Prediction of Equivalent Strength of Hydrated Cement Paste Based on Neural Networks
-
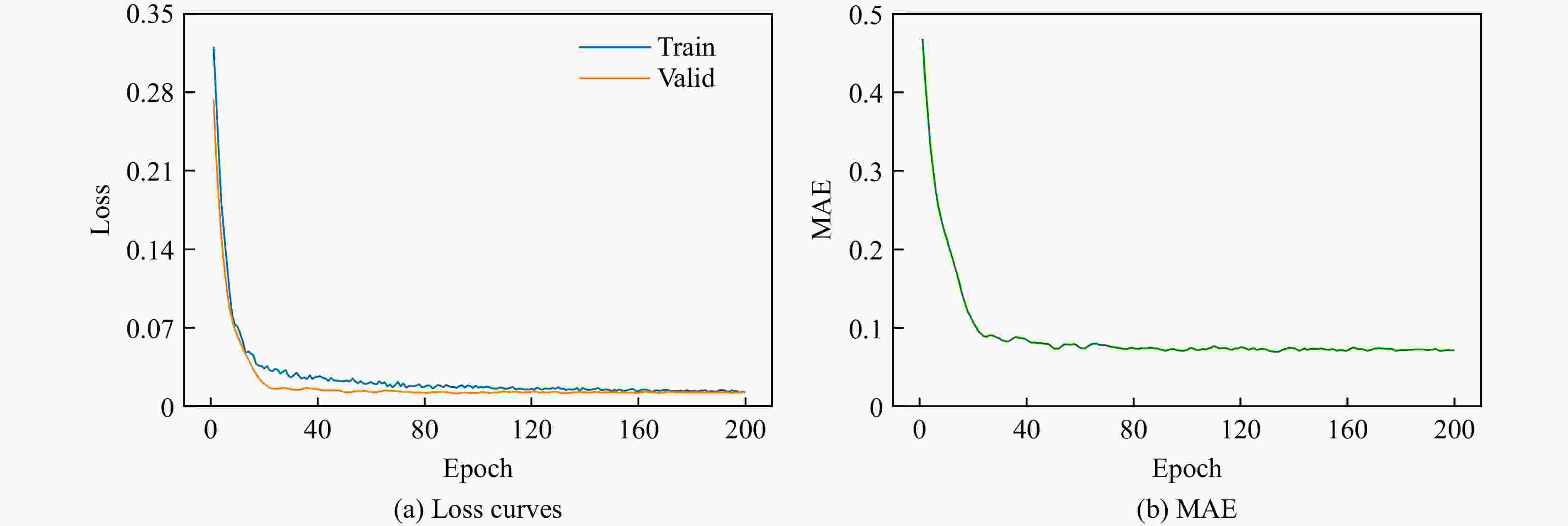
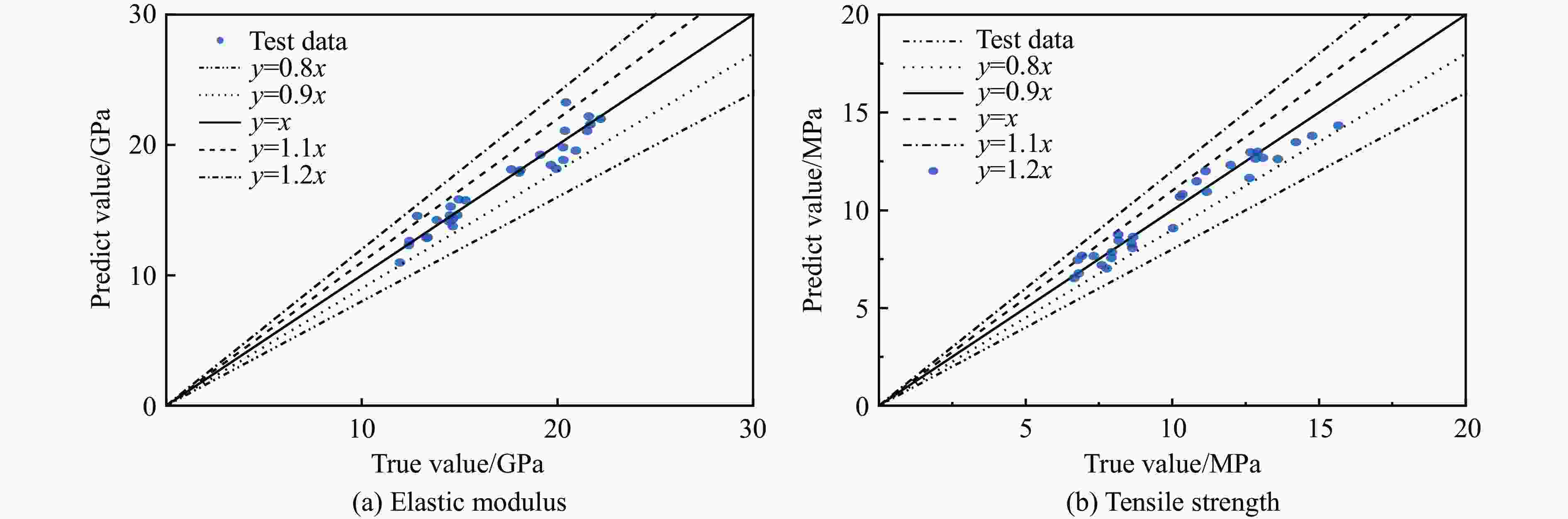
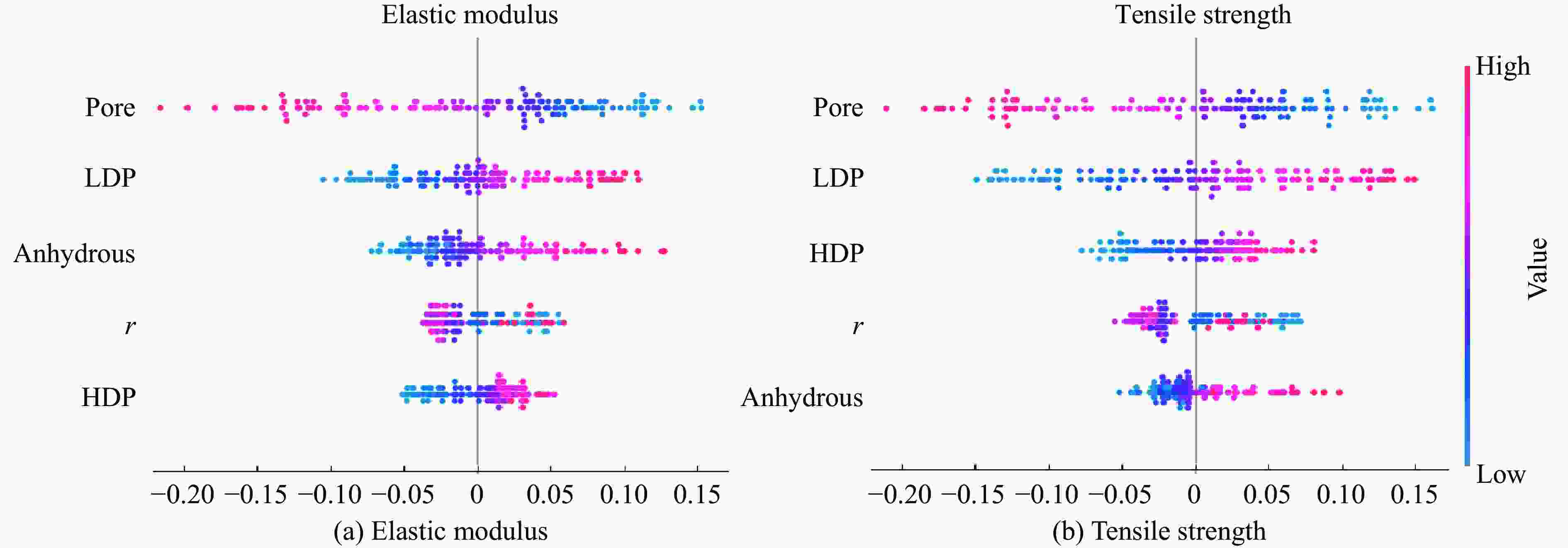
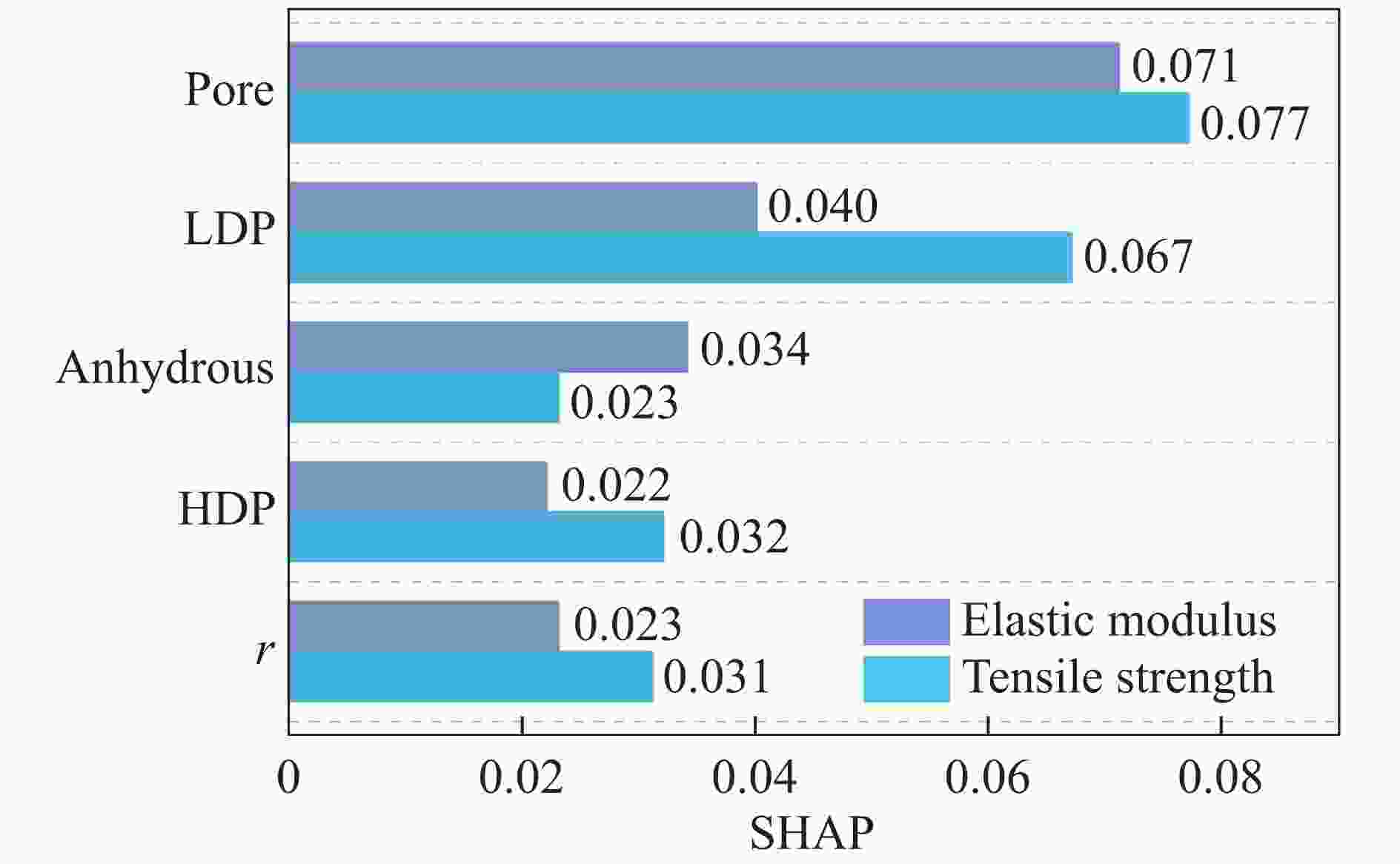
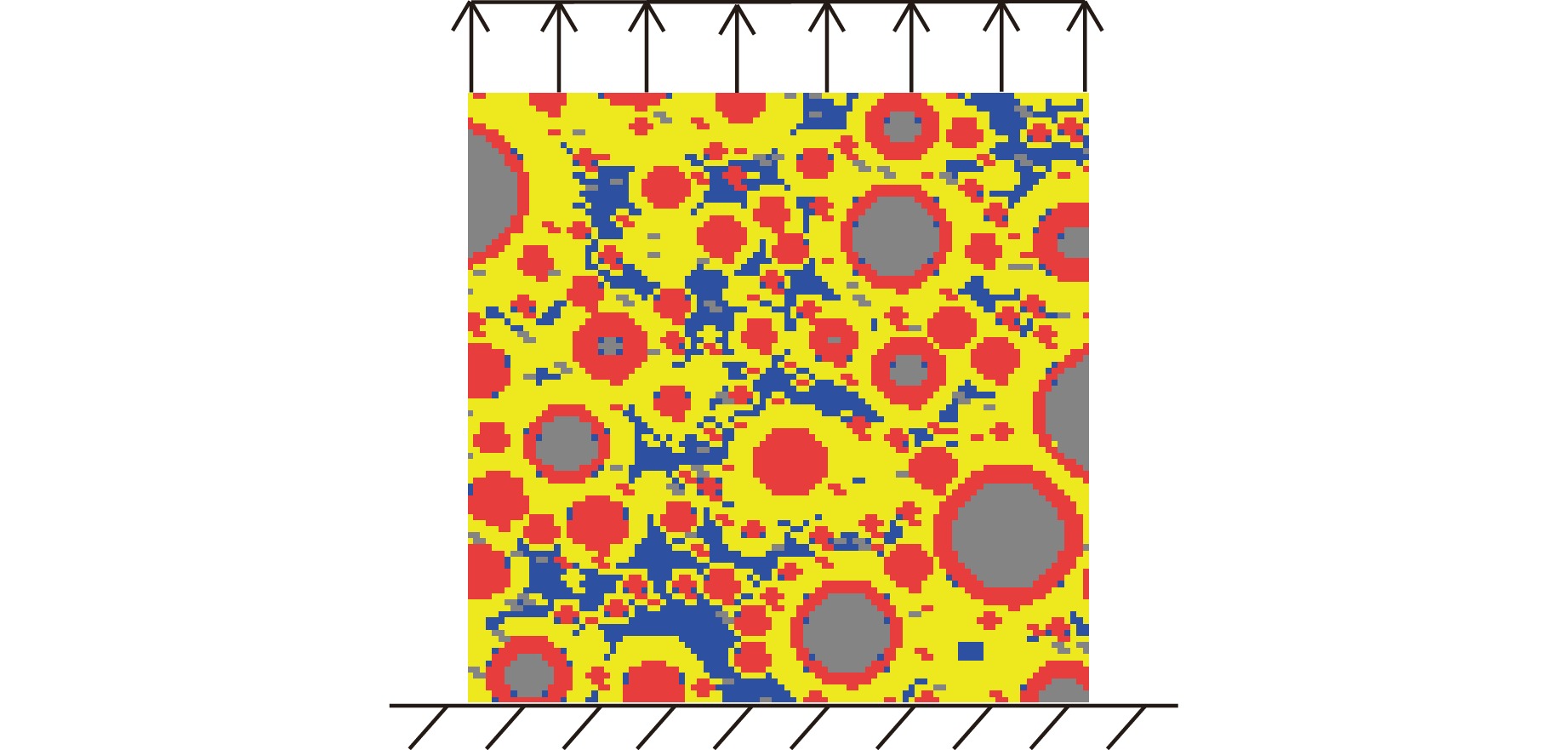
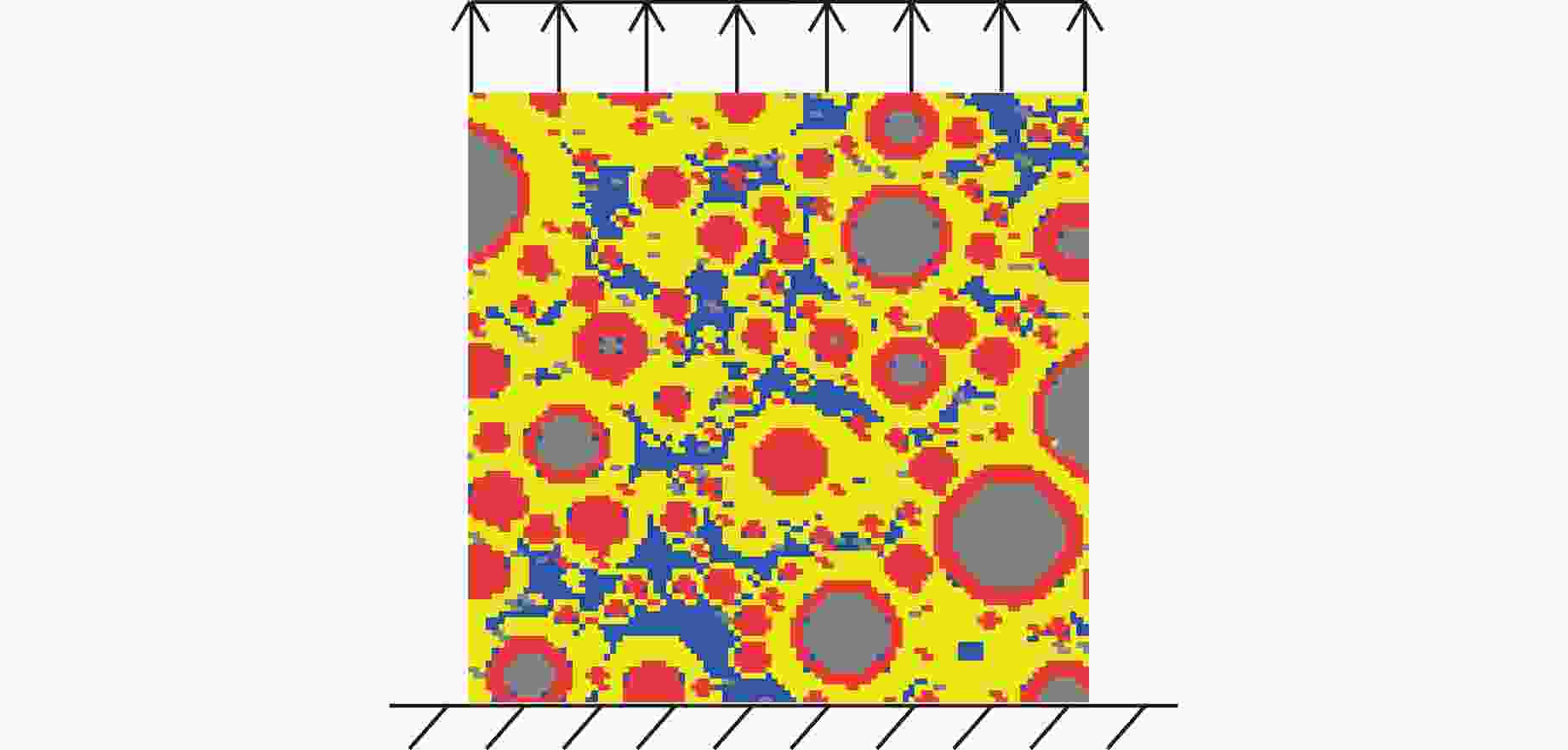
摘要: 为实现材料性能优化并保障工程结构安全,需要研究具有复杂结构的水泥水化模型的力学性能。为此,考察了水灰比及各相体积分数对水泥浆体等效力学性能的影响,提出了一种基于数据驱动的模型,用于预测水化水泥结构的力学性能。通过HYMOSTRUC 3D软件生成波特兰硬化水泥浆体三维结构切片,基于Python编写的批处理程序,将切片批量转换为ABAQUS模型。通过拉伸仿真模拟,得到结构的等效弹性性能和等效强度,运用数据驱动方法建立反向传播预测模型。模型的超参数优化采用K折交叉验证方法,以提高模型的泛化能力。最终训练得到的神经网络模型能够准确预测水泥水化结构的力学性能,显著降低传统分析方法在材料微观尺度研究中的复杂性。研究结果为水泥基材料的性能预测提供了一种高效且可靠的解决方案。Abstract: To optimize material performance and ensure the safety of engineering structures, it is essential to investigate the mechanical properties of cement hydration models with complex structures. This study aims to investigate the influence of the water-to-cement ratio and phase volume fractions on the equivalent mechanical properties of cement paste, particularly focusing on how these parameters influence the behavior of the material. A data-driven model is proposed to predict the mechanical performance of hydrated cement structures. Three-dimensional structural slices of Portland hydrated cement paste were created by utilizing the HYMOSTRUC 3D software. Subsequently, an automated batch-processing script coded in Python was applied to transform these slices into ABAQUS models. Tensile simulations were performed to determine the equivalent elastic modulus and equivalent strength of the structures. Based on the simulation results, a backpropagation prediction model was developed using a data-driven approach. Hyperparameter optimization of the model was performed using K-fold cross-validation to improve its generalization capability. Consequently, the trained neural network model demonstrates high accuracy in predicting the mechanical properties of hydrated cement structures. This approach not only ensures reliable predictions but also significantly reduces the complexity associated with traditional microscale material analysis methods. Overall, this study offers an efficient and robust solution for performance prediction of cement-based materials.
-
Key words:
- hydrated cement paste /
- finite element method /
- neural network /
- data-driven approach /
- uniaxial tension
-
表 1 水泥的化学组分(质量分数)
Table 1. Each chemical component in cement (mass fraction)
% CaO SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 SO3 MgO Others 65.24 21.12 5.34 4.63 1.58 1.25 0.84 表 2 不同水灰比HCP中各组分的平均体积分数
Table 2. Average volume fraction of each component for HCP with different water-to-cement ratios
r Volume fraction/% LDP HDP Pore Anhydrous 0.375 49.8439 24.4324 10.9256 14.7981 0.400 48.6137 23.9870 12.9135 14.4858 0.425 48.0042 23.9356 14.7209 13.3585 0.450 46.8344 23.4919 17.1533 12.5203 0.475 45.5721 23.3070 19.8090 11.3119 0.500 44.9101 23.1363 21.1294 10.8241 表 3 HCP各成分的力学参数
Table 3. Mechanical parameters of each component in HCP
Component Young’s modulus/GPa Tensile strength/MPa Poisson’s ratio HDP 31.6 92 0.2 LDP 25.2 66 0.2 Anhydrous 99.2 683 0.2 Pore 1×10−6 0 -
[1] WU X G, ZHENG S Y, FENG Z B, et al. Prediction of the frost resistance of high-performance concrete based on RF-REF: a hybrid prediction approach [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 333: 127132. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127132 [2] GUO F Q, ZHANG Z H, YANG Z J. A continuous hydration model for cement paste with realistic CT image-based particles and simulation of microstructural evolution [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2024, 184: 107607. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2024.107607 [3] NGUYEN-TUAN L, KLEINER F, RÖBLER C, et al. Numerical simulation of model cement hydration using level set based method [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2024, 186: 107674. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2024.107674 [4] BENTZ D P. Three-dimensional computer simulation of Portland cement hydration and microstructure development [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1997, 80(1): 3–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1997.tb02785.x [5] VAN BREUGEL K. Numerical simulation of hydration and microstructural development in hardening cement-based materials (Ⅰ) theory [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1995, 25(2): 319–331. doi: 10.1016/0008-8846(95)00017-8 [6] 曹秀丽, 刘元寿, 张红飞, 等. 水泥水化计算机模拟研究进展 [J]. 材料导报, 2013, 27(1): 157–160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-023X.2013.01.032CAO X L, LIU Y S, ZHANG H F, et al. A review on computer simulation of cement hydration models [J]. Materials Review, 2013, 27(1): 157–160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-023X.2013.01.032 [7] QIAN Z W. Multiscale modeling of fracture processes in cementitious materials [D]. Delft: Delft University of Technology, 2012. [8] YU P, REN Z Y, CHEN Z, et al. A multiscale finite element model for prediction of tensile strength of concrete [J]. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 2023, 215: 103877. doi: 10.1016/j.finel.2022.103877 [9] SHERZER G, GAO P, SCHLANGEN E, et al. Upscaling cement paste microstructure to obtain the fracture, shear, and elastic concrete mechanical LDPM parameters [J]. Materials, 2017, 10(3): 242. doi: 10.3390/ma10030242 [10] QIAN Z W, SCHLANGEN E, YE G, et al. Modeling framework for fracture in multiscale cement-based material structures [J]. Materials, 2017, 10(6): 587. doi: 10.3390/ma10060587 [11] KAMALI-BERNARD S, BERNARD F. Effect of tensile cracking on diffusivity of mortar: 3D numerical modelling [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2009, 47(1): 178–185. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2009.07.005 [12] HLOBIL M, KUMPOVÁ I, HLOBILOVÁ A. Surface area and size distribution of cement particles in hydrating paste as indicators for the conceptualization of a cement paste representative volume element [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2022, 134: 104798. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2022.104798 [13] PUTTBACH C, PRINZ G S, MURRAY C D. Estimation of cement paste stiffness and UHPC elastic modulus through measured phase-property upscaling [J]. Cement, 2024, 17: 100110. doi: 10.1016/j.cement.2024.100110 [14] LE V T, BUI H H, NGUYEN G D, et al. Meso to macro connections to capture fatigue damage in cemented materials [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2023, 176: 107890. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2023.107890 [15] 巨凯萱, 赵婷婷, 刘嘉英, 等. 级配对颗粒材料力学特性影响的卷积神经网络分析 [J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2025, 55(1): 115–132. doi: 10.1360/SST-2024-0187JU K X, ZHAO T T, LIU J Y, et al. Convolution neural network analysis of the effect of gradation on the mechanical properties of granular materials [J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2025, 55(1): 115–132. doi: 10.1360/SST-2024-0187 [16] MURR J, ALAM S Y, GRONDIN F. Micromechanics and microstructure based machine learning approach: unveiling the role of porosity and hydrated phases on the tensile behaviour of cement pastes [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2024, 312: 110613. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2024.110613 [17] KIM J, LEE D, UBYSZ A. Comparative analysis of cement grade and cement strength as input features for machine learning-based concrete strength prediction [J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2024, 21: e03557. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03557 [18] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土结构设计规范: GB/T 5001—2010 [S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2011.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Code for design of concrete structures: GB/T 5001—2010 [S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2011. [19] ZHANG H Z, ŠAVIJA B, FIGUEIREDO S C, et al. Microscale testing and modelling of cement paste as basis for multi-scale modelling [J]. Materials, 2016, 9(11): 907. doi: 10.3390/ma9110907 [20] 卢振宇, 李文彬, 姚文进, 等. 不同应变率下两种岩石的压缩破碎特征试验研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2021, 35(1): 014101. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200605LU Z Y, LI W B, YAO W J, et al. Experimental study on compression and fracture characteristics of two kinds of rocks under different strain rates [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2021, 35(1): 014101. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200605 [21] 马昊, 陈美多, 袁良柱, 等. 中等应变率下纸蜂窝结构的力学性能研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2024, 38(4): 044104. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240701MA H, CHEN M D, YUAN L Z, et al. Study on mechanical properties of paper honeycomb structure at medium strain rates [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2024, 38(4): 044104. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240701 [22] 洛绒邓珠, 刘潇如, 杨佳, 等. 不同应变率下高强钢的拉伸行为及力学性能分析 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2024, 38(3): 030104. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240702LUORONG D Z, LIU X R, YANG J, et al. Tensile behavior and mechanical performance analysis of high-strength steels at varying strain rates [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2024, 38(3): 030104. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240702 [23] 张春春, 王艳超, 黄争鸣. 横观各向同性基体复合材料的等效弹性常数 [J]. 应用数学和力学, 2018, 39(7): 750–765. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.380267ZHANG C C, WANG Y C, HUANG Z M. Effective elastic properties of transversely isotropic matrix based composites [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2018, 39(7): 750–765. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.380267 [24] 朱俊, 桂林, 李果, 等. 基于结构参数的平纹机织复合材料等效弹性性能预测 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(2): 804–813. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220424.004ZHU J, GUI L, LI G, et al. Prediction of the effective elastic properties for plain woven fabric composite based on the structural parameters [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(2): 804–813. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220424.004 [25] 顾春苗, 刘冠琳, 周风华, 等. 人造结石的静动态巴西劈裂试验研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2024, 38(5): 054105. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240738GU C M, LIU G L, ZHOU F H, et al. Study on static and dynamic Brazilian splitting test of artificial stones [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2024, 38(5): 054105. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240738 -






 下载:
下载: