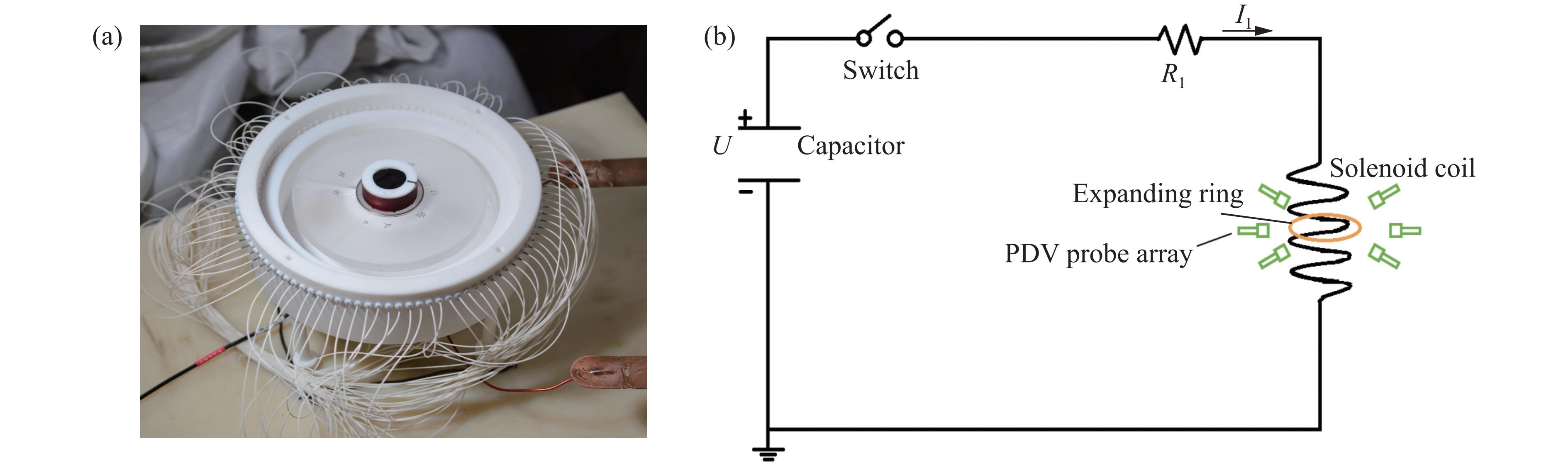
Statistical Law of Dynamic Fracture Strain Distribution of 6061 Aluminum Electromagnetic Expansion Ring
-
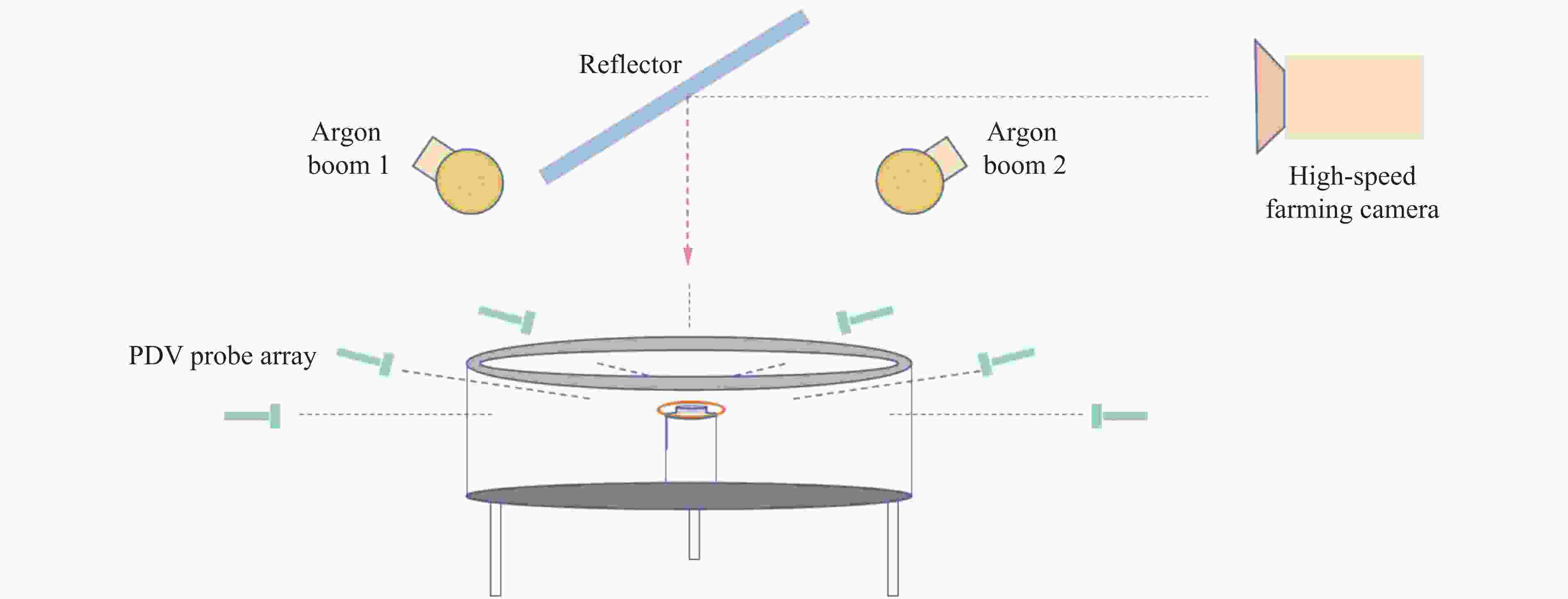
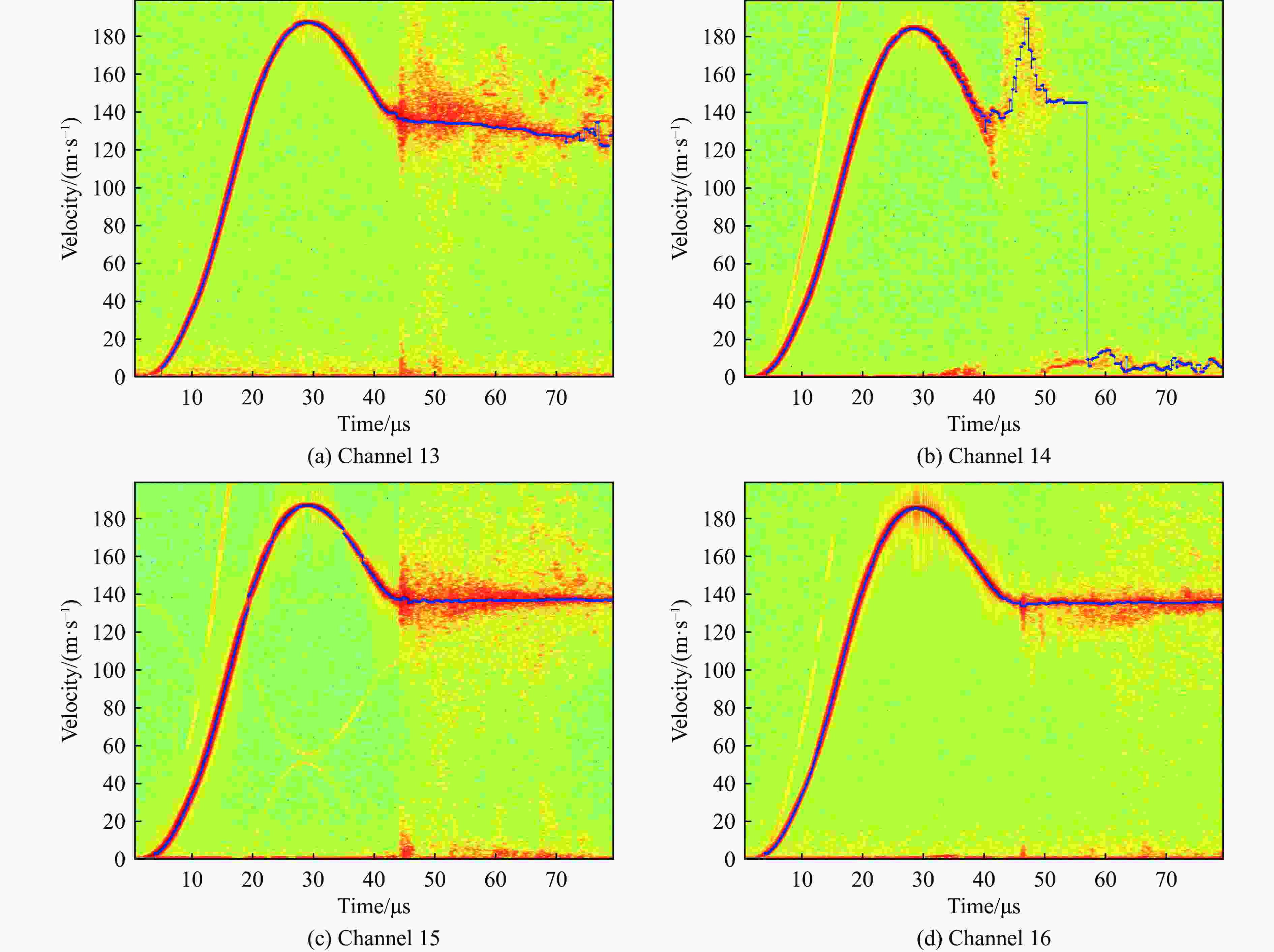
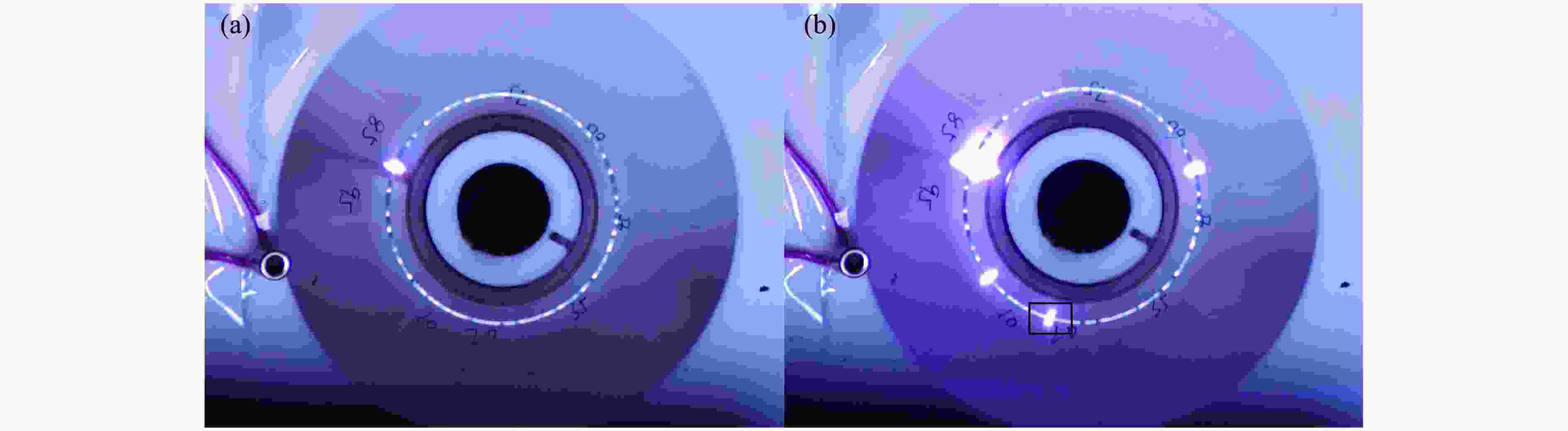
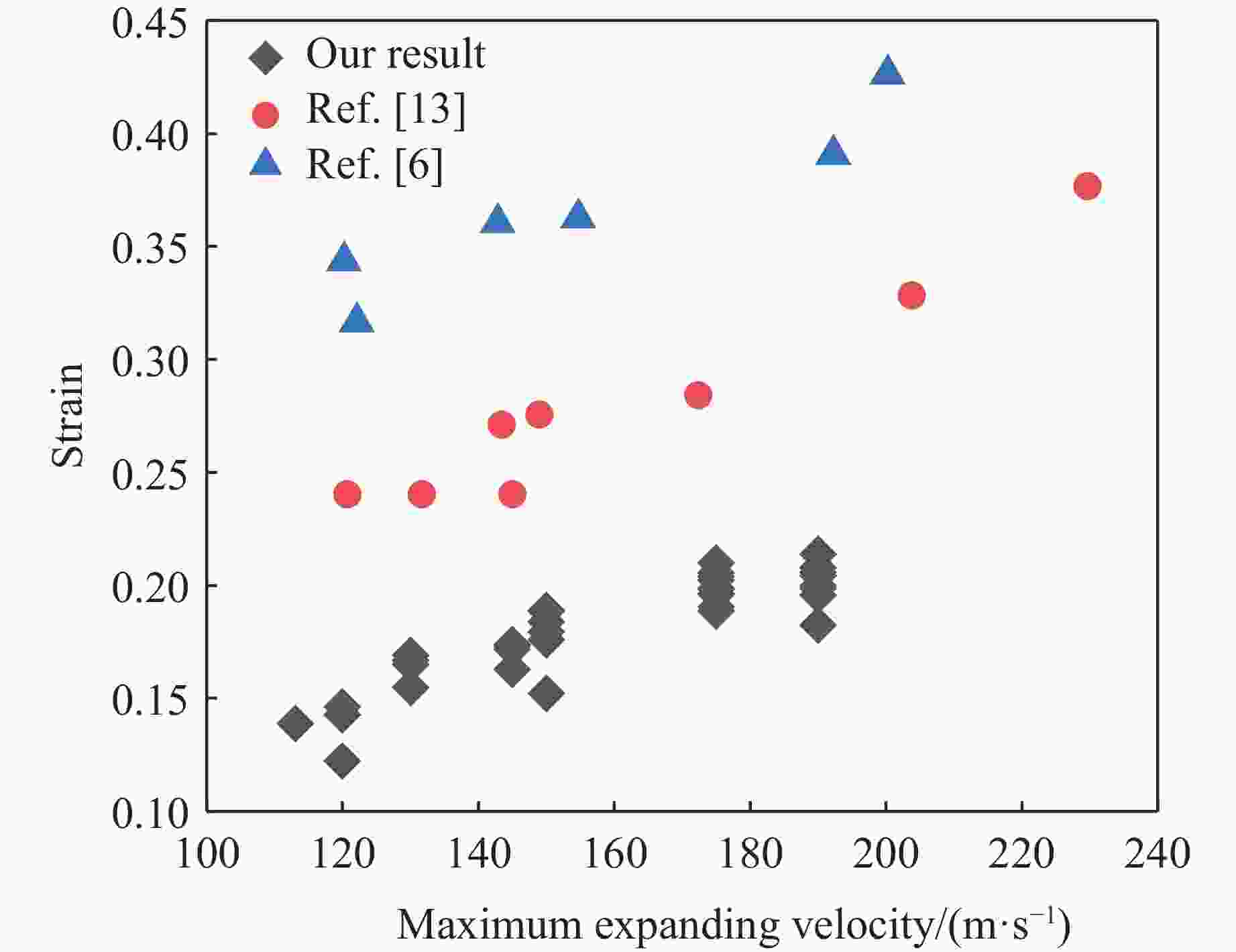
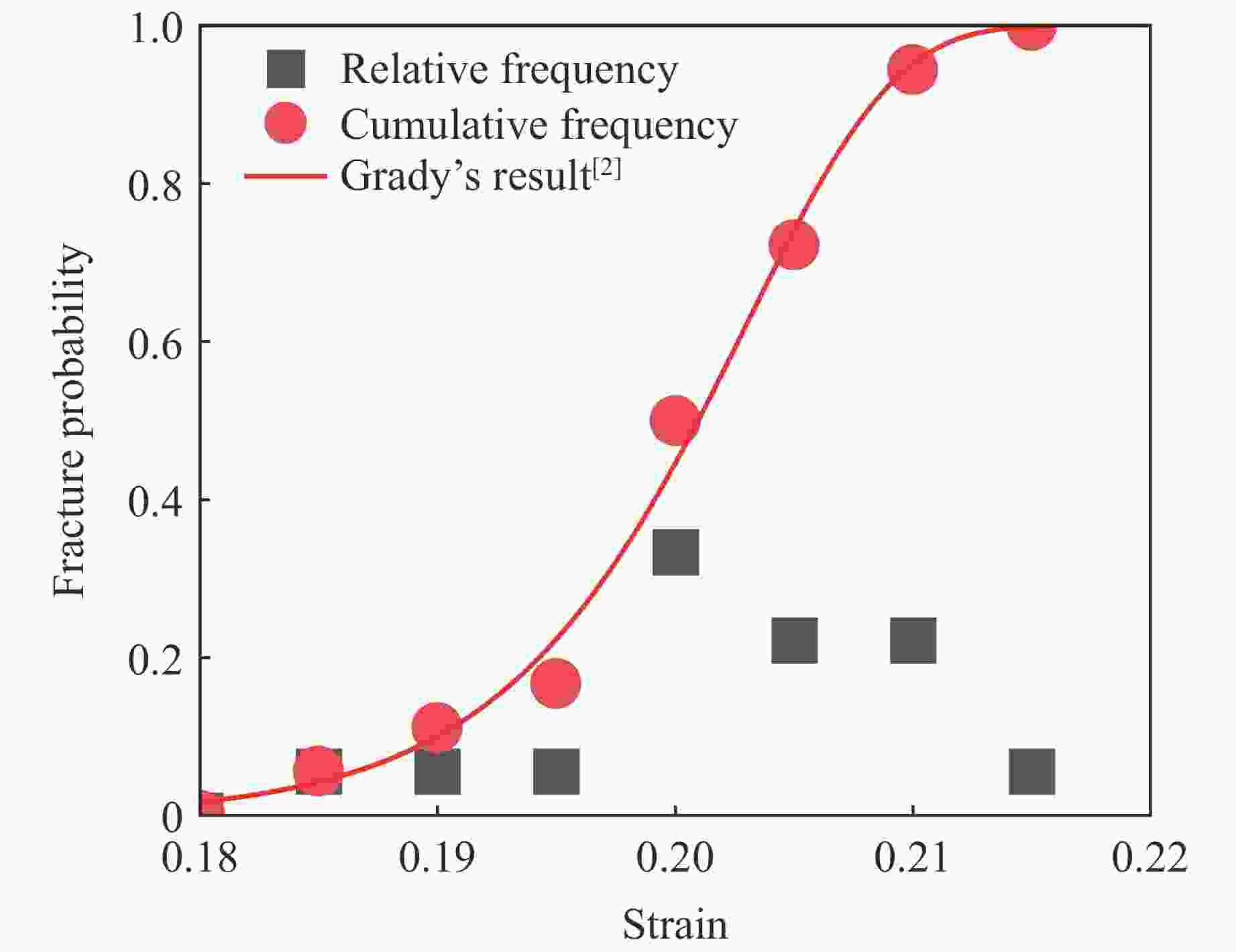
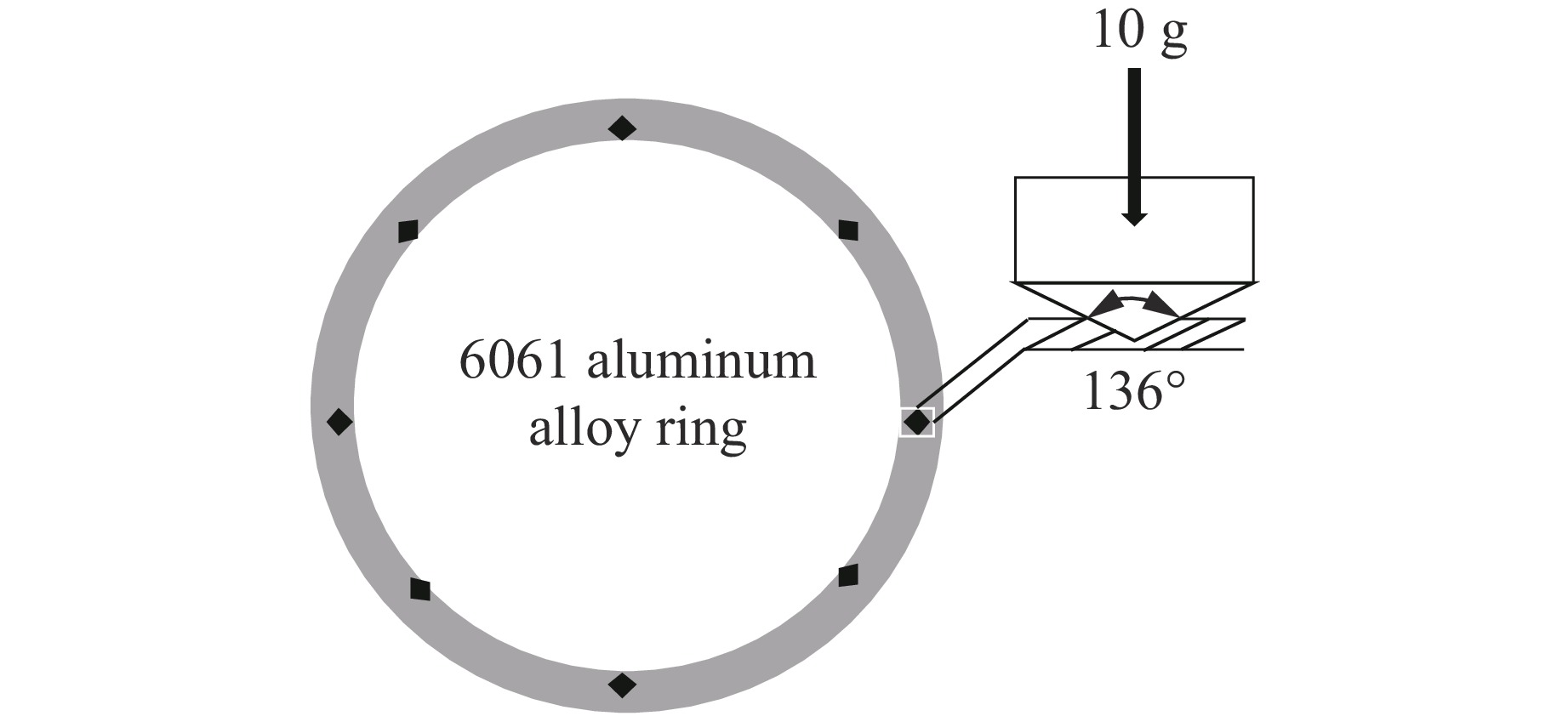
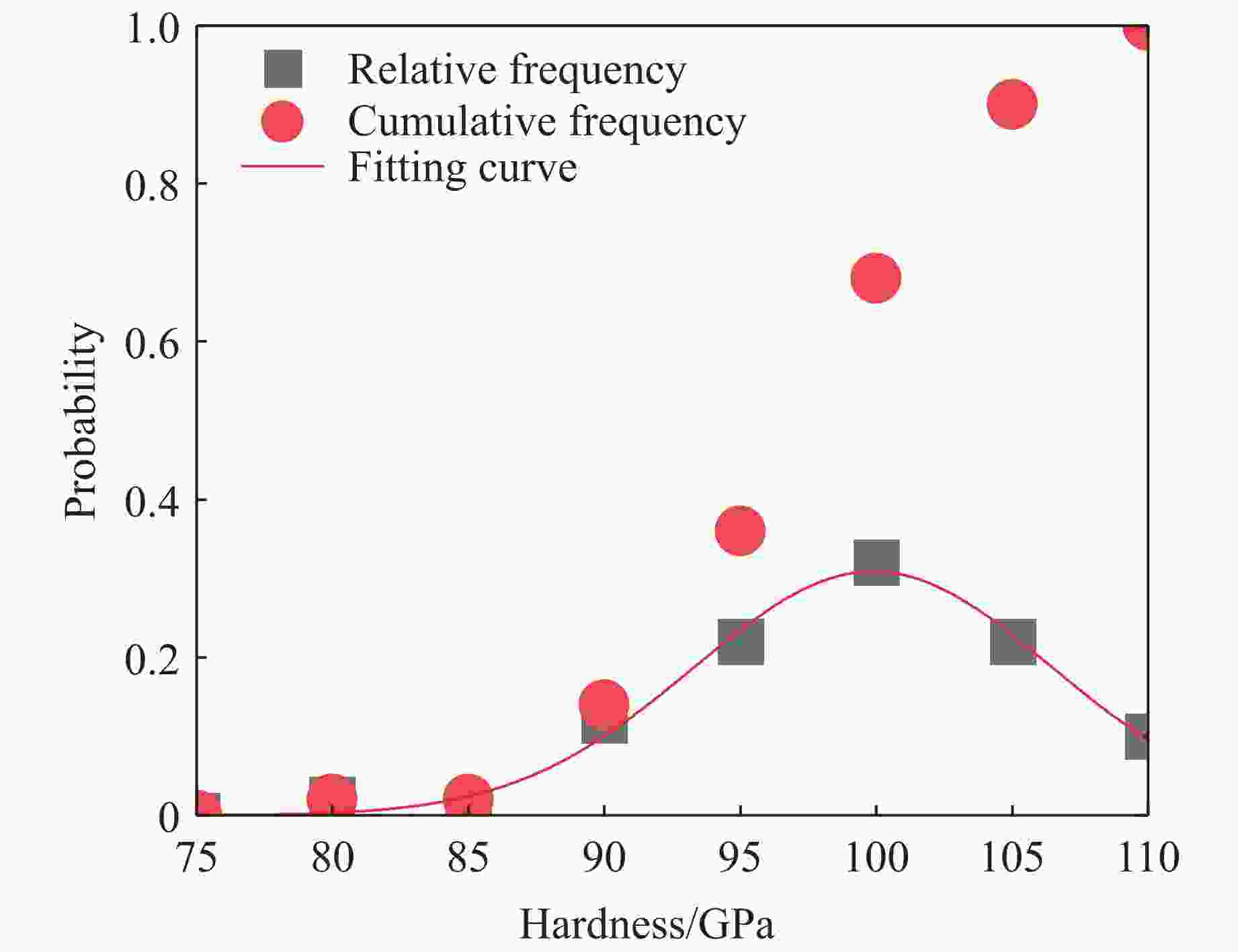
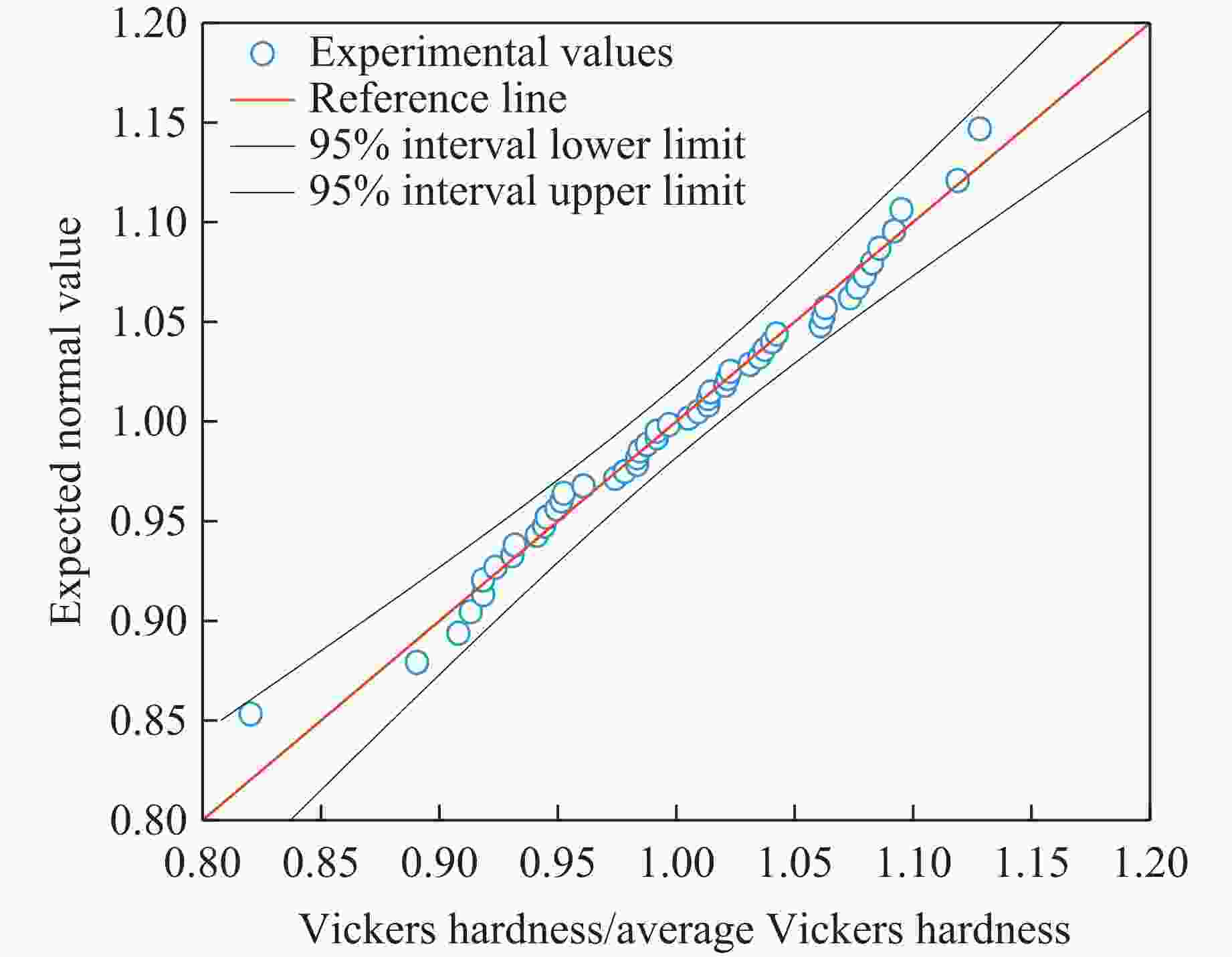
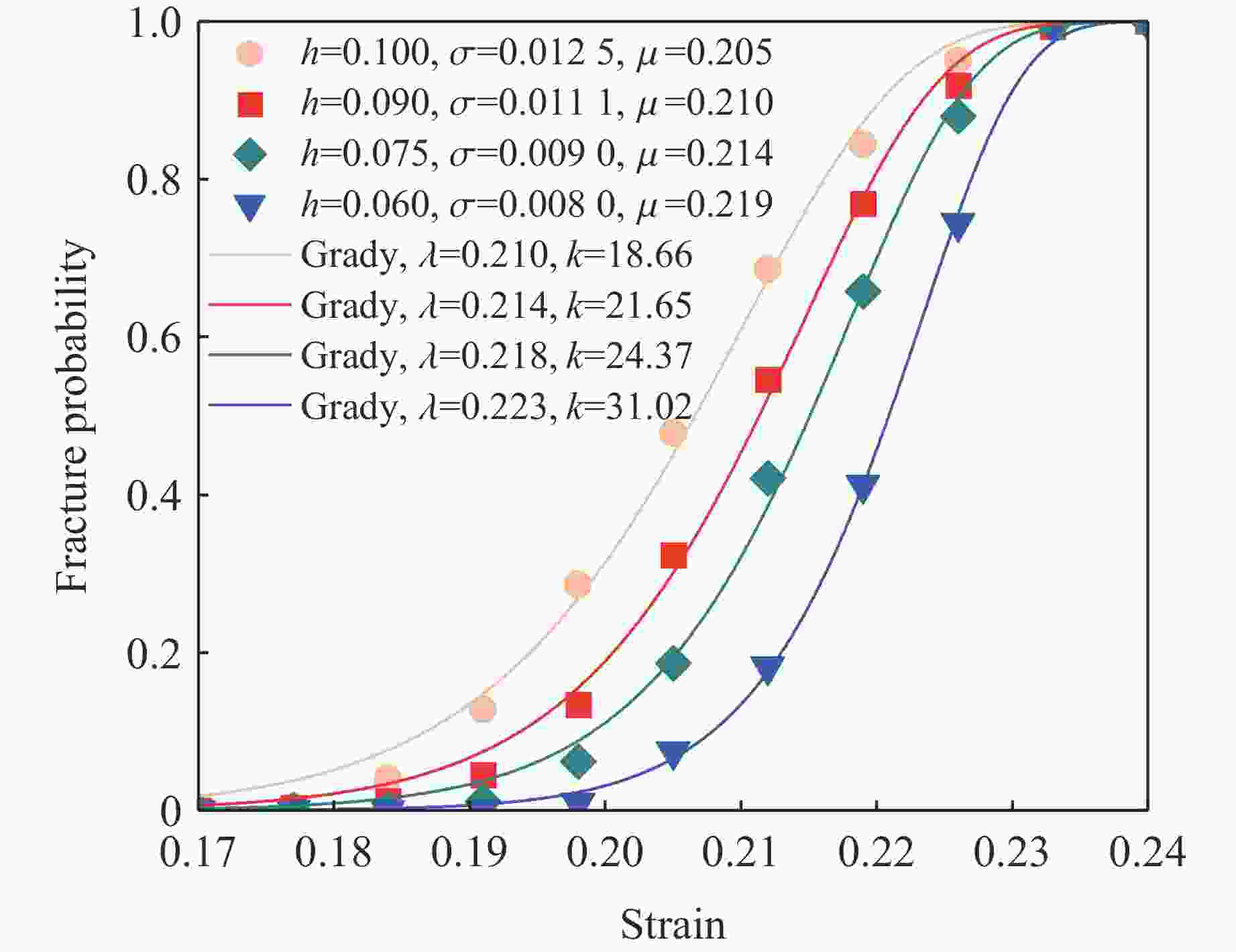
摘要: 研究延性金属环在动态加载下的断裂应变分布规律具有重要意义,电磁膨胀环装置是常用的实验加载手段。然而,目前实验上缺乏有效的原位观测技术,无法获得高精度的断裂应变统计数据。为此,将新研制的密排光子多普勒测速仪阵列应用于电磁膨胀环实验,获得了大量高置信度的断裂应变实验数据;通过硬度测量获得了材料屈服强度的统计分布规律,建立了含概率的本构模型,并进行了大规模计算,得到了大量的断裂应变模拟结果。结合实验与模拟结果,分析了6061铝电磁膨胀环动态断裂应变的应变率效应以及断裂应变韦伯分布假设的合理性。
-
关键词:
- 密排多普勒测速仪阵列 /
- 电磁膨胀环 /
- 断裂应变统计规律 /
- 应变率效应
Abstract: The fracture strain distribution of ductile metal rings under dynamic loading has significant application value, and the electromagnetic expansion ring is a commonly used experimental loading method. However, currently there is a lack of effective in-situ observation technology in experiments, making it impossible to obtain high-precision fracture strain statistical data. In this paper, the newly developed close-packed photonic Doppler velocimetry (PDV) array testing technology was applied to the electromagnetic expanding ring experiment, and a large amount of high-confidence fracture strain experimental data were obtained. The statistical distribution of material yield strength was obtained through hardness measurements, a probabilistic constitutive model was established, and large-scale computations were carried out to obtain a wealth of fracture strain simulation results. By combining experiments with simulations, the strain rate effect of dynamic fracture strain in 6061 aluminum electromagnetic expanding ring and the rationality of the Weibull distribution assumption for fracture strain were analyzed. -
表 1 实验样品的最大扩展速度及断口数量
Table 1. Maximum expansion velocity and number of fractures of experimental samples
Test No. Charging voltage/kV Maximum expansion velocity/(m·s–1) Number of fractures 1 5.25 113 1 2 5.50 120 3 3 5.50 130 4 4 6.00 145 4 5 6.00 150 6 6 6.25 175 10 7 6.50 190 8 表 2 6061铝的J-C模型参数
Table 2. Parameters of the J-C model of the 6061 aluminum
ρ/(g·cm−3) G/GPa A/GPa B/GPa n C $ \dot{\varepsilon}_0/\mathrm{s}^{-1} $ Tm/K Tr/K m cp/(J∙kg−1∙K−1) 2.703 27 0.278 0.245 0.817 0.0256 1.0 925 300 1.34 876 -
[1] MOTT N F. Fragmentation of shell cases [J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1947, 189(1018): 300–308. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1947.0042 [2] GRADY D. Fragmentation of rings and shells: the legacy of N. F. Mott [M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2006. [3] ROBSON J D. Exploring effects of property variation on fragmentation of metal rings using a simple model [J]. Defence Technology, 2023, 23: 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2022.08.014 [4] TODINOV M T. Is Weibull distribution the correct model for predicting probability of failure initiated by non-interacting flaws? [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2009, 46(3/4): 887–901. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2008.09.033 [5] NIORDSON F I. A unit for testing materials at high strain rates: by using ring specimens and electromagnetic loading, high strain rates are obtained in a tension test in a homogeneous, uniaxial strain field [J]. Experimental Mechanics, 1965, 5(1): 29–32. doi: 10.1007/BF02320901 [6] ZHANG H, RAVI-CHANDAR K. On the dynamics of necking and fragmentation—Ⅰ. real-time and post-mortem observations in Al 6061-O [J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2006, 142(3): 183–217. doi: 10.1007/s10704-006-9024-7 [7] ZHANG H, RAVI-CHANDAR K. On the dynamics of necking and fragmentation—Ⅱ. effect of material properties, geometrical constraints and absolute size [J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2008, 150(1): 3–36. doi: 10.1007/s10704-008-9233-3 [8] JANISZEWSKI J. Ductility of selected metals under electromagnetic ring test loading conditions [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2012, 49(7/8): 1001–1008. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2012.01.005 [9] DAN J K, GUO Z L, CHEN Y, et al. Preliminary investigations on dynamic fracture of ductile metals by using electromagnetically driven expanding ring [J]. AIP Advances, 2020, 10(10): 105001. doi: 10.1063/5.0016527 [10] JIANG Y, CHEN Y, GUO Z L, et al. Effect of strain rate on ductility of Cu TU1 in electromagnetic ring expansion [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2024, 184: 104832. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104832 [11] BARKER L M, HOLLENBACH R E. Laser interferometer for measuring high velocities of any reflecting surface [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1972, 43(11): 4669–4675. doi: 10.1063/1.1660986 [12] STRAND O T, GOOSMAN D R, MARTINEZ C, et al. Compact system for high-speed velocimetry using heterodyne techniques [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2006, 77(8): 083108. doi: 10.1063/1.2336749 [13] ALTYNOVA M, HU X Y, DAEHN G S. Increased ductility in high velocity electromagnetic ring expansion [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1996, 27(7): 1837–1844. doi: 10.1007/BF02651933 [14] LIU M T, REN G W, FAN C, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on the expanding fracture behavior of an explosively driven 1045 steel cylinder [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 109: 240–252. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.07.008 [15] HUANG S, CHEN H Y, ZHANG R, et al. Uncovering the fracture behavior of metallic cylindrical shells under internal explosive loadings via careful design of densely-arranged multi-point photon Doppler velocimetry measurements [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 180: 104679. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104679 [16] ZHANG H, PEI X Y, PENG H, et al. Phase-field modeling of spontaneous shear bands in collapsing thick-walled cylinders [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2021, 249: 107706. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2021.107706 [17] LOVINGER Z, RITTEL D, ROSENBERG Z. Modeling spontaneous adiabatic shear band formation in electro-magnetically collapsing thick-walled cylinders [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2018, 116: 130–145. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2017.01.010 [18] 邓云飞, 张永, 吴华鹏, 等. 6061-T651铝合金动态力学性能及J-C本构模型的修正 [J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(20): 74–81. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.20.074DENG Y F, ZHANG Y, WU H P, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties and modification of J-C constitutive model of 6061-T651 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(20): 74–81. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.20.074 [19] CAI J Z, GRIESBACH C, AHNEN S G, et al. Dynamic hardness evolution in metals from impact induced gradient dislocation density [J]. Acta Materialia, 2023, 249: 118807. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2023.118807 -






 下载:
下载: