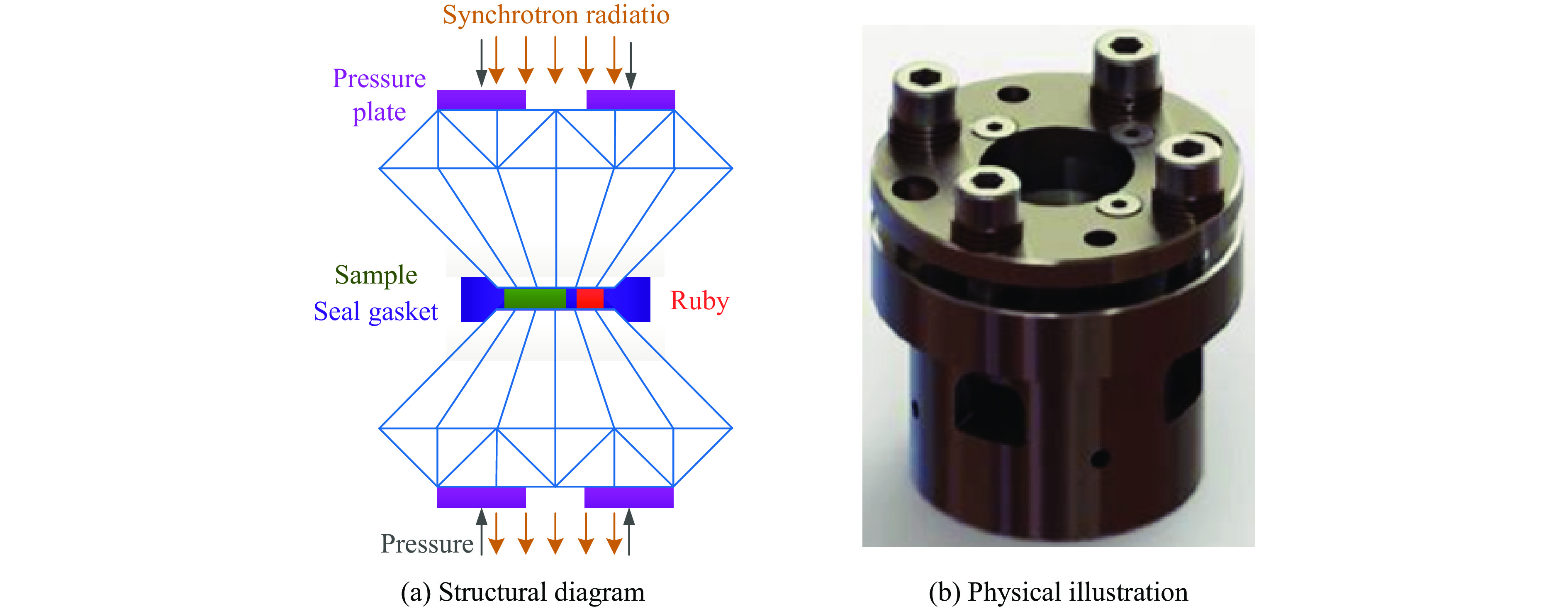
Research Progress of Static Ultra-High Pressure Device
-
摘要: 超高压技术作为极端条件制造领域的重要手段,其应用已从凝聚态物理、地球科学等基础研究拓展至超硬材料合成及高密度储能器件制造等工程实践,并逐步向精密能场调控等前沿方向延伸。尽管我国超高压装置需求激增,但是受限于大尺寸硬质合金烧结技术壁垒,国产超高压装置占比较低。为此,系统梳理了对顶砧、两面顶、多面顶、分球式4类主流静态超高压装置的结构特征与技术瓶颈,并对未来超高压装置的发展和技术方向进行了展望。Abstract: Ultra-high pressure (UHP) technology, a core technique in manufacturing under extreme conditions, has expanded its scope from fundamental research in areas like condensed matter physics and geosciences to practical engineering applications such as superhard material synthesis and high-density energy storage device fabrication. Furthermore, UHP techniques are increasingly being used in cutting-edge fields such as the precise control of energy fields. Despite the surging demand for ultra-high pressure equipment in China, the market share of domestically produced ultra-high pressure equipment remains relatively low due to the technical barriers in large-size cemented carbide sintering. This study systematically reviews the design features and technical limitations of four mainstream static ultra-high-pressure devices: opposed anvil presses, belt-type presses, multi-anvil presses, and split-sphere apparatus. Finally, it presents an outlook on potential future advancements and technological pathways for UHP equipment.
-
表 1 静态超高压装置性能对比
Table 1. Performance evaluation of static ultra-high pressure devices
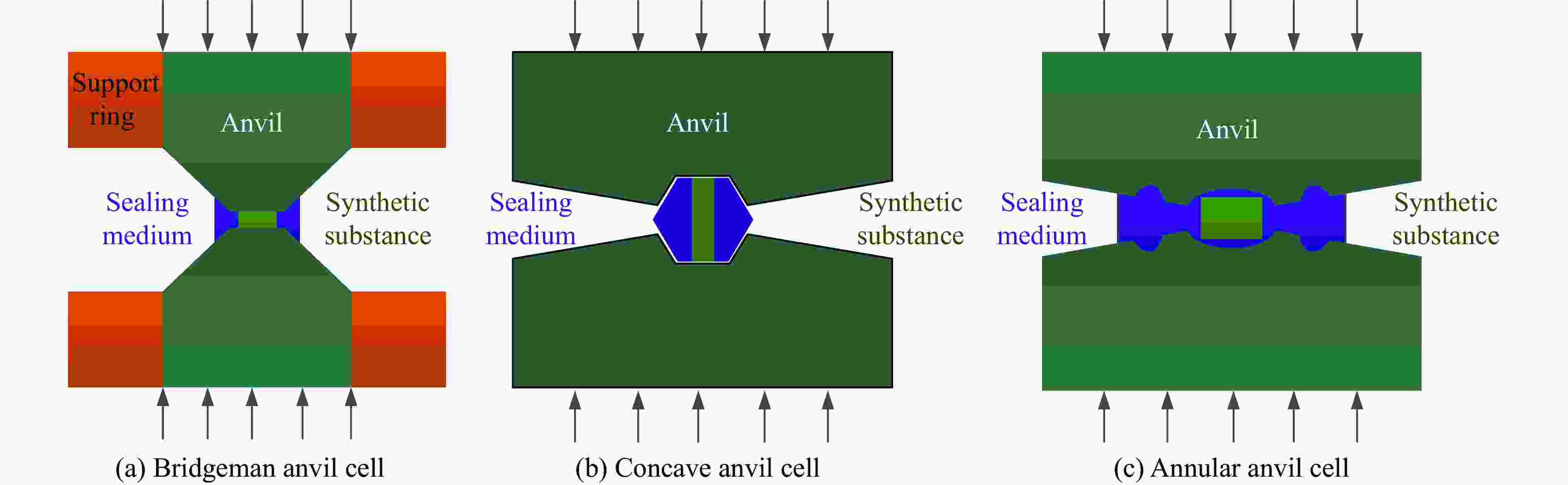
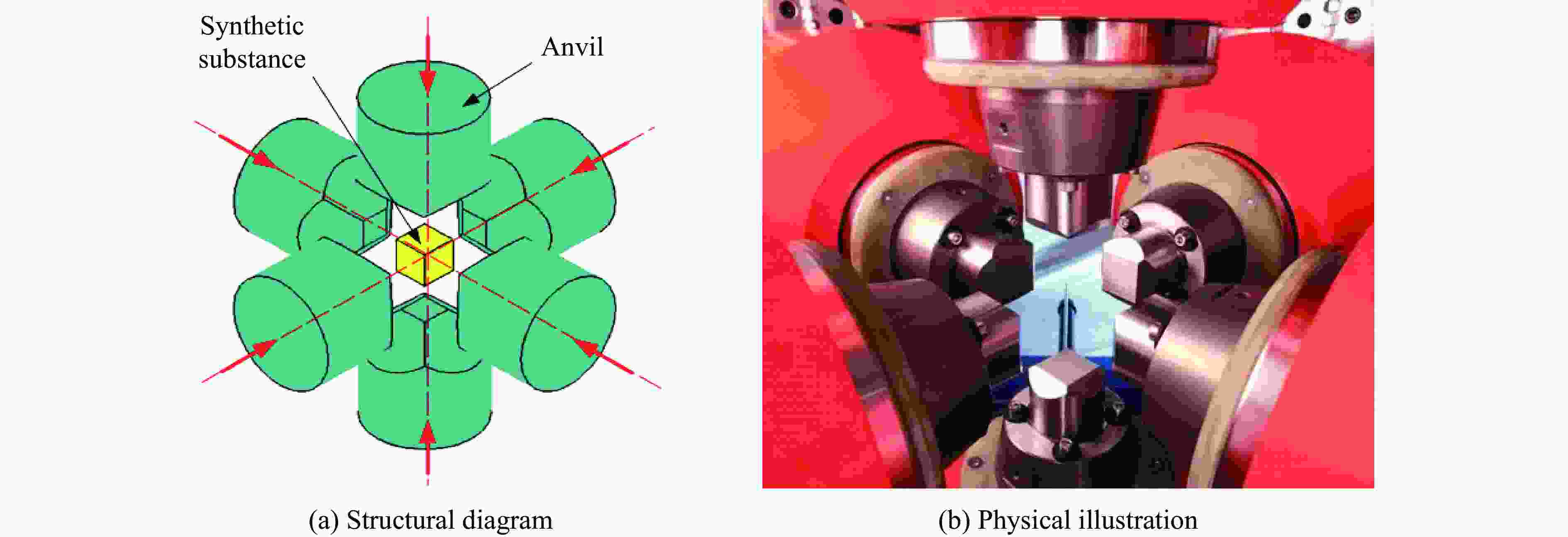
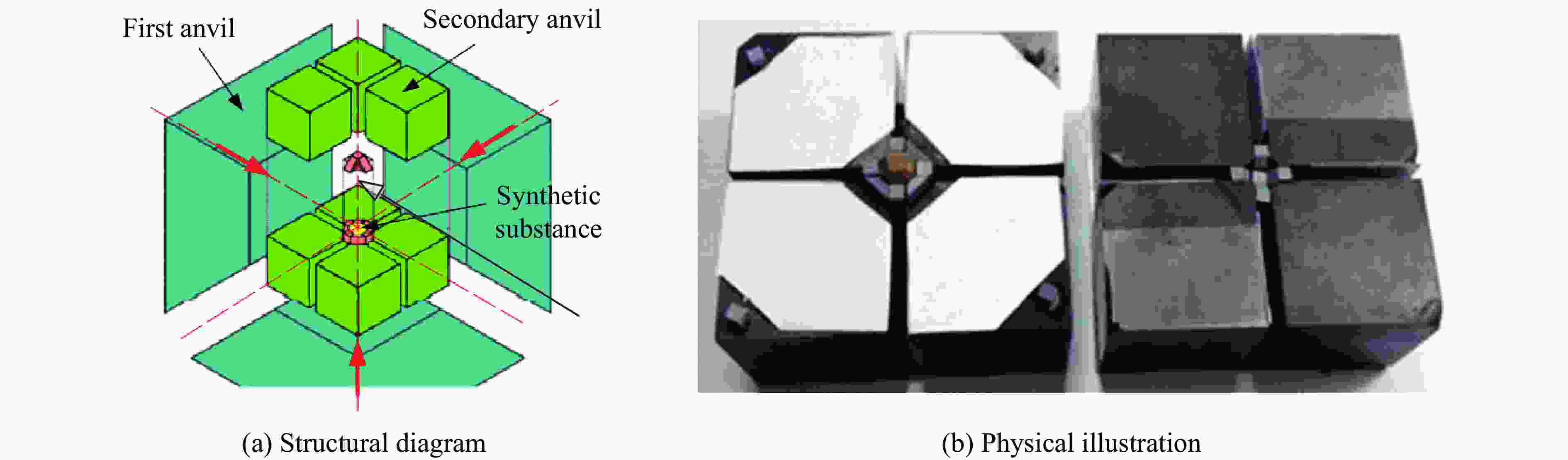
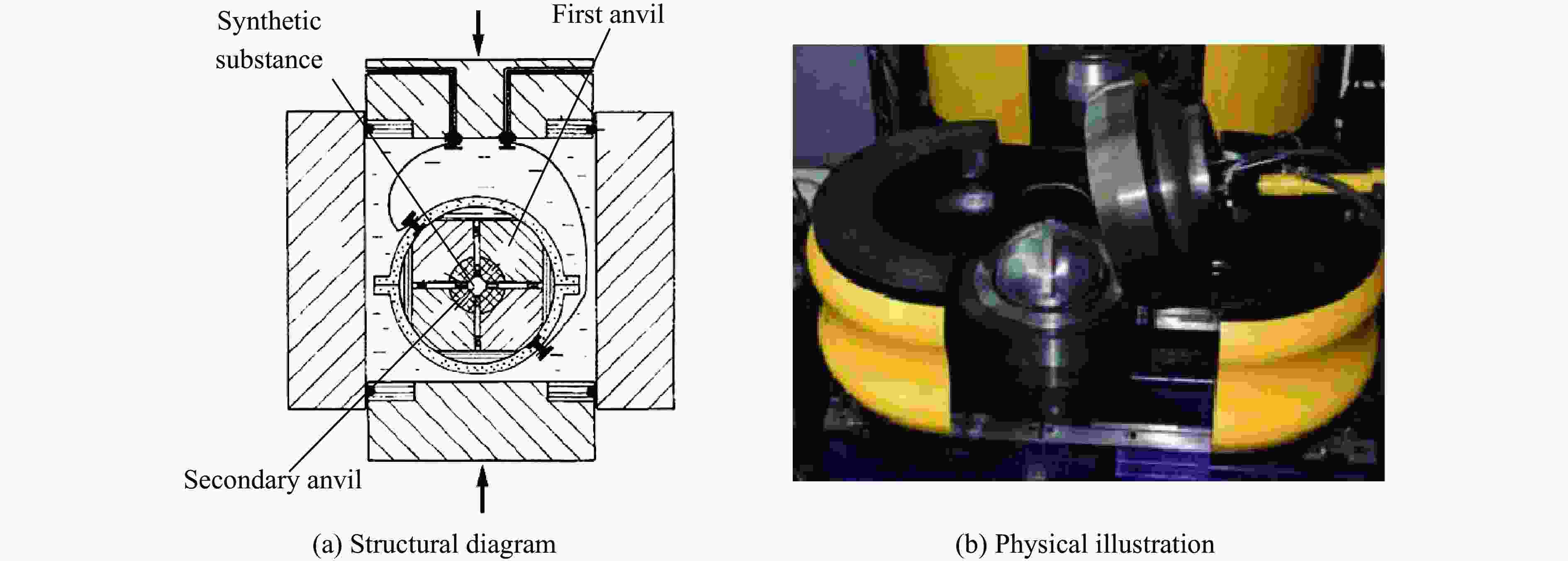
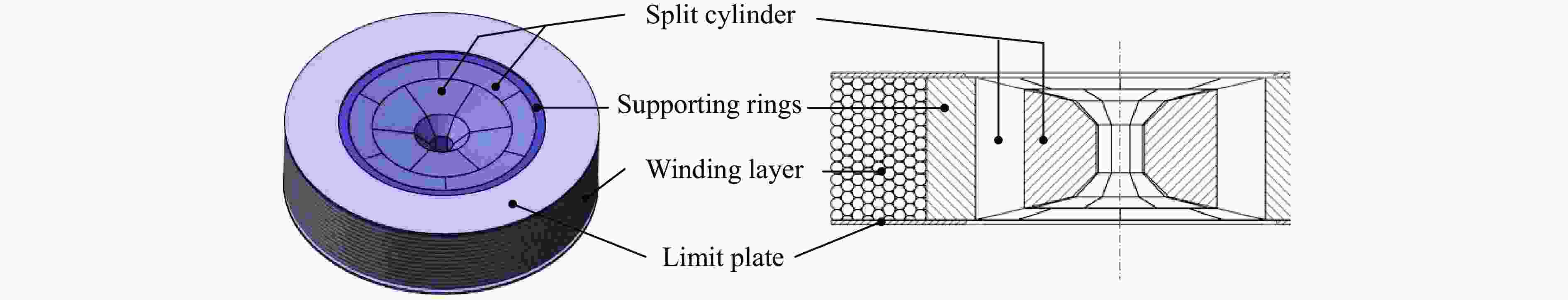
Device type Pressure range/GPa Cavity dimensions Primary applications Technical features Diamond anvil
cell setup0−550 Cavity diameter: 0.3−0.5 mm In-situ characterization techniques, ultrahigh-pressure research (e.g., planetary interior simulations, metallic hydrogen synthesis) Single-crystal diamond
anvil cell (DAC);
piston-cylinder/four-column
pressure systems;
transparent anvils enabling
in-situ optical characterizationBridgeman anvil cell setup 0−25 Extremely
smallPhase transition mechanisms and cryogenic rheology of advanced materials Cemented carbide flat anvils; interference-fit high-strength
steel support rings;
metal gasket sealing assemblyAnnular anvil
cell setup20−30 3 mm3
(Optimized
Haberl)Neutron scattering characterization, high-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) studies in large-volume press systems Axisymmetric hemispherical
concave anvils;
peripheral gradient annular
groove design;
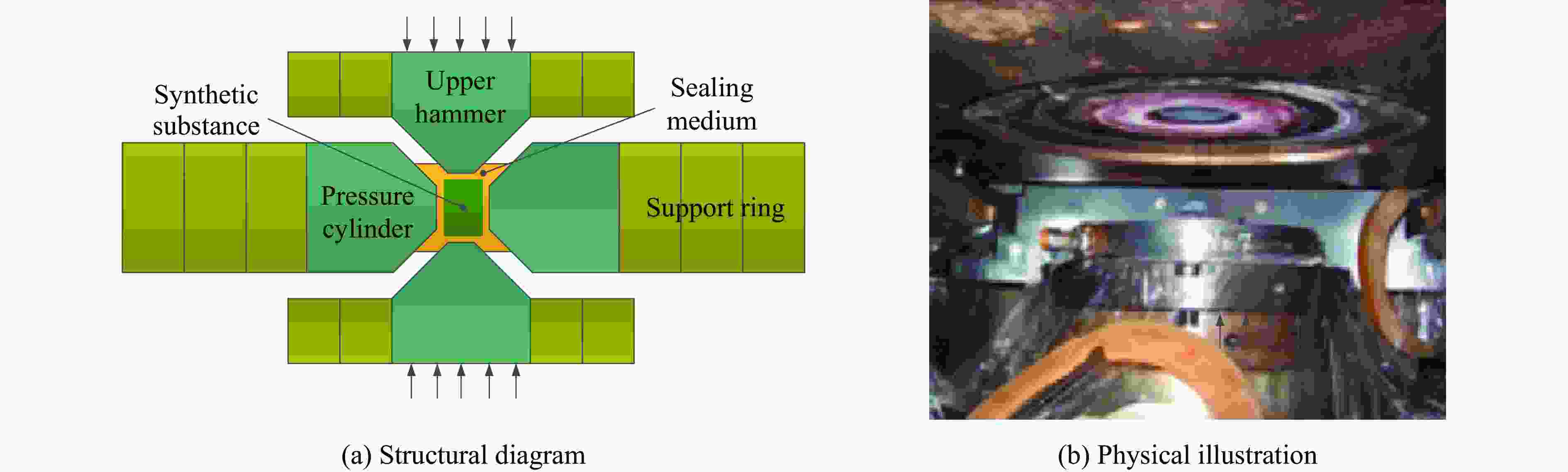
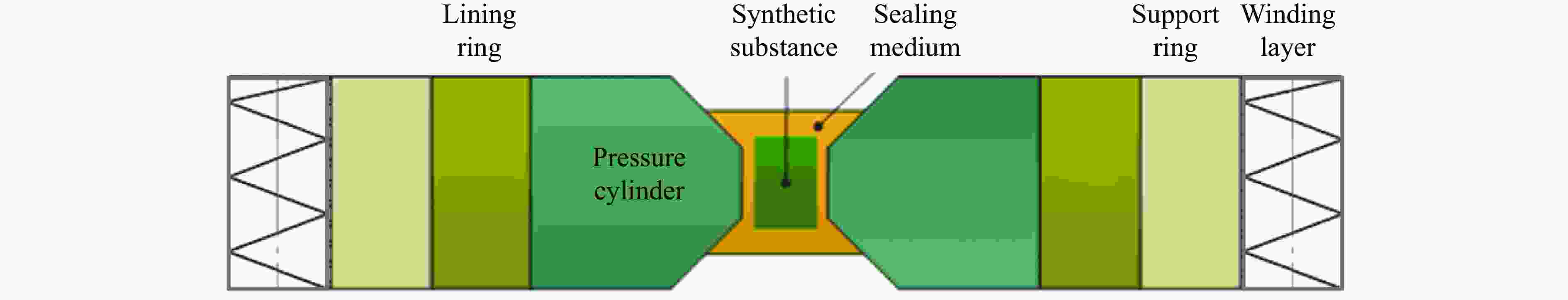
split-type sealing gaskets (pyrophyllite+metal)Belt-type ultra-high pressure device 0−6.5 Cavity diameter:
250 mm[29–30],
135 mm[31]Industrial diamond production (polycrystalline diamond compacts) Belt-type multi-layered support die; cemented carbide pressure cylinder
with steel support rings;
isostatic pressing loading mechanismMulti-anvil
high pressure apparatus0−12 Regular
tetrahedral
cavityPioneering advancements
in XRD instrumentationAsymmetric configuration of four cemented-carbide top anvils;
regular tetrahedral sealed chamber;
manual loading systemCubic anvil ultra-high pressure system 0−6.5 28000 mm3Scalable production of mid-to-low grade diamonds Orthogonal configuration of six
cemented carbide top anvil;
electrically heated graphite tube for precise temperature control;
hydraulically synchronized
driving system6-8 type multi-anvil ultra-high pressure system 20−55 Side length:
14 mm[52],2000 mm3[54]Phase transitions under HPHT conditions (e.g., magnesium silicate perovskite) Two-stage pressurization structure (8 sintered diamond top anvils);
regular octahedral sample chamber;
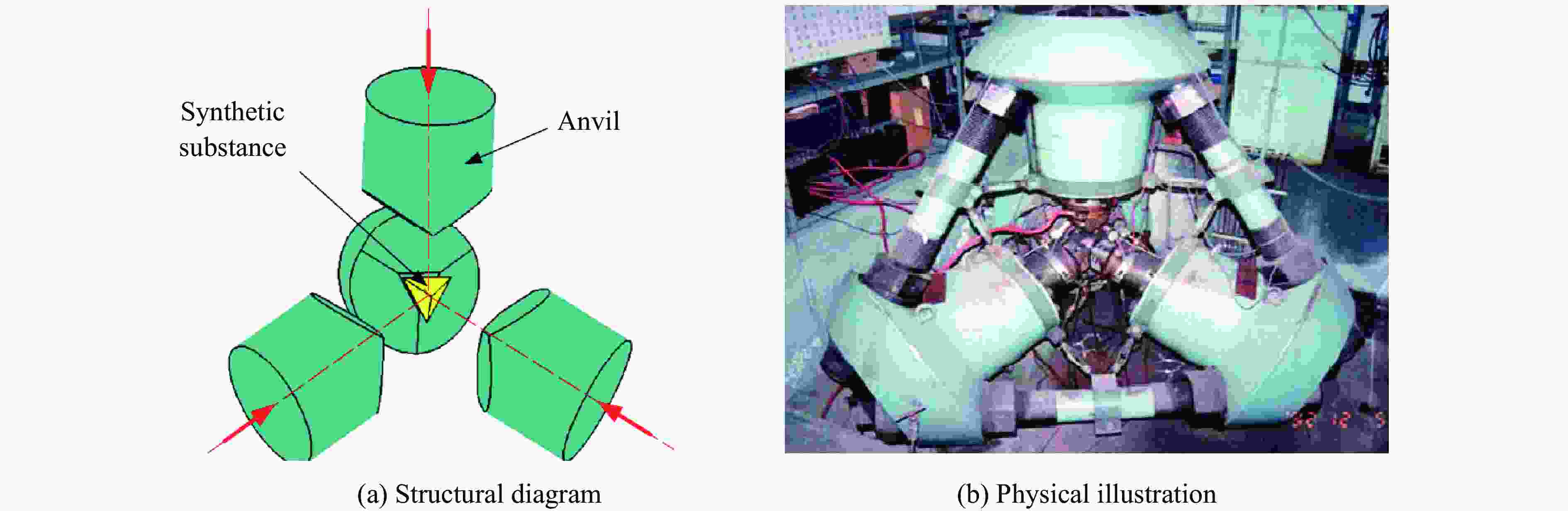
pre-sealed edge technologySplit-sphere
high pressure apparatuses0−10 Experimental diamond synthesis Multi-stage hydraulic driven top anvils; rubber membrane-sealed oil chamber; embedded graphite tube heating system -
[1] 翟航, 杨锦坭, 王建云, 等. 高压下主族金属富氮化合物的结构与含能特性 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2024, 38(4): 040101. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230810ZHAI H, YANG J N, WANG J Y, et al. Structure and energy properties of nitrogen-rich compounds of main group metals under high pressure [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2024, 38(4): 040101. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230810 [2] 王莹莹. 高压下典型金属硫族化合物和氢化物的结构及超导电性研究 [D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2022.WANG Y Y. Structures and superconductivity of typical metal chalcogenides and hydrides under high pressure [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2022. [3] 吴杰, 甘波, 宋文豪, 等. 冲击下黄铁矿脱硫及其对地球早期环境的影响 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2025, 39(3): 030101. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240916WU J, GAN B, SONG W H, et al. Shock-induced desulfurization of natural pyrite and its implications for the early Earth’s environment [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2025, 39(3): 030101. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240916 [4] YANG X X, YE Q L. Synthesis of high-quality octahedral cBN crystals with large size using lithium metal as a catalyst [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 580: 1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.05.095 [5] WANG X M, ZENG X Q, YAO S S, et al. The corrosion behavior of Ce-implanted magnesium alloys [J]. Materials Characterization, 2008, 59(5): 618–623. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2007.05.006 [6] XIE L J, YONEDA A, YOSHINO T, et al. Graphite-boron composite heater in a Kawai-type apparatus: the inhibitory effect of boron oxide and countermeasures [J]. High Pressure Research, 2016, 36(2): 105–120. doi: 10.1080/08957959.2016.1164151 [7] YI Z, FU W Z, LI M Z, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental verification of a novel double-layered split die for high pressure apparatus used for synthesizing superhard materials [J]. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials, 2019, 26(3): 377–385. doi: 10.1007/s12613-019-1747-3 [8] MAO H K, BELL P M, HEMLEY R J. Ultrahigh pressures: optical observations and Raman measurements of hydrogen and deuterium to 1.47 Mbar [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1985, 55(1): 99–102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.55.99 [9] FORMAN R A, PIERMARINI G J, BARNETT J D, et al. Pressure measurement made by the utilization of ruby sharp-line luminescence [J]. Science, 1972, 176(4032): 284–285. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4032.284 [10] XU J A, MAO H K, BELL P M. High-pressure ruby and diamond fluorescence: observations at 0.21 to 0.55 terapascal [J]. Science, 1986, 232(4756): 1404–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4756.1404 [11] SCHULTZ E, MEZOUAR M, CRICHTON W, et al. Double-sided laser heating system for in situ high pressure-high temperature monochromatic X-ray diffraction at the esrf [J]. High Pressure Research, 2005, 25(1): 71–83. doi: 10.1080/08957950500076031 [12] JAMIESON J C, LAWSON A W, NACHTRIEB N D. New device for obtaining X-ray diffraction patterns from substances exposed to high pressure [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1959, 30(11): 1016–1019. doi: 10.1063/1.1716408 [13] BELL P M, MAO H K, GOETTEL K. Ultrahigh pressure: beyond 2 megabars and the ruby fluorescence scale [J]. Science, 1984, 226(4674): 542–544. doi: 10.1126/science.226.4674.542 [14] GREGORYANZ D S. Comment on “evidence of a first-order phase transition to metallic hydrogen” [J]. Physical Review B, 2017, 96(15): 52–54. [15] DIAS R P, SILVERA I F. Observation of the Wigner-Huntington transition to metallic hydrogen [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6326): 715–718. doi: 10.1126/science.aal1579 [16] ZHANG L J, WANG Y C, LV J, et al. Materials discovery at high pressures [J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2(4): 17005. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2017.5 [17] FASOL G, SCHILLING J S. New hydrostatic pressure cell to 90 kilobars for precise electrical and magnetic measurements at low temperatures [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1978, 49(12): 1722–1724. doi: 10.1063/1.1135323 [18] YANG Y F, LI M Z, WANG B L. Study on stress distribution of tangent split high pressure apparatus and its pressure bearing capacity [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2015, 58: 180–184. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2015.07.010 [19] ZHAO L, LI M Z, LI R, et al. Stress analysis of the multi-layer stagger-split die for synthesizing gem quality large single crystal diamond [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2018, 83: 54–59. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2018.01.024 [20] JACCARD D, HOLMES A T, BEHR G, et al. Superconductivity of ε-Fe: complete resistive transition [J]. Physics Letters A, 2002, 299(2/3): 282–286. doi: 10.1016/S0375-9601(02)00725-9 [21] EREMETS M I. High pressure experimental methods [M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1996: 102–107. [22] KLOTZ S, BESSON J M, HAMEL G, et al. Neutron powder diffraction at pressures beyond 25 GPa [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1995, 66(14): 1735–1737. doi: 10.1063/1.113350 [23] KHVOSTANTSEV L G, SLESAREV V N, BRAZHKIN V V. Toroid type high-pressure device: history and prospects [J]. High Pressure Research, 2004, 24(3): 371–383. doi: 10.1080/08957950412331298761 [24] NI P Y, HUA R D, LV Z L, et al. Performance analysis of compact thermoelectric generation device for harvesting waste heat [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2023, 291: 117333. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2023.117333 [25] NELMES R J, LOVEDAY J S, WILSON R M, et al. Neutron diffraction study of the structure of deuterated ice Ⅷ to 10 GPa [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1993, 71(8): 1192–1195. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.1192 [26] BIANCA H, JAMIE J M, JOERG C N, et al. Modified Bridgman anvils for high pressure synthesis and neutron scattering [J]. High Pressure Research, 2019, 39(3): 1–13. [27] BILYALOV Y R, KAUROV A A, TSVYASHCHENKO A V. Pressure generation by a double-stage system using sintered diamond as the last stage anvil [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1992, 63(4): 2311–2314. doi: 10.1063/1.1143155 [28] HALL H T. Ultra-high-pressure, high-temperature apparatus: the “belt” [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1960, 31(2): 125–131. doi: 10.1063/1.1716907 [29] PETROVA A E, SIDOROV V A, STISHOV S M. High-pressure helium gas apparatus and hydrostatic toroid cell for low-temperatures applications [J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2005, 359/360/361: 1463–1465. doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2005.01.454 [30] YANG Y F, LI M Z, WANG B L, et al. A novel split-belt apparatus: the stress distribution and performance of its tangent split die [J]. High Pressure Research, 2015, 35(3): 247–253. doi: 10.1080/08957959.2015.1058934 [31] SUMIYA H, IRIFUNE T. Indentation hardness of nano-polycrystalline diamond prepared from graphite by direct conversion [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2004, 13(10): 1771–1776. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2004.03.002 [32] 姚裕成. 人造金刚石和超高压高温技术 [M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 1996: 152–157.YAO Y C. Synthetic diamond and ultra-high pressure high temperature technology [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 1996: 152–157. [33] ZHAO L, LI M Z, YANG Y F, et al. Finite element analysis and experiment on high pressure apparatus with split cylinder [J]. High Pressure Research, 2017, 37(3): 377–388. doi: 10.1080/08957959.2017.1318130 [34] GROENBAEK J, THUN N. Forming tool for a pressable material: 2001052977 [P]. 2001-07-26. [35] GROENBAEK J. High-pressure tool: 2001036080 [P]. 2001-05-25. [36] 刘长海, 唐立强. 超高压容器损伤自增强的应力分析 [J]. 压力容器, 2005, 22(5): 20–22, 58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4837.2005.05.006LIU C H, TANG L Q. Stress analysis of vessel with self-reinforced damage under super-high pressure [J]. Pressure Vessel Technology, 2005, 22(5): 20–22, 58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4837.2005.05.006 [37] 吴俊飞. 绕丝式超高压容器模糊优化设计 [J]. 压力容器, 2008, 25(1): 11–13, 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4837.2008.01.003WU J F. Fuzzy optimization design of wire-wounded ultra-high pressure vessel [J]. Pressure Vessel Technology, 2008, 25(1): 11–13, 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4837.2008.01.003 [38] 刘志卫, 余其成, 胡海霞. 金属挤压筒结构研究进展 [J]. 塑性工程学报, 2021, 28(10): 1–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2021.10.001LIU Z W, YU Q C, HU H X. Research progress of metal extrusion container structure [J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2021, 28(10): 1–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2021.10.001 [39] 刘志卫, 吴承伟, 童明俊, 等. 钢丝缠绕剖分式超高压模具等张力预紧分析 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2021, 35(1): 013302. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200591LIU Z W, WU C W, TONG M J, et al. Analysis of equal tension pre-tightening of steel wire winding split ultra-high pressure die [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2021, 35(1): 013302. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200591 [40] 陈孔军, 王强, 赵东, 等. 钢带缠绕预应力模具缠绕过程的数值模拟 [J]. 制造技术与机床, 2012(5): 33–36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2402.2012.05.010CHEN K J, WANG Q, ZHAO D, et al. Numerical simulation on the winding process of strip wound prestressed die [J]. Manufacturing Technology & Machine Tool, 2012(5): 33–36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2402.2012.05.010 [41] 来小丽, 王强, 蔡冬梅, 等. 钢带缠绕预应力模具缠绕层数的确定方法 [J]. 塑性工程学报, 2008, 15(3): 152–156.LAI X L, WANG Q, CAI D M, et al. Approach to determine winding layers of prestressed strip-wound dies [J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2008, 15(3): 152–156. [42] HALL H T. Some high-pressure, high-temperature apparatus design considerations: equipment for use at 100000 atmospheres and3000 ℃ [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1958, 29(4): 267–275. doi: 10.1063/1.1716172[43] HALL H T, MERRILL L, BARNETT J D. High pressure polymorphism in cesium [J]. Science, 1964, 146(3649): 1297–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3649.1297 [44] 姚裕成, 胡光亚, 佟学礼. 从两面顶、六面顶、凹模的特点论我国合成金刚石装备大型化的方向 [J]. 人工晶体学报, 1999, 28(1): 103–107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.1999.01.021YAO Y C, HU G Y, TONG X L. Discussing on the developing direction of large sized apparatus for making synthetic diamond in China according to the characteristics of belt-type press, cubic press and recess dies [J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 1999, 28(1): 103–107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.1999.01.021 [45] 韩奇钢. 人造金刚石的制备方法及其超高压技术 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2015, 29(4): 313–320. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2015.04.012HAN Q G. Preparation methods and ultra-high pressure technologies of synthetic diamonds [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2015, 29(4): 313–320. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2015.04.012 [46] HAN Q G, LIU B, HU M H, et al. Design an effective solution for commercial production and scientific research on gem-quality, large, single-crystal diamond by high pressure and high temperature [J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2011, 11(4): 1000–1005. doi: 10.1021/cg100940b [47] 许俊杰, 鲁森远, 陈孝鹏, 等. 新锤面顶锤在六面顶压机合成工业金刚石中的应用 [J]. 超硬材料工程, 2021, 33(2): 24–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1433.2021.02.008XU J J, LU S Y, CHEN X P, et al. Application of a new hammer face anvil in the synthesis of industrial diamond by hexahedron press [J]. Superhard Material Engineering, 2021, 33(2): 24–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1433.2021.02.008 [48] 韩奇钢, 班庆初, 易政, 等. 超高压碳化钨顶砧新结构的设计与研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2014, 28(6): 686–690. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2014.06.007HAN Q G, BAN Q C, YI Z, et al. Study on new structure of ultra-high pressure WC anvil [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2014, 28(6): 686–690. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2014.06.007 [49] WANG D J, LI H P, LIU C Q, et al. Electrical conductivity of synthetic quartz crystals at high temperature and pressure from complex impedance measurements [J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2002, 19(8): 1211–1213. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/19/8/354 [50] 何强, 唐俊杰, 王霏, 等. 一种适用于极端高温条件的六面顶压机实验组装 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2014, 28(2): 145–151. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2014.02.003HE Q, TANG J J, WANG F, et al. High temperature stable assembly designed for cubic press [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2014, 28(2): 145–151. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2014.02.003 [51] KAWAI N, TOGAYA M, ONODERA A. A new device for pressure vessels [J]. Proceedings of the Japan Academy, 1973, 49(8): 623–626. doi: 10.2183/pjab1945.49.623 [52] ITO E, KATSURA T, AIZAWA Y, et al. Chapter 22: high-pressure generation in the Kawai-type apparatus equipped with sintered diamond anvils: application to the wurtzite-rocksalt transformation in GaN [M]//CHEN J H, WANG Y B, DUFFY T S, et al. Advances in High-Pressure Technology for Geophysical Applications. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2005: 451–460. [53] YAMAZAKI D, ITO E. High pressure generation in the Kawai-type multianvil apparatus equipped with sintered diamond anvils [J]. High Pressure Research, 2020, 40(1): 3–11. doi: 10.1080/08957959.2019.1689975 [54] TETSUO I, FUTOSHI I, TORU S. A novel large-volume Kawai-type apparatus and its application to the synthesis of sintered bodies of nano-polycrystalline diamond [J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2014, 228(22): 255–261. [55] MUELLER H J, BECKMANN F, DOBSON D P, et al. New techniques for high pressure falling sphere viscosimetry in DIA-type large volume presses [J]. High Pressure Research, 2014, 34(3): 345–354. doi: 10.1080/08957959.2014.950262 [56] 王文丹, 贺端威, 王海阔, 等. 二级6-8型大腔体装置的高压发生效率机理研究 [J]. 物理学报, 2010, 59(5): 3107–3115. doi: 10.7498/aps.59.3107WANG W D, HE D W, WANG H K, et al. Research on pressure generation efficiency of 6-8 type multianvil high pressure apparatus [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2010, 59(5): 3107–3115. doi: 10.7498/aps.59.3107 [57] 张佳威, 李强, 王俊普, 等. 二次加压对六面顶压腔压力发生效率和压力密封性能的影响 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2019, 33(2): 020105. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190703ZHANG J W, LI Q, WANG J P, et al. Effect of re-compression on the pressure-generation efficiency and pressure-seal capability of large volume cubic press [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2019, 33(2): 020105. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190703 [58] KAWAI N, ENDO S. The generation of ultrahigh hydrostatic pressures by a split sphere apparatus [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1970, 41(8): 1178–1181. doi: 10.1063/1.1684753 [59] REZA A, HENRY Z, CARTER C. High pressure-high temperature growth of diamond crystals using split sphere apparatus [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2005, 14(11/12): 1916–1919. [60] YELISSEYEV A, NADOLINNY V, FEIGELSON B, et al. Spatial distribution of impurity defects in synthetic diamonds obtained by the BARS technology [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 1996, 5(10): 1113–1117. doi: 10.1016/0925-9635(96)00511-0 -






 下载:
下载: