Research Progress on the Ultra-High Pressure Preparation of Typical Transition Metal Carbides (Group ⅣB −ⅥB)
-
摘要: 过渡金属碳化物具有高硬度、高熔点、高电导率、耐腐蚀等优异的综合性能,在航空航天、切削加工等极端环境领域具有广阔的应用前景。由于过渡金属碳化物具有强共价键和低扩散系数,其烧结制备所需的温度极高,制备高致密度且性能优异的块体陶瓷具有挑战性。高温高压烧结方法具有可有效降低烧结温度、缩短烧结时间、抑制晶粒生长、提高致密化程度并保持物相纯净等优点。本文从高温高压合成角度,综述了数种典型过渡金属碳化物(ⅣB~ⅥB族)的制备、力学性能、微观机制的研究进展,总结并展望了过渡金属碳化物陶瓷的应用前景和未来发展方向。Abstract: Transition metal carbides (TMCs) exhibit exceptional properties, including high hardness, high melting point, excellent electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance, making them promising candidates for extreme environments such as aerospace and cutting tools. However, the strong covalent bonding and low diffusion coefficients inherent to TMCs necessitate extremely high sintering temperatures, posing significant challenges for fabricating dense bulk ceramics with superior properties. The high pressure and high temperature (HPHT) sintering technique offers distinct advantages, effectively lowering sintering temperatures, reducing processing times, suppressing grain growth, enhancing densification, and preserving phase purity. This review summarizes recent advances in the HPHT synthesis, mechanical properties, and underlying mechanisms of several typical TMCs (Groups ⅣB to ⅥB). The application prospects and future research directions for TMC ceramics are also discussed and outlined.
-
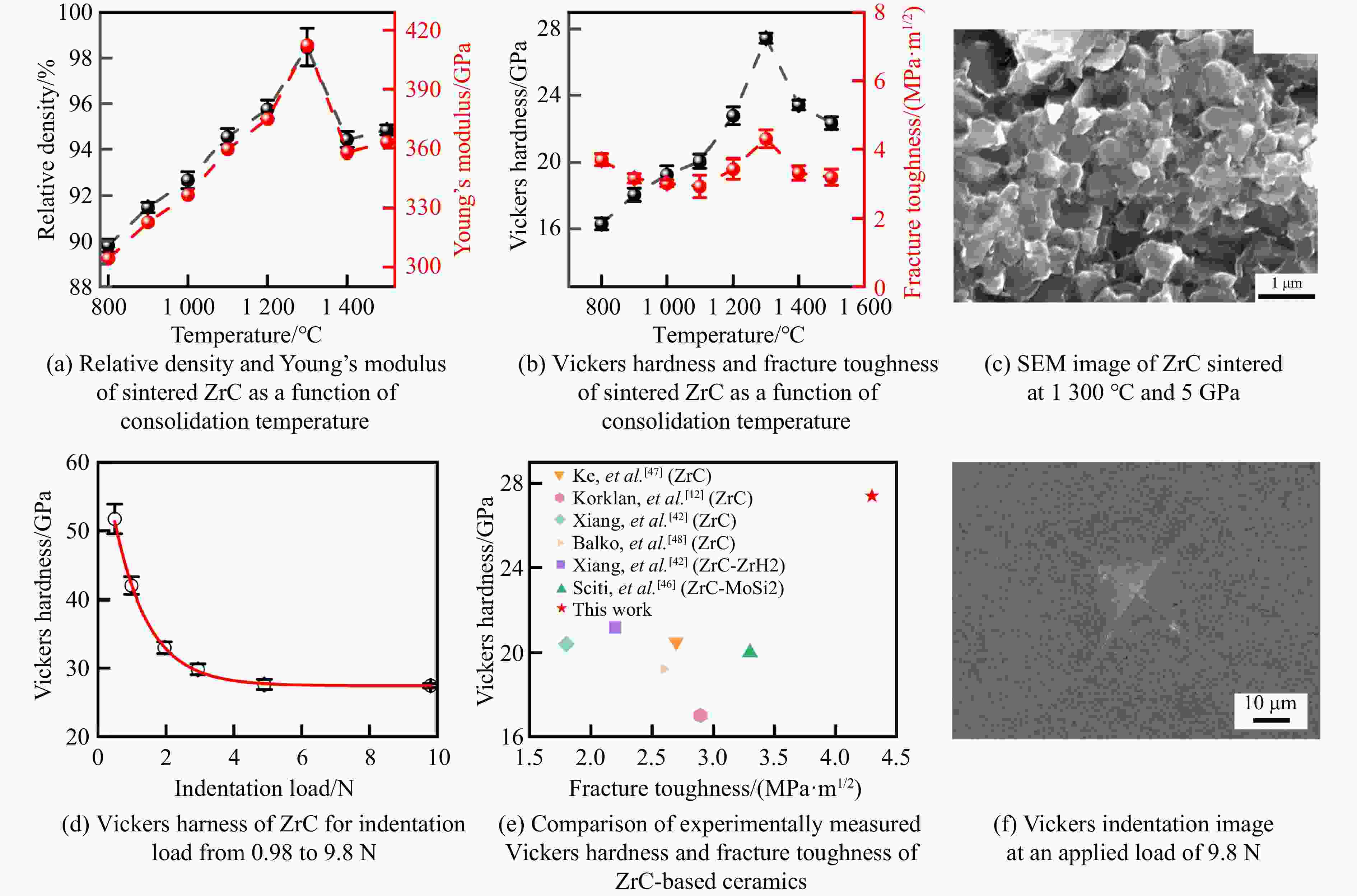
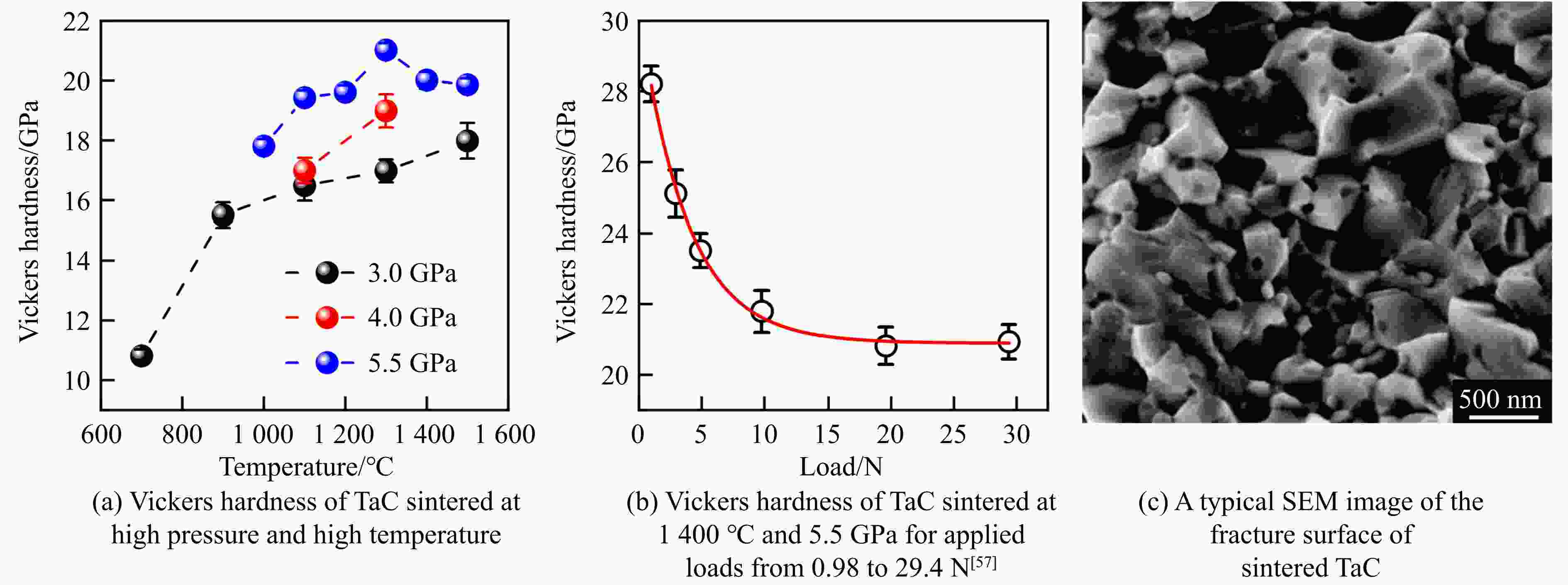
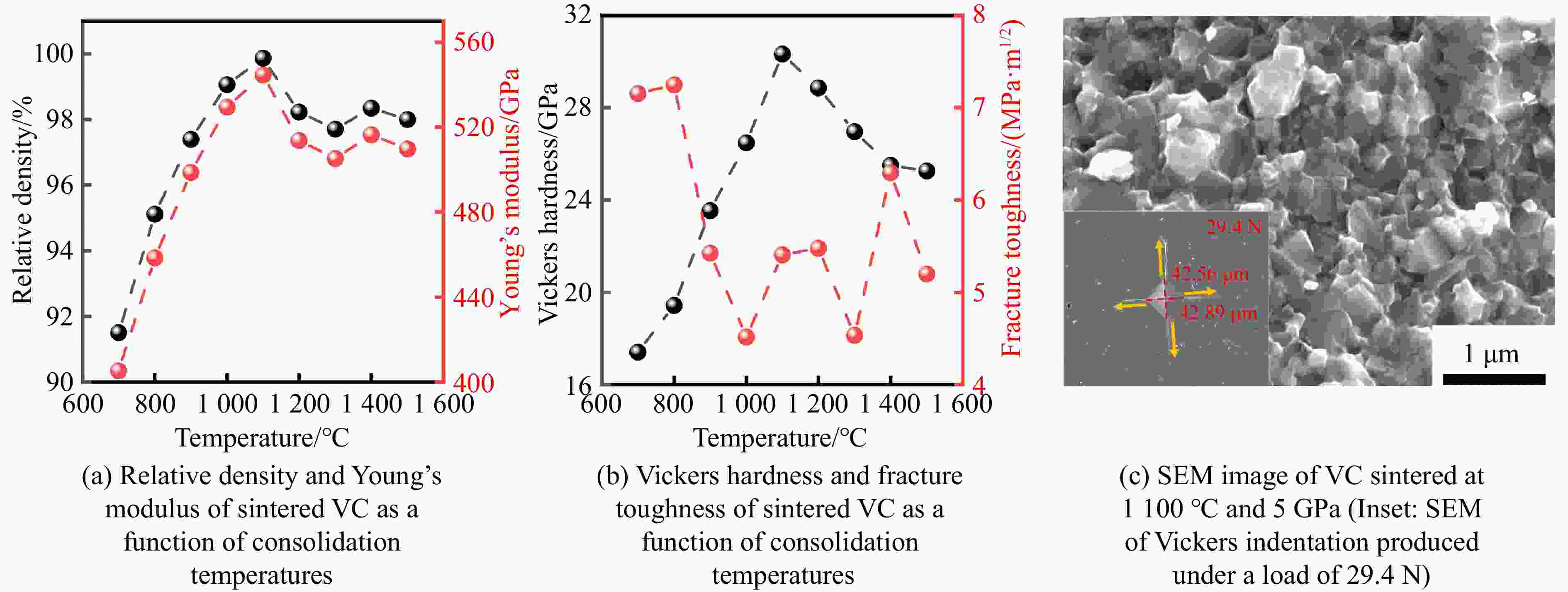
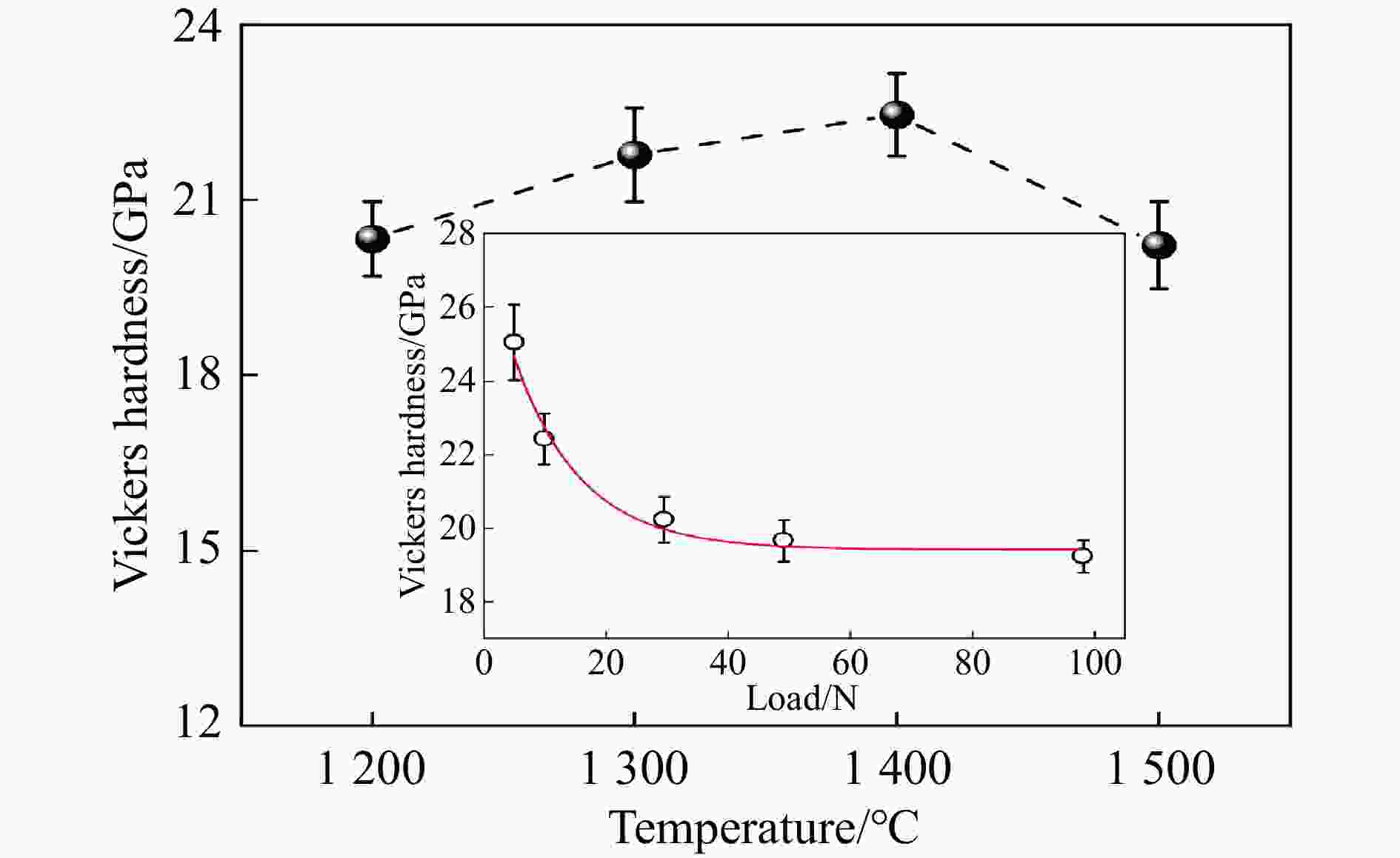
表 1 典型过渡金属碳化物的烧结工艺参数、合成条件与性能的对比
Table 1. Comparison of sintering parameters, synthesis conditions, and performances of typical transition metal carbides
TMCs Synthetic method Synthesis condition Vickers
hardness/GPaE/GPa KIC/
(MPa·m1/2)Relative
density/%Thermal
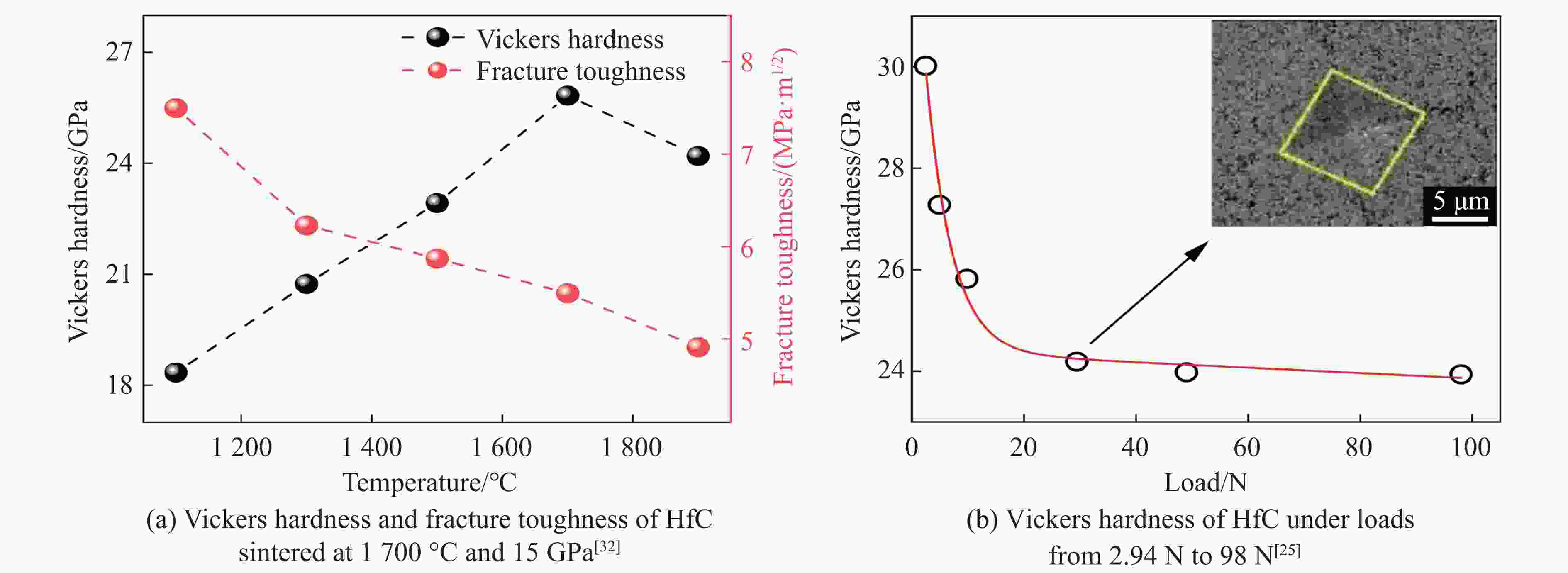
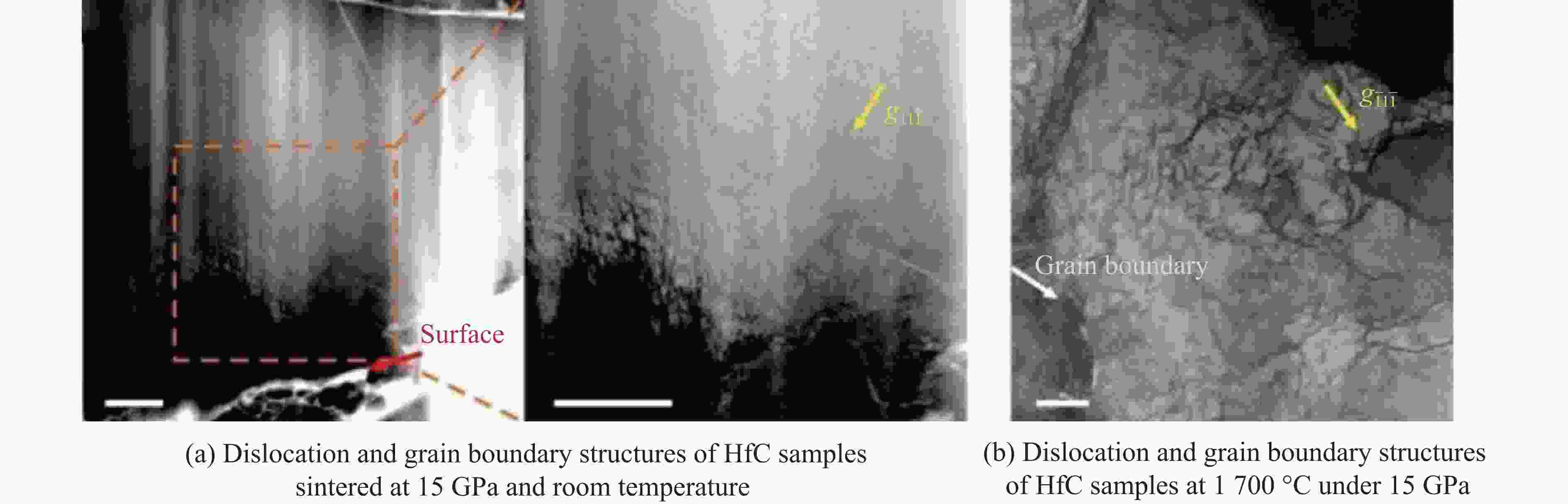
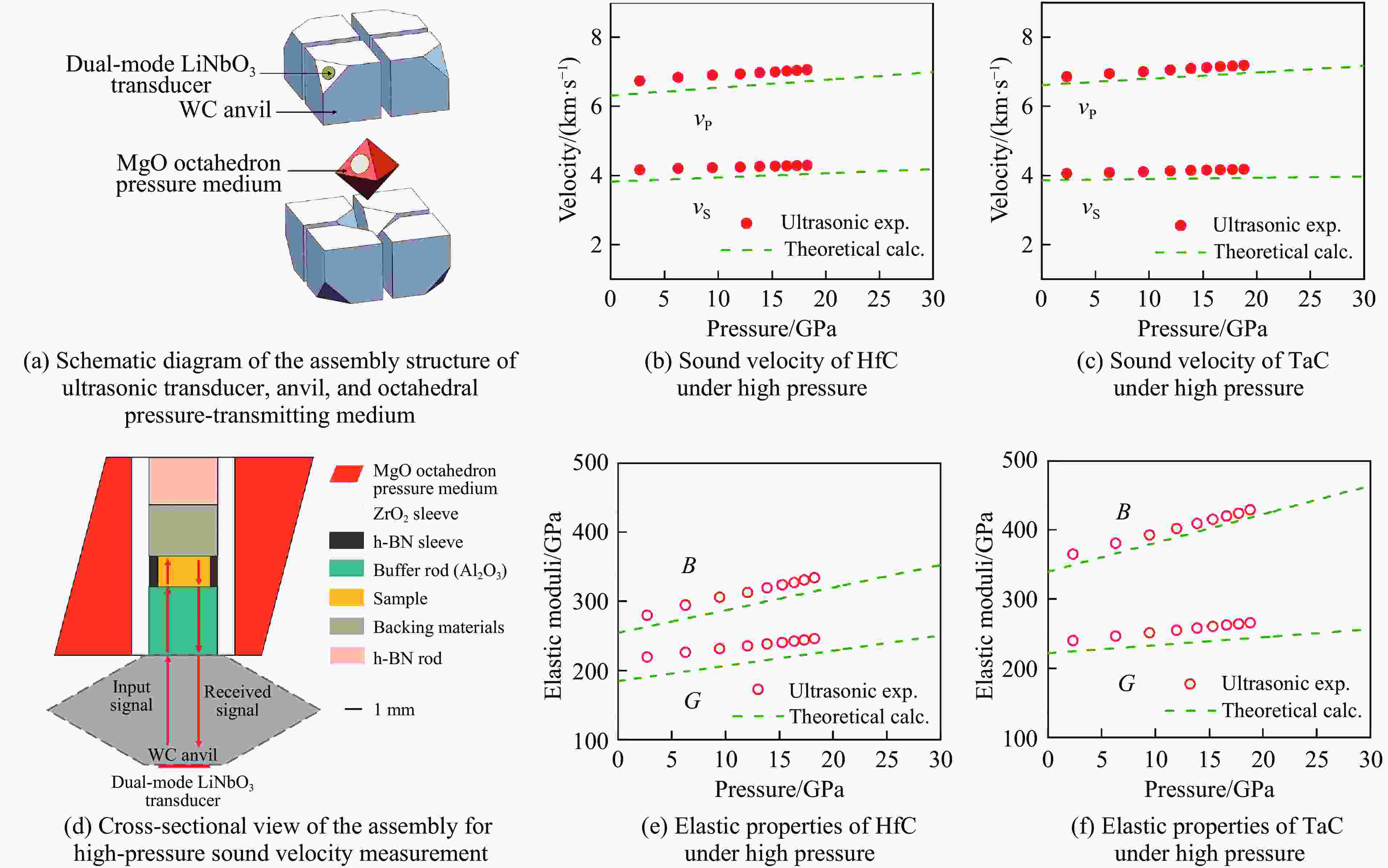
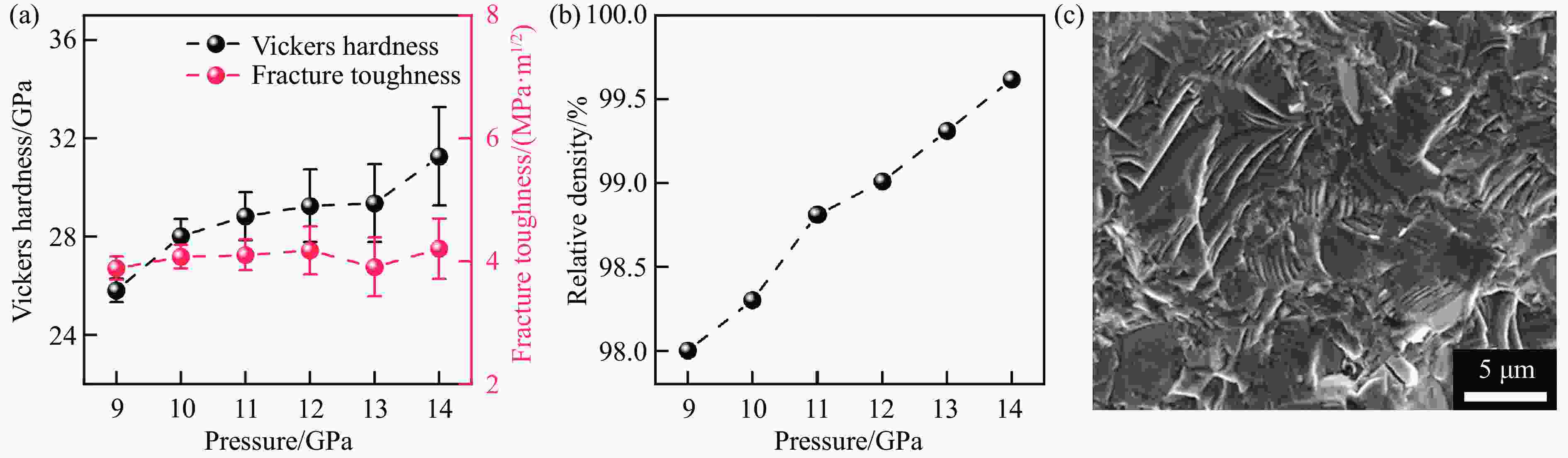
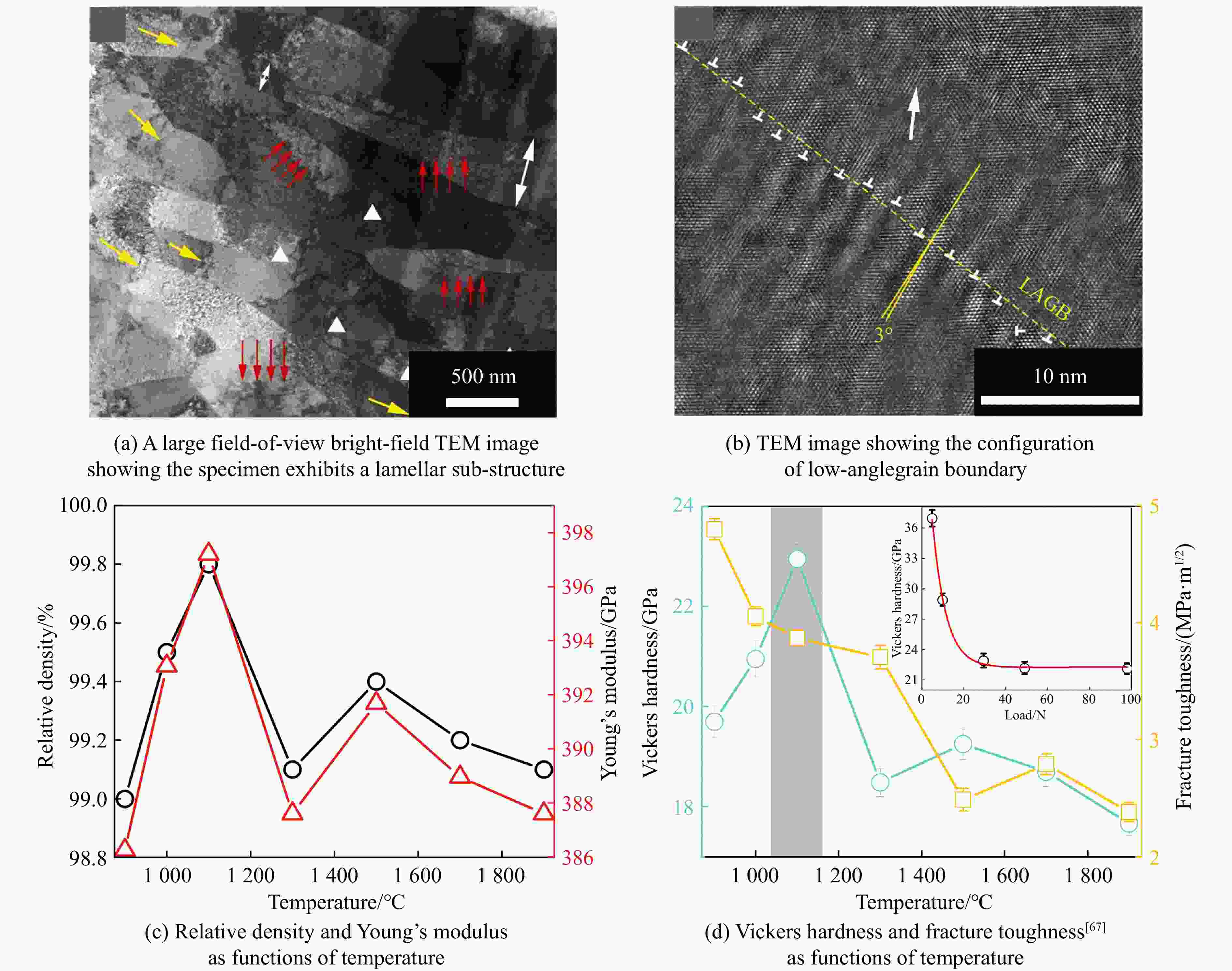
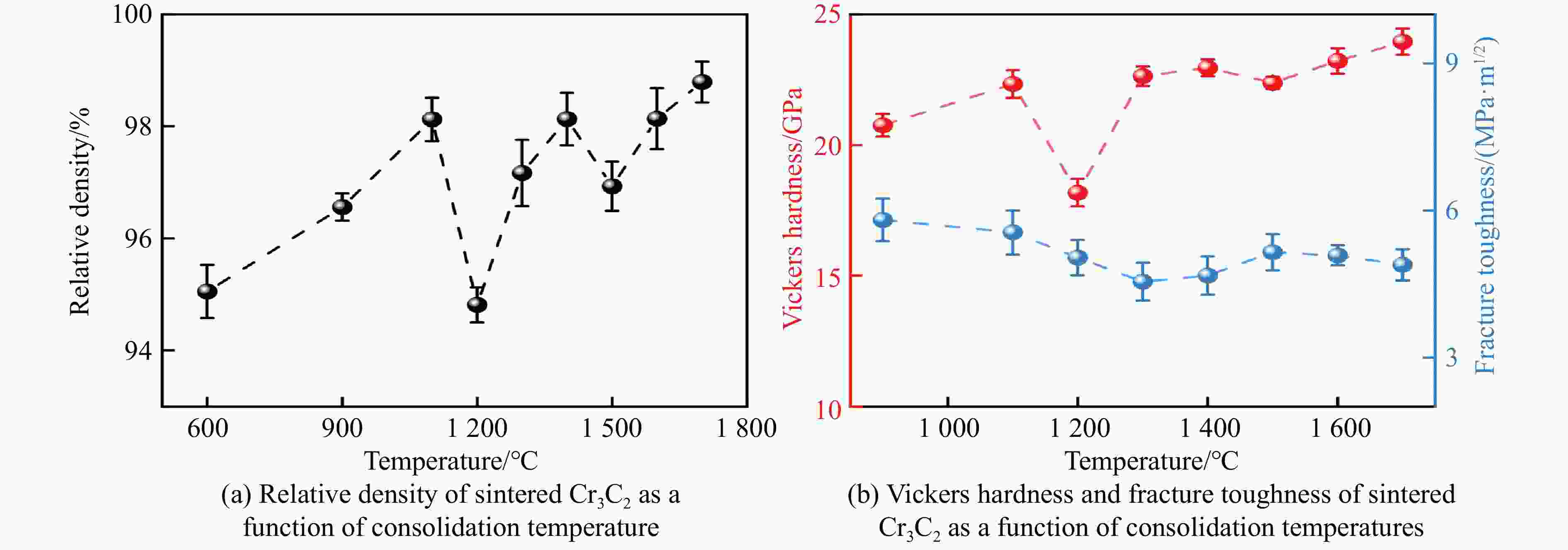
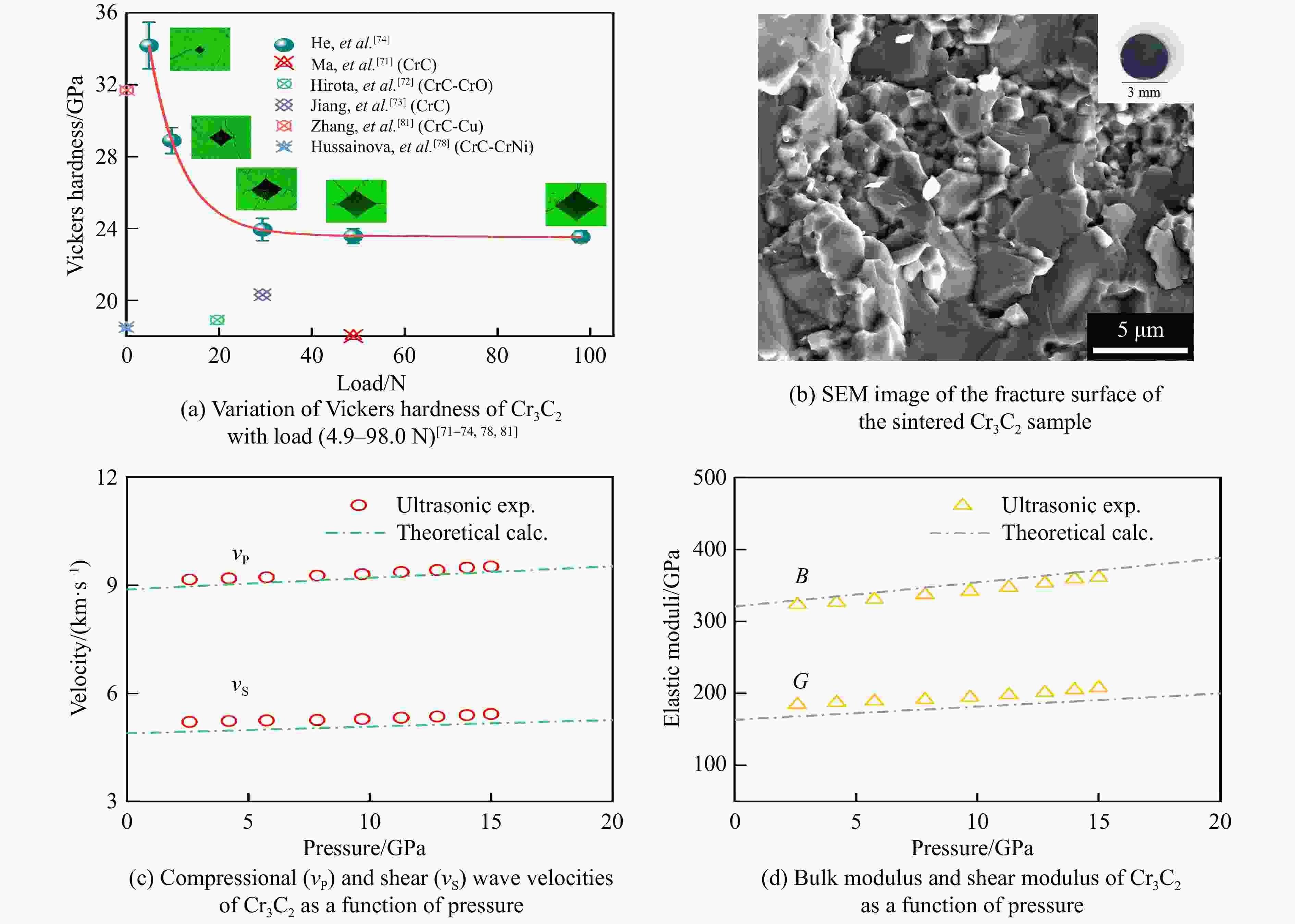
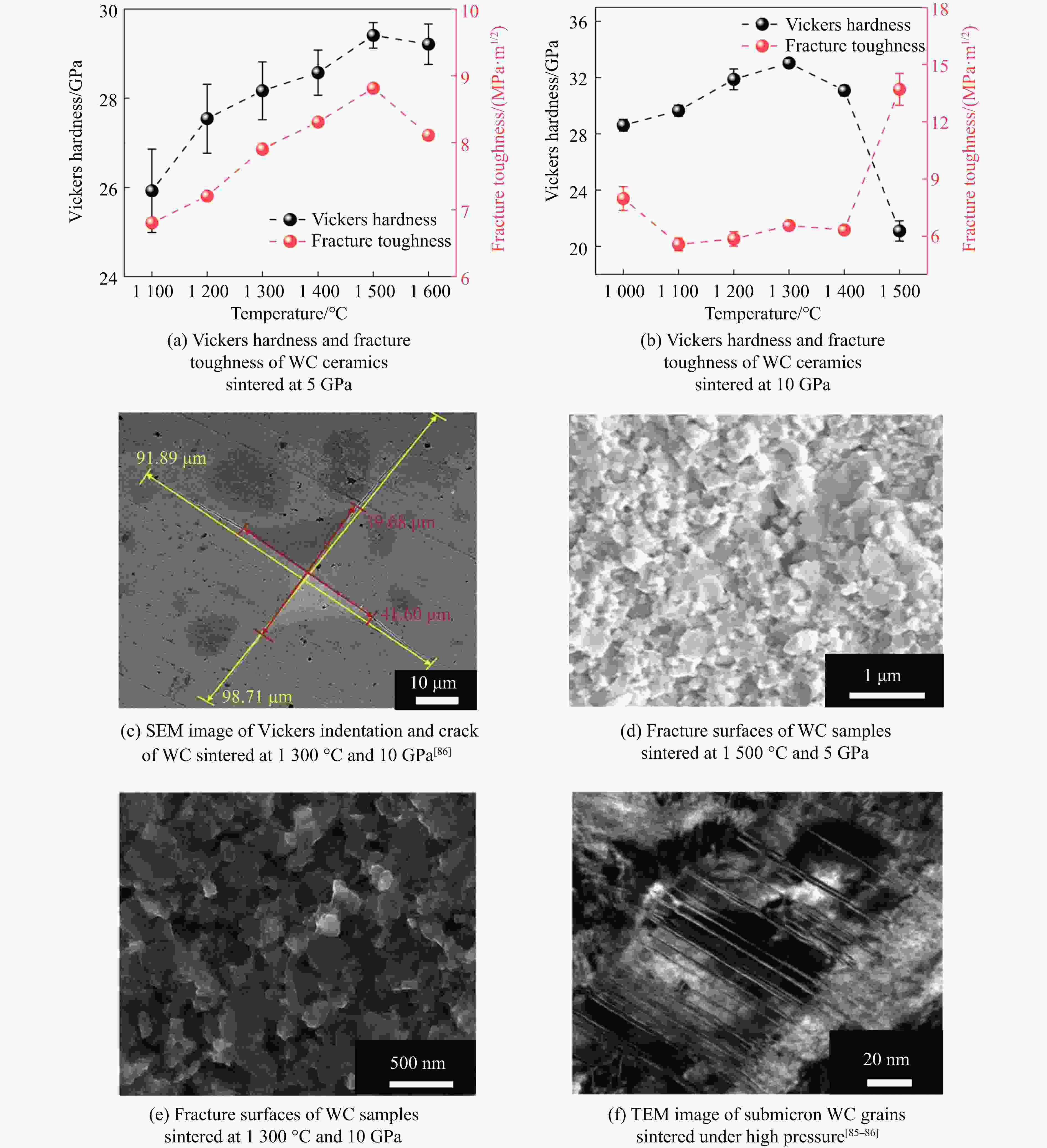
stability/℃TiC SPS 1 650 ℃, 100 MPa[38–39] 25.7/27 97.9/95.1 HFIHS 80 MPa[16] 25.7 99 PS 1 700 ℃[40] 20.3 95.7 HPHT 1 500 ℃, 14 GPa[41] 31.2 4.2 99.7 ZrC SPS 1 850 ℃, 100 MPa[42] 20.4 376 1.8 98 1 800 ℃, 40 MPa[43] 17.6 3.3 95.5 PS 2 100 ℃[89] 8.9 94.4 HPHT 1 300 ℃, 5 GPa[44] 27.4 412 4.3 98.2 713 HfC SPS 2 200 ℃, 65 MPa[31] 19 500 98 2 300 ℃, 38 MPa[13] 10.2 283 2.9 85 HPS 1 900 ℃, 30 MPa[10] 5.79 1.88 89 HPHT 1 700 ℃, 15 GPa[32] 25.8 455 5.5 99.5 860 VC HPHT 1 100 ℃, 5 GPa[59] 30.4 544 5.4 99.8 655 NbC HPHT 1400 ℃, 5 GPa[63]19.2 7.7 99.4 TaC SPS 2 350 ℃, 38 MPa[13] 13.9 458 2.7 98 HPS 2 300 ℃, 30 MPa[52] 14 3 94 2 000 ℃, 40 MPa[54] 15.7 4.1 97 HFIHS 80 MPa[53] 22 5.1 96 HPHT 1 300 ℃, 5.5 GPa[56] 21 457 97.7 Cr3C2 HPS 1 300 ℃, 40 MPa[70] 18.5 5.6 HIP 1 330 ℃, 150 MPa[70] 17 5 GPCS 727 ℃, 100 MPa[71] 18 5.6 PECPS 1 300 ℃, 30 MPa[72] 18.9 7.1 98.9 HPHT 1 700 ℃, 15 GPa[74] 24 459 4.9 99 Mo2C HPS 1 550 ℃, 50 MPa[66] 16 400 100 HPHT 1 100 ℃, 15 GPa[67] 23 397 3.9 99.8 655 WC SPS 1 400 ℃, 80 MPa[88] 27 7.2 99.3 HPHT 1 500 ℃, 5 GPa[85] 29.3 8.9 99.2 1 300 ℃, 10 GPa[86] 33 6.6 -
[1] FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E. Ultra-high temperature ceramics: materials for extreme environments [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2017, 129: 94–99. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.10.018 [2] SAVINO R, DE STEFANO FUMO M, PATERNA D, et al. Aerothermodynamic study of UHTC-based thermal protection systems [J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2005, 9(2): 151–160. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2004.12.003 [3] 董绍明, 王京阳, 倪德伟. 结构陶瓷——承载人类文明的基石 [J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 569–570. doi: 10.15541/jim20240000DONG S M, WANG J Y, NI D W. Structural ceramics—the cornerstone of human civilization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 569–570. doi: 10.15541/jim20240000 [4] 张幸红, 王义铭, 程源, 等. 超高温陶瓷复合材料研究进展 [J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 571–590. doi: 10.15541/jim20230609ZHANG X H, WANG Y M, CHENG Y, et al. Research progress on ultra-high temperature ceramic composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 571–590. doi: 10.15541/jim20230609 [5] WOO Y C, KANG H J, KIM D J. Formation of TiC particle during carbothermal reduction of TiO2 [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2007, 27(2/3): 719–722. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2006.04.090 [6] UL-HAMID A. Microstructure, properties and applications of Zr-carbide, Zr-nitride and Zr-carbonitride coatings: a review [J]. Materials Advances, 2020, 1(5): 1012–1037. doi: 10.1039/D0MA00233J [7] LEVASHOV E A, MUKASYAN A S, ROGACHEV A S, et al. Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of advanced materials and coatings [J]. International Materials Reviews, 2017, 62(4): 203–239. doi: 10.1080/09506608.2016.1243291 [8] BOLOKANG S, BANGANAYI C, PHASHA M. Effect of C and milling parameters on the synthesis of WC powders by mechanical alloying [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2010, 28(2): 211–216. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2009.09.006 [9] RAJKUMAR K, ARAVINDAN S. Microwave sintering of copper-graphite composites [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(15/16): 5601–5605. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2009.05.017 [10] SILVESTRONI L, BELLOSI A, MELANDRI C, et al. Microstructure and properties of HfC and TaC-based ceramics obtained by ultrafine powder [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2011, 31(4): 619–627. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.10.036 [11] WOYDT M, MOHRBACHER H. The use of niobium carbide (NbC) as cutting tools and for wear resistant tribosystems [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2015, 49: 212–218. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2014.07.002 [12] KORKLAN N, HILMAS G E, FAHRENHOLTZ W G. Processing and room temperature mechanical properties of a zirconium carbide ceramic [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2021, 104(1): 413–418. doi: 10.1111/jace.17442 [13] CEDILLOS-BARRAZA O, GRASSO S, NASIRI N A, et al. Sintering behaviour, solid solution formation and characterisation of TaC, HfC and TaC-HfC fabricated by spark plasma sintering [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(7): 1539–1548. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.02.009 [14] BABAPOOR A, ASL M S, AHMADI Z, et al. Effects of spark plasma sintering temperature on densification, hardness and thermal conductivity of titanium carbide [J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(12): 14541–14546. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.05.071 [15] KELLY J P, GRAEVE O A. Mechanisms of pore formation in high-temperature carbides: case study of TaC prepared by spark plasma sintering [J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 84: 472–483. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2014.11.005 [16] SHON I J, KIM B R, DOH J M, et al. Consolidation of binderless nanostructured titanium carbide by high-frequency induction heated sintering [J]. Ceramics International, 2010, 36(6): 1797–1803. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2010.03.007 [17] KIM H C, YOON J K, DOH J M, et al. Rapid sintering process and mechanical properties of binderless ultra fine tungsten carbide [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A Structural Materials: Properties, Microstructure and Processing, 2006, 435/436: 717–724. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.07.127 [18] KIM B R, WOO K D, YOON J K, et al. Mechanical properties and rapid consolidation of binderless niobium carbide [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 481(1/2): 573–576. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.03.036 [19] TOTH L E. Transition metal carbides and nitrides [M]. New York: Elsevier, 2014. [20] YOUNG C, ZHANG C, LOGANATHAN A, et al. Densification and oxidation behavior of spark plasma sintered hafnium diboride-hafnium carbide composite [J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10): 14625–14631. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.263 [21] ZHANG J, MA S, ZHU J W, et al. Microstructure and compression strength of W/HfC composites synthesized by plasma activated sintering [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2019, 25(2): 416–424. doi: 10.1007/s12540-018-0190-8 [22] IRIFUNE T, KAWAKAMI K, ARIMOTO T, et al. Pressure-induced nano-crystallization of silicate garnets from glass [J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 13753. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13753 [23] SOLOZHENKO V L, KURAKEVYCH O O, LE GODEC Y. Creation of nanostuctures by extreme conditions: high-pressure synthesis of ultrahard nanocrystalline cubic boron nitride [J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(12): 1540–1544. doi: 10.1002/adma.201104361 [24] FENG L, LEE S H, WANG H L, et al. Synthesis and densification of nano-crystalline hafnium carbide powder [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(15): 4073–4081. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.08.004 [25] LIANG H, FANG L M, GUAN S X, et al. Insights into the bond behavior and mechanical properties of hafnium carbide under high pressure and high temperature [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2021, 60(2): 515–524. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c02800 [26] HE R Q, FANG L M, HAN T X, et al. Elasticity, mechanical and thermal properties of polycrystalline hafnium carbide and tantalum carbide at high pressure [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(13): 5220–5228. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2022.06.039 [27] KURBATKINA V V, PATSERA E I, LEVASHOV E A, et al. SHS processing and consolidation of Ta-Ti-C, Ta-Zr-C, and Ta-Hf-C carbides for ultra-high-temperatures application [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2018, 20(8): 1701075. doi: 10.1002/adem.201701075 [28] GOLLA B R, MUKHOPADHYAY A, BASU B, et al. Review on ultra-high temperature boride ceramics [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2020, 111: 100651. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100651 [29] CEDILLOS-BARRAZA O, MANARA D, BOBORIDIS K, et al. Investigating the highest melting temperature materials: a laser melting study of the TaC-HfC system [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 37962. doi: 10.1038/srep37962 [30] ZHONG Y, XIA X H, SHI F, et al. Transition metal carbides and nitrides in energy storage and conversion [J]. Advanced Science, 2016, 3(5): 1500286. doi: 10.1002/advs.201500286 [31] SCITI D, GUICCIARDI S, NYGREN M. Densification and mechanical behavior of HfC and HfB2 fabricated by spark plasma sintering [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(5): 1433–1440. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2007.02248.x [32] LIANG H, LIN W T, FANG L M, et al. Achieving dislocation strengthening in hafnium carbide through high pressure and high temperature [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(43): 24254–24262. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c08086 [33] LI B S, LIEBERMANN R C. Study of the Earth’s interior using measurements of sound velocities in minerals by ultrasonic interferometry [J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2014, 233: 135–153. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2014.05.006 [34] DURLU N. Titanium carbide based composites for high temperature applications [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1999, 19(13/14): 2415–2419. doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(99)00101-6 [35] NEDFORS N, TENGSTRAND O, LEWIN E, et al. Structural, mechanical and electrical-contact properties of nanocrystalline-NbC/amorphous-C coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2011, 206(2/3): 354–359. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.07.021 [36] OGUNTUYI S D, JOHNSON O T, SHONGWE M B. Spark plasma sintering of ceramic matrix composite of TiC: microstructure, densification, and mechanical properties: a review [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 116(1): 69–82. doi: 10.1007/s00170-021-07471-y [37] ONO T, ENDO H, UEKI M. Hot-pressing of TiC-graphite composite materials [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 1993, 2(5): 659–664. doi: 10.1007/BF02650054 [38] TEBER A, SCHOENSTEIN F, TÊTARD F, et al. Effect of SPS process sintering on the microstructure and mechanical properties of nanocrystalline TiC for tools application [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2012, 30(1): 64–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2011.06.013 [39] ABDERRAZAK H, SCHOENSTEIN F, ABDELLAOUI M, et al. Spark plasma sintering consolidation of nanostructured TiC prepared by mechanical alloying [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2011, 29(2): 170–176. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2010.10.003 [40] FU Z Z, KOC R. Pressureless sintering of submicron titanium carbide powders [J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(18): 17233–17237. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.09.050 [41] WANG Z W, KOU Z L, ZHANG Y F, et al. Micrometer-sized titanium carbide with properties comparable to those of nanocrystalline counterparts [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 125(16): 165901. doi: 10.1063/1.5087754 [42] XIANG M Y, XIE J J, JI W, et al. Low temperature consolidation for fine-grained zirconium carbide from nanoparticles with ZrH2 as sintering additive [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(8): 3003–3007. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.03.002 [43] ACICBE R B, GOLLER G. Densification behavior and mechanical properties of spark plasma-sintered ZrC-TiC and ZrC-TiC-CNT composites [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2013, 48(6): 2388–2393. doi: 10.1007/s10853-012-7024-8 [44] YANG P, PENG F, XIAO X, et al. Sintering pure polycrystalline zirconium carbide ceramics with enhanced mechanical properties under high-pressure and high-temperature [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2025, 45(5): 117115. doi: 10.1016/J.JEURCERAMSOC.2024.117115 [45] NIELSEN L F. Elasticity and damping of porous materials and impregnated materials [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1984, 67(2): 93–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1984.tb09622.x [46] SCITI D, GUICCIARDI S, NYGREN M. Spark plasma sintering and mechanical behaviour of ZrC-based composites [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 59(6): 638–641. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.05.026 [47] KE B R, JI W, ZOU J, et al. Densification mechanism, microstructure and mechanical properties of ZrC ceramics prepared by high-pressure spark plasma sintering [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(8): 3053–3061. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2023.02.038 [48] BALKO J, CSANÁDI T, SEDLÁK R, et al. Nanoindentation and tribology of VC, NbC and ZrC refractory carbides [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(14): 4371–4377. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.04.064 [49] DOLLÉ M, GOSSET D, BOGICEVIC C, et al. Synthesis of nanosized zirconium carbide by a sol-gel route [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2007, 27(4): 2061–2067. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2006.06.005 [50] DA A Y, LONG F, WANG J L, et al. Preparation of nano-sized zirconium carbide powders through a novel active dilution self-propagating high temperature synthesis method [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology Materials Science Edition, 2015, 30(4): 729–734. doi: 10.1007/s11595-015-1220-8 [51] ZHANG X H, HILMAS G E, FAHRENHOLTZ W G. Densification and mechanical properties of TaC-based ceramics [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A Structural Materials: Properties, Microstructure and Processing, 2009, 501(1/2): 37–43. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2008.09.024 [52] ZHANG X H, HILMAS G E, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, et al. Hot pressing of tantalum carbide with and without sintering additives [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2007, 90(2): 393–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2006.01416.x [53] KIM B R, WOO K D, DOH J M, et al. Mechanical properties and rapid consolidation of binderless nanostructured tantalum carbide [J]. Ceramics International, 2009, 35(8): 3395–3400. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2009.06.012 [54] REZAEI F, KAKROUDI M G, SHAHEDIFAR V, et al. Densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of hot pressed tantalum carbide [J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(4): 3489–3494. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.10.067 [55] CHEN H H, LIANG H, LIU L X, et al. Hardness measurements for high-pressure prepared TaB and nano-TaC ceramics [J]. Results in Physics, 2017, 7: 3859–3862. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2017.10.006 [56] ZHANG Z G, LIANG H, CHEN H H, et al. Exploring physical properties of tantalum carbide at high pressure and temperature [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2020, 59(3): 1848–1852. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b03055 [57] SUN W G, KUANG X Y, LIANG H, et al. Mechanical properties of tantalum carbide from high-pressure/high-temperature synthesis and first-principles calculations [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2020, 22(9): 5018–5023. doi: 10.1039/C9CP06819H [58] DODD S P, CANKURTRAN M, JAMES B. Ultrasonic determination of the elastic and nonlinear acoustic properties of transition-metal carbide ceramics: TiC and TaC [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2003, 38(6): 1107–1115. doi: 10.1023/A:1022845109930 [59] CHEN J, PENG F, WANG Y P, et al. Mechanisms and mechanical properties of high-temperature high-pressure sintered vanadium carbide ceramics [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2024, 118: 106483. doi: 10.1016/J.IJRMHM.2023.106483 [60] WU L L, YAO T K, WANG Y C, et al. Understanding the mechanical properties of vanadium carbides: nano-indentation measurement and first-principles calculations [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 548: 60–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.09.014 [61] HUANG S G, VAN DER BIEST O, LI L, et al. Properties of NbC-Co cermets obtained by spark plasma sintering [J]. Materials Letters, 2007, 61(2): 574–577. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2006.05.011 [62] VOJVODIC A, HELLMAN A, RUBERTO C, et al. From electronic structure to catalytic activity: a single descriptor for adsorption and reactivity on transition-metal carbides [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(14): 146103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.146103 [63] LIU F M, LIU P P, PENG F, et al. Hardness and compression behavior of niobium carbide [J]. High Pressure Research, 2017, 37(2): 244–255. doi: 10.1080/08957959.2017.1297810 [64] WANG X H, HAO H L, ZHANG M H, et al. Synthesis and characterization of molybdenum carbides using propane as carbon source [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2006, 179(2): 538–543. doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2005.11.009 [65] DÍAZ BARRIGA ARCEO L, OROZCO E, MENDOZA-LEÓN H, et al. Nanostructures obtained from a mechanically alloyed and heat treated molybdenum carbide [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 434/435: 799–802. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.08.193 [66] NINO A, TANAKA A, SUGIYAMA S, et al. Indentation size effect for the hardness of refractory carbides [J]. Materials Transactions, 2010, 51(9): 1621–1626. doi: 10.2320/matertrans.M2010110 [67] LIANG H, HE R Q, LIN W T, et al. Strain-induced strengthening in superconducting β-Mo2C through high pressure and high temperature [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(1): 88–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2022.09.031 [68] LU K, LU L, SURESH S. Strengthening materials by engineering coherent internal boundaries at the nanoscale [J]. Science, 2009, 324(5925): 349–352. doi: 10.1126/science.1159610 [69] DOHERTY R D, HUGHES D A, HUMPHREYS F J, et al. Current issues in recrystallization: a review [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A Structural Materials: Properties, Microstructure and Processing, 1997, 238(2): 219–274. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(97)00424-3 [70] FURUKAWA M, SATO M, NAKANO O, et al. Hot isostatic pressing of chromium carbide [J]. Nippon Tungsten Review, 1989, 22: 73–82. [71] MA X F, TANIHATA K, MIYAMOTO Y. Gas-pressure combustion sintering and properties of Cr3C2 ceramic and its composite with TiC [J]. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 1992, 100(1160): 605–607. doi: 10.2109/jcersj.100.605 [72] HIROTA K, MITANI K, YOSHINAKA M, et al. Simultaneous synthesis and consolidation of chromium carbides (Cr3C2, Cr7C3 and Cr23C6) by pulsed electric-current pressure sintering [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A Structural Materials: Properties, Microstructure and Processing, 2005, 399(1/2): 154–160. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2005.02.062 [73] JIANG B L, KOU Z L, MA D J, et al. Mechanical behavior of the Cr3C2 compound at high pressure and high temperature [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2015, 1120/1121: 1187–1193. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1120-1121.1187 [74] HE R Q, FANG L M, SUN J C, et al. Abnormal sintering behaviors of chromium carbide under high pressure and high temperature [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2025, 45(1): 116822. doi: 10.1016/J.JEURCERAMSOC.2024.116822 [75] HE R Q, FANG L M, CHEN X P, et al. Experimental study of covalent Cr3C2 with high ionicity: sound velocities, elasticity, and mechanical properties under high pressure [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2023, 224: 115146. doi: 10.1016/J.SCRIPTAMAT.2022.115146 [76] OYAMA S T. The chemistry of transition metal carbides and nitrides [M]. London: Springer Dordrecht, 1996. [77] ZHAI W Y, GAO Y M, SUN L, et al. High pressure in-situ synthesis and physical properties of Cr3C2-Ni cermets [J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(18): 17202–17205. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.09.145 [78] HUSSAINOVA I, JASIUK I, SARDELA M, et al. Micromechanical properties and erosive wear performance of chromium carbide based cermets [J]. Wear, 2009, 267(1): 152–159. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2008.12.104 [79] JELLAD A, LABDI S, BENAMEUR T. On the hardness and the inherent ductility of chromium carbide nanostructured coatings prepared by RF sputtering [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 483(1/2): 464–467. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.07.220 [80] SINGH V, DIAZ R, BALANI K, et al. Chromium carbide-CNT nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical properties [J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(2): 335–344. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2008.09.023 [81] ZHANG L, PANG X L, GAO K W, et al. Mechanical properties of a bi-continuous Cu-Cr3C2 composite [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A Structural Materials: Properties, Microstructure and Processing, 2015, 623: 4–9. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.10.074 [82] KIM H C, OH D Y, SHON I J. Synthesis of WC and dense WC-xvol.%Co hard materials by high-frequency induction heated combustion method [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2004, 22(1): 41–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2003.12.002 [83] BAO R, YI J H. Densification and alloying of microwave sintering WC-8wt.%Co composites [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2014, 43: 269–275. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2013.12.010 [84] WANG X, FANG Z Z, SOHN H Y. Grain growth during the early stage of sintering of nanosized WC-Co powder [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2008, 26(3): 232–241. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2007.04.006 [85] MA D J, KOU Z L, LIU Y J, et al. Sub-micron binderless tungsten carbide sintering behavior under high pressure and high temperature [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2016, 54: 427–432. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2015.10.001 [86] ZHANG Y F, KOU Z L, WANG Z W, et al. Magic high-pressure strengthening in tungsten carbide system [J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(7): 8721–8726. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.01.195 [87] CHUVIL'DEEV V N, BLAGOVESHCHENSKIY Y V, NOKHRIN A V, et al. Spark plasma sintering of tungsten carbide nanopowders obtained through DC arc plasma synthesis [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 708: 547–561. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.035 [88] GRASSO S, POETSCHKE J, RICHTER V, et al. Low-temperature spark plasma sintering of pure nano WC powder [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2013, 96(6): 1702–1705. doi: 10.1111/jace.12365 [89] ZHAO L Y, JIA D C, DUAN X M, et al. Pressureless sintering of ZrC-based ceramics by enhancing powder sinterability [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2011, 29(4): 516–521. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2011.03.001 -






 下载:
下载: