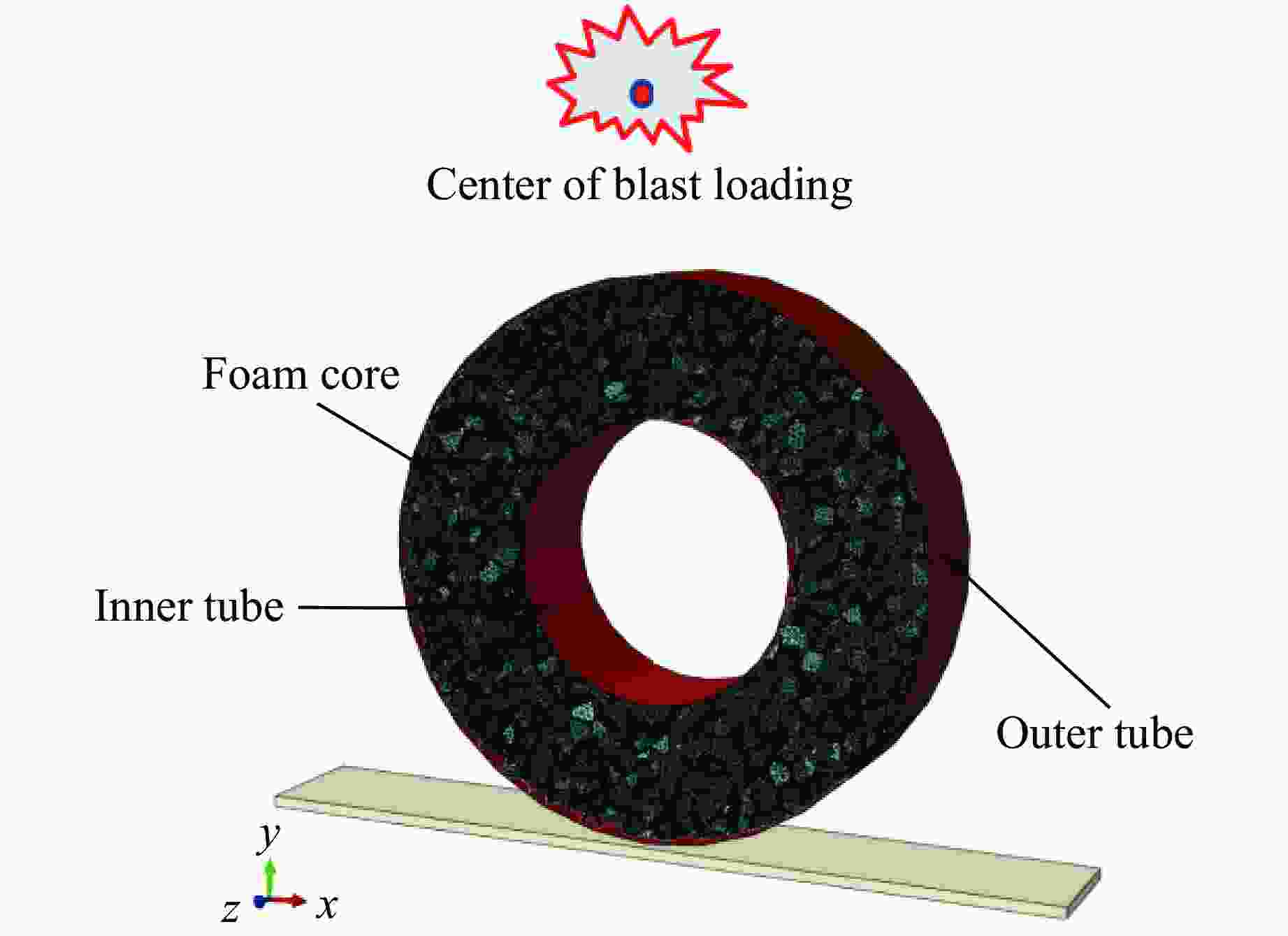
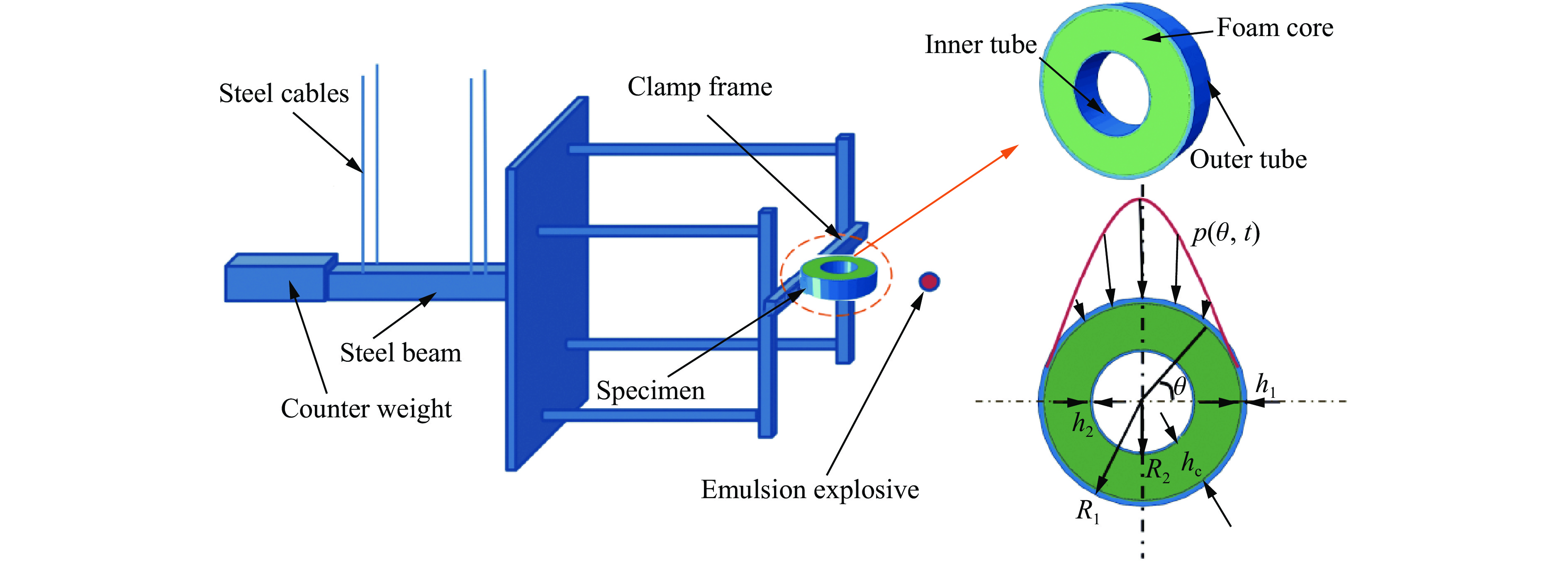
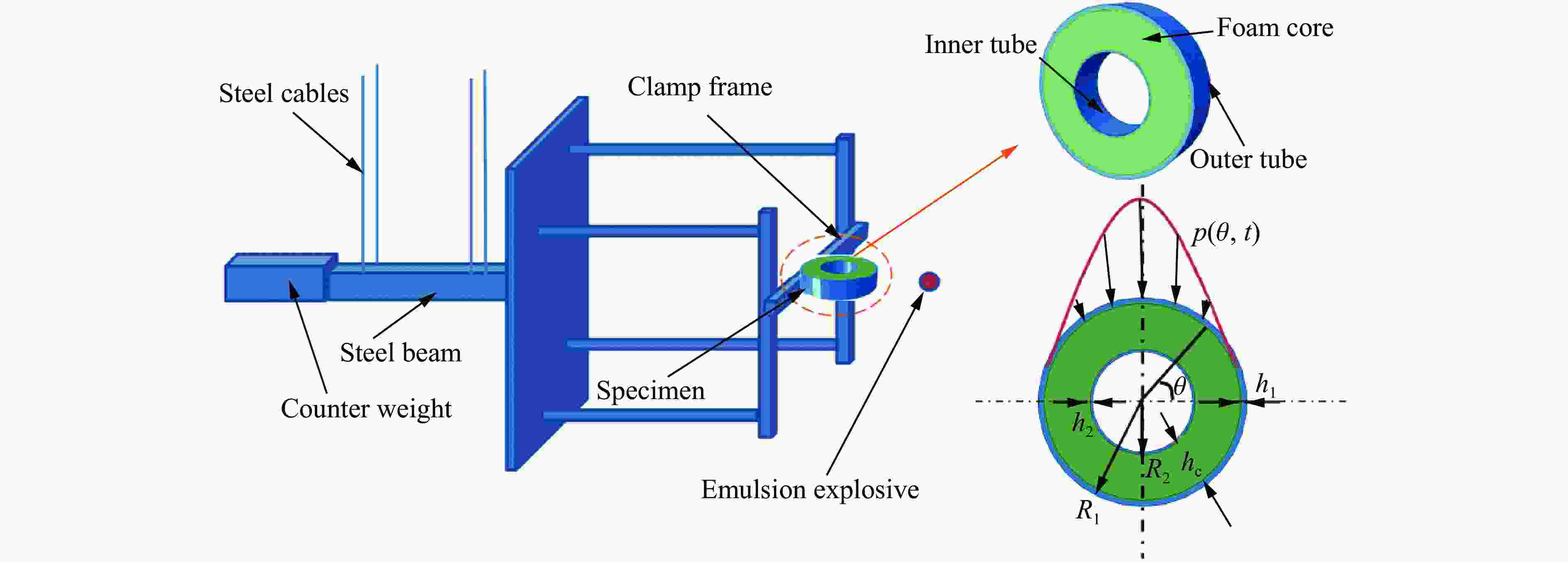
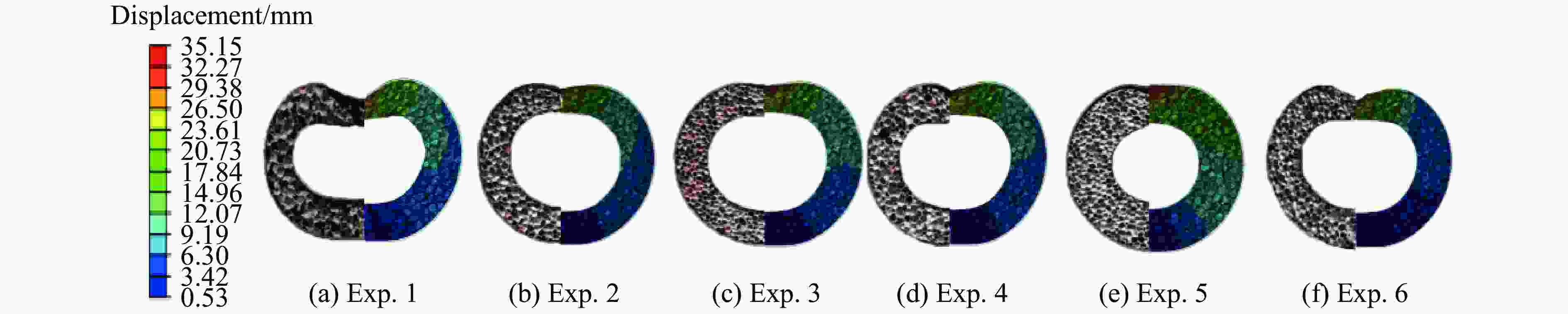Response Characteristics and Deformation Mechanism of Sandwich Tubes under Lateral Explosive Loads
-
摘要: 结合实验与数值模拟,系统地分析了泡沫铝夹芯管在侧向爆炸载荷下的动态响应和能量吸收性能。通过弹道摆锤系统,开展了一系列侧向爆炸实验,分析了结构的几何参数、泡沫铝的相对密度以及炸药质量对泡沫铝夹芯管变形模态和抗爆性能的影响,获得了泡沫铝夹芯管在爆炸载荷作用下的最终变形模态和挠度。基于实验结果,通过数值模拟进一步比较了泡沫铝夹芯管和空心圆管夹芯管的抗爆性能,对空心圆管夹芯管在梯度与非梯度设计下的表现进行了对比分析。结果显示:在相同条件下,空心圆管夹芯管的最终变形均大于泡沫铝夹芯管,但两者之间的差异并不显著。在梯度空心圆管夹芯管结构中,最外层壁厚最大、中间层最薄的梯度配置在提升抗爆性能方面具有最佳的效果。此外,梯度空心圆管夹芯管的抗爆性能明显优于非梯度结构。Abstract: The dynamic response and energy absorption performance of foam aluminum sandwich tubes under lateral explosive loads were systematically investigated using a combination of experimental research and numerical simulation. A series of lateral explosion experiments were conducted using a ballistic pendulum system to analyze the effects of structural geometric parameters, foam aluminum density, and the explosive mass on the deformation mode and blast resistance performance. Based on the experimental results, numerical simulations were performed to further compare the blast resistance performance of foam aluminum sandwich tubes and circular tube core sandwich tubes, comparing gradient and non-gradient designs of circular tube core sandwich tubes. The results show that, the final deformation of circular tube core sandwich tubes is greater than that of foam aluminum sandwich tubes, although the difference is not significant. Among the gradient circular tube core sandwich tubes, the configuration with the largest outer wall thickness and the thinnest middle layer exhibits the best improvement in blast resistance performance. Furthermore, the blast resistance performance of gradient circular tube core sandwich tubes is significantly superior to that of non-gradient structures.
-
Key words:
- explosive loads /
- sandwich tubes /
- deformation modes /
- energy absorption /
- blast resistance performance
-
表 1 材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters
Material Density/(kg·m−3) Young’s modulus/GPa Poisson’s ratio Yield stress/MPa Tangent modulus/MPa Stainless steel 7830 193 0.25 205 787.5 Foam core/
circular tube core2700 70 0.30 80 700.0 表 2 泡沫铝夹芯管的几何参数和实验结果
Table 2. Geometric parameters and experimental results for the aluminum foam sandwich tubes
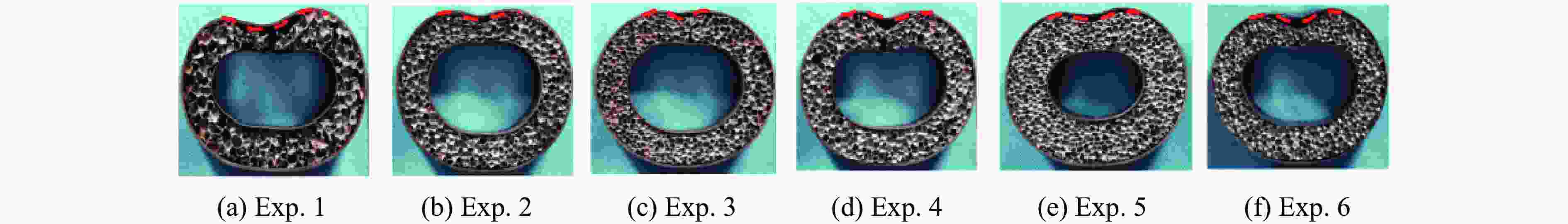
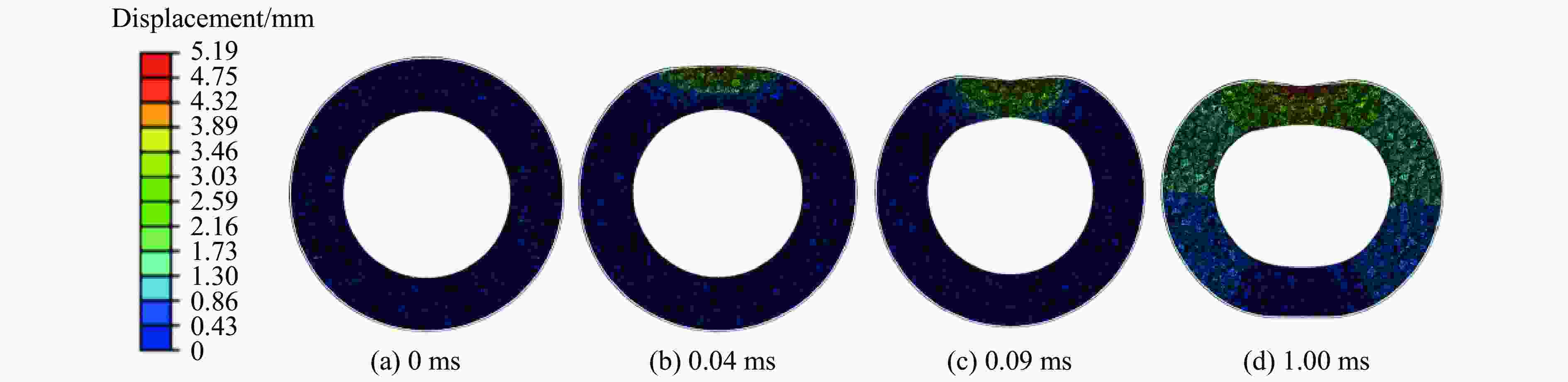
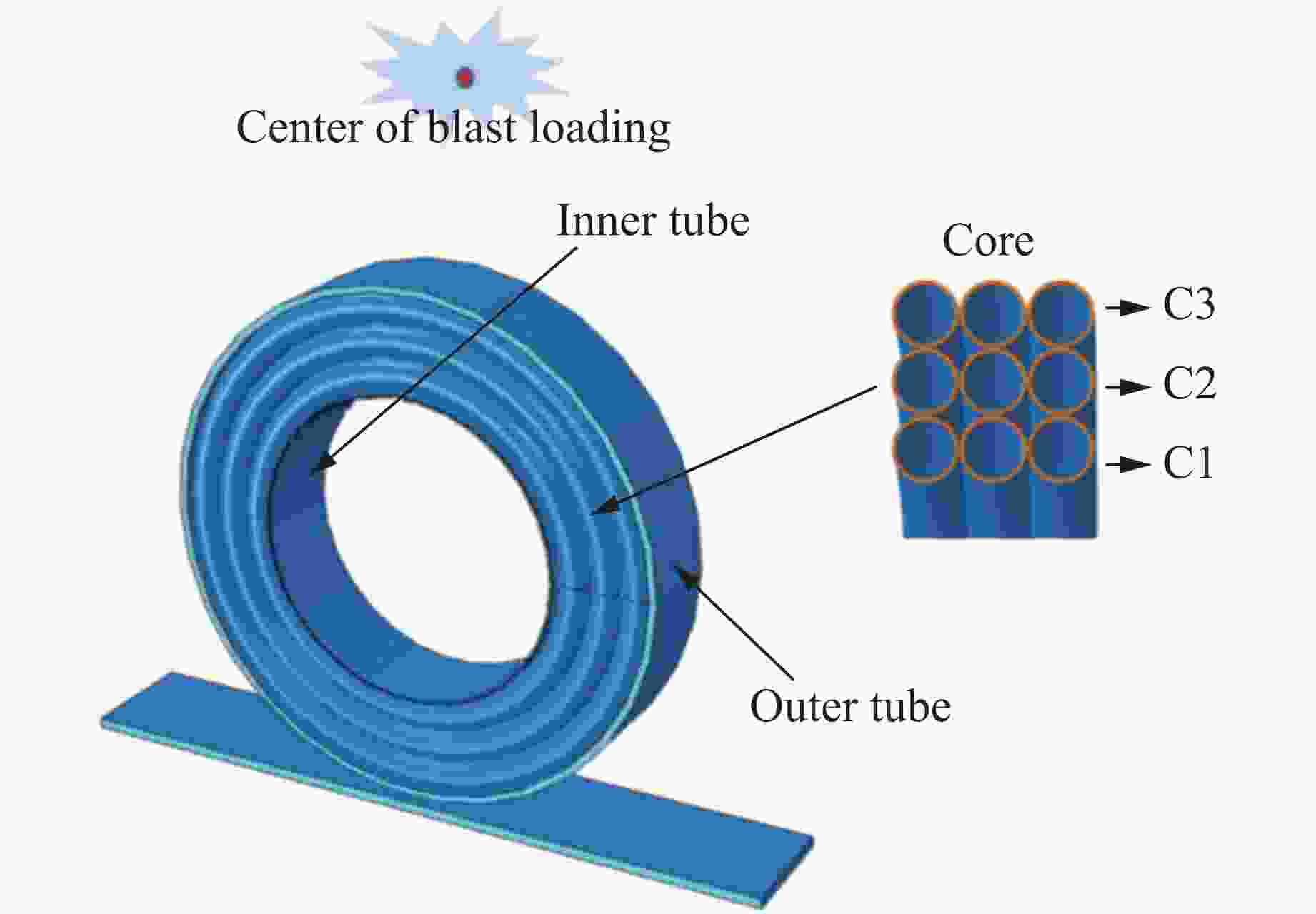
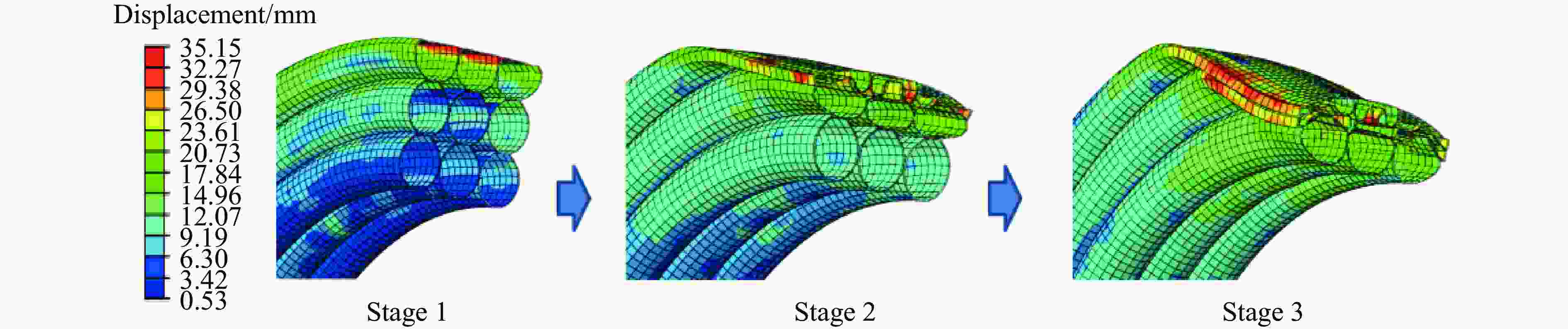
Exp. No. R1/mm h1/mm R2/mm h2/mm w/g ρ U1/mm U2/mm 1 50.5 1.5 31.5 0.6 60 0.10 37.7 28.4 2 50.5 1.5 31.5 1.2 50 0.15 24.1 14.6 3 50.5 1.5 31.5 0.6 50 0.15 25.0 14.2 4 50.5 1.5 31.5 0.6 60 0.15 33.9 23.1 5 50.5 1.5 25.5 0.6 50 0.15 23.4 12.9 6 50.5 1.0 31.5 0.6 50 0.15 33.6 21.8 表 3 实验冲量与理论冲量的对比
Table 3. Comparison of the experimental and theoretical impulse
Exp. No. IE/(N·s) I/(N·s) Error/% Exp. No. IE/(N·s) I/(N·s) Error/% 1 6.08 6.17 1.48 4 5.20 6.17 18.70 2 5.23 5.68 8.60 5 5.24 5.68 8.40 3 5.19 5.68 9.40 6 5.68 表 4 中点挠度的误差
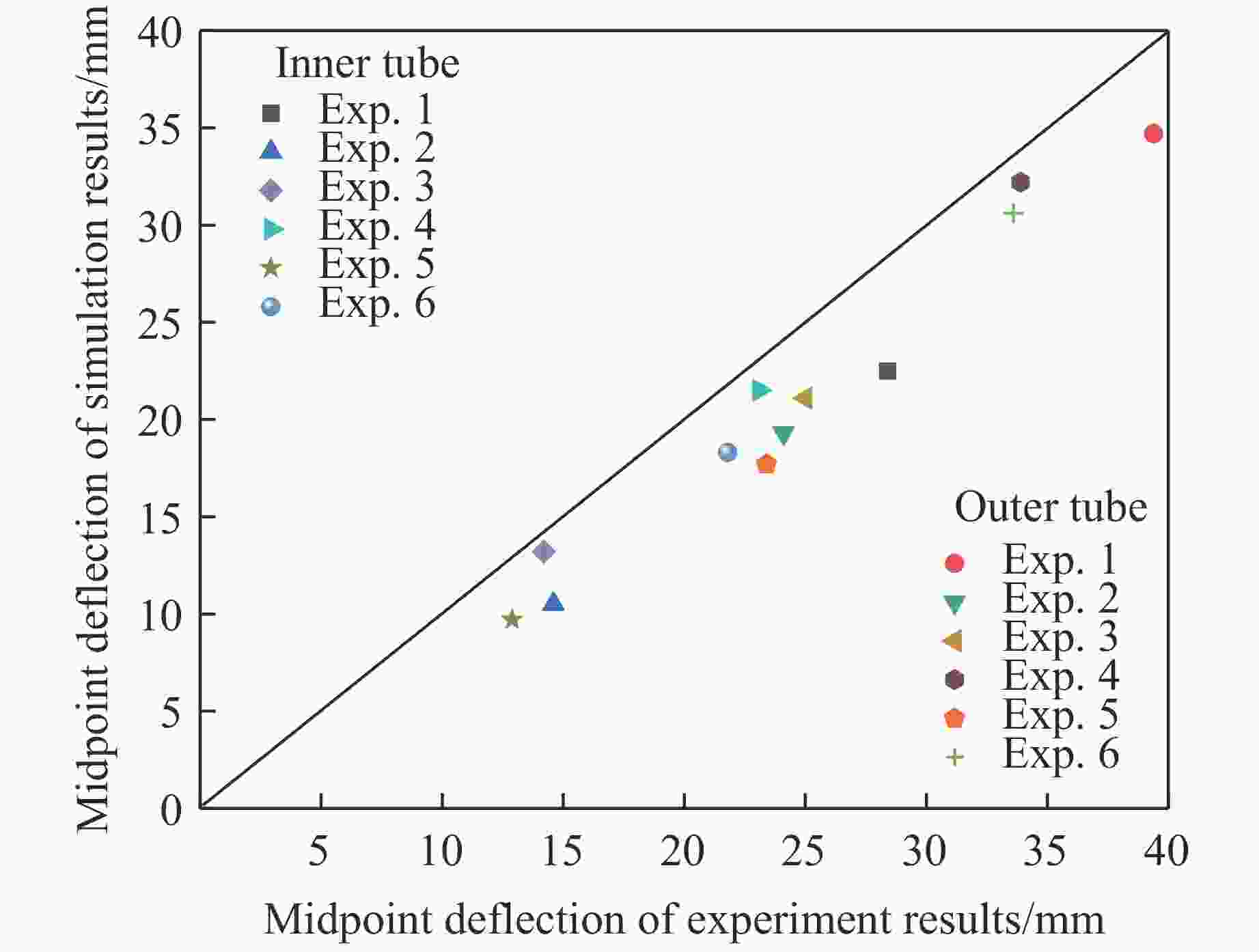
Table 4. Errors of the midpoint deflection
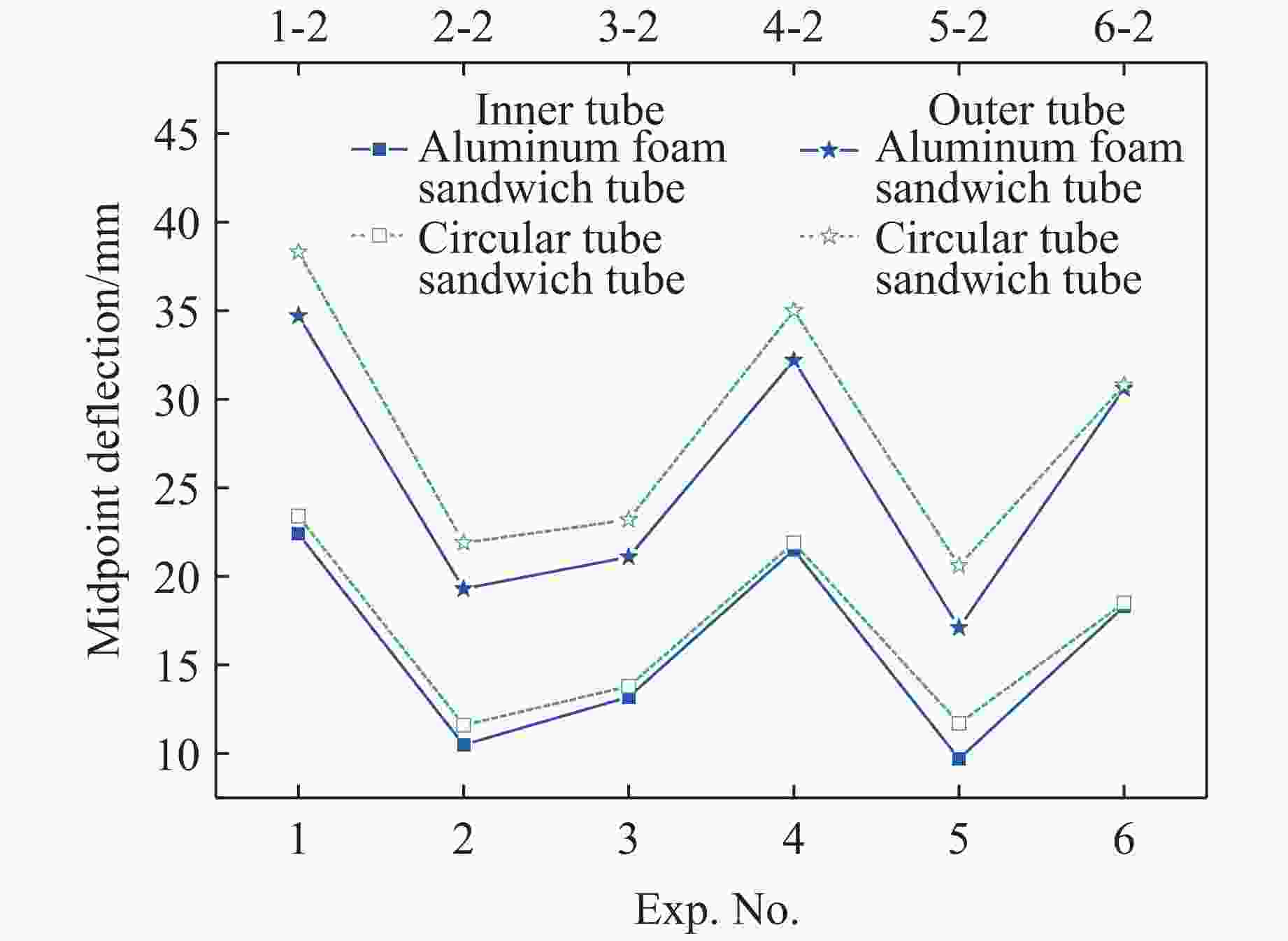
Exp. No. U1 U2 Exp./mm Sim./mm Error/% Exp./mm Sim./mm Error/% 1 39.4 34.7 11.9 28.4 22.5 20.8 2 24.1 19.3 19.9 14.6 10.5 28.1 3 25.0 21.1 15.6 14.2 13.2 7.0 4 33.9 32.2 5.0 23.1 21.5 6.9 5 23.4 17.7 24.4 12.9 9.7 24.8 6 33.6 30.6 8.9 21.8 18.3 16.1 表 5 空心圆管壁厚
Table 5. Wall thickness of circular tubes
Exp. No. hct/mm Exp. No. hct/mm 1-2 0.3 4-2 0.4 2-2 0.4 5-2 0.4 3-2 0.4 6-2 0.4 表 6 空心圆管芯层排列组合
Table 6. Core arrangement groups of sandwich tubes with circular tube core
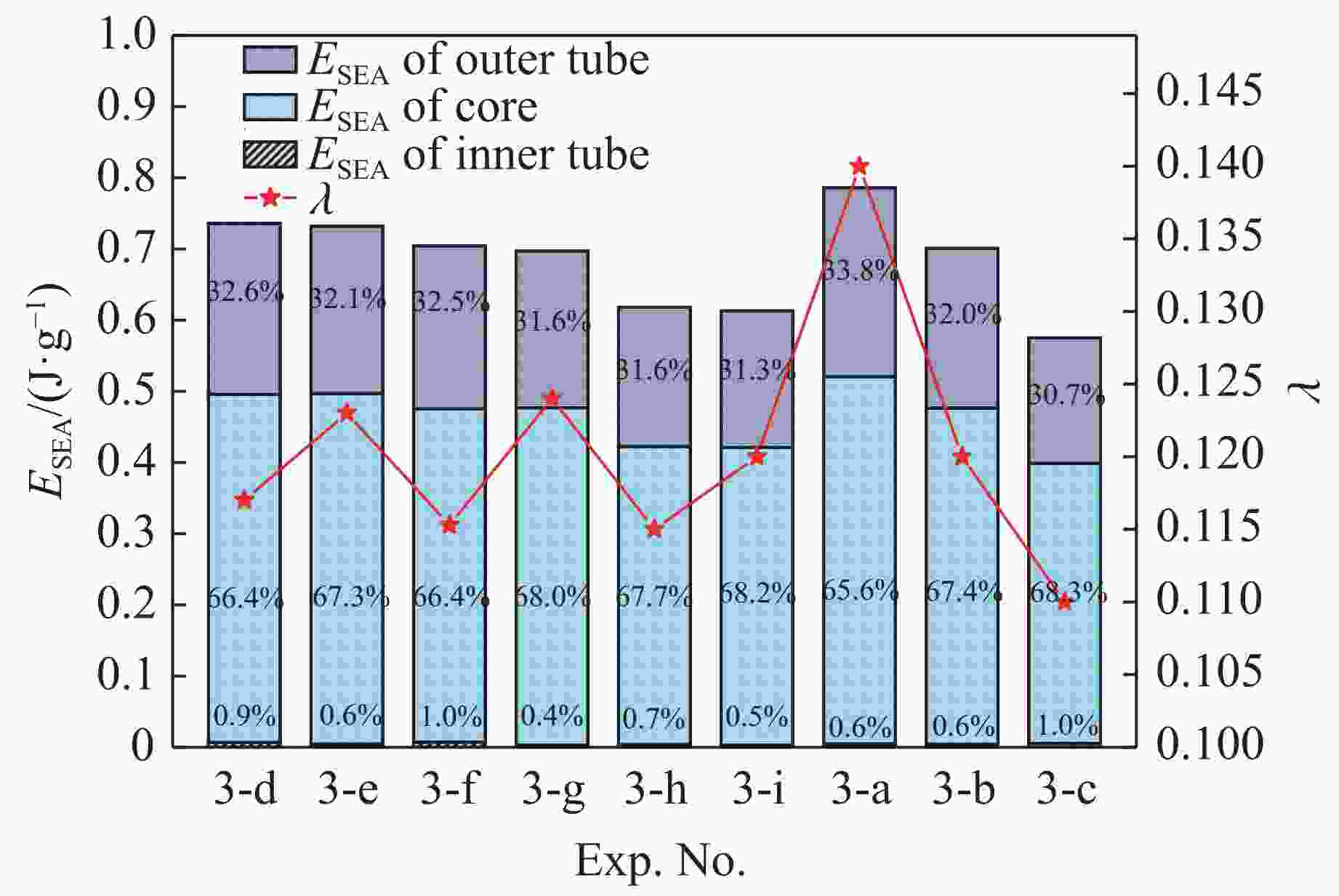
Group hC3/mm hC2/mm hC1/mm Group hC3/mm hC2/mm hC1/mm a 0.4 0.4 0.4 f 0.5 0.4 0.6 b 0.5 0.5 0.5 g 0.5 0.6 0.4 c 0.6 0.6 0.6 h 0.6 0.4 0.5 d 0.4 0.5 0.6 i 0.6 0.5 0.4 e 0.4 0.6 0.5 表 7 Exp. 3-b与Exp. 3-f的抗爆性能对比
Table 7. Simulation results for Exp. 3-b and Exp. 3-f
Exp. No. $ m^* $/g ESEA/(J·g−1) no/% ni/% nc/% λ 3-b 178 0.7 32.0 0.6 67.4 0.12 3-f 178 0.7 32.5 1.0 66.4 0.11 -
[1] BIRMAN V, KARDOMATEAS G A. Review of current trends in research and applications of sandwich structures [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2018, 142: 221–240. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.01.027 [2] GARGANO A, DAS R, MOURITZ A P. Comparative experimental study into the explosive blast response of sandwich structures used in naval ships [J]. Composites Communications, 2022, 30: 101072. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2022.101072 [3] LU W K, ZHANG J Y. Mechanical response of aluminum foam sandwich structure under impact load [J]. Materials Research Express, 2022, 9(1): 016515. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ac493e [4] SONG J F, XU S C, XU L H, et al. Experimental study on the crashworthiness of bio-inspired aluminum foam-filled tubes under axial compression loading [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2020, 155: 106937. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.106937 [5] NIKNEJAD A, OROJLOO P H. A novel nested system of tubes with special cross-section as the energy absorber [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2016, 100: 113–123. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2015.12.009 [6] XUE Z Y, HUTCHINSON J W. A comparative study of impulse-resistant metal sandwich plates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2004, 30(10): 1283–1305. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2003.08.007 [7] SEITZBERGER M, RAMMERSTORFER F G, GRADINGER R, et al. Experimental studies on the quasi-static axial crushing of steel columns filled with aluminium foam [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2000, 37(30): 4125–4147. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7683(99)00136-5 [8] HALL I W, GUDEN M, CLAAR T D. Transverse and longitudinal crushing of aluminum-foam filled tubes [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 46(7): 513–518. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6462(02)00024-6 [9] FAN Z H, SHEN J H, LU G X. Investigation of lateral crushing of sandwich tubes [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 14: 442–449. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.07.055 [10] SHEN J H, LU G X, ZHAO L M, et al. Short sandwich tubes subjected to internal explosive loading [J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 55: 56–65. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2011.12.005 [11] JING L, WANG Z H, ZHAO L M. Dynamic response of cylindrical sandwich shells with metallic foam cores under blast loading: numerical simulations [J]. Composite Structures, 2013, 99: 213–223. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.12.013 [12] JING L, WANG Z H, SHIM V P W, et al. An experimental study of the dynamic response of cylindrical sandwich shells with metallic foam cores subjected to blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 71: 60–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.03.009 [13] LIU Z F, ZHANG T H, LI S Q, et al. Experiment and numerical simulation on the dynamic response of foam-filled tubes under lateral blast loading [J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2021, 34(6): 937–953. doi: 10.1007/s10338-021-00285-1 [14] NIKNEJAD A, ELAHI S A, LIAGHAT G H. Experimental investigation on the lateral compression in the foam-filled circular tubes [J]. Materials & Design (1980–2015), 2012, 36: 24–34. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2011.10.047 [15] ZHANG B Y, WANG L, ZHANG J, et al. Deformation and energy absorption properties of cenosphere/aluminum syntactic foam-filled circular tubes under lateral quasi-static compression [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2021, 192: 106126. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.106126 [16] FAN Z H, SHEN J H, LU G X, et al. Dynamic lateral crushing of empty and sandwich tubes [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2013, 53: 3–16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2012.09.006 [17] BAROUTAJI A, GILCHRIST M D, SMYTH D, et al. Analysis and optimization of sandwich tubes energy absorbers under lateral loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 82: 74–88. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.01.005 [18] 鲁文科. 泡沫铝夹芯结构动态力学响应的数值模拟研究[D]. 湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2022.LU W K. Numerical simulation of dynamic mechanical response of aluminum foam sandwich structures [D]. Xiangtan: Xiangtan University, 2022. [19] YUEN S C K, NURICK G N, BRINCKMANN H B, et al. Response of cylindrical shells to lateral blast load [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2013, 4(3): 209–230. doi: 10.1260/2041-4196.4.3.209 [20] WIERZBICKI T, FATT M S H. Damage assessment of cylinders due to impact and explosive loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1993, 13(2): 215–241. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(93)90094-N [21] 刘志芳, 王军, 秦庆华. 横向冲击载荷下泡沫铝夹芯双圆管的吸能研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(11): 2259–2267. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.11.024LIU Z F, WANG J, QIN Q H. Research on energy absorption of aluminum foam-filled double circular tubes under lateral impact loadings [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2017, 38(11): 2259–2267. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.11.024 [22] LIANG M Z, ZHANG G D, LU F Y, et al. Blast resistance and design of sandwich cylinder with graded foam cores based on the Voronoi algorithm [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2017, 112: 98–106. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2016.12.016 [23] 于学会, 李婷, 王安帅, 等. 极坐标下连续密度梯度多孔金属材料设计及其夹芯管的抗爆性能研究 [J]. 固体力学学报, 2024, 45(6): 831–845. doi: 10.19636/j.cnki.cjsm42-1250/o3.2024.035YU X H, LI T, WANG A S, et al. Design of continuous-density-graded porous metal materials in polar coordinates and study on the blast resistance of sandwich tubes [J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2024, 45(6): 831–845. doi: 10.19636/j.cnki.cjsm42-1250/o3.2024.035 [24] WANG A S, YU X H, WANG H, et al. Dynamic response of sandwich tubes with continuously density-graded aluminum foam cores under internal explosion load [J]. Materials, 2022, 15(19): 6966. doi: 10.3390/ma15196966 [25] 李世强. 分层梯度多孔金属夹芯结构的冲击力学行为[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2015.LI S Q. The dynamic behavior of sandwich structure with layered graded porous metallic cores [D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2015. [26] LI Z H, ZHANG T H, TANG B, et al. Blast response and optimization of cylindrical sandwich shells with toroidal tubular cores [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2025, 196: 105157. doi: 10.1016/J.IJIMPENG.2024.105157 [27] HENRYCH J. The dynamics of explosion and its use [M]. New York: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, 1979. [28] GOEL M D, MATSAGAR V A, GUPTA A K, et al. An abridged review of blast wave parameters [J]. Defence Science Journal, 2012, 62(5): 300–306. doi: 10.14429/dsj.62.1149 -






 下载:
下载: