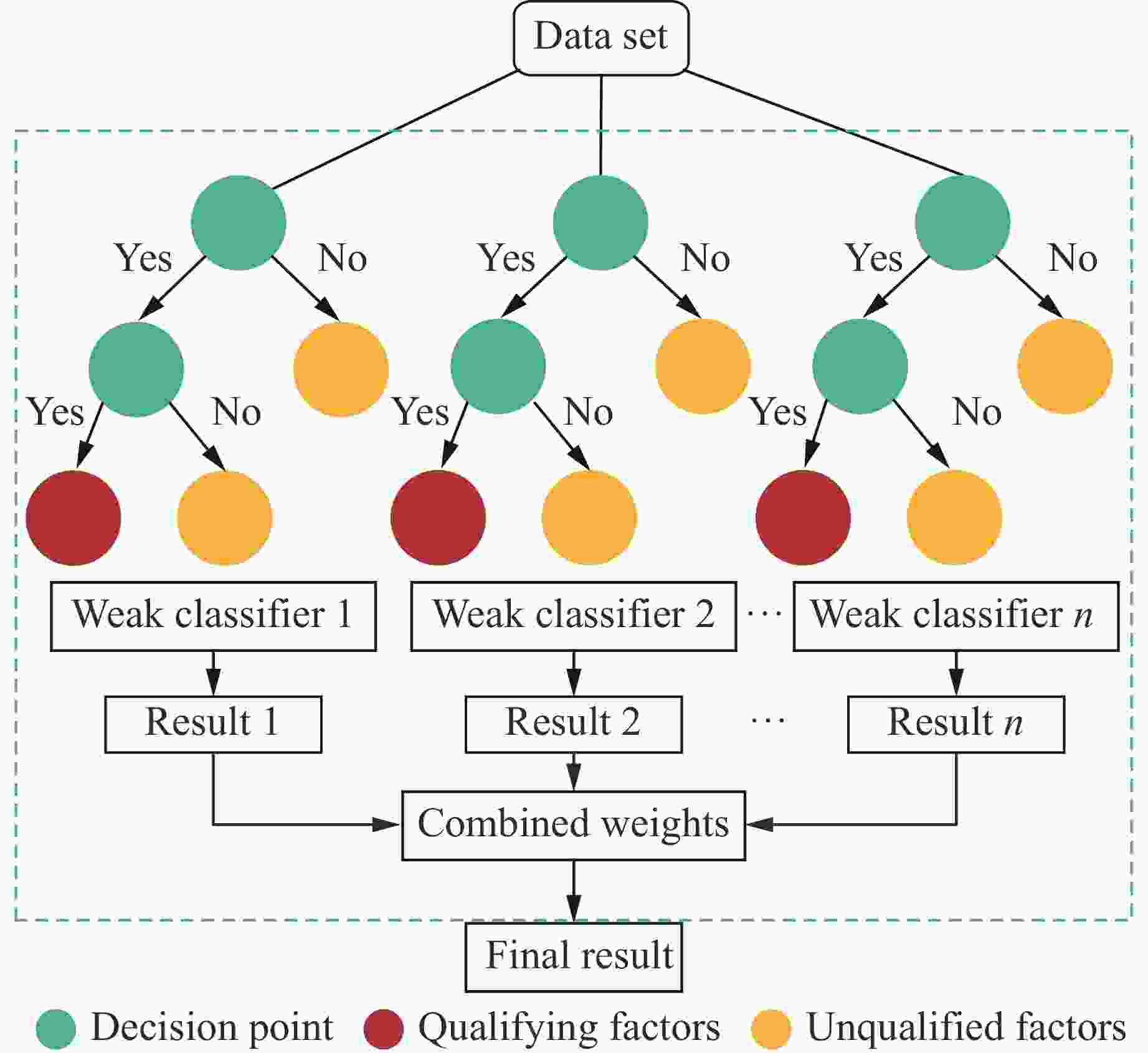
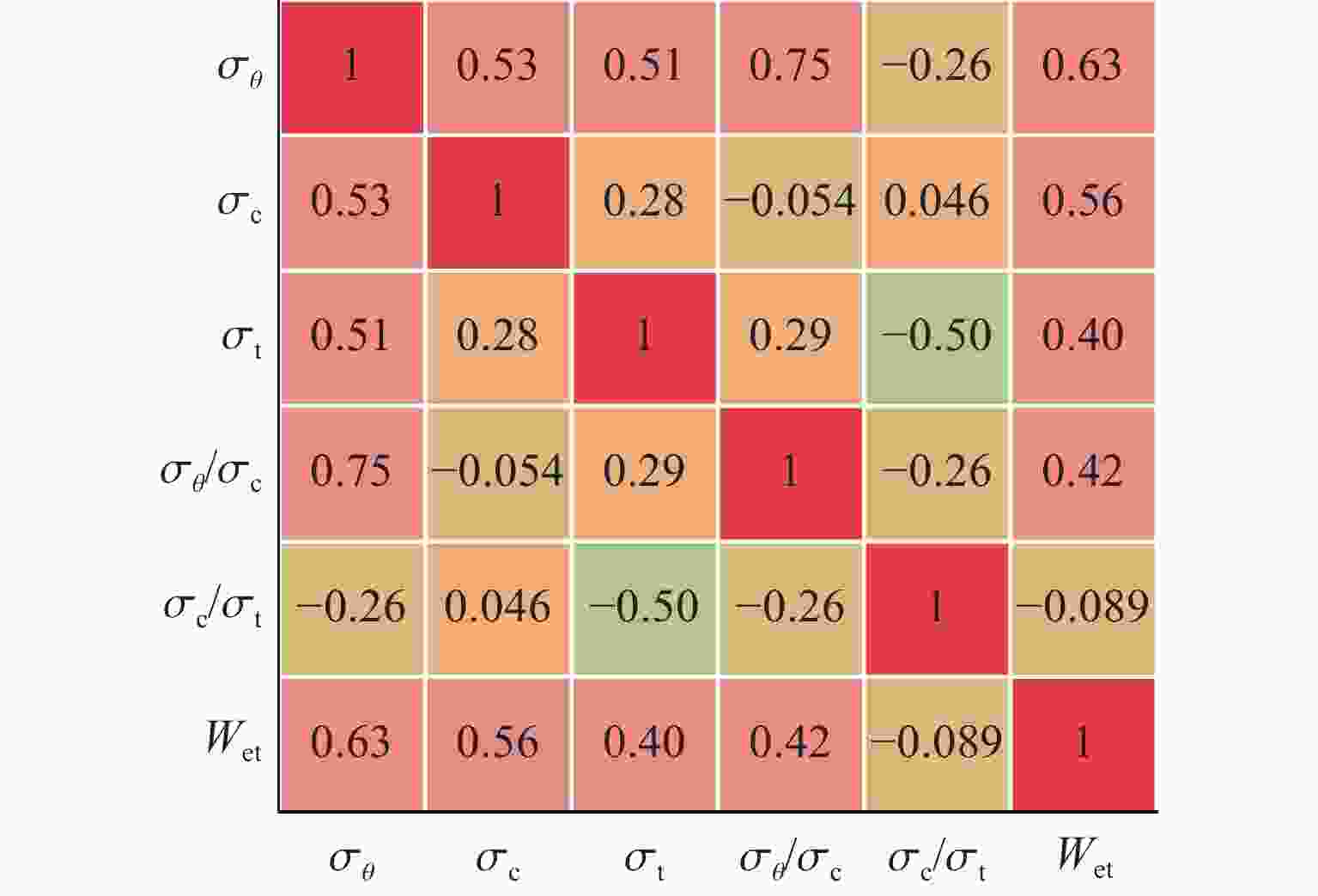
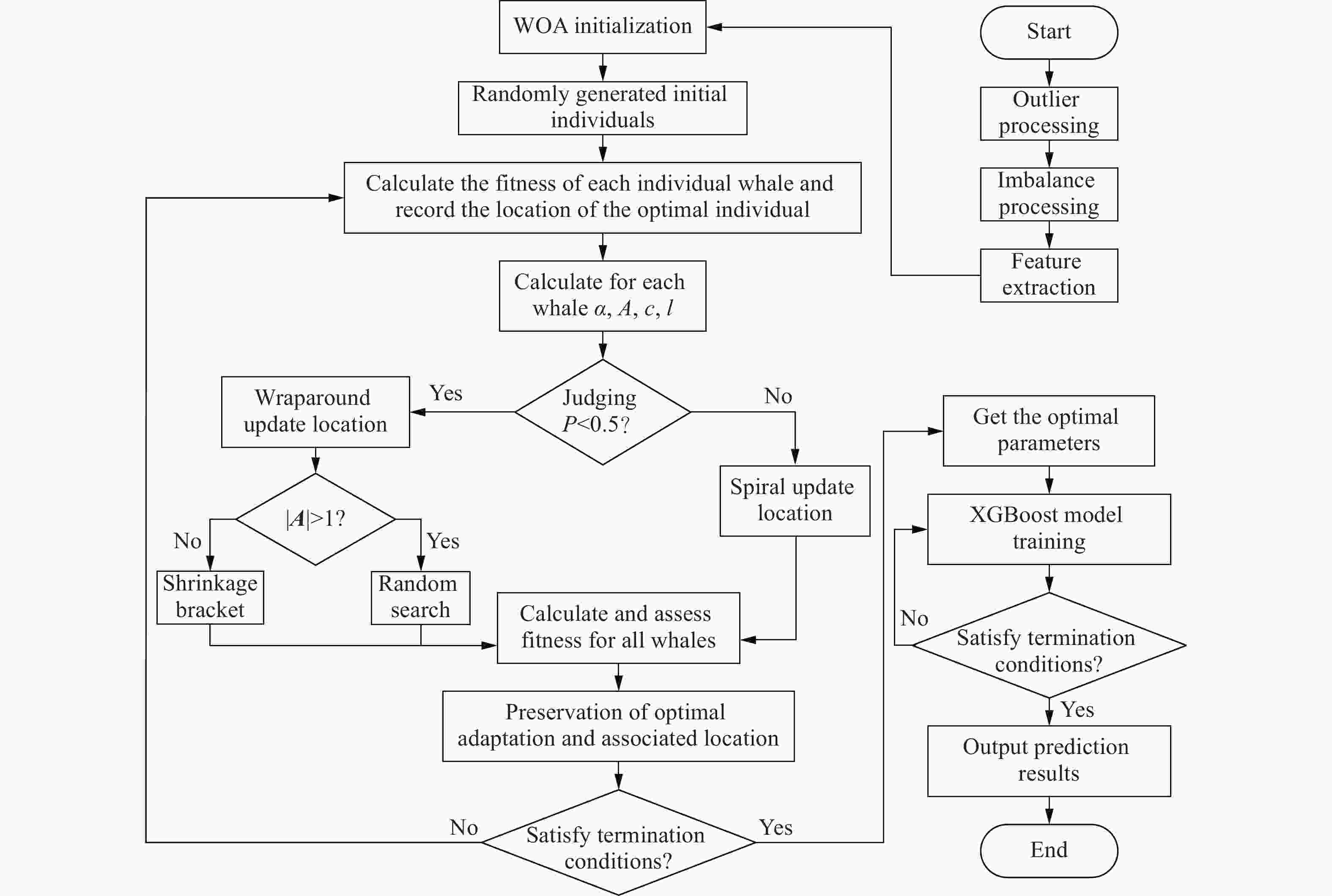
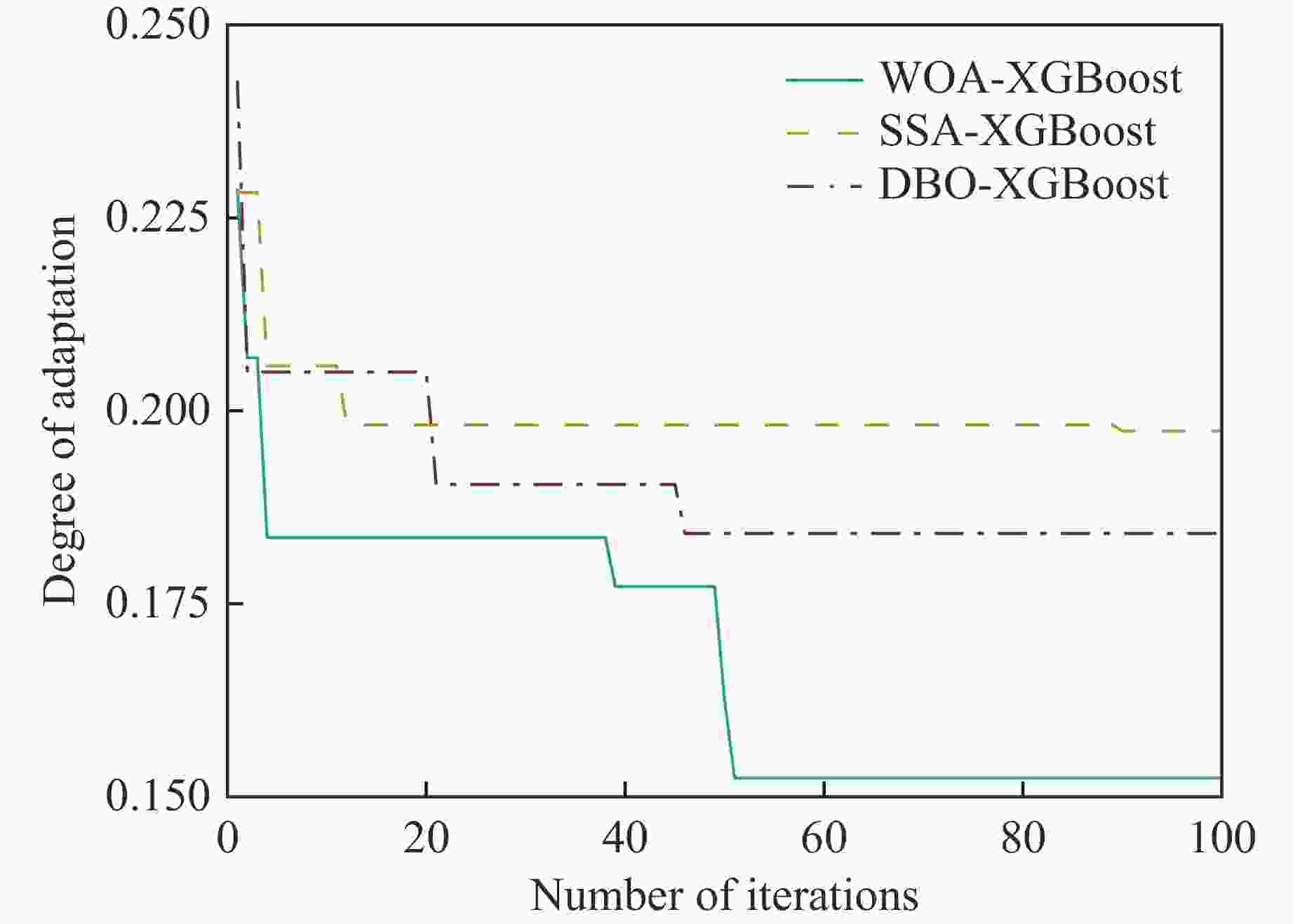
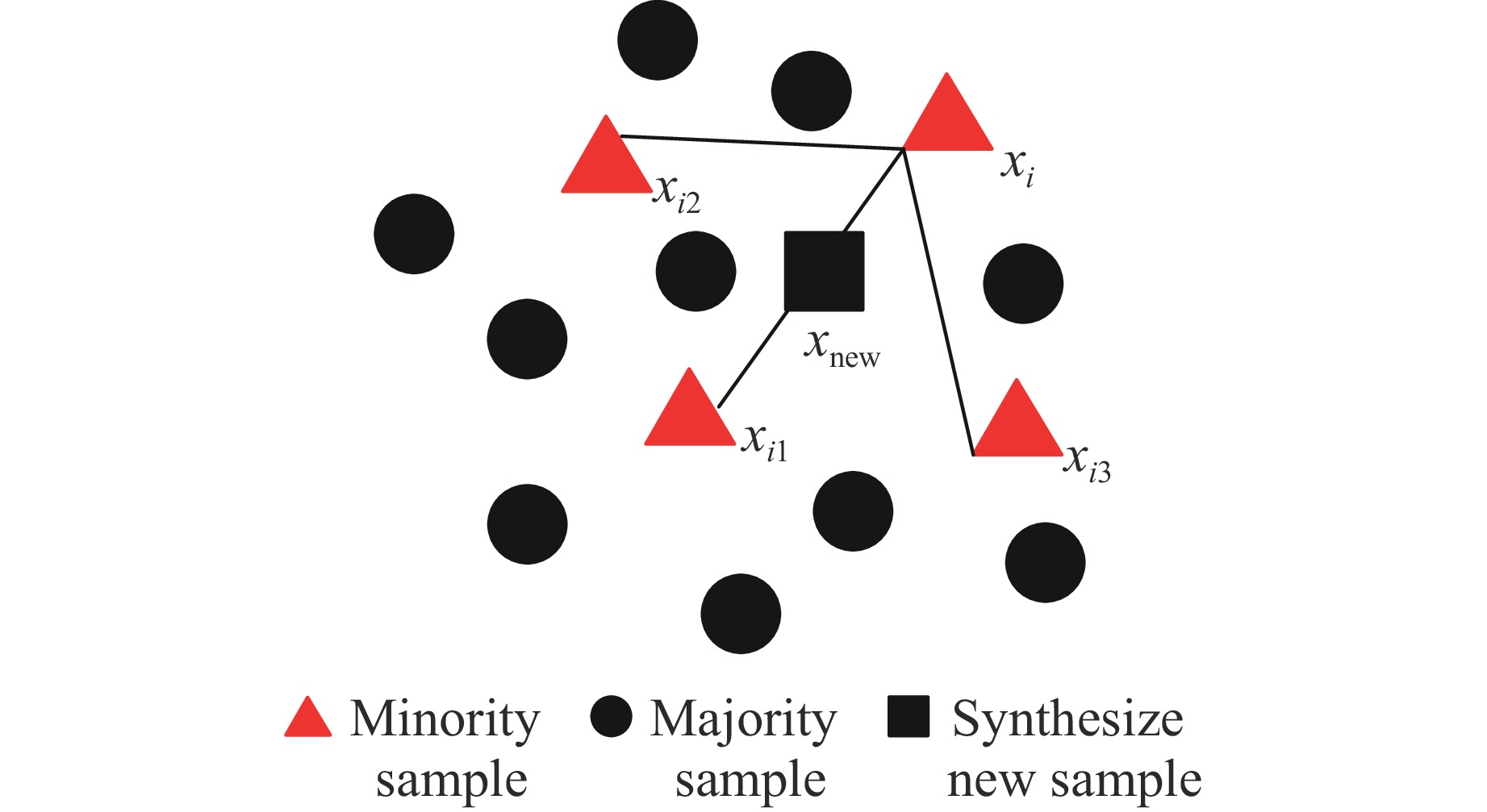
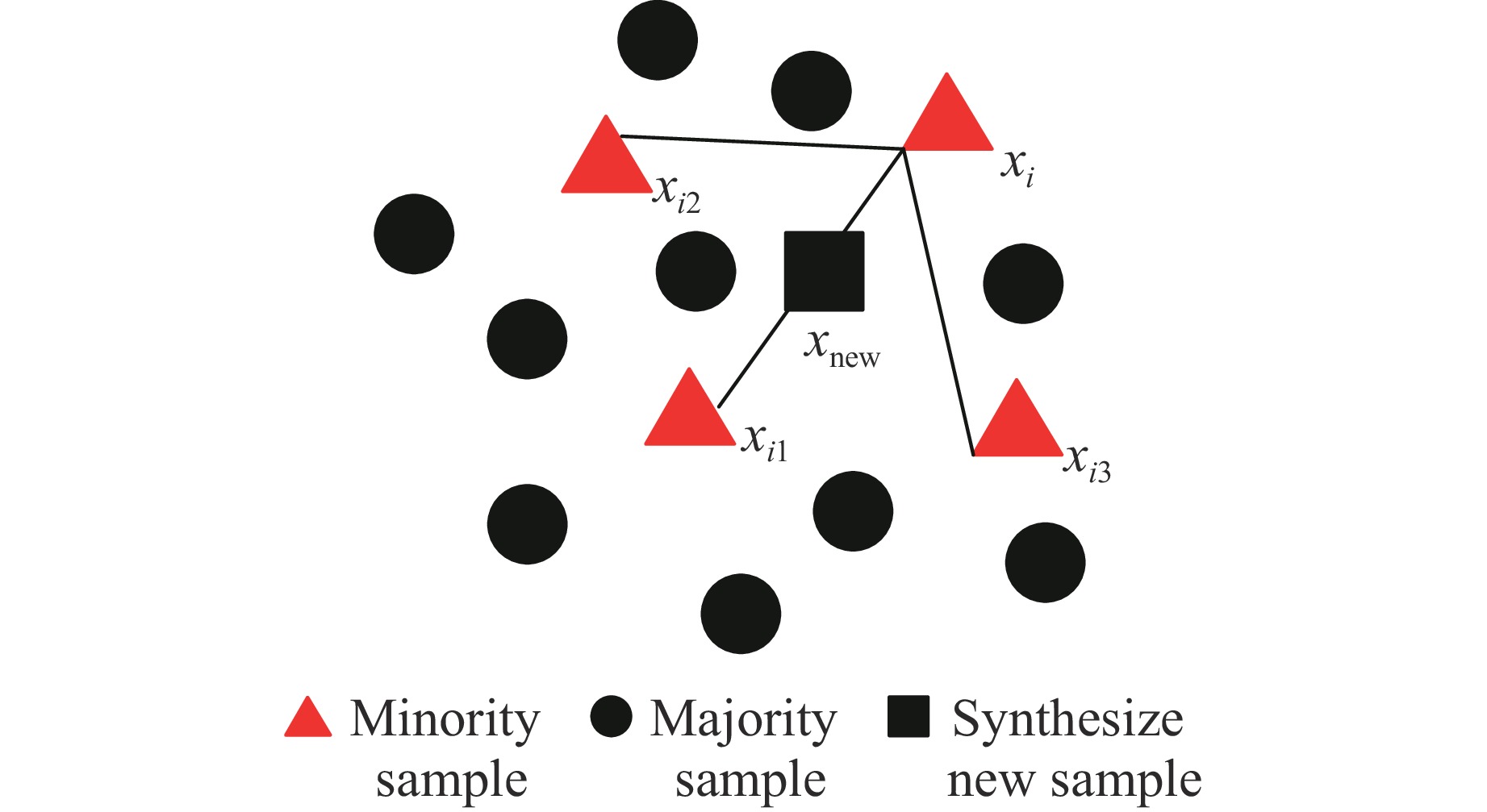
摘要: 为确保深部高应力区岩土工程的施工安全,提升岩爆烈度等级预测的精准度,针对岩爆的突发性和复杂性,提出了一种基于鲸鱼优化算法(whale optimization algorithm,WOA)与极端梯度提升树(extreme gradient boosting,XGBoost)的组合岩爆烈度等级预测模型。首先,分析了影响岩爆烈度等级的主控因素,选取单轴抗压强度、最大切向应力、单轴抗拉强度、脆性系数、应力系数和弹性能量指数建立岩爆烈度等级预测指标体系,引入Pearson相关系数、链式方程多重插补法、合成少数类过采样技术(synthetic minority oversampling technique,SMOTE)和主成分分析法处理原始样本。其次,通过WOA优化XGBoost模型的最大迭代次数、树的最大深度和学习率,并采用准确率、精准度、召回率、F1分数和科恩卡帕系数综合评价所建模型的预测结果。最后,将该模型应用于秦岭终南山公路隧道和江边水电站引水系统预测岩爆烈度等级。结果表明:经WOA优化后XGBoost模型的最大迭代次数、树的最大深度和学习率分别为51、13和
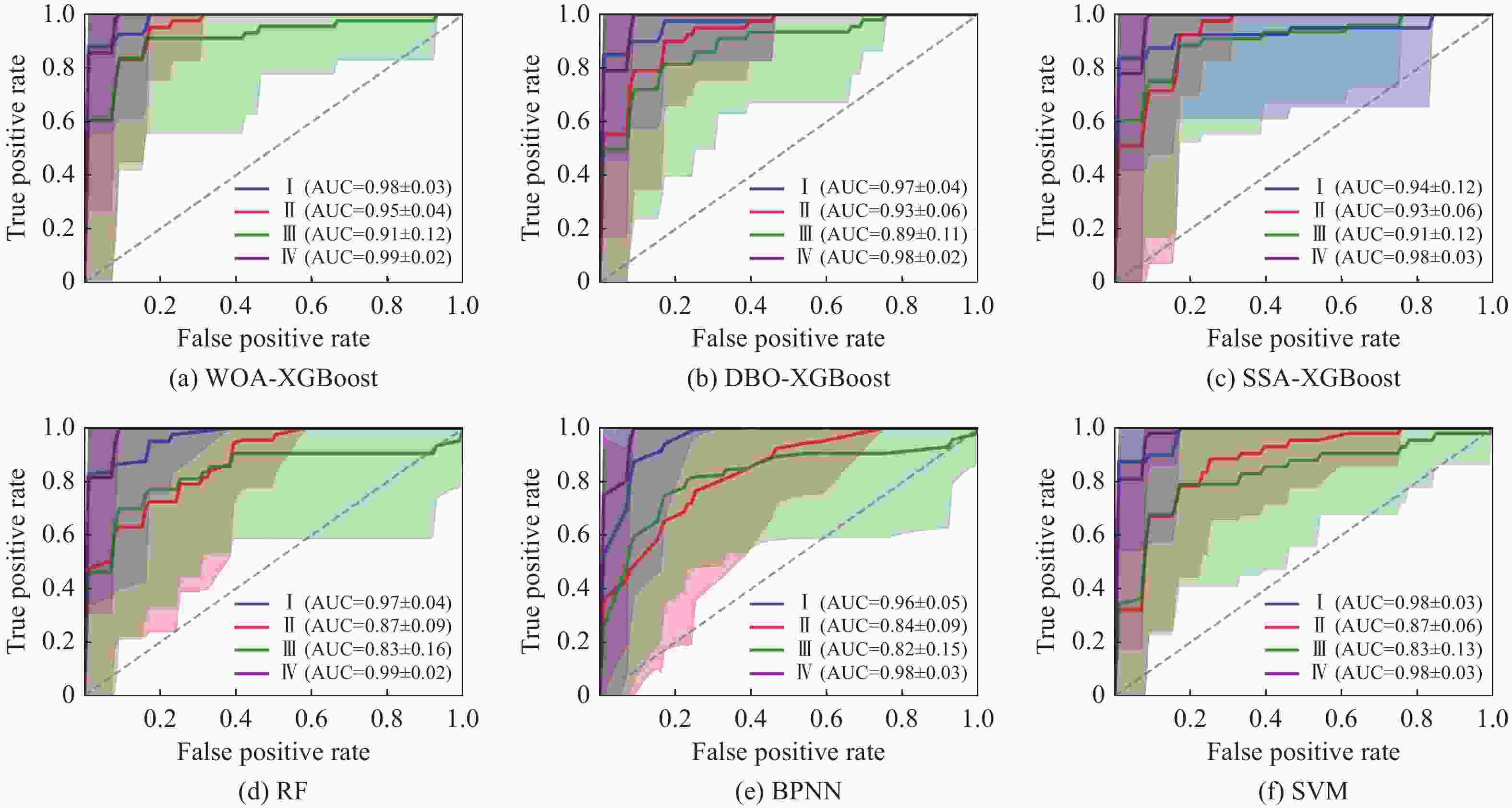
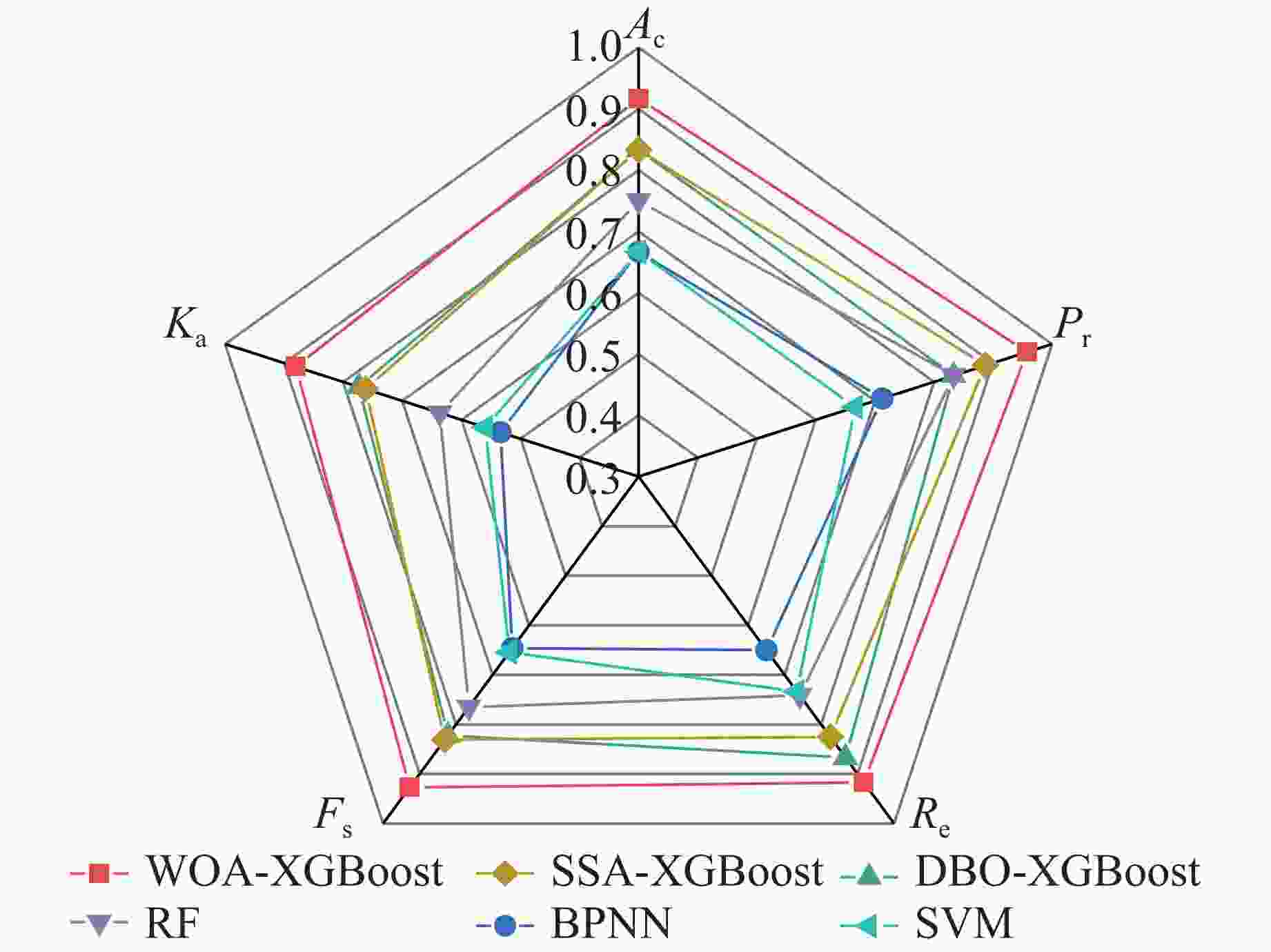
0.7325 时效果最佳;基于WOA-XGBoost岩爆烈度等级预测模型得到的结果与实际等级的拟合度优于传统智能算法模型;通过将WOA-XGBoost模型应用于工程实践中,验证了该模型预测岩爆烈度等级具有较高的准确度和可靠性。-
关键词:
- 岩爆 /
- 鲸鱼优化算法(WOA) /
- 极端梯度提升树(XGBoost) /
- 链式方程多重插补法(MICE) /
- 合成少数类过采样技术(SMOTE)
Abstract: To ensure the construction safety of geotechnical engineering in deep high stress areas, a combined rock burst intensity prediction model based on whale optimization algorithm (WOA) and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) is proposed to address the suddenness and complexity of rock burst. Firstly, the main controlling factors that affect the intensity level of rock burst are analyzed, and the uniaxial compressive strength, maximum tangential stress, uniaxial tensile strength, brittleness coefficient, stress coefficient, and elastic energy index are selected to establish a prediction index system for rock burst intensity level. The original samples are processed using the Pearson correlation coefficient, multiple imputation by chained equations (MICE), synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE), and principal component analysis (PCA). Secondly, the maximum number of iterations, maximum depth of the tree, and learning rate of the XGBoost model were optimized through WOA, and the prediction results of the model were comprehensively evaluated using accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and Cohen Kappa coefficient. Finally, the model was applied to predict the rock burst intensity level of the Qinlingzhongnanshan highway tunnel and the water diversion system for hydropower stations. Results show that the WOA-optimized XGBoost model achieves optimal performance when the maximum number of iterations, maximum tree depth, and learning rate are 51, 13, and0.7325 , respectively. Prediction results for rock burst intensity level using the WOA-XGBoost model outperform those of other intelligent algorithm models, verifying the model’s high accuracy and reliability in predicting rock burst intensity level. -
表 1 岩爆烈度等级分类标准
Table 1. Criteria for classification of rock burst intensity levels
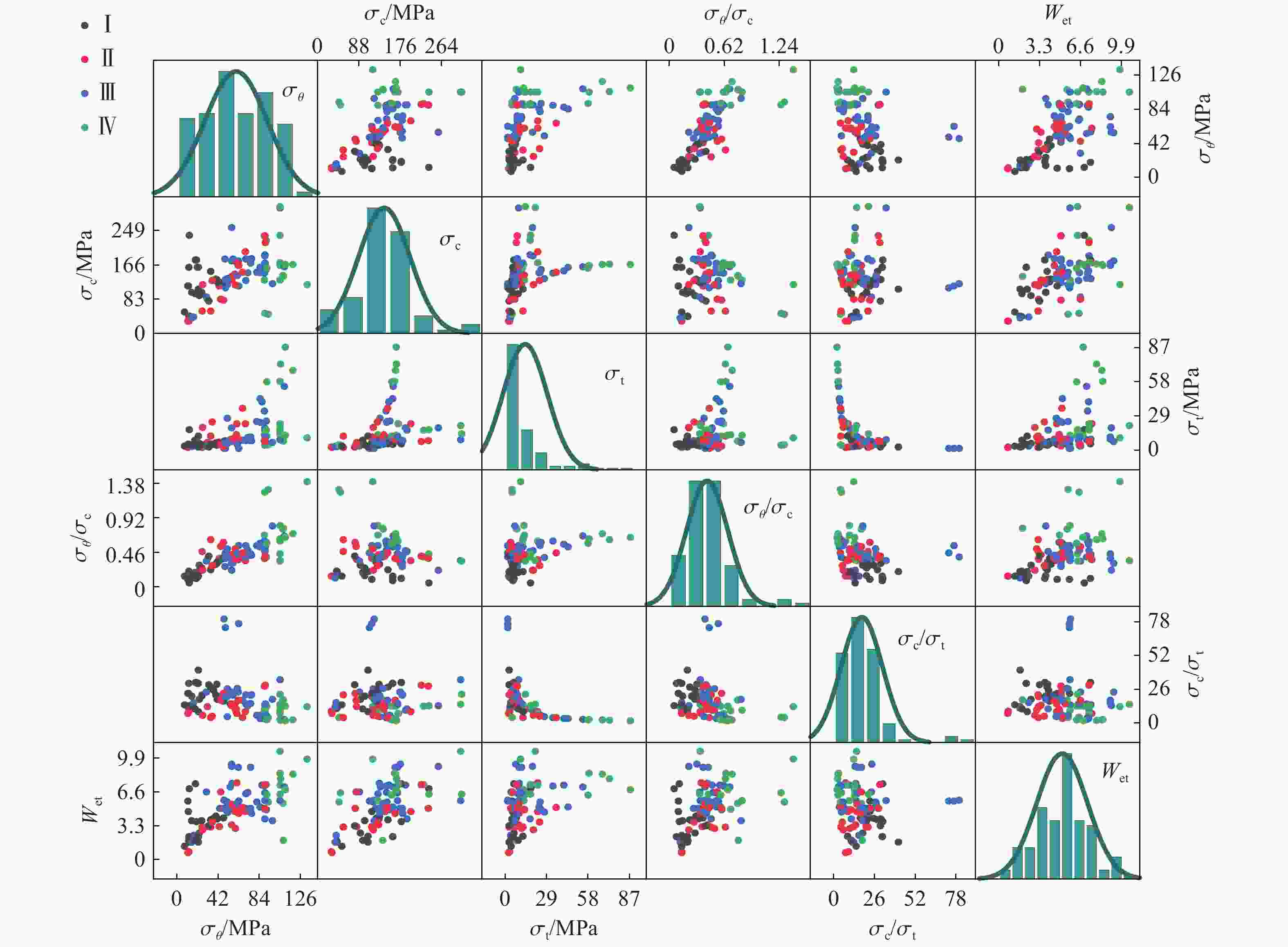
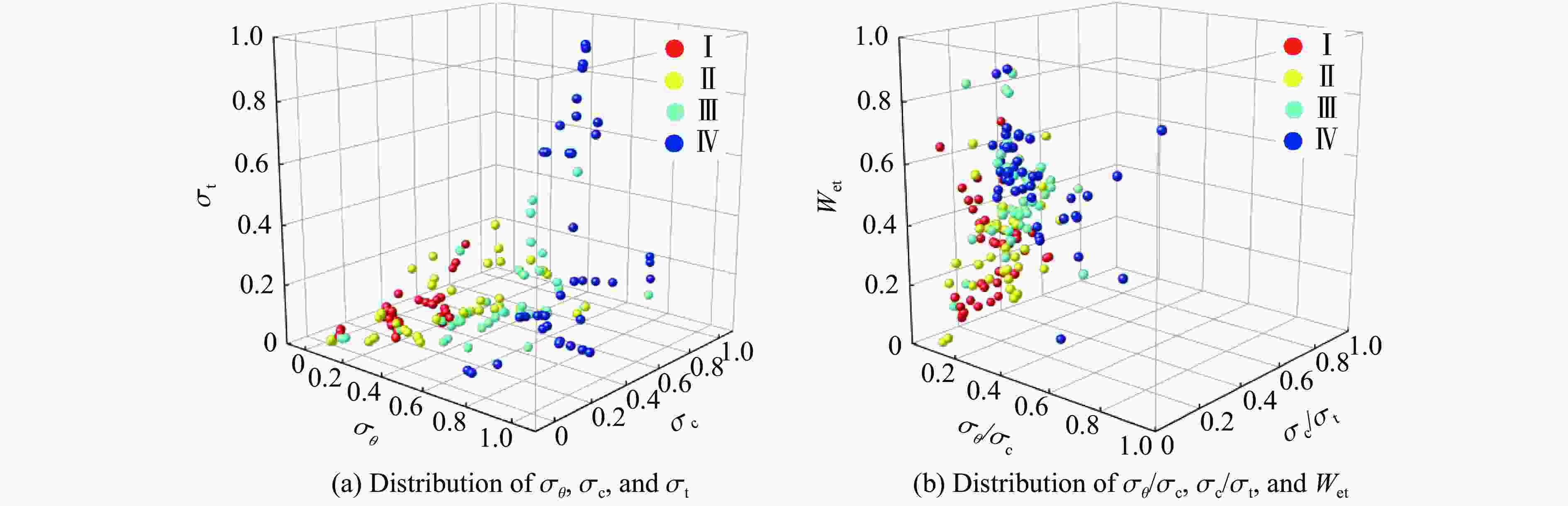
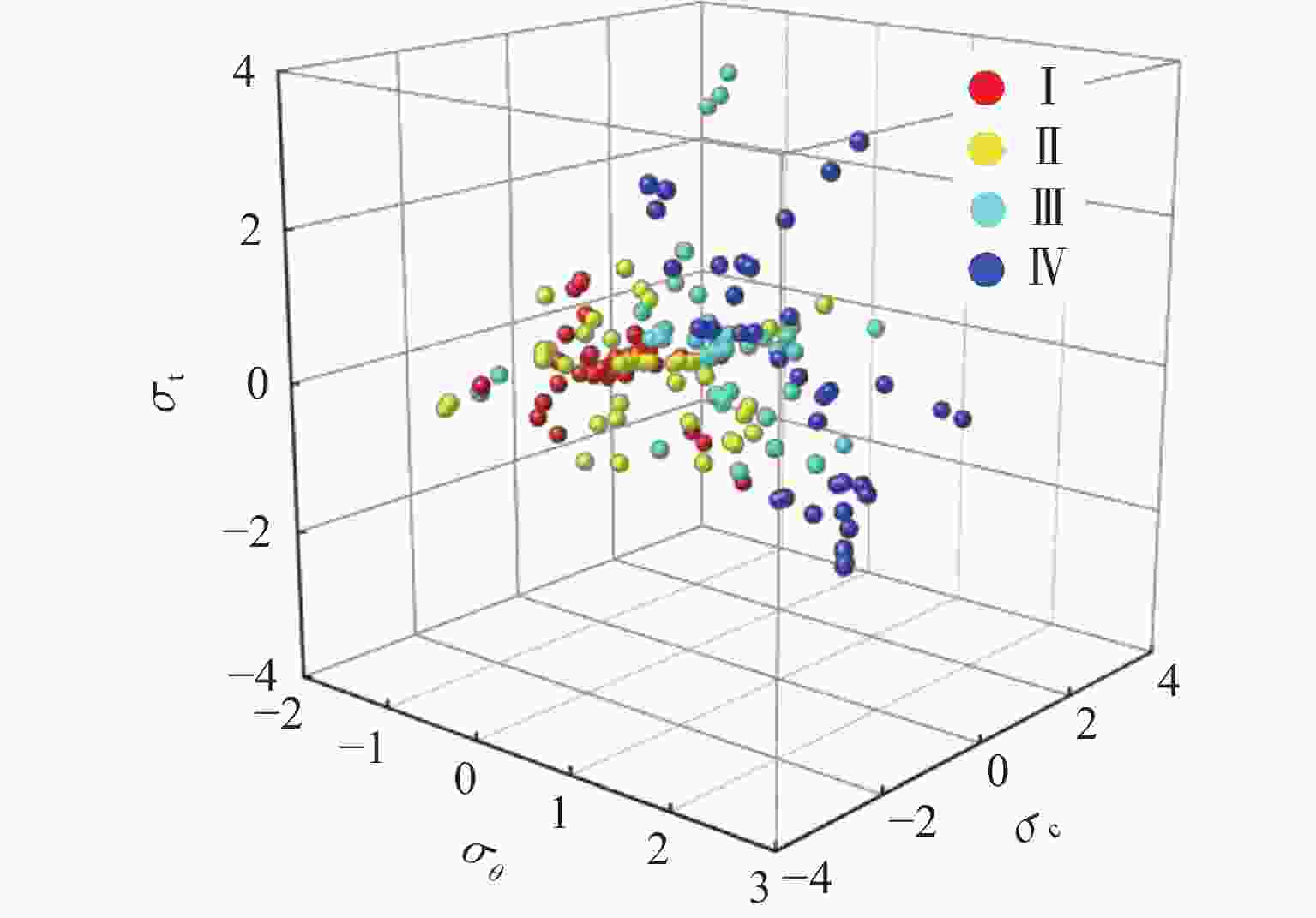
Rock burst level σc/MPa σθ/MPa σt/MPa σc/σt σθ/σc Wet No rock burst (Ⅰ) <80 <24 <5 >40.0 <0.3 <2.0 Minor rock burst (Ⅱ) 80−120 24−60 5−7 26.7−40.0 0.3−0.5 2.0−4.0 Moderate rock burst (Ⅲ) 120−180 60−126 7−9 14.5−26.7 0.5−0.7 4.0−6.0 Strong rock burst (Ⅳ) >180 126−200 9−30 <14.5 >0.7 >6.0 Serial No. σθ/MPa σc/MPa σt/MPa σc/σt σθ/σc Wet Rock burst level 1 22.40 91.20 5.99 15.23 0.25 2.60 Ⅰ 2 12.60 41.70 3.15 13.24 0.30 1.70 Ⅰ … … … … … … … … 105 110.35 167.19 87.53 1.91 0.66 6.83 Ⅳ 106 26.06 118.46 19.61 6.04 0.22 2.89 Ⅱ 表 3 变量的基本信息
Table 3. Basic information of variables
Statistic σθ/MPa σc/MPa σt/MPa σθ/σc σc/σt Wet Average 60.20 141.75 13.76 0.43 17.74 5.11 Standard deviation 31.97 55.12 15.55 0.23 13.22 2.05 Minimum value 7.50 29.45 1.50 0.05 1.91 0.70 Maximum value 132.60 306.58 87.53 1.40 80.00 10.57 25% percentile (Q1) 34.24 115.45 5.20 0.29 9.79 3.80 50% percentile (Q2) 57.92 140.00 8.30 0.40 14.90 5.00 75% percentile (Q3) 89.53 169.52 13.73 0.54 21.75 6.50 Median 57.92 140.00 8.30 0.40 14.90 5.00 Mode 105.00 115.00 8.30 0.38 17.50 5.00 表 4 部分标准化数据
Table 4. Partial standardized data
Serial No. σθ/MPa σc/MPa σt/MPa σc/σt σθ/σc Wet Rock burst level 1 0.12 0.22 0.05 0.15 0.17 0.19 Ⅰ 2 0.04 0.04 0.02 0.19 0.15 0.10 Ⅰ … … … … … … … … 105 0.82 0.50 1.00 0.45 0 0.62 Ⅳ 106 0.15 0.32 0.21 0.13 0.05 0.22 Ⅱ 表 5 各指标缺失情况及剩余样本量
Table 5. Missing conditions of each indicator and remaining sample size
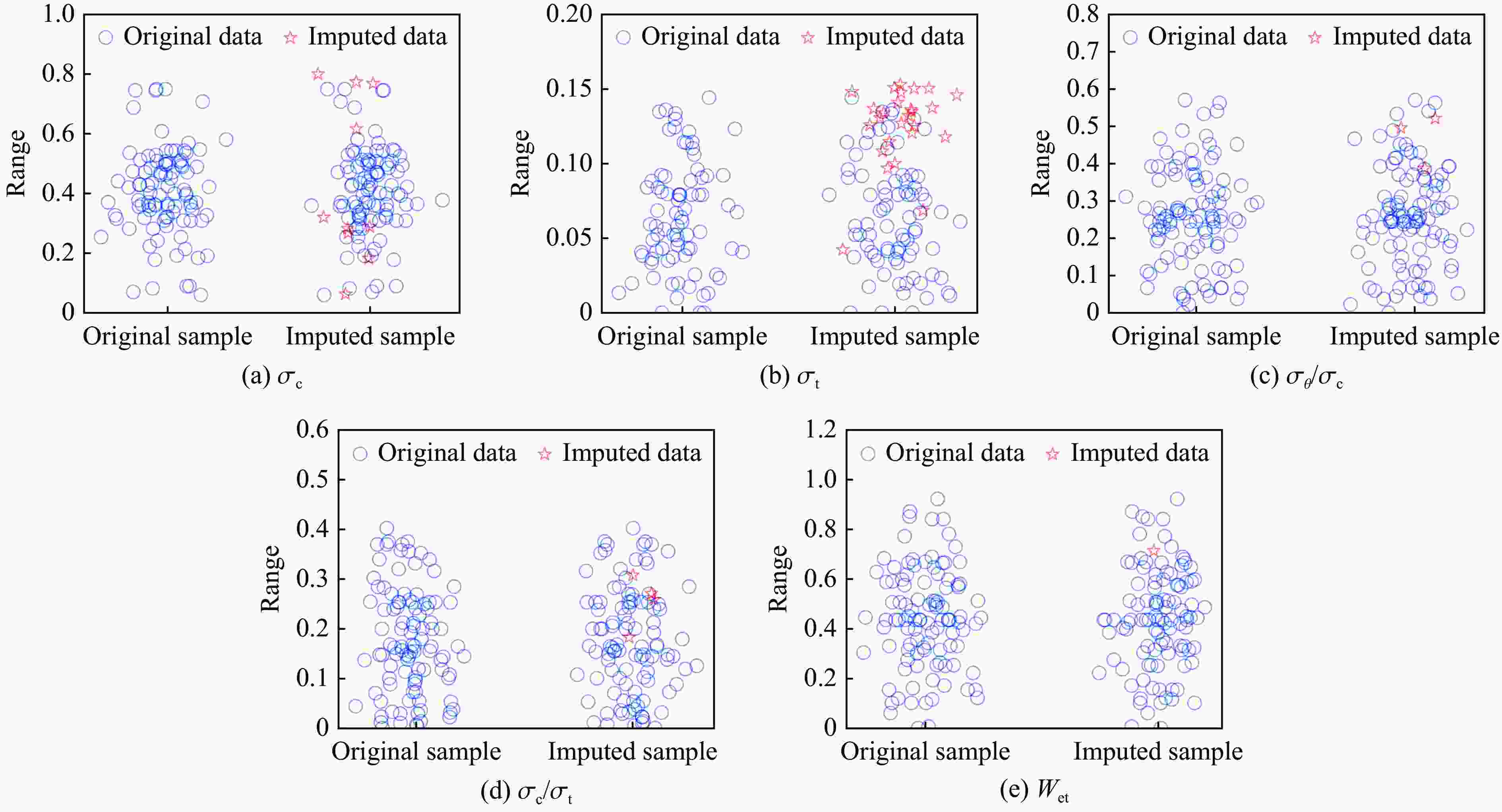
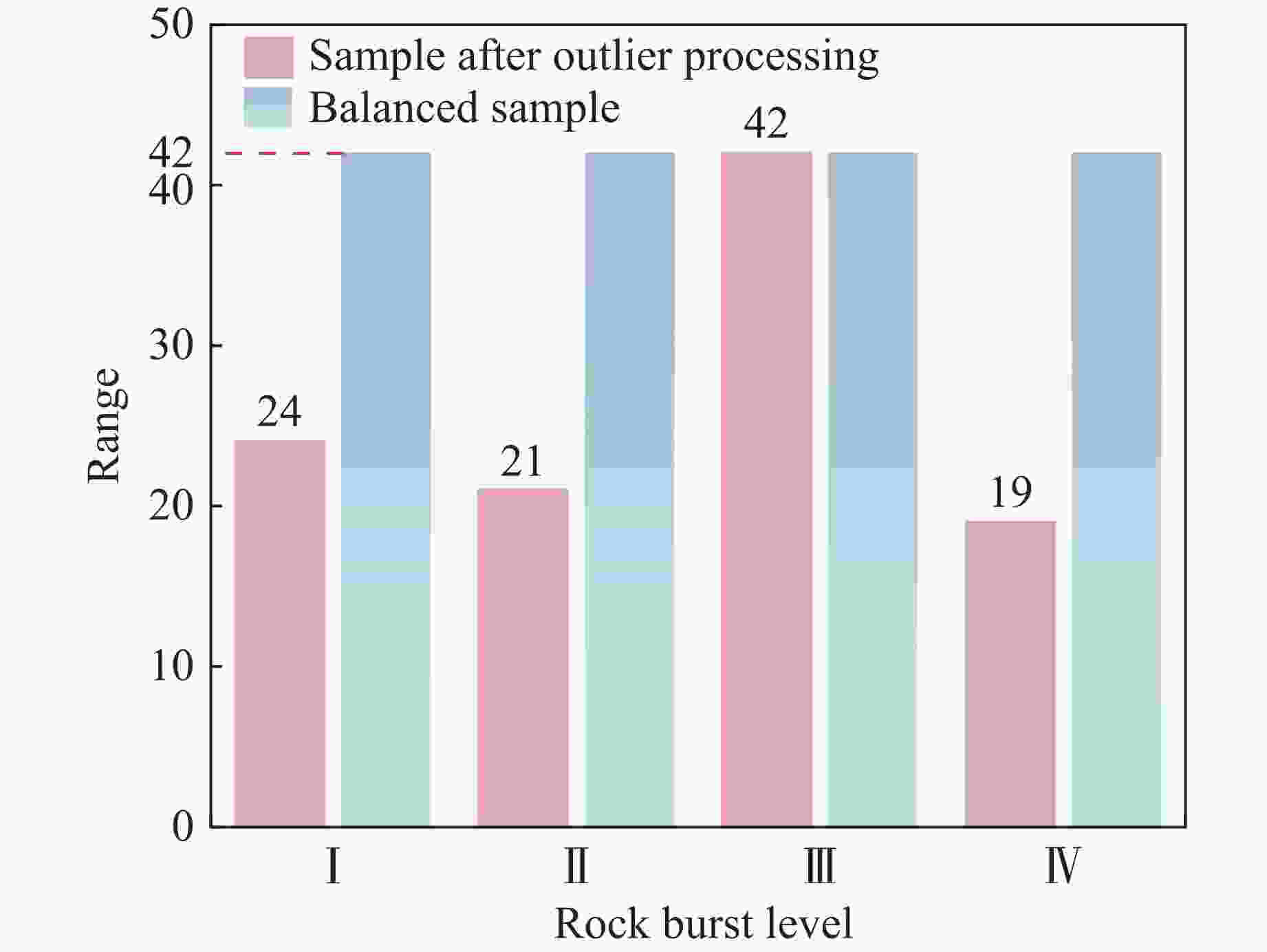
Statistic Missing quantity Remaining sample size σθ 0 106 σc 10 96 σt 11 95 σθ/σc 3 103 σc/σt 4 102 Wet 1 105 表 6 特征提取后部分样本数据
Table 6. Partial sample data after feature extraction
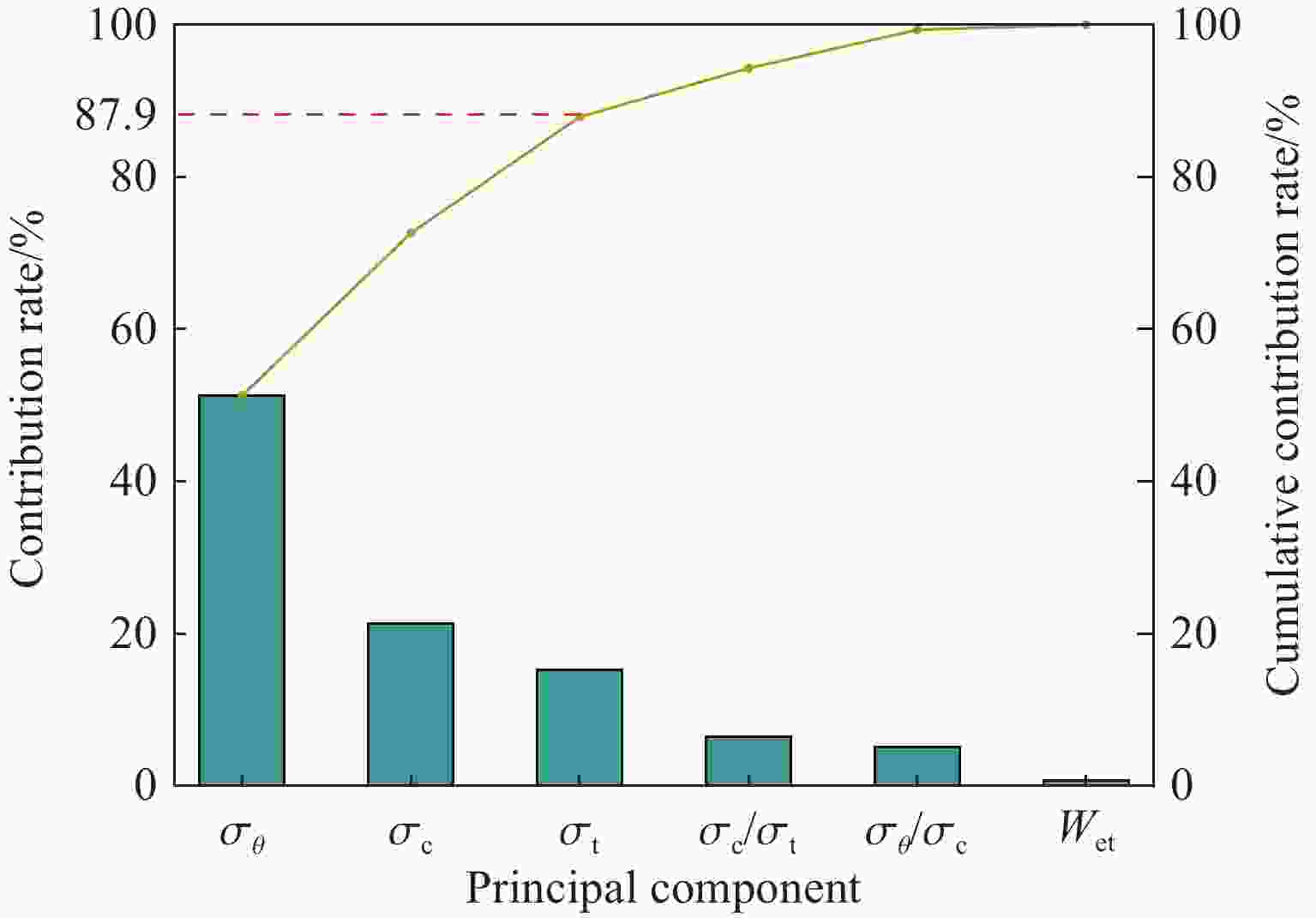
Serial No. σθ σc σt Rock burst level 1 −1.12 −0.57 −0.17 Ⅰ 2 −1.51 −1.40 −0.44 Ⅰ 3 0.24 1.69 0.22 Ⅲ … … … … … 167 1.46 2.46 −0.73 Ⅳ 168 2.12 −0.96 −1.72 Ⅳ 表 7 XGBoost超参数的初始值和预定的搜索范围
Table 7. Initial values of XGBoost hyperparameters and predetermined search scope
Parameter Parameter meaning Range Initial value Num_iters Maximum number of iterations [10, 100] 30 Max_depth Maximum depth of tree [1, 18] 6 Eta Learning rate [0, 1] 0.3 表 8 模型各等级预测情况
Table 8. Prediction of each level of the model
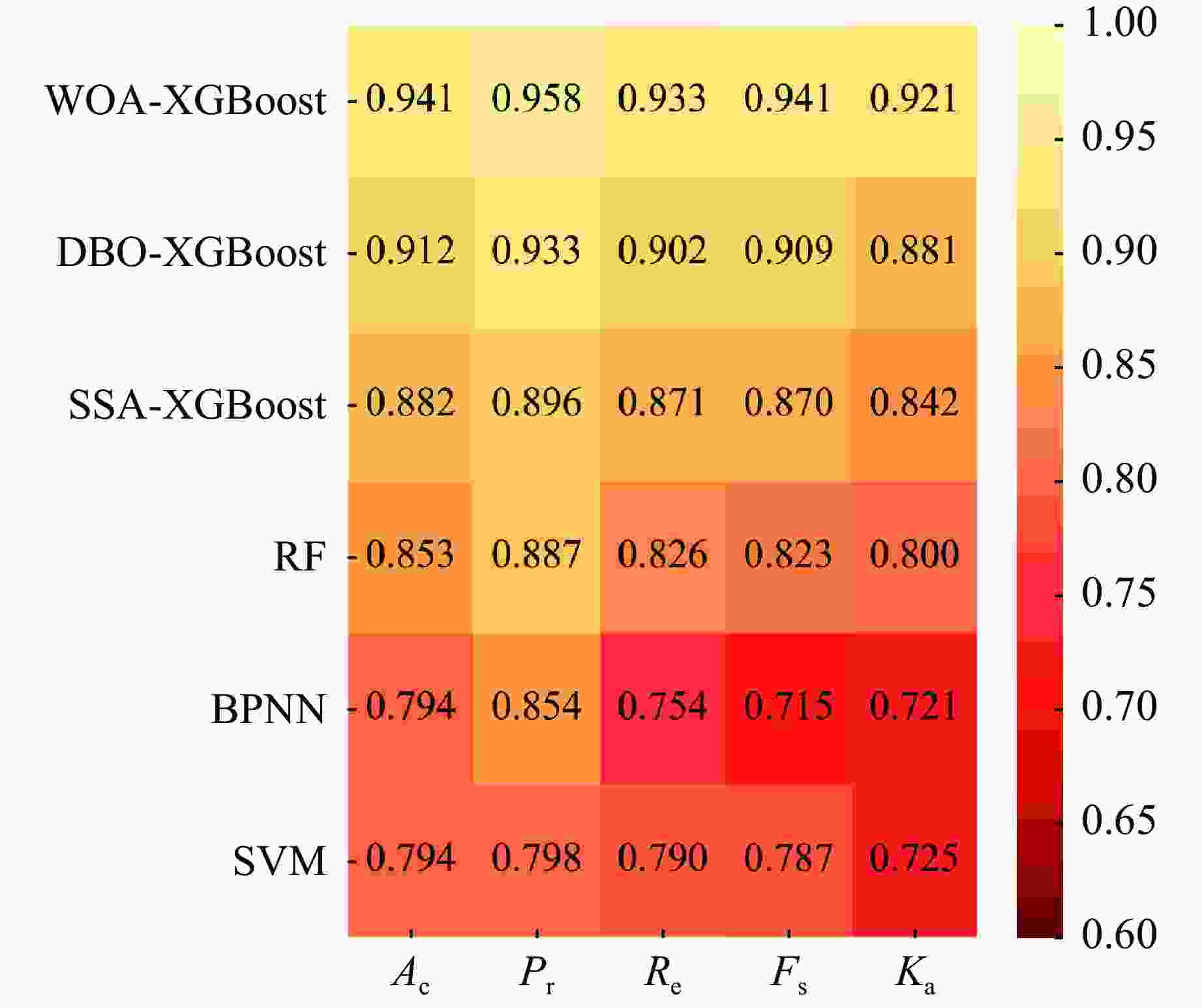
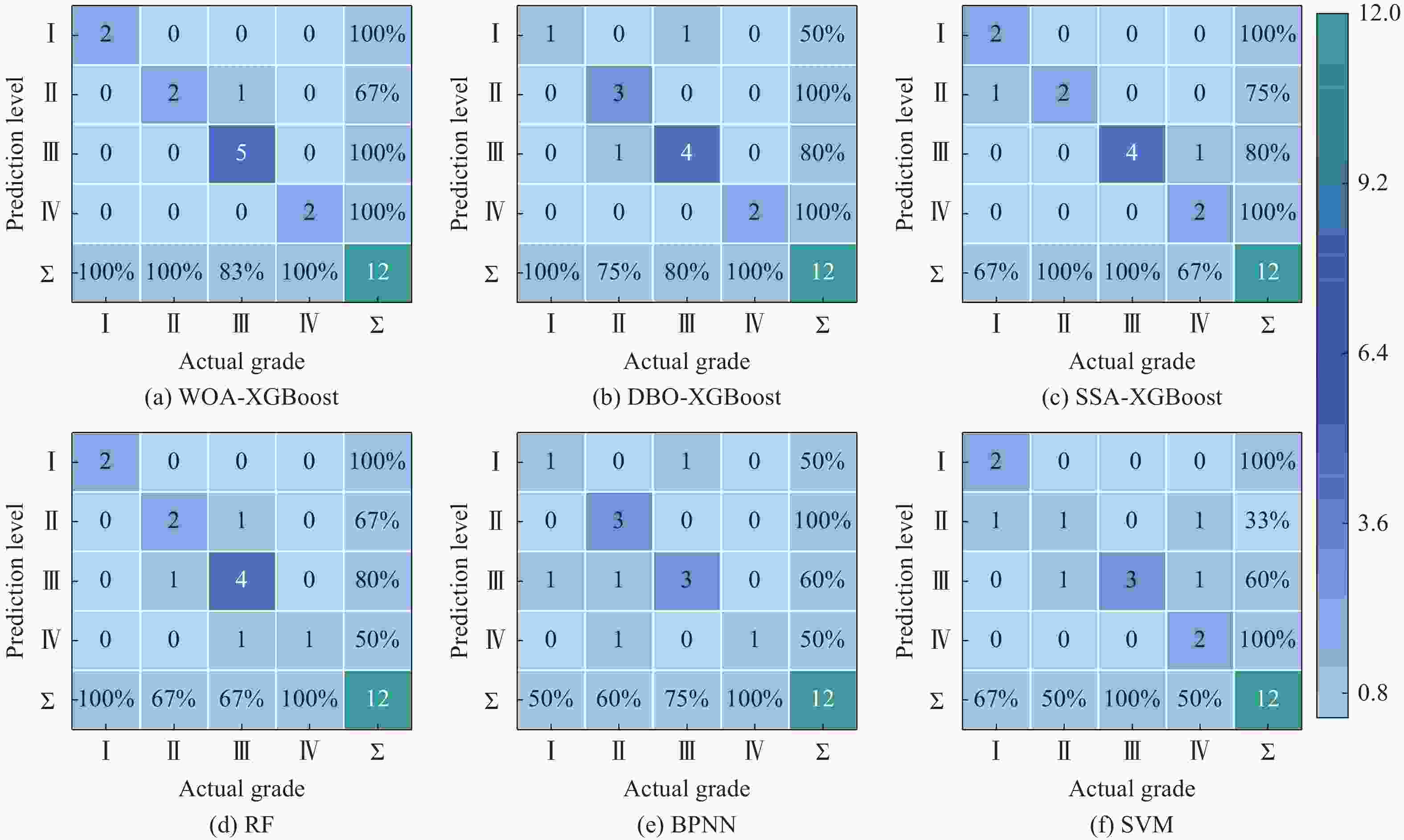
Rock burst level Actual quantity Predicted quantity WOA-XGBoost DBO-XGBoost SSA-XGBoost RF BPNN SVM Ⅰ 8 7 7 6 6 6 5 Ⅱ 8 7 7 7 7 6 7 Ⅲ 8 8 6 7 6 7 7 Ⅳ 8 8 8 7 7 6 6 Total 32 30 28 27 26 25 25 表 9 原始及特征提取后岩爆工程实例样本
Table 9. Sample examples of rock burst engineering after original and feature extraction
Engineering name Serial No. σθ/MPa σc/MPa σt/MPa σc/σt σθ/σc Wet F1 F2 Rock burst
levelQinlingzhongnanshan
highway tunnel1 43.1 122.0 5.38 22.68 0.35 3.31 −0.83 −0.25 Ⅱ 2 62.8 120.0 6.45 18.60 0.52 4.16 0.38 0.40 Ⅲ 3 54.2 134.0 9.09 14.74 0.4 7.08 1.35 −0.70 Ⅲ 4 79.1 124.0 8.64 14.35 0.64 7.74 2.20 0.75 Ⅳ 5 70.3 128.5 8.73 14.72 0.55 6.43 1.70 0.08 Ⅲ 6 56.1 132.0 9.44 13.98 0.43 7.44 1.57 −0.52 Ⅲ 7 56.2 119.0 7.21 16.50 0.47 5.52 0.59 0.29 Ⅲ 8 87.5 121.0 8.73 13.86 0.72 9.05 2.73 1.29 Ⅳ Water diversion system for
hydropower stations9 19.4 106.3 2.76 38.52 0.18 2.03 −3.35 0.25 Ⅰ 10 9.7 88.5 2.16 40.97 0.11 1.77 −4.28 0.96 Ⅰ 11 34.9 151.7 7.47 20.31 0.23 3.17 −0.23 −2.37 Ⅱ 12 33.9 117.5 4.23 27.77 0.29 2.37 −1.81 −0.17 Ⅱ -
[1] LI P, CAI M F. Challenges and new insights for exploitation of deep underground metal mineral resources [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2021, 31(11): 3478–3505. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65744-8 [2] 江飞飞, 周辉, 刘畅, 等. 地下金属矿山岩爆研究进展及预测与防治 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(5): 956–972. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.1190JIANG F F, ZHOU H, LIU C, et al. Progress, prediction and prevention of rockbursts in underground metal mines [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(5): 956–972. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.1190 [3] ZHANG J F, WANG Y H, SUN Y T, et al. Strength of ensemble learning in multiclass classification of rockburst intensity [J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2020, 44(13): 1833–1853. doi: 10.1002/nag.3111 [4] 张镜剑, 傅冰骏. 岩爆及其判据和防治 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(10): 2034–2042. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.10.010ZHANG J J, FU B J. Rockburst and its criteria and control [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(10): 2034–2042. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.10.010 [5] 汤志立, 徐千军. 基于9种机器学习算法的岩爆预测研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(4): 773–781. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2019.0686TANG Z L, XU Q J. Rockburst prediction based on nine machine learning algorithms [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(4): 773–781. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2019.0686 [6] 刘慧敏, 徐方远, 刘宝举, 等. 基于CNN-LSTM的岩爆危险等级时序预测方法 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(3): 659–670. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.03.001LIU H M, XU F Y, LIU B J, et al. Time-series prediction method for risk level of rockburst disaster based on CNN-LSTM [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2021, 52(3): 659–670. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.03.001 [7] 刘剑, 周宗红, 刘军, 等. 基于主成分分析和改进Bayes判别的岩爆等级预测 [J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报, 2022, 4(5): 053014. doi: 10.13532/j.jmsce.cn10-1638/td.2022.05.004LIU J, ZHOU Z H, LIU J, et al. Prediction of rockburst grade based on principal component analysis and improved Bayesian discriminant analysis [J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering, 2022, 4(5): 053014. doi: 10.13532/j.jmsce.cn10-1638/td.2022.05.004 [8] 李康楠, 吴雅琴, 杜锋, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的岩爆烈度等级预测 [J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2023, 51(10): 94–103. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.01.0018LI K N, WU Y Q, DU F, et al. Prediction of rockburstintensity grade based on convolutional neural network [J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2023, 51(10): 94–103. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.01.0018 [9] 高梅, 张成良, 张华超, 等. 基于SMOTEENN-CGAN-Stacking的岩爆烈度等级预测研究 [J]. 工程地质学报, 2024, 32(6): 2264–2276. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2024-0112GAO M, ZHANG C L, ZHANG H C, et al. Rockburst intensity level prediction based on SMOTEENN-CGAN-Stacking [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2024, 32(6): 2264–2276. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2024-0112 [10] 满轲, 武立文, 刘晓丽, 等. 基于灰色关联分析和GRU模型的岩爆等级预测 [J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2025, 21(2): 695–708, 719. doi: 10.20174/j.JUSE.2025.02.37MAN K, WU L W, LIU X L, et al. Rockburst grade prediction based on grey correlation analysis and GRU model [J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2025, 21(2): 695–708, 719. doi: 10.20174/j.JUSE.2025.02.37 [11] 祁云, 白晨浩, 代连朋, 等. 改进双向长短期记忆神经网络的瓦斯涌出量预测 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2024, 24(12): 4630–4637. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2024.0383QI Y, BAI C H, DAI L P, et al. Enhanced Bi-directional long short-term memory neural network for gas emission forecasting [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2024, 24(12): 4630–4637. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2024.0383 [12] CHAWLA N V, BOWYER K W, KEGELMEYER W P, et al. SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique [J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2002, 16: 321–357. doi: 10.1613/jair.953 [13] MIRJALILI S, LEWIS A. The whale optimization algorithm [J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2016, 95: 51–67. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008 [14] BENTÉJAC C, CSÖRGŐ A, MARTÍNEZ-MUÑOZ G. A comparative analysis of gradient boosting algorithms [J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2021, 54(3): 1937–1967. doi: 10.1007/s10462-020-09896-5 [15] JIANG H, HE Z, YE G, et al. Network intrusion detection based on PSO-XGBoost model [J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 58392–58401. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2982418 [16] 邱士利, 冯夏庭, 张传庆, 等. 深埋硬岩隧洞岩爆倾向性指标RVI的建立及验证 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30(6): 1126–1141.QIU S L, FENG X T, ZHANG C Q, et al. Development and validation of rockburst vulnerability index (RVI) in deep hard rock tunnels [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(6): 1126–1141. [17] 宫凤强, 闫景一, 李夕兵. 基于线性储能规律和剩余弹性能指数的岩爆倾向性判据 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(9): 1993–2014. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0232GONG F Q, YAN J Y, LI X B. A new criterion of rock burst proneness based on the linear energy storage law and the residual elastic energy index [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(9): 1993–2014. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0232 [18] 张如九, 张延杰, 高仝, 等. 基于最大能量耗散率的岩爆倾向性指标研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(12): 2993–3009. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2023.0363ZHANG R J, ZHANG Y J, GAO T, et al. A novel index of rockburst proneness based on maximum energy dissipation rate [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(12): 2993–3009. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2023.0363 [19] 葛启发, 冯夏庭. 基于AdaBoost组合学习方法的岩爆分类预测研究 [J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(4): 943–948. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.04.017GE Q F, FENG X T. Classification and prediction of rockburst using AdaBoost combination learning method [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(4): 943–948. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.04.017 [20] 吴顺川, 张晨曦, 成子桥. 基于PCA-PNN原理的岩爆烈度分级预测方法 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(9): 2767–2776. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.1519WU S C, ZHANG C X, CHENG Z Q. Prediction of intensity classification of rockburst based on PCA-PNN principle [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(9): 2767–2776. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.1519 [21] 邱道宏, 李术才, 张乐文, 等. 基于模型可靠性检查的QGA-SVM岩爆倾向性分类研究 [J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2015, 23(5): 981–991. doi: 10.16058/j.issn.1005-0930.2015.05.012QIU D H, LI S C, ZHANG L W, et al. Research on QGA-SVM rock burst orientation classification based on model reliability examination [J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2015, 23(5): 981–991. doi: 10.16058/j.issn.1005-0930.2015.05.012 [22] 周科平, 雷涛, 胡建华. 深部金属矿山RS-TOPSIS岩爆预测模型及其应用 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(Suppl 2): 3705–3711.ZHOU K P, LEI T, HU J H. RS-TOPSIS model of rockburst prediction in deep metal mines and its application [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(Suppl 2): 3705–3711. [23] 王克忠, 谢添, 李梅, 等. 基于数值样本和随机森林分类器的岩爆风险快速预测代理模型 [J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 64(7): 1203–1214. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2024.26.027WANG K Z, XIE T, LI M, et al. A surrogate model for the rapid prediction of rockburst risk based on numerical samples and random forest classifier [J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2024, 64(7): 1203–1214. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2024.26.027 [24] 吴菡. 基于支持向量机的岩爆预测方法研究 [D]. 林芝: 西藏农牧学院, 2023. [25] 武立文. 基于SSA-RF模型的岩爆预测方法及应用研究 [D]. 北京: 北方工业大学, 2024.WU L W. Research on rockburst prediction method and application based on SSA-RF model [D]. Beijing: North China University of Technology, 2024. -






 下载:
下载: