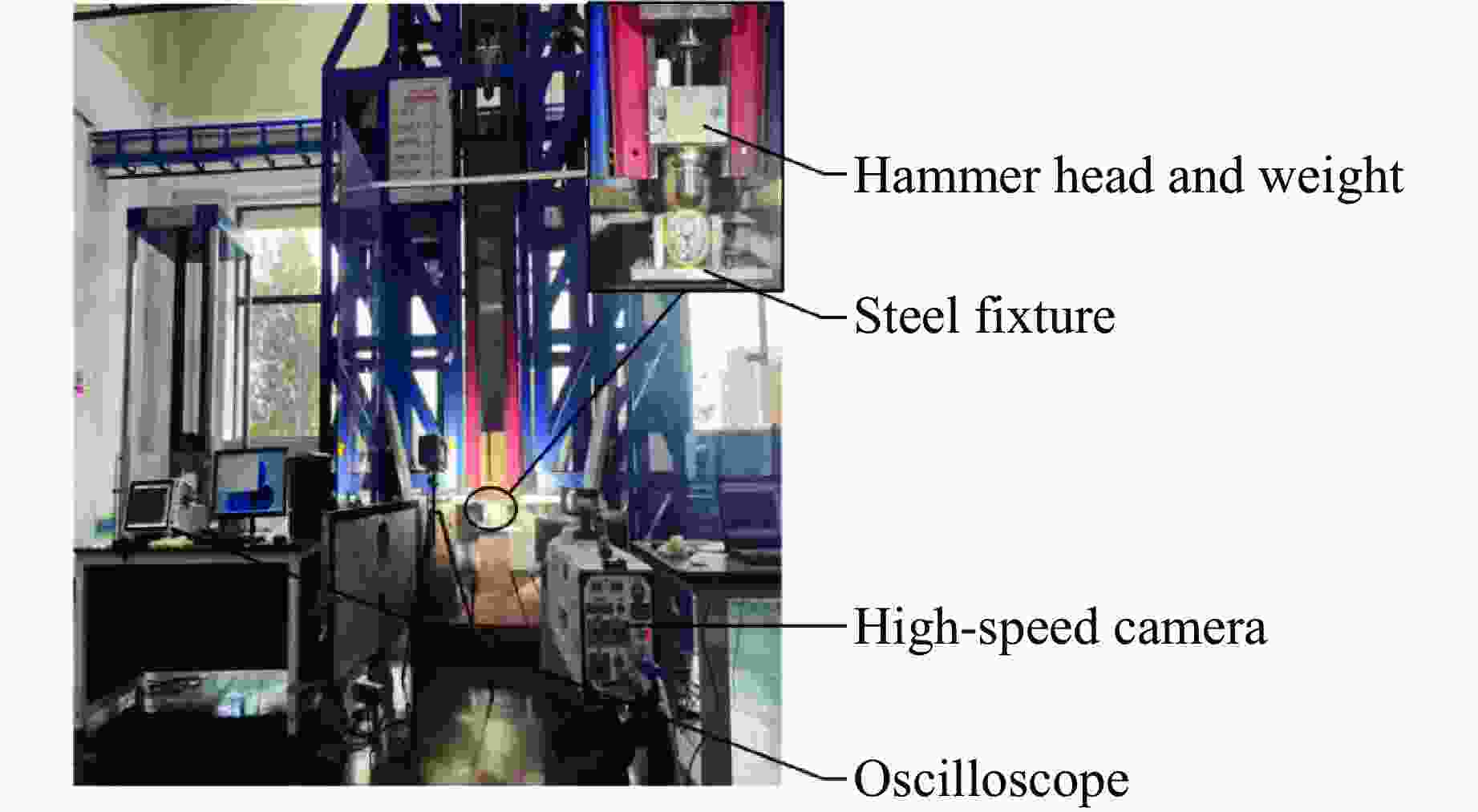
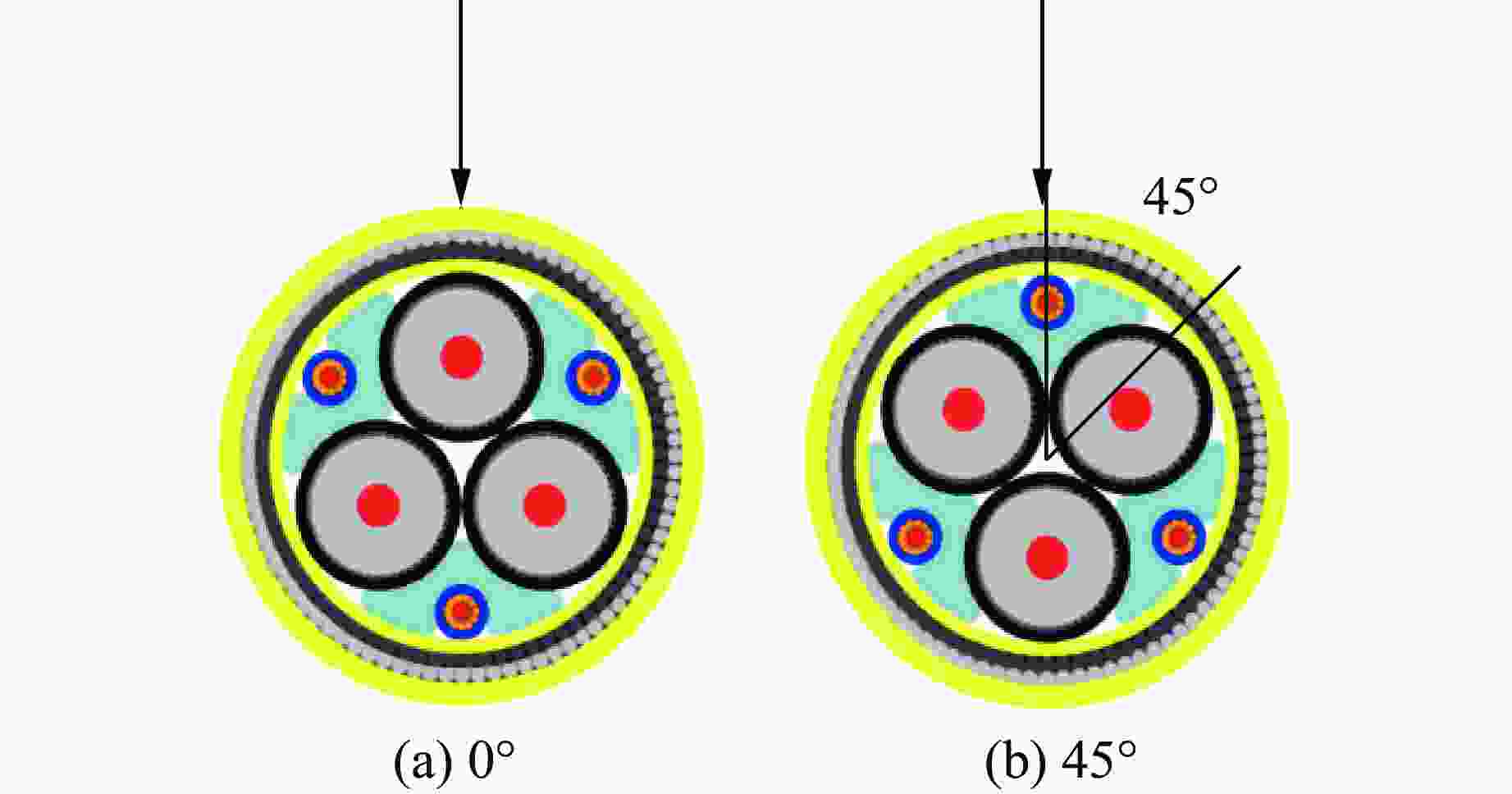
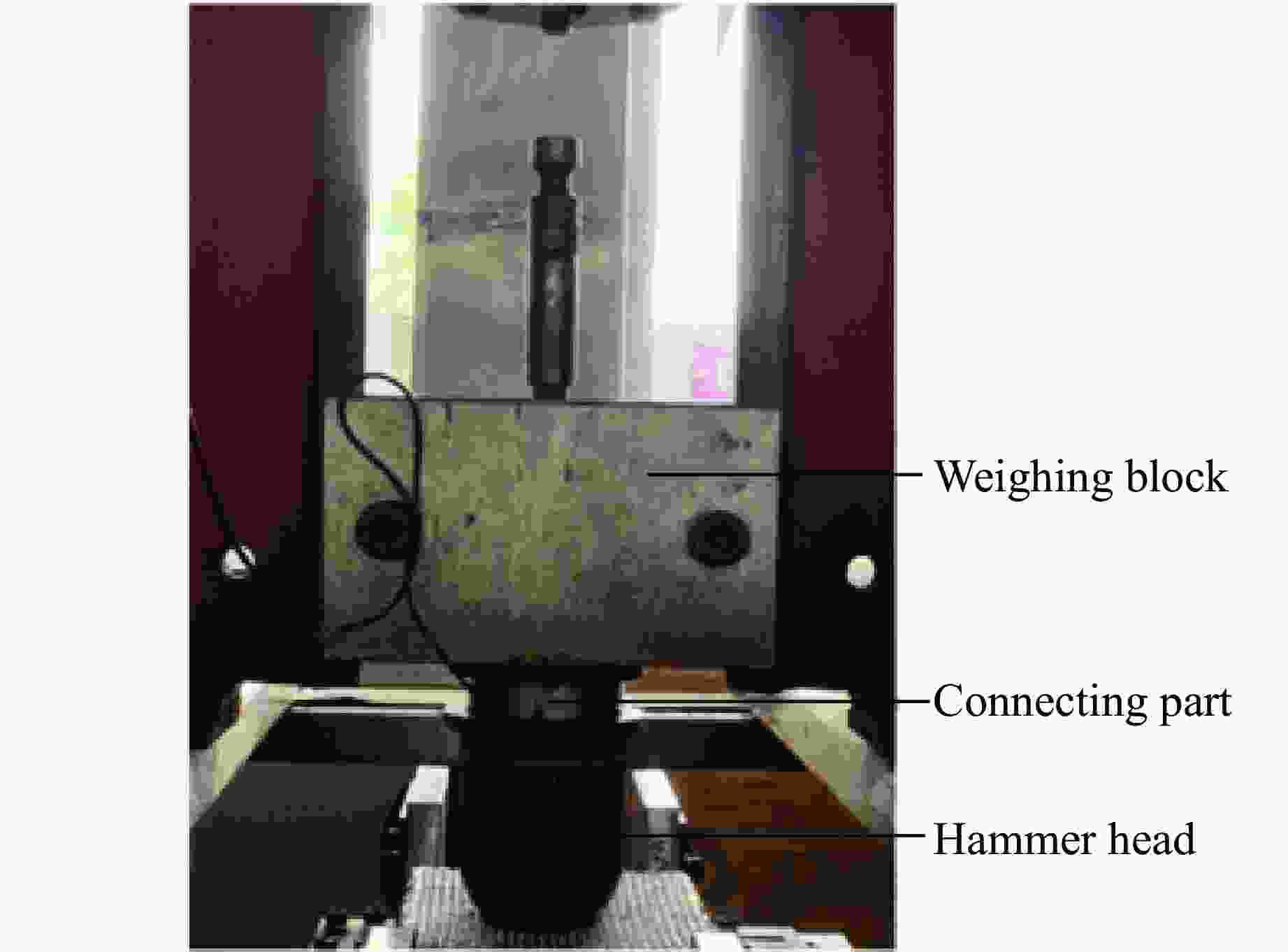
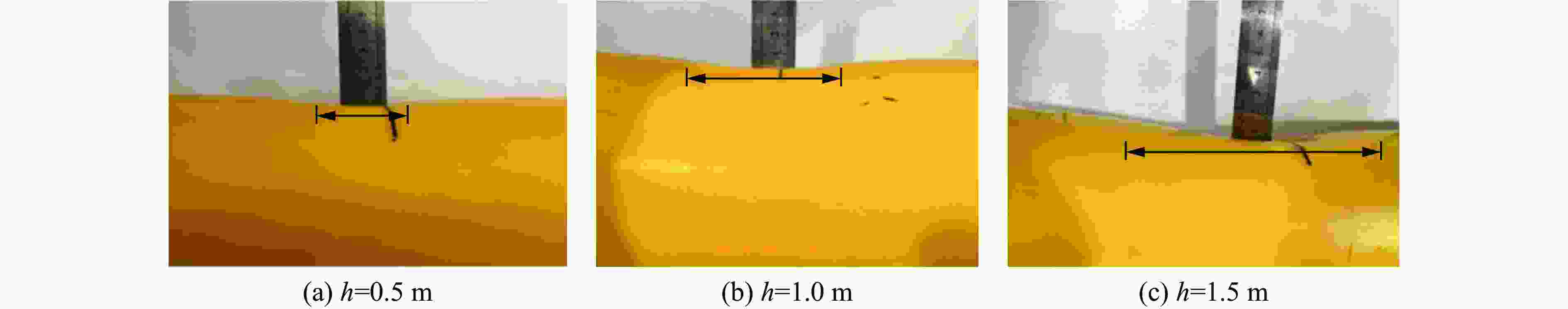
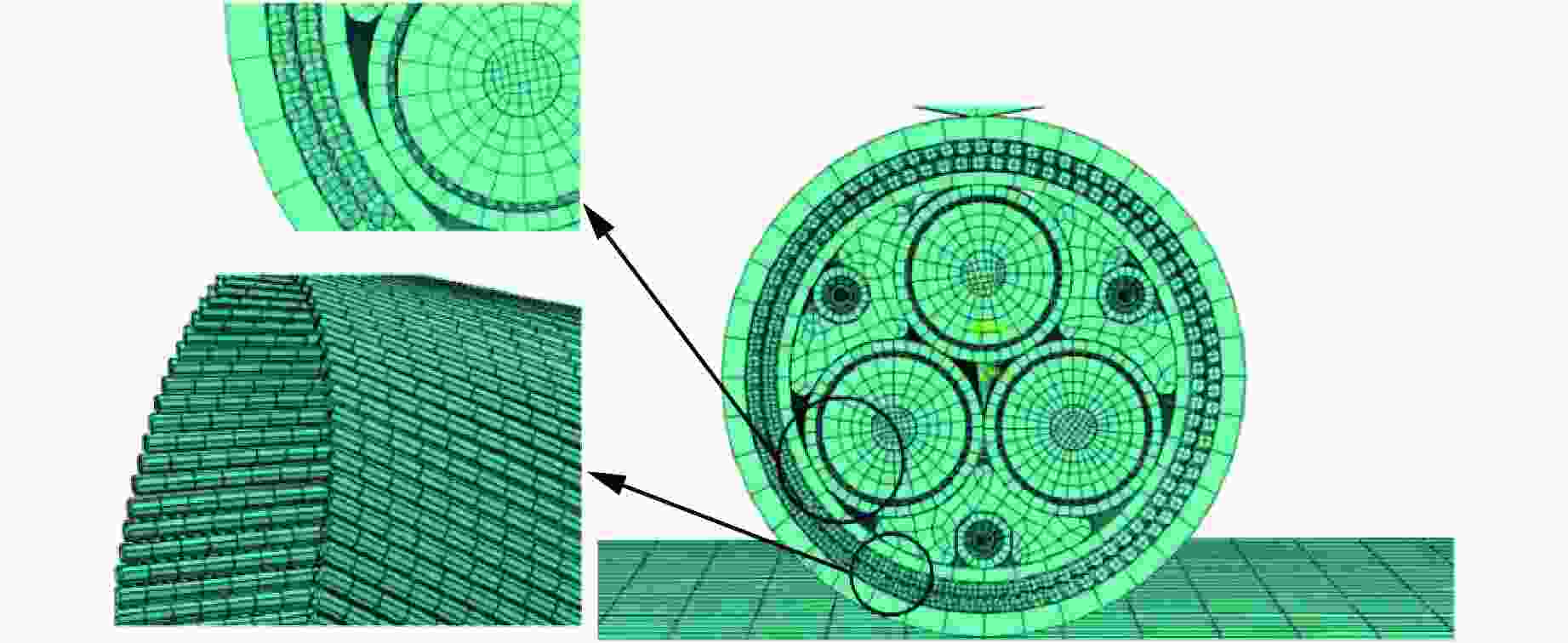
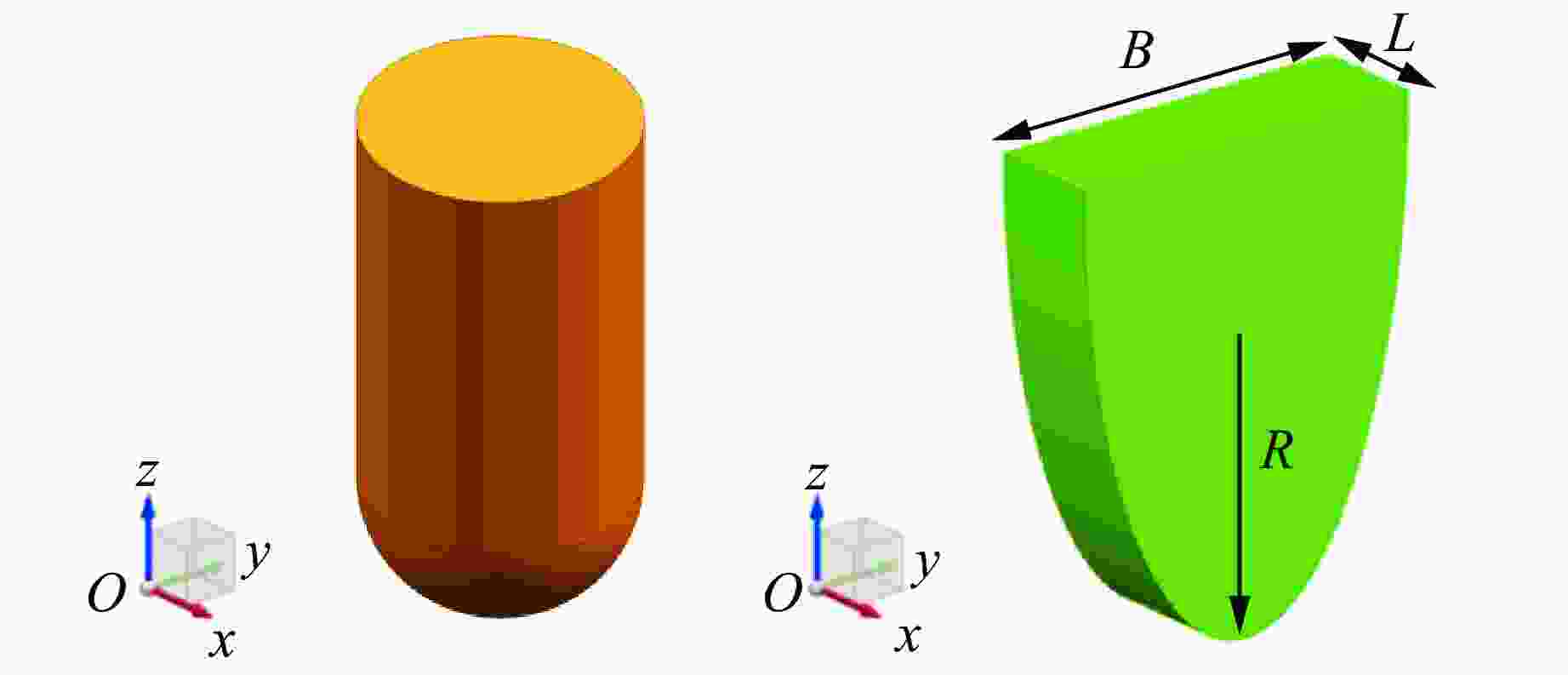Test and Simulation Study on Impact Response of Submarine Optoelectronic Composite Cables
-
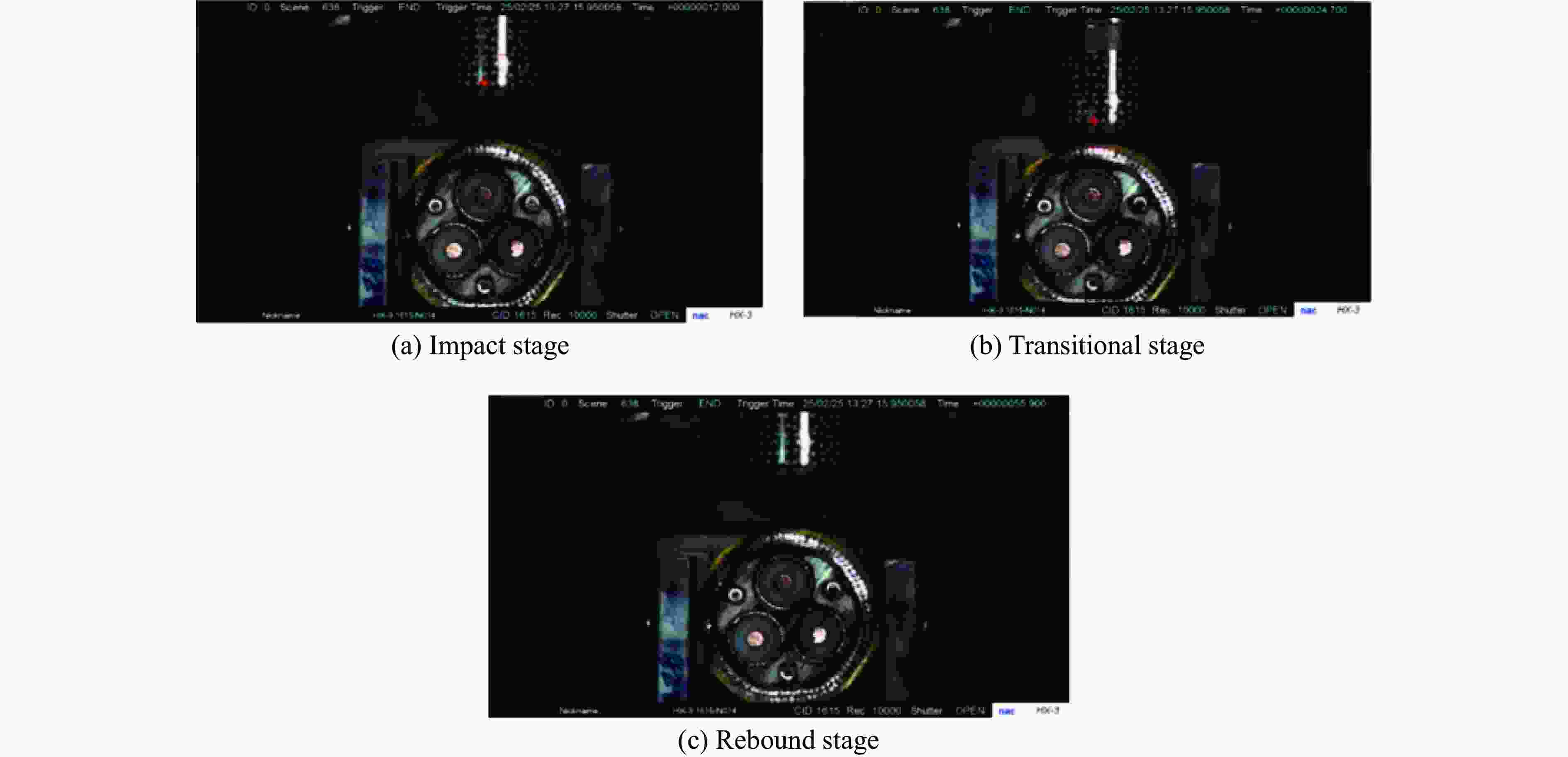
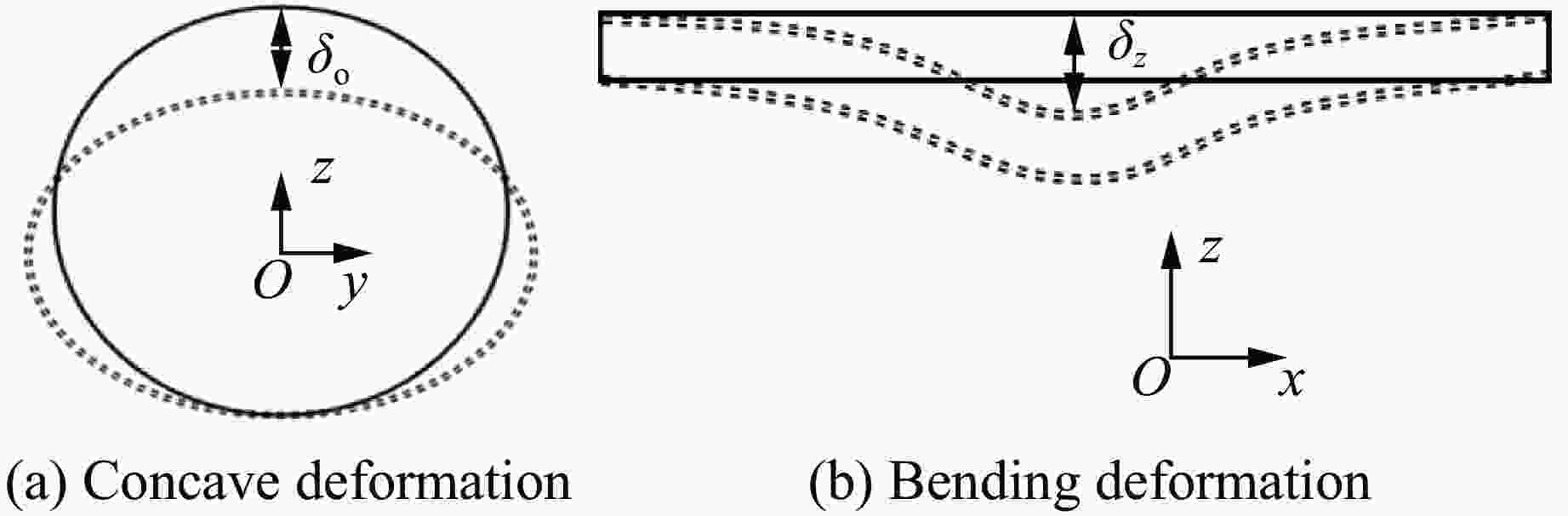
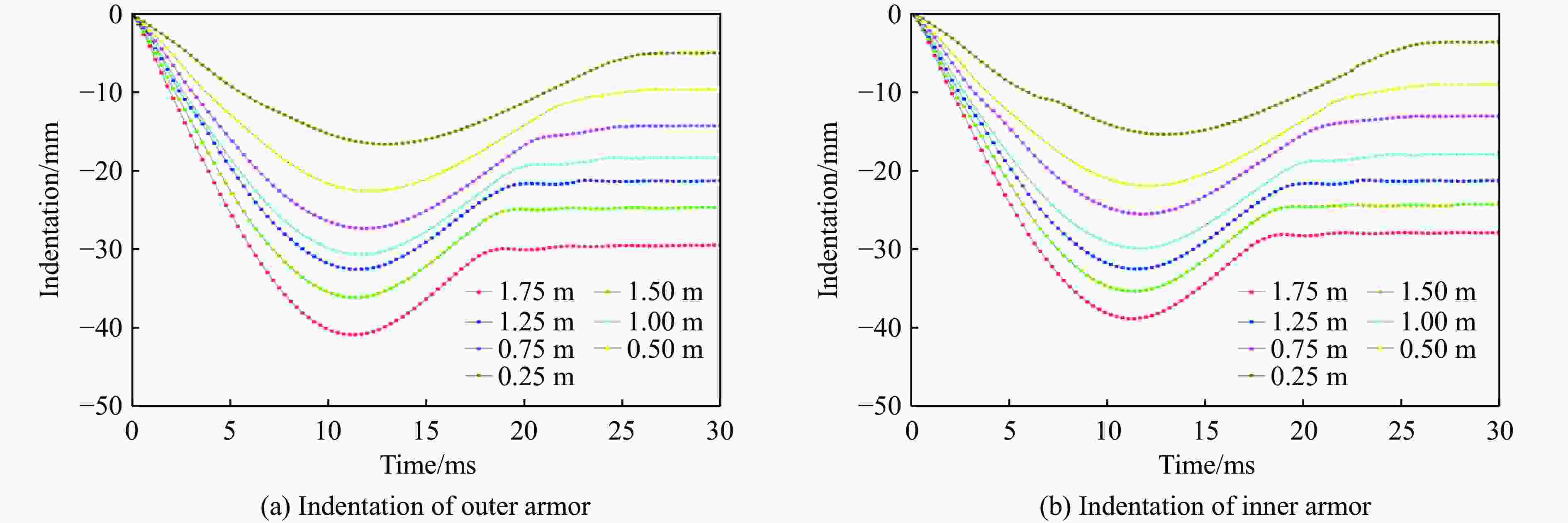
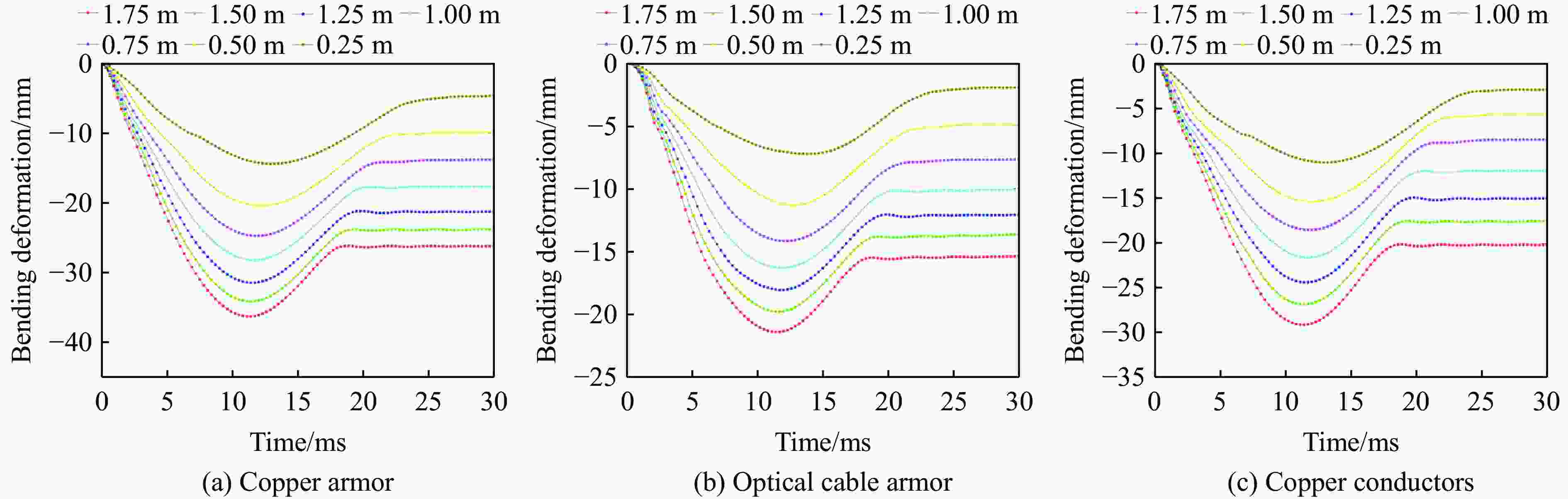
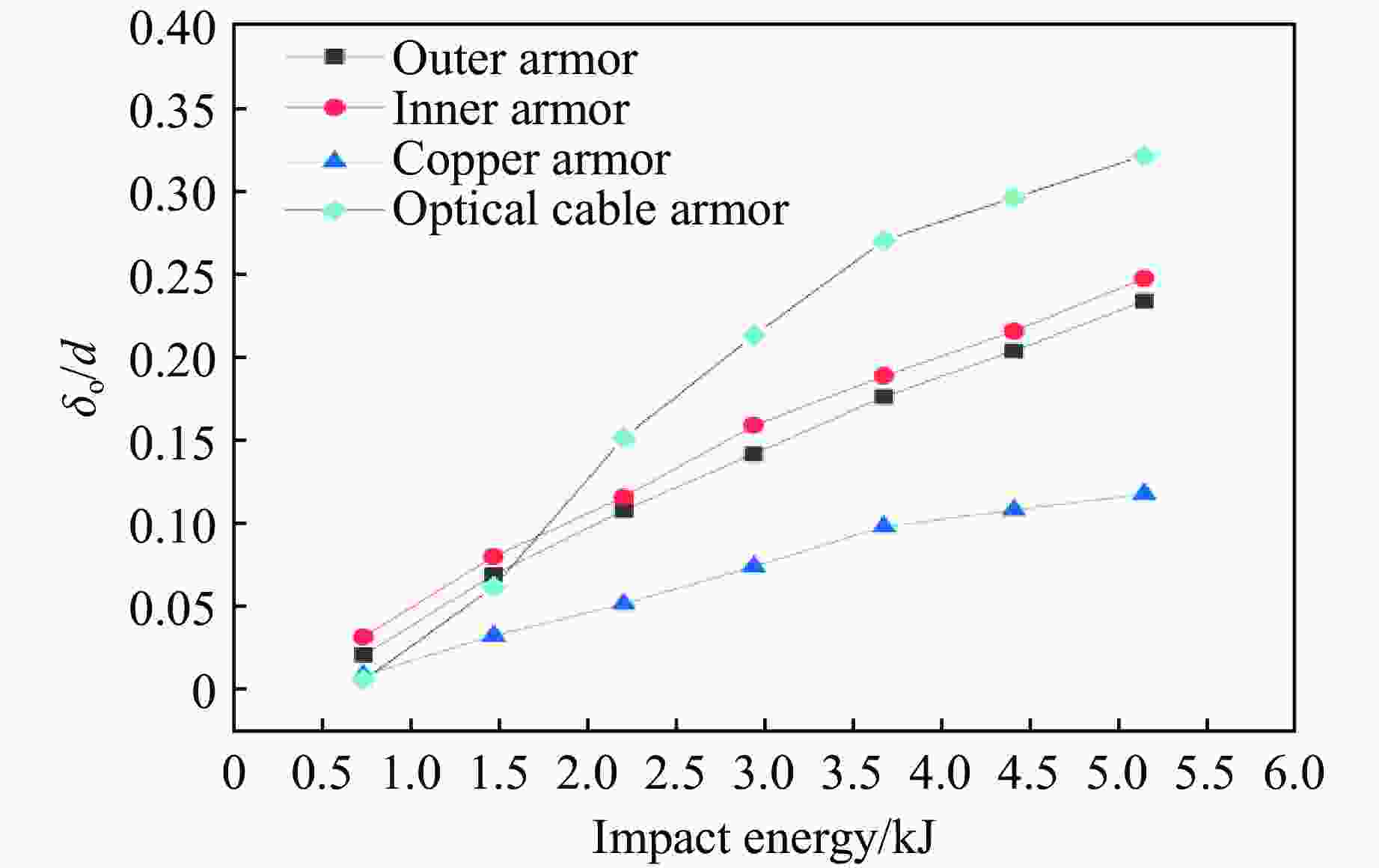
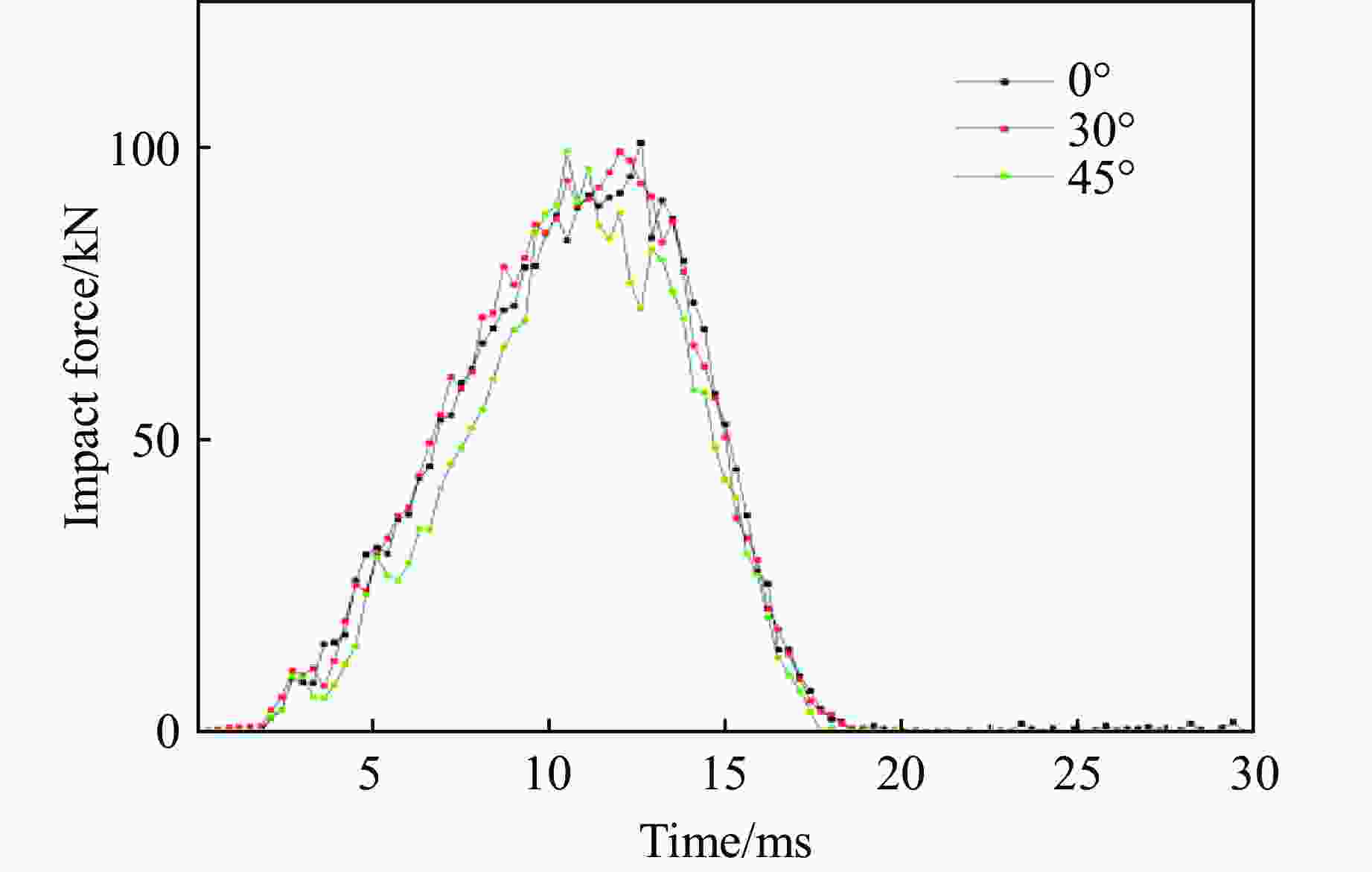
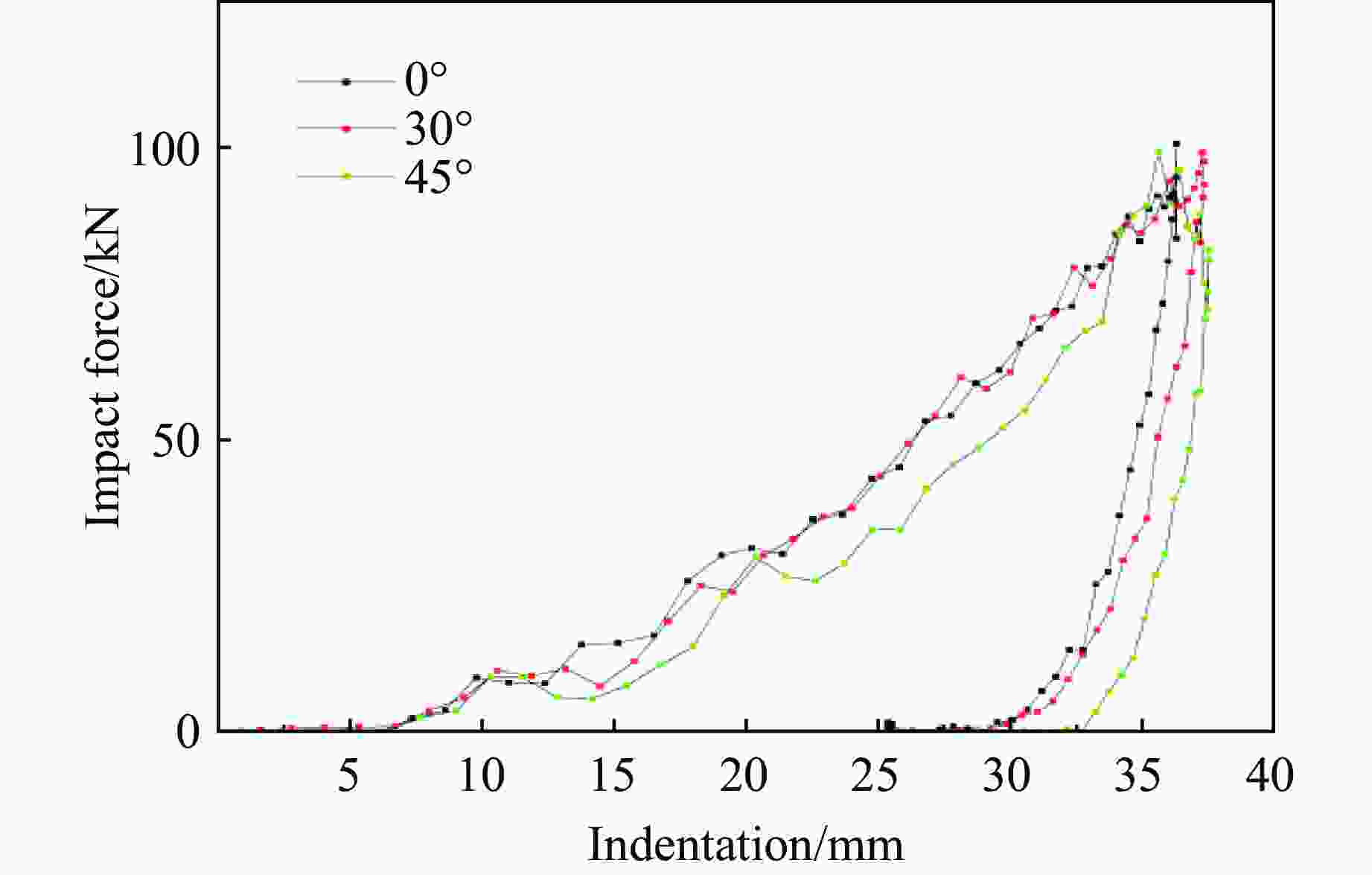
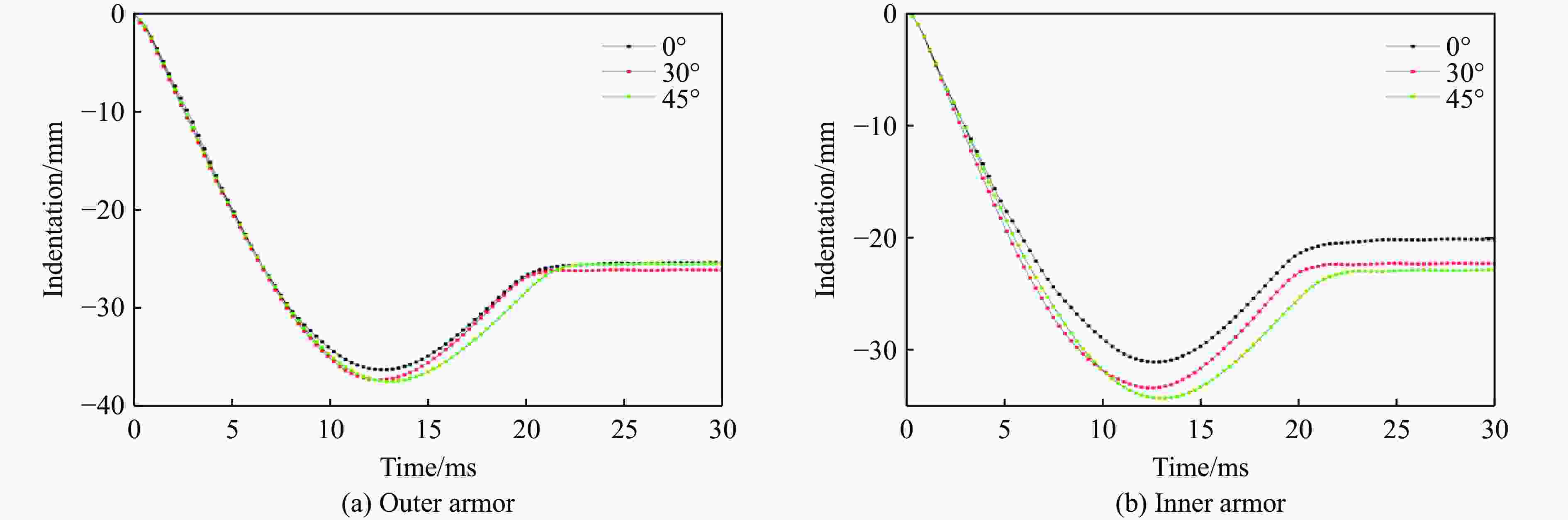
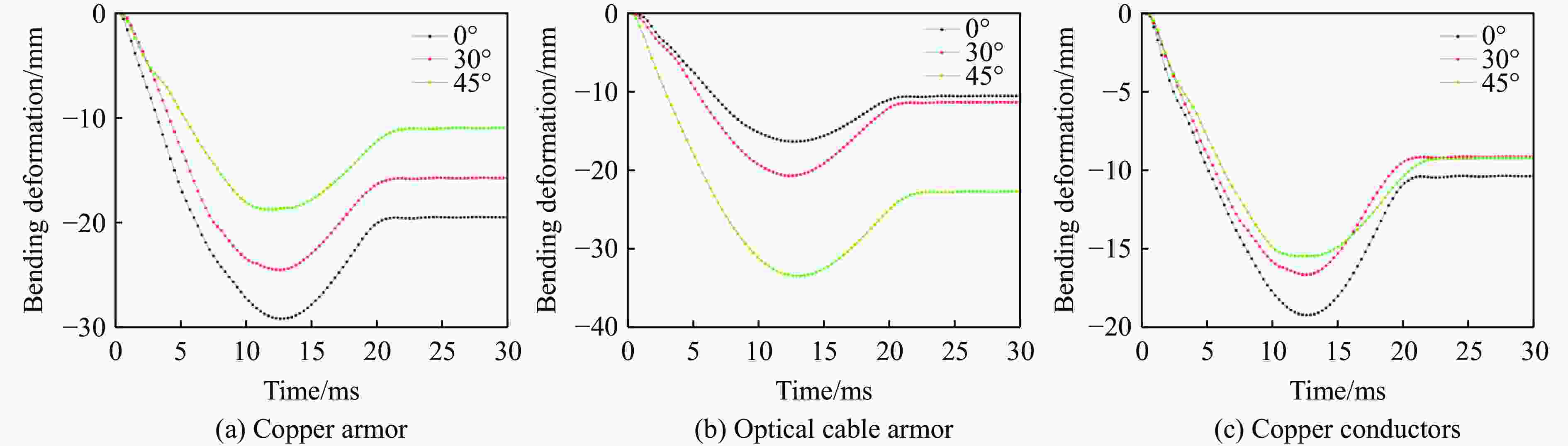
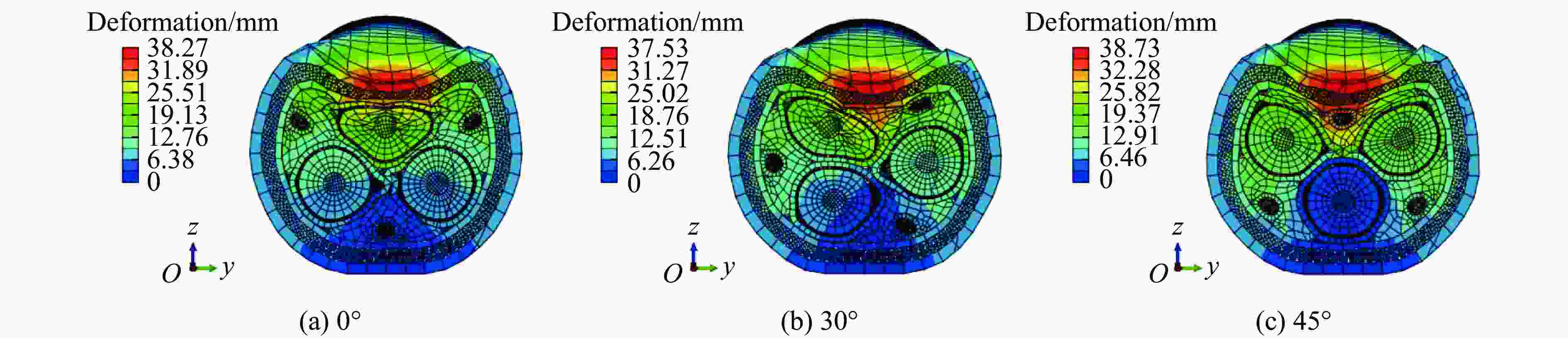
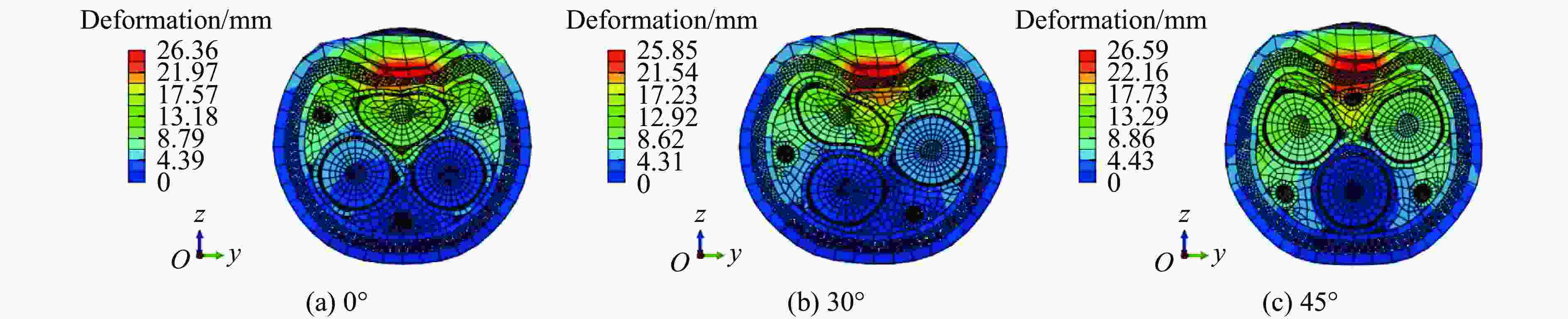
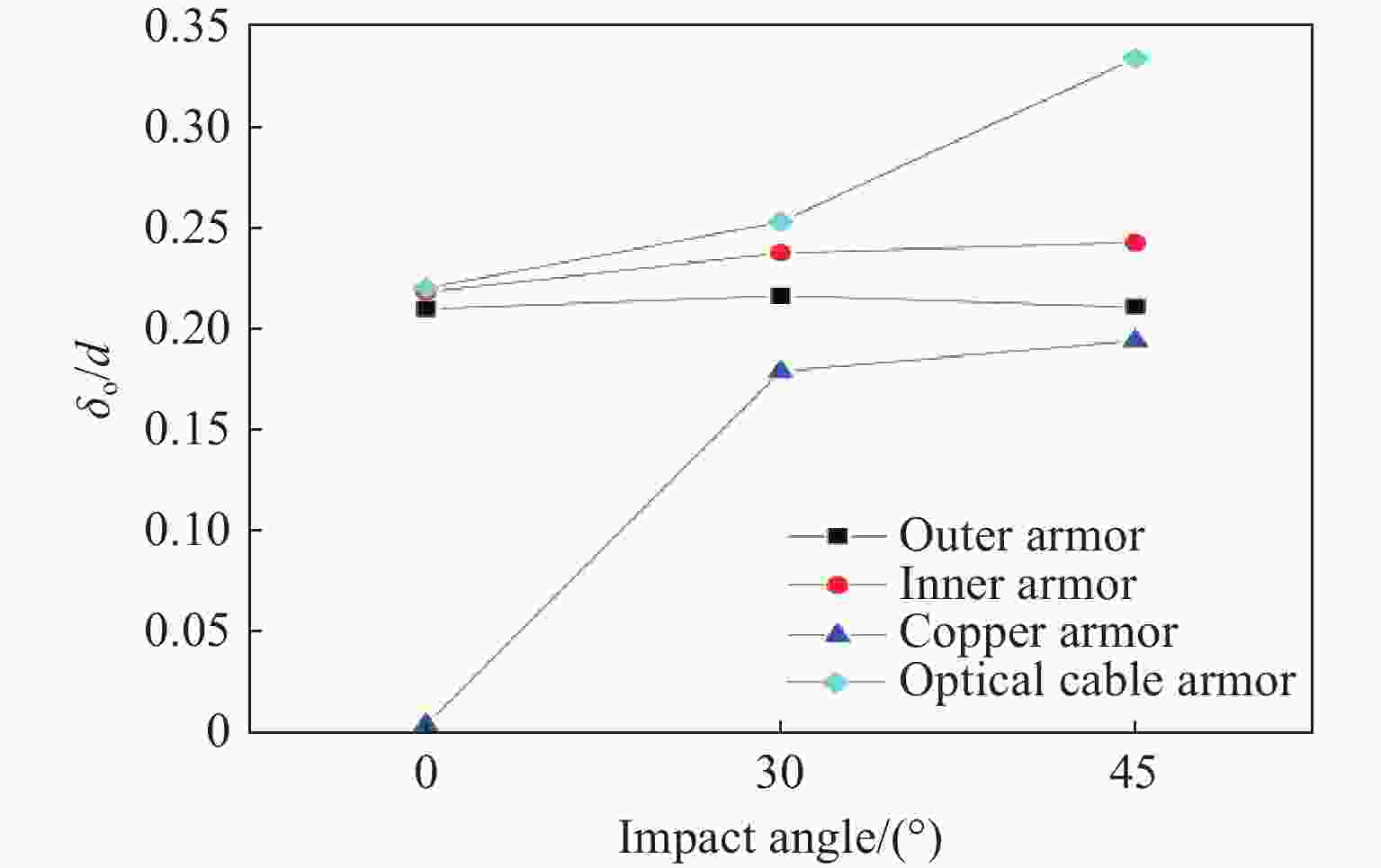
摘要: 为探讨海底光电复合电缆(submarine optical-electrical composite cable,SOCC)在不同工况下的抗冲击力学性能,对SOCC开展落锤冲击试验,揭示不同变量下其外铠装的结构变形特征,记录冲击演化过程和最大凹陷变形程度;然后,对SOCC开展有限元模拟,并与试验结果进行对比分析;最后,探讨了SOCC在不同参数影响下的变形特征。结果表明:内外铠装均发生了凹陷变形,铜铠装、铜导体和光缆铠装主要表现为弯曲变形,同时耦合局部凹陷变形;随着冲击能量的增大,金属构件达到最大变形所需时间缩短、回弹加快;冲击角度对内外铠装凹陷变形的影响不明显,对内部其他构件产生了显著破坏,其中上方构件的变形破坏最为严重。研究结果有利于对SOCC的动力学性能评估,并为工程中SOCC保护措施设计提供参考。Abstract: This thesis aims to explore the impact resistance mechanical properties of submarine optical-electrical composite cable (SOCC) under different working conditions. Firstly, a hammer impact test was carried out on SOCC to reveal the structural deformation characteristics of the outer armour under different variables, and to record the impact evolution process and the maximum degree of concave deformation; secondly, a finite element simulation analysis was carried out on SOCC, and a comparison analysis was made with the test results; lastly, the deformation characteristics of SOCC under the influence of different parameters were explored. The results show that both the inner and outer armour undergoes depression deformation, while the copper armour, copper conductor and optical cable armour mainly show bending deformation, coupled with local depression deformation. With the increase of impact energy, the time required for metal components to reach the maximum deformation decreases, and the faster the rebound is; the impact angle does not have a significant effect on the depression deformation of the inner and outer armour, and produces significant damage to other internal components, of which the upper component has the most serious deformation damage. This paper is conducive to the evaluation of the dynamic performance of SOCC and provides a reference for the design of SOCC protection measures in engineering.
-
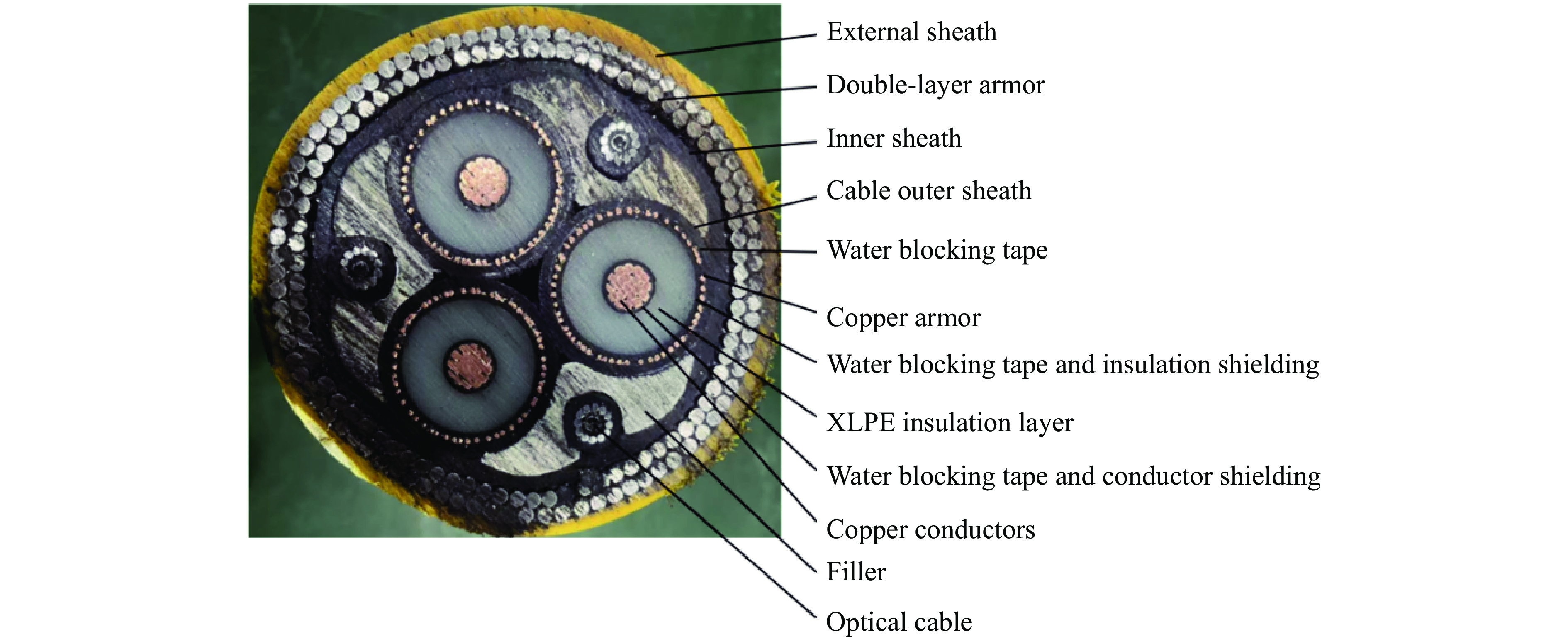
表 1 SOCC尺寸参数
Table 1. Dimension parameters of SOCC
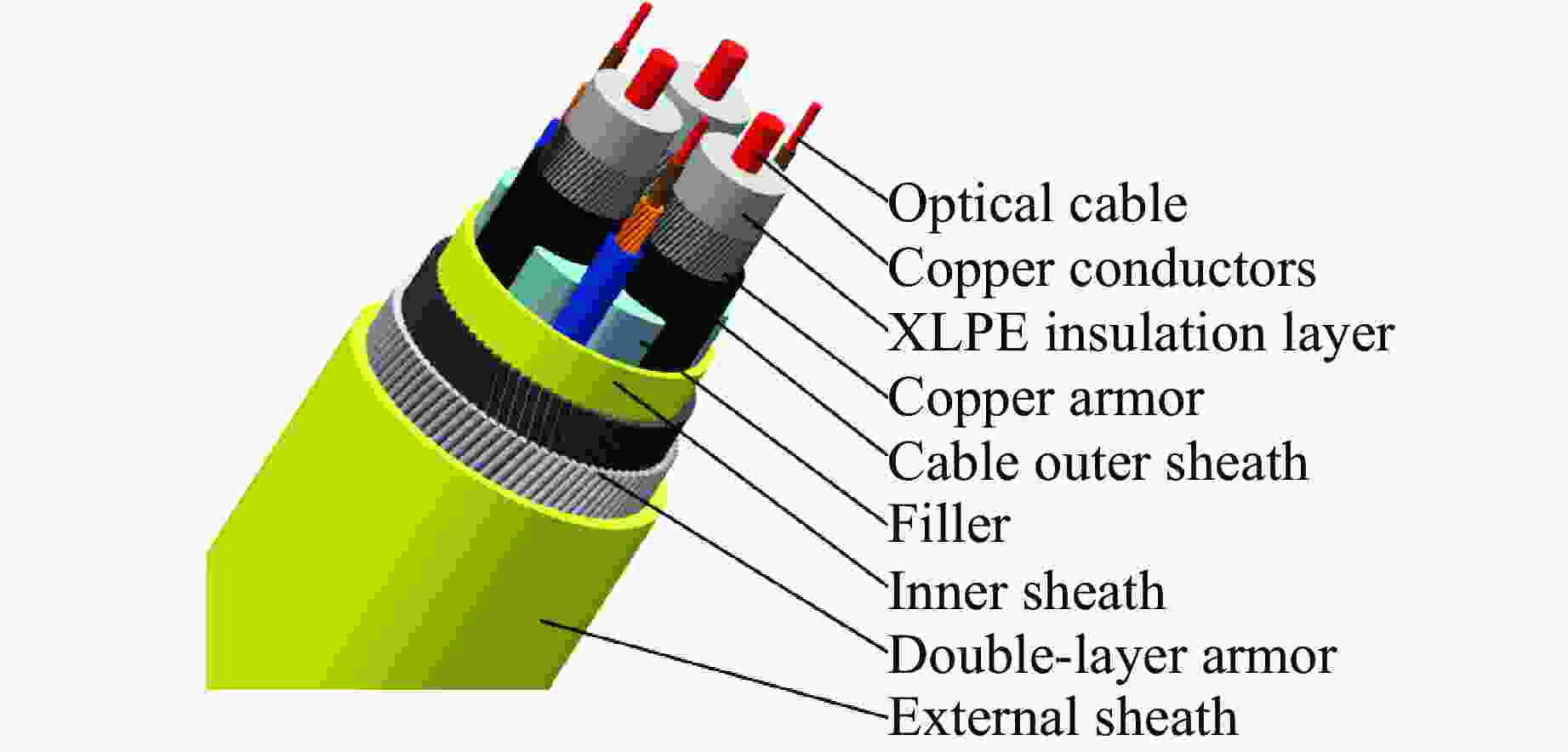
Position Component type Raw materials Quantity hn/mm douter/mm θ/(°) Optical cable Optical fiber Inner sheath Polyethylene 1.0 5.8 Armor Steel 2.0 9.8 10 External sheath Polyethylene 2.5 14.8 Power cable Copper conductors Copper 3 11.4 Water-blocking tape Semiconductor water-blocking tape 0.3 11.4 Conductor shielding Semiconductor compounds 0.8 13.0 XLPE insulation layer Crosslinked polyethylene 10.5 34.0 Insulated shielding Semiconductor compounds 1.0 36.0 Water-blocking tape Semiconductor water-blocking tape 0.3 36.9 Copper armor Copper 52 1.1 39.2 10 Copper belt Copper 0.1 39.5 Water-blocking tape Semiconductor water-blocking tape 0.3 40.4 Cableouter sheath Polyethylene 2.5 45.4 Inner layer Filler Polyethylene 97.9 Inner cover tape Nylon tape 0.3 98.8 Inner sheath Polyethylene 3.0 104.8 Double-layer armor Armor Steel 77/84 4.0 112.8/121.7 10 Adhesive tape Nylon tape 0.3 113.7/122.6 External sheath Polyethylene 5.0 132.6 表 2 重物尺寸
Table 2. Dimensions of weight
No. Photo Shape Mass/kg Dimension/(mm×mm) Material Hardness/MPa 1 
Cylinder 6.7 $ \mathrm{\varnothing } $100×150 Cr12MoV 4.71 2 
Semi-sphere 6.0 $ \mathrm{\varnothing } $100×150 Cr12MoV 4.71 表 3 试验分组情况
Table 3. Test grouping situation
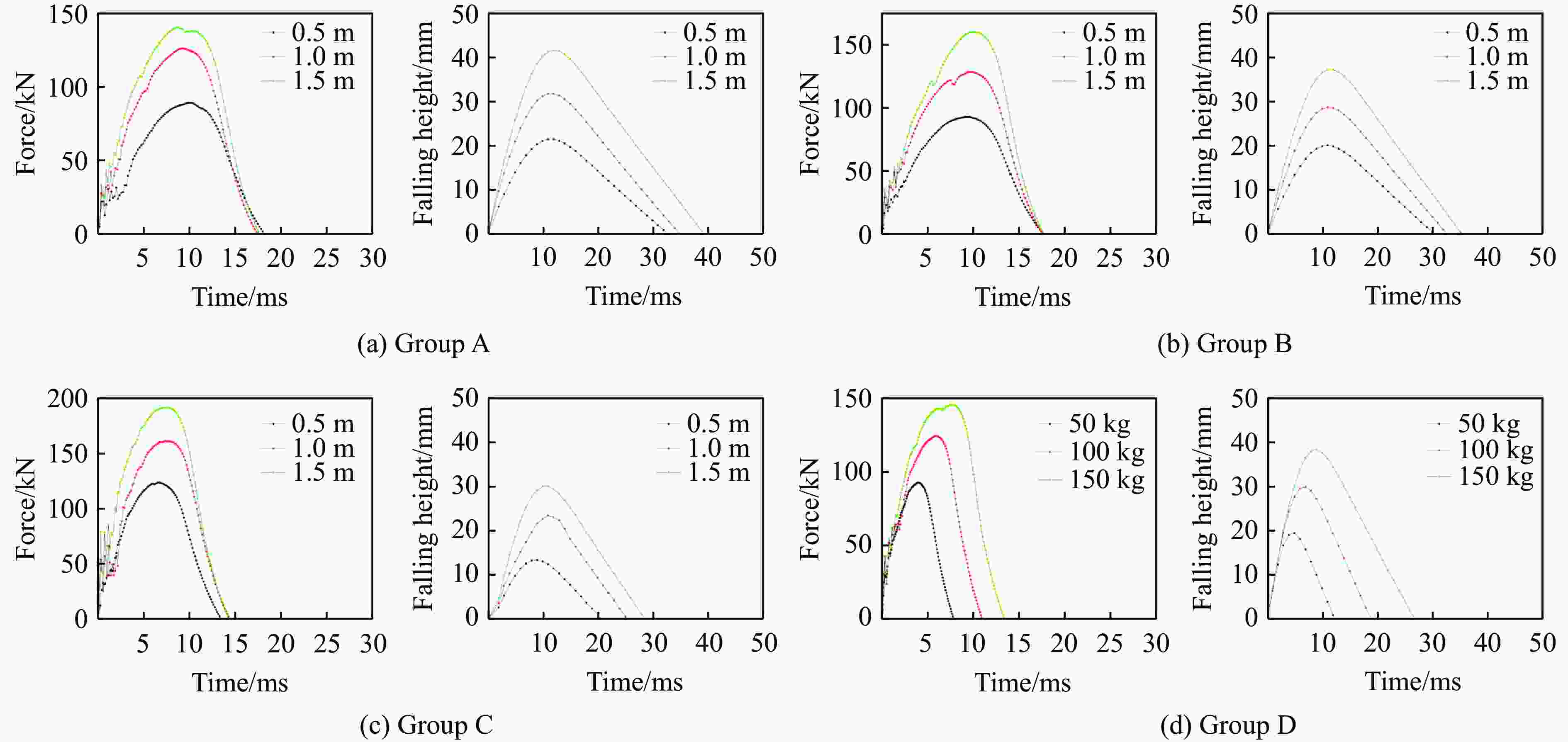
Group Weight shape Impact angle/(°) Mass/kg h/m A Semi-sphere 0 300 0.5 1.0 1.5 B Semi-sphere 45 300 0.5 1.0 1.5 C Cylinder 0 300 0.5 1.0 1.5 D Semi-sphere 0 50 3.0 100 3.0 150 3.0 表 4 试验结果
Table 4. Test results
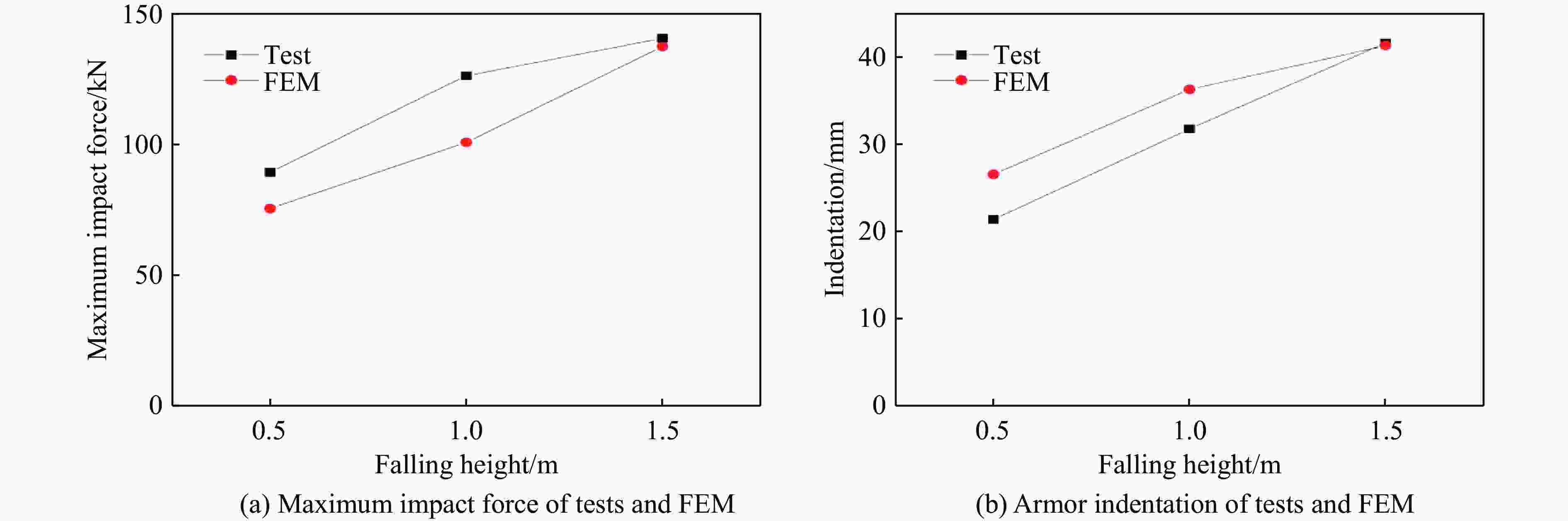
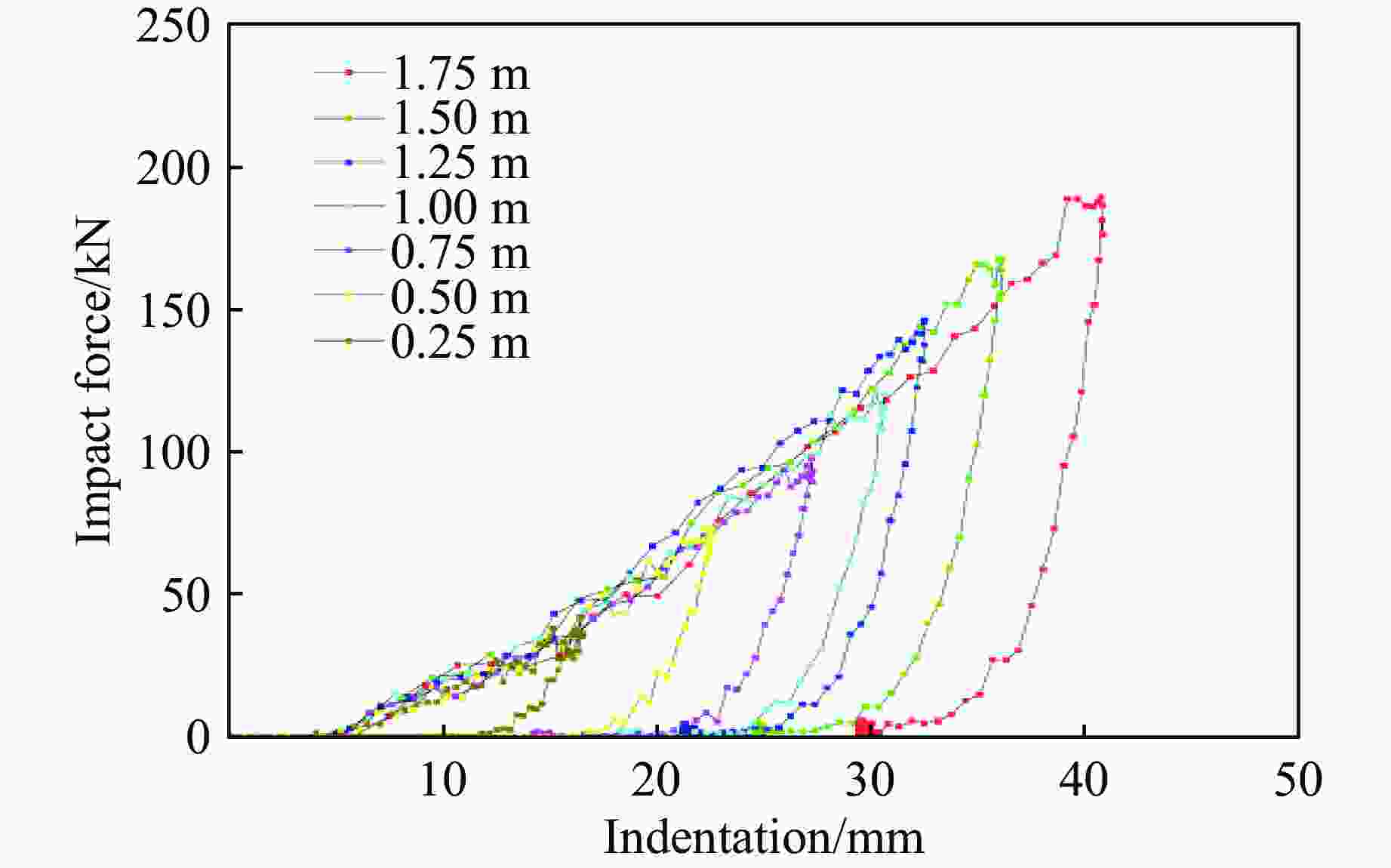
Group Weight shape Impact angle/(°) Mass/kg h/m Maximum deformation of
the outer armor/mmPeak force of
impact/kNA Semi-sphere 0 300 0.5 21.42 89.2 1.0 31.79 126.1 1.5 41.63 140.4 B Semi-sphere 45 300 0.5 20.03 92.7 1.0 28.67 128.3 1.5 37.21 159.8 C Cylinder 0 300 0.5 13.87 123.6 1.0 22.02 161.1 1.5 30.09 191.7 D Semi-sphere 0 50 3.0 19.21 92.8 100 3.0 29.99 124.5 150 3.0 38.33 145.8 Material Density/(kg·m−3) Elastic modulus/GPa Poisson’s ratio Yield strength/MPa XLPE 930 0.3 0.30 20 PE 958 0.883 0.46 20 Cu 8960 108 0.33 305 Steel 7960 210 0.30 340 表 6 冲击能量参数
Table 6. Impact energy parameters
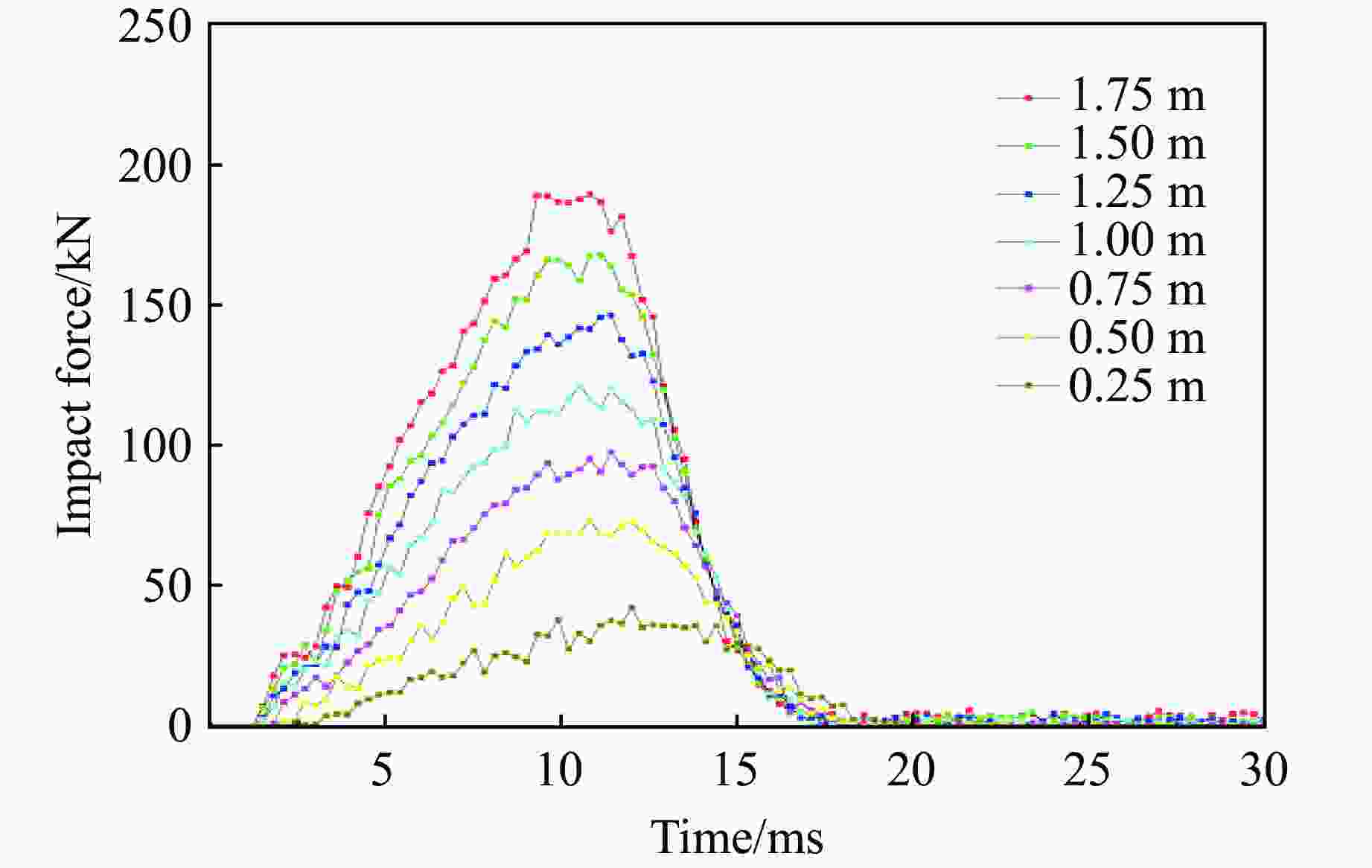
Falling height/m Mass/kg Velocity/(m·s–1) Impact energy/kJ 0.25 300 2.213 0.735 0.50 300 3.130 1.470 0.75 300 3.830 2.205 1.00 300 4.427 2.940 1.25 300 4.949 3.675 1.50 300 5.422 4.410 1.75 300 5.856 5.145 -
[1] 阎军, 胡海涛, 苏琦, 等. 海洋电缆中关键力学问题的研究进展与展望 [J]. 力学学报, 2022, 54(4): 846–861. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-22-113YAN J, HU H T, SU Q, et al. Prospect and progression of key mechanical problems in marine cables [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2022, 54(4): 846–861. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-22-113 [2] 王少华, 阎黎冰, 李特, 等. 交流500 kV交联聚乙烯绝缘海缆设计关键问题 [J]. 高压电器, 2018, 54(8): 225–230, 236. doi: 10.13296/j.1001-1609.hva.2018.08.035WANG S H, YAN L B, LI T, et al. Key problems of design for AC 500 kV cross-linked polyethylene insulation submarine cable [J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2018, 54(8): 225–230, 236. doi: 10.13296/j.1001-1609.hva.2018.08.035 [3] PENG L J, XU S Y, HE M C. Numerical simulation study on through-anchor cable reinforcement control of inter-roadway coal pillars in double-roadway layouts [J]. Sustainability, 2025, 17(6): 2416. doi: 10.3390/su17062416 [4] SUN X M, WANG L, CUI L, et al. Numerical study on mechanical properties and energy conversion characteristics of soft rock anchored by CRLD anchor cables containing random cracks [J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2025, 25(6): 04025079. doi: 10.1061/IJGNAI.GMENG-10281 [5] TAORMINA B, BALD J, WANT A, et al. A review of potential impacts of submarine power cables on the marine environment: knowledge gaps, recommendations and future directions [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 96: 380–391. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2018.07.026 [6] 李晓骏, 张维佳, 左干清, 等. 深水区大截面海底电缆打捞受力分析 [J]. 应用科技, 2022, 49(6): 86–91. doi: 10.11991/yykj.202208017LI X J, ZHANG W J, ZUO G Q, et al. Analysis of lifting up force of large section submarine cable in deep water [J]. Applied Science and Technology, 2022, 49(6): 86–91. doi: 10.11991/yykj.202208017 [7] CHANG H C, CHEN B F. Mechanical behavior of submarine cable under coupled tension, torsion and compressive loads [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 189: 106272. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106272 [8] 祝茂宇, 于治雨, 肖龙, 等. 不同填充形式对动态海底电缆力学性能的影响 [J]. 海洋工程装备与技术, 2022, 9(4): 10–17. doi: 10.12087/oeet.2095-7297.2022.04.02ZHU M Y, YU Z Y, XIAO L, et al. Influence of different filling forms on mechanical properties of dynamic submarine cables [J]. Ocean Engineering Equipment and Technology, 2022, 9(4): 10–17. doi: 10.12087/oeet.2095-7297.2022.04.02 [9] VASILESCU V F, DINU D. Installation of submarine cables in the offshore wind industry and their impact on the marine environment [J]. Journal of Marine Technology and Environment, 2021, 1: 43–51. doi: 10.53464/JMTE.01.2021.07 [10] LIU Z, IGLAND R, BRUASETH S. Local and global assessments of a subsea riser-spool connection under dropped impact loads [J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2021, 1201: 012049. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/1201/1/012049 [11] HOU F H, CHEN Y F, YAN Y F, et al. Structural response and damage assessment method for subsea pipe-in-pipe subjected to anchor impact [J]. Marine Structures, 2025, 99: 103714. doi: 10.1016/j.marstruc.2024.103714 [12] TIAN Y H, CHAI W S, EL BORGI S, et al. Assessment of submarine pipeline damages subjected to falling object impact considering the effect of seabed [J]. Marine Structures, 2021, 78: 102963. doi: 10.1016/j.marstruc.2021.102963 [13] ZHAO E J, NIE C H, HE L, et al. Numerical study on dynamic responses of submarine pipeline and porous seabed under internal solitary waves [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 320: 120285. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.120285 [14] MAO Y D, YANG Z X, WANG G, et al. A study on the mechanical behavior of umbilical cables under impact loads using experimental and numerical methods [J]. Marine Structures, 2025, 99: 103700. doi: 10.1016/j.marstruc.2024.103700 [15] OSTHOFF D, HEINS E, GRABE J. Impact on submarine cables due to ship anchor-soil interaction [J]. Geotechnik, 2017, 40(4): 265–270. doi: 10.1002/gete.201600027 [16] GAO Q, DUAN M L, LIU X X, et al. Damage assessment for submarine photoelectric composite cable under anchor impact [J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2018, 73: 42–58. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2018.01.006 [17] ZHANG T, LI L T, DU A Q, et al. Research on anchor damage and protection of three-core composite submarine cable considering impact angle [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 265: 112668. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112668 [18] WANG F W, DAI Z L, NAKAHARA Y, et al. Experimental study on impact behavior of submarine landslides on undersea communication cables [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 148: 530–537. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.11.050 [19] ZHOU H, YAN X, HU D A, et al. A hamiltonian global nodal position finite element method for dynamics analysis of submarine cables [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 266: 112992. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112992 [20] 国家技术监督局. 海军锚: GB/T 545—1996 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1996.State Bureau of Technical Supervision. Admiralty anchor: GB/T 545—1996[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1996. [21] OPGÅRD M F. Torsion instability of dynamic cables during installation [D]. Trondheim: Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2017. [22] TRAVANCA J, HAO H. Numerical analysis of steel tubular member response to ship bow impacts [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 64: 101–121. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.10.007 [23] YAMADA H, SHIMIZU Y, OGASAWARA N, et al. Effect of strain rate on load-displacement relations by instrumented sharp indentation [J]. Journal of the Japanese Society for Experimental Mechanics, 2012, 12(2): 88–93. doi: 10.11395/jjsem.12.88 [24] WASKITO R, ARTANA K B, PRATIWI E. Risk assessment of Subsea pipeline using standard DNVGL-RP-F107 [J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2020, 557: 012069. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/557/1/012069 -






 下载:
下载: