Preparation, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mo Layer and CoCrFeNiMn High Entropy Alloy Hard Coating Layer
-
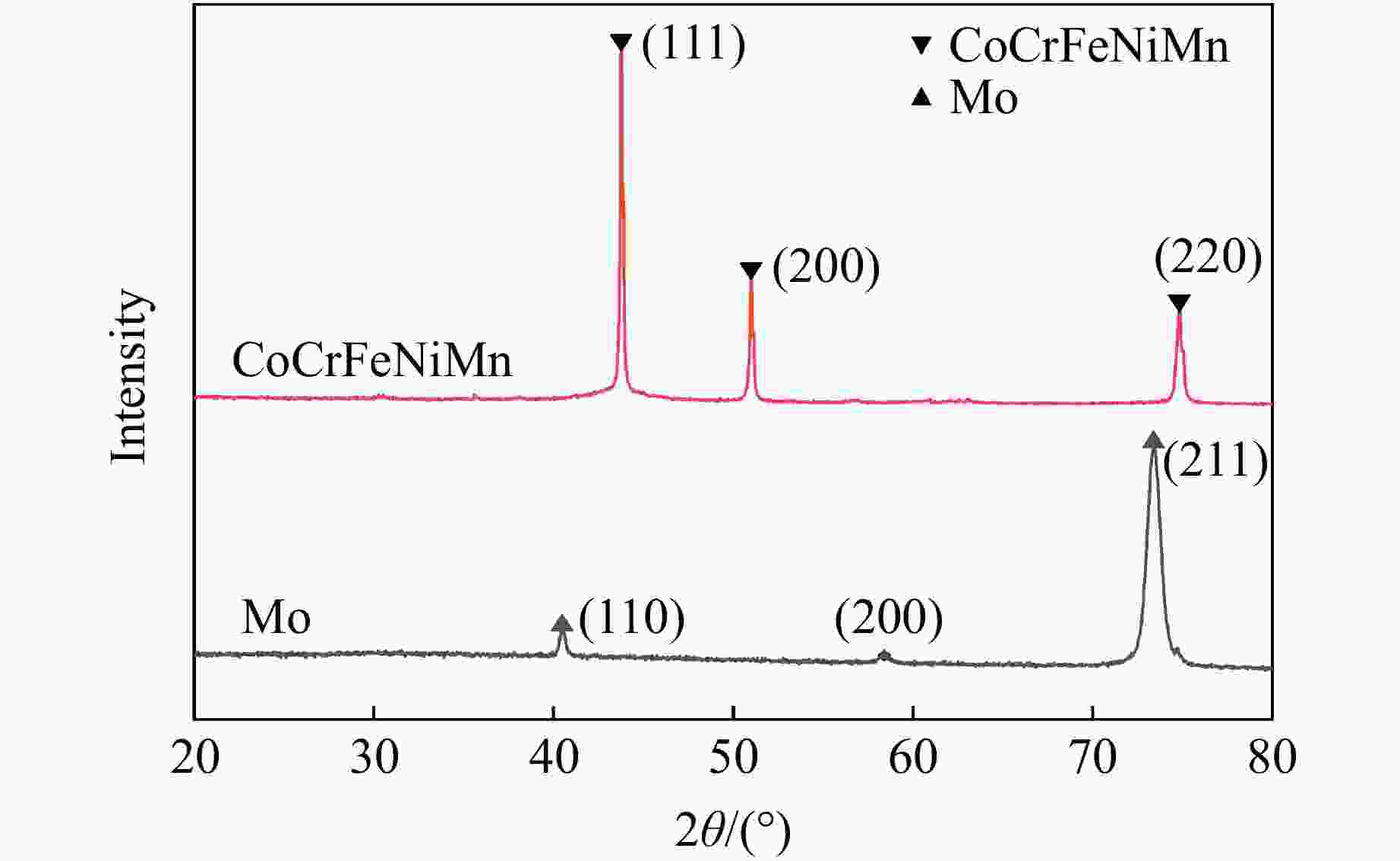
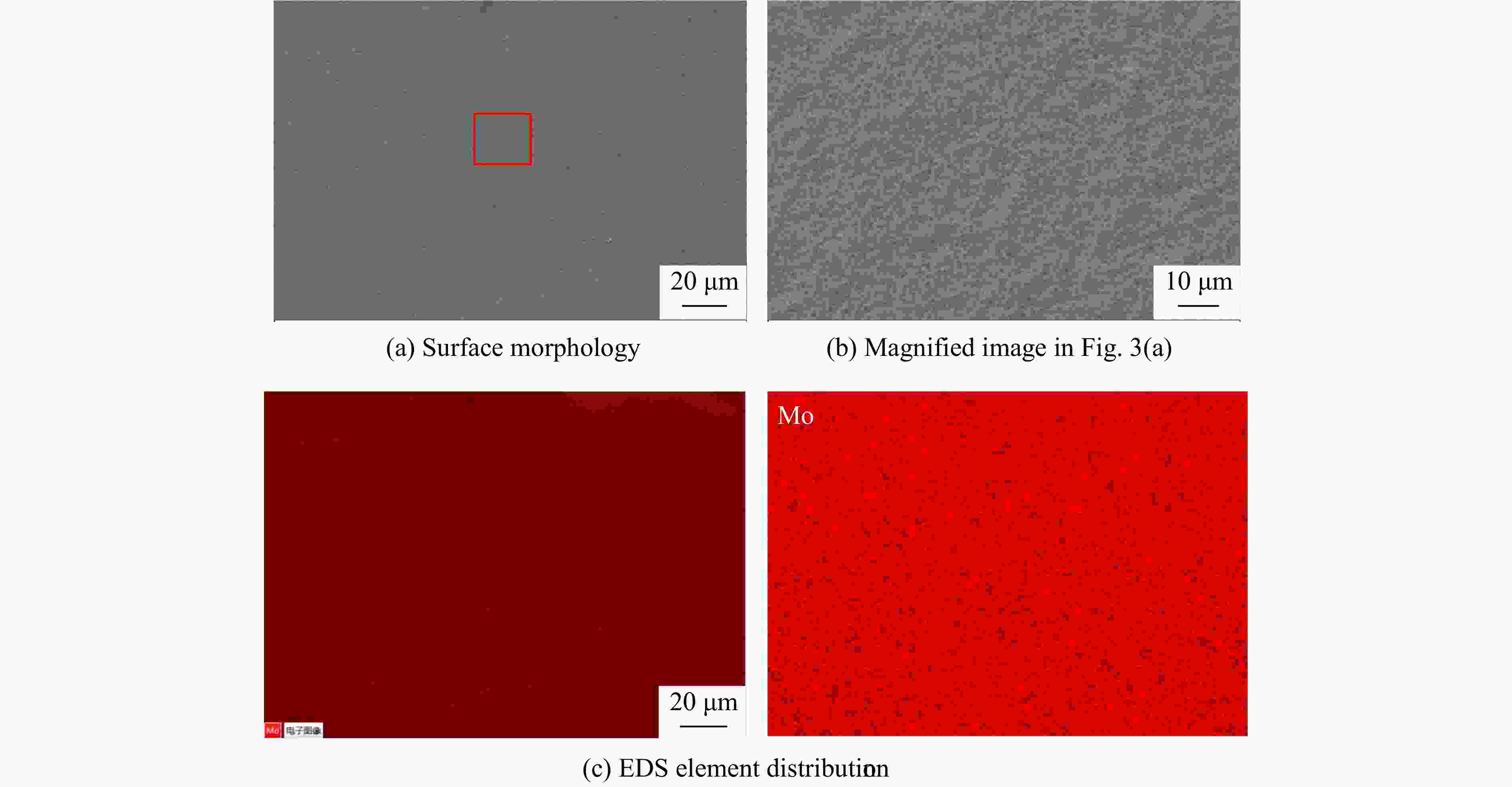
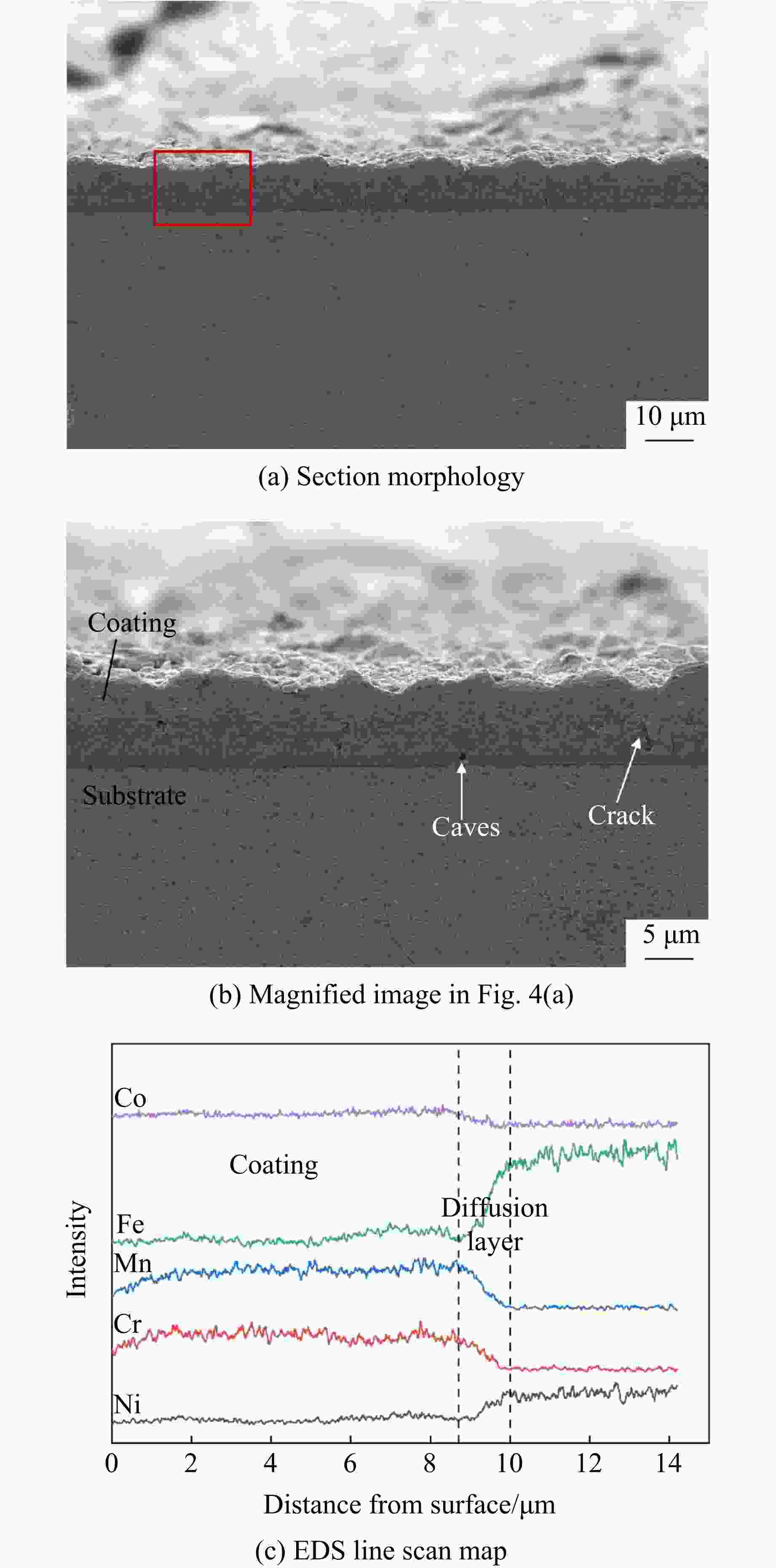
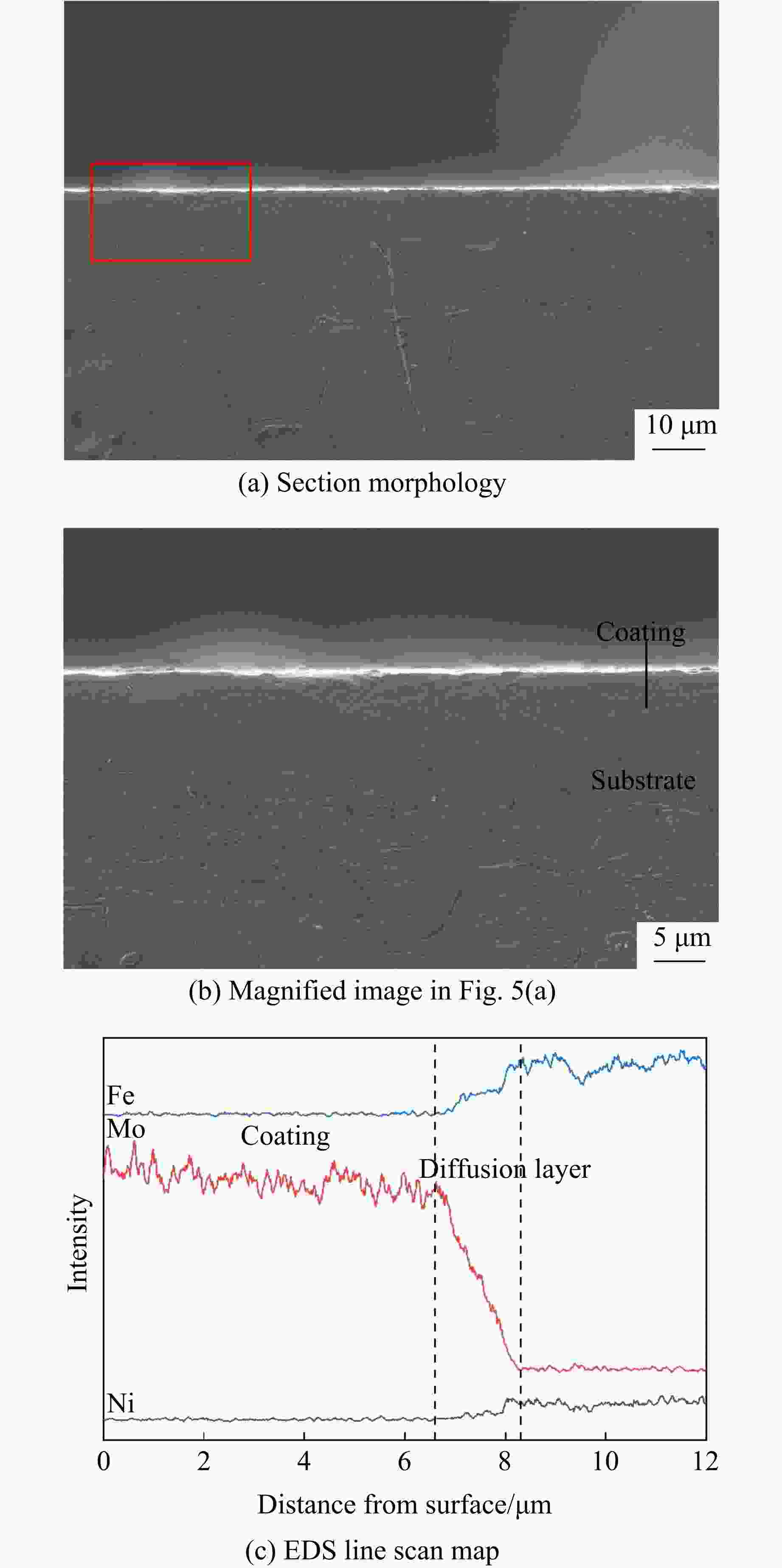
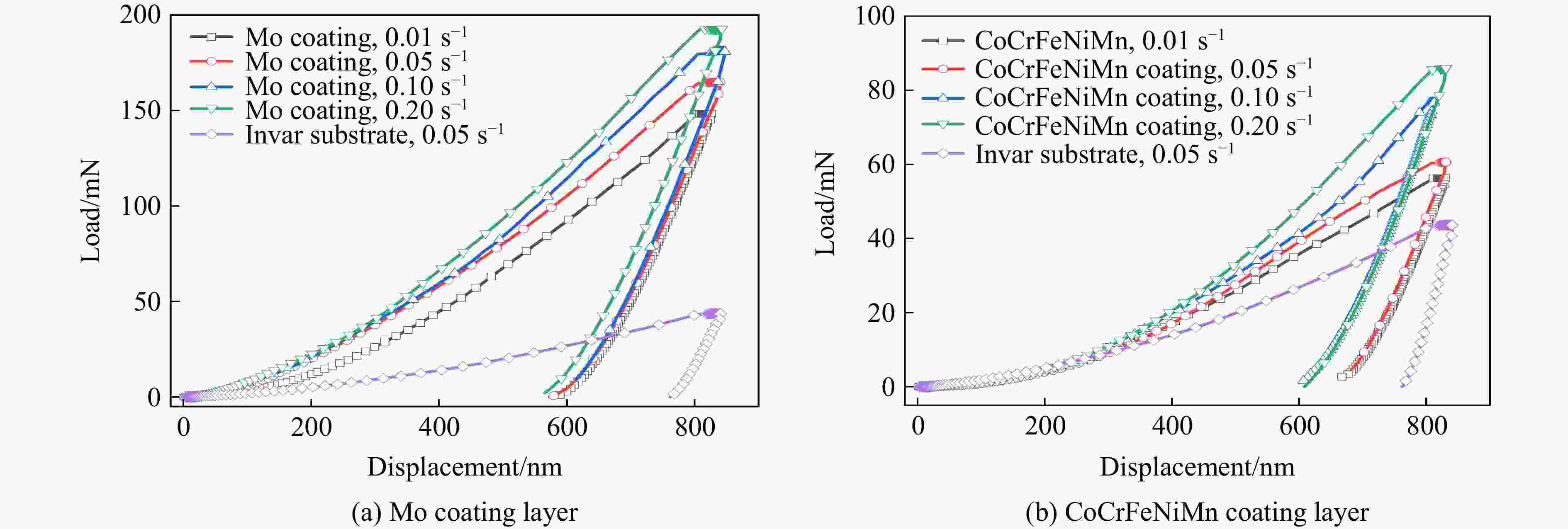
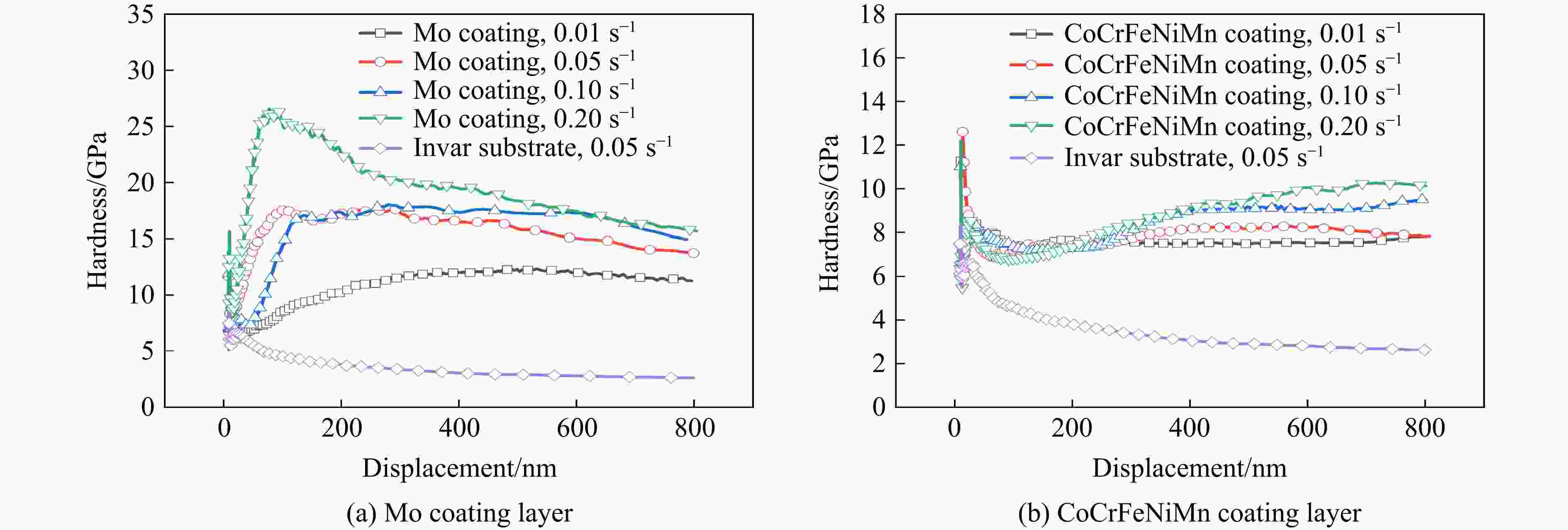
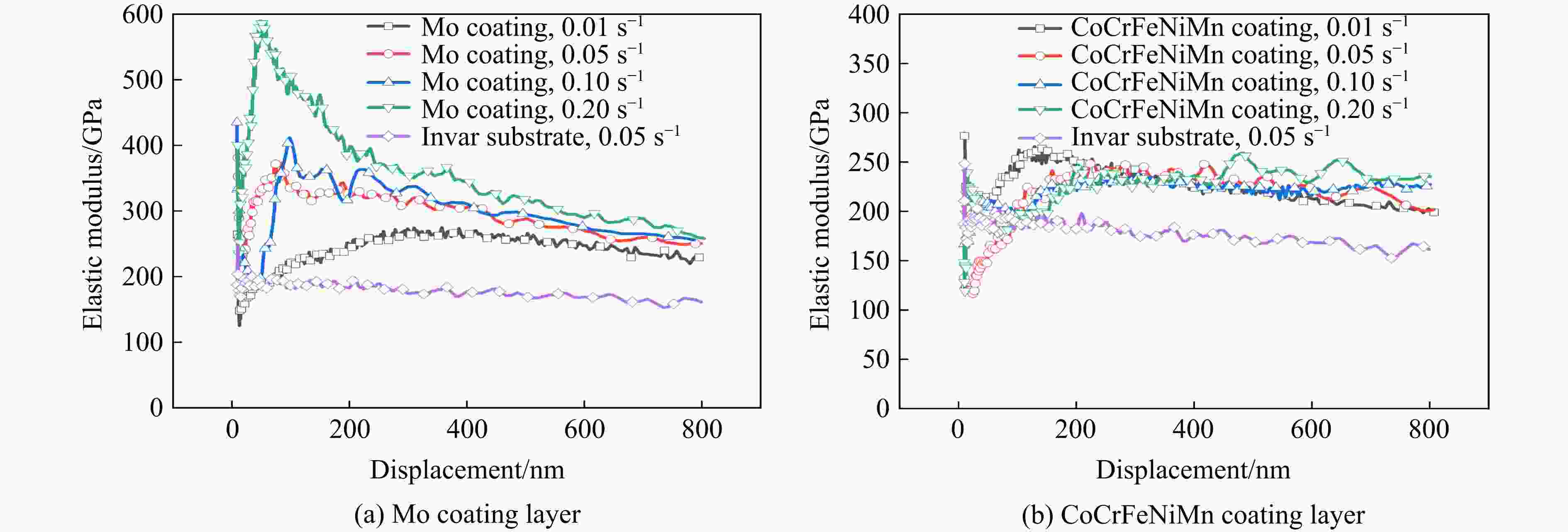
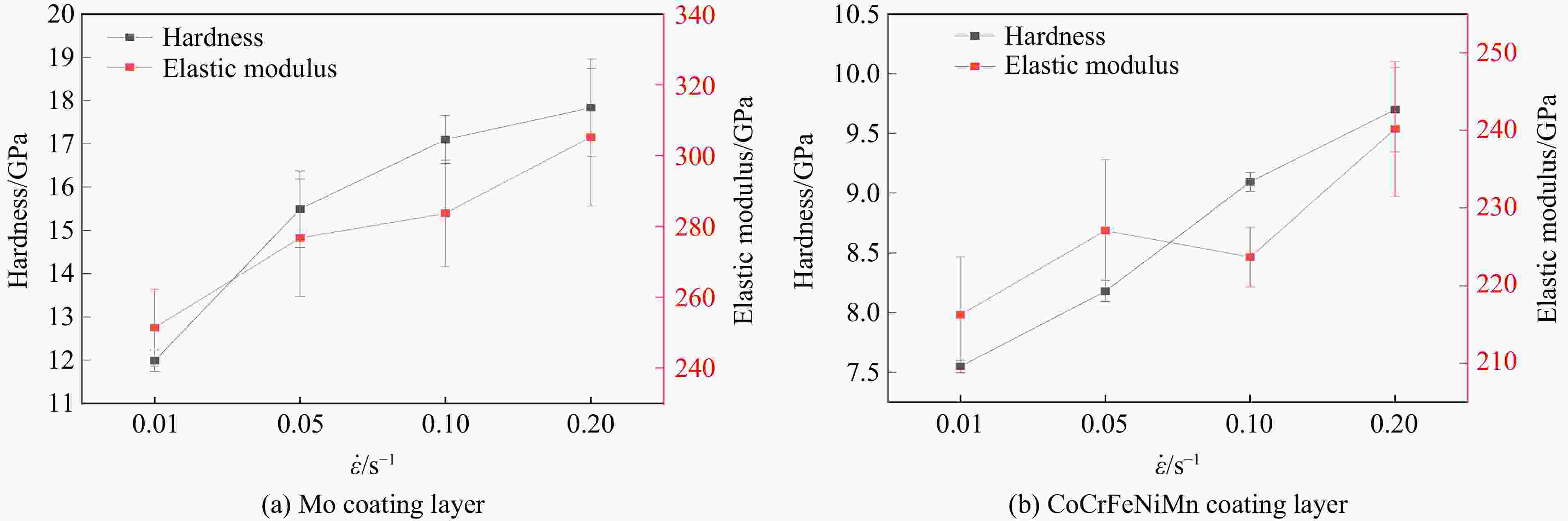
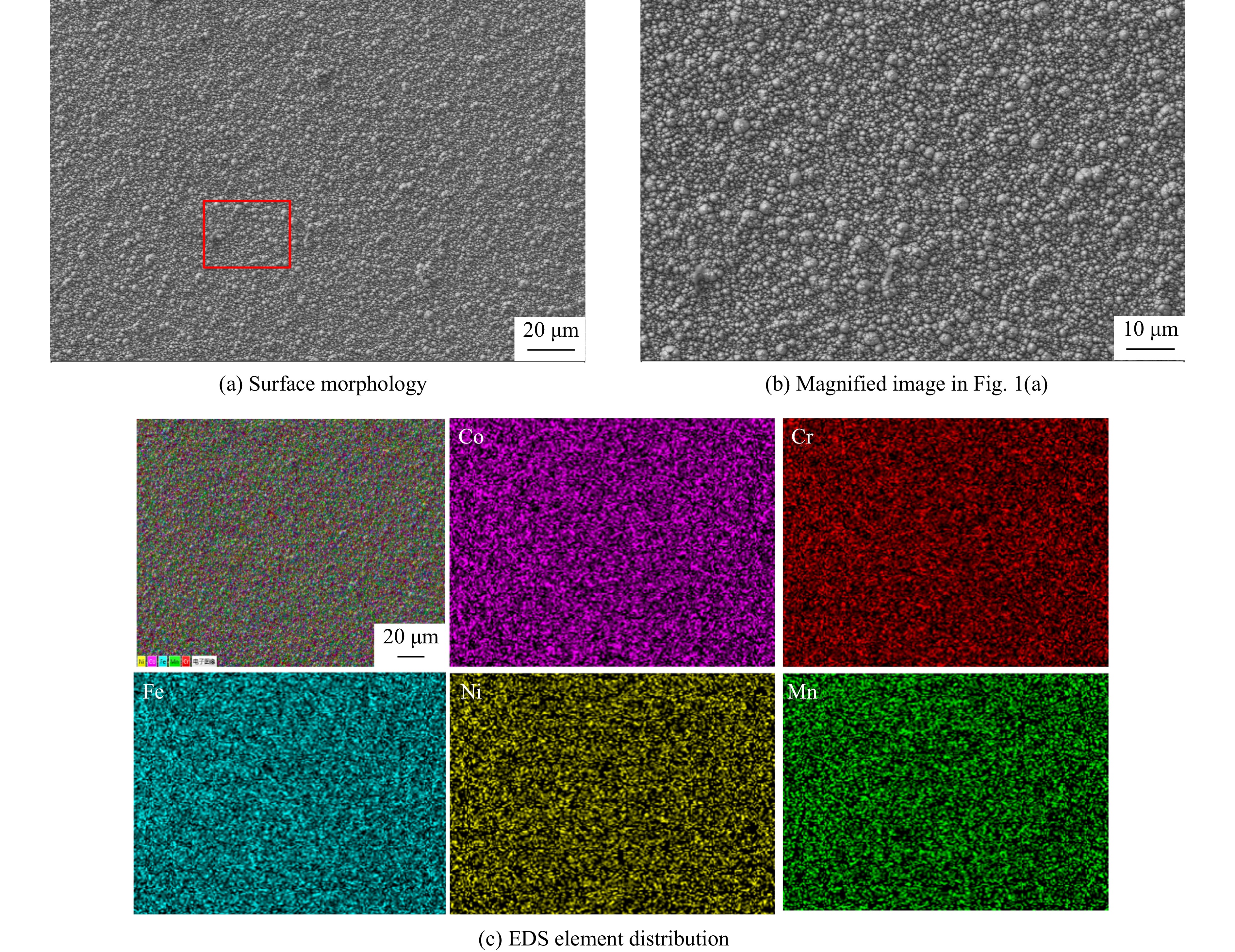
摘要: 为解决Invar合金在实际应用中硬度低、使用寿命有限的问题,采用双辉等离子表面合金化技术(double glow plasma surface alloying,DGPSA)在Invar合金表面制备了Mo及CoCrFeNiMn硬质涂层,使用X射线衍射、扫描电子显微镜和X射线能谱仪研究了2种涂层的相结构、微观结构及元素分布。采用纳米压痕法研究了加载应变率对2种硬质涂层表面硬度、弹性模量和蠕变性能的影响。结果显示:制备的Mo涂层厚度约为8.3 μm,涂层内部致密均匀,涂层具有体心立方结构;制备的CoCrFeNiMn涂层厚度约为10 μm,涂层内部存在少量孔隙,涂层具有面心立方结构。纳米压痕实验测得Mo涂层和CoCrFeNiMn涂层的硬度分别为15.49和8.18 GPa,弹性模量分别为278.70和227.12 GPa,2种硬质涂层均显著提高了Invar合金的表面硬度和弹性模量,且2种涂层均具有足够的韧性。2种涂层的硬度均随应变率的增大而增大,展现出明显的应变率效应,弹性模量基本保持稳定。同时,2种涂层的蠕变行为会受到加载应变率的影响,纳米压痕蠕变行为主要表现为位错运动,Mo涂层的改性效果优于CoCrFeNiMn涂层。
-
关键词:
- 双辉等离子表面合金化技术 /
- 纳米压痕 /
- 应变率效应 /
- 蠕变性能
Abstract: To address the issue of low hardness and limited service life of the Invar alloy in practical applications, this study employs double-glow plasma surface alloying (DGPSA) technique to fabricate Mo and CoCrFeNiMn hard coating layers on the surface of the Invar alloy. The phase structure, microstructure, and element distribution of the two coating layers were investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). The effects of loading strain rate on surface hardness, elastic modulus, and creep behavior of the two hard coating layers were systematically studied via nanoindentation. The thickness of the Mo coating layer is approximately 8.3 μm, with a dense and uniform internal structure and a body-centered cubic (BCC) structure. The thickness of the CoCrFeNiMn coating layer is approximately 10 μm, with some internal porosity and presents a face-centered cubic (FCC) structure. The nanoindentation tests show that the hardness of the Mo and CoCrFeNiMn coating layers is 15.49 and 8.18 GPa, respectively, while their elastic modulus are 278.70 and 227.12 GPa. The two hard coating layers significantly enhance the surface hardness and elastic modulus of the Invar alloy, and exhibit sufficient toughness. Hardness of the two coating layers increases with increasing strain rate, showing a pronounced strain rate sensitivity, while the elastic modulus remains relatively stable. Additionally, the creep behavior of the two coatings layers is influenced by the applied strain rate, with nanoindentation creep primarily governed by dislocation motion. The modification effect of the Mo coating layer is superior to that of the CoCrFeNiMn coating layer. -
表 1 Mo/CoCrCFeNiMn涂层的合金化工艺参数
Table 1. Process parameters of the Mo/CoCrFeNiMn coating layer
Distance between the source
and sample/mmVoltage of the
source/VVoltage of the
cathode/VWorking
pressure/PaHolding
time/hHolding
temperature/℃14–16 −920–−790 −620–−490 30 3 900 表 2 不同应变率下CoCrFeNiMn涂层的总功、弹性功、塑性功和塑性指数
Table 2. Total work, elastic work, plastic work and plastic index of the CoCrFeNiMn coating layer at different strain rates
$\dot \varepsilon $/s−1 Wtot/(10−9 J) We/(10−9 J) Wp/(10−9 J) i 0.01 33.52 10.71 22.81 0.68 0.05 44.38 15.62 28.76 0.65 0.10 46.71 18.96 27.75 0.59 0.20 61.29 24.36 36.93 0.60 表 3 不同应变率下Mo涂层的总功、弹性功、塑性功和塑性指数
Table 3. Total work, elastic work, plastic work and plastic index of the Mo coating layer at different strain rates
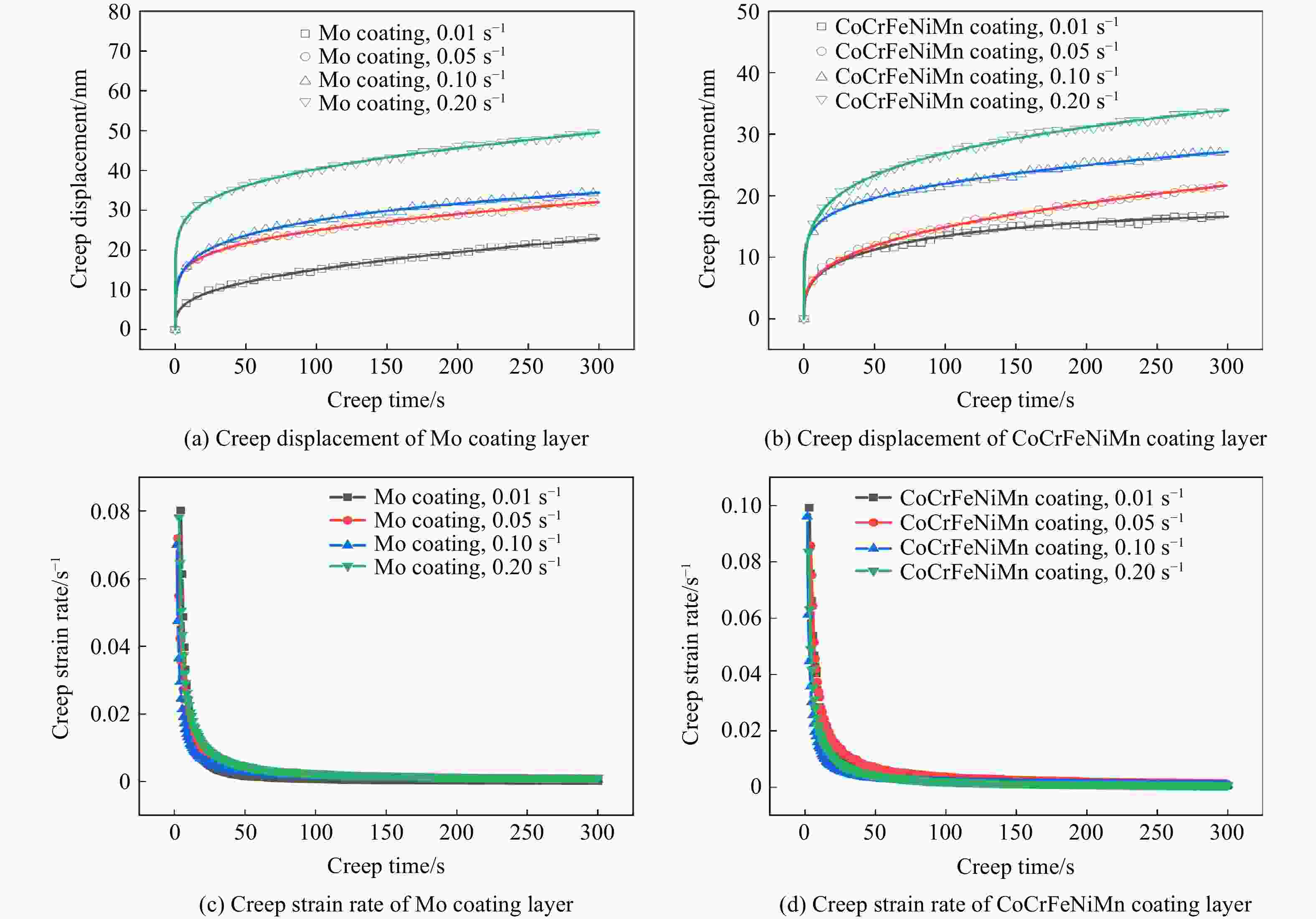
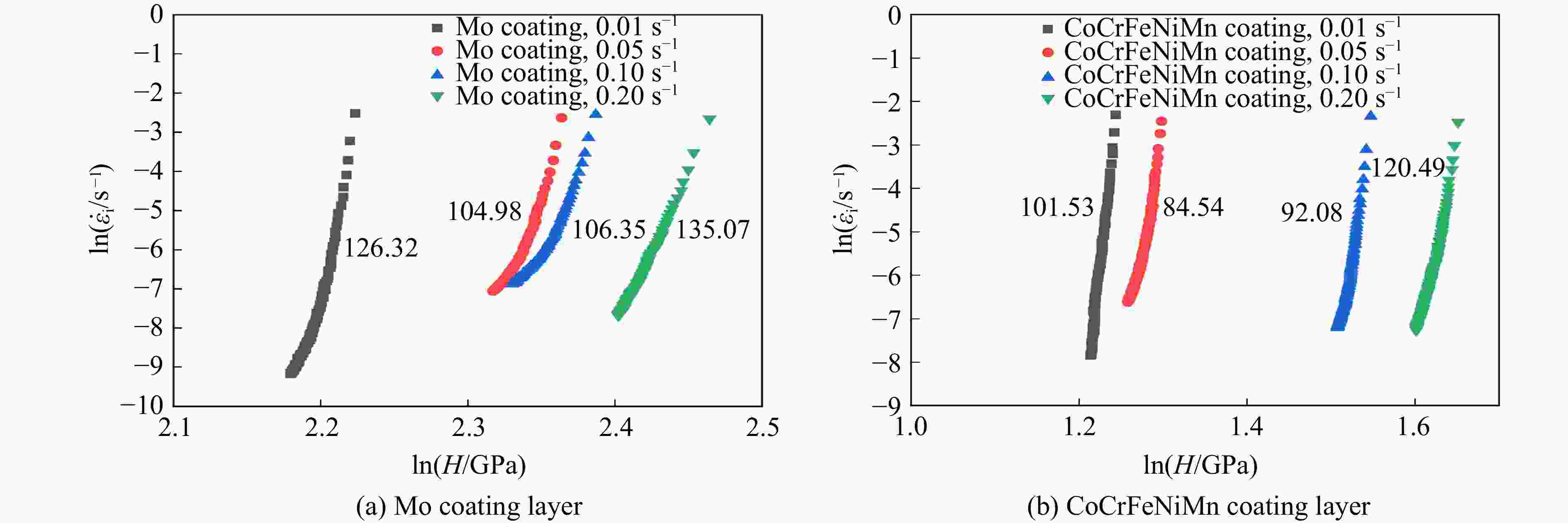
$\dot \varepsilon$/s−1 Wtot/(10−9 J) We/(10−9 J) Wp/(10−9 J) i 0.01 75.81 23.51 52.30 0.69 0.05 78.47 23.62 54.85 0.70 0.10 87.36 31.32 56.04 0.64 0.20 97.32 34.82 62.50 0.64 表 4 不同应变率下 Mo涂层的蠕变位移拟合结果
Table 4. Creep displacement fitting results of the Mo coating layer at different strain rates
$\dot \varepsilon $/s−1 A b k R2 0.01 3.53710 0.29675 0.01199 0.99583 0.05 10.99365 0.16660 0.01215 0.99604 0.10 10.11826 0.21823 − 0.00258 0.99658 0.20 21.23843 0.12993 0.01640 0.99750 表 5 不同应变率下CoCrFeNiMn 涂层的蠕变位移拟合结果
Table 5. Creep displacement fitting results of the CoCrFeNiMn coating layer at different strain rates
$\dot \varepsilon $/s−1 A b k R2 0.01 3.36007 0.32704 − 0.01699 0.98791 0.05 3.57775 0.29970 0.00631 0.99523 0.10 11.15359 0.13845 0.00858 0.99193 0.20 10.30795 0.20805 0.00379 0.99692 -
[1] VAN SCHILFGAARDE M, ABRIKOSOV I A, JOHANSSON B. Origin of the Invar effect in iron-nickel alloys [J]. Nature, 1999, 400(6739): 46–49. doi: 10.1038/21848 [2] 陈昀, 李明光, 张艳红, 等. 因瓦合金发展现状及应用前景 [J]. 机械研究与应用, 2009, 22(4): 9–11, 14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4414.2009.04.003CHEN Y, LI M G, ZHANG Y H, et al. The development actuality and application prospect of Invar alloy [J]. Mechanical Research & Application, 2009, 22(4): 9–11, 14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4414.2009.04.003 [3] 杨博, 李宏, 曹正华. 殷钢在复合材料成形模具中的应用 [J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2010(6): 68–69, 44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2010.06.016YANG B, LI H, CAO Z H. Application of Invar in mould for composites [J]. Composites Science and Engineering, 2010(6): 68–69, 44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2010.06.016 [4] HAN X L, LIU P, SUN D L, et al. The role of incoherent interface in evading strength-ductility trade-off dilemma of Ti2AlN/TiAl composite: a combined in-situ TEM and atomistic simulations [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2020, 185: 107794. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.107794 [5] 陈正涵, 孙晓峰, 李占明, 等. 镍铝青铜基冷喷涂Cu402F与Cu涂层的力学性能 [J]. 材料导报, 2018, 32(10): 1618–1622. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.10.009CHEN Z H, SUN X F, LI Z M, et al. Mechanical properties of cold sprayed Cu402F and Cu coating deposited on nickel aluminum bronze [J]. Materials Reports, 2018, 32(10): 1618–1622. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.10.009 [6] EISSEL A, ENGELKING L, GUSTUS R, et al. Alloy modification for additive manufactured Ni alloy components—part Ⅰ: effect on microstructure and hardness of Invar alloy [J]. Welding in the World, 2023, 67(4): 1049–1057. doi: 10.1007/s40194-023-01510-w [7] 张文凯, 彭放, 郭振堂, 等. 高压烧结镀Cr、Ti膜金刚石/铜复合材料热导率研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2012, 26(3): 306–312. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2012.03.010ZHANG W K, PENG F, GUO Z T, et al. Research on thermal conductivity of diamond with Cr, Ti coating/copper composite materials by sintering under high pressure [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2012, 26(3): 306–312. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2012.03.010 [8] WANG G C, ZHU X B, LIU L Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy subjected to laser cladding [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2025, 34(3): 2484–2497. doi: 10.1007/s11665-024-09200-4 [9] 韩晶晶, 贺端威, 马迎功, 等. 类金刚石微球的高温高压制备 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2017, 31(3): 215–222. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2017.03.002HAN J J, HE D W, MA Y G, et al. Synthesis of diamond-like carbon spheres under high temperature and high pressure [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2017, 31(3): 215–222. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2017.03.002 [10] DU M Z, WANG L L, GAO Z N, et al. Microstructure and element distribution characteristics of Y2O3 modulated WC reinforced coating on Invar alloys by laser cladding [J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2022, 153: 108205. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2022.108205 [11] NAGAYAMA T, YAMAMOTO T, NAKAMURA T, et al. Properties of electrodeposited Invar Fe-Ni alloy/SiC composite film [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2017, 322: 70–75. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.05.023 [12] JIAO Z J, YU C, WANG X M, et al. Corrosion resistance enhanced by an atomic layer deposited Al2O3/micro-arc oxidation coating on magnesium alloy AZ31 [J]. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(3): 5541–5551. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.11.309 [13] 徐重, 张艳梅, 张平则, 等. 双层辉光等离子表面冶金技术 [J]. 热处理, 2009, 24(1): 1–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1690.2009.01.001XU Z, ZHANG Y M, ZHANG P Z, et al. Double glow plasma surface metallurgy technology [J]. Heat Treatment, 2009, 24(1): 1–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1690.2009.01.001 [14] LEI X, LIN N M, YUAN S, et al. Combining laser surface texturing and double glow plasma surface chromizing to improve tribological performance of Ti6Al4V alloy [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2024, 478: 130418. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2024.130418 [15] ZHU X B, DANG B, LI F K, et al. Tribocorrosion behavior of Nb coating deposited by double-glow plasma alloying [J]. Materials Research Express, 2021, 8(1): 016411. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/abdc39 [16] 徐一斐, 张楠, 许培鑫, 等. EHLA原位熔覆Ti(C,B)/Ni60A复合涂层的界面特征与表面磨损机理 [J/OL]. 金属学报 (2024-02-29)[2024-12-26]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1139.TG.20240228.1145.008.html.XU Y F, ZHANG N, XU P X, et al. Interfacial characterization and surface wear mechanism of in-situ Ti(C,B)/Ni60A composite coating prepared by EHLA [J/OL]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (2024-02-29)[2024-12-26]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1139.TG.20240228.1145.008.html. [17] MA Y, ZHANG Y, YAO X H, et al. Characterization of Mo surface modified Ti by indentation techniques [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2013, 226: 75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.03.038 [18] WANG Z, WANG C, ZHAO Y L, et al. Fatigue studies of CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy films using nanoindentation dynamic mechanical analyses [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2021, 410: 126927. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.126927 [19] WANG Y D, WANG H F, JIA Y W, et al. Nano-mechanical properties of Mo coating prepared on Invar alloy substrate by double glow plasma surface alloying [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 447: 128850. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128850 [20] OLIVEIRA J P, PONDER K, BRIZES E, et al. Combining resistance spot welding and friction element welding for dissimilar joining of aluminum to high strength steels [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019, 273: 116192. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.04.018 [21] OLIVER W C, PHARR G M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 1992, 7(6): 1564–1583. doi: 10.1557/JMR.1992.1564 [22] YAGHOOBI M, VOYIADJIS G Z. The effects of temperature and strain rate in fcc and bcc metals during extreme deformation rates [J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 151: 1–10. [23] XING X G, WANG Y S, XIAO G S, et al. Rate-dependent indentation size effect on hardness and creep behavior of a titanium metallization film on alumina substrate [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 15: 4662–4671. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.10.101 [24] XIAO G S, YUAN G Z, JIA C N, et al. Strain rate sensitivity of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder investigated by nanoindentation [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 613: 336–339. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.06.113 [25] LIU E Q, XIAO G S, JIA W F, et al. Strain-induced phase transformation behavior of stabilized zirconia ceramics studied via nanoindentation [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2017, 75: 14–19. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.07.006 [26] ZHAI H M, MA X, CHENG B, et al. Room temperature nanoindentation creep behavior of detonation sprayed Fe-based amorphous coating [J]. Intermetallics, 2022, 141: 107426. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2021.107426 [27] LI H, NGAN A H W. Size effects of nanoindentation creep [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2004, 19(2): 513–522. doi: 10.1557/jmr.2004.19.2.513 [28] MAYO M J, NIX W D. A micro-indentation study of superplasticity in Pb, Sn, and Sn-38 wt% Pb [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1988, 36(8): 2183–2192. doi: 10.1016/0001-6160(88)90319-7 [29] LLOYD G E. Creep of crystals: high-temperature deformation processes in metals, ceramics and minerals: Poirier, J. -P. 1985. Cambridge University Press. 260 pp. price: paperback £10.95 [J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1986, 8(2): 213–214. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(86)90116-1 [30] MA X K, LI F G, ZHAO C, et al. Indenter load effects on creep deformation behavior for Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al alloy at room temperature [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 709: 322–328. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.175 [31] LANGDON T G. Identifiying creep mechanisms at low stresses [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2000, 283(1/2): 266–273. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(00)00624-9 [32] MAHMUDI R, ROUMINA R, RAEISINIA B. Investigation of stress exponent in the power-law creep of Pb-Sb alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2004, 382(1/2): 15–22. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.05.078 [33] SHARMA G, RAMANUJAN R V, KUTTY T R G, et al. Hot hardness and indentation creep studies of a Fe-28Al-3Cr-0.2C alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2000, 278(1/2): 106–112. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(99)00590-0 [34] DE LA TORRE A, ADEVA P, ABALLE M. Indentation creep of lead and lead-copper alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1991, 26(16): 4351–4354. doi: 10.1007/BF00543650 -






 下载:
下载: