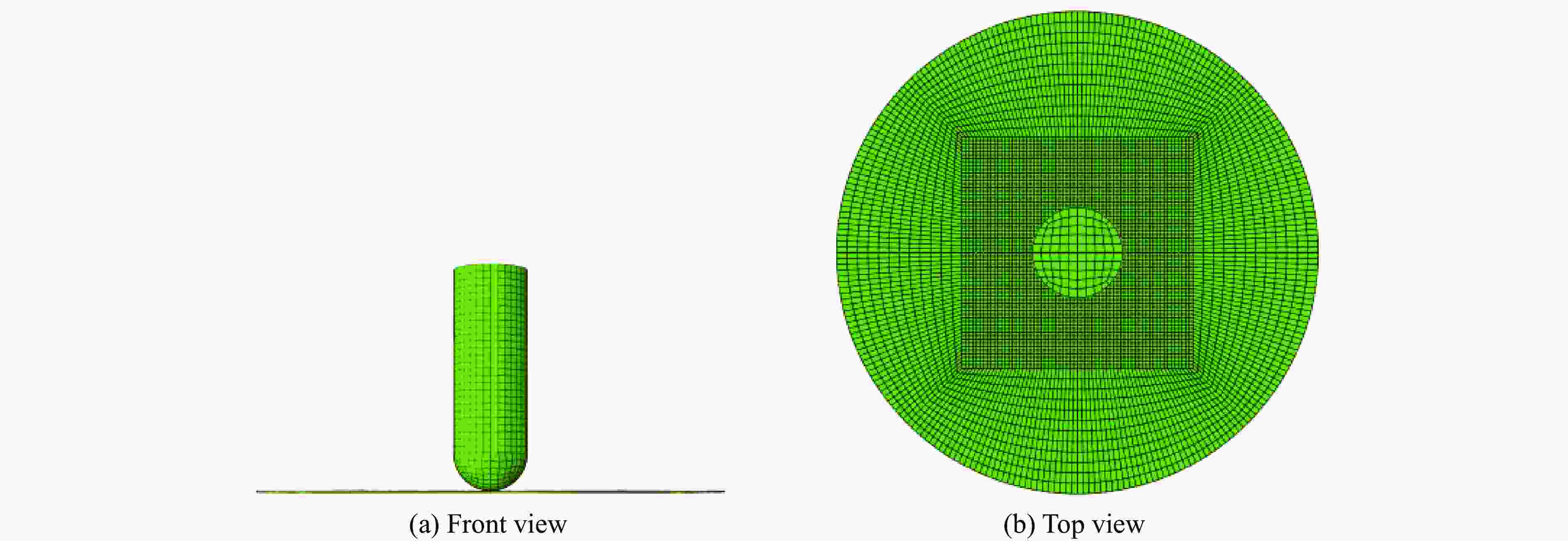
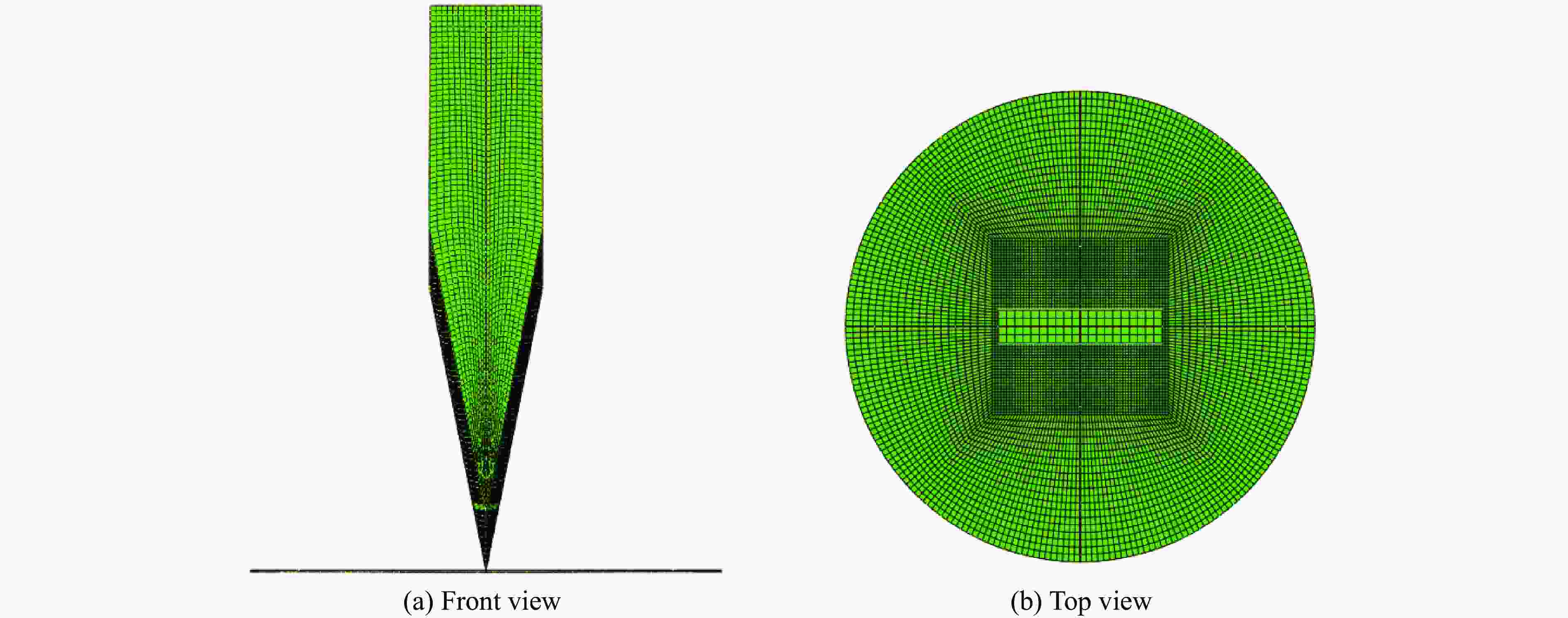
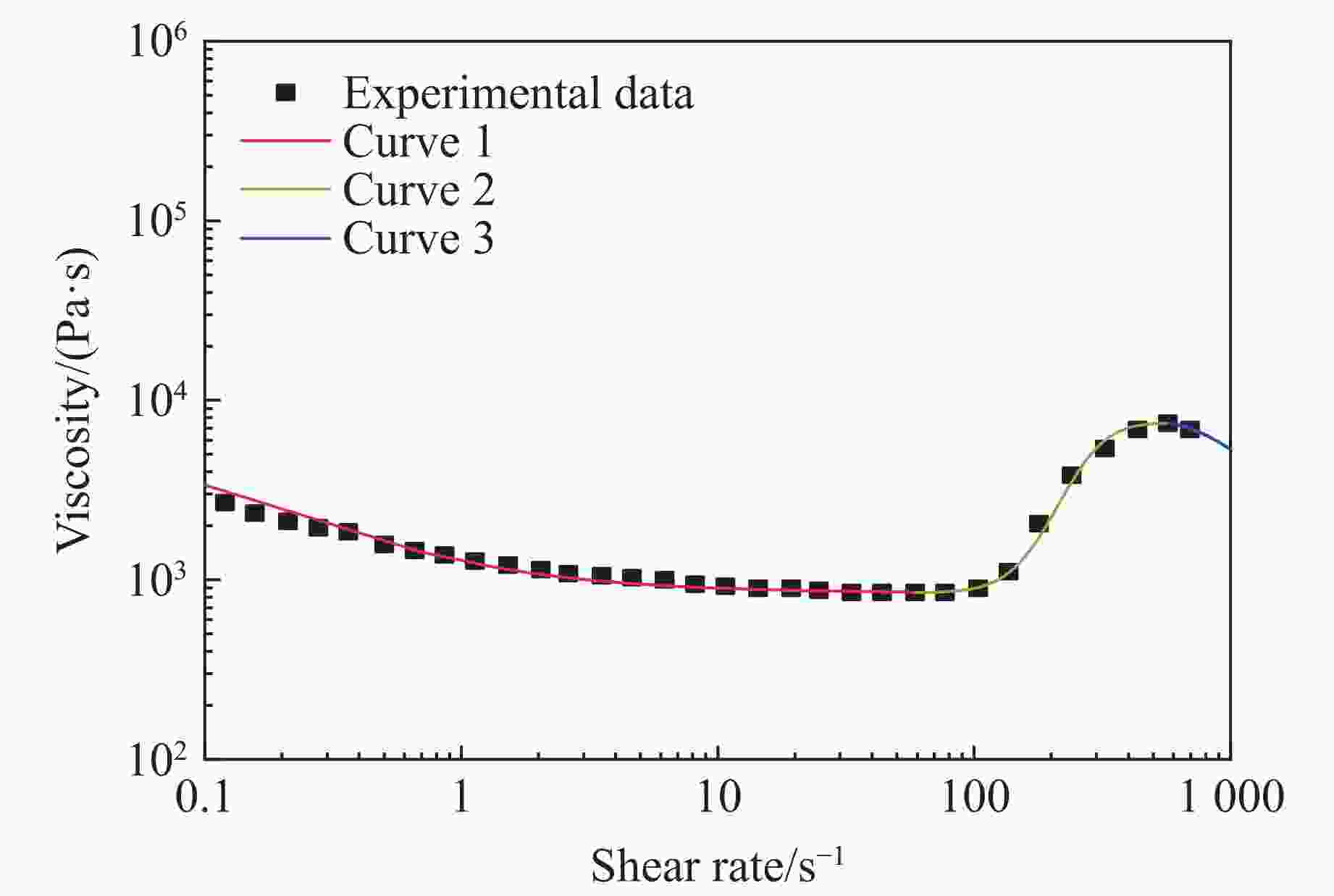
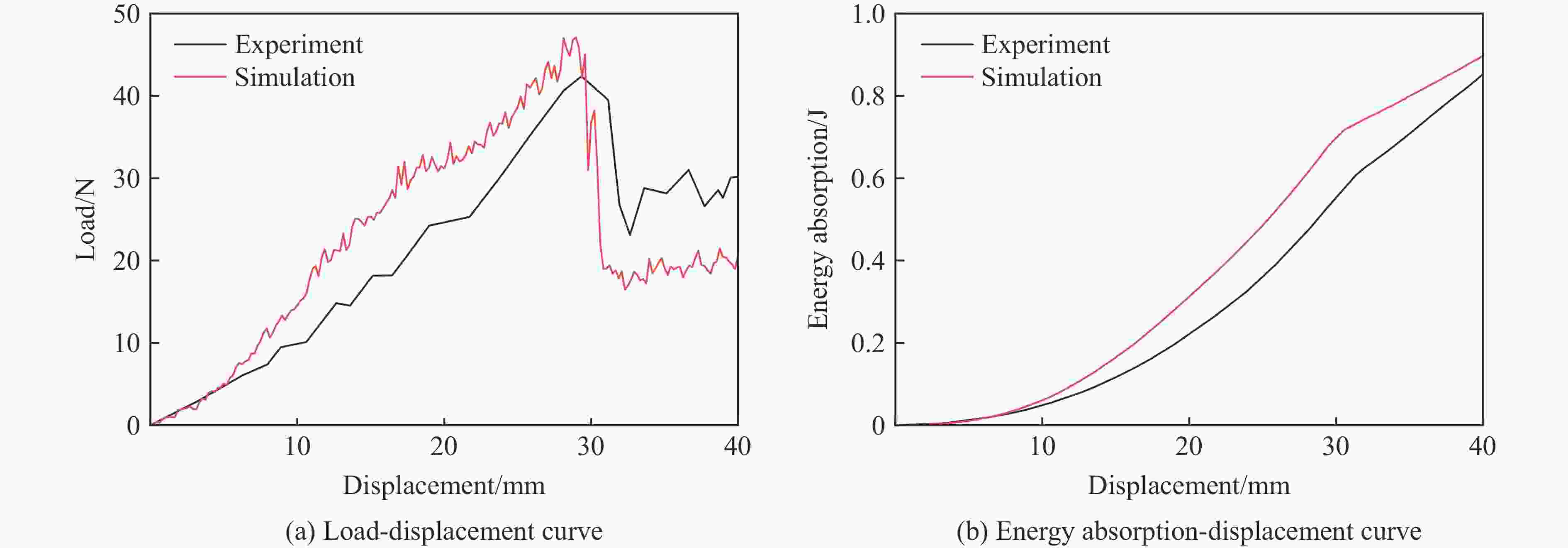
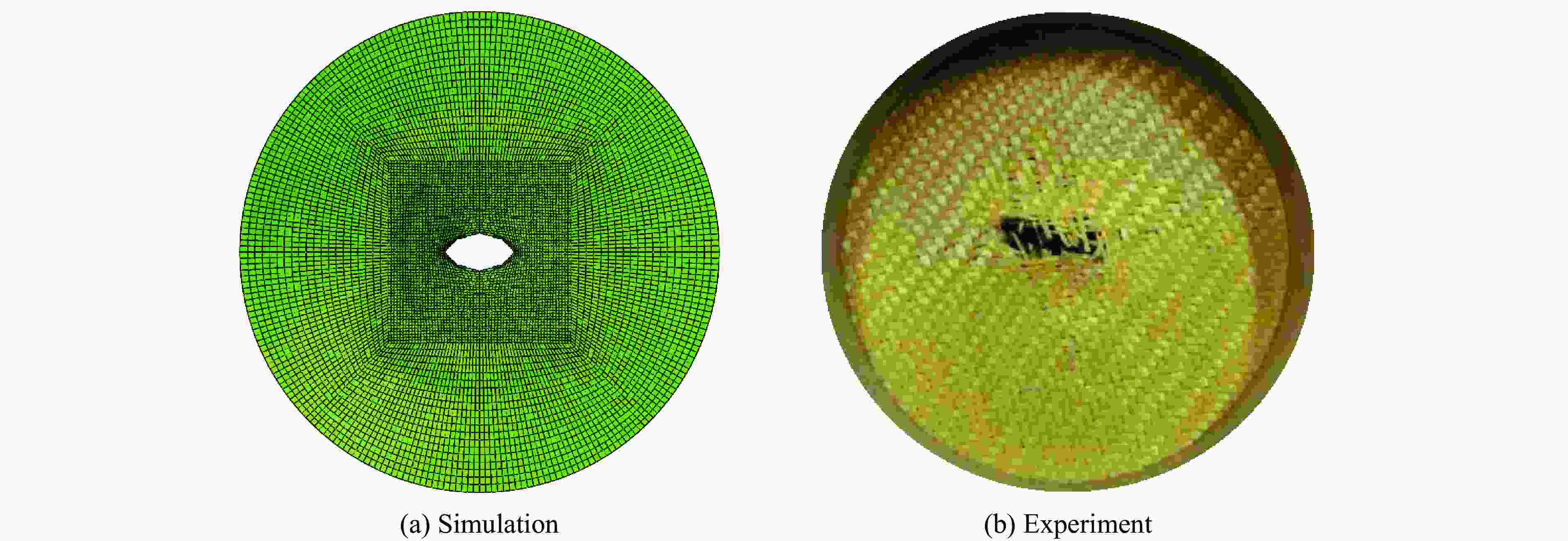
A Dynamic Constitutive Model for Shear Thickening Fluid Impregnated Kevlar Fabric
-
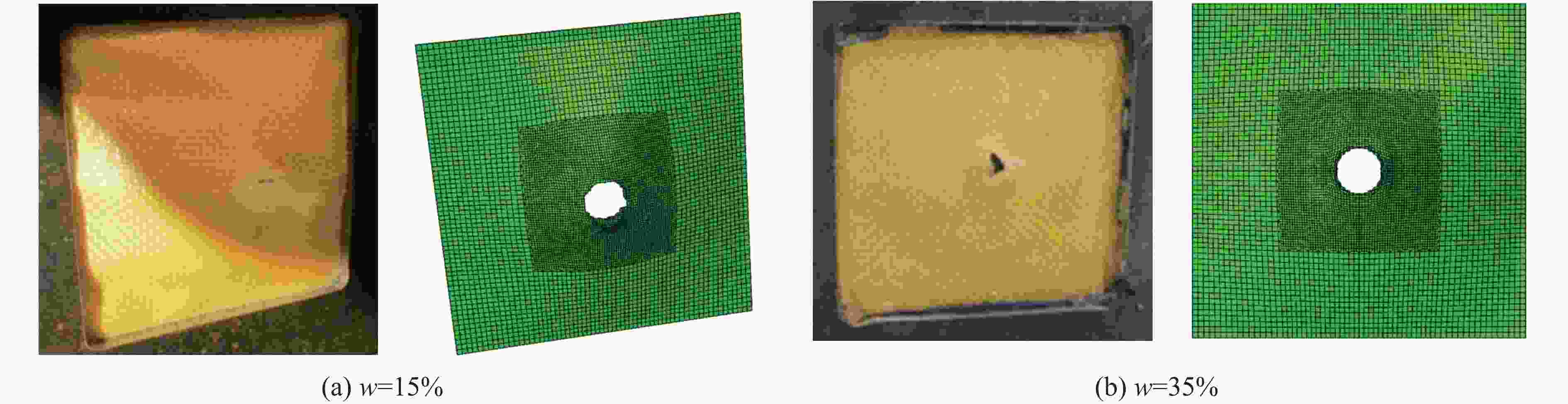
摘要: 剪切增稠液(shear thickening fluid, STF)浸渍凯夫拉(Kevlar)织物是一种新型复合材料,相比纯Kevlar织物,具有更好的抗冲击性能,研究其动态本构模型具有重要的理论意义和应用价值。首先,通过引入动态增强因子(应变率效应)和残余强度因子,结合STF的流变特性和纱线拔出实验结果,发展了STF浸渍Kevlar织物的连续介质损伤力学本构模型;然后,利用提出的本构模型,开展了不同冲击速度下STF浸渍Kevlar织物侵彻的数值模拟;最后,将模拟结果与文献中的相关实验结果进行对比分析。结果表明:所建立的本构模型能够预测STF浸渍Kevlar织物在冲击载荷作用下的力学响应和破坏形貌,并且能够描述STF浸渍后Kevlar织物抗冲击性能的增强效应。
-
关键词:
- 剪切增稠液 /
- Kevlar织物 /
- 连续介质损伤力学本构模型 /
- 流变特性 /
- 纱线间摩擦
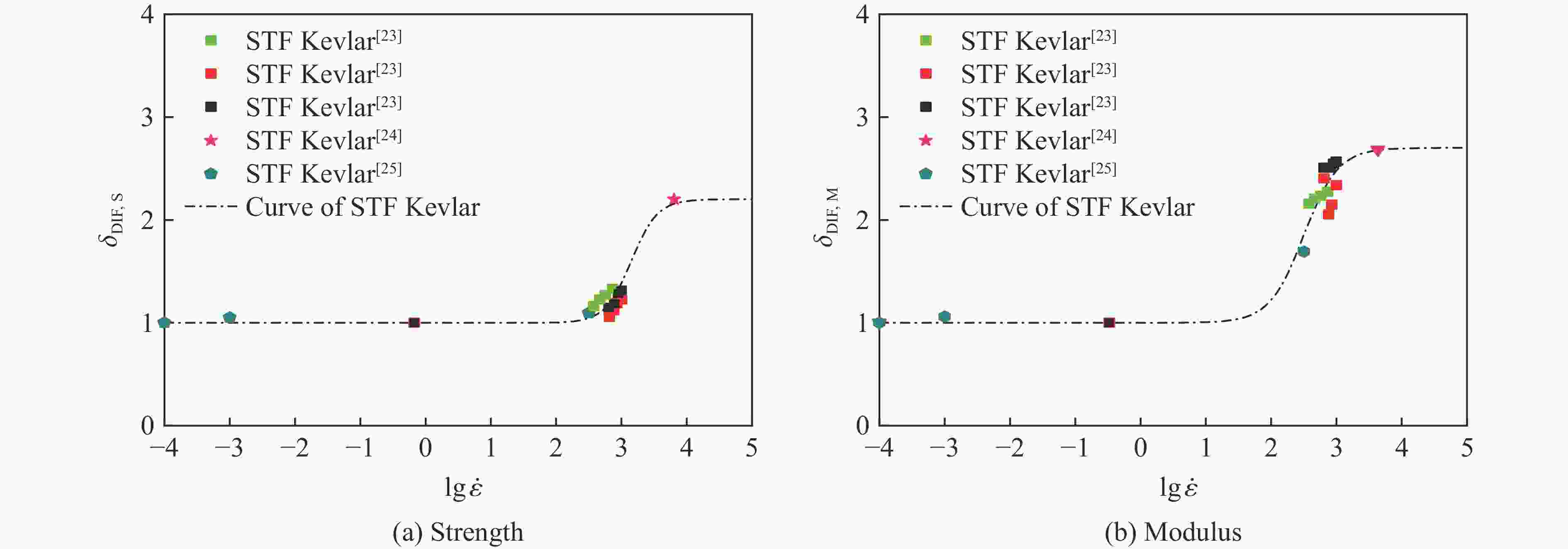
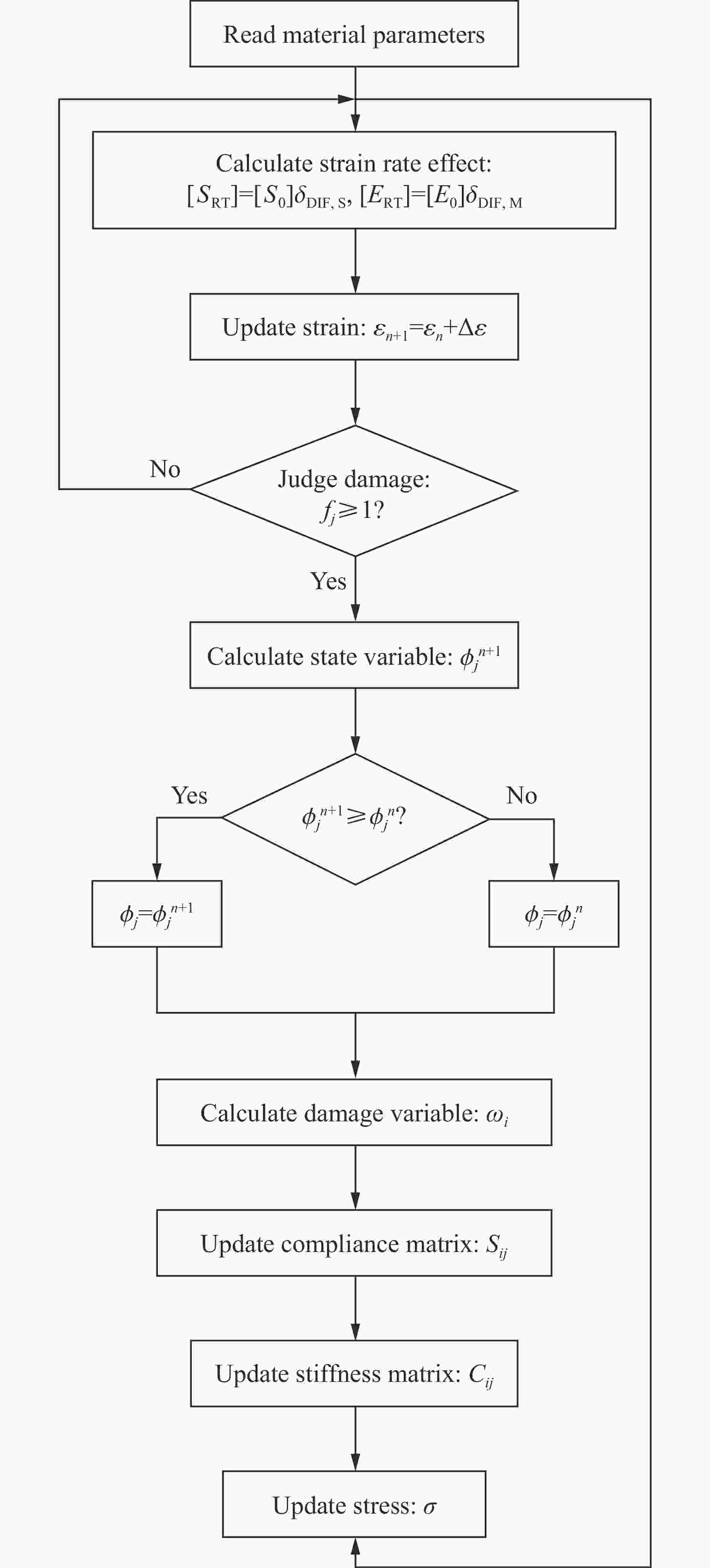
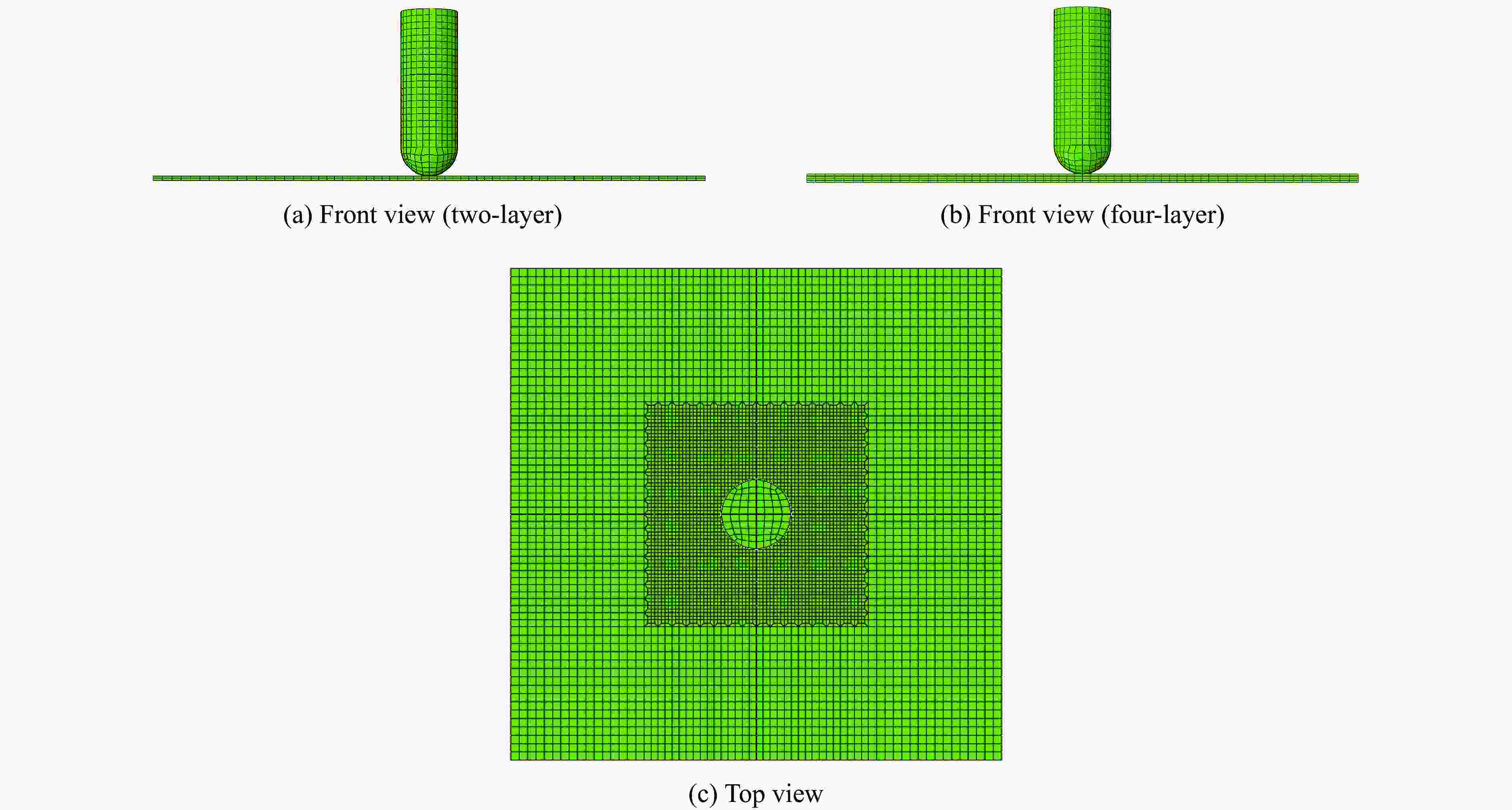
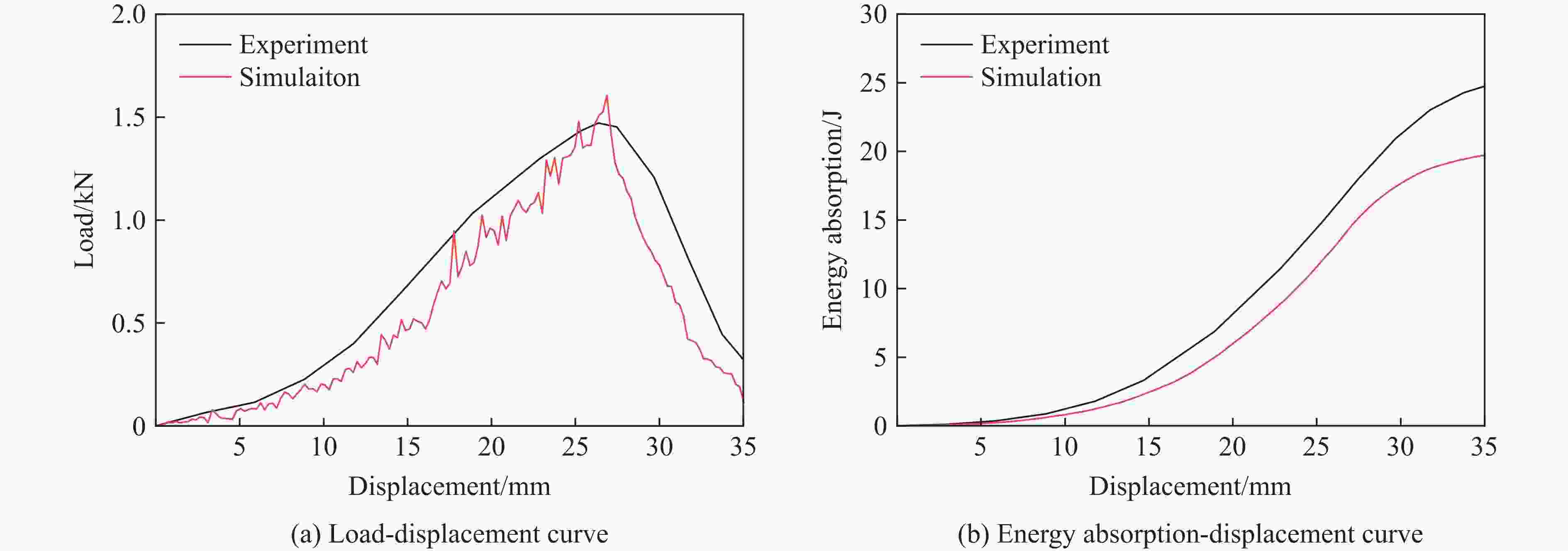
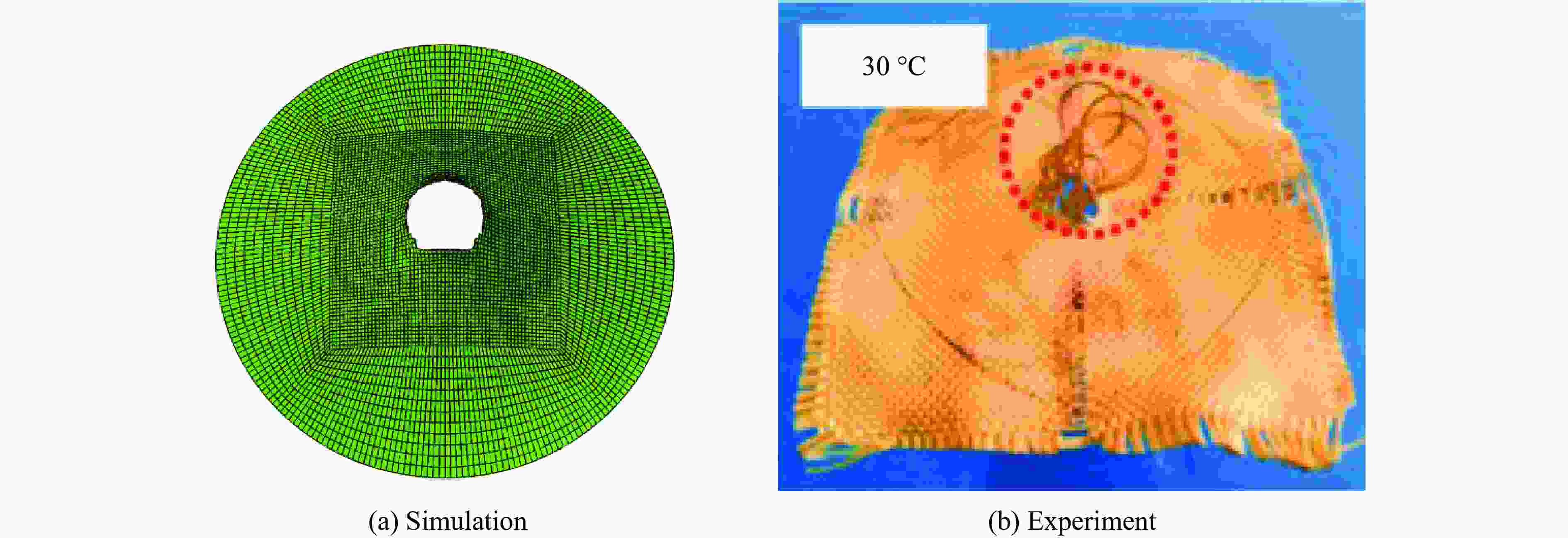
Abstract: Shear thickening fluid (STF) impregnated Kevlar fabric is a new type of composite materials which has better impact resistance as compared with neat Kevlar fabric. On the basis of previous work, a dynamic constitutive model for STF impregnated Kevlar fabric is firstly developed by introducing dynamic increase factor (strain rate effect) and residual strength factor in combination with the rheological properties of STF and yarn pull out test results. Numerical simulations of STF impregnated Kevlar fabric at different impact velocities are then conducted using the proposed constitutive model. Finally, the numerical results are compared with the relevant experimental data. It is shown that the present constitutive model can predict well the impact response of STF impregnated Kevlar fabrics in terms of residual velocity, load-displacement curve and damage morphology, lending support to the accuracy and usefulness of the dynamic constitutive model for STF impregnated Kevlar fabric. -
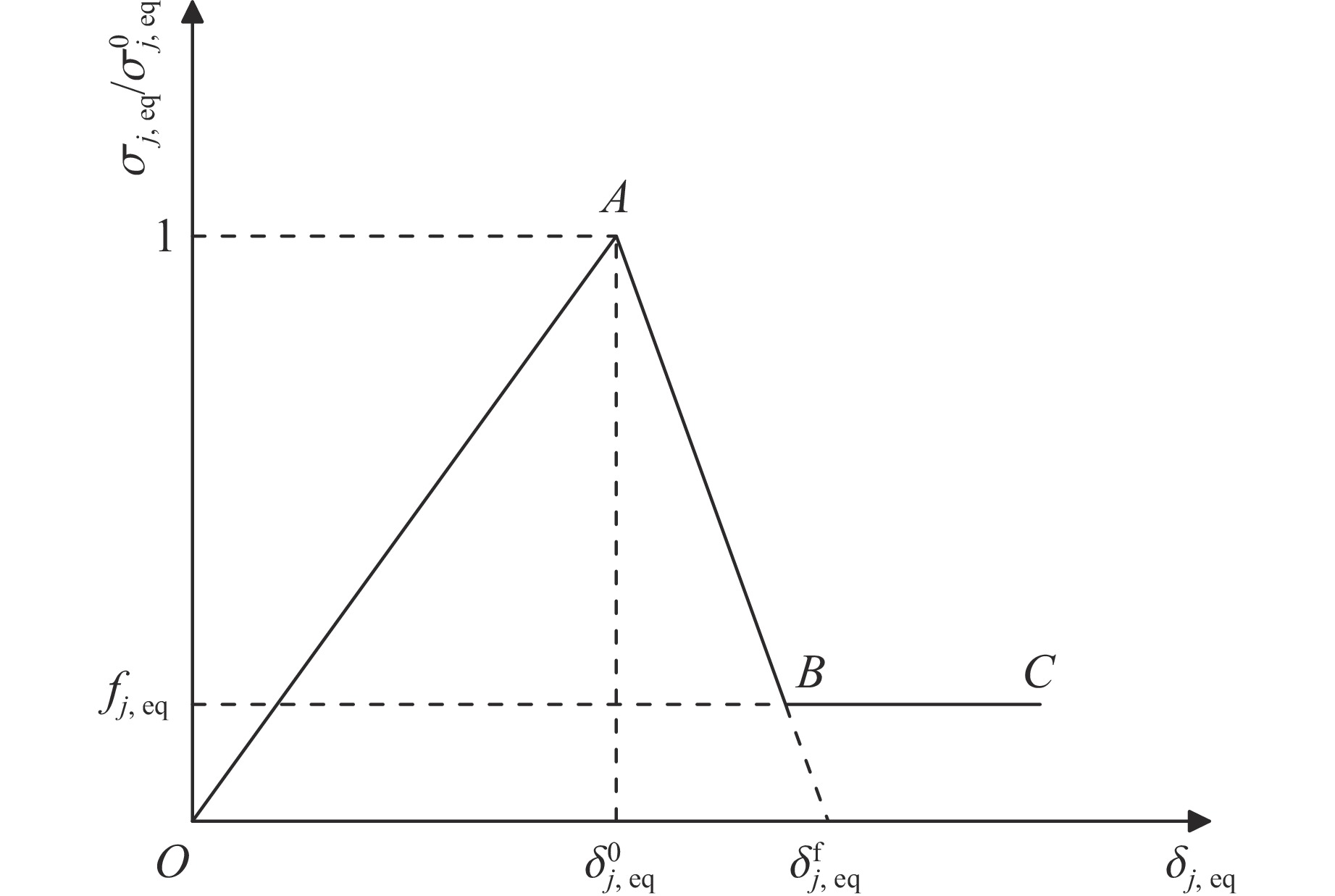
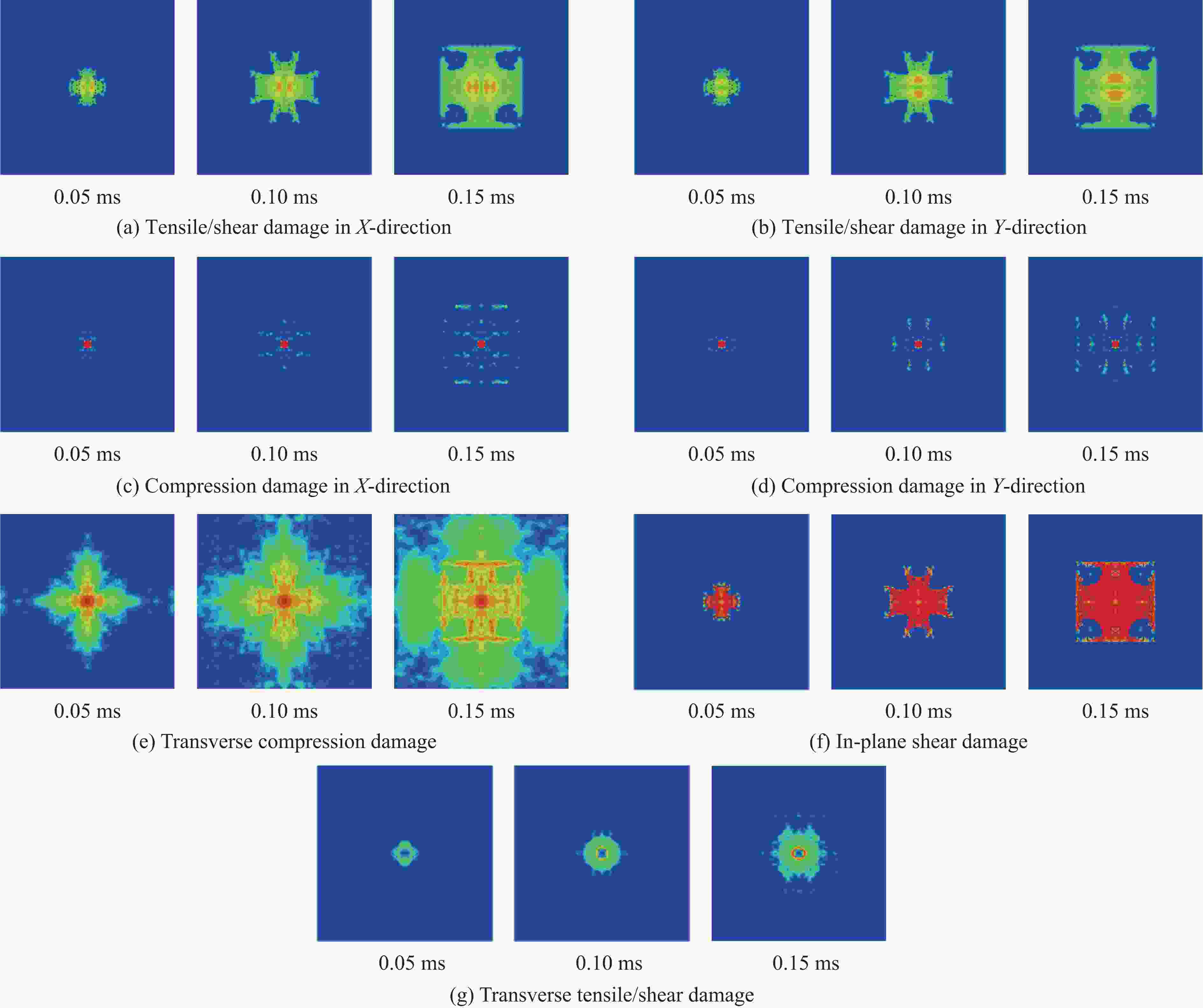
Damage mode ${\delta _{j,{\rm{eq}}}}$ ${\sigma _{j,{\rm{eq}}}}$ Tensile/shear damage in X-direction ${L_{\rm{c}}}\sqrt {{{\left\langle {{\varepsilon _{11}}} \right\rangle }^2}+{{{{\gamma _{12}^2}} }}+{{ {{\gamma _{31}^2}} }}} $ ${L_{\rm{c}}}\left( {{E_{11}}{{\left\langle {{\varepsilon _{11}}} \right\rangle }^2}+{G_{12}}{{{{\gamma _{12}^2}} }}+{G_{31}}{{{{\gamma _{31}^2}} }}} \right)/{\delta _{\rm{1,eq}}}$ Tensile/shear damage in Y-direction ${L_{\rm{c}}}\sqrt {{{\left\langle {{\varepsilon _{22}}} \right\rangle }^2}+{{ {{\gamma _{12}^2}} }}+{{ {{\gamma _{23}^2}} }}} $ ${L_{\rm{c}}}\left( {{E_{22}}{{\left\langle {{\varepsilon _{22}}} \right\rangle }^2}+{G_{12}}{{ {{\gamma _{12}^2}} }}+{G_{23}}{{{{\gamma _{23}^2}}}}} \right)/{\delta _{\rm{2,eq}}}$ Compression damage in X-direction ${L_{\rm{c}}}\sqrt {{{\left\langle {{{\varepsilon }_{11}'}} \right\rangle }^2}} $ ${L_{\rm{c}}}\left( {{E_{11}}{{\left\langle {{{\varepsilon}_{11} '}} \right\rangle }^2}} \right)/{\delta _{\rm{3,eq}}}$ Compression damage in Y-direction ${L_{\rm{c}}}\sqrt {{{\left\langle {{{\varepsilon }_{22}'}} \right\rangle }^2}} $ ${L_{\rm{c}}}\left( {{E_{22}}{{\left\langle {{{\varepsilon }_{22}'}} \right\rangle }^2}} \right)/{\delta _{\rm{4,eq}}}$ Transverse compression damage ${L_{\rm{c}}}\sqrt {{{\left\langle {{{\varepsilon }_{33}'}} \right\rangle }^2}} $ ${L_{\rm{c}}}\left( {{E_{33}}{{\left\langle {{{\varepsilon }_{33}'}} \right\rangle }^2}} \right)/{\delta _{\rm{5,eq}}}$ In-plane shear damage ${L_{\rm{c}}}\sqrt {{{{{\gamma _{12}^2}} }}} $ ${L_{\rm{c}}}\left( {{G_{12}}{{ {{\gamma _{12}^2}} }}} \right)/{\delta _{\rm{6,eq}}}$ Transverse tensile/shear damage ${L_{\rm{c}}}\sqrt {{{\left\langle {{\varepsilon _{33}}} \right\rangle }^2}+{{{{\gamma _{23}^2}} }}+{{{{\gamma _{31}^2}} }}} $ ${L_{\rm{c}}}\left( {{E_{33}}{{\left\langle {{\varepsilon _{33}}} \right\rangle }^2}+{G_{23}}{{ {{\gamma _{23}^2}} }}+{G_{31}}{{ {{\gamma _{31}^2}} }}} \right)/{\delta _{\rm{7,eq}}}$ 表 2 数值模拟中STF浸渍Kevlar织物的材料参数[23, 28–34]
Table 2. Material parameters of STF impregnated Kevlar fabric in the numerical simulations[23, 28–34]
E11/GPa E22/GPa E33/GPa G12/GPa G23/GPa G31/GPa ${\nu _{12}}$ ${\nu _{23}}$ ${\nu _{31}}$ 70 70 7 16.4 1.8 1.8 0.33 0.40 0.40 Xt/MPa Yt/MPa Zt/MPa Xc/MPa Yc/MPa Zc/MPa S12/MPa S23/MPa S31/MPa 2 758 2 758 24 580 580 60 180 180 180 表 3 弹道冲击实验中STF流变特性的拟合参数[26]
Table 3. Parameters for fitting the rheological properties of STF used in ballistic impact experiments[26]
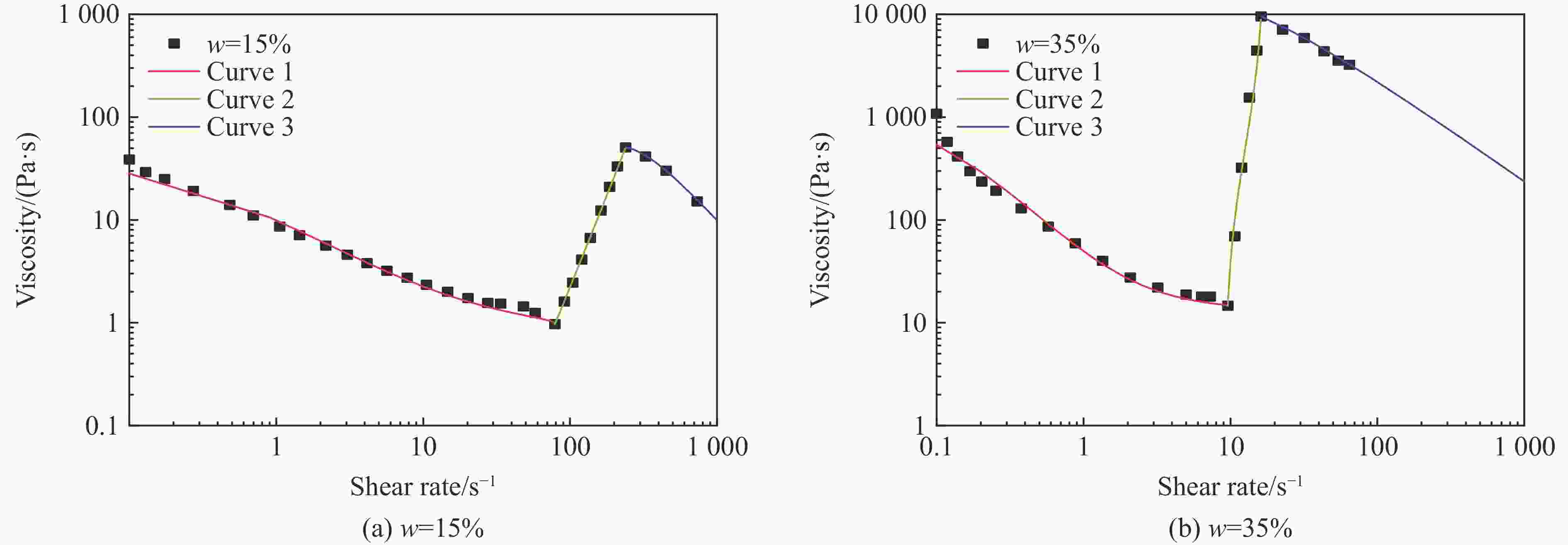
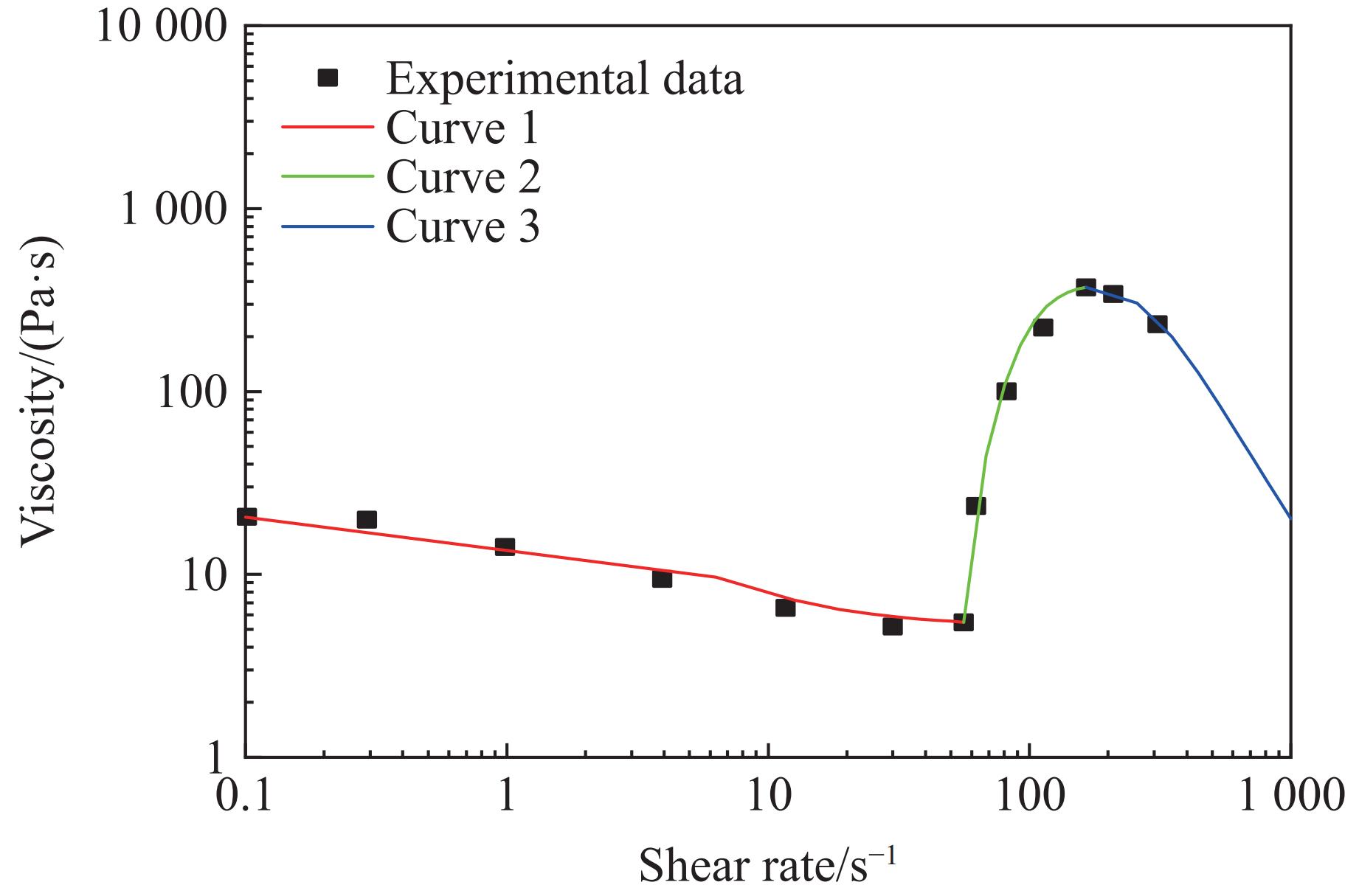
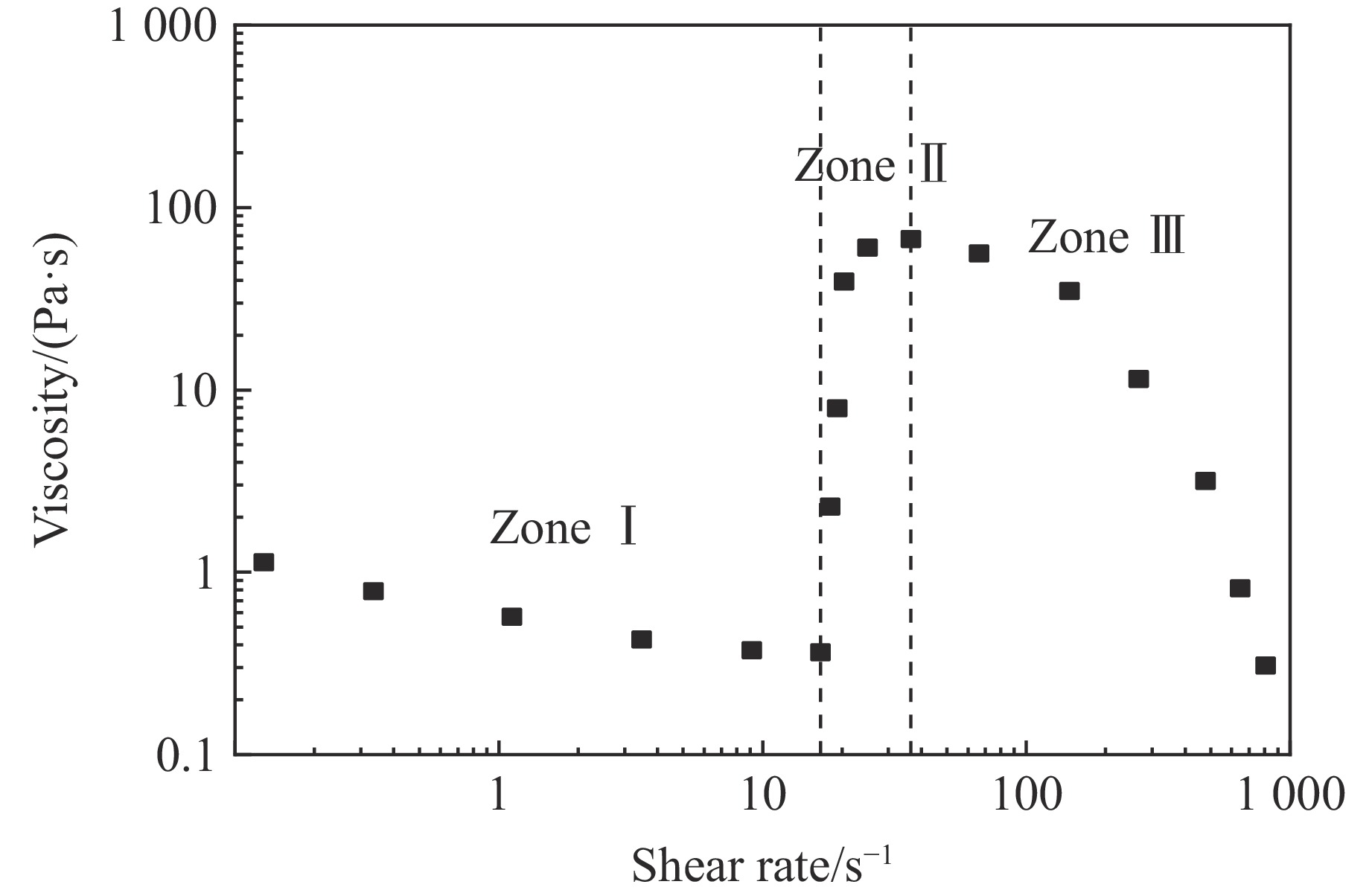
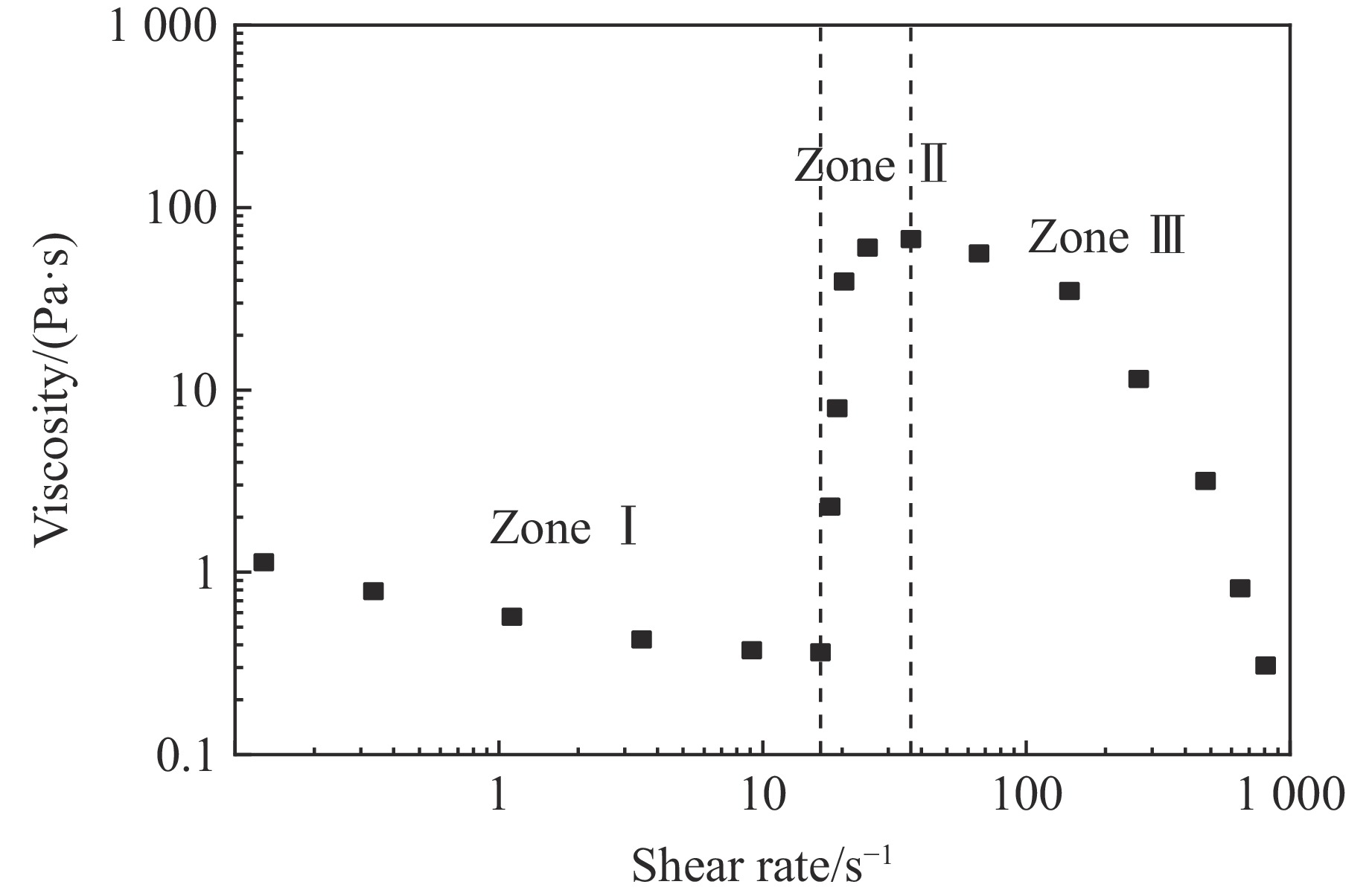
w/% ${\eta _0}/({\rm{Pa}} \cdot{\rm{ s}})$ ${\eta _{\rm{c}}}/({\rm{Pa}} \cdot{\rm{ s}})$ ${\eta _{\rm{max}}}/({\rm{Pa}} \cdot{\rm{ s}})$ ${\dot \gamma _{\rm{c}}}$/s−1 ${\dot \gamma _{\rm{max}}}$/s−1 KⅠ KⅡ KⅢ nⅠ nⅡ nⅢ 15 38.775 0.972 50.624 78.952 238.946 −1 000 −0.001 7 0.003 6 0.46 1.0 1.4 35 1 078.201 14.663 9 540.340 9.603 16.151 −1 000 −0.006 5 0.040 0 0.71 1.1 1.0 表 4 弹道冲击实验中数值模拟的材料参数[26]
Table 4. Material parameters for the numerical simulations of ballistic impact experiments[26]
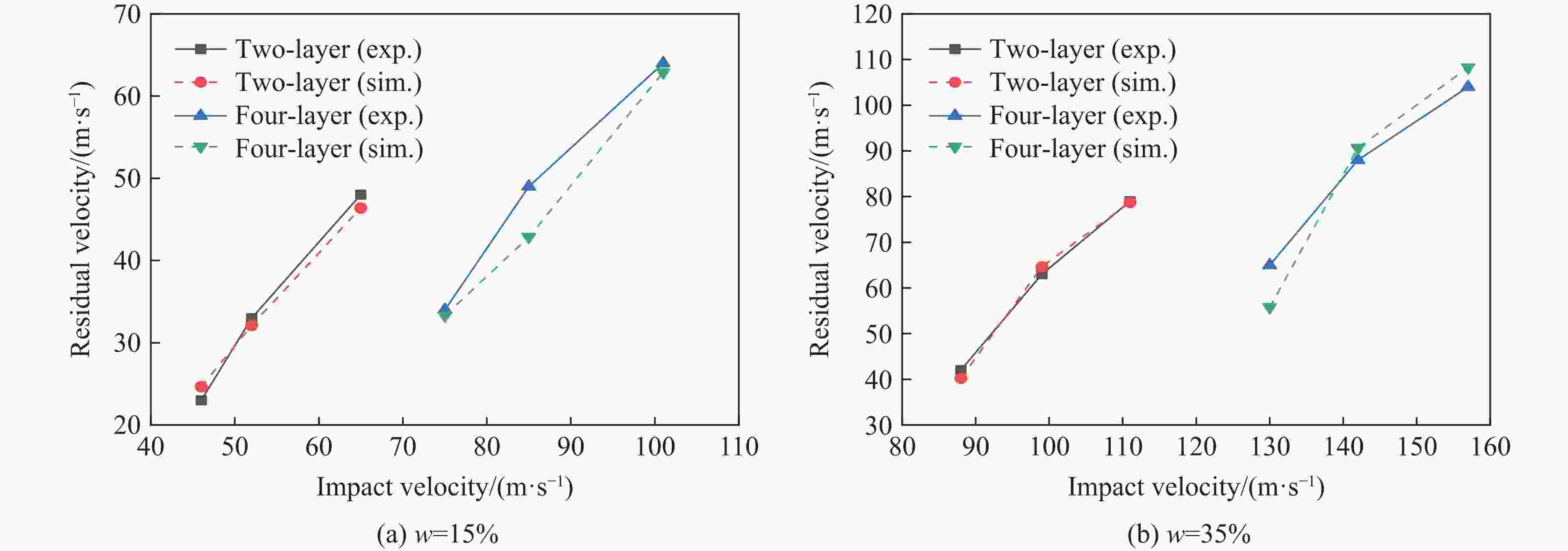
w/% $ {\rho _{\rm{areal}}} $/(kg·m−2) $ {f_{\rm{rs0}}} $ $ k $ $ \xi $ 15 0.523 0.4 0.272 0.444 35 0.722 0.4 0.957 0.321 表 5 低速冲击实验中STF流变特性的拟合参数[35]
Table 5. Parameters for fitting the rheological properties of STF used in low velocity impact experiments[35]
${\eta _0}/({\rm{Pa}} \cdot{\rm{ s}})$ ${\eta _{\rm{c}}}/({\rm{Pa}} \cdot{\rm{ s}})$ ${\eta _{\rm{max}}}/({\rm{Pa}} \cdot{\rm{ s}})$ ${\dot \gamma _{\rm{c}}}$/s−1 ${\dot \gamma _{\rm{max}}}$/s−1 KⅠ KⅡ KⅢ nⅠ nⅡ nⅢ 20.677 5.26 362 54.5 164.725 −5 −0.02 0.005 0.7 1.2 2.0 Table 6. Material parameters for the numerical simulations of low velocity impact experiments[35–36]
$ {\rho _{\rm{{areal}}}} $/(kg·m−2) $ {f_{\rm{rs0}}} $ $ k $ $ \xi $ 0.3032 0.16 0.814 0.796 表 7 准静态穿刺实验中STF流变特性的拟合参数[36]
Table 7. Parameters for fitting the rheological properties of STF used in quasi-static puncture experiments[36]
${\eta _0}/({\rm{Pa}} \cdot {\rm{s}})$ ${\eta _{\rm{c}}}/({\rm{Pa}} \cdot{\rm{ s}})$ ${\eta _{\rm{max}}}/({\rm{Pa}} \cdot{\rm{ s}})$ ${\dot \gamma _{\rm{c}}}$/s−1 ${\dot \gamma _{\rm{max}}}$/s−1 KⅠ KⅡ KⅢ nⅠ nⅡ nⅢ 2845 852 7449 58.808 570.207 − 20000 −0.006 0.0012 0.47 1.7 1.4 -
[1] LI T T, DAI W N, WU L W, et al. Effects of STF and fiber characteristics on quasi-static stab resistant properties of shear thickening fluid (STF)-impregnated UHMWPE/Kevlar composite fabrics [J]. Fibers and Polymers, 2019, 20(2): 328–336. doi: 10.1007/s12221-019-8446-6 [2] LIU L L, YANG Z Z, ZHAO Z H, et al. The influences of rheological property on the impact performance of Kevlar fabrics impregnated with SiO2/PEG shear thickening fluid [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2020, 151: 106717. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.106717 [3] LIU B, LIU Q, PAN Y C, et al. An impact-resistant and flame-retardant CNTs/STF/Kevlar composite with conductive property for safe wearable design [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2023, 168: 107489. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2023.107489 [4] MAWKHLIENG U, MAJUMDAR A. Deconstructing the role of shear thickening fluid in enhancing the impact resistance of high-performance fabrics [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 175: 107167. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107167 [5] MAJUMDAR A, LAHA A. Effects of fabric construction and shear thickening fluid on yarn pull-out from high-performance fabrics [J]. Textile Research Journal, 2016, 86(19): 2056–2066. doi: 10.1177/0040517515619357 [6] LI D Y, WANG R, LIU X, et al. Shear-thickening fluid using oxygen-plasma-modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes to improve the quasi-static stab resistance of Kevlar fabrics [J]. Polymers, 2018, 10(12): 1356. doi: 10.3390/polym10121356 [7] QIN J B, GUO B R, ZHANG L, et al. Soft armor materials constructed with Kevlar fabric and a novel shear thickening fluid [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2020, 183: 107686. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107686 [8] LIU M, ZHANG S S, LIU S, et al. CNT/STF/Kevlar-based wearable electronic textile with excellent anti-impact and sensing performance [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2019, 126: 105612. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105612 [9] KORDANI N, VANINI A S, AMIRI H. Numerical solution of penetration into woven fabric target impregnated with shear thickening fluid [J]. Polymers and Polymer Composites, 2016, 24(4): 281–287. doi: 10.1177/096739111602400407 [10] KHODADADI A, LIAGHAT G H, SABET A R, et al. Experimental and numerical analysis of penetration into Kevlar fabric impregnated with shear thickening fluid [J]. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, 2018, 31(3): 392–407. doi: 10.1177/0892705717704485 [11] SEN S, BIN JAMAL M N, SHAW A, et al. Numerical investigation of ballistic performance of shear thickening fluid (STF)-Kevlar composite [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2019, 164: 105174. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105174 [12] XIE Z H, CHEN W, LIU Y Y, et al. Design of the ballistic performance of shear thickening fluid (STF) impregnated Kevlar fabric via numerical simulation [J]. Materials & Design, 2023, 226: 111599. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2023.111599 [13] LIU L L, CAI M, LUO G, et al. Macroscopic numerical simulation method of multi-phase STF-impregnated Kevlar fabrics. part 2: material model and numerical simulation [J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 262: 113662. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.113662 [14] LIAO J B, WEN H M. A constitutive model for shear thickening fluid (STF) impregnated Kevlar fabric subjected to impact loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2024, 191: 104990. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2024.104990 [15] XIN S H, WEN H M. A progressive damage model for fiber reinforced plastic composites subjected to impact loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 75: 40–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.07.014 [16] GALINDO-ROSALES F J, RUBIO-HERNÁNDEZ F J, SEVILLA A. An apparent viscosity function for shear thickening fluids [J]. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 2011, 166(5/6): 321–325. doi: 10.1016/j.jnnfm.2011.01.001 [17] 王敏, 文鹤鸣. 碳纳米管/碳纤维增强复合材料层合板低速冲击响应和破坏的数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(3): 033102. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0050WANG M, WEN H M. Numerical simulations of response and failure of carbon nanotube/carbon fibre reinforced plastic laminates under impact loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(3): 033102. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0050 [18] LIAO J B, WANG M, WEN H M. A dynamic constitutive model for carbon nanotubes (CNTs) modified unidirectional fibre reinforced plastic laminates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2024, 183: 104793. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104793 [19] BAI R X, LI W K, LEI Z K, et al. Experimental study of yarn friction slip and fabric shear deformation in yarn pull-out test [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2018, 107: 529–535. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.02.001 [20] BAI R X, MA Y, LEI Z K, et al. Shear deformation and energy absorption analysis of flexible fabric in yarn pullout test [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2020, 128: 105678. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105678 [21] LEE B W, KIM I J, KIM C G. The influence of the particle size of silica on the ballistic performance of fabrics impregnated with silica colloidal suspension [J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2009, 43(23): 2679–2698. doi: 10.1177/0021998309345292 [22] PARK J L, YOON B I, PAIK J G, et al. Ballistic performance of p-aramid fabrics impregnated with shear thickening fluid; part I–effect of laminating sequence [J]. Textile Research Journal, 2012, 82(6): 527–541. doi: 10.1177/0040517511420753 [23] LIU L L, CAI M, LUO G, et al. Macroscopic numerical simulation method of multi-phases STF impregnated Kevlar fabrics. part 1: quasi-static and dynamic mechanical test [J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 266: 113780. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.113780 [24] CAO S S, CHEN Q, WANG Y P, et al. High strain-rate dynamic mechanical properties of Kevlar fabrics impregnated with shear thickening fluid [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2017, 100: 161–169. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.04.015 [25] LIU L L, YANG Z Z, LIU X, et al. Yarn dynamic tensile behavior and meso-scale numerical simulation method for STF-Kevlar fabrics [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 159: 107319. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.107319 [26] KHODADADI A, LIAGHAT G, VAHID S, et al. Ballistic performance of Kevlar fabric impregnated with nanosilica/PEG shear thickening fluid [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 162: 643–652. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.12.121 [27] MA Y, HONG X, LEI Z K, et al. Shear response behavior of STF/Kevlar composite fabric in picture frame test [J]. Polymer Testing, 2022, 113: 107652. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2022.107652 [28] NATH R B, FENNER D N, GALIOTIS C. Elasto-plastic finite element modelling of interfacial failure in model Kevlar 49 fibre-epoxy composites [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 1996, 27(9): 821–832. doi: 10.1016/1359-835X(96)00053-X [29] ZHENHUA Z, LULU L, WEI C, et al. Numerical simulation methodology of multi-layer Kevlar 49 woven fabrics in aircraft engine containment application [J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2019, 24(1): 86–99. doi: 10.1080/13588265.2017.1422374 [30] DETERESA S J, ALLEN S R, FARRIS R J, et al. Compressive and torsional behaviour of Kevlar 49 fibre [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1984, 19(1): 57–72. doi: 10.1007/BF02403111 [31] YEUNG K K H, RAO K P. Mechanical properties of Kevlar-49 fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites [J]. Polymers and Polymer Composites, 2012, 20(5): 411–424. doi: 10.1177/096739111202000501 [32] FISCHER M, SCHMID R. Matrix properties and composite failure [J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 1986, 264(5): 387–398. doi: 10.1007/BF01419542 [33] LEAL A A, DEITZEL J M, GILLESPIE JR J W. Compressive strength analysis for high performance fibers with different modulus in tension and compression [J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2009, 43(6): 661–674. doi: 10.1177/0021998308088589 [34] HUANG J Z, LI Q H, YANG Q, et al. Measurement and research of the transverse mechanical properties of high performance fibers [J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2011, 492: 384–387. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.492.384 [35] XIE Z H, LIU Y Y, LIU L L, et al. Research on the adaptability of STF-Kevlar to ambient temperature under low-velocity impact conditions [J]. Polymer Testing, 2024, 133: 108416. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2024.108416 [36] QIN J B, WANG T W, YUN J, et al. Response and adaptability of composites composed of the STF-treated Kevlar fabric to temperature [J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 260: 113511. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.113511 -






 下载:
下载: