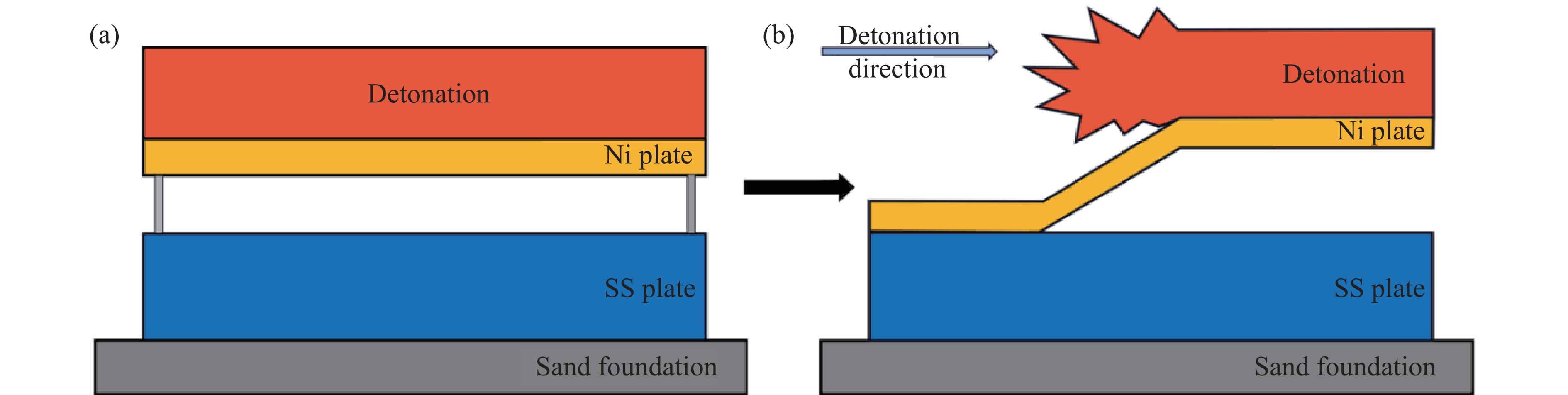
Experimental Study and Numerical Simulation of Explosive Welding of Nickel/304 Stainless Steel
-
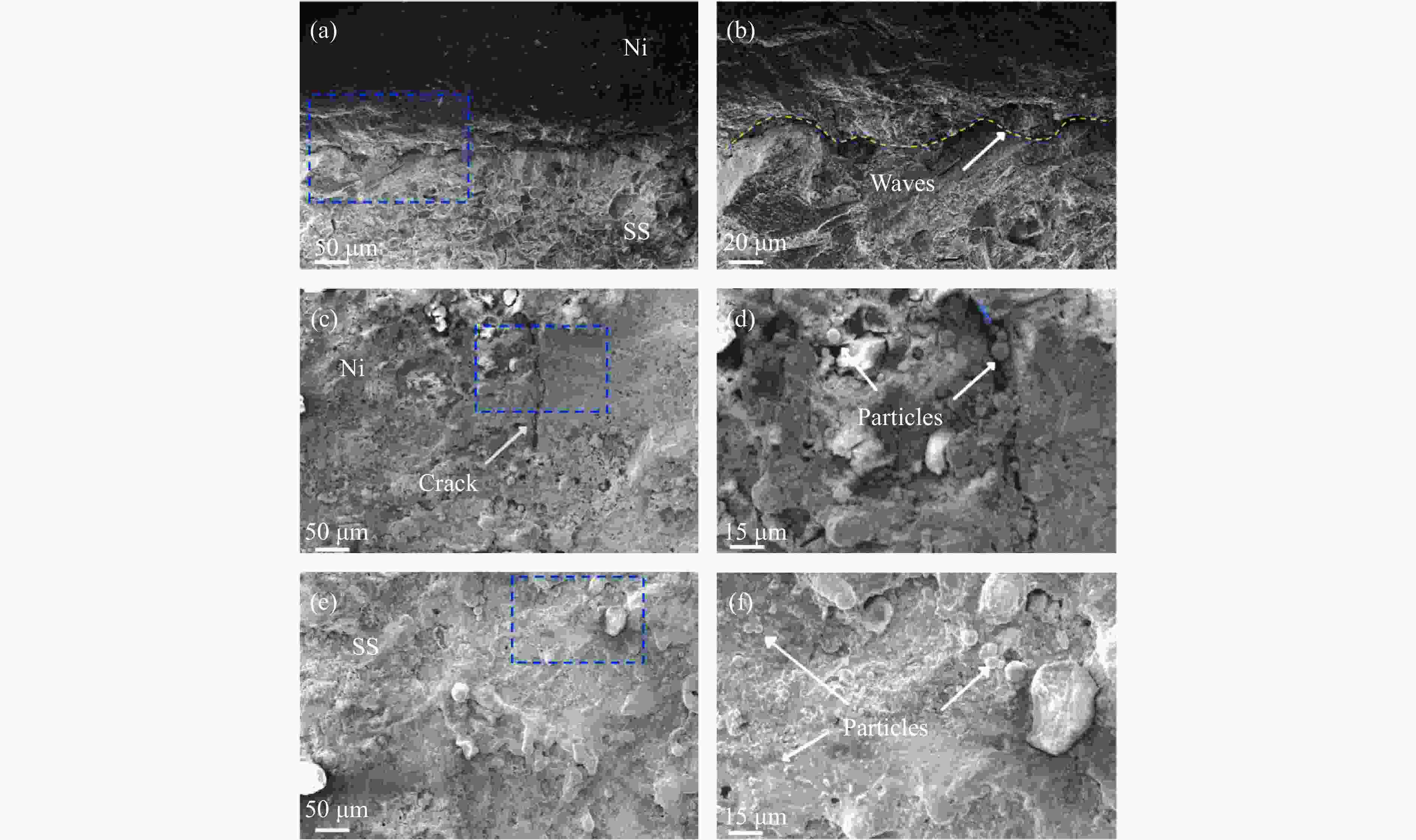
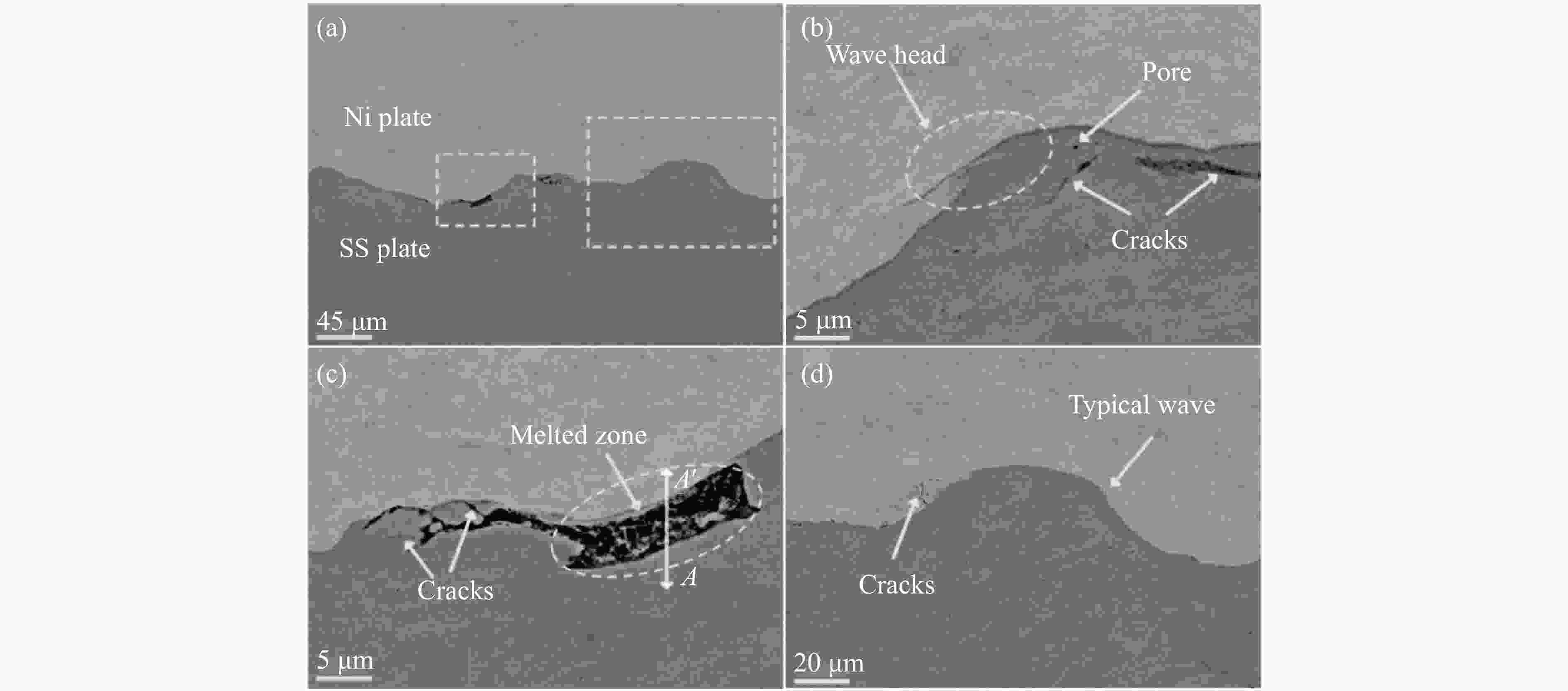
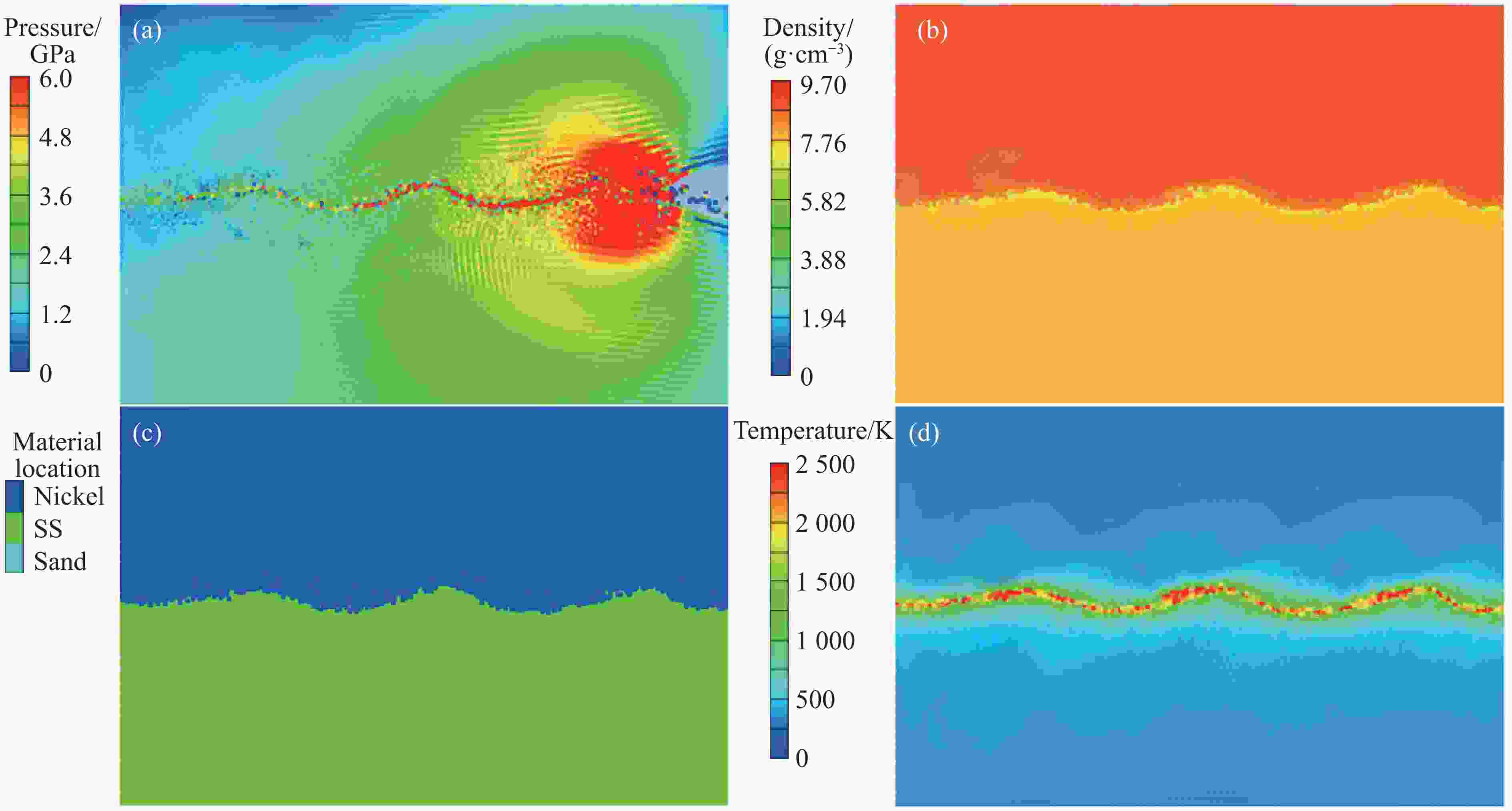
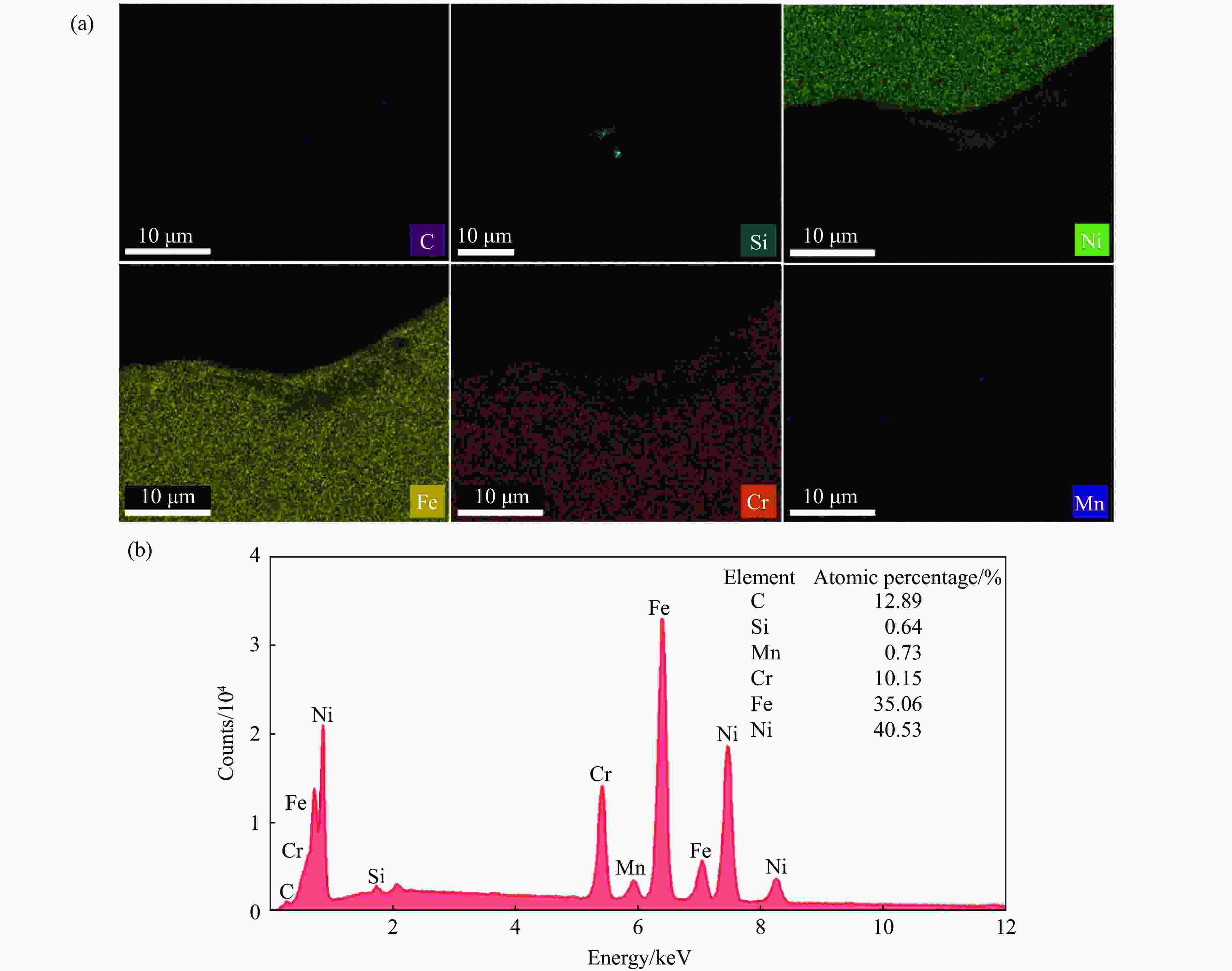
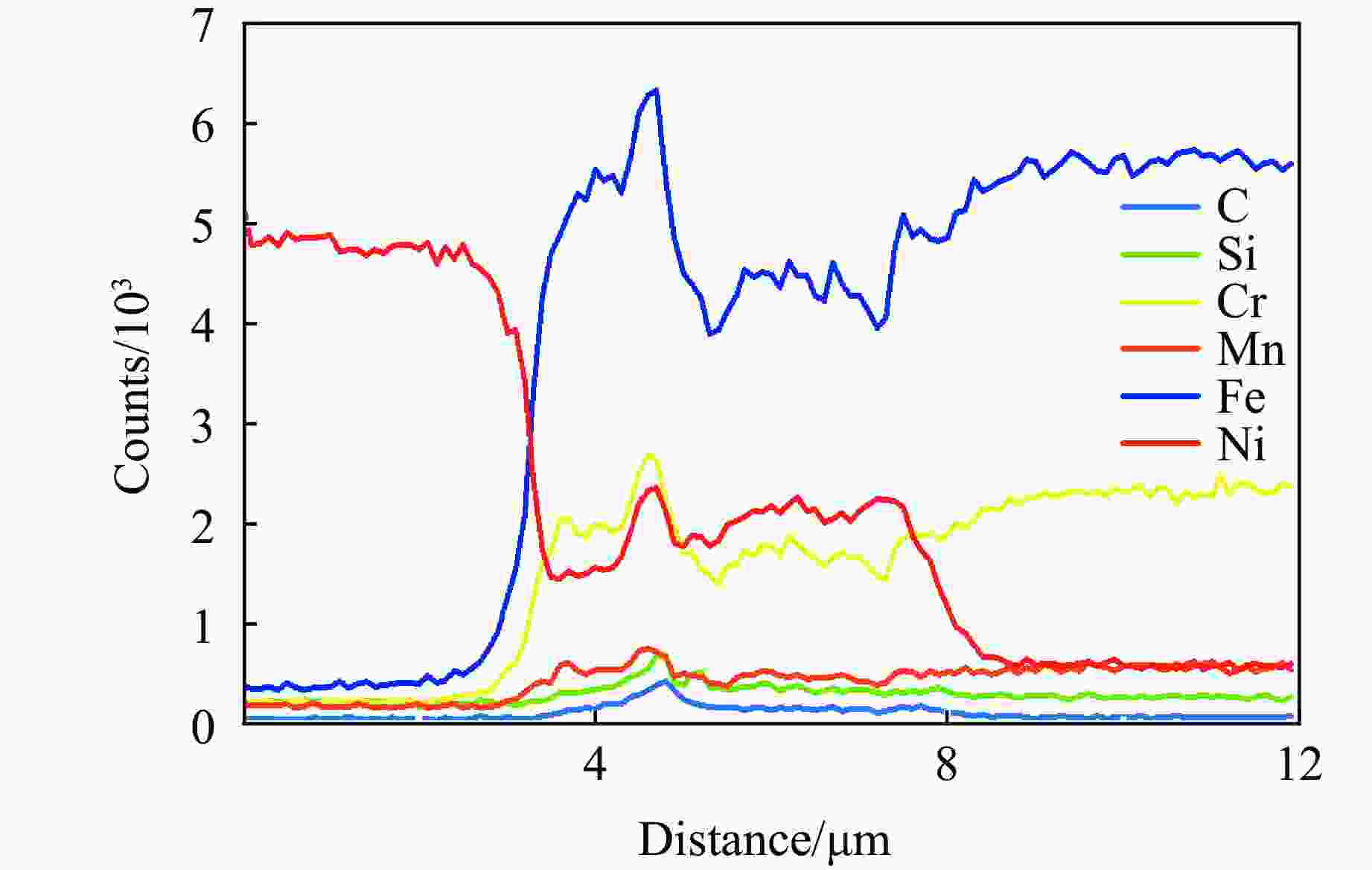
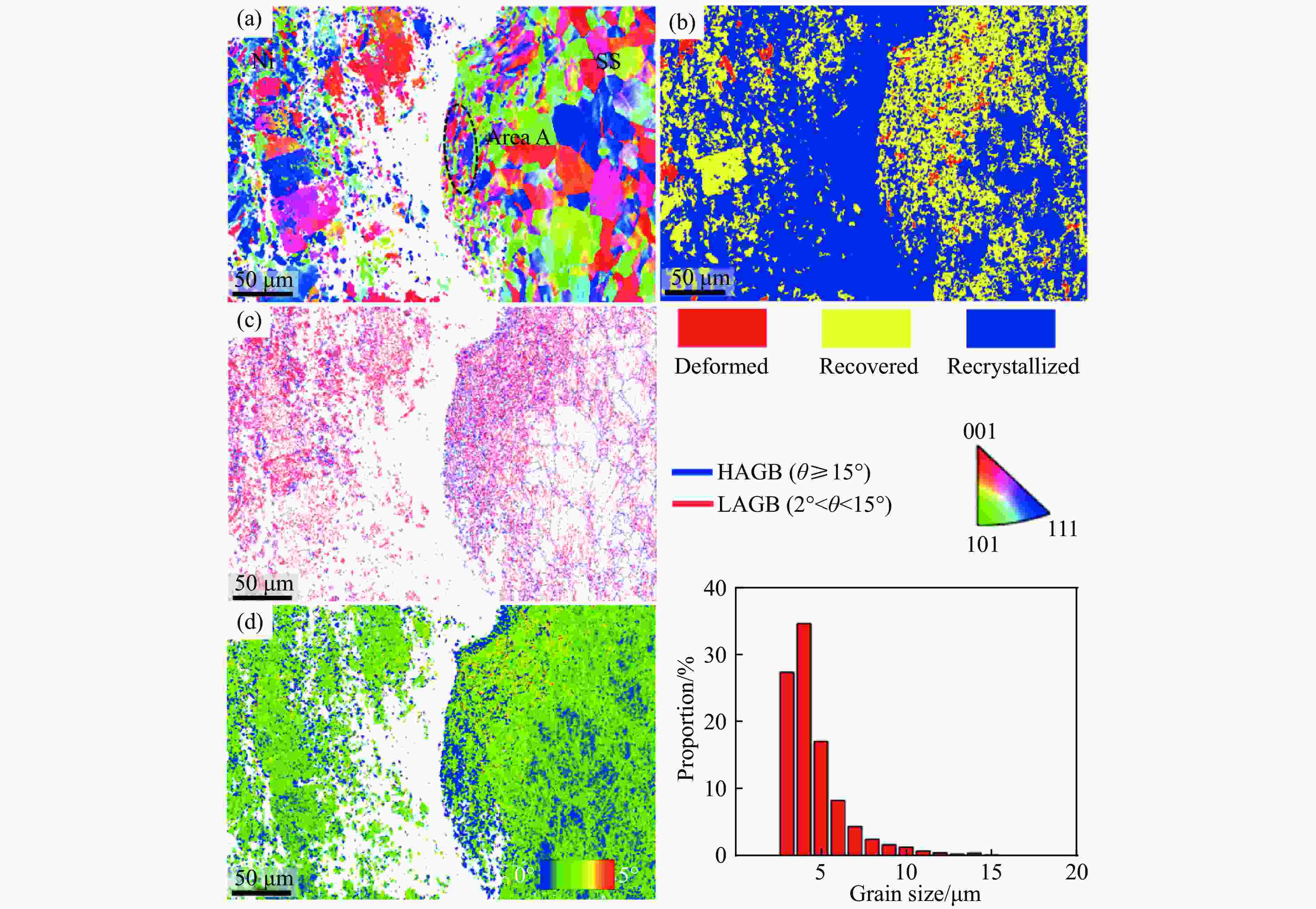
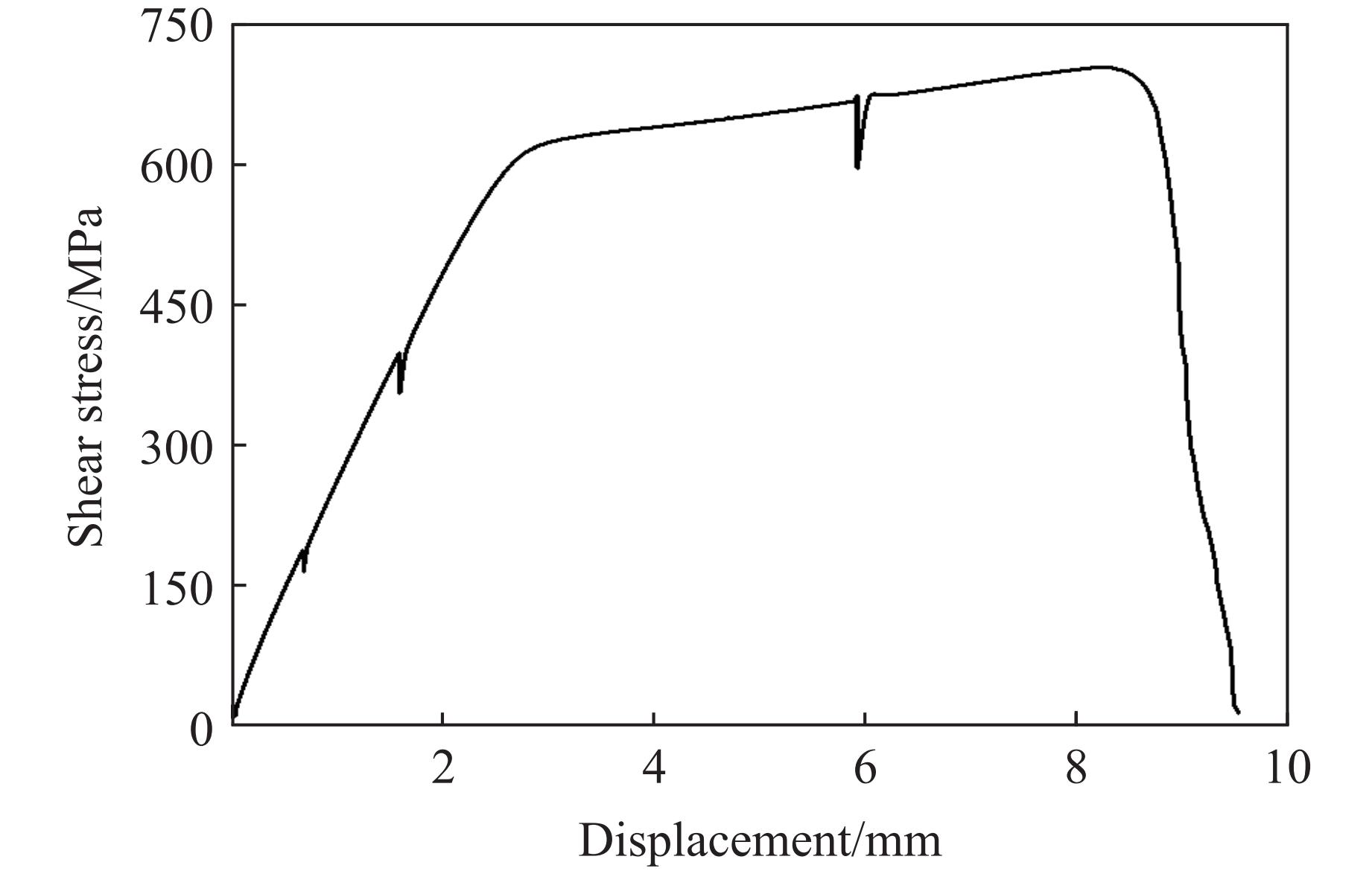
摘要: 为了研究镍/304不锈钢层状复合板界面的微观结构及形成机理,采用爆炸焊接技术,成功制备了镍/304不锈钢层状复合材料,通过扫描电子显微镜、能谱仪和电子背散射衍射仪研究了复合板的微观组织特征,利用拉伸试验测试了复合板的力学性能,并运用光滑粒子流体动力学方法对高速斜向冲击焊接过程进行了数值模拟。模拟结果再现了波状界面和射流的形成过程,支持和扩展了试验结果。结合界面密度的变化促进了元素扩散,晶粒弯曲反映了波形成过程中材料的运动特征,再结晶过程受到位错密度的影响,在结合界面形成了细晶粒区域。拉伸试样断裂后结合界面没有分层,金属板的抗拉强度和断裂伸长率分别达到705 MPa和24%。
-
关键词:
- 爆炸焊接 /
- 光滑粒子流体动力学模拟 /
- 力学性能 /
- 结合界面 /
- 微观形貌
Abstract: Ni/304 stainless steel laminated composite materials were successfully fabricated using explosive welding to investigate the microstructural characteristics and the formation mechanism of interface. The microstructural characteristics of the composite plate were analyzed using scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD). The mechanical properties of the composite plate were evaluated through tensile tests. Additionally, the smooth particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method was employed to numerically simulate the high-speed oblique impact welding process. The results indicate that the Ni/304 stainless steel composite plate exhibits a continuous wave bonding interface, which is consistent with the numerical simulation results. The variation in interface density promotes elemental diffusion, while the bending of grains reflects the material movement characteristics during wave formation. The recrystallization process is influenced by dislocation density, leading to the formation of fine-grained regions at the Ni/304 stainless steel interface. The tensile strength and elongation at fracture of the composite plate reach 705 MPa and 24%, respectively. The high bonding strength is primarily attributed to the formation of a continuous wavy interface structure. -
表 1 试验材料的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of experimental materials
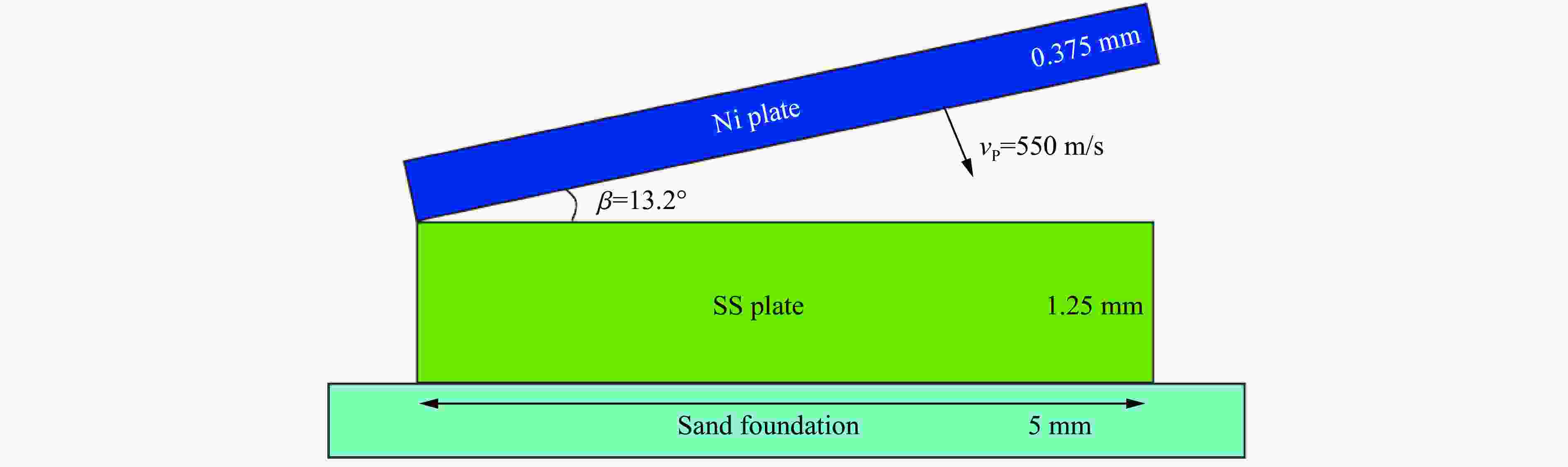
Materials Ingredient Mass fraction/% Materials Ingredient Mass fraction/% Ni Ni 99.990 SS Fe 71.199 Si 0.001 C 0.780 W 0.001 Si 1.000 Ta 0.001 Mn 1.950 Fe 0.001 P 0.033 Nb 0.001 S 0.028 C 0.001 Ni 8.010 O 0.002 Cr 17.000 N 0.002 表 2 基板和复板材料参数
Table 2. Material parameters of base plate and flyer plate
Materials Yield strength/MPa Melting point/℃ Thermal conductivity/
(W·m−1·℃−1)Specific heat capacity/
(J·kg−1·K−1)Ni 380 1453 91 444 SS 550 1440 16 500 表 3 乳化基质组分
Table 3. Components of emulsified matrix
Ingredient Mass fraction/% NH4NO3 73 NaNO3 8 H2O 10 C18H38 6 C24H44O6 3 表 4 Mie-Grüneisen shock状态方程和Steinberg-Guinan强度模型材料参数
Table 4. Material parameters of Mie-Grüneisen shock equation of state and Steinberg-Guinan intensity model
Materials Density/(g·cm−3) γ Initial shear modulus/GPa Initial yield stress/GPa Hardening constant Ni 8.9 1.93 85.5 0.14 46 SS 7.9 1.93 77.0 0.34 43 表 5 拉伸试验得到的Ni/SS复合板的力学数据
Table 5. Mechanical properties of Ni/SS plate obatined by tensile test
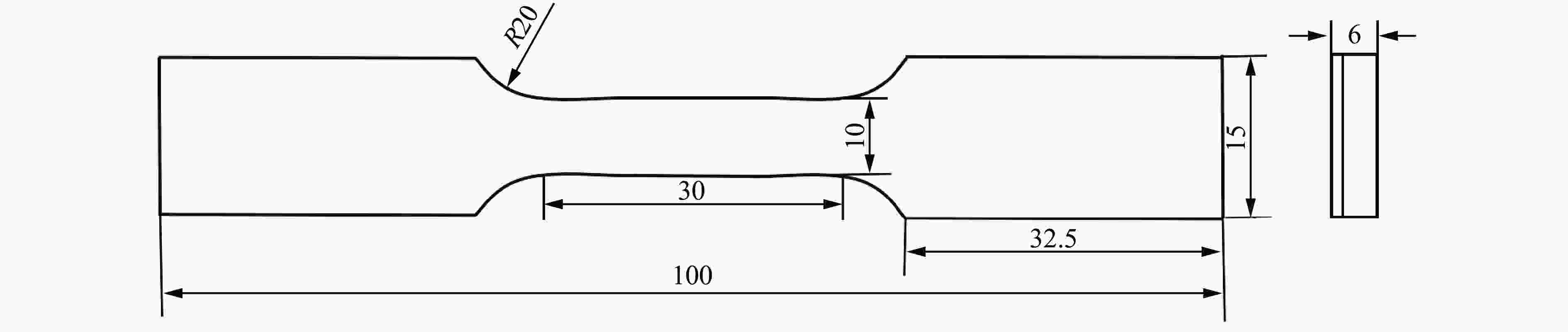
Tensile strength/MPa Yield strength/MPa Fracture elongation/% 709 581 24 -
[1] LI J H, LIANG X P, TAO H, et al. Study on the interface formation mechanism and properties of CoCrNi/316L composites prepared by explosive welding [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2025, 35: 4587–4598. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2025.02.122 [2] CORIGLIANO P, CRUPI V, GUGLIELMINO E. Non linear finite element simulation of explosive welded joints of dissimilar metals for shipbuilding applications [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 160: 346–353. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.04.070 [3] ZHANG C H, SONG C B, ZHU W G, et al. Interfaces of the 5083Al/1060Al/TA1/Ni/SUS304 five-layer composite plate fabricated by explosive welding [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022, 19: 314–331. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.04.157 [4] PETUSHKOV V G. Physical interpretation of explosion welding near its lower boundary [J]. Combustion, Explosion and Shock Waves, 2000, 36(6): 771–776. doi: 10.1023/A:1002810908014 [5] AFROUZIAN A, GRODEN C J, FIELD D P, et al. Additive manufacturing of Ti-Ni bimetallic structures [J]. Materials & Design, 2022, 215: 110461. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2022.110461 [6] ZHOU J N, LUO N, LIANG H L, et al. Multi-scale simulation and microstructure characteristics of TC4 ELI/Al 6013 plates by explosive welding [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2024, 124: 1180–1192. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2024.07.014 [7] SHMORGUN V G, BOGDANOV A I, TAUBE A O, et al. Evaluation of heat resistance and thermal conductivity of Ni-Cr-Al system layered coatings [J]. Metallurgist, 2022, 66(7/8): 934–941. doi: 10.1007/s11015-022-01405-z [8] LIPIŃSKA M, URA-BIŃCZYK E, MRÓZ S J, et al. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of Ni-Ti-Al multi-layer laminates manufactured by explosive welding with subsequent rolling [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2023, 105: 84–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.09.046 [9] YUAN J X, SHAO F, BAI L Y, et al. Interface characteristics and mechanical properties of titanium/aluminum composites with an interlayer fabricated by explosive welding [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2024, 31(1): 43–58. doi: 10.1007/s11771-023-5476-4 [10] SUN Z R, SHI C G, SHI H, et al. Comparative study of energy distribution and interface morphology in parallel and double vertical explosive welding by numerical simulations and experiments [J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 195: 109027. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109027 [11] 缪广红, 马宏昊, 沈兆武, 等. 蜂窝结构炸药及其应用 [J]. 含能材料, 2014, 22(5): 693–697. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2014.05.022MIAO G H, MA H H, SHEN Z W, et al. Explosives with structure of honeycomb and its application [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2014, 22(5): 693–697. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2014.05.022 [12] ZHA Y C, ZHANG C H, ZHU W G, et al. Experimental and numerical investigations on the microstructural features and mechanical properties of explosively welded aluminum/titanium/steel trimetallic plate [J]. Materials Characterization, 2024, 209: 113669. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2024.113669 [13] CHEN X, XIE X Q, HU J N, et al. Experimental and numerical study on the mechanism of interlayer explosive welding [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2024, 30: 5529–5546. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.04.209 [14] WANG X, ZHENG Y Y, LIU H X, et al. Numerical study of the mechanism of explosive/impact welding using smoothed particle hydrodynamics method [J]. Materials & Design, 2012, 35: 210–219. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2011.09.047 [15] KHALAJ G, MORADI M, ASADIAN E. Exploring the impact of rolling temperature on interface microstructure and mechanical properties of steel-bronze explosive welded bilayer composite sheets [J]. Welding in the World, 2023, 67(6): 1411–1425. doi: 10.1007/s40194-023-01495-6 [16] DERIBAS A A, KUDINOV V M, MATVEENKOV F I, et al. Determination of the impact parameters of flat plates in explosive welding [J]. Combustion, Explosion and Shock Waves, 1967, 3(2): 182–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00748745 [17] DERIBAS A A, KUDINOV V M, MATVEENKOV F I. Effect of the initial parameters on the process of wave formation in explosive welding [J]. Combustion, Explosion and Shock Waves, 1967, 3(4): 344–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00741684 [18] ZHOU J N, LUO N, JIANG L, et al. Interface microstructure and numerical simulation investigations of Ni/TC18 composite tube fabricated by explosive welding [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2025, 34(7): 5735–5750. doi: 10.1007/s11665-024-09544-x [19] PENG J X, HU C M, LI Y L, et al. Determination of parameters of Steinberg-Guinan constitutive model with shock wave experiments [J]. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 2008, 22: 1111–1116. doi: 10.1142/S0217979208046396 [20] LIANG H L, LUO N, CHEN Y L, et al. Interface microstructure and phase constitution of AA1060/TA2/SS30408 trimetallic composites fabricated by explosive welding [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022, 18: 564–576. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.02.109 [21] MAĆKOWIAK P, PŁACZEK D. Numerical simulation of the welding process for the prediction of temperature distribution on Al/steel explosion welded joint [J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2024, 2714: 012020. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2714/1/012020 [22] CHU Q L, CAO Q L, ZHANG M, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties investigation of explosively welded titanium/copper/steel trimetallic plate [J]. Materials Characterization, 2022, 192: 112250. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2022.112250 [23] CHU Q L, ZHANG M, LI J H, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of microstructure and mechanical behavior of titanium/steel interfaces prepared by explosive welding [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2017, 689: 323–331. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.02.075 [24] KODUKULA S, MANNINEN T, PORTER D. Estimation of Lankford coefficients of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels using mean grain orientations from micro-texture measurements [J]. ISIJ International, 2021, 61(1): 401–407. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2020-256 [25] ZHOU Q, LIU R, ZHOU Q, et al. Microstructure characterization and tensile shear failure mechanism of the bonding interface of explosively welded titanium-steel composite [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 820: 141559. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141559 -






 下载:
下载: