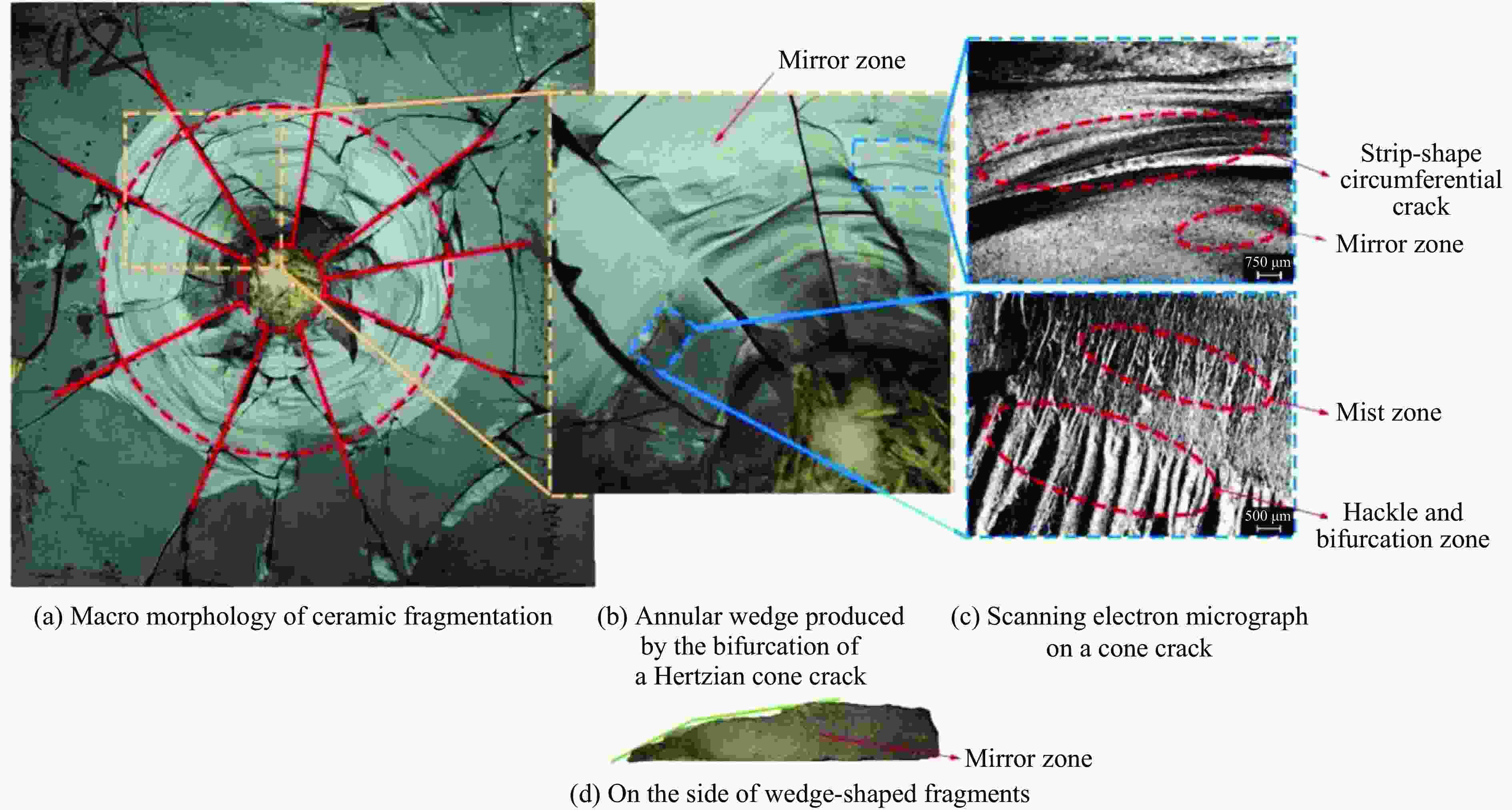
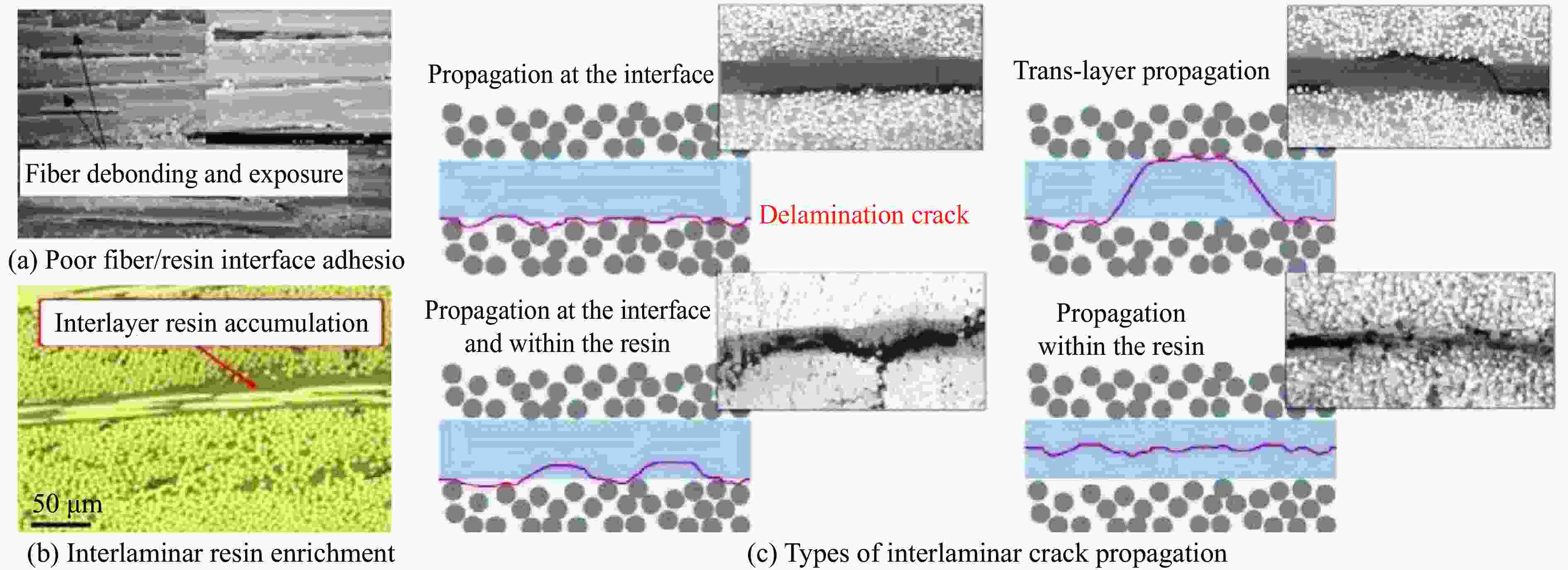
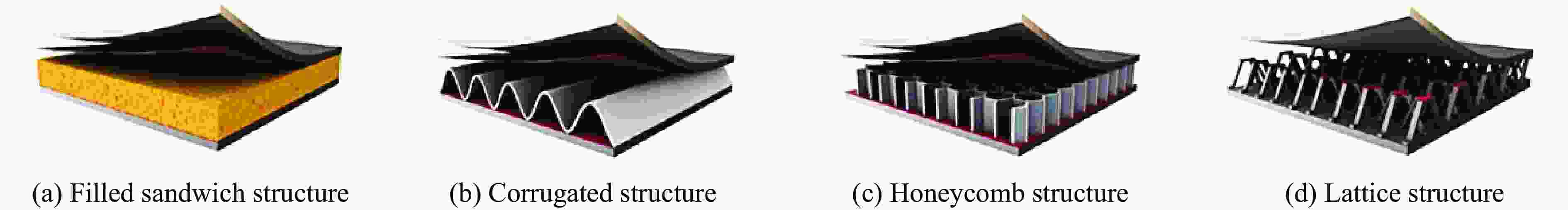
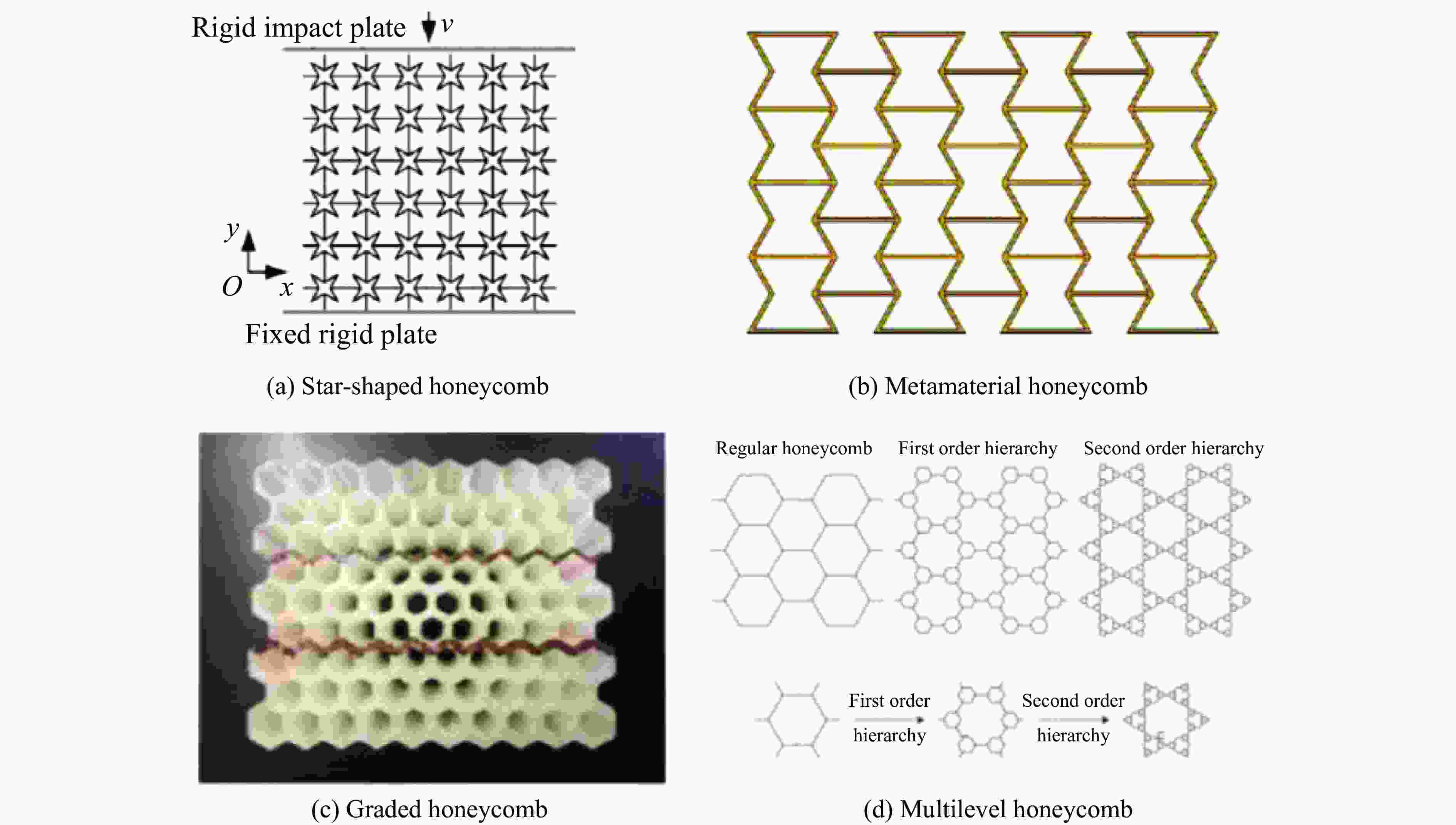
Research Progress on Dynamic Mechanical Response Characteristics of High-Velocity Particle Flow Impacting Multilayer Sandwich Composite Structures
-
摘要: 多层夹芯复合结构在抗冲击防护领域具有重要应用,尤其在应对爆炸破片颗粒群冲击中展现出优越的防护性能。在分析单层材料抗冲击性能及失效机制的基础上,综述了单颗粒和多颗粒冲击下复合结构的动态力学响应特性研究进展,结果表明:金属材料主要出现塑性变形、裂纹扩展及局部热软化等特征;陶瓷依靠其高硬度和脆性破坏可迅速分散冲击能量;纤维增强复合材料则利用连续纤维网络实现多级能量耗散。针对多层夹芯复合结构,颗粒高速冲击靶板会出现局部应力波传播、微裂纹产生和界面分层等现象,结构的抗冲击机理复杂。当前研究主要聚焦于结构在单次冲击下的抗冲击性能,多颗粒冲击下的防护机理仍不明确,且研究手段相对单一。其中,实验研究方法主要采用改装分离式霍普金森压杆(split Hopkinson pressure bar,SHPB)等装置实现颗粒群的高速加载,但二次冲击和速度极限问题仍未得到有效解决。数值模拟方面,SPH-FEM(smoothed particle hydrodynamics-finite element method)耦合方法是目前颗粒群冲击研究的主流方法,但其模型准确性问题仍需进一步研究。Abstract: Multilayer sandwich composite structures have significant applications in impact protection. In particular, they demonstrate superior protective performance when subjected to impacts from explosive fragment particle clusters. Based on an analysis of the impact resistance and failure mechanisms of single-layer materials, this paper reviews the research progress regarding the dynamic mechanical response characteristics of composite structures under both single-particle and multi-particle impacts. The results indicate that metallic materials predominantly exhibit features such as plastic deformation, crack propagation, and localized thermal softening. By contrast, ceramics rapidly disperse impact energy due to their high hardness and propensity for brittle fracture. Meanwhile, fiber-reinforced composites achieve hierarchical energy dissipation through their continuous fiber network. Studies on multilayer sandwich structures show that high-speed particle impacts on the target plate have been found to induce phenomena such as localized stress wave propagation, micro-crack formation, and interfacial delamination. The mechanisms underlying impact resistance in these structures are complex. However, current research primarily focuses on the impact resistance of structures under single-impact conditions. The protective mechanisms under multi-particle impacts remain unclear, and the employed research methods are relatively limited. Experimentally, approaches such as the modified split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) apparatus are predominantly utilized to achieve high-speed loading of particle clusters. Nevertheless, issues regarding secondary impacts and velocity limitations in these experiments have yet to be effectively resolved. In numerical simulations, the smoothed particle hydrodynamics-finite element method (SPH-FEM) coupling approach remains the mainstream method for investigating particle cluster impacts. However, concerns regarding the accuracy of these models still warrant further investigation.
-
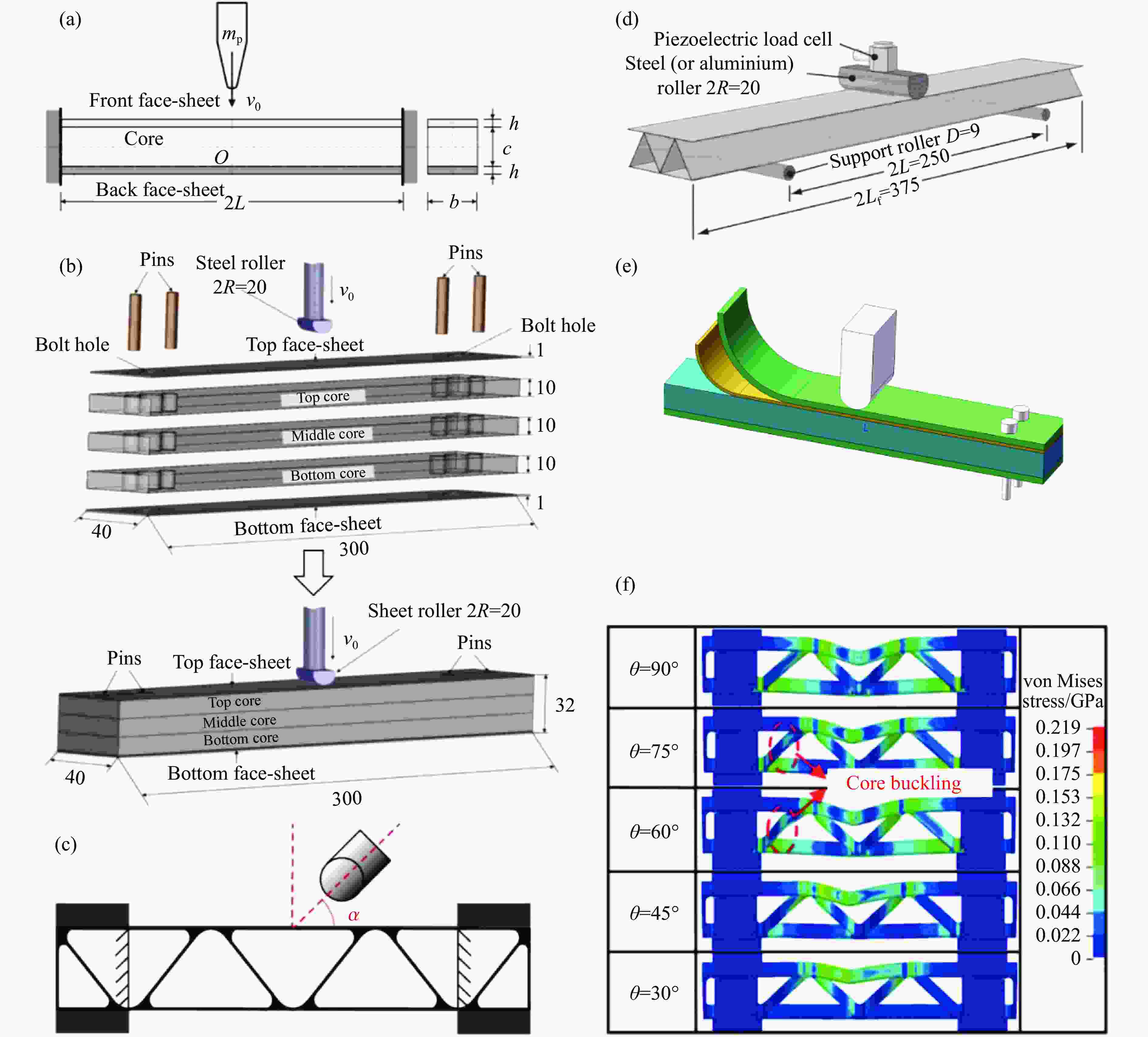
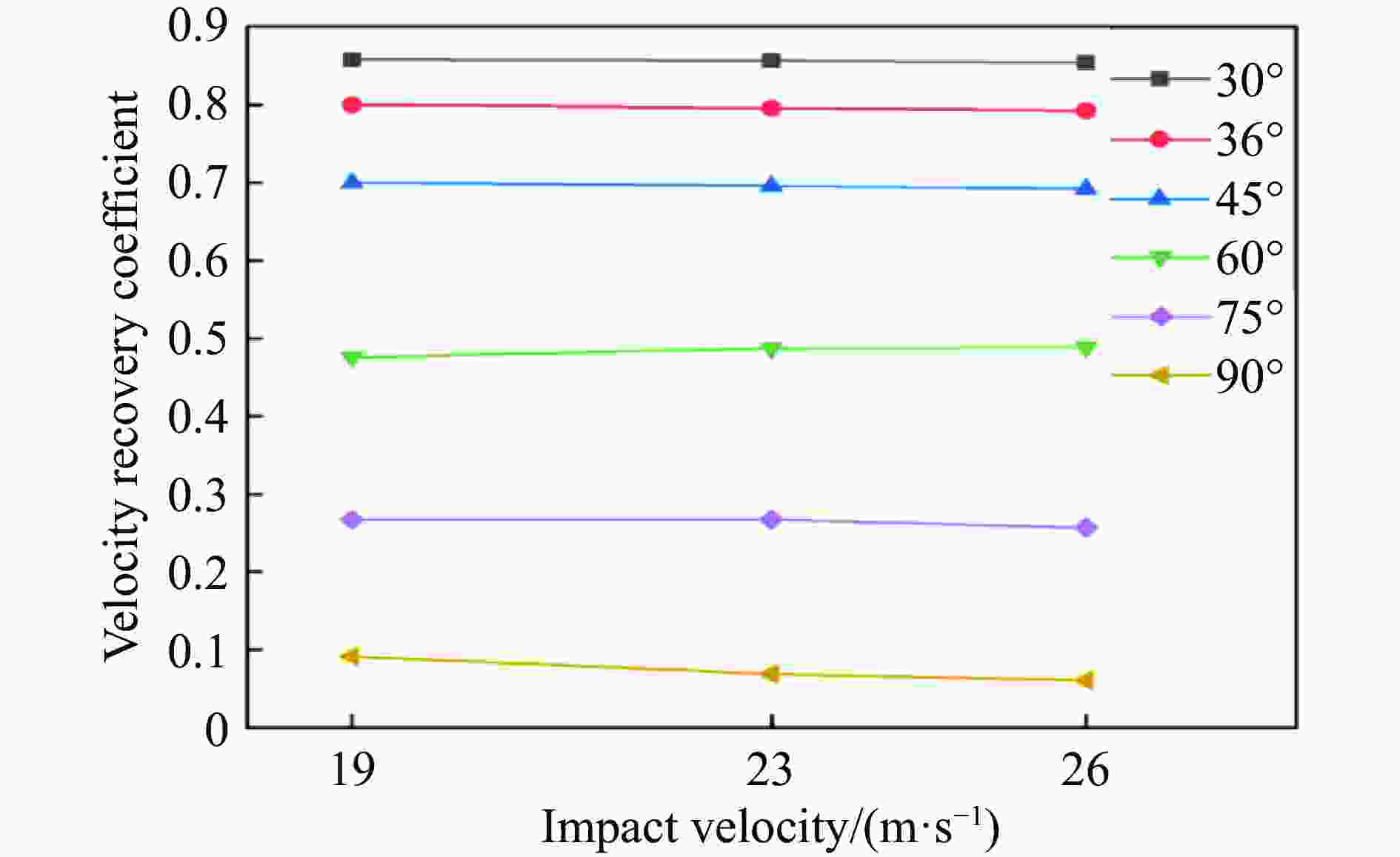
图 6 各类夹芯结构梁的变形与承载能力研究[57]:(a)完全固支的非对称细长夹层梁受重物横向冲击示意图;(b)梯度夹层梁装配示意图;(c)波纹夹层梁斜向冲击示意图;(d) 简支波纹芯夹层梁落锤冲击实验装置示意图;(e)用于夹层梁分析的几何模型及边界条件;(f) 波纹夹层梁在不同冲击角度下的最终数值变形模式(单位:mm)
Figure 6. Research on the deformation and bearing capacity of various types of sandwich structural beams[57]: (a) sketch of a fully clamped asymmetric slender sandwich beam transversely struck by a heavy mass; (b) schematic diagram of the assembly of graded sandwich beams; (c) schematic diagram of the oblique impact of corrugated sandwich beam; (d) sketch of the experimental setup of drop-weight test for simply-supported corrugated core sandwich beam; (e) geometry and boundary conditions used for the analysis of sandwich beams; (f) final numerical deformation modes of corrugated sandwich beams under different impact angles (Unit: mm)
-
[1] SHIRBHATE P A, GOEL M D. Performance of honeycomb sandwich structure under combined blast and impact of fragments [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Structures and Buildings, 2024, 177(2): 177–191. doi: 10.1680/jstbu.22.00167 [2] LI J, SHI S Q, LUO W M, et al. Study on explosion-resistance of biomimetic layered honeycomb structure [J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020, 2020(1): 5356145. doi: 10.1155/2020/5356145 [3] ZAID N Z M, REJAB M R M, MOHAMED N A N. Sandwich structure based on corrugated-core: a review [J]. MATEC Web of Conferences, 2016, 74: 00029. doi: 10.1051/matecconf/20167400029 [4] 唐方红, 文周. 碳纤维增强聚醚醚酮材料动态冲击数值模拟 [J]. 工程塑料应用, 2024, 52(5): 101–107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2024.05.015TANG F H, WEN Z. Numerical simulation of dynamic impact of carbon fiber reinforced PEEK material [J]. Engineering Plastics Application, 2024, 52(5): 101–107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2024.05.015 [5] REN J W, SUN M Q, ZHOU Y L, et al. Impact response of a sandwich with a foam aluminum core enhanced by a ceramic tile: an experimental study [J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials, 2023, 25(6): 625–644. doi: 10.1177/10996362221130967 [6] 俎政, 原天宇, 汤双双, 等. 蜂窝夹芯板多次低速冲击及冲击后剩余强度 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(28): 101–109.ZU Z, YUAN T Y, TANG S S, et al. Repeated low velocity impacts on honeycomb sandwich panels and residual strength after impacts [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(28): 101–109. [7] KUCUKKALFA E, GHADERIARAM A, YILDIZ K, et al. Damage detection of CNT/CNC-reinforced foam-cored sandwich composites by acoustic emission tests under flexural load [C]//AIAA SCITECH 2023 Forum. National Harbor: AIAA, 2023. [8] WANG X, HU Y C. Preparation and bending properties of lattice sandwich structure for wooden truss [C]//3rd Annual International Conference on Advanced Material Engineering (AME 2017). Shanghai: Atlantis Press, 2017: 343–349. [9] RANAWEERA P, BAMBACH M R, WEERASINGHE D, et al. Ballistic impact response of monolithic steel and tri-metallic steel-titanium-aluminium armour to nonrigid NATO FMJ M80 projectiles [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 182: 110200. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2022.110200 [10] WANG Y L, HUI S X, LIU R, et al. Evaluation of dynamic performance and ballistic behavior of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr-1Zr alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(2): 429–436. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63620-2 [11] DENG Y F, HU A, XIAO X K, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on the ballistic resistance of ZK61m magnesium alloy plates struck by blunt and ogival projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 158: 104021. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.104021 [12] 文周, 杨丽君, 舒润泽, 等. 胞元尺寸对聚醚醚酮蜂窝夹芯板动态冲击性能的影响 [J]. 塑料工业, 2025, 53(1): 111–118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5770.2025.01.017WEN Z, YANG L J, SHU R Z, et al. Influence of cell size on the dynamic impact performances of polyetheretherketone honeycomb sandwich panels [J]. China Plastics Industry, 2025, 53(1): 111–118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5770.2025.01.017 [13] JIANG K, ZHANG Q, LI J G, et al. Abnormal hardening and amorphization in an FCC high entropy alloy under extreme uniaxial tension [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2022, 159: 103463. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2022.103463 [14] KHAN M A, WANG Y W, YASIN G, et al. Microstructure characteristic of spray formed 7055 Al alloy subjected to ballistic impact by two different steel core projectiles impact [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2019, 8(6): 6177–6190. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.10.012 [15] YANG J B, HAN J Z, TIAN H D, et al. Structural and magnetic properties of nanocomposite Nd-Fe-B prepared by rapid thermal processing [J]. Engineering, 2020, 6(2): 132–140. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2019.12.008 [16] SUN P, SU B L, TAN C S, et al. The influence of heat treatment on the high temperature tensile properties of a Near-α as-cast titanium alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2025, 1010: 178148. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2024.178148 [17] GAO X Z, JIANG W, LU Y P, et al. Excellent strength-ductility combination of Cr26Mn20Fe20Co20Ni14 high-entropy alloy at cryogenic temperatures [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 154: 166–177. doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2023.01.023 [18] CHEN J L, LI S T, MA S, et al. The anti-penetration performance and mechanism of metal materials: a review [J]. Engineering, 2024, 40: 131–157. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2024.03.023 [19] ZHANG W L, HE L J, LU Z G, et al. Microstructural characteristics and formation mechanism of adiabatic shear bands in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy under dynamic shear loading [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2020, 791: 139430. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.139430 [20] ZHOU S Y, DENG C, LIU S F, et al. Microstructure, texture, and fracture of pure magnesium adiabatic shear band under high strain rate compression [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 822: 141632. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141632 [21] CHEN X Z, WU H B, LIU H, et al. Microstructure and properties of pressureless-sintered zirconium carbide ceramics with MoSi2 addition [J]. Materials, 2024, 17(9): 2155. doi: 10.3390/ma17092155 [22] HUANG C Y, CHEN Y L. Design and impact resistant analysis of functionally graded Al2O3-ZrO2 ceramic composite [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 91: 294–305. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.11.091 [23] WANG W R, YE W, HUANG K S, et al. Impact-resistance mechanism of gradient ceramic/high entropy alloy composite structure [J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2024, 31(25): 6885–6897. doi: 10.1080/15376494.2023.2239814 [24] TAN W K, ZOU J, WANG W M, et al. Integrated preparation of B4C-TiB2 multilayer graded ceramics with high hardness and high toughness [J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2024, 21(5): 3453–3461. doi: 10.1111/ijac.14746 [25] WANG J L, MA D J, SUN L. The influence of crack forms on indentation hardness test results for ceramic materials [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2015, 50(18): 6096–6102. doi: 10.1007/s10853-015-9162-2 [26] ZHENG Z J, WANG E Z, LIU X L, et al. The dynamic response of brittle materials under impact loading [J]. International Journal of Nonlinear Sciences and Numerical Simulation, 2017, 18(2): 115–127. doi: 10.1515/ijnsns-2016-0019 [27] WANG M F, LI Y T, LUO H S, et al. Experiment and numerical simulation of damage progression in transparent sandwich structure under impact load [J]. Materials, 2022, 15(11): 3809. doi: 10.3390/ma15113809 [28] YU Y L, WU Y D, MA M H, et al. Fracture mechanics of ceramic layers in composite armor: effects of impact velocity [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2025, 198: 105211. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2024.105211 [29] ÖZSOY M İ. Investigation of the energy absorption behavior and damage mechanisms of aramid/carbon/jute fiber hybrid epoxy composites [J]. Polymer Composites, 2024, 45(12): 11515–11531. doi: 10.1002/pc.28583 [30] WANG B, XIONG J, WANG X J, et al. Energy absorption efficiency of carbon fiber reinforced polymer laminates under high velocity impact [J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 50: 140–148. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.01.046 [31] MOUSAVI M V, KHORAMISHAD H. Investigation of energy absorption in hybridized fiber-reinforced polymer composites under high-velocity impact loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 146: 103692. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103692 [32] SEBAEY T A, RAJAK D K, MEHBOOB H. Internally stiffened foam-filled carbon fiber reinforced composite tubes under impact loading for energy absorption applications [J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 255: 112910. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112910 [33] YANG H Y, REN Y R. On energy absorption capability and controllable failure modes of CFRP circular tube using numerical simulation [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2024, 205: 112423. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2024.112423 [34] JIANG H Y, WANG Y H, REN Y R. Controllable energy-absorption behaviors of the perforated CFRP tube with an adhesively bonded CFRP patch [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2022, 181: 110015. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2022.110015 [35] LIU Z D, WANG S, HAN Z Q. Experiments and numerical simulations on ceramic-metal composite targets penetrated by a 7.62 mm armour-piercing projectile [J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2024, 2891: 052020. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2891/5/052020 [36] GOLEWSKI P, SADOWSKI T. Description of thermal protection against heat transfer of carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) coated by stiffened ceramic mat (TBC) [J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 229: 111489. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111489 [37] 王旭康. 碳纤维增强聚醚醚酮复合材料构件层间性能增强方法研究 [D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2024.WANG X K. Research on interlaminar properties enhancement of carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone composite components [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2024. [38] TANG E L, YIN H T, CHEN C, et al. Simulation of CFRP/aluminum foam sandwich structure under high velocity impact [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(4): 7273–7287. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.04.093 [39] WANG B, ZHANG G Q, WANG S X, et al. High velocity impact response of composite lattice core sandwich structures [J]. Applied Composite Materials, 2014, 21(2): 377–389. doi: 10.1007/s10443-013-9345-4 [40] 吴丽丽, 徐翔, 李远, 等. 多胞圆管夹芯组合板落锤冲击试验及数值仿真 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2024, 43(23): 38–46, 55. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2024.23.005WU L L, XU X, LI Y, et al. Drop hammer impact tests and numerical simulation of multi-cell circular tube sandwich composite panel [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2024, 43(23): 38–46, 55. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2024.23.005 [41] YU S, YU X F, AO Y L, et al. The impact resistance of composite Y-shaped cores sandwich structure [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 169: 108389. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2021.108389 [42] 田策. 低温环境中复合夹芯结构抗冲击性能研究 [D]. 北京: 军事科学院, 2024.TIAN C. Research on the impact resistance of composite sandwich structures in low-temperature environments [D]. Beijing: Academy of Military Science, 2024. [43] LIU C J, ZHANG Y X, YE L. High velocity impact responses of sandwich panels with metal fibre laminate skins and aluminium foam core [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 100: 139–153. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.09.004 [44] LUO G, MO Y M, WU C B, et al. Experimental study of ice impact on aluminium/carbon fiber reinforced composite dual plate [J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2022, 27(2): 510–521. doi: 10.1080/13588265.2020.1816438 [45] KUMAR S J A, KUMAR S J A. Low-velocity impact damage and energy absorption characteristics of stiffened syntactic foam core sandwich composites [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 246: 118412. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118412 [46] ZHAO Y, YANG Z H, YU T L, et al. Mechanical properties and energy absorption capabilities of aluminium foam sandwich structure subjected to low-velocity impact [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 273: 121996. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121996 [47] WANG H, XIE S C, JING K K, et al. Closed-cell polyurethane in-situ foaming honeycomb for enhanced energy absorption and water intrusion resistance [J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2025, 114: 572–587. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2024.12.011 [48] HAMID W L H W A, AMINANDA Y, DAWOOD M S. Experimental investigation on the energy absorption capability of foam-filled nomex honeycomb structure [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 393: 460–466. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.393.460 [49] 王凡, 熊景毅, 王文群, 等. 低速冲击下碳纤维面板泡沫夹芯复合材料的损伤分析 [J]. 力学季刊, 2024, 45(3): 739–749.WANG F, XIONG J Y, WANG W Q, et al. Damage analysis of carbon fiber panel and foam core sandwich composites under low speed impact [J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2024, 45(3): 739–749. [50] 赵相江, 马小敏, 李世强, 等. 爆炸载荷下双层梯度夹芯板的抗爆性能 [J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2021, 52(6): 1022–1028.ZHAO X J, MA X M, LI S Q, et al. The explosion resistance of double-layer honeycomb sandwich panel under blast load [J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021, 52(6): 1022–1028. [51] WANG Z G, LI Z D, XIONG W. Experimental investigation on bending behavior of honeycomb sandwich panel with ceramic tile face-sheet [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 164: 280–286. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.10.077 [52] ZHAO S C, GAO X, LOU J J, et al. Experimental study on impact and flexural behaviors of CFRP/aluminum-honeycomb sandwich panel [J]. E-Polymers, 2024, 24(1): 20240044. doi: 10.1515/epoly-2024-0044 [53] MEI J, LIU J Y, ZHANG M G, et al. Experimental and numerical study on the ballistic impact resistance of the CFRP sandwich panel with the X-frame cores [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2022, 232: 107649. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107649 [54] GAO G W, TANG E L, YANG G L, et al. Energy absorption performance and optimization of combination modes for carbon fiber reinforced plastics/aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels [J]. Polymer Composites, 2022, 43(1): 52–67. doi: 10.1002/pc.26356 [55] ZHANG J X, YUAN H, LI J F, et al. Dynamic response of multilayer curved aluminum honeycomb sandwich beams under low-velocity impact [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2022, 177: 109446. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2022.109446 [56] HE W T, LIU J X, TAO B, et al. Experimental and numerical research on the low velocity impact behavior of hybrid corrugated core sandwich structures [J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 158: 30–43. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.09.009 [57] GUO H Y, YUAN H, ZHANG J X, et al. Review of sandwich structures under impact loadings: experimental, numerical and theoretical analysis [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2024, 196: 111541. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.111541 [58] TANG E L, ZHANG X Q, HAN Y F. Experimental research on damage characteristics of CFRP/aluminum foam sandwich structure subjected to high velocity impact [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2019, 8(5): 4620–4630. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.08.006 [59] ZHAO N, YE R C, TIAN A L, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on the anti-penetration performance of metallic sandwich plates for marine applications [J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials, 2019, 22(2): 494–522. doi: 10.1177/1099636219855335 [60] PALOMBA G, EPASTO G, SUTHERLAND L, et al. Aluminium honeycomb sandwich as a design alternative for lightweight marine structures [J]. Ships and Offshore Structures, 2022, 17(10): 2355–2366. doi: 10.1080/17445302.2021.1996109 [61] SHIH C H, YOU J L, LEE Y L, et al. Design and ballistic performance of hybrid plates manufactured from aramid composites for developing multilayered armor systems [J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(22): 5026. doi: 10.3390/polym14225026 [62] KIREMITCI S C, ELALDI F. High velocity impact performance of double ceramic stacking on multilayer sandwich armor structures [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2025, 16(4): 1006–1018. doi: 10.1177/20414196241304038 [63] ALAM S, NGUYEN D. An investigation of the ballistic impact behavior of multi-layered armor structure [J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 2025, 44(17/18): 1357–1374. doi: 10.1177/07316844241239711 [64] ZNIKER H, OUAKI B, BOUZAKRAOUI S, et al. Energy absorption and damage characterization of GFRP laminated and PVC-foam sandwich composites under repeated impacts with reduced energies and quasi-static indentation [J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2022, 16: e00844. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2021.e00844 [65] ZOU Y C, XIONG C, YIN J H, et al. Research on dynamic cumulative damage effect of metal rubber and stress wave propagation characteristics of layered composite structure [J]. Science of Advanced Materials, 2021, 13(5): 981–990. doi: 10.1166/sam.2021.3997 [66] BIKAKIS G S E, SAVAIDIS A, ZALIMIDIS P, et al. Influence of the metal volume fraction on the permanent dent depth and energy absorption of GLARE plates subjected to low velocity impact [J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2016, 161: 012055. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/161/1/012055 [67] SUN J, HUANG L H, DAI Y F. Dynamic response and damage accumulation of laminated composites under repeated low-velocity impacts [J]. Materials, 2023, 16(2): 778. doi: 10.3390/ma16020778 [68] LIAO B B, ZHOU J W, LI Y, et al. Damage accumulation mechanism of composite laminates subjected to repeated low velocity impacts [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2020, 182: 105783. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105783 [69] 夏鑫, 孔祥韶, 郑成, 等. 金属面复合材料波纹夹层结构多次冲击性能及其剩余强度 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(9): 5016–5031. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20240419.002XIA X, KONG X S, ZHENG C, et al. Performance and residual strength of metal-faced composite corrugated sandwich structure under multiple impacts [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(9): 5016–5031. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20240419.002 [70] LIU X F, REN Q X, JIA L G. Temperature field analysis of concrete filled steel tube reinforced concrete columns in fire [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 644: 5019–5022. [71] LI Y C, WANG W, WANG X. Finite element analysis of deformation effect of concrete filled steel tubular composite frame under high temperature [J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 676: 012076. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/676/1/012076 [72] GAO X C, XIA H, WANG X Y, et al. Experimental study on dynamic mechanical characteristics and energy evolution of sandstone under cyclic impact loading [J]. Shock and Vibration, 2022, 2022(1): 4805589. [73] CHEN Y L, WU H S, PU H, et al. Investigations of damage characteristics in rock material subjected to the joint effect of cyclic loading and impact [J]. Energies, 2020, 13(9): 2154. doi: 10.3390/en13092154 [74] TANG H P, WANG J Z, AO Q B, et al. Effect of pore structure on performance of porous metal fiber materials [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2015, 44(8): 1821–1826. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5372(15)30107-7 [75] SINGH J P, PANDEY P M. Fabrication and assessment of mechanical properties of open cell porous regular interconnected metallic structure through rapid manufacturing route [J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2018, 24(1): 138–149. doi: 10.1108/RPJ-04-2015-0043 [76] ZHU Z Y, LI X W, CHEN Q L, et al. Simulations and tests of composite marine structures under low-velocity impact [J]. Polish Maritime Research, 2021, 28(1): 59–71. doi: 10.2478/pomr-2021-0006 [77] ELAMIN M, LI B, TAN K T. Impact damage of composite sandwich structures in arctic condition [J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 192: 422–433. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.03.015 [78] WANG Y Q. Auxetic composite laminates with through-thickness negative Poisson’s ratio for mitigating low velocity impact damage: a numerical study [J]. Materials, 2022, 15(19): 6963. doi: 10.3390/ma15196963 [79] 王易航, 吴先前, 黄晨光. 颗粒群冲击诱导光伏电池性能衰减的特性与机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(1): 015901.WANG Y H, WU X Q, HUANG C G. Performance deterioration behavior of photovoltaic cells subjected to massive-particles impact environment [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(1): 015901. [80] JUNG S, YANG E, JUNG W, et al. Anti-erosive mechanism of a grooved surface against impact of particle-laden flow [J]. Wear, 2018, 406/407: 166–172. [81] 张凯雄. 砂石颗粒群冲击条件下圆弧型结构靶板的抗冲蚀机理及反弹特性的数值研究 [D]. 太原: 太原科技大学, 2024.ZHANG K X. Numerical study on erosion resistance mechanism and rebound characteristics of arc-shaped structure target under the impact of sand particles swarm [D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, 2024. [82] 胡朝磊, 孙海亮, 王志鹏, 等. 高速颗粒流冲击下负泊松比力学超材料夹芯梁的动态响应及缓冲吸能机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(12): 123101. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0045HU C L, SUN H L, WANG Z P, et al. Dynamic response and mechanism of mitigation and energy absorption of sandwich beams with a mechanical metamaterial core of negative Poisson’s ratio subjected to high-velocity impact of granular slug [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(12): 123101. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0045 [83] TAKAFFOLI M, PAPINI M. Numerical simulation of solid particle impacts on Al6061-T6 part Ⅱ: materials removal mechanisms for impact of multiple angular particles [J]. Wear, 2012, 296(1/2): 648–655. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2012.07.022 [84] LI W Y, WANG J, ZHU H T, et al. On ultrahigh velocity micro-particle impact on steels—a multiple impact study [J]. Wear, 2014, 309(1/2): 52–64. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2013.10.011 [85] 陈高飞. 微细颗粒高速撞击沟槽结构叶片靶板抗冲蚀机理研究 [D]. 太原: 太原科技大学, 2023.CHEN G F. Study on anti-erosion mechanism of high speed impact of fine particles on grooved blade target [D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, 2023. -






 下载:
下载: