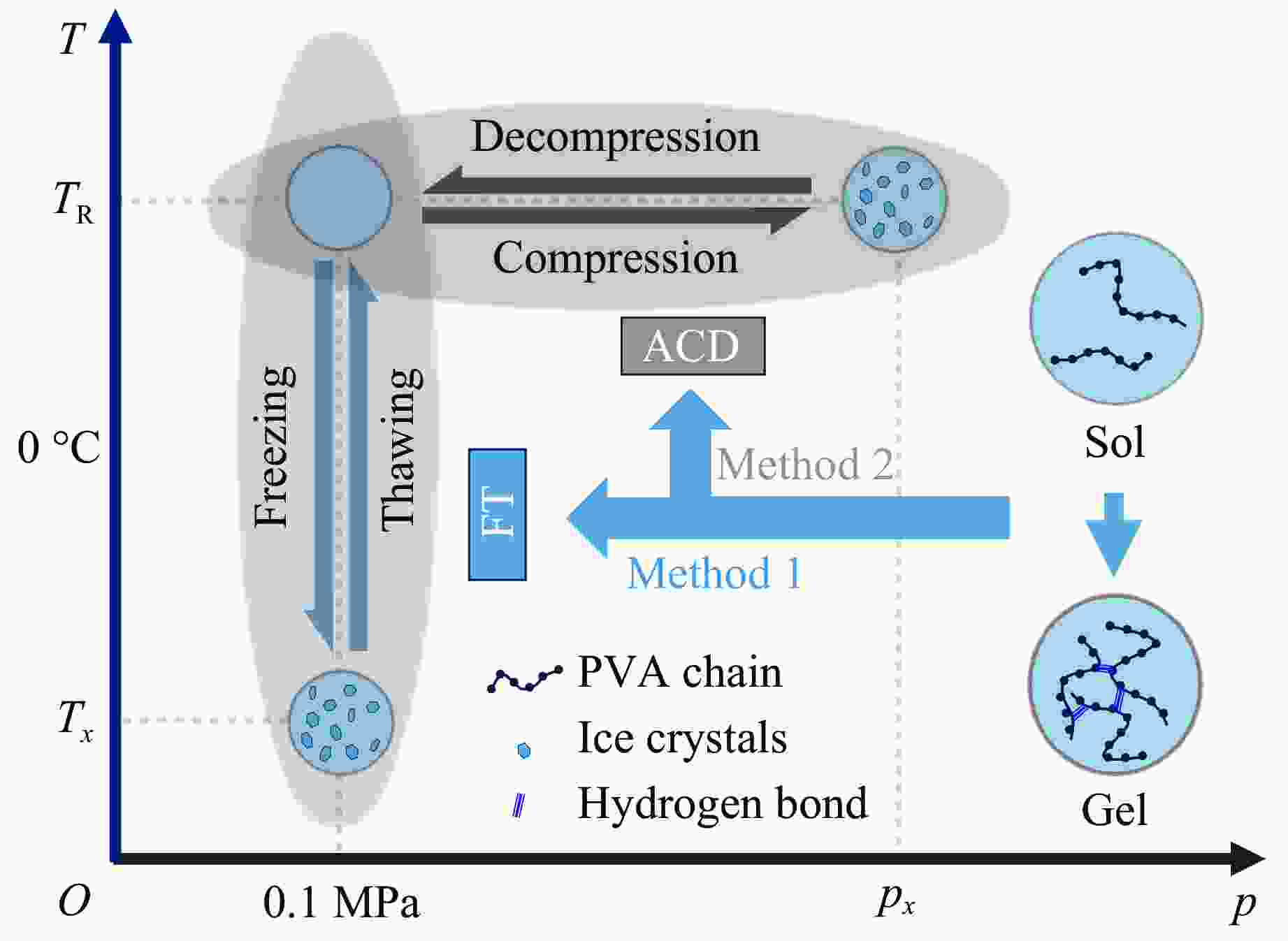
Preparation of Polymeric Hydrogel via Alternate Compression-Decompression
-
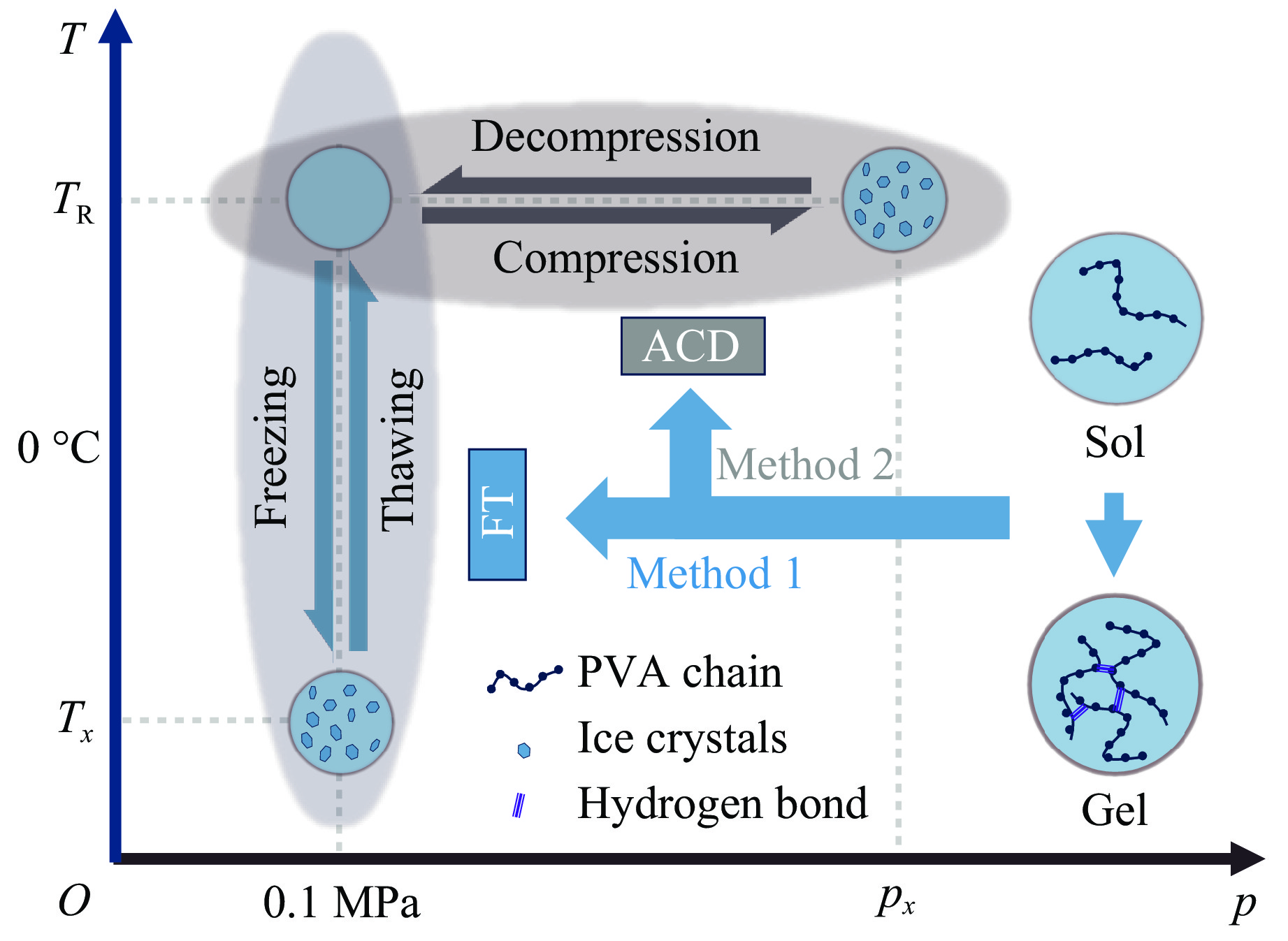
摘要: 基于冷冻-解冻法制备凝胶原理及相关的研究成果,依托自主设计的动态加载装置,从压力调控的角度出发,系统探究了不同加载方式(加载幅度、加载速率、加载频次)对高分子水溶液胶凝过程的影响。结果表明:采用循环加压-卸压法,能够高效、快速地合成一系列具备优异机械强度的水凝胶,其潜在应用涵盖生物医学、环境保护、电子器件等多个领域。循环加压-卸压技术作为一种创新方法,不仅极大地拓展了水凝胶的制备策略,还显著提升了水凝胶在软物质科学领域的应用潜力,为该领域的进一步发展提供了新的思路和方向。Abstract: Based on the principles of gel preparation via freeze-thaw method and research progress in hydrogel synthesis, this study explores the effects of different pressure parameters systematically from the perspective of pressure regulation. Pressure magnitude, pressure compression and decompression rate, and number of cyclic loading were investigated during the gelation process of polymer solutions. By using the alternate compression-decompression (ACD) method, efficient and rapid synthesis of a series of hydrogels with excellent mechanical strength is enabled. These hydrogels have potential applications in diverse fields, including biomedicine, environmental protection, and electronic devices. As an innovative approach, the ACD method not only expands the preparation strategies for hydrogels significantly but also enhances the application potential of hydrogels in the field of soft matter science, providing new insights and directions for further development in this field.
-
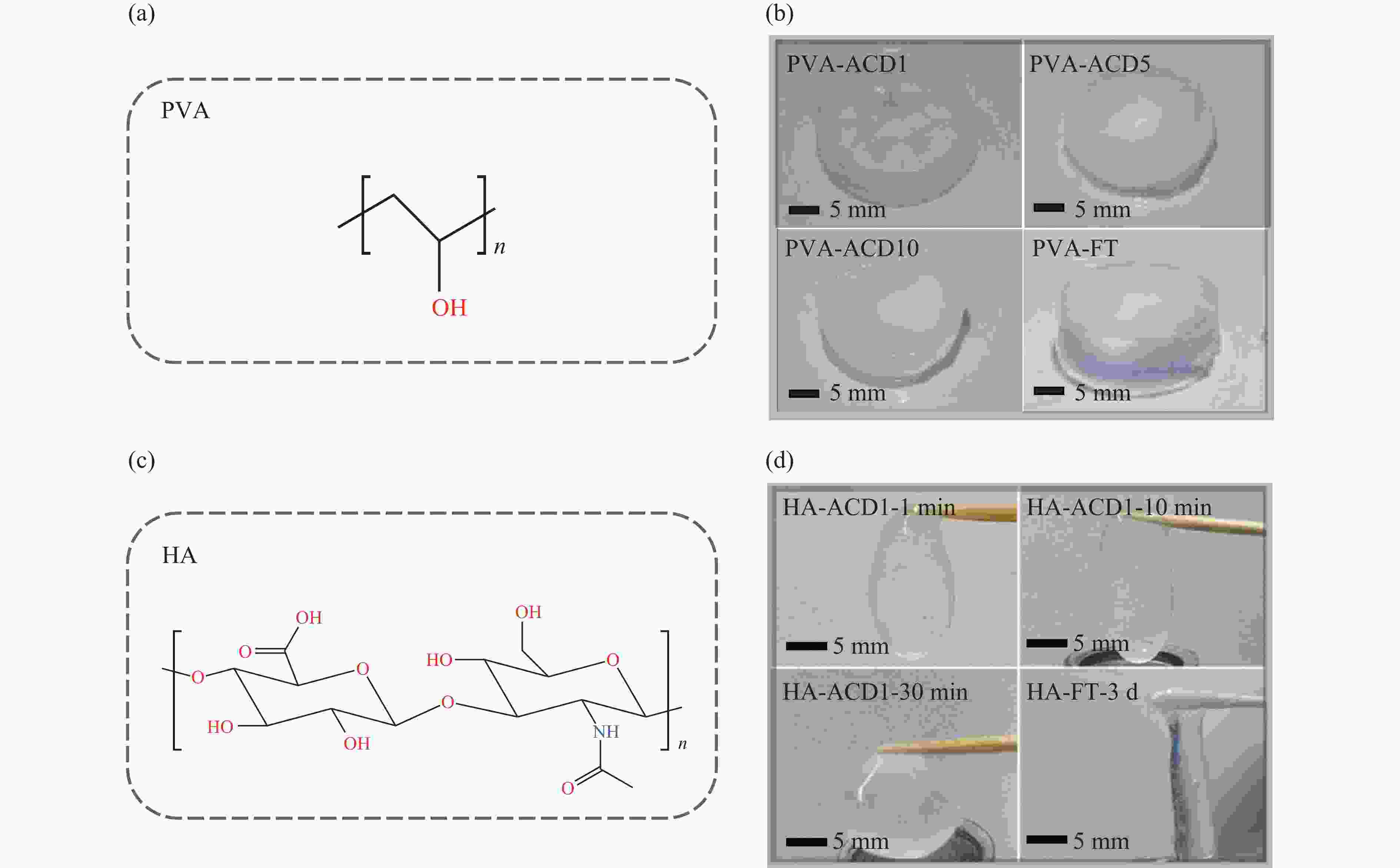
图 2 (a) 聚乙烯醇的化学式;(b) 循环加压-卸压法和冷冻-解冻法制备的聚乙烯醇水凝胶的外观,其中ACDm(m=1,5,10)代表反复加压、卸压次数;(c) 透明质酸的化学式;(d) 循环加压-卸压法和冷冻-解冻法制备的透明质酸水凝胶的外观,其中ACD1-t(t=1,10,30 min)代表单次加压高压的保持时间为1、10、30 min,FT-3 d表示冷冻处理样品保持时间为3 d[15]
Figure 2. (a) Chemical formula of polyvinyl alcohol; (b) appearance of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels prepared by pressure method and freeze-thaw method, where ACDm (m=1, 5, 10) represents the number of repeated pressurization and depressurization cycles; (c) chemical formula of hyaluronic acid; (d) appearance of hyaluronic acid hydrogels prepared by pressure method and freeze-thaw method, where ACD1-t (t=1, 10, 30 min) represents the single pressurization and high-pressure holding time of 1, 10, and 30 min respectively, and FT-3 d indicates the sample held for 3 d after freeze treatment[15]
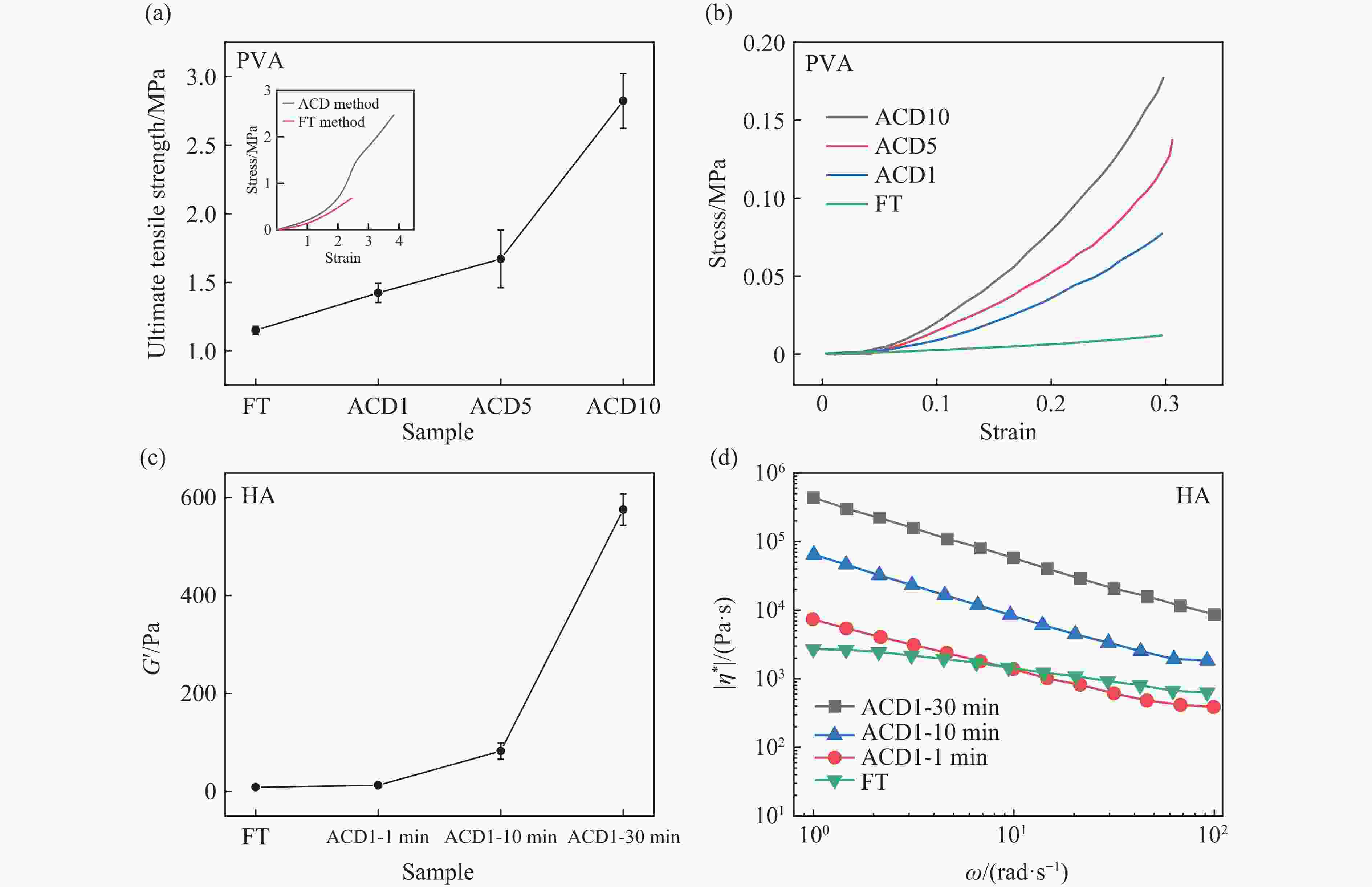
图 3 凝胶力学测试结果[15–16]:(a) 聚乙烯醇拉伸测试结果,不同循环次数加压-卸压法和冷冻-解冻法制备凝胶的极限抗拉强度对比,插图为加压-卸压法和冷冻-解冻法制备凝胶的应力-应变曲线;(b) 聚乙烯醇抗压测试结果,30%应变压缩聚乙烯醇凝胶的应力-应变曲线;(c) 加压-卸压法和冷冻-解冻法制备透明质酸凝胶的储能模量;(d) 加压-卸压法和冷冻-解冻法制备透明质酸凝胶的复黏度
Figure 3. Mechanical test results of gels[15–16]: (a) tensile test results of polyvinyl alcohol, the small figure shows the stress-strain curves of gels prepared by the compression and unloading method and the freeze-thaw method, and the large figure shows the comparison of the ultimate tensile strength of gels prepared by the compression and unloading method and freeze-thaw method with different number of cycles; (b) compressive test of polyvinyl alcohol, the stress-strain curve of polyvinyl alcohol gel compressed at 30% strain; (c) storage modulus of hyaluronic acid gels prepared by compression and unloading method and freeze-thaw method; (d) reversibility viscosity of hyaluronic acid gels prepared by compression and unloading method and freeze-thaw method
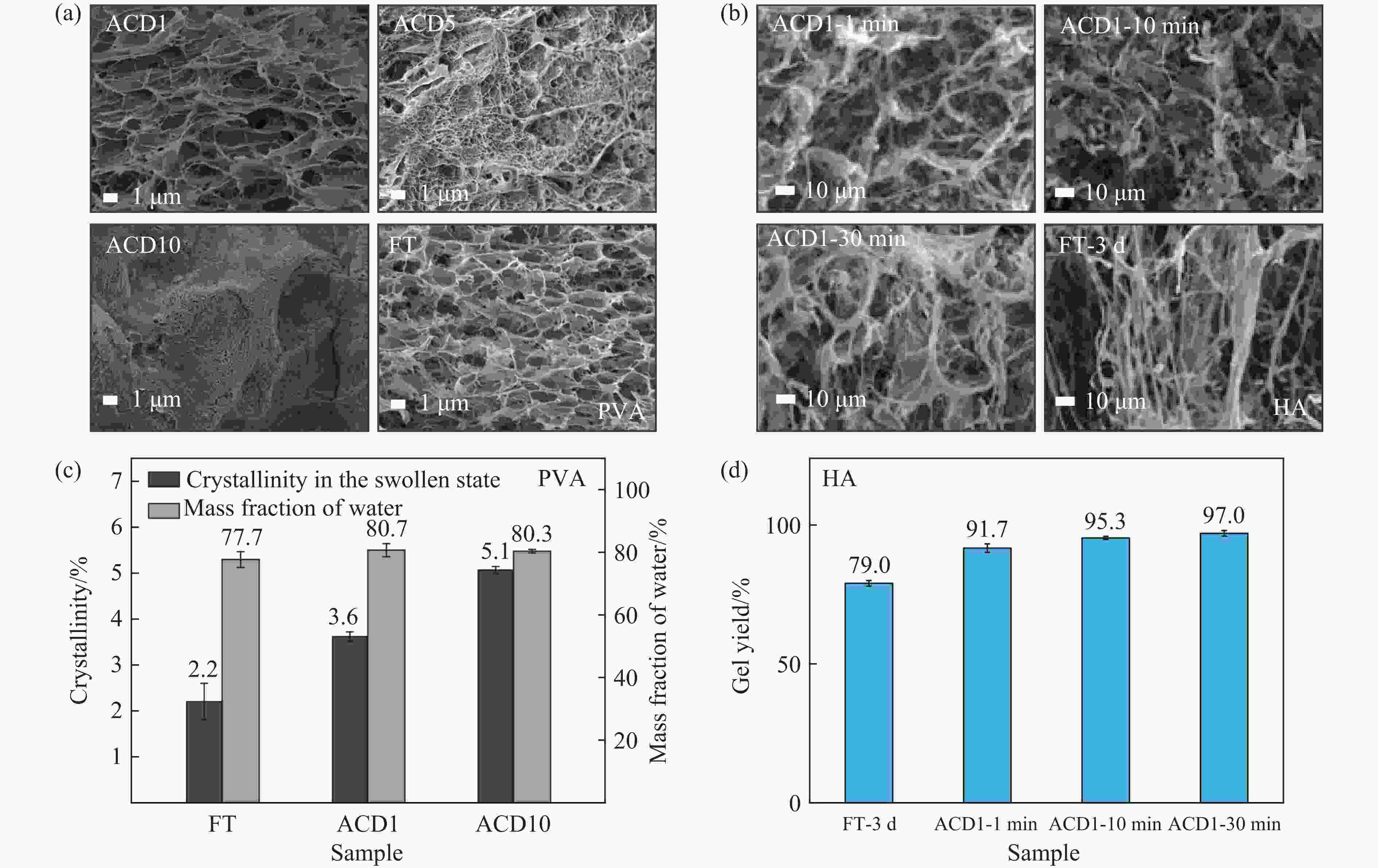
图 4 加压-卸压法和冷冻-解冻法制备的聚乙烯醇凝胶(a)和透明质酸凝胶(b)的SEM影像,(c) 不同制备方法得到的聚乙烯醇凝胶的结晶度和含水量,(d) 不同制备方法得到的透明质酸凝胶的凝胶产率
Figure 4. SEM images of polyvinyl alcohol gel (a) and hyaluronic acid gel (b) prepared by alternate compression-decompression method and freeze-thaw method; (c) crystallinity and water content of polyvinyl alcohol gel prepared by different methods; (d) gel yield of hyaluronic acid gel prepared by different methods
-
[1] 王薇, 关国平, 王璐. 生物医用水凝胶研究进展 [J]. 生物医学工程学进展, 2015, 36(4): 221–225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1242.2015.04.008WANG W, GUAN G P, WANG L. Research progress in biomedical hydrogels [J]. Progress in Biomedical Engineering, 2015, 36(4): 221–225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1242.2015.04.008 [2] 谭燕, 刘曦, 袁芳. 魔芋葡甘聚糖的结构、性质及其在食品中的应用 [J]. 中国调味品, 2019, 44(2): 168–174, 178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2019.02.038TAN Y, LIU X, YUAN F. Structure, properties of konjac glucomannan and its application in food industry [J]. China Condiment, 2019, 44(2): 168–174, 178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2019.02.038 [3] CHEN X L, YANG T, CAI X L, et al. Eco-friendly hydrogel based on locust bean gum for water retaining in sandy soil [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 275: 133490. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133490 [4] ZHANG Y S, KHADEMHOSSEINI A. Advances in engineering hydrogels [J]. Science, 2017, 356(6337): eaaf3627. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf3627 [5] 饶涛, 何显儒. 高强度物理交联水凝胶综述 [J]. 塑料工业, 2022, 50(7): 6–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5770.2022.07.002RAO T, HE X R. Review of high strength physical hydrogels [J]. China Plastics Industry, 2022, 50(7): 6–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5770.2022.07.002 [6] LOZINSKY V I, PLIEVA F M, GALAEV I Y, et al. The potential of polymeric cryogels in bioseparation [J]. Bioseparation, 2001, 10: 163–188. doi: 10.1023/A:1016386902611 [7] PEPPAS N A. Turbidimetric studies of aqueous poly (vinyl alcohol) solutions [J]. Die Makromolekulare Chemie, 1975, 176(11): 3433–3440. doi: 10.1002/macp.1975.021761125 [8] LOZINSKY V I, DAMSHKALN L G, BROWN R, et al. Study of cryostructuring of polymer systems. XIX. on the nature of intermolecular links in the cryogels of locust bean gum [J]. Polymer International, 2000, 49(11): 1434–1443. doi: 10.1002/1097-0126(200011)49:11<1434::AID-PI525>3.0.CO;2-F [9] 程慧茹, 张德坤. PVA-Silk复合水凝胶的摩擦磨损性能研究 [J]. 润滑与密封, 2010, 35(3): 14–18, 40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2010.03.004CHENG H R, ZHANG D K. Research on the friction and wear properties of PVA-Silk composite hydrogel [J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2010, 35(3): 14–18, 40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2010.03.004 [10] GRIGORYAN B, PAULSEN S J, CORBETT D C, et al. Multivascular networks and functional intravascular topologies within biocompatible hydrogels [J]. Science, 2019, 364(6439): 458–464. doi: 10.1126/science.aav9750 [11] LEE J H, RIM Y S, MIN W K, et al. Biocompatible and biodegradable neuromorphic device based on hyaluronic acid for implantable bioelectronics [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(50): 2107074. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202107074 [12] SEDLAČÍK T, NONOYAMA T, GUO H L, et al. Preparation of tough double- and triple-network supermacroporous hydrogels through repeated cryogelation [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(19): 8576–8586. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c02911 [13] ADELNIA H, ENSANDOOST R, SHEBBRIN MOONSHI S, et al. Freeze/thawed polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels: present, past and future [J]. European Polymer Journal, 2022, 164: 110974. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2021.110974 [14] MIAO M S, SUN Y H, ZUREK E, et al. Chemistry under high pressure [J]. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2020, 4(10): 508–527. doi: 10.1038/s41570-020-0213-0 [15] QIAO P, SHI K Y, WANG Y L, et al. Ultrafast gelation of hyaluronan hydrogels via alternate compression-decompression [J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2023, 141: 108732. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108732 [16] QIAO P, LI B, HE Y, et al. High-performance hydrogels via alternate compression-decompression [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2022, 126(51): 21825–21832. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.2c06997 [17] SU L, SHI K Y, ZHANG L, et al. Static and dynamic diamond anvil cell (s-dDAC): a bidirectional remote controlled device for static and dynamic compression/decompression [J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2022, 7(1): 018401. doi: 10.1063/5.0061583 [18] LOZINSKY V I. Cryogels on the basis of natural and synthetic polymers: preparation, properties and application [J]. Russian Chemical Reviews, 2002, 71(6): 489–511. doi: 10.1070/RC2002v071n06ABEH000720 [19] DE BRITO CARDOSO G, SOUZA I N, PEREIRA M M, et al. Poly(vinyl alcohol) as a novel constituent to form aqueous two-phase systems with acetonitrile: phase diagrams and partitioning experiments [J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2015, 94: 317–323. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2014.08.009 [20] LIN S T, YUK H, ZHANG T, et al. Stretchable hydrogel electronics and devices [J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(22): 4497–4505. doi: 10.1002/adma.201504152 [21] BAKER M I, WALSH S P, SCHWARTZ Z, et al. A review of polyvinyl alcohol and its uses in cartilage and orthopedic applications [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part B, Applied Biomaterials, 2012, 100(5): 1451–1457. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.32694 [22] XU X, JHA A K, HARRINGTON D A, et al. Hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels: from a natural polysaccharide to complex networks [J]. Soft Matter, 2012, 8(12): 3280–3294. doi: 10.1039/C2SM06463D [23] BAKSH D, SONG L, TUAN R S. Adult mesenchymal stem cells: characterization, differentiation, and application in cell and gene therapy [J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2004, 8(3): 301–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2004.tb00320.x [24] ANSETH K S, METTERS A T, BRYANT S J, et al. In situ forming degradable networks and their application in tissue engineering and drug delivery [J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2002, 78(1/2/3): 199–209. doi: 10.1016/S0168-3659(01)00500-4 -






 下载:
下载: