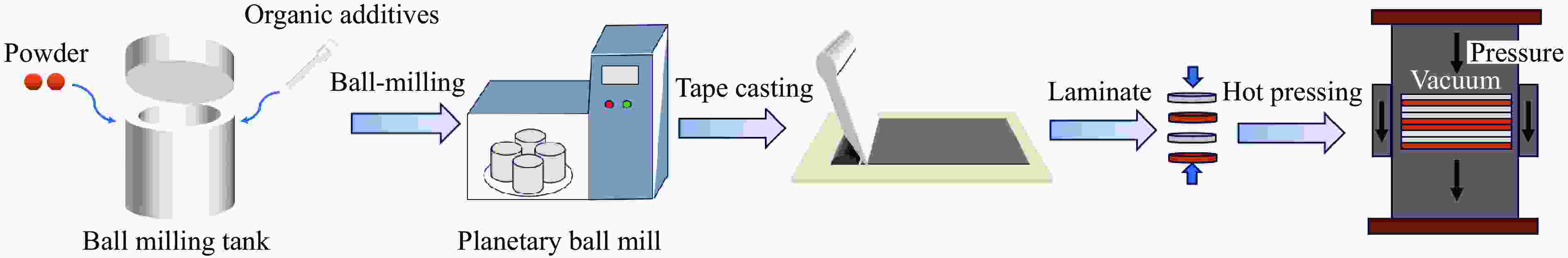
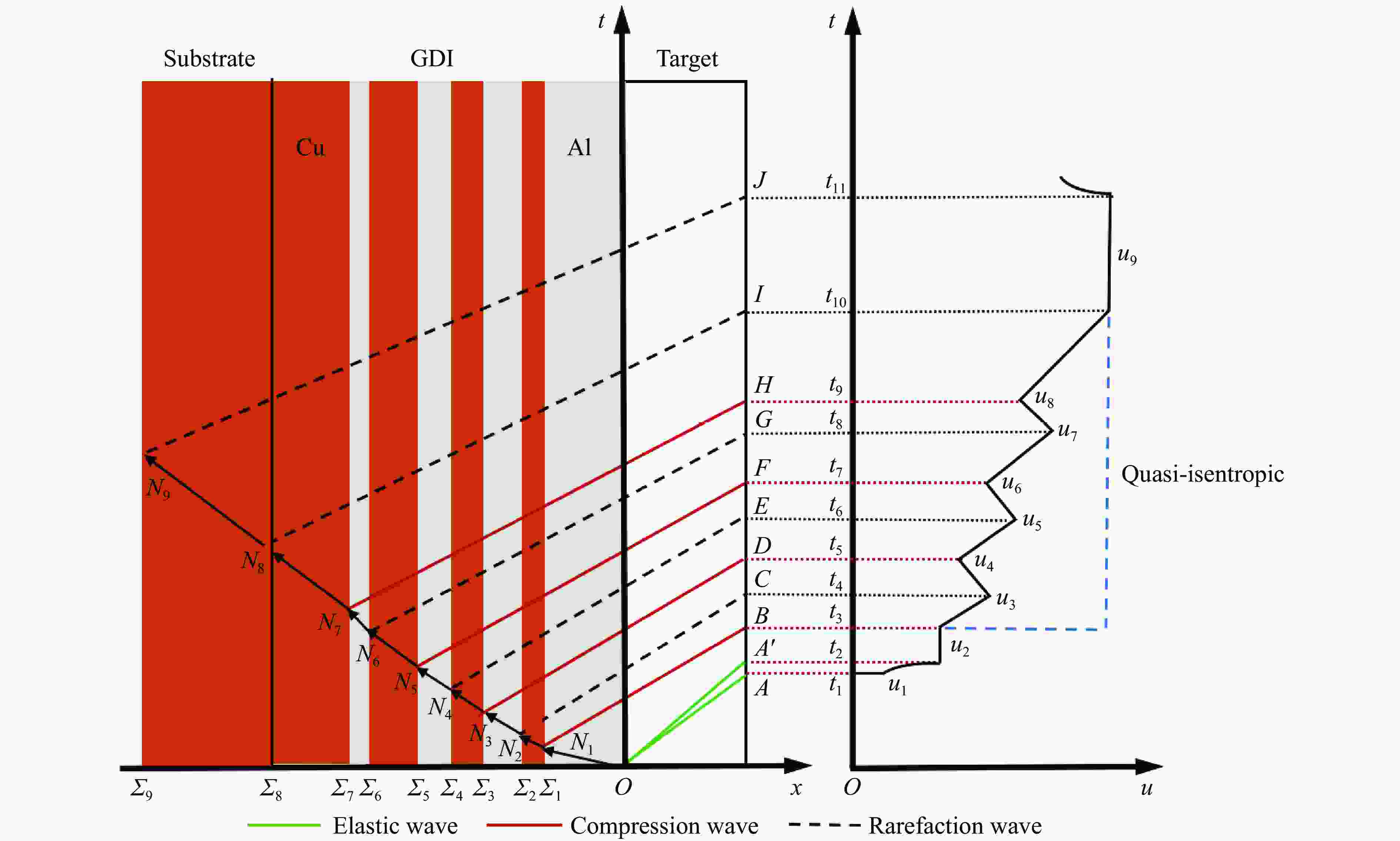
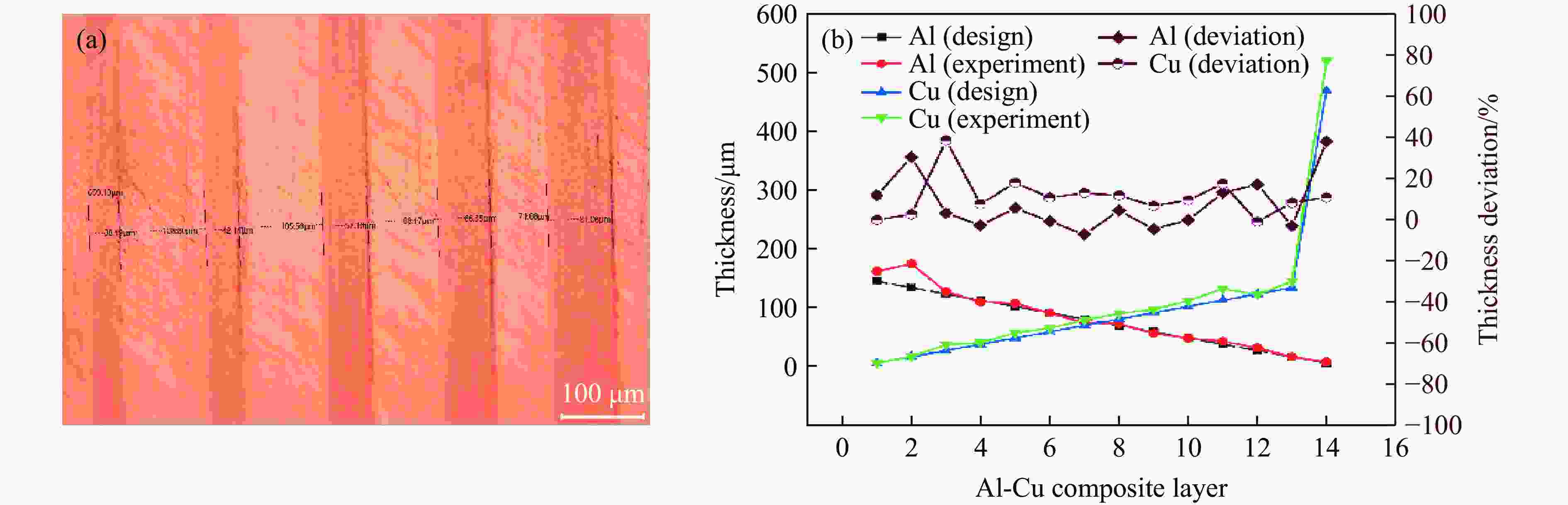
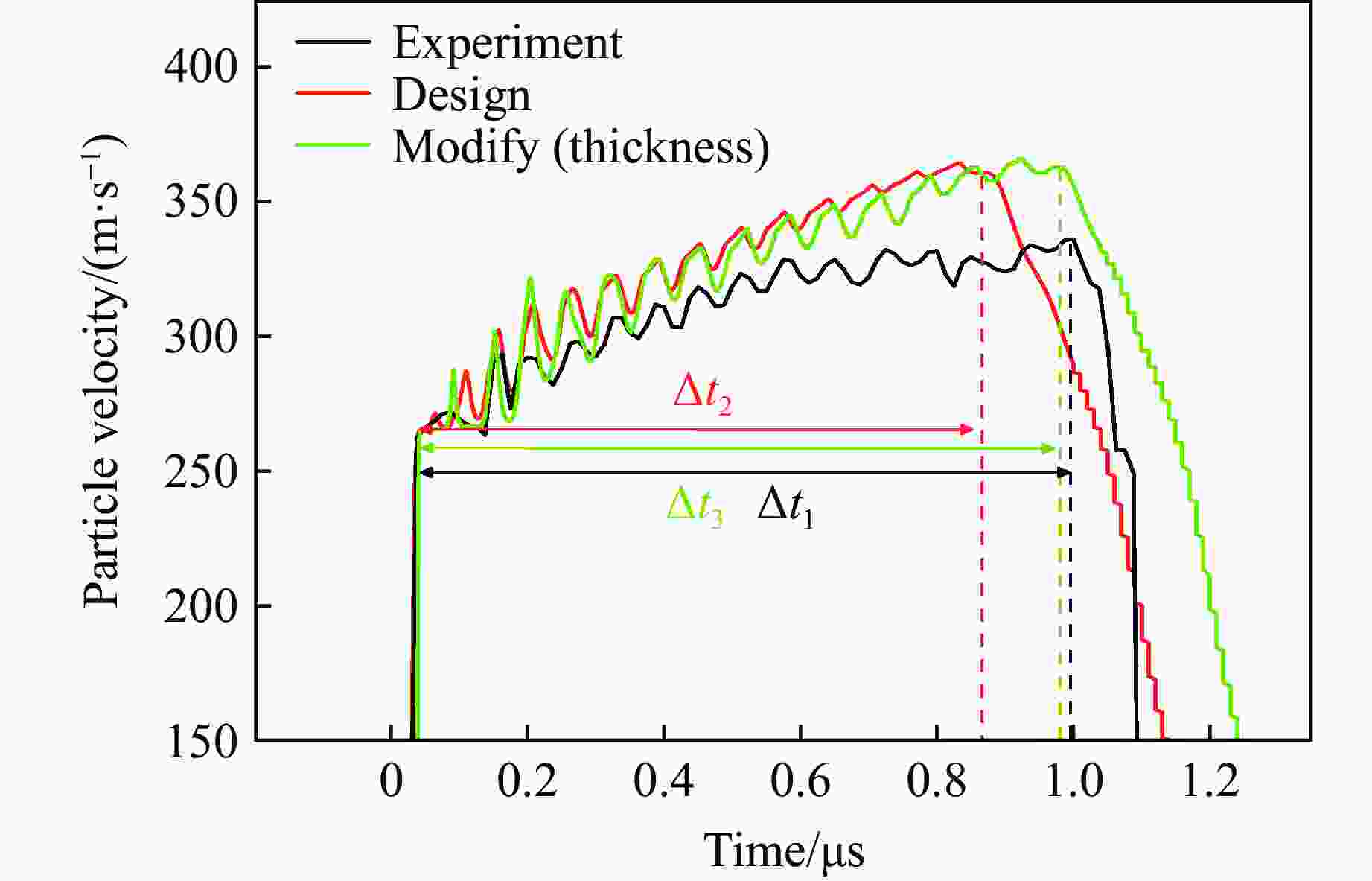
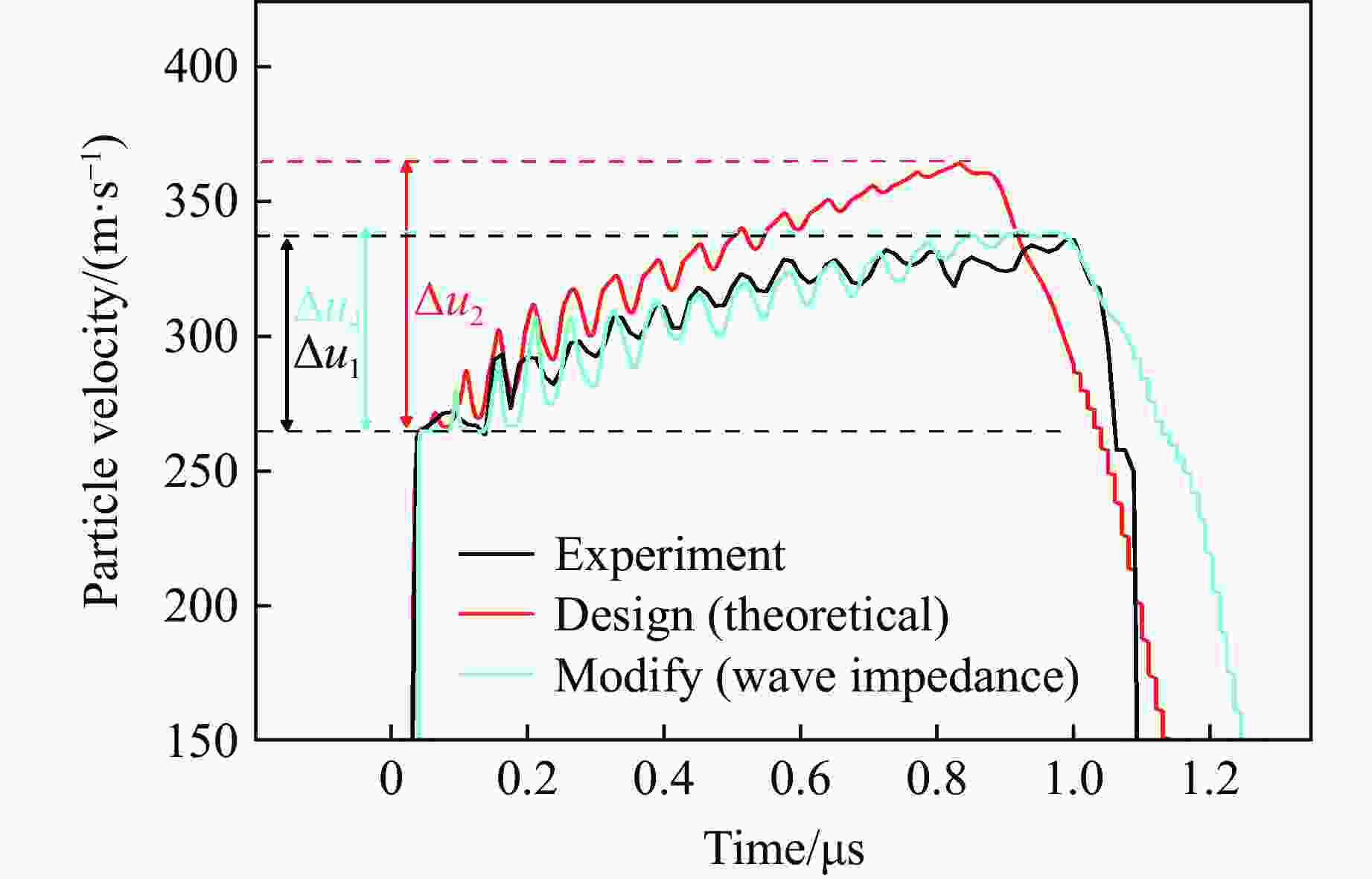
Tape Casting Preparation and Quasi-Isentropic Loading Properties of Al-Cu Periodic Laminated Gradient Materials
-
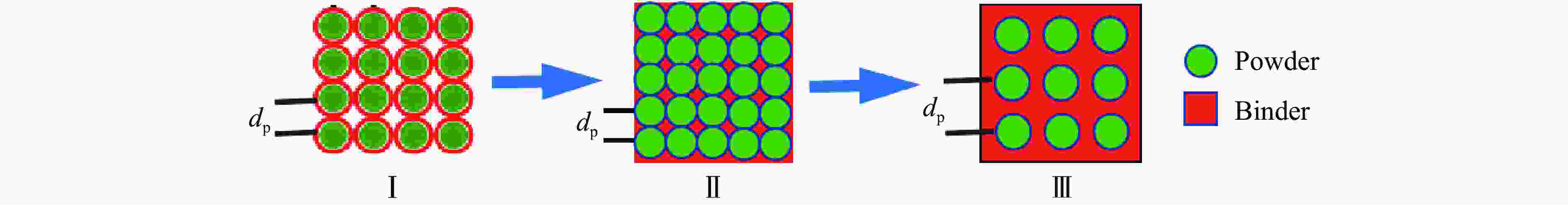
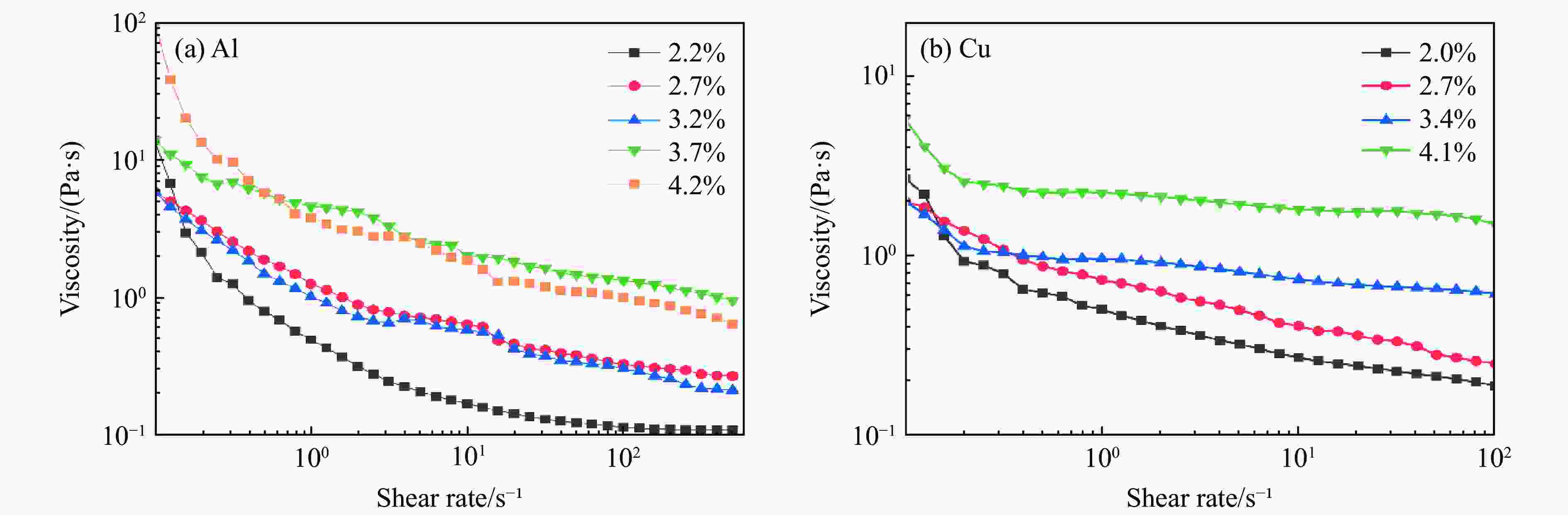
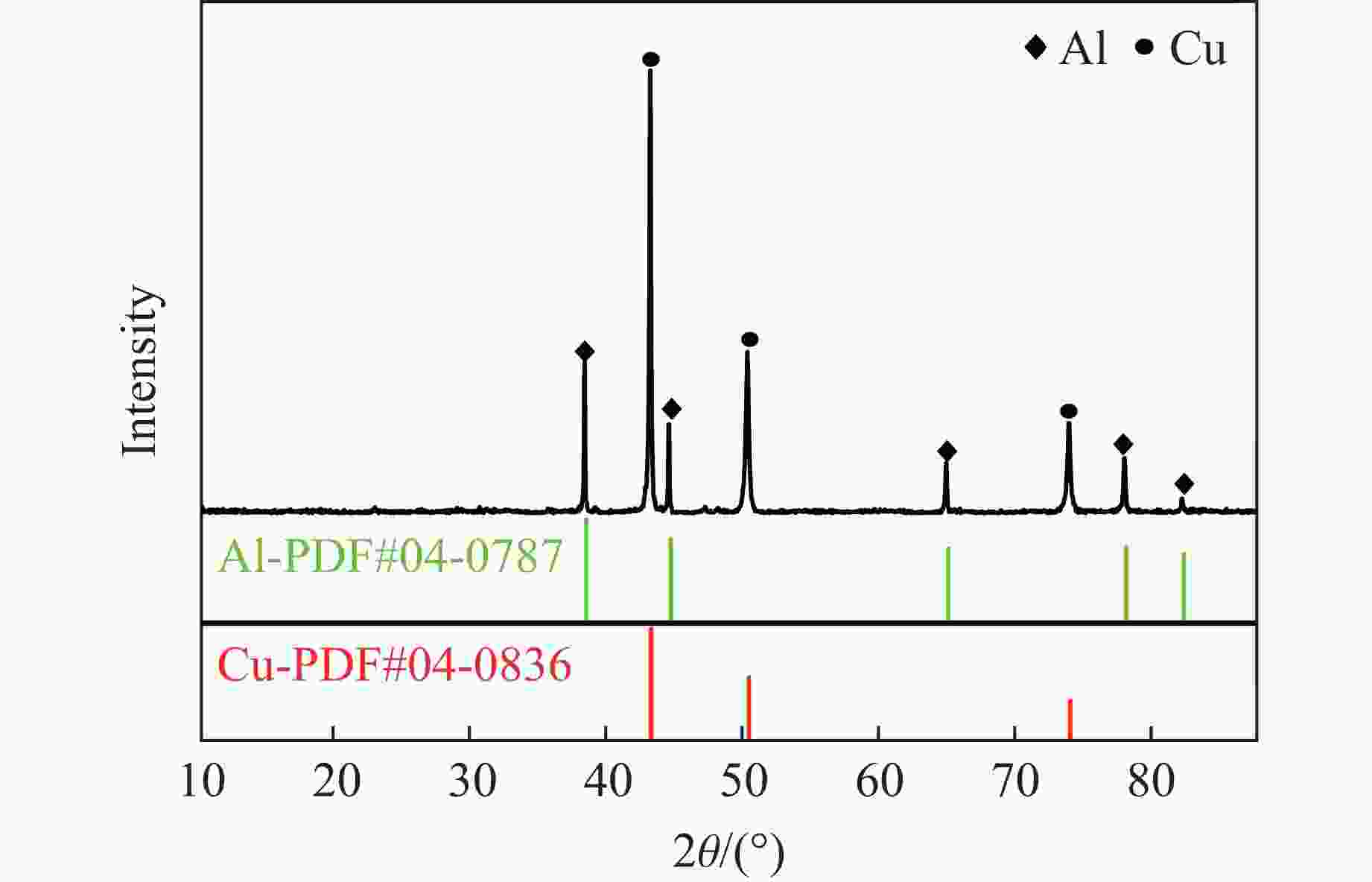
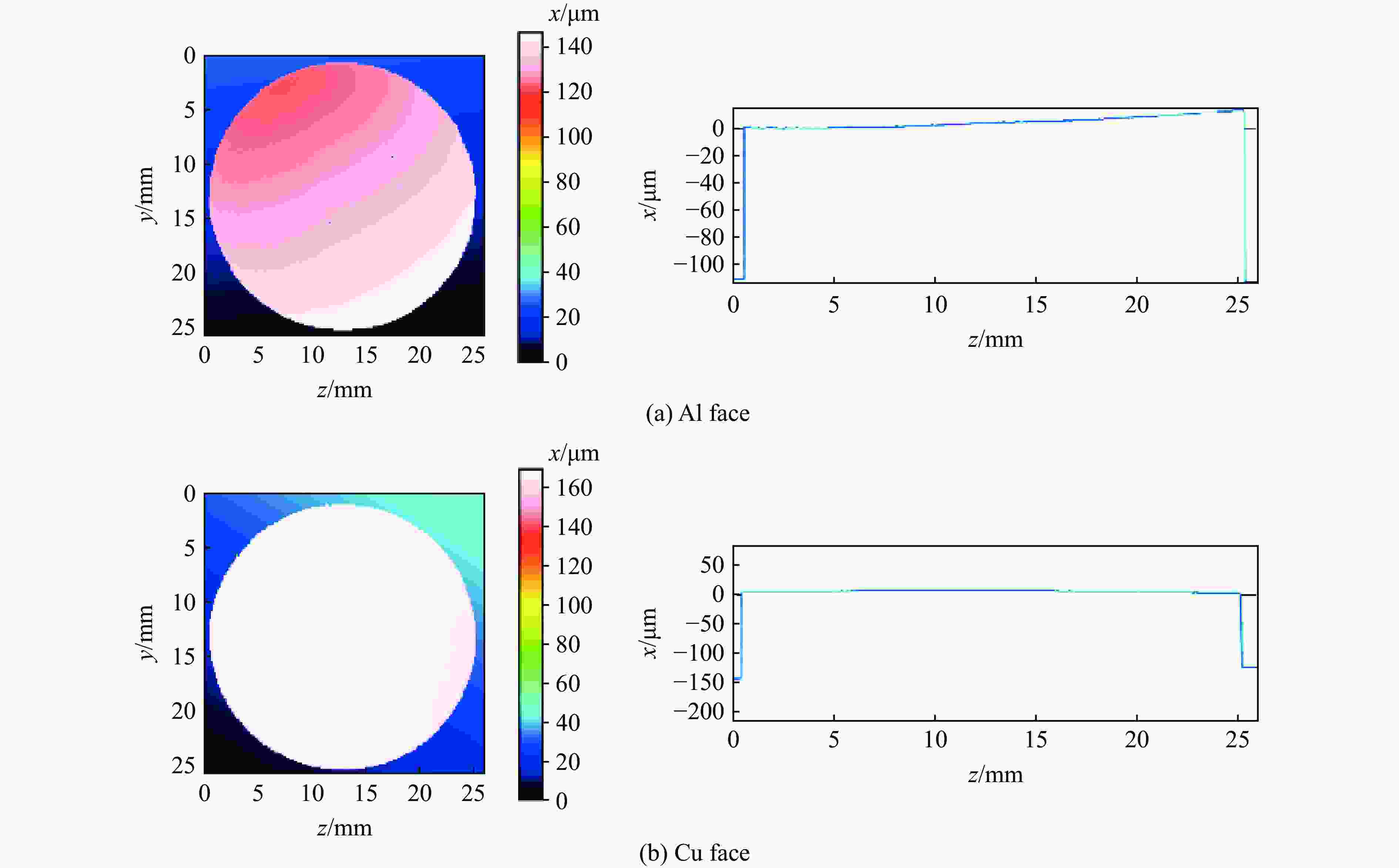
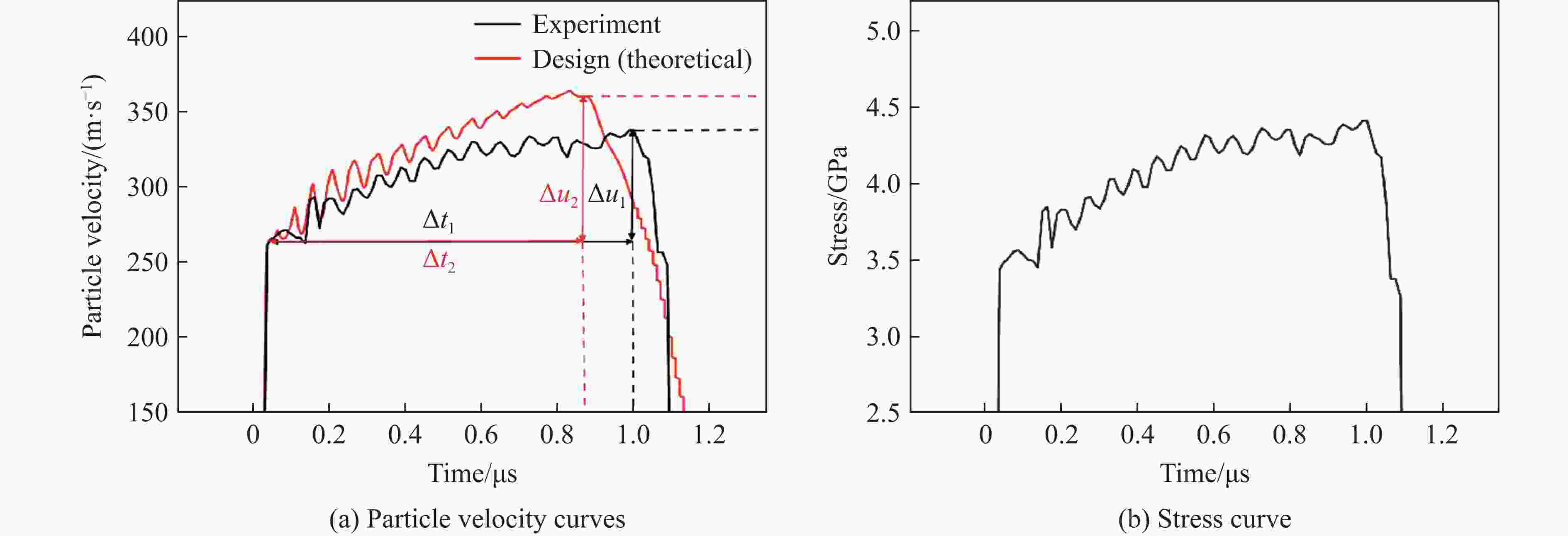
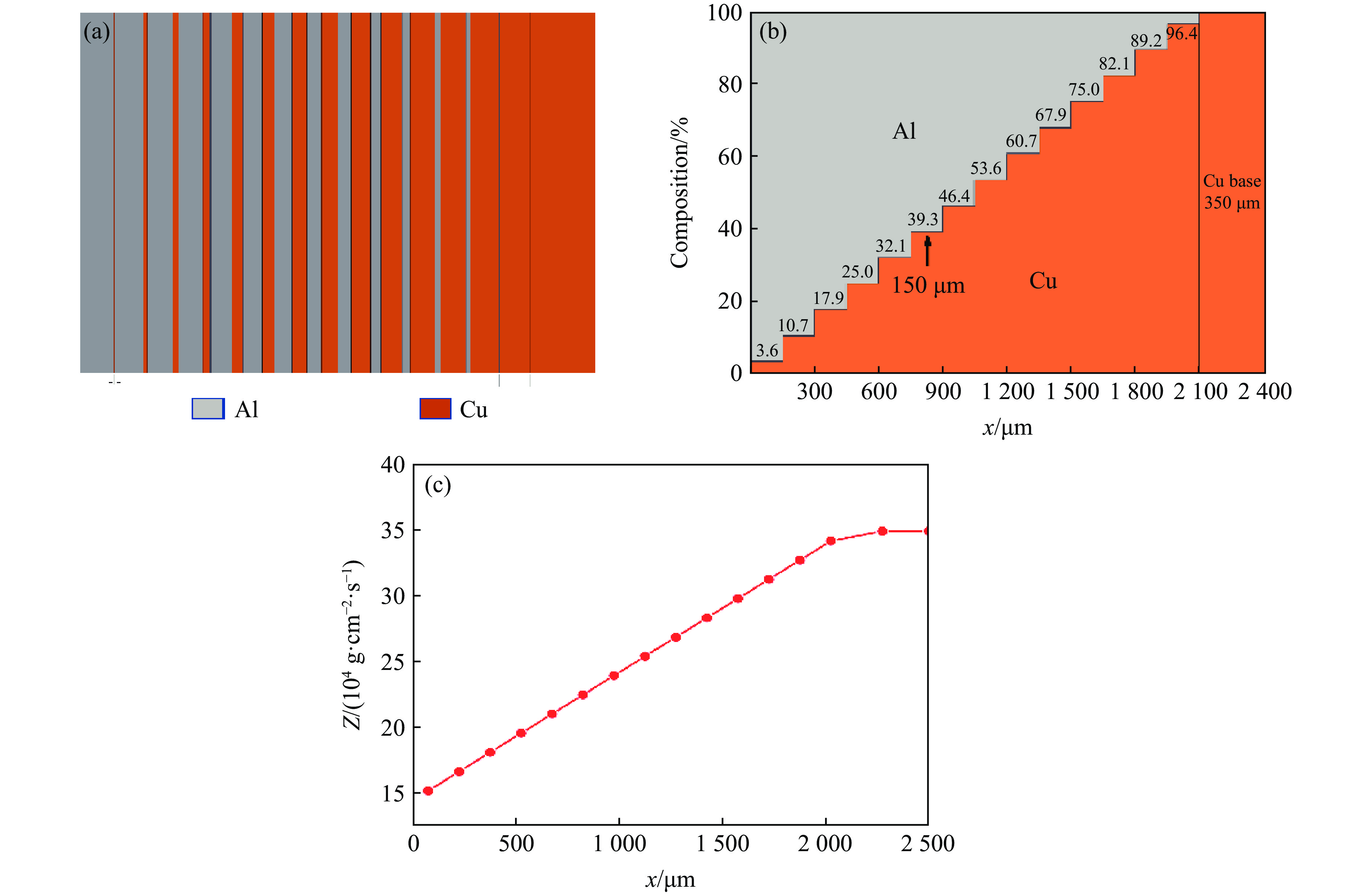
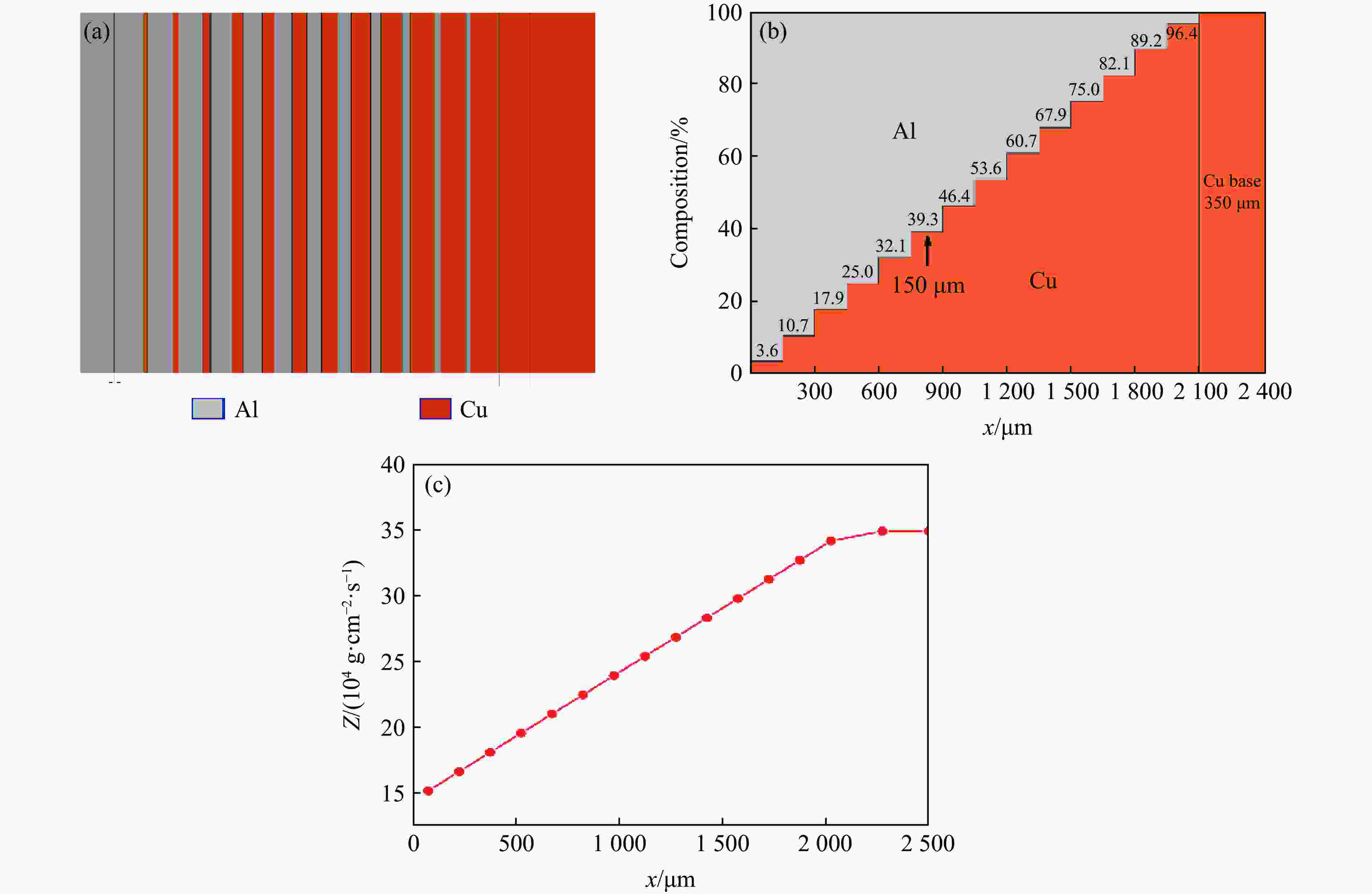
摘要: 周期叠层梯度材料具有独立可控的波阻抗分布和极少的物相反应,已被用于实现准等熵加载。然而,由于制备技术的局限性,目前制备的周期叠层梯度材料的波系作用时间只有纳秒量级,难以获得更高量级的加载时间。为此,系统探究了流延技术,成功通过流延法结合低温致密化技术制备出大尺寸Al-Cu周期叠层梯度材料。通过微观结构表征和动态加载实验,验证了其质量和准等熵加载特性。结果表明:材料梯度结构明显,层间平行度高,层界面结合良好,无裂纹缺陷,且无金属间化合物生成;材料致密度达95.8%,整体变形量小于15 μm。Al-Cu周期叠层梯度材料以510.6 m/s的驱动速度加载6 μm厚Al靶时,加载波形振荡上升,加载时间接近1 μs。通过对实验材料Al/Cu周期层厚和Cu层波阻抗进行修正,设计模拟结果与实验曲线在加载趋势上吻合较好,表现出良好的准等熵加载特性。研究结果可为周期叠层梯度材料制备技术提供理论依据和技术支持。Abstract: Periodic laminated gradient materials with independently controllable wave impedance distributions and minimal physical phase reactions are now being used for quasi-isentropic loading. However, the wave system action time of the currently periodic laminated gradient materials are on the order of nanoseconds due to limitations in preparation technology, which makes it difficult to achieve loading times of significantly larger magnitudes. In this study, the tape casting process was systematically investigated, and large-size Al-Cu periodic laminated gradient materials were successfully prepared using a combined technique of tape casting and low-temperature densification. The quality and quasi-isentropic loading properties were verified through microstructural characterization and dynamic loading experiments. The results show that the gradient structure of the material is well-defined, the interlayer parallelism is high, the layer interface is well bonded, and that no crack defects or intermetallic compounds generated. The material exhibits a densification of 95.8% and a total deformation less than 15 μm. When the Al-Cu periodic laminated gradient material was loaded with a 6 μm-thick Al target at a driving speed of 510.6 m/s, the loading waveform oscillated and increased with a loading time approaching 1 μs. The loading trends of simulation results agree well with the experimental curves through correcting Al/Cu periodic layer thickness and Cu layer wave impedance. The materials demonstrate excellent quasi-isentropic loading characteristics. This study provides theoretical basis, technical support and new preparation techniques for the application of periodic laminated gradient materials.
-
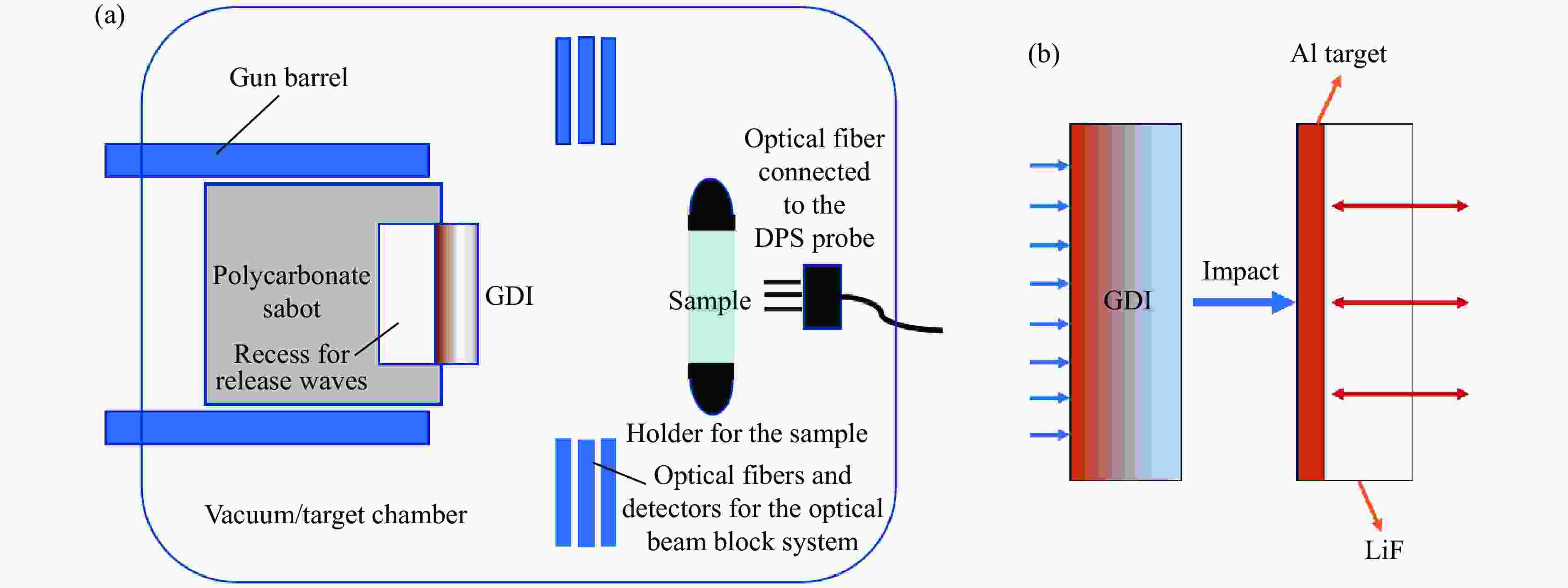
图 3 (a) 基于轻气炮的飞片冲击实验装置示意图,(b) 冲击实验侧视图(直径为16 mm的GDI冲击直径为18 mm的6 μm厚铝靶和6 mm厚LiF窗口)
Figure 3. (a) Schematic diagram of flyer plate impact experiments using a light-gas gun; (b) side view of an impact experiment in which the GDI with a diameter of 16 mm impacts a 6 μm-thick Al target and 6 mm-thick LiF window, both with a diameter of 18 mm
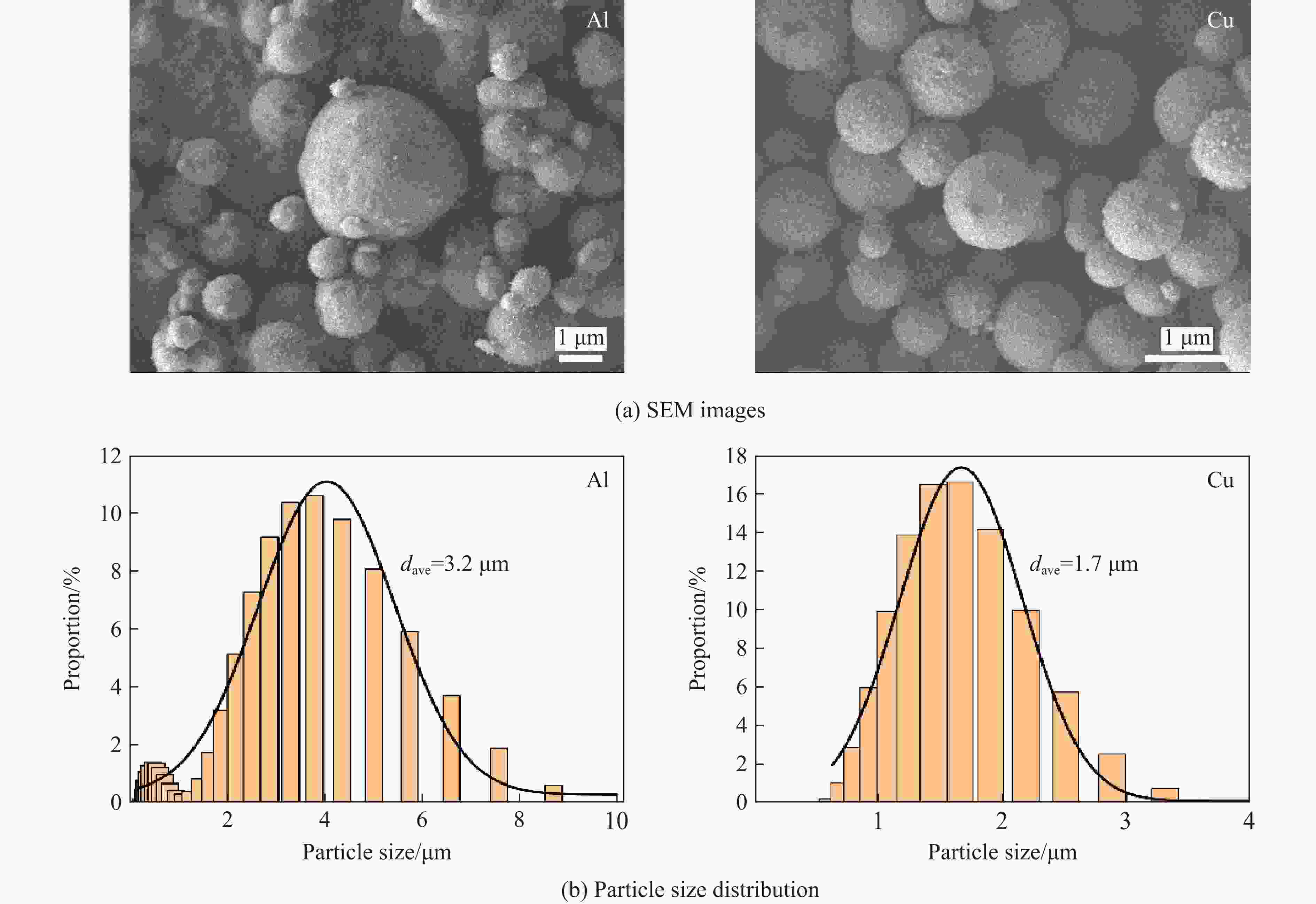
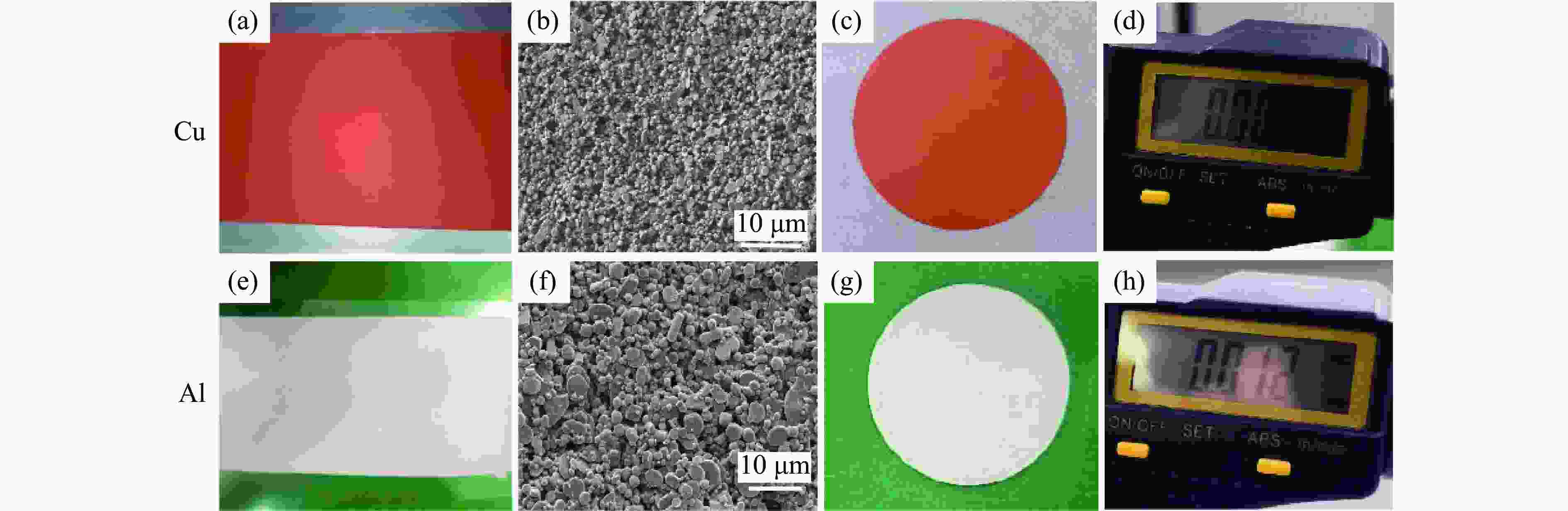
图 8 纯Cu和纯Al流延素片的表征:(a)~(d) Cu素片的宏观形貌、微观形貌、加工形貌、厚度,(e)~(h) Al素片的宏观形貌、微观形貌、加工形貌、厚度
Figure 8. Characterization of the pure Cu and pure Al cast vein sheets: (a)−(d) macroscopic morphology, microscopic morphology, processed morphology and thickness of Cu cast vein sheet; (e)−(h) macroscopic morphology, microscopic morphology, processed morphology and thickness of Al cast vein sheet
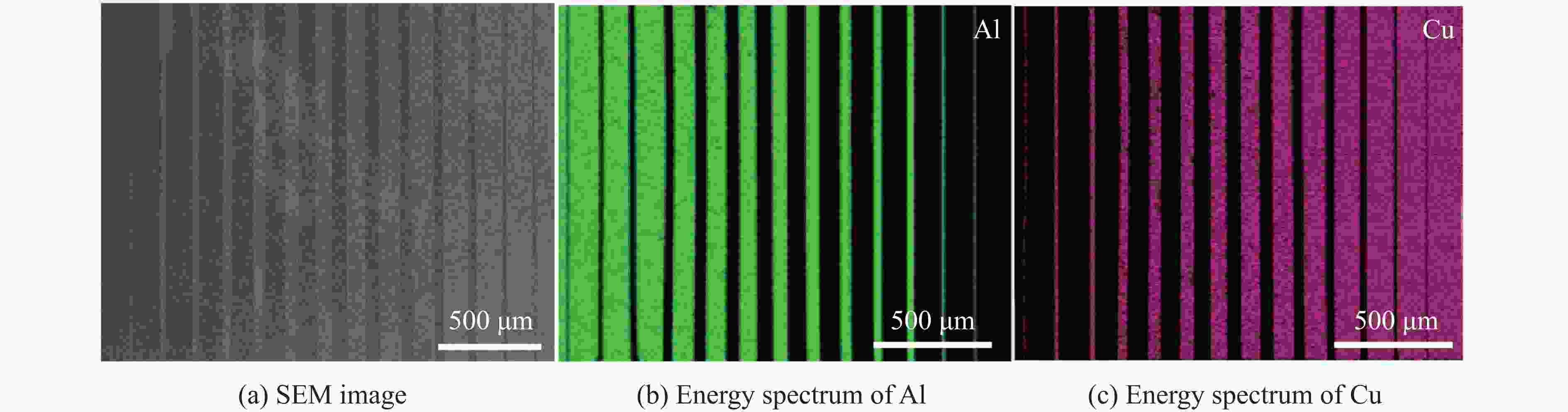
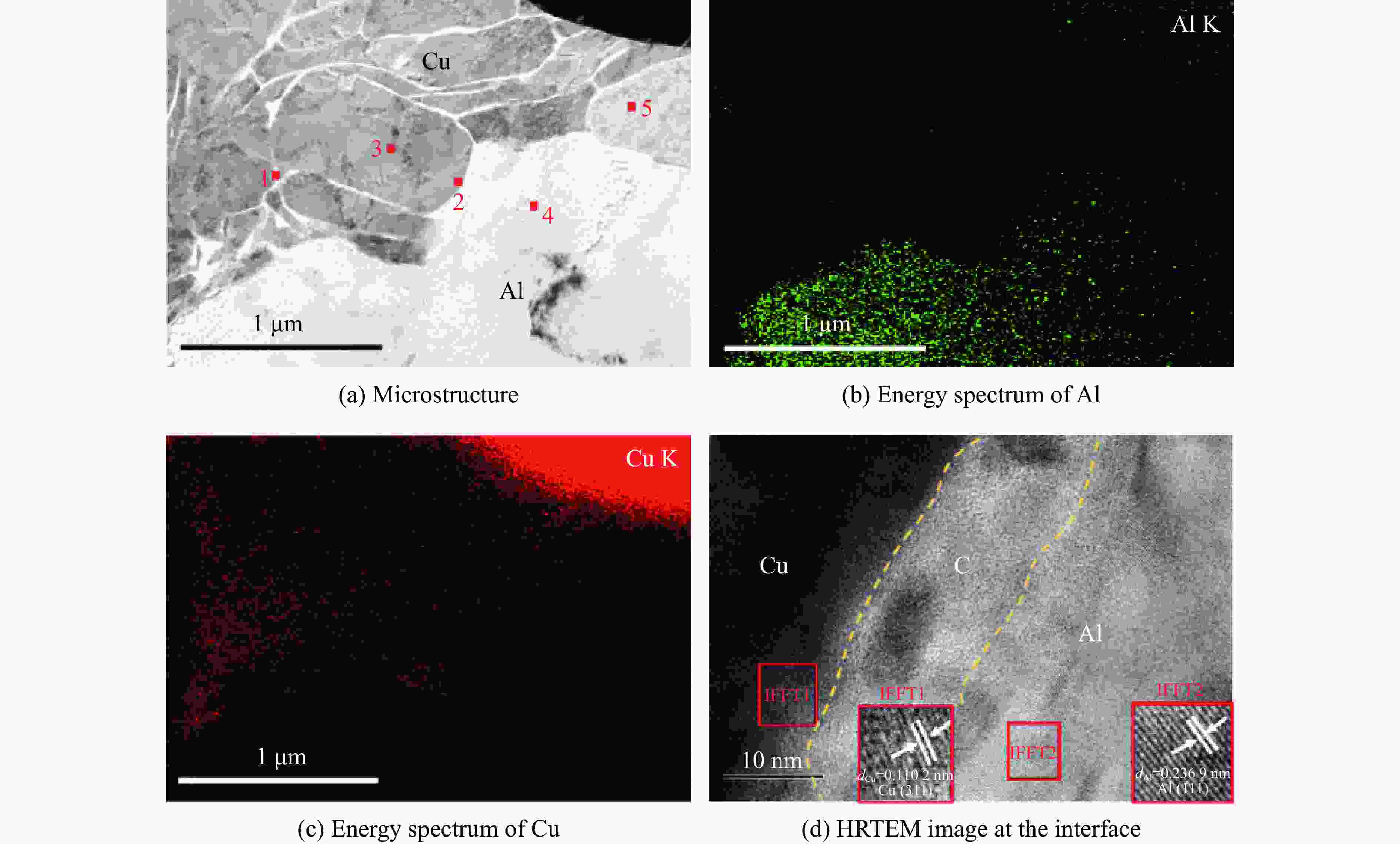
表 1 Al-Cu周期叠层梯度材料层间界面的能谱点分析数据
Table 1. Energy spectral point analysis data for the interlayer interface of the Al-Cu periodic laminated gradient materials
Point Atom fraction/% Al Cu C O 1 0 95.75 1.22 3.02 2 8.06 88.51 3.43 0 3 0 94.45 2.73 2.82 4 95.64 0 3.03 1.33 5 7.28 92.72 0 0 表 2 Al-Cu周期叠层梯度材料不同物相的物性参数
Table 2. Physical parameters of different physical phases of the Al-Cu periodic laminated gradient material
Phase Density/(g·cm−3) Sound velocity/(km·s−1) Wave impedance/(g·cm−2·μs−1) C 2.203 4.45 9.80 Al 2.712 5.33 14.45 Cu 8.924 3.91 34.89 -
[1] GLEASON A E, BOLME C A, LEE H J, et al. Time-resolved diffraction of shock-released SiO2 and diaplectic glass formation [J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 1481. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01791-y [2] MILLOT M, HAMEL S, RYGG J R, et al. Experimental evidence for superionic water ice using shock compression [J]. Nature Physics, 2018, 14(3): 297–302. doi: 10.1038/s41567-017-0017-4 [3] FRATANDUONO D E, MILLOT M, BRAUN D G, et al. Establishing gold and platinum standards to 1 terapascal using shockless compression [J]. Science, 2021, 372(6546): 1063–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.abh0364 [4] 单连强, 高宇林, 辛建婷, 等. 激光驱动气库靶对铝的准等熵压缩实验研究 [J]. 物理学报, 2012, 61(13): 135204. doi: 10.7498/aps.61.135204SHAN L Q, GAO Y L, XIN J T, et al. Laser-driven reservoir target for quasi-isentropic compression in aluminum [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(13): 135204. doi: 10.7498/aps.61.135204 [5] 刘海庆, 段卓平, 蔡进涛, 等. 准等熵加载下PBXC03炸药起爆响应特性实验研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2018, 38(8): 792–796. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.08.004LIU H Q, DUAN Z P, CAI J T, et al. Experimental research of characteristics of initiation response of PBXC03 under quasi-isentropic loading [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2018, 38(8): 792–796. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.08.004 [6] NGUYEN J H, ORLIKOWSKI D, STREITZ F H, et al. Specifically prescribed dynamic thermodynamic paths and resolidification experiments [J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2004, 706(1): 1225–1230. doi: 10.1063/1.1780459 [7] JARMAKANI H, MCNANEY J M, KAD B, et al. Dynamic response of single crystalline copper subjected to quasi-isentropic, gas-gun driven loading [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2007, 463(1/2): 249–262. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.09.118 [8] DARGAUD M, FORQUIN P. A shockless plate-impact spalling technique, based on wavy-machined flyer-plates, to evaluate the strain-rate sensitivity of ceramic tensile strength [J]. Journal of Dynamic Behavior of Materials, 2022, 8(1): 73–88. doi: 10.1007/s40870-021-00317-4 [9] 贺芝宇, 周华珍, 黄秀光, 等. 激光加载下铝材料的冲击温度测量 [J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28(4): 042002. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.122002HE Z Y, ZHOU H Z, HUANG X G, et al. Measurements of aluminum’s shock temperature on SG-Ⅱ high-power laser facility [J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28(4): 042002. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.122002 [10] DUAN X X, ZHANG C, GUAN Z Y, et al. Transparency measurement of lithium fluoride under laser-driven accelerating shock loading [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 128(1): 015902. doi: 10.1063/5.0003869 [11] 薛全喜, 江少恩, 王哲斌, 等. 基于神光Ⅲ原型装置开展的激光直接驱动准等熵压缩研究进展 [J]. 物理学报, 2018, 67(4): 045202. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20172159XUE Q X, JIANG S E, WANG Z B, et al. Progress of laser-driven quasi-isentropic compression study performed on SHENGUANG Ⅲ prototype laser facility [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(4): 045202. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20172159 [12] HALL C A, ASAY J R, KNUDSON M D, et al. Experimental configuration for isentropic compression of solids using pulsed magnetic loading [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2001, 72(9): 3587–3595. doi: 10.1063/1.1394178 [13] KNUDSON M D, HANSON D L, BAILEY J E, et al. Principal Hugoniot, reverberating wave, and mechanical reshock measurements of liquid deuterium to 400 GPa using plate impact techniques [J]. Physical Review B, 2004, 69(14): 144209. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.69.144209 [14] AO T, ASAY J R, CHANTRENNE S, et al. A compact strip-line pulsed power generator for isentropic compression experiments [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2008, 79(1): 013903. doi: 10.1063/1.2827509 [15] BROWN N P, SPECHT P E, BROWN J L. Quasi-isentropic compression of an additively manufactured aluminum alloy to 14.8 GPa [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2022, 132(22): 225106. doi: 10.1063/5.0127989 [16] REMINGTON T P, HAHN E N, ZHAO S, et al. Spall strength dependence on grain size and strain rate in tantalum [J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 158: 313–329. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.07.048 [17] ZHONG T, LIU X, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Penetration dynamics of a carbonate sand: a synchrotron phase contrast imaging study [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 152: 103839. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.103839 [18] YE S J, XU Y F, ZHOU Y, et al. Penetration dynamics of steel spheres into a ballistic gelatin: experiments, nondimensional analysis, and finite element modeling [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 162: 104144. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.104144 [19] 沈强, 张联盟, 王传彬, 等. 梯度飞片材料的波阻抗分布设计与优化 [J]. 物理学报, 2003, 52(7): 1663–1667. doi: 10.7498/aps.52.1663SHEN Q, ZHANG L M, WANG C B, et al. Design and optimization of wave impedance distribution for flyer materials [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2003, 52(7): 1663–1667. doi: 10.7498/aps.52.1663 [20] 窦金锋. W-Mo-Ti体系波阻抗梯度飞片的设计及相关物性研究 [D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2002.DOU J F. Design of W-Mo-Ti flier-plate with graded wave impedanceand study on its relative physical properties [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2002. [21] HAYASHI T, UGO R, MORIMOTO Y. Experimental observation of stress waves propagating in laminated composites [J]. Experimental Mechanics, 1986, 26(2): 169–174. doi: 10.1007/BF02320011 [22] ANDERSON M U, CHHABILDAS L C, REINHART W D. Simultaneous PVDF/VISAR measurement technique for isentropic loading with graded density impactors [J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1998, 429(1): 841–844. doi: 10.1063/1.55681 [23] CHHABILDAS L C, KMETYK L N, REINHART W D, et al. Enhanced hypervelocity launcher-capabilities to 16 km/s [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1995, 17(1): 183–194. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)99845-I [24] SUN L, SNELLER A, KWON P. Fabrication of alumina/zirconia functionally gradedmaterial: from optimization of processing parameters to phenomenological constitutive models [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 488(1/2): 31–38. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2007.10.044 [25] MARTIN L P, PATTERSON J R, ORLIKOWSKI D, et al. Application of tape-cast graded impedance impactors for light-gas gun experiments [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102(2): 023507. doi: 10.1063/1.2756058 [26] SUN W, LI X J, HOKAMOTO K. Fabrication of graded density impactor via underwater shock wave and quasi-isentropic compression testing at two-stage gas gun facility [J]. Applied Physics A, 2014, 117(4): 1941–1946. doi: 10.1007/s00339-014-8663-1 [27] ZHANG L M, ZHOU X Z, LUO G Q, et al. Microstructure and properties of aluminum-copper composites prepared by hot-pressure sintering [J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2014, 616: 212–216. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.616.212 [28] YEP S J, BELOF J L, ORLIKOWSKI D A, et al. Fabrication and application of high impedance graded density impactors in light gas gun experiments [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2013, 84(10): 103909. doi: 10.1063/1.4826565 [29] KELLY J P, NGUYEN J H, LIND J, et al. Application of Al-Cu-W-Ta graded density impactors in dynamic ramp compression experiments [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 125(14): 145902. doi: 10.1063/1.5055398 [30] BROWN J L, ADAMS D P, ALEXANDER C S, et al. Estimates of Ta strength at ultrahigh pressures and strain rates using thin-film graded-density impactors [J]. Physical Review B, 2019, 99(21): 214105. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.99.214105 [31] GAO W L, ZHANG R Z, WANG J, et al. Enhancing laser-driven flyer velocity by optimizing of modulation period of Al/Ti reactive multilayer films [J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A, 2023, 41(6): 063414. doi: 10.1116/6.0003066 [32] 江宇达, 张睿智, 吴楯, 等. Ti-Pt周期调制梯度材料的制备及准等熵加载特性 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2024, 38(6): 064205. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240816JIANG Y D, ZHANG R Z, WU D, et al. Preparation and quasi-isentropic loading characteristics of Ti-Pt periodically modulated gradient material [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2024, 38(6): 064205. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240816 [33] KE B Y, ZHANG C C, CHENG S L, et al. Tape-casting electrode architecture permits low-temperature manufacturing of all-solid-state thin-film microbatteries [J]. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2024, 3(4): 621–631. doi: 10.1002/idm2.12174 [34] 李代颖, 刘济宽, 陈学通. 超细球形铜粉研究进展 [J]. 船电技术, 2013, 33(3): 42–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4862.2013.03.014LI D Y, LI J K, CHEN X T. Progress in preparation of ultrafine spherical copper powder [J]. Marine Electric & Electronic Technology, 2013, 33(3): 42–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4862.2013.03.014 [35] SHANG Q S, WANG Z J, LI J, et al. Gel-tape-casting of aluminum nitride ceramics [J]. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2017, 6(1): 67–72. doi: 10.1007/s40145-016-0211-3 [36] LUO G Q, LI P B, HU J N, et al. Synergistic effect of Ag and C addition into Al-Cu matrix composites [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2022, 57(24): 11013–11025. doi: 10.1007/s10853-022-07189-6 [37] HU J N, TAN Y, LI X M, et al. Structure characterization and impact effect of Al-Cu graded materials prepared by tape casting [J]. Materials, 2022, 15(14): 4834. doi: 10.3390/ma15144834 [38] GU J F, FU S, PING H, et al. Idea of macro-scale and micro-scale prestressed ceramics [J]. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2024, 3(6): 897–906. doi: 10.1002/idm2.12224 [39] 郭浩天. Cu/Mo叠层复合材料热响应行为数值模拟研究 [D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018.GUO H T. Numerical simulation of thermal response behaviorof Cu/Mo laminated composite materials [D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2018. [40] HUANG J, ZHANG J, ZHU K, et al. Using graded density impactor to achieve quasi-isentropic loading with stress and strain-rate controlled [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2024, 135(8): 085901. doi: 10.1063/5.0189243 -






 下载:
下载: