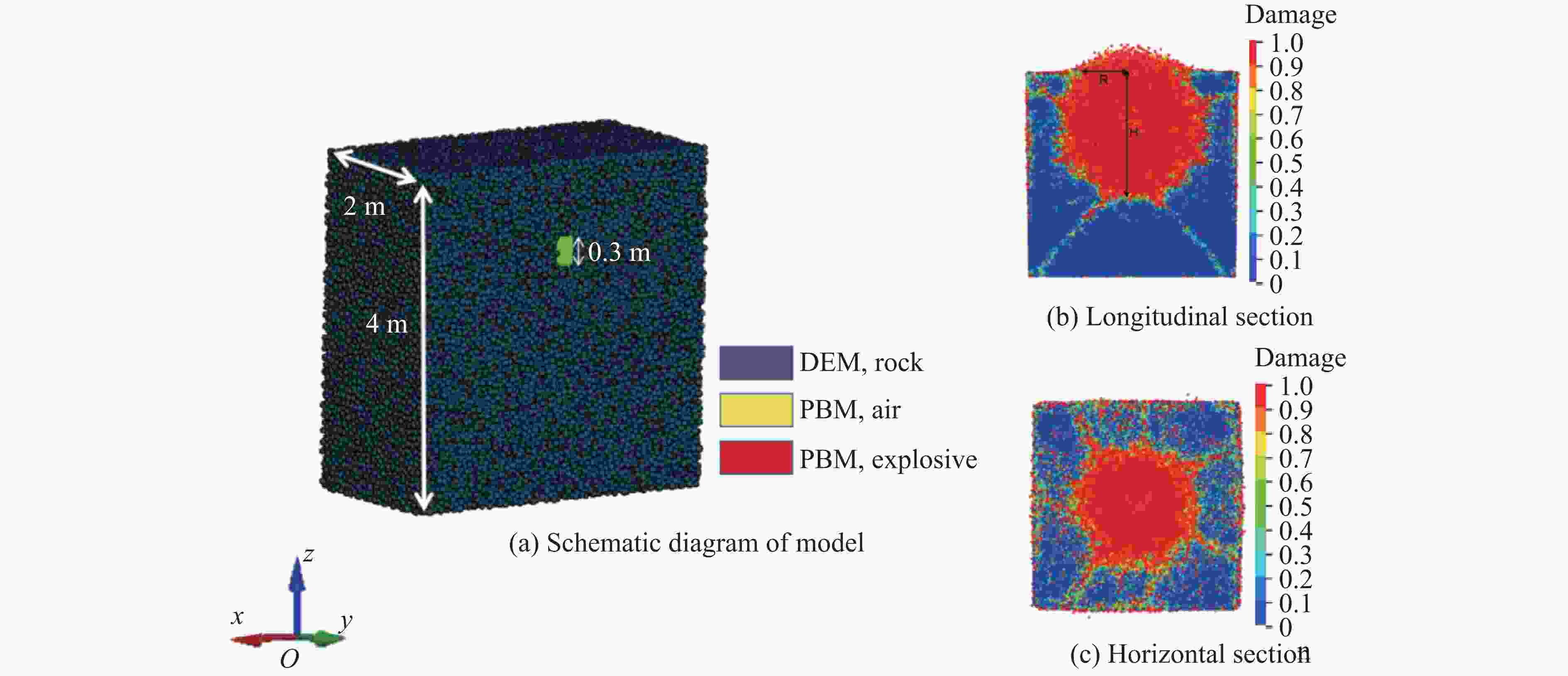
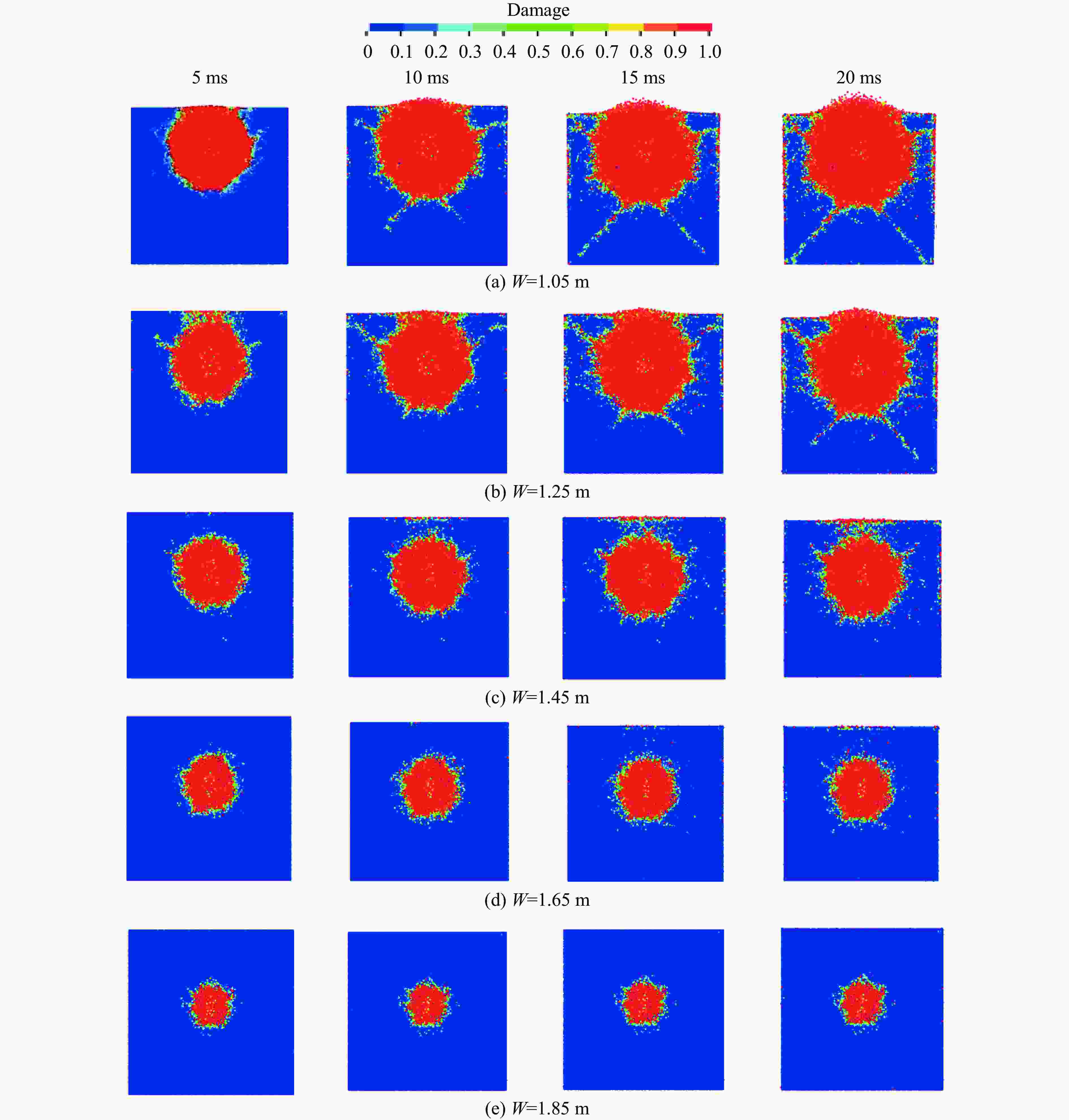
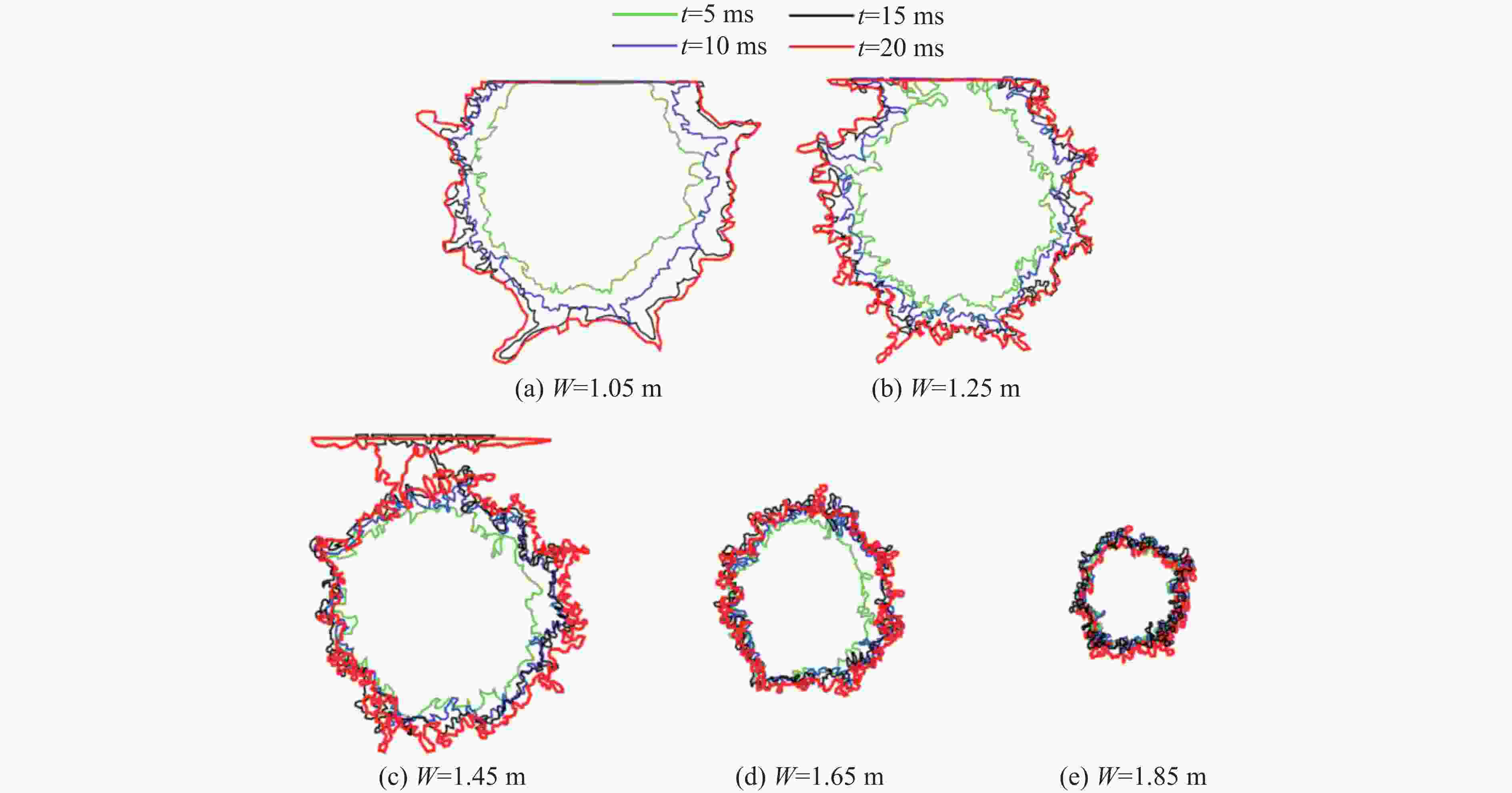
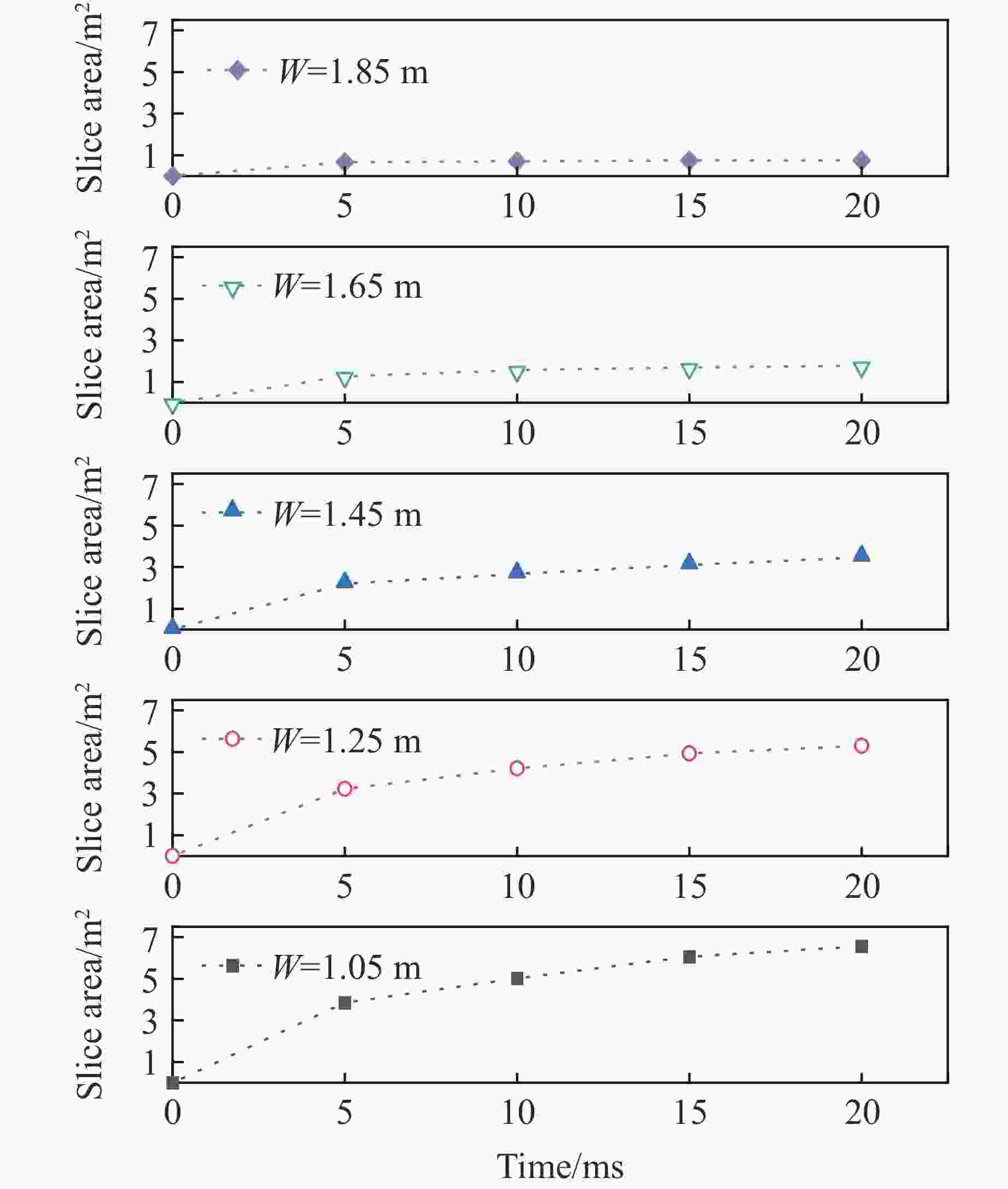
Blasting Crater Test Law under Different Resistance Lines Based on DEM-PBM Method
-
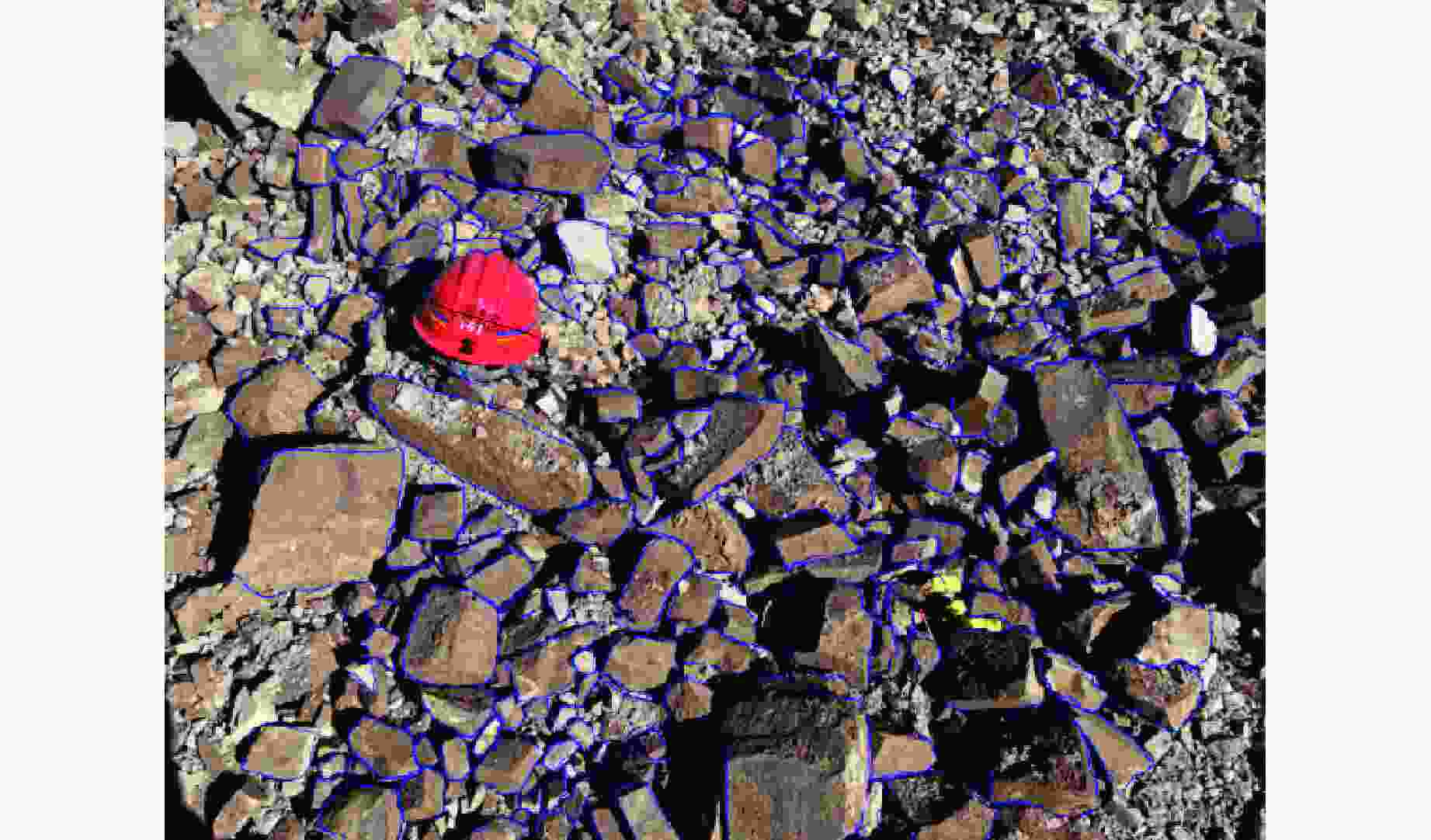
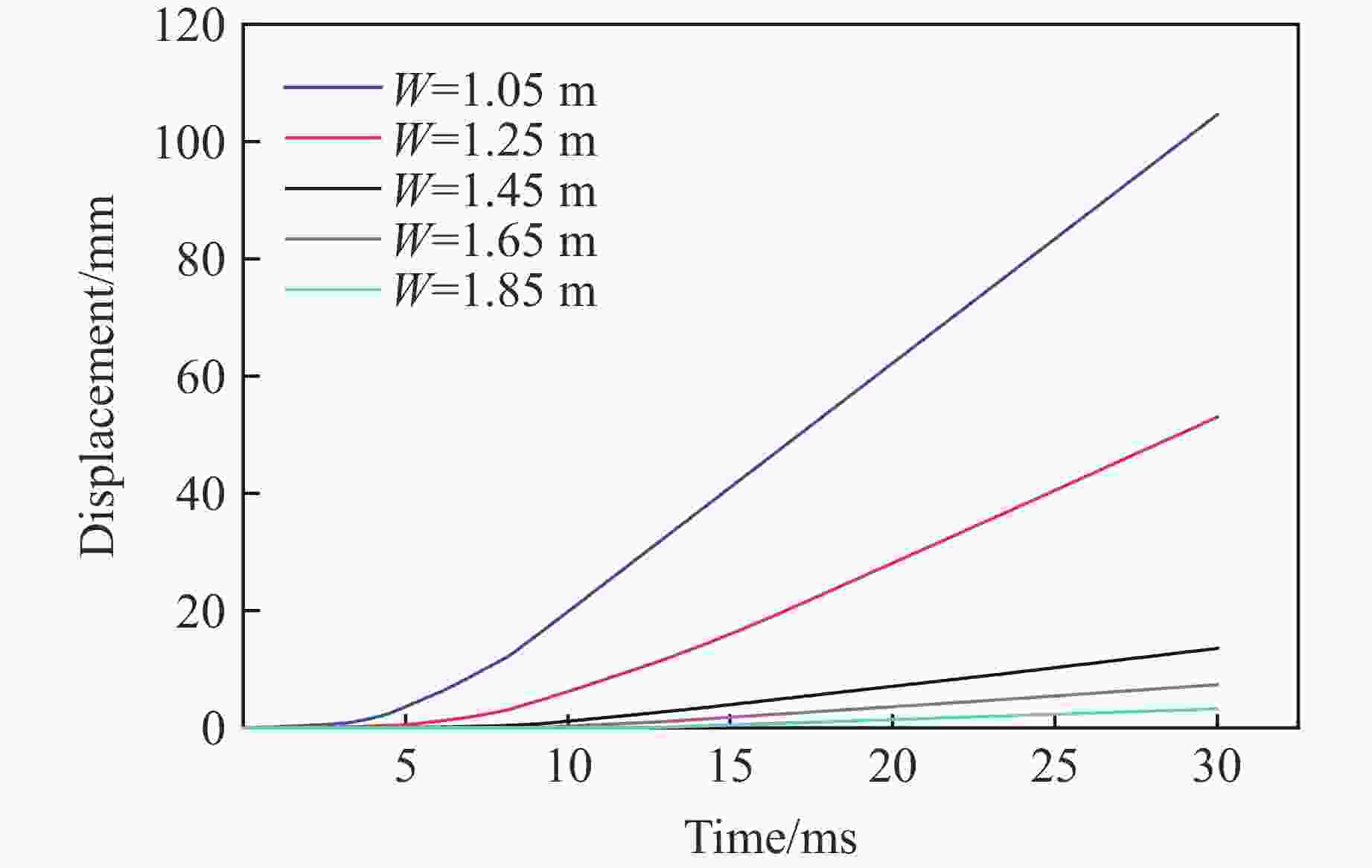
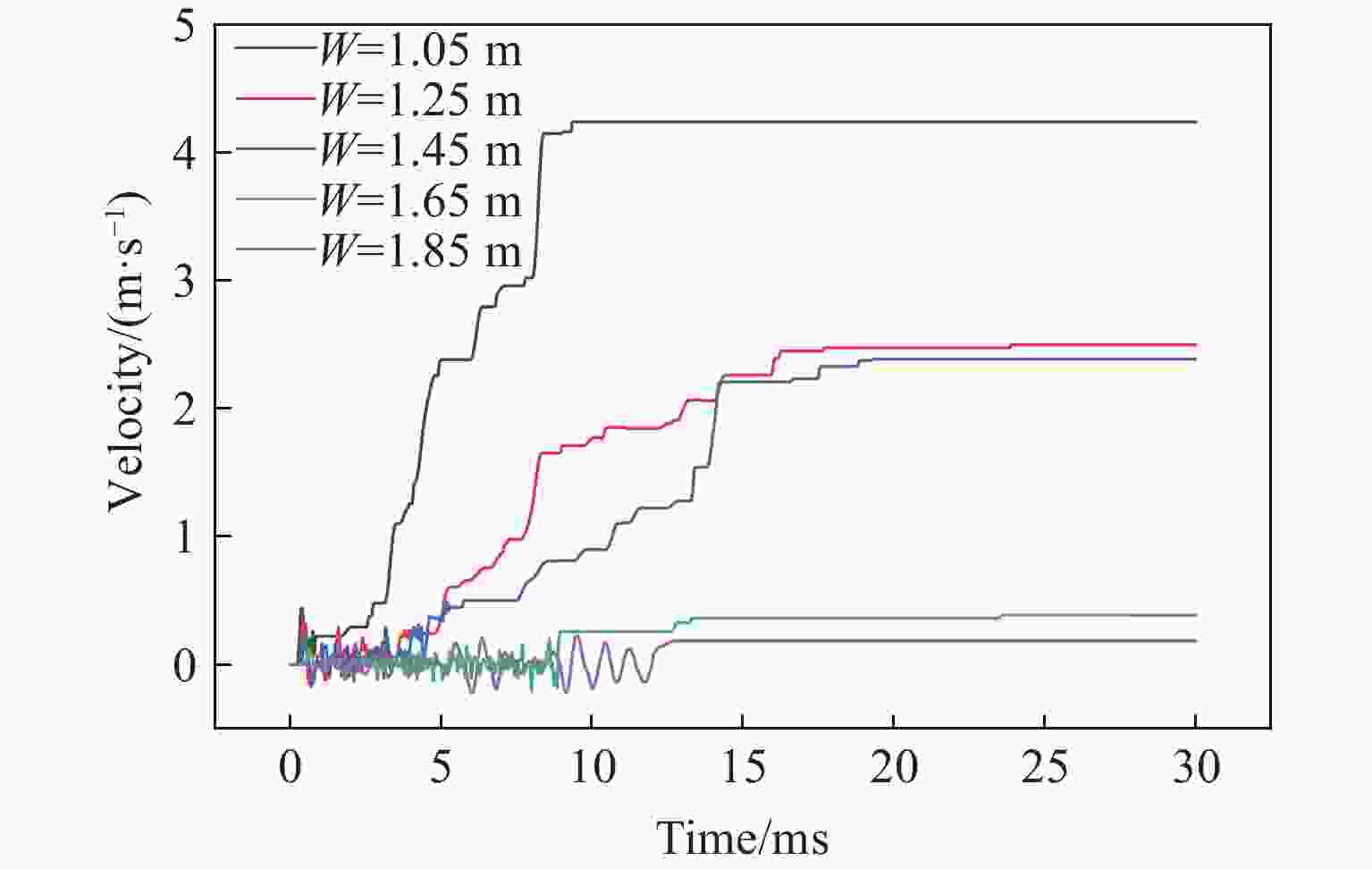
摘要: 在露天爆破中,最小抵抗线决定了爆破能量释放的主导方向和岩石运动速度的方向,是控制爆破作用范围、岩石破碎效果及抛掷路径的核心因素。基于DEM-PBM(discrete element method-population balance model)耦合的爆破漏斗数值模拟方法,通过多尺度建模与试验数据协同分析,结合现场爆破漏斗试验,对不同最小抵抗线下爆破漏斗破岩规律进行了研究,以优化爆破参数,提高爆破效率和安全性。数值模拟结果表明:当抵抗线长度为1.05 m时,20 ms时的爆破扩腔面积比5 ms时增长70.33%;当抵抗线长度为1.85 m时,爆破扩腔面积增长11.42%。对比不同抵抗线下破碎块度的抛掷作用效果,当抵抗线长度为1.05 m时,抛掷效果最佳。现场爆破漏斗试验结果显示:当抵抗线长度增大时,爆破漏斗体积变小;当抵抗线长度为1.05 m时,爆破漏斗体积最大,与数值模拟得到的爆破扩腔规律相似。现场爆破块度尺寸分形规律分析结果表明,当抵抗线长度为1.05 m、炮孔深度为1.2 m时,抛掷岩石块体较多,块度分布适中,破碎块体抛掷作用效果最佳。研究结果可为现场钻爆参数优化提供一定参考。Abstract: In open-pit blasting project, the minimum resistance line (W) determines the dominant direction of blasting energy release and the maximum direction of rock velocity. This parameter is the core factor controlling the blasting action range, crushing effect and throwing path of the rock. Based on discrete element method-population balance model (DEM-PBM) coupling numerical simulation method of blasting crater, field blasting crater test was carried out through multi-scale modeling and test data collaborative analysis. The rock breaking law of blasting crater test under different minimum resistance lines was studied in order to optimize blasting parameters and improve blasting efficiency and safety. Based on the comparison of numerical simulation results, the blasting expansion area at 20 ms increases by 70.33% compared with that at 5 ms when W=1.05 m, and the blasting expansion area increases by 11.42% when W=1.85 m. By comparing the throwing effect of fragmentation under different minimum resistance lines, the throwing effect is the best when W=1.05 m. According to the results of field blasting crater test, when the length of the resistance line increases, the volume of the blasting crater becomes smaller, and the volume of the blasting crater is the largest when W=1.05 m, which is similar to the blasting cavity expansion law obtained through numerical simulation. The fractal law of fragmentation size in field blasting was analyzed. When W=1.05 m and the depth of blast hole is 1.2 m, more rock blocks are thrown, the fragmentation distribution is moderate, and the throwing effect of broken blocks is the best. This study provides reference for the optimization of field drilling and blasting parameters.
-
Key words:
- DEM-PBM method /
- blasting crater /
- throwing action /
- blasting fragmentation
-
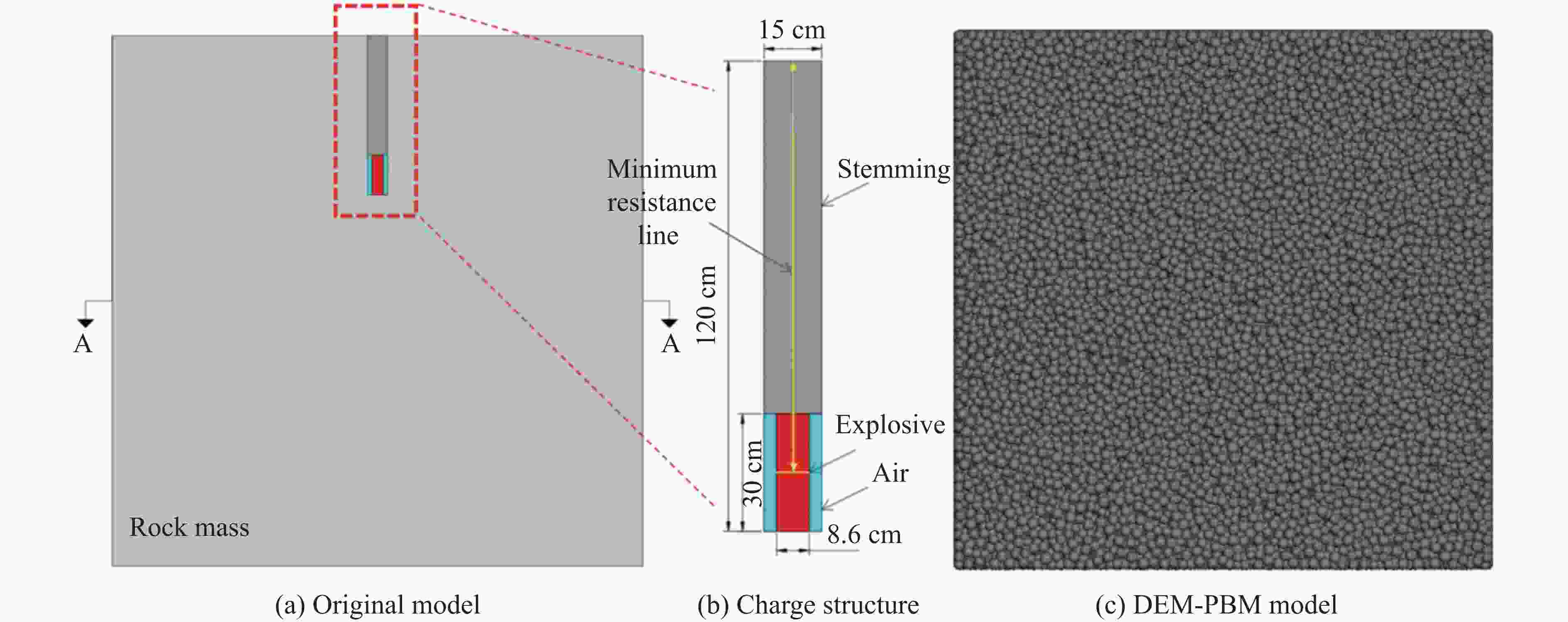
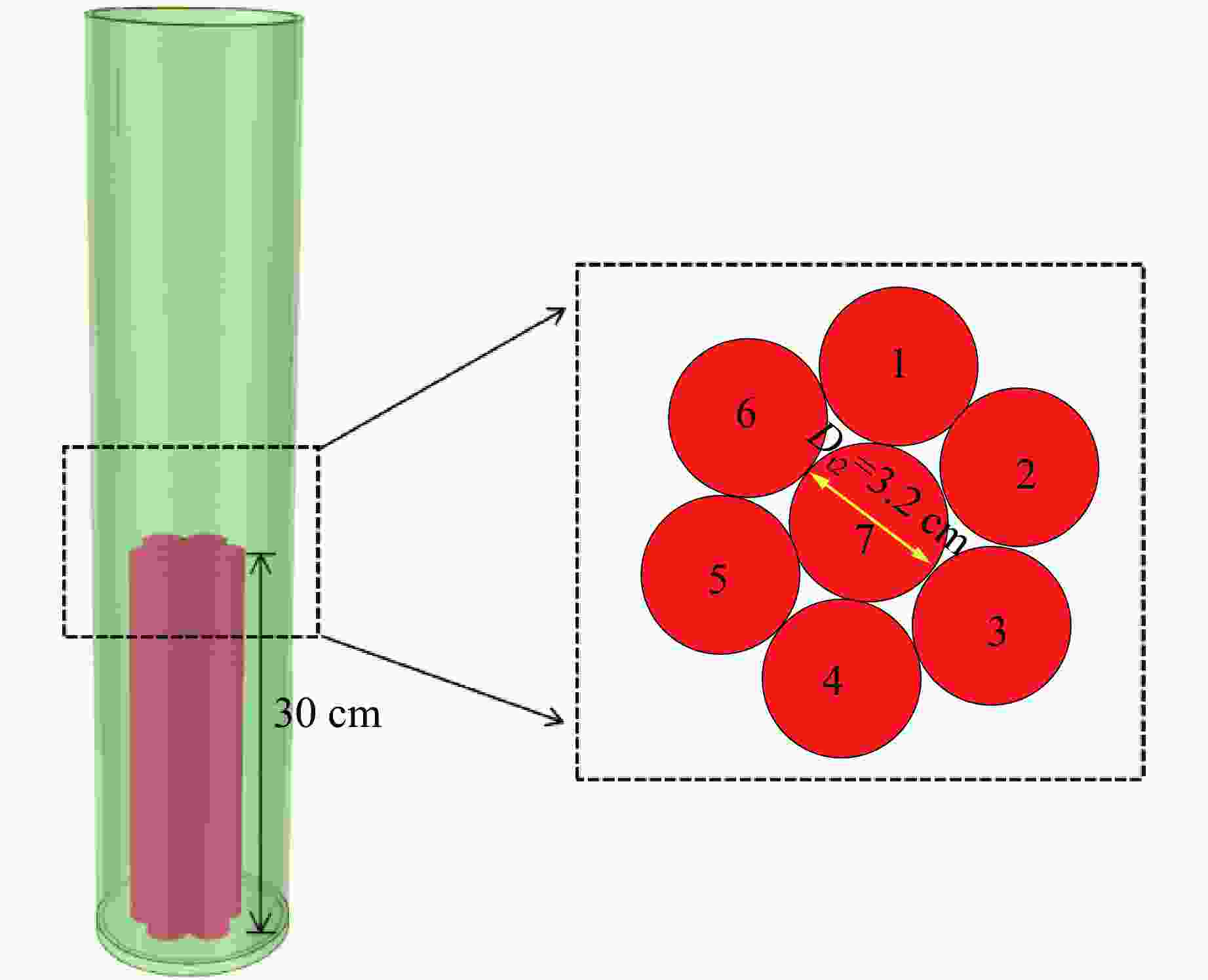
表 1 不同最小抵抗线参数
Table 1. Parameters of different minimum resistance lines
No. Aperture/cm Charge diameter/cm Hole depth/m Charge mass/kg Charge height/cm Minimum resistance
line length/m1 15 8.6 1.2 2.1 30 1.05 2 1.4 1.25 3 1.6 1.45 4 1.8 1.65 5 2.0 1.85 表 2 磷矿石的HJC本构参数
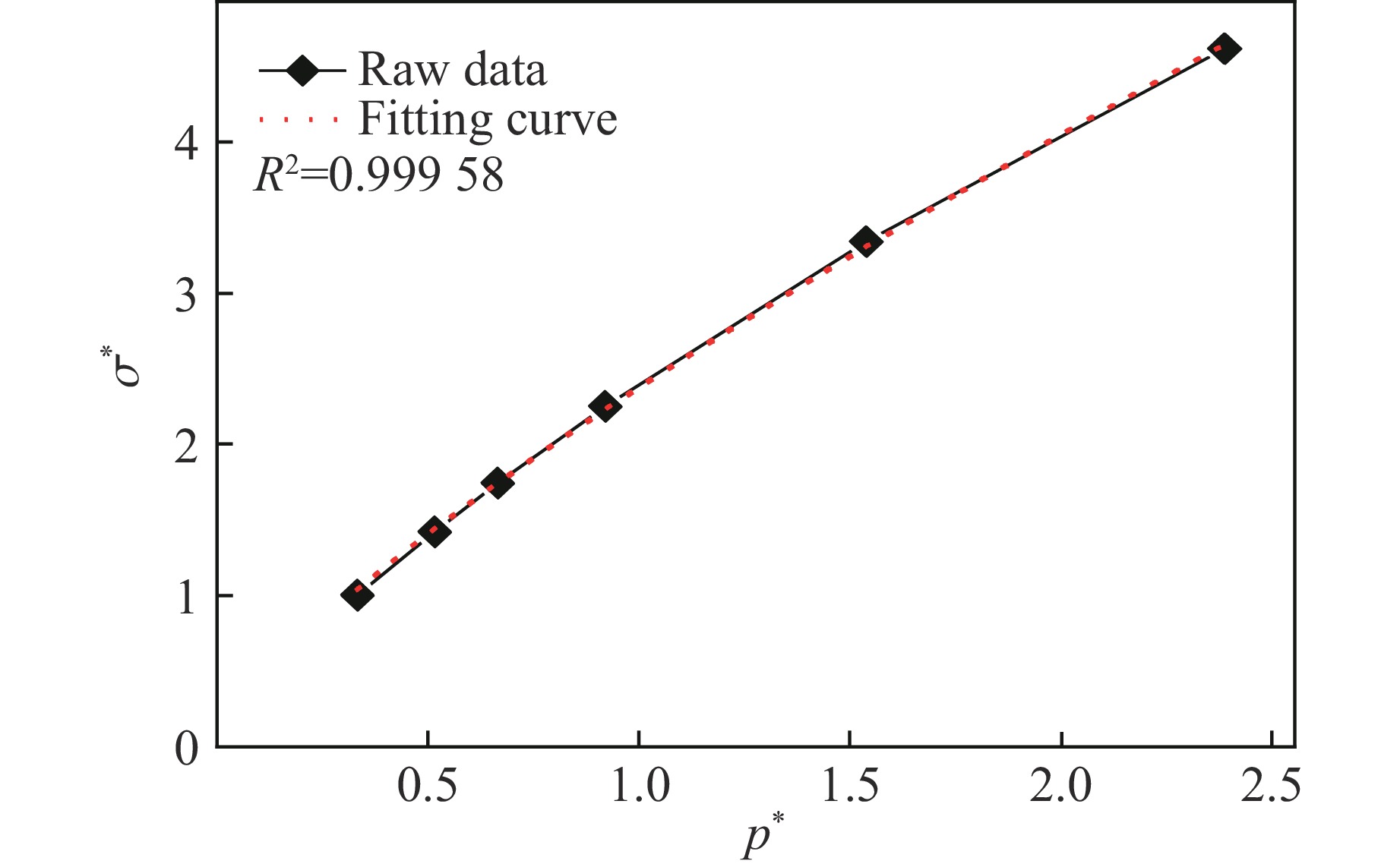
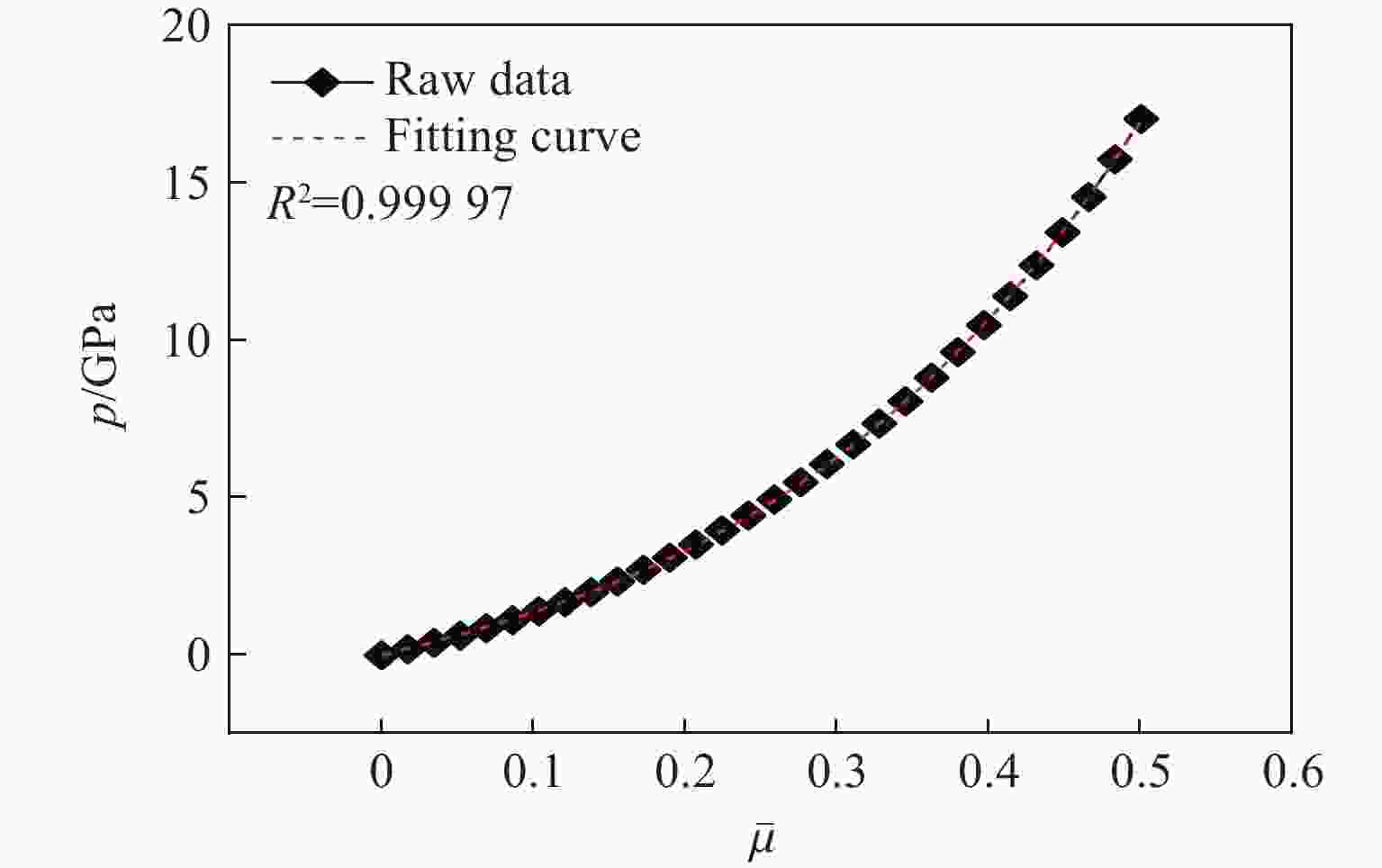
Table 2. HJC constitutive parameters of phosphate ore
ρ0/(kg·m−3) G/GPa A B C N fc/MPa 2 415 47.2 0.053 8 2.321 47 0.024 9 0.783 37 118 T/MPa pc/MPa ρl/(kg·m−3) K1/GPa K2/GPa K3/GPa 6.78 39.33 2 444.33 12 8.64 69.98 表 3 炸药的相关参数
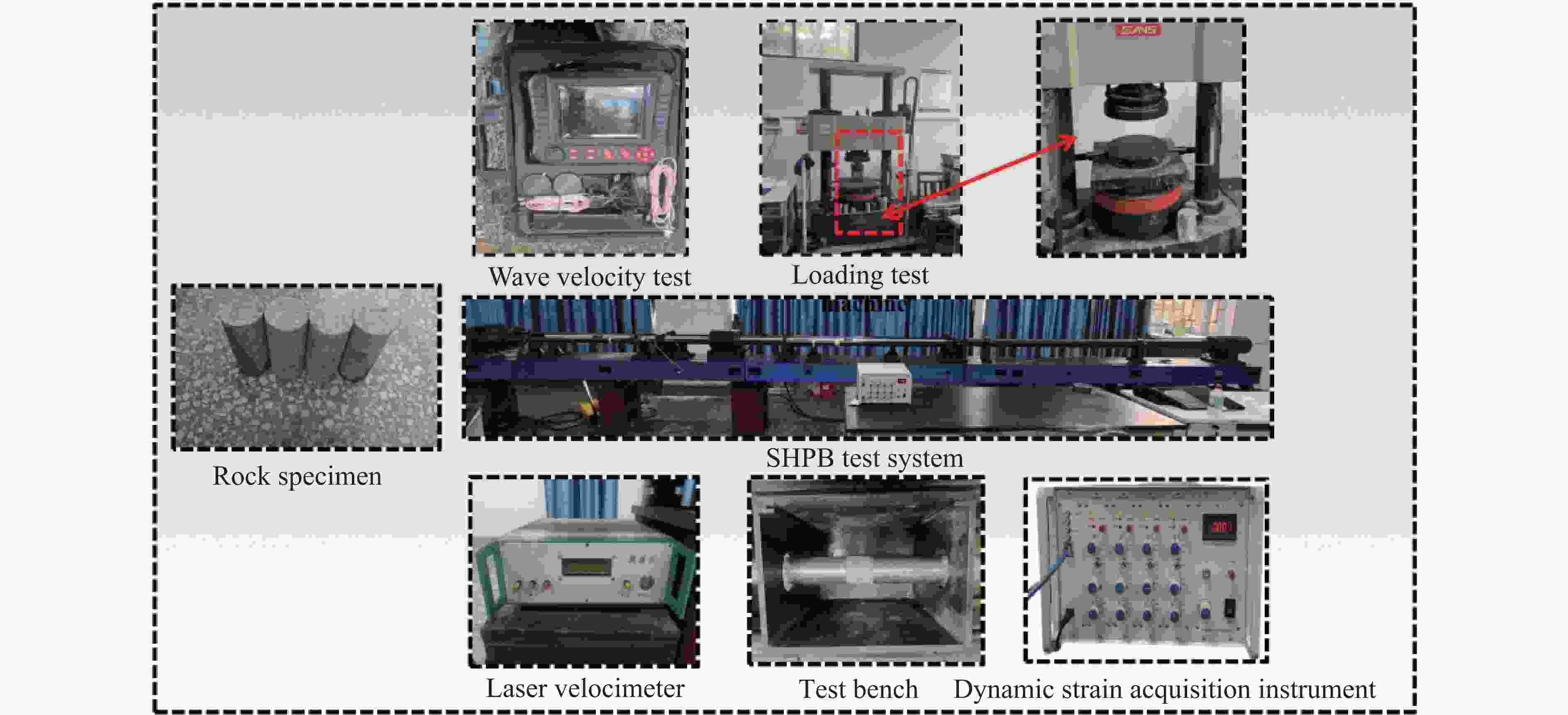
Table 3. Relevant parameters of explosives
Dt2/cm L/cm m/kg D0/(m·s−1) Explosive force value/mL Ferocity/mm Burst distance/cm 3.2 30 0.3 4500 320 16 4 表 4 爆破漏斗半径
Table 4. Blasting crater radius
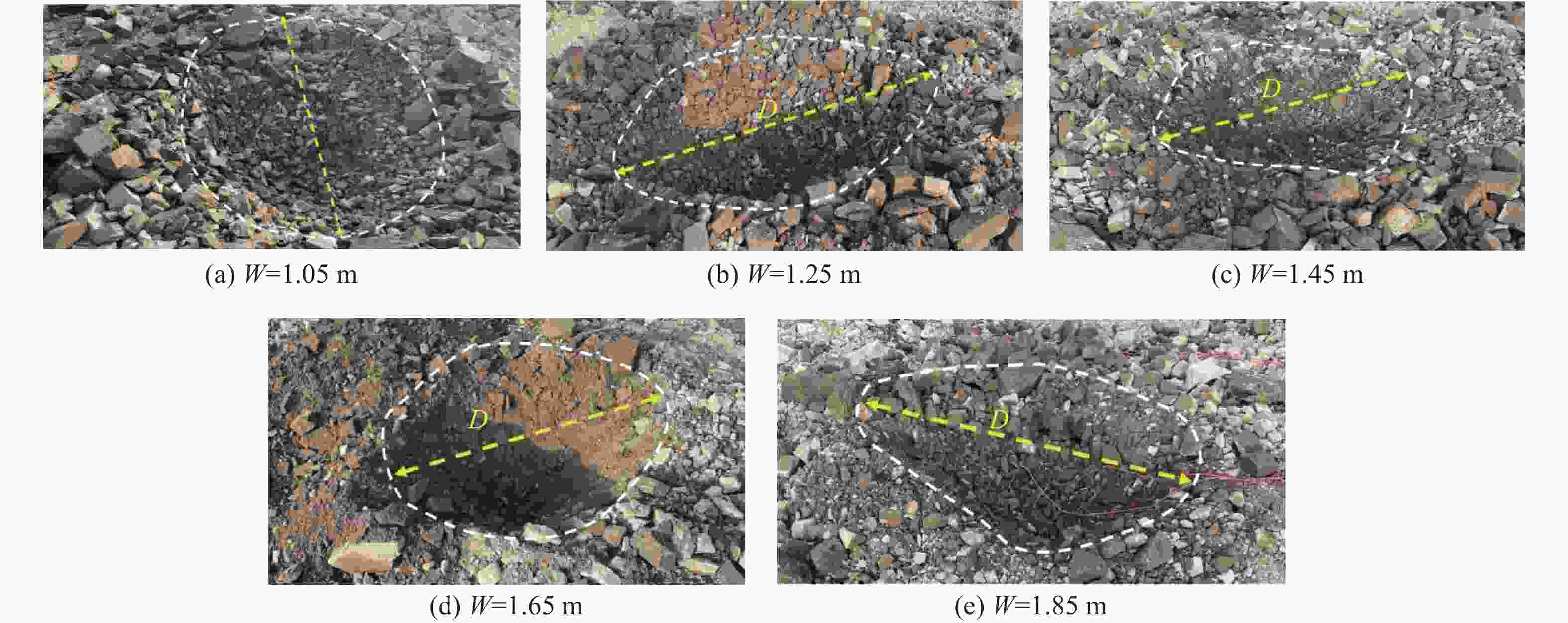
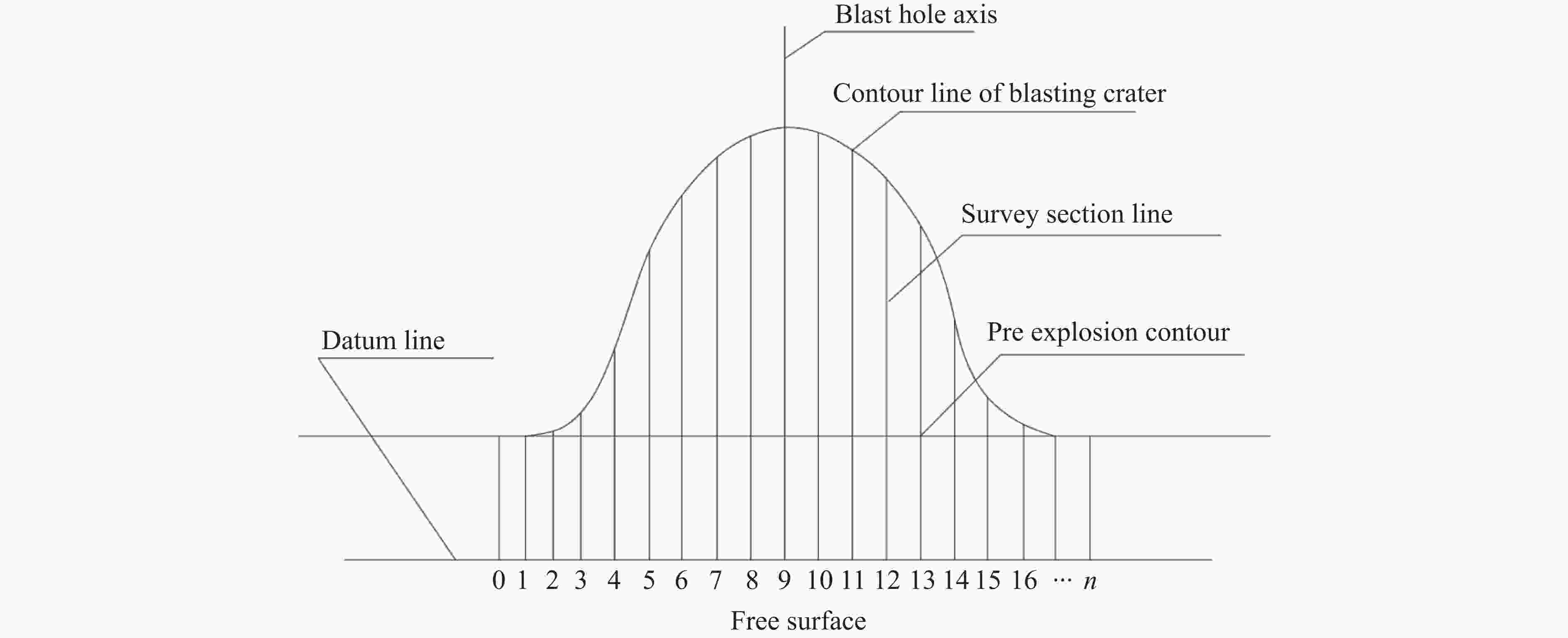
W/m r/m 1.05 0.934 1.25 0.851 1.45 0.382 1.65 0.215 1.85 0.034 表 5 现场试验数据
Table 5. Field test data
No. Hole depth/m Resistance line length/m Funnel depth/m Funnel radius/m Funnel volume/m³ 1 1.2 1.05 0.931 0.934 1.043 2 1.4 1.25 0.851 0.851 0.947 3 1.6 1.45 0.421 0.382 0.269 4 1.8 1.65 0.334 0.215 0.193 5 2.0 1.85 0.230 0.034 0.105 表 6 不同抵抗线长度下的平均块度分布
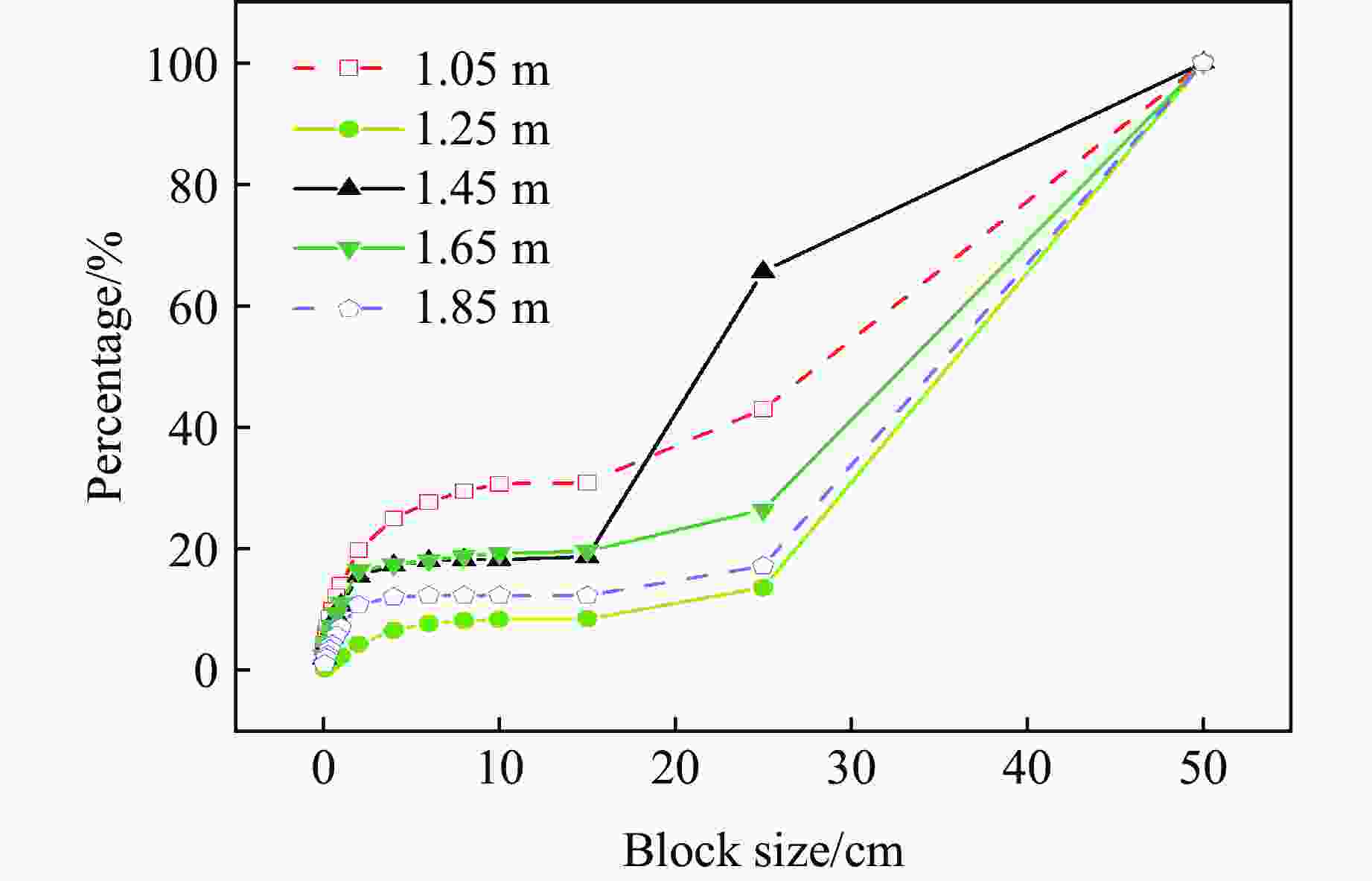
Table 6. Average block size distribution under different resistance lines
W/m d50/cm 1.05 28 1.25 36 1.45 22 1.65 34 1.85 35 -
[1] 李祥龙, 刘俊轩, 胡涛, 等. 黑岱沟露天煤矿高台阶抛掷爆破混凝土模型的相似材料配比试验研究 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2015, 40(Suppl 2): 359–366. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.0934LI X L, LIU J X, HU T, et al. Proportioning test study on similar material of concrete model of high bench cast blasting in Heidaigou open pit [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(Suppl 2): 359–366. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.0934 [2] GRAETTINGER A H, VALENTINE G A, SONDER I, et al. Maar-diatreme geometry and deposits: subsurface blast experiments with variable explosion depth [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2014, 15(3): 740–764. doi: 10.1002/2013GC005198 [3] 张俊兵, 潘卫东, 傅洪贤. 青藏铁路多年高含冰量冻土爆破漏斗的试验研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(6): 1077–1081. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.06.032ZHANG J B, PAN W D, FU H X. Experimental study on the explosion crater of ice-rich frozen soil along Qinghai-Tibet railway [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(6): 1077–1081. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.06.032 [4] 张智宇, 陈春超, 黄永辉, 等. 爆破漏斗鼓包运动模型的构建及验证 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2020, 40(8): 810–817. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.219ZHANG Z Y, CHEN C C, HUANG Y H, et al. Construction and validation for the model of bulging movement in explosion [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2020, 40(8): 810–817. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.219 [5] 王鹏, 周传波, 耿雪峰, 等. 多孔同段爆破漏斗形成机理的数值模拟研究 [J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(3): 993–997. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.03.056WANG P, ZHOU C B, GENG X F, et al. Numerical simulation of formation mechanism of multi hole and same delay time of blasting crater [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(3): 993–997. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.03.056 [6] 龙尧, 肖源杰, 陈俊桦. 基于爆破漏斗试验的单孔爆破损伤范围研究 [J]. 工程爆破, 2023, 29(6): 68–74. doi: 10.19931/j.EB.20220273LONG Y, XIAO Y J, CHEN J H. Study on damage zone of single-hole blasting based on blasting funnel test [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2023, 29(6): 68–74. doi: 10.19931/j.EB.20220273 [7] 张若棋, 丁育青, 汤文辉, 等. 混凝土HJC、RHT本构模型的失效强度参数 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2011, 25(1): 15–22. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2011.01.003ZHANG R Q, DING Y Q, TANG W H, et al. The failure strength parameters of HJC and RHT concrete constitutive models [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2011, 25(1): 15–22. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2011.01.003 [8] 何家辉, 胡义锋. 基于HJC模型的深部岩石爆破裂纹受不耦合系数影响的模拟研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2025, 44(3): 171–181. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2025.03.020HE J H, HU Y F. Simulation of deep rock blasting cracks affected by decoupling coefficient based on HJC model [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2025, 44(3): 171–181. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2025.03.020 [9] 张鑫, 刘泽功, 常帅, 等. 爆破荷载作用下煤岩本构模型参数特性研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2025, 44(5): 263–277. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2025.05.029ZHANG X, LIU Z G, CHANG S, et al. Parametric characteristics of coal rock constitutive model under blasting load [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2025, 44(5): 263–277. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2025.05.029 [10] ZHANG H, LI T C, DU Y T, et al. Theoretical and numerical investigation of deep-hole cut blasting based on cavity cutting and fragment throwing [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2021: 103854. [11] SHEN W G, ZHAO T, CROSTA G B, et al. Analysis of impact-induced rock fragmentation using a discrete element approach [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2017, 98: 33–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.07.014 [12] 李廷春, 刘洪强. 煤矿下山巷道爆破掘进技术试验研究 [J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(1): 35–40, 47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.01.006LI T C, LIU H Q. Experimental study of blasting technology of dip roadway excavation in coal mine [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(1): 35–40, 47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.01.006 [13] 毕程程. 华山花岗岩HJC本构参数标定及爆破损伤数值模拟 [D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2018.BI C C. Calibration of HJC constitutive parameters of Huashan granite and its blasting damage numerical simulation [D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2018. [14] HOLMQUIST T J, JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A computational constitutive model for concrete subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high pressures [C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Ballistics. Quebec: American Defense Preparedness Association, 1993: 591–600. [15] BANADAKI M M D. Stress-wave induced fracture in rock due to explosive action [D]. Toronto: University of Toronto, 2010. [16] 黄永辉, 占宇飞, 张洪波, 等. 极高地应力条件下光面爆破围岩损伤规律研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2025, 44(6): 104–112. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2025.06.011HUANG Y H, ZHAN Y F, ZHANG H B, et al. Damage patterns of surrounding rock under high-stress conditions in smooth blasting [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2025, 44(6): 104–112. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2025.06.011 [17] 周传波, 罗学东, 何晓光. 爆破漏斗试验在一次爆破成井中的应用研究 [J]. 金属矿山, 2005(8): 20–23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2005.08.007ZHOU C B, LUO X D, HE X G. Investigation on application of blasting crater test in shaft excavation by one blasting [J]. Metal Mine, 2005(8): 20–23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2005.08.007 [18] 江飞飞, 陈良, 李向东. 爆破漏斗体积多方法测量及其比较分析 [J]. 采矿技术, 2013, 13(4): 126–128, 153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2013.04.045JIANG F F, CHEN L, LI X D. Multi method measurement and comparative analysis of blasting funnel volume [J]. Mining Technology, 2013, 13(4): 126–128, 153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2013.04.045 [19] 孟佳乐, 黄永辉, 张智宇, 等. 基于SPH露天台阶的爆破优化 [J]. 有色金属工程, 2024, 14(5): 120–129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2024.05.016MENG J L, HUANG Y H, ZHANG Z Y. Optimization of open pit step blasting based on SPH [J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2024, 14(5): 120–129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2024.05.016 -






 下载:
下载: