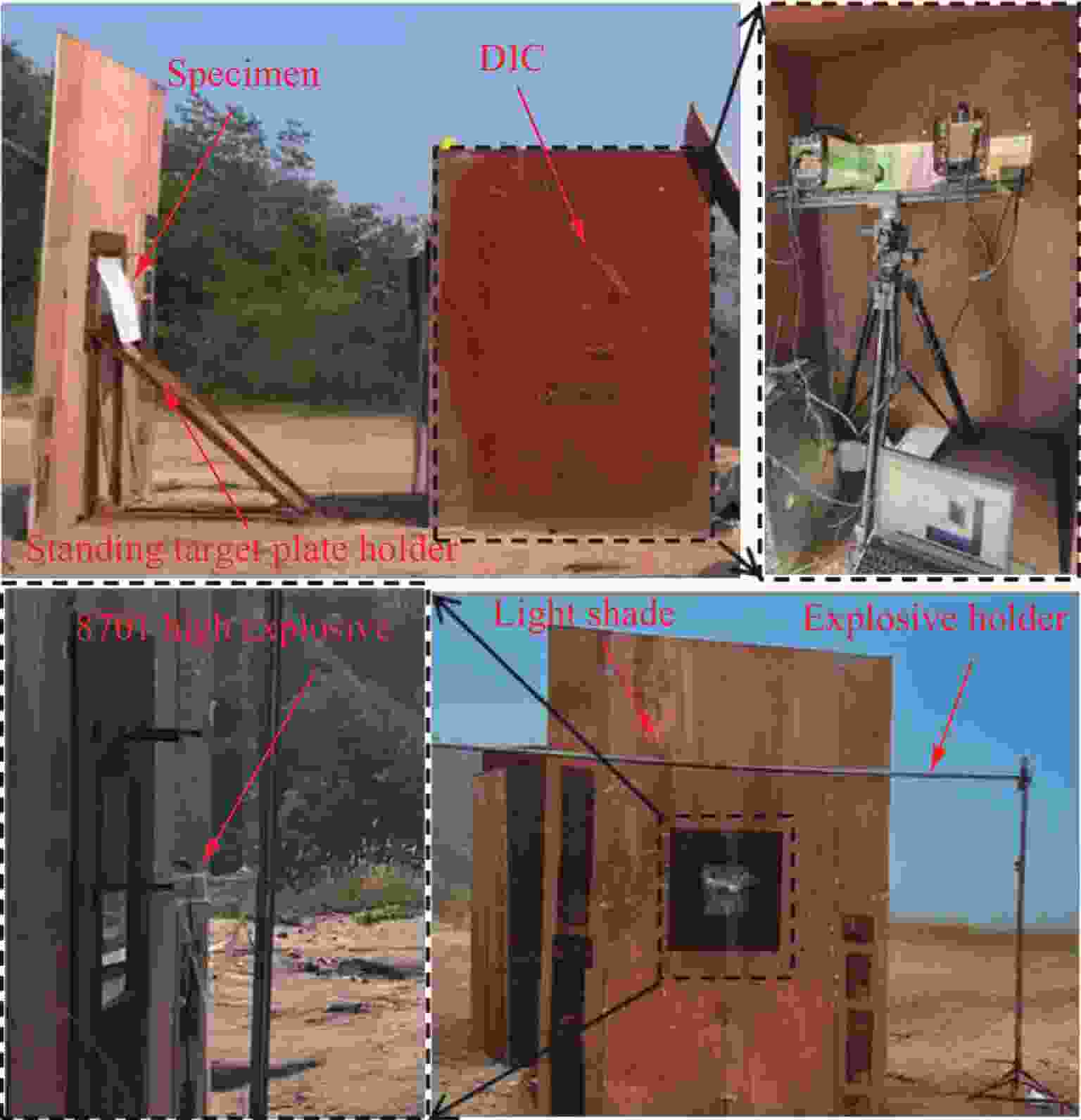
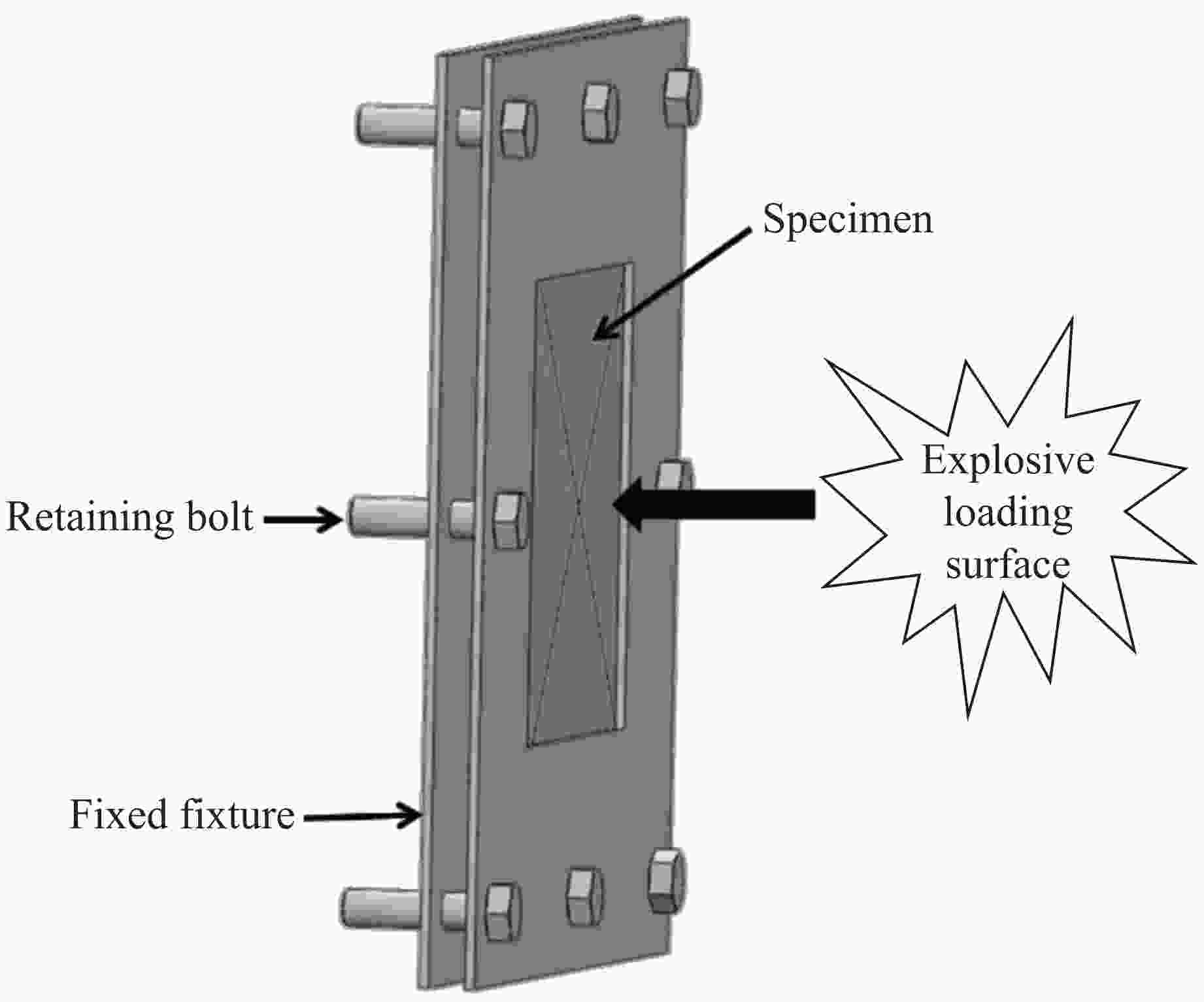
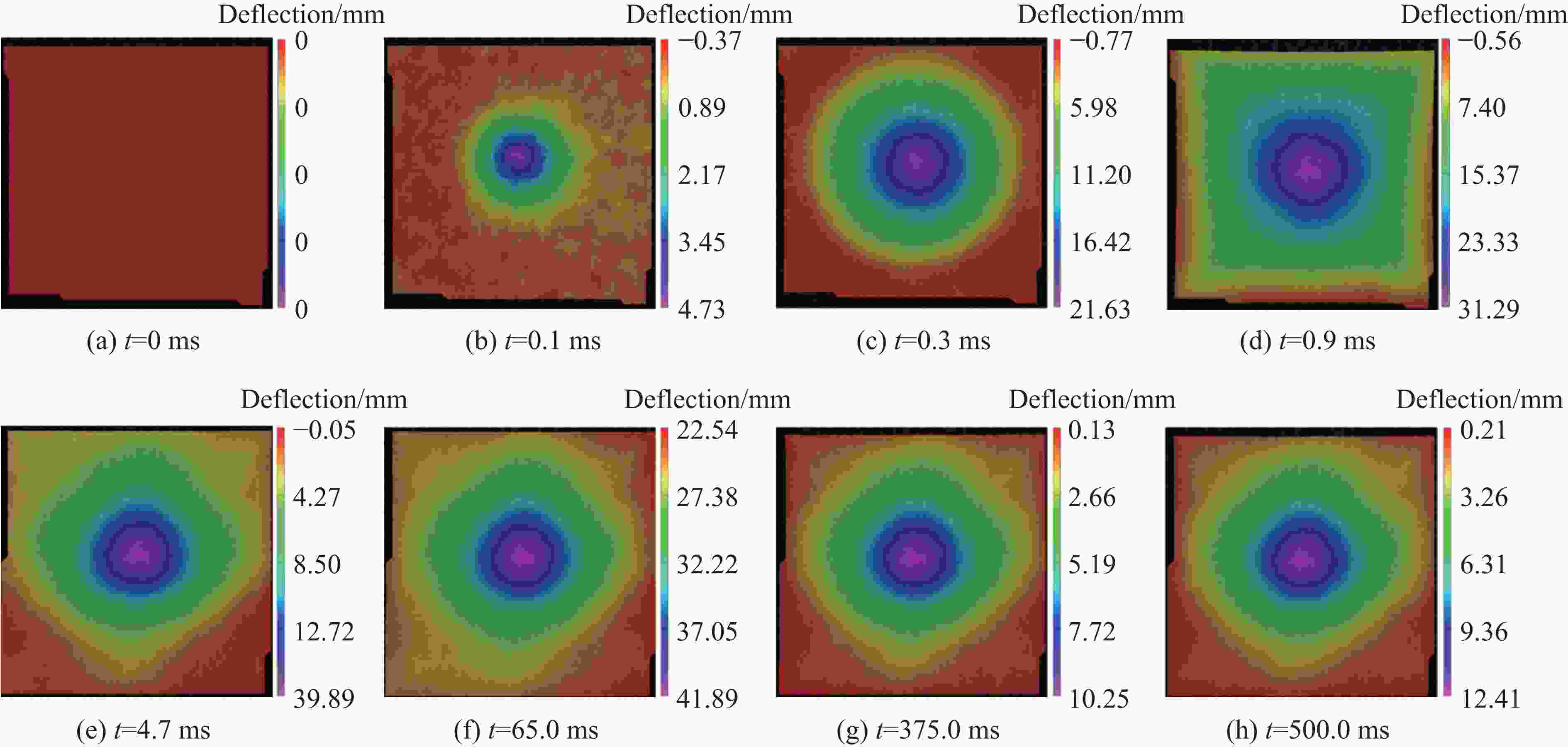
Dynamic Response of Shear Thickening Gel-Filled Honeycomb Sandwich Panels under Blast Loading: Experimental Research
-
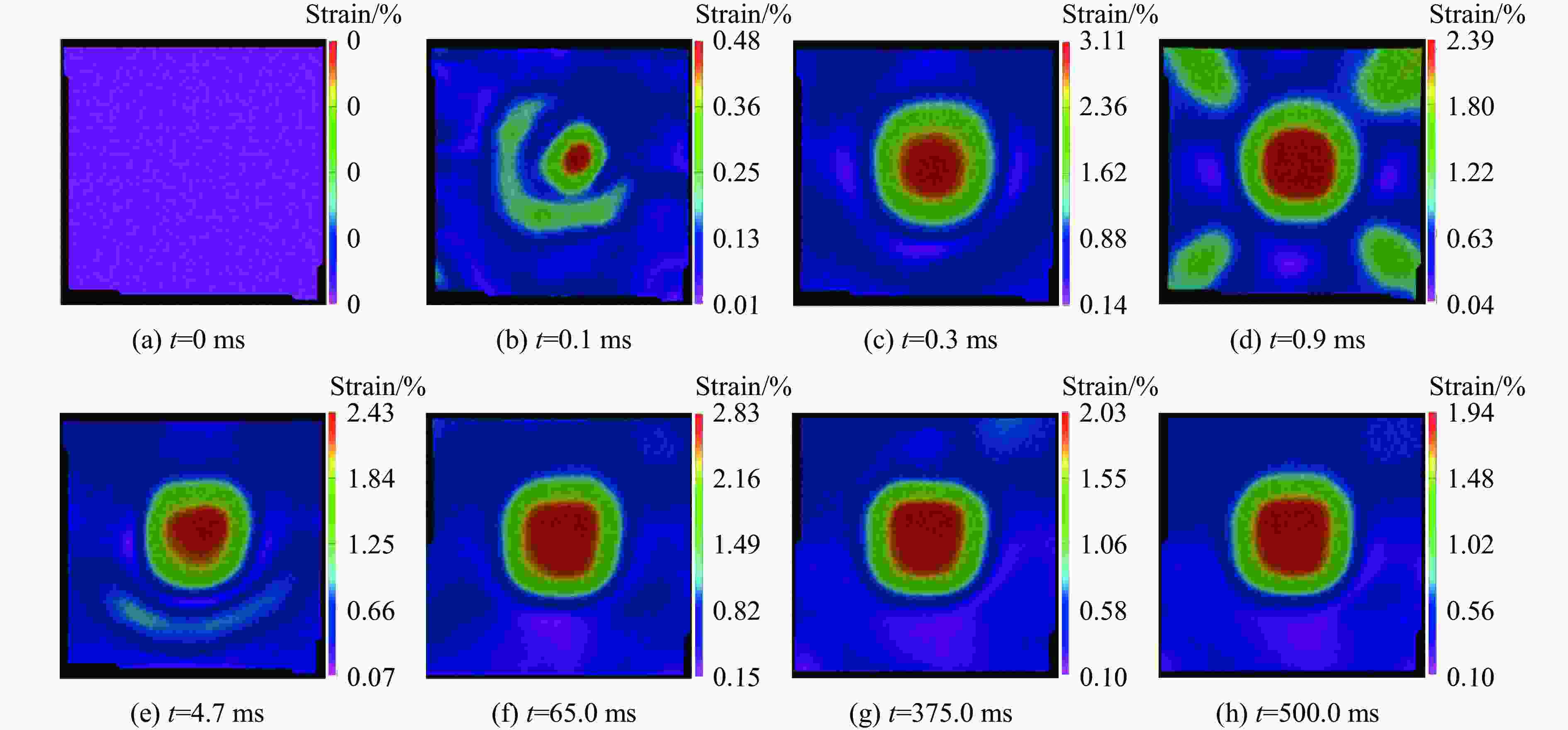
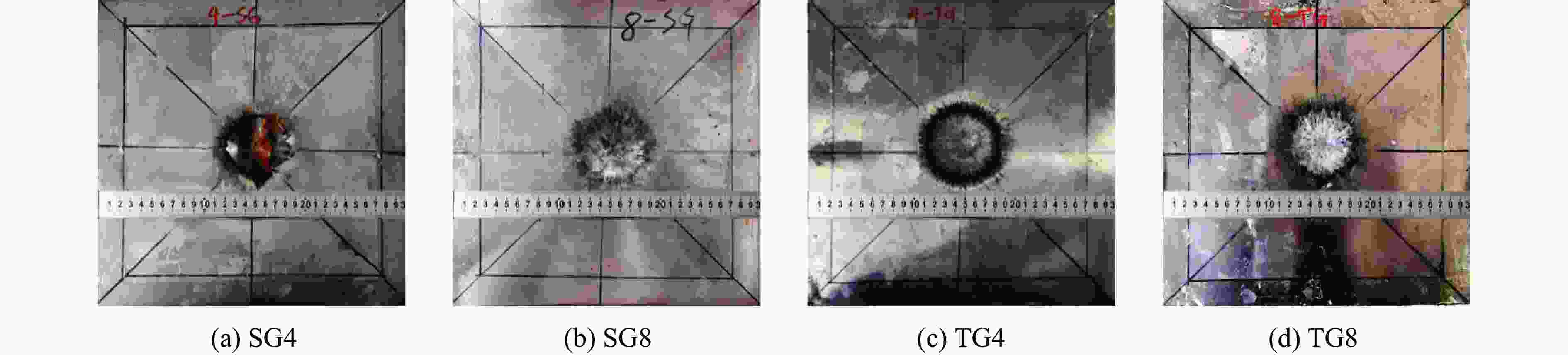
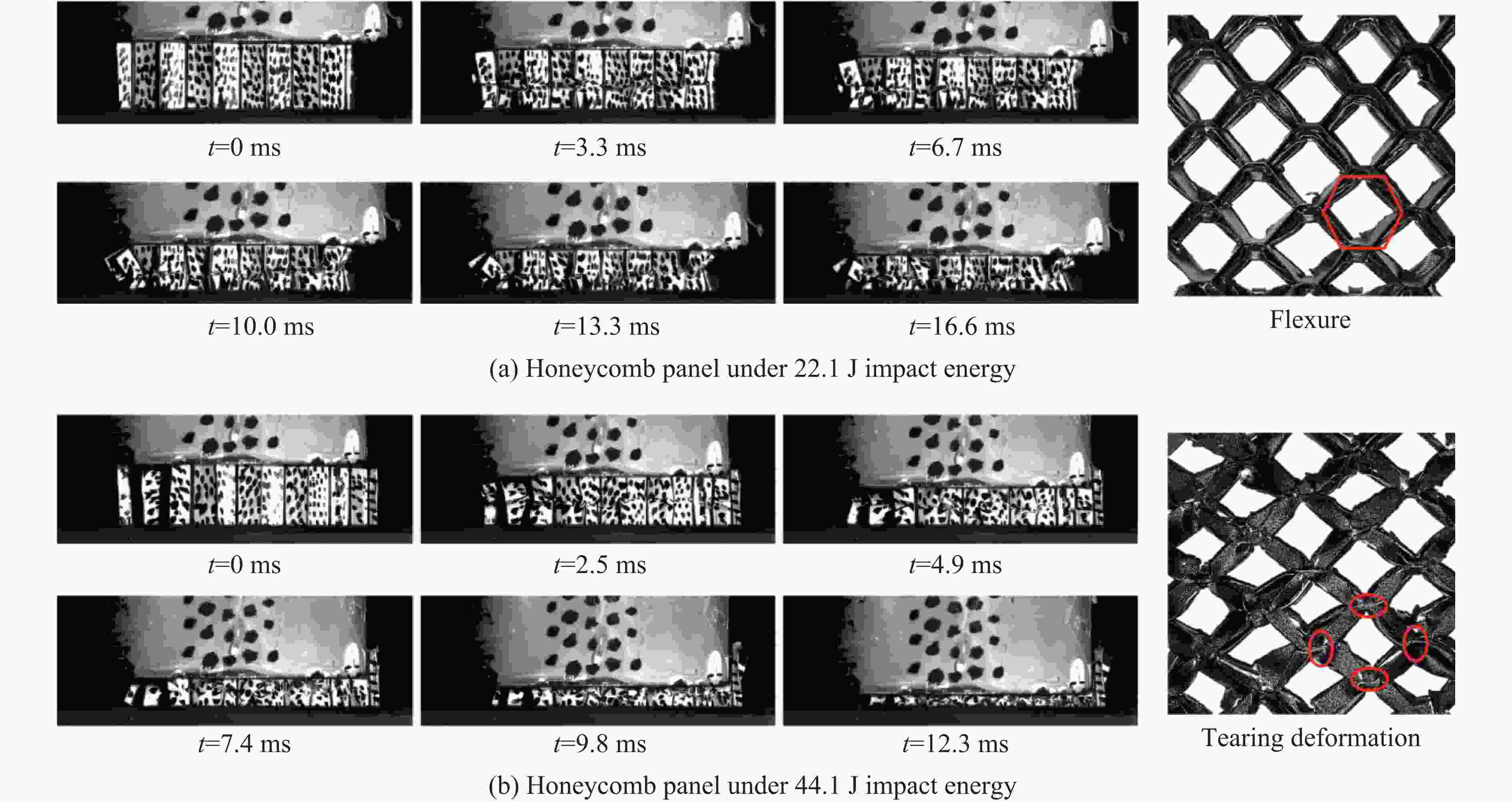
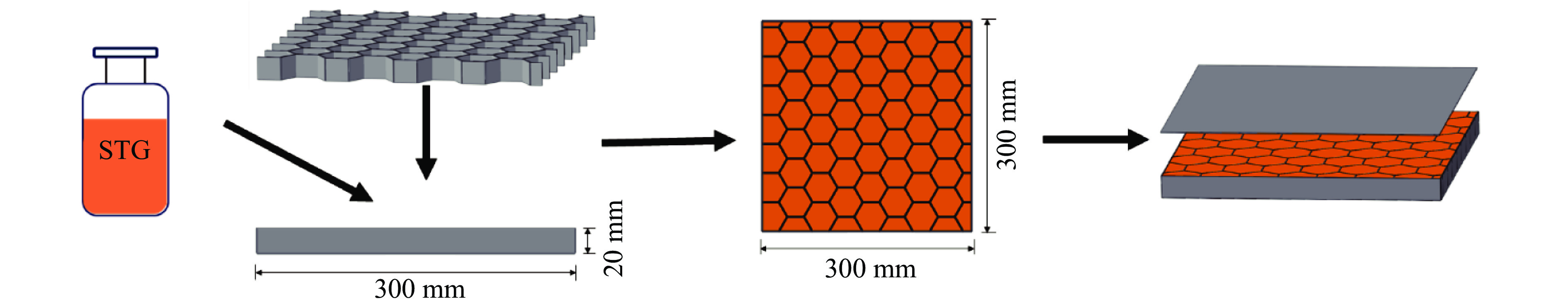
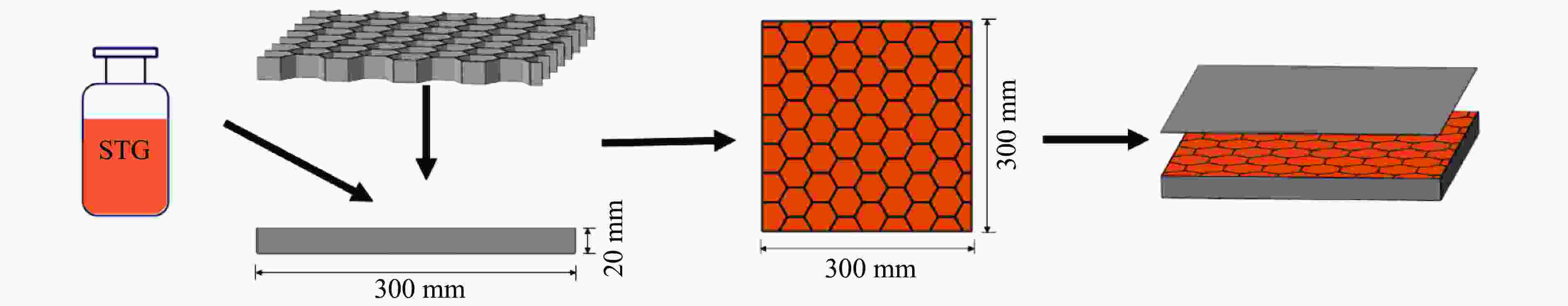
摘要: 将2种不同配比的剪切增稠胶(shear thickening gel,STG)SG和TG分别填充到铝合金蜂窝芯层中,设计并制备了一种具有优良抗爆性能的夹芯板结构。通过一系列实验,研究了其在爆炸载荷下的动态响应,采用数字图像相关(digital image correlation,DIC)技术记录并分析了夹芯板结构的实验过程,探究了STG填充材料与蜂窝芯层的耦合作用机制对夹芯结构动力学行为的影响规律。此外,通过分析不同夹芯结构前后面板及芯层的变形模态、应变历程和失效模式,得出了不同蜂窝边长及STG类型对夹芯板结构的抗爆炸冲击性能的影响。实验发现:未填充STG的蜂窝夹芯板的前后面板均出现了明显的破坏,防护性能较弱;填充STG能够有效地增强结构的抗爆炸冲击性能,而具有更高剪切增稠效应的TG填充夹芯板相较于SG填充夹芯板拥有更好的防护效果。当蜂窝边长为4 mm时,SG填充夹芯板的前面板发生破裂,而TG填充夹芯板的前面板则发生较均匀的塑性凹陷,且背面板挠度降低了61.0%;当蜂窝边长为8 mm时,相较于SG填充夹芯板,TG填充夹芯板的前面板和背面板挠度分别降低了5.6%和17.7%。实验结果表明,通过改变填充胶类型和蜂窝结构参数可以调控结构的抗爆性能。Abstract: A sandwich panel with superior blast resistance was designed and fabricated by filling aluminum honeycomb cores with two shear thickening gels (STGs) of different compositions, SG and TG. A series of blast experiments were conducted to investigate its dynamic response. The digital image correlation (DIC) technique was used to record and analyze the experimental process, exploring the coupling mechanism between the STG filling and the honeycomb core and its effect on the dynamic behavior of the structure. In addition, by analyzing the deformation modes, strain histories, and failure patterns of the front and back face sheets as well as the core layer, the effects of honeycomb cell size and STG type on the blast resistance of the sandwich panel were determined. Experimental results showed that the unfilled honeycomb sandwich panel suffered severe damage to both face sheets, indicating poor protective performance. The STG filling significantly enhanced the blast resistance, and the TG-filled panel achieved better protection than the SG-filled panel due to its stronger shear thickening effect. When the honeycomb cell size was 4 mm, the front face sheet of the SG-filled panel fractured, whereas the TG-filled panel exhibited more uniform plastic indentation, and the back face sheet deflection was reduced by 61.0%. When the honeycomb cell size was 8 mm, the TG-filled panel achieved reductions of 5.6% (front panel) and 17.7% (back panel) in deflection compared to the SG-filled panel. The experimental results indicate that optimizing the type of STG and honeycomb structural parameters can effectively modulate the blast resistance of the sandwich panel.
-
Key words:
- shear thickening gel (STG) /
- sandwich structure /
- blast loading /
- dynamic response /
- honeycomb core
-
Material ρ/(kg·m−3) E/GPa μ σY/MPa Et/GPa 201 stainless steel 7740 184 0.31 275 85.75 Al6061-T6 aluminum alloy 2700 69 0.33 275 26.69 表 2 实验工况
Table 2. Experimental conditions
Specimen Honeycomb side length/mm STG type Total mass/g E4 4 Empty 1318.6 SG4 4 SG 2759.7 SG8 8 SG 2758.5 TG4 4 TG 2786.8 TG8 8 TG 2781.4 ρ/(kg·m−3) $ D $/(m·s−1) $ {p}_{\mathrm{C}\mathrm{J}} $/GPa $ {A}_{1} $/GPa $ {B}_{1} $/GPa $ {R}_{1} $ $ {R}_{2} $ $ \omega $ $ {E}_{\rm a} $/GPa 1700 8315 28.6 524.23 7.678 4.2 1.1 0.34 8.499 表 4 剪切频率测试中STG样品的$ G'_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x}} $、$ G'_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $和相对剪切增稠效应
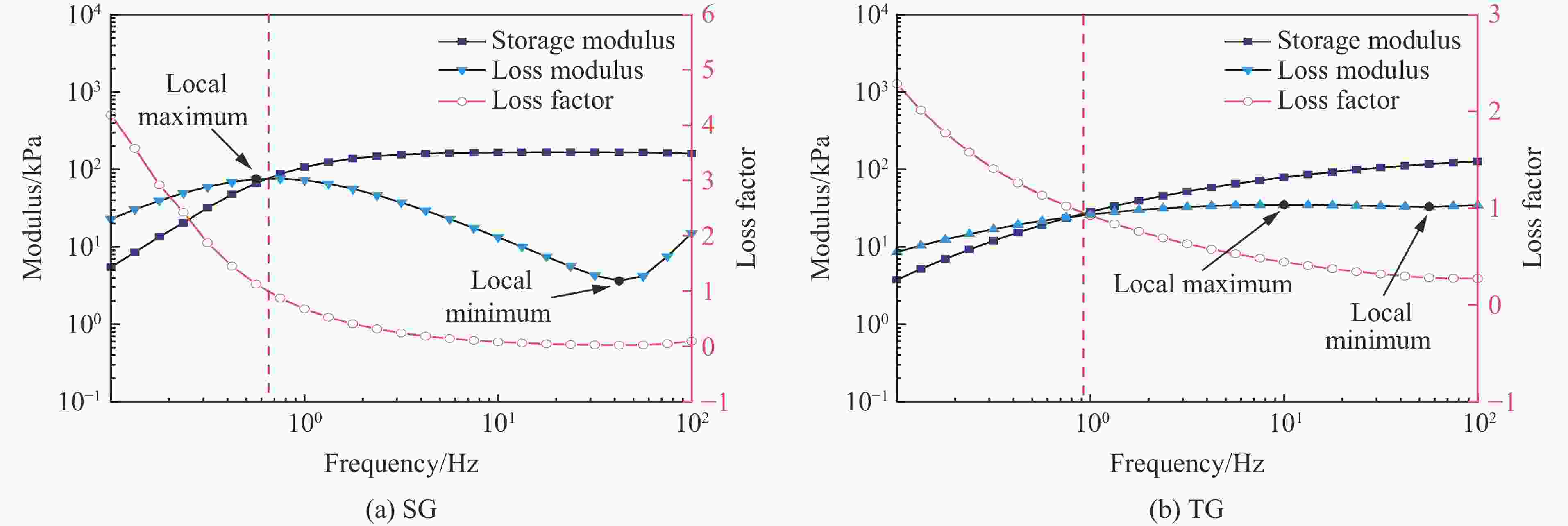
Table 4. $ G'_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x}} $, $ G'_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $ and relative shear thickening effect of STG samples in shear frequency tests
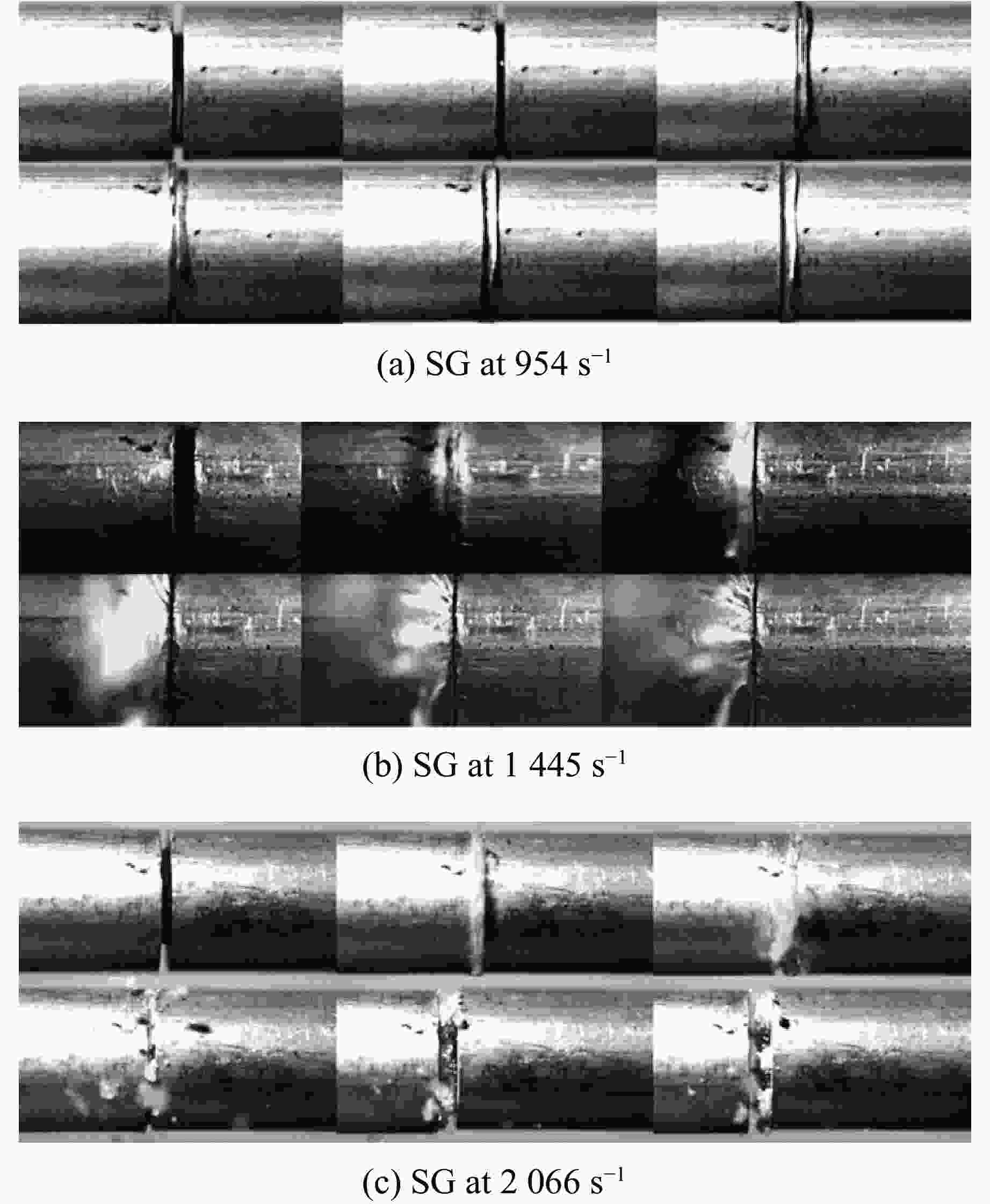
Specimen $ G'_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x}} $/kPa $ G'_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $/kPa $ \theta $/% SG 159.710 5.4672 2821.2 TG 120.640 3.7694 3100.5 表 5 前面板变形
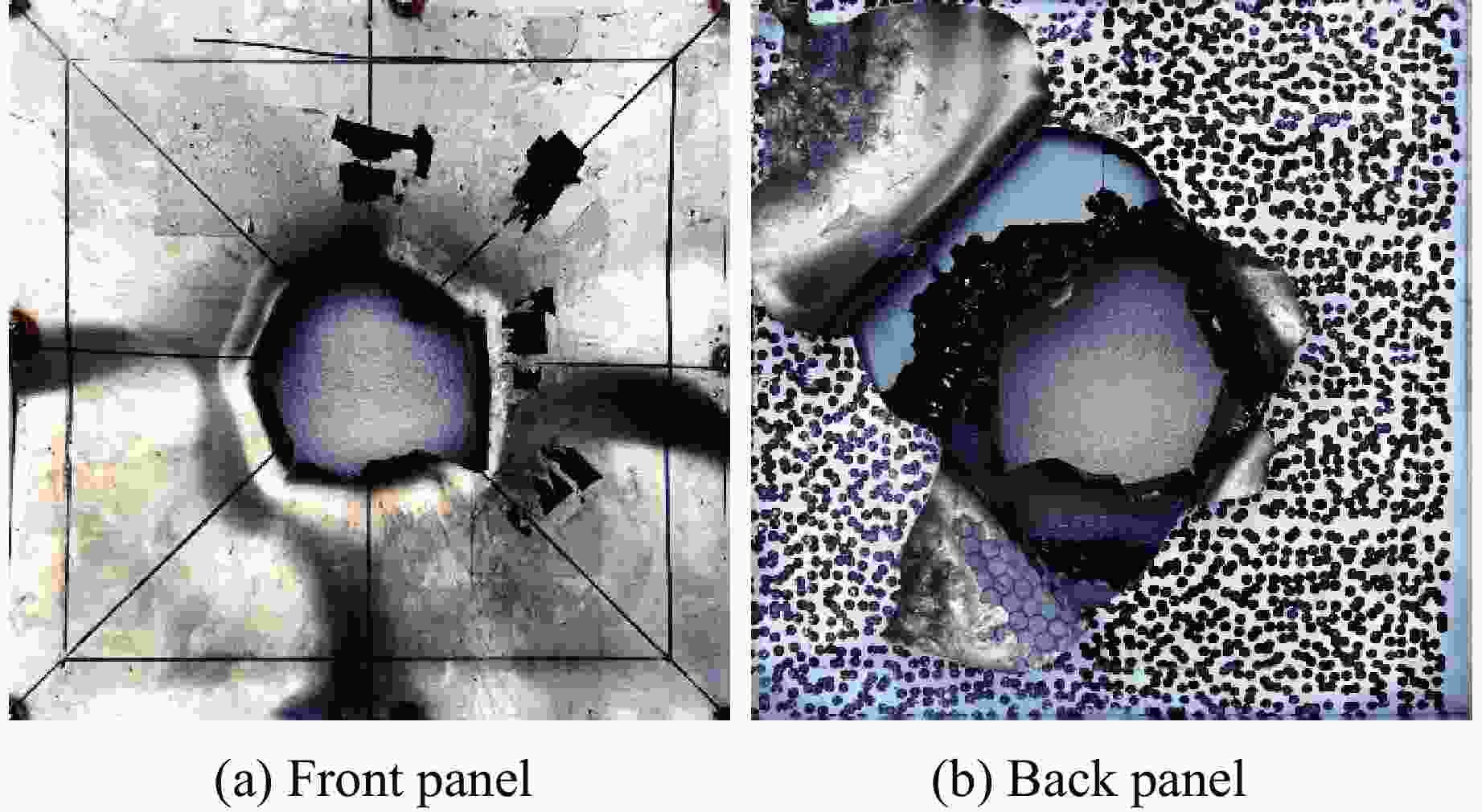
Table 5. Deformation of the front panel
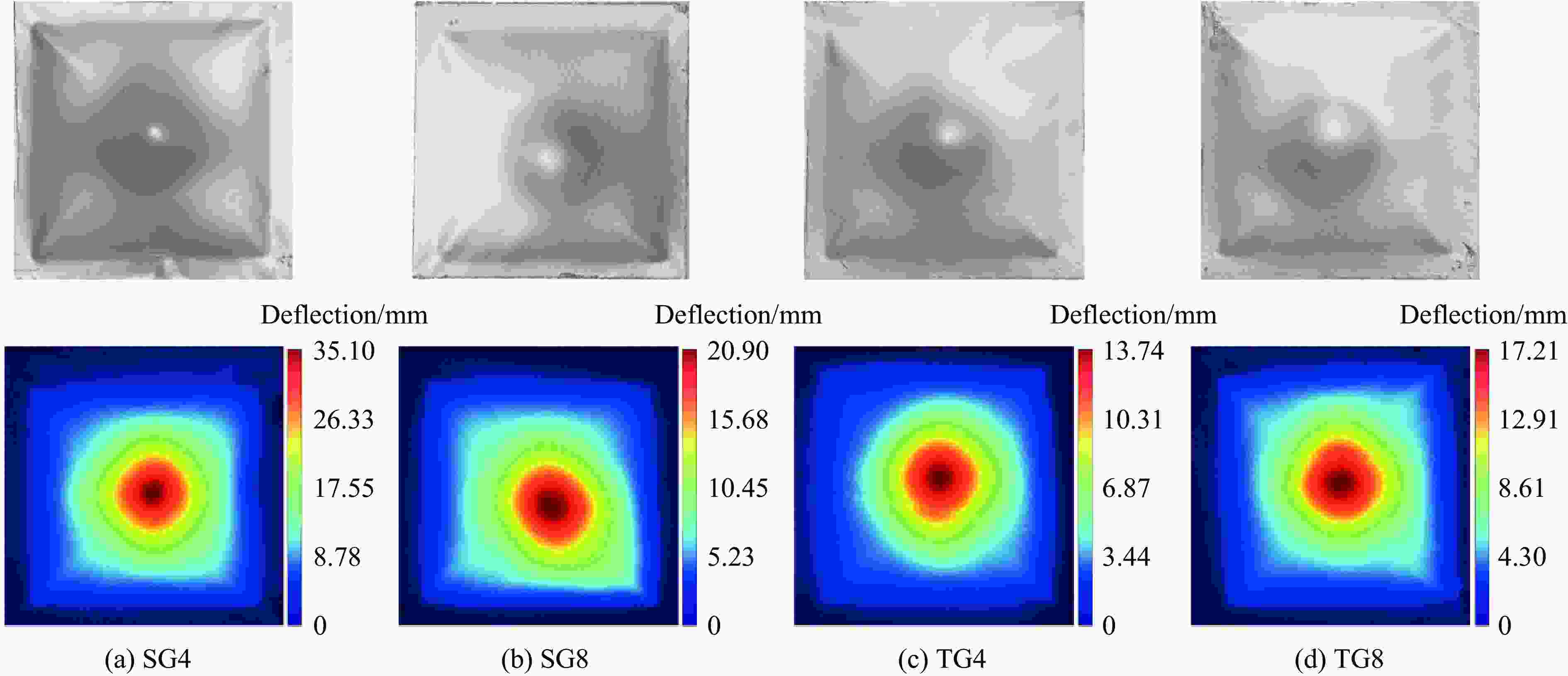
Specimen Diameter/mm Deflection/mm SG4 75 Punch failure SG8 72 9.0 TG4 78 12.0 TG8 69 8.5 表 6 DIC和3D扫描仪测量的背面板残余挠度
Table 6. Residual deflection of the back panel measured by DIC and 3D scanner
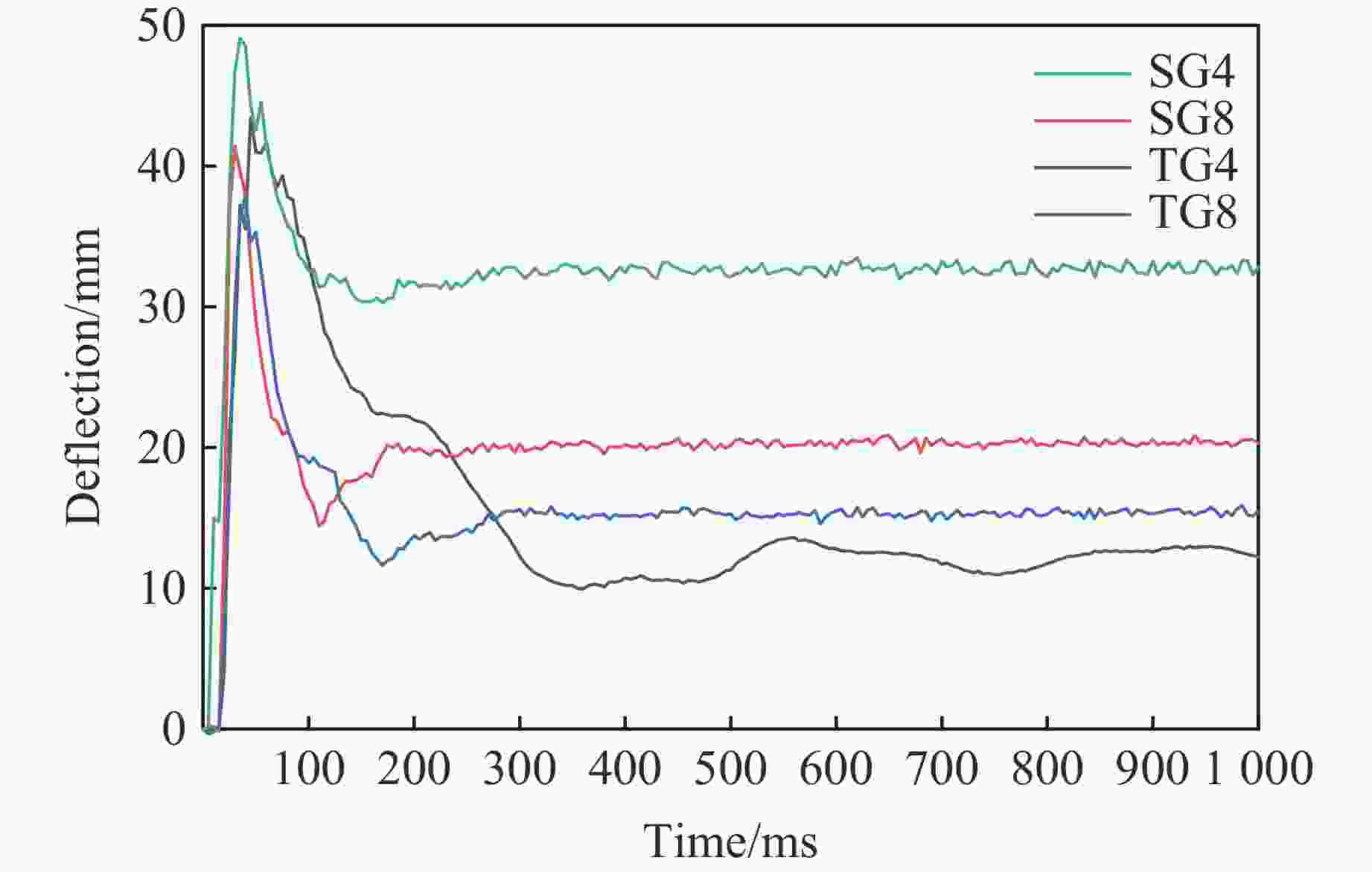
Specimen Residual deflection/mm DIC 3D scanner SG4 33.6 35.1 SG8 20.2 20.9 TG4 12.4 13.7 TG8 15.7 17.2 -
[1] GUO H Y, YUAN H, ZHANG J X, et al. Review of sandwich structures under impact loadings: experimental, numerical and theoretical analysis [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2024, 196: 111541. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.111541 [2] YANG X F, SUN Y X, YANG J L, et al. Out-of-plane crashworthiness analysis of bio-inspired aluminum honeycomb patterned with horseshoe mesostructure [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2018, 125: 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2018.01.014 [3] LIU S T, ZHANG Y C, LIU P. New analytical model for heat transfer efficiency of metallic honeycomb structures [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2008, 51(25/26): 6254–6258. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2007.07.055 [4] HONG S T, PAN J, TYAN T, et al. Quasi-static crush behavior of aluminum honeycomb specimens under non-proportional compression-dominant combined loads [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2006, 22(6): 1062–1088. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2005.07.003 [5] 周文华, 周百能. 夹芯泡沫材料性能及其在风电叶片上的应用 [J]. 天津科技, 2023, 50(1): 75–78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8945.2023.01.020ZHOU W H, ZHOU B N. Applied research of sandwich foam in wind turbine blades [J]. Tianjin Science & Technology, 2023, 50(1): 75–78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8945.2023.01.020 [6] RADFORD D D, DESHPANDE V S, FLECK N A. The use of metal foam projectiles to simulate shock loading on a structure [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 31(9): 1152–1171. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2004.07.012 [7] YUAN H, WU X W, ZHANG J X. Cutting failure behavior of foam core sandwich plates [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2024, 303: 113009. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2024.113009 [8] WU X W, GUO H Y, ZHANG J X. Bi-surface induction in biomimetic multi-gradient foam-filled tubes with enhanced energy absorption: theory, experiment, and simulation [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2025, 92(5): 051010. doi: 10.1115/1.4068061 [9] PAZ J, DÍAZ J, ROMERA L, et al. Size and shape optimization of aluminum tubes with GFRP honeycomb reinforcements for crashworthy aircraft structures [J]. Composite Structures, 2015, 133: 499–507. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.07.077 [10] LURIE S, VOLKOV-BOGORODSKIY D, SOLYAEV Y, et al. Impact behavior of a stiffened shell structure with optimized GFRP corrugated sandwich panel skins [J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 248: 112479. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112479 [11] ANSARI M M, CHAKRABARTI A. Ballistic performance of unidirectional glass fiber laminated composite plate under normal and oblique impact [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2017, 173: 161–168. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.12.053 [12] 潘腾, 卞晓兵, 袁名正, 等. 爆炸冲击波作用下聚氨酯-半球夹芯结构的动态响应 [J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(12): 3580–3589. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0645PAN T, BIAN X B, YUAN M Z, et al. Dynamic response of polyurethane-hemisphere sandwich structure under action of explosive shock wave [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(12): 3580–3589. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0645 [13] ZHOU N, WANG J X, JIANG D K, et al. Study on the failure mode of a sandwich composite structure under the combined actions of explosion shock wave and fragments [J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 196: 109166. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109166 [14] FU K K, WANG H J, CHANG L, et al. Low-velocity impact behaviour of a shear thickening fluid (STF) and STF-filled sandwich composite panels [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2018, 165: 74–83. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.06.013 [15] CAGLAYAN C, OSKEN I, ATAALP A, et al. Impact response of shear thickening fluid filled polyurethane foam core sandwich composites [J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 243: 112171. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112171 [16] WARREN J, COLE M, OFFENBERGER S, et al. Hypervelocity impacts on honeycomb core sandwich panels filled with shear thickening fluid [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 150: 103803. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103803 [17] LING J, LI J Q, LI F, et al. Low-velocity impact response of sandwich composite panels with shear thickening gel filled honeycomb cores [J]. Composites Communications, 2022, 32: 101136. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2022.101136 [18] WANG Y P, GONG X L, XUAN S H. Study of low-velocity impact response of sandwich panels with shear-thickening gel cores [J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2018, 27(6): 065008. doi: 10.1088/1361-665X/aab7dc [19] HE Q Y, CAO S S, WANG Y P, et al. Impact resistance of shear thickening fluid/kevlar composite treated with shear-stiffening gel [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2018, 106: 82–90. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.12.019 [20] AKRAM S, JAFFERY S H I, KHAN M, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation of Johnson-Cook material models for aluminum (Al 6061-T6) alloy using orthogonal machining approach [J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 10(9): 1–14. doi: 10.1177/1687814018797794 [21] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard specification for chromium and chromium-nickel stainless steel plate, sheet, and strip for pressure vessels and for general applications: ASTM A240/A240M-20a [S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2004: 12. [22] LIU B, DU C B, DENG H X, et al. Study on the shear thickening mechanism of multifunctional shear thickening gel and its energy dissipation under impact load [J]. Polymer, 2022, 247: 124800. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2022.124800 [23] WU L W, ZHAO F, LU Z Q, et al. Impact energy absorption composites with shear stiffening gel-filled negative Poisson’s ratio skeleton by Kirigami method [J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 298: 116009. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116009 [24] WANG S, JIANG W Q, JIANG W F, et al. Multifunctional polymer composite with excellent shear stiffening performance and magnetorheological effect [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2014, 2(34): 7133–7140. doi: 10.1039/C4TC00903G [25] LI S Q, LI X, WANG Z H, et al. Finite element analysis of sandwich panels with stepwise graded aluminum honeycomb cores under blast loading [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2016, 80: 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.09.025 [26] LI X, ZHANG P W, WANG Z H, et al. Dynamic behavior of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels under air blast: experiment and numerical analysis [J]. Composite Structures, 2014, 108: 1001–1008. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.10.034 [27] LI S Q, LI X, WANG Z H, et al. Sandwich panels with layered graded aluminum honeycomb cores under blast loading [J]. Composite Structures, 2017, 173: 242–254. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.04.037 -






 下载:
下载: