Effect of Explosive Impact on Ignition Head Damage and Ignition Time of Electronic Detonator
-
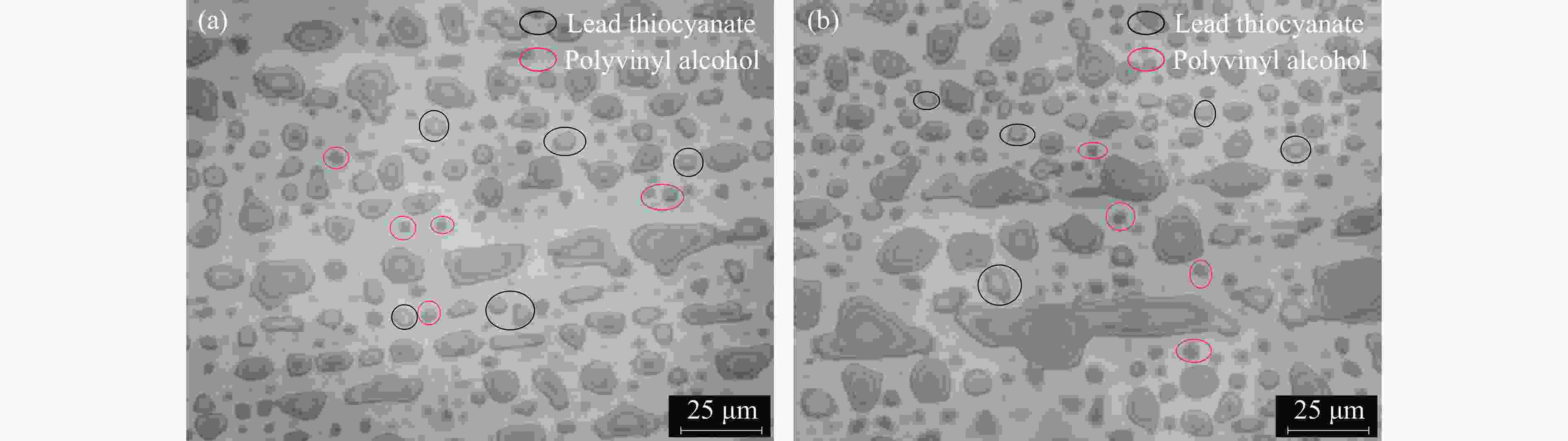
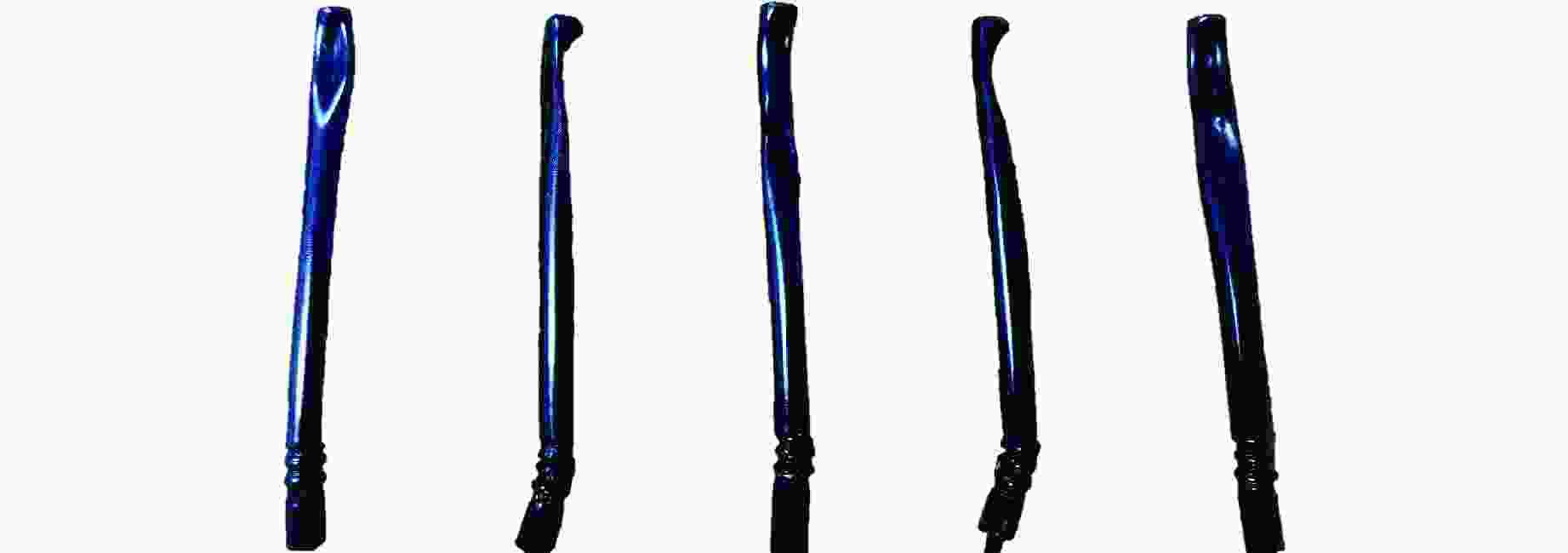
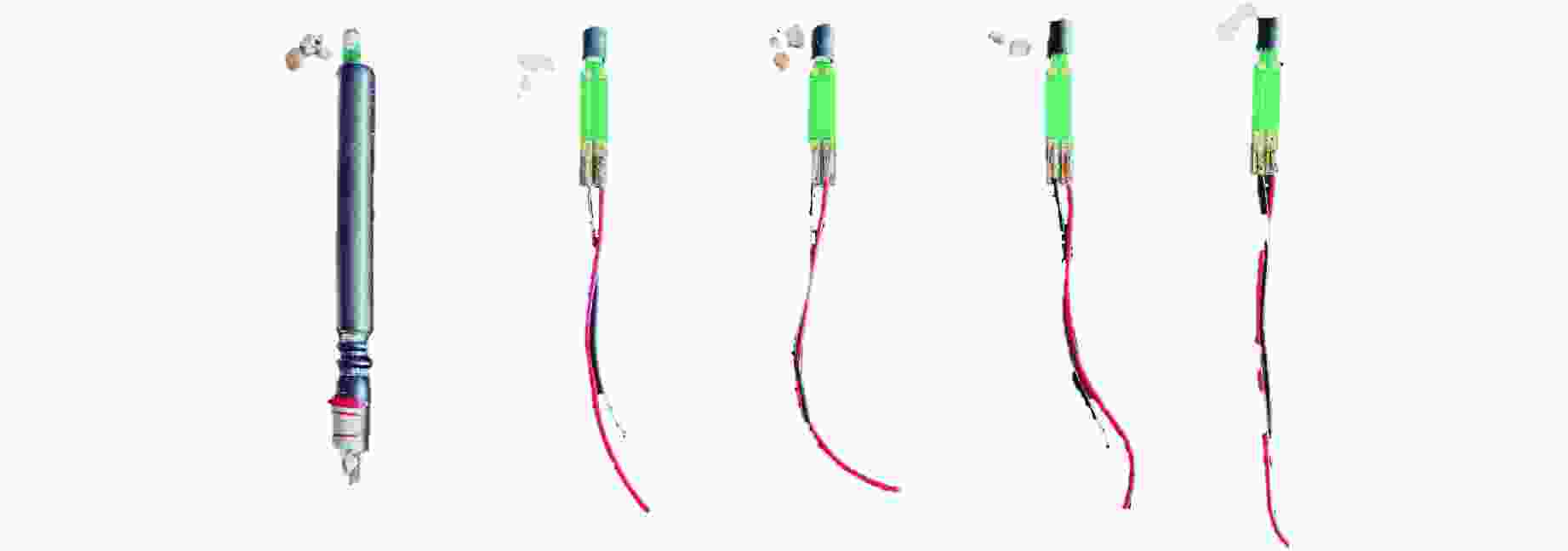
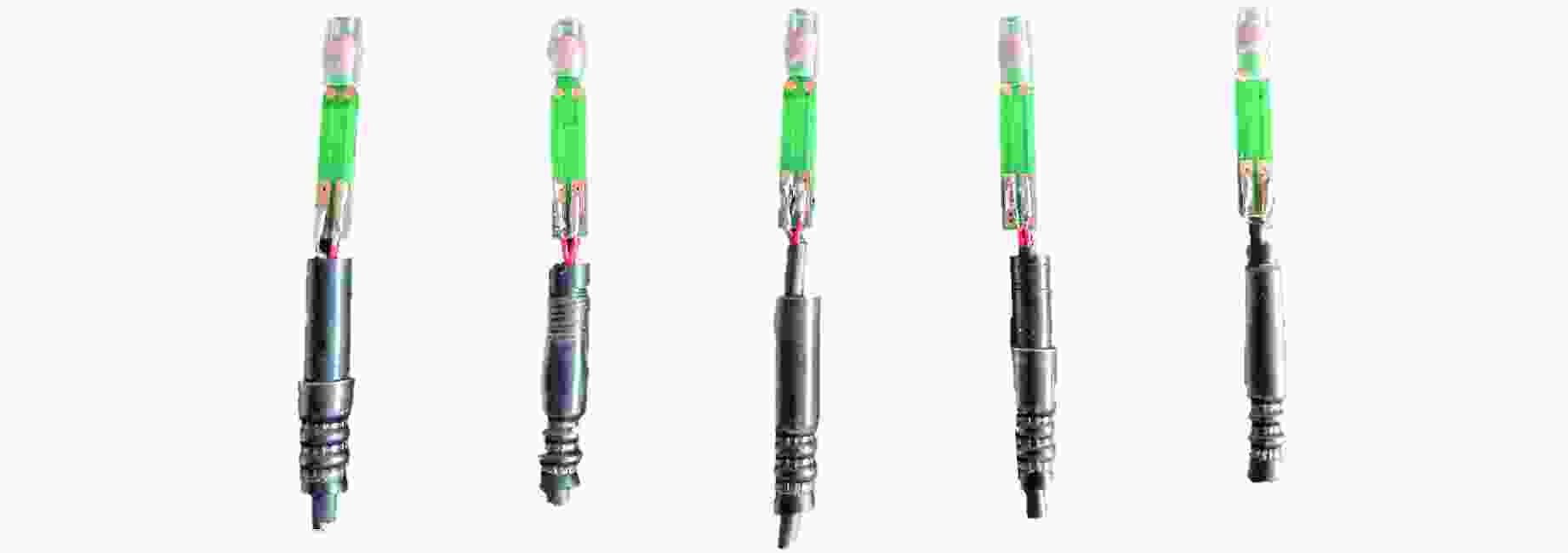
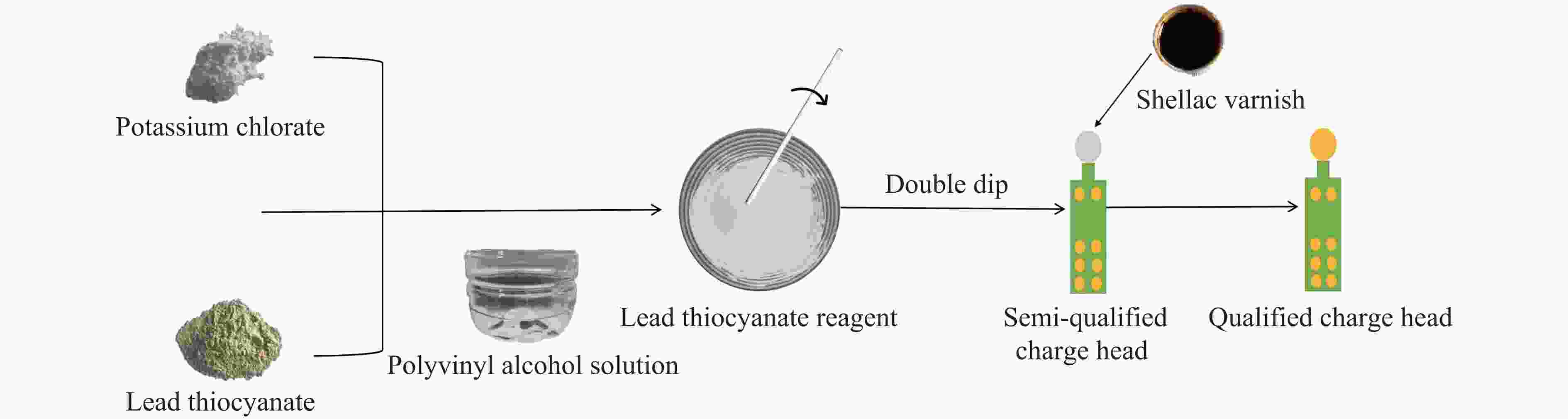
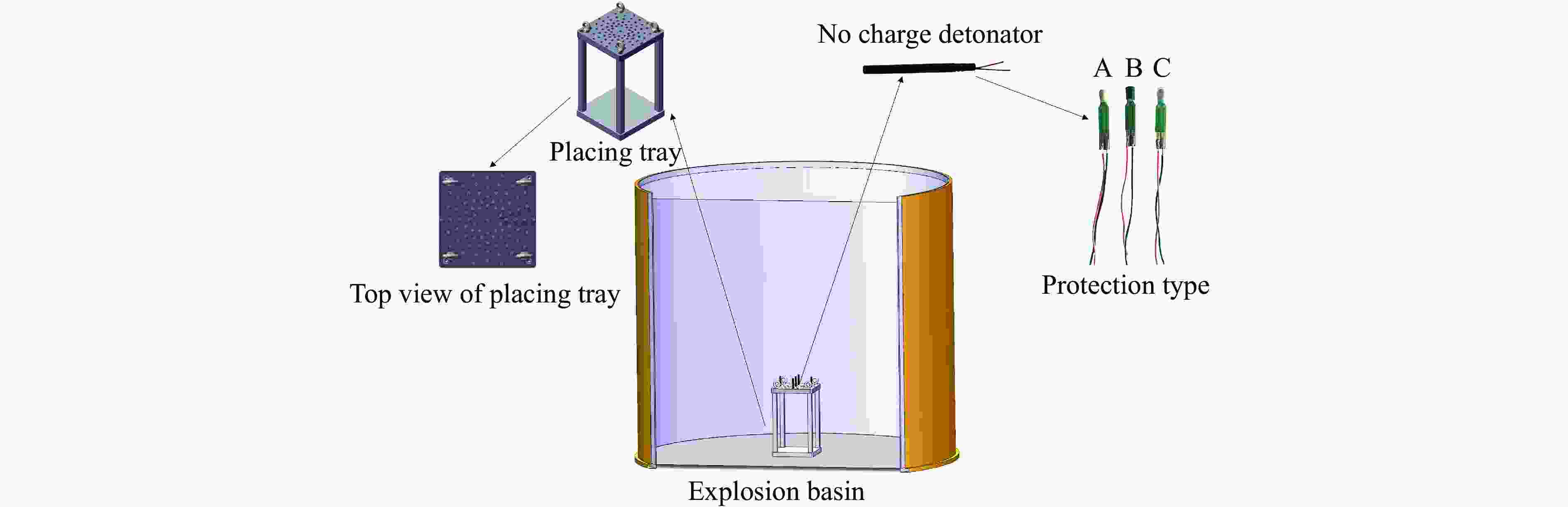
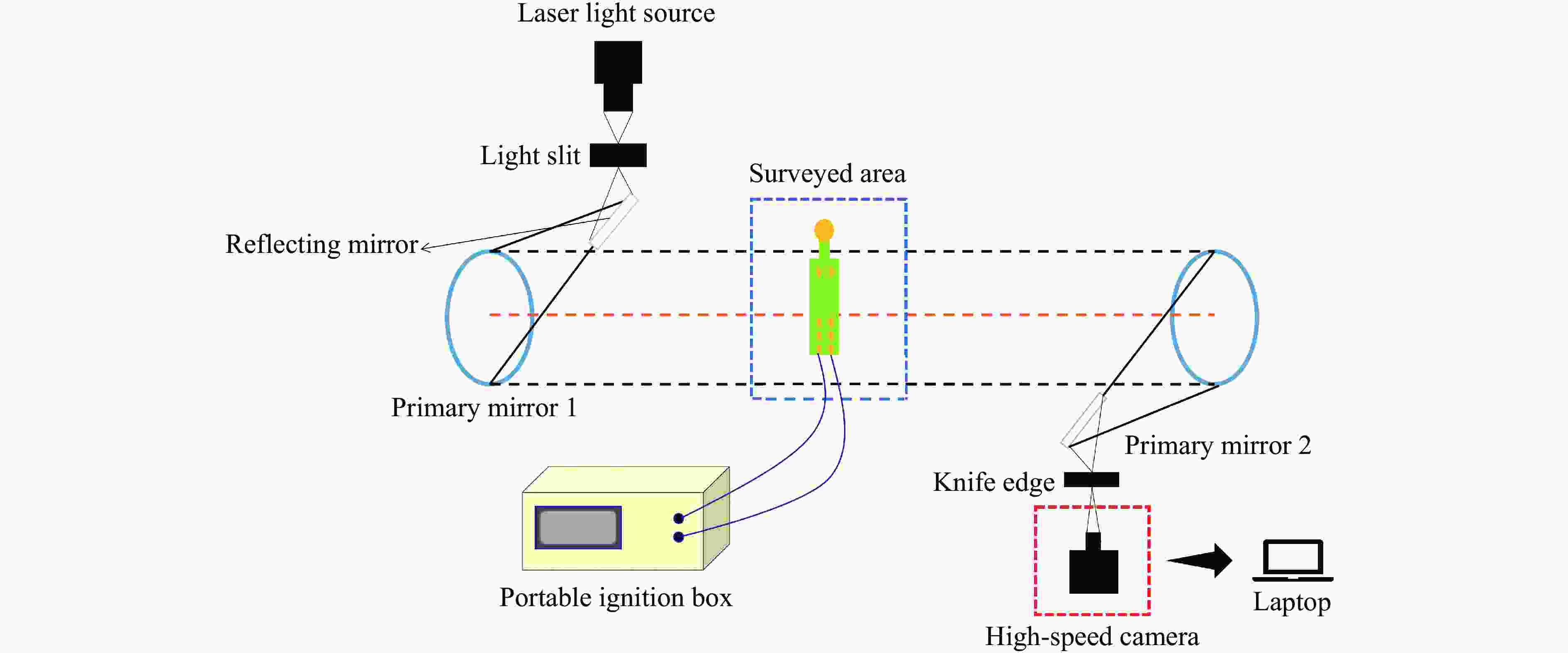
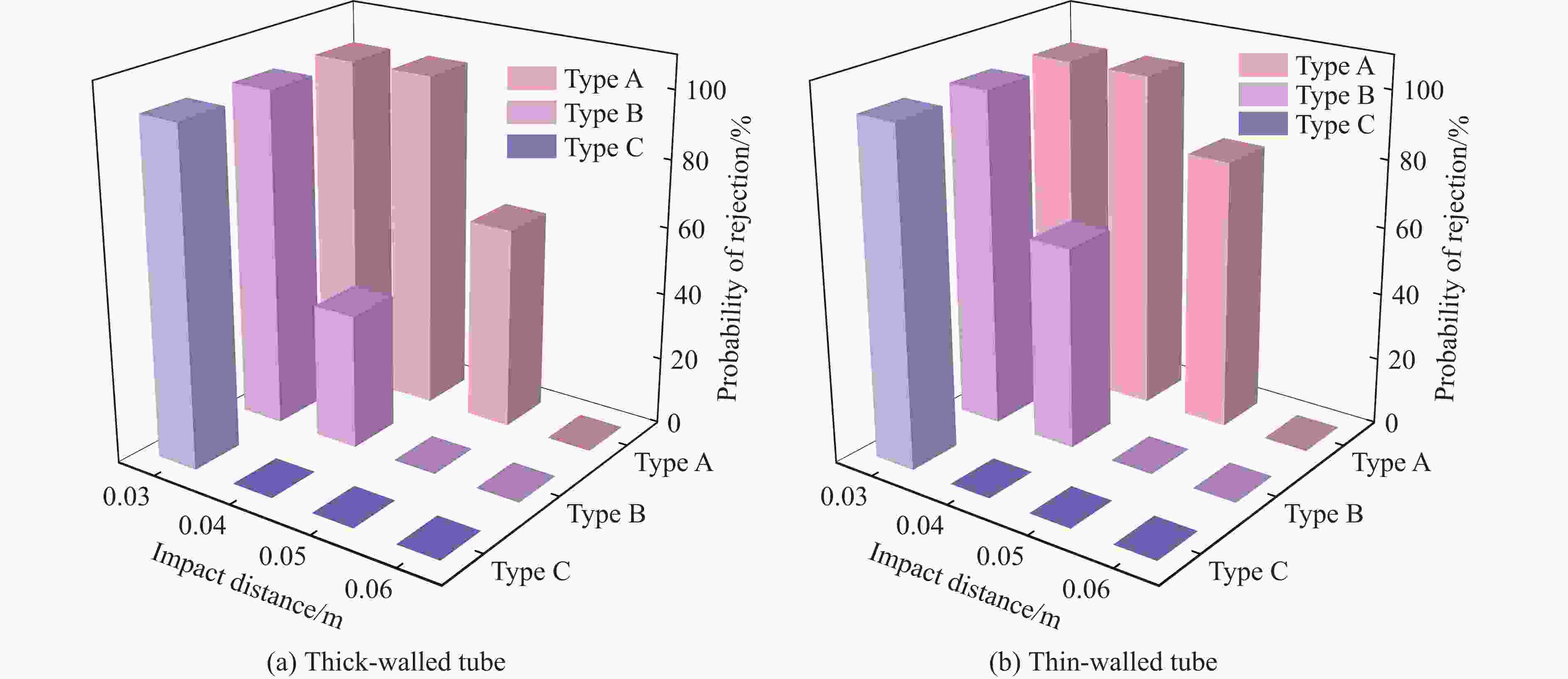
摘要: 为研究爆炸冲击作用对电子雷管引火药头损伤及发火时间的影响,制备了硫氰酸铅系引火药剂,并对其进行微观结构观测,对蘸药的引火药头样品进行发火电压测定以检验其质量。通过水下爆炸测试方法对无基础装药的雷管进行冲击,拆解冲击后的雷管,观察引火药头的损伤情况,并利用高速纹影系统对无明显损伤的引火药头进行发火试验。结果表明:无防护型、热缩型、硅胶型引火药头抗冲击的极限压力分别为98.22、117.12、156.27 MPa,3种防护型引火药头在高于极限压力时均会出现不同程度的损伤。在0.38和0.50 mm 2种管壳壁厚下,3种防护型引火药头的拒爆率均呈现随冲击强度降低而变小的趋势,其中,硅胶型引火药头的防护效果优于热缩型,无防护型引火药头的效果最差。在98.22 MPa下,无防护型引火药头因高压气体使药头碎片飞散,导致用于发火的药剂质量减少,发火剧烈程度减弱,最终导致发火时间明显缩短。热缩型引火药头在117.12 MPa下的发火时间较未冲击下增加8.30%,可能影响电子雷管的延期精度。硅胶型引火药头在156.27 MPa下的发火时间几乎不受影响。Abstract: In order to study the effect of explosion impact on the damage and ignition time of the ignition head of the electronic detonator, the lead thiocyanate ignition agent was prepared and its microstructure was observed, and the ignition voltage of the ignition head sample dipped in was measured to test its quality. The underwater explosion method was used to impact the sample detonator without basic charge, and the damage of the ignition head was observed by disassembling the impact detonator, and the high-speed schlieren system was used to carry out the ignition test on the ignition head without obvious damage. The results show that the ultimate pressures of the unguarded, heat-shrinkable and silica gel ignition heads were 98.22, 117.12 and 156.27 MPa, respectively. The three types of protection ignition heads were damaged to varying degrees above the ultimate pressure. Under the wall thickness of 0.38 and 0.50 mm, the explosion miss-fire rate of the three types of protective ignition head showed a trend of decreasing with the decrease of impact strength, and the protective effect of silicone type was better than heat shrinkable type, and the effect of non-protective type was the worst. Under 98.22 MPa, the high pressure gas causes the fragments of the ignition head to fly away, resulting in the reduction of the quality of the ignition head used for ignition, the reduction of the intensity of ignition, and finally the obvious shortening of the ignition time. The ignition time of the heat-shrinkable ignition head at 117.12 MPa was increased by 8.30% compared with no impact, which may affect the delay accuracy of the electronic detonator. The ignition time of the silicone ignition head at 156.27 MPa was almost unaffected.
-
Key words:
- electronic detonator /
- ignition head /
- underwater explosion /
- impact resistance /
- ignition time
-
表 1 发火电压升降法试验结果
Table 1. Test results of ascending and descending ignition voltage method
Voltage/V i ni $n' _i $ ini i2ni $in' _i$ $i^2 in' _i $ 10.5 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 10.7 1 3 6 3 3 6 6 10.9 2 6 6 12 24 12 24 11.1 3 5 11 15 45 33 99 11.3 4 10 0 40 160 0 0 表 2 厚壁管样品的冲击试验结果
Table 2. Impact test results of thick-walled tube samples
Impact
distance/mOverpressure/
MPaProtection
typeNumber of impact test Totality Over-
grindingMild
grindingPartial
ruptureNo obvious
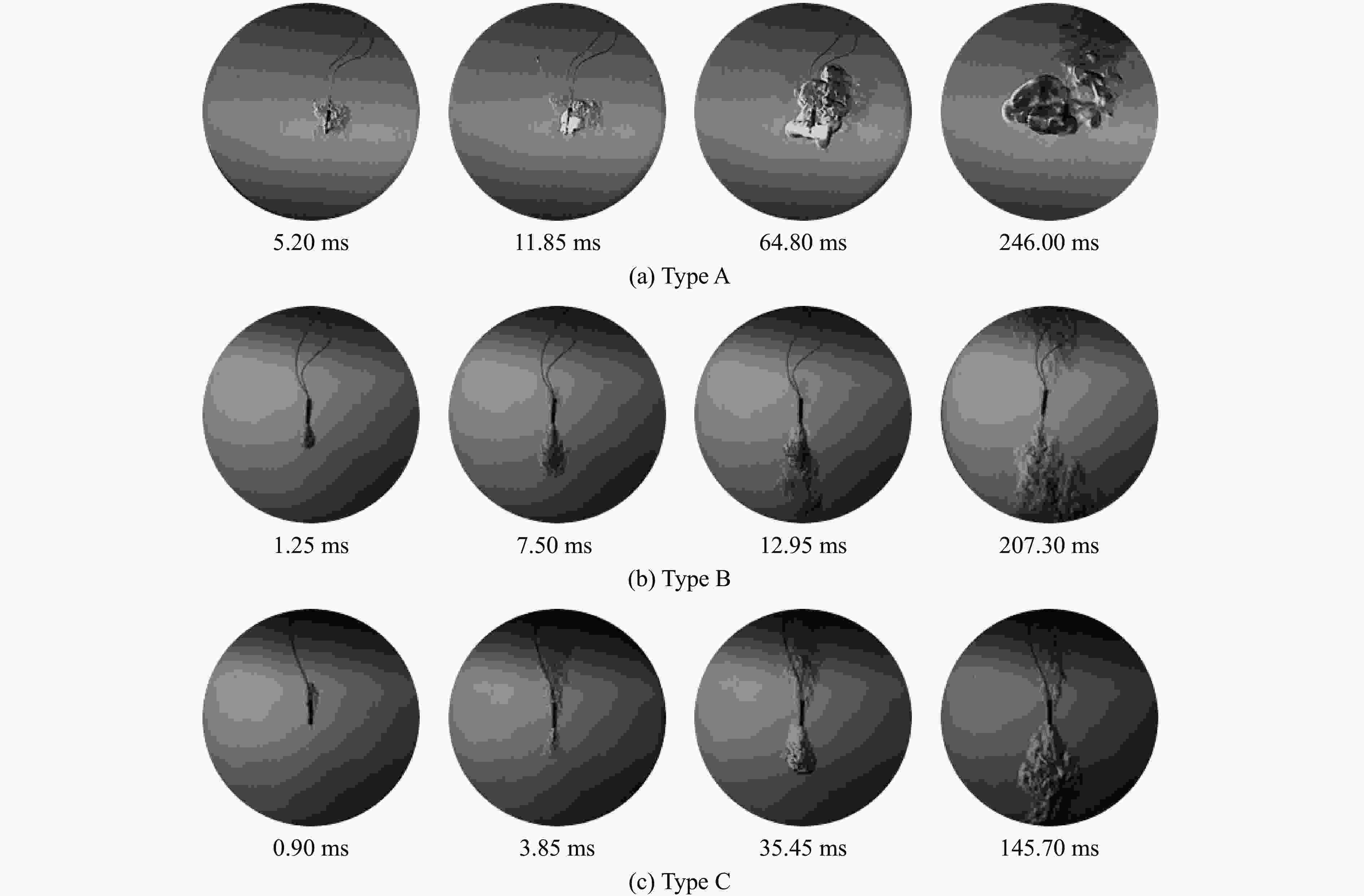
damage0.03 221.89 A 10 10 0 0 0 B 10 0 4 2 4 C 10 0 0 4 6 0.04 156.27 A 10 0 10 0 0 B 10 0 0 4 6 C 10 0 0 0 10 0.05 117.12 A 10 0 4 0 6 B 10 C 10 0.06 98.22 A 10 0 0 0 10 B 10 C 10 表 3 薄壁管样品的冲击试验结果
Table 3. Impact test results of thin-walled tube samples
Impact
distance/mOverpressure/
MPaProtection
typeNumber of impact test Totality Compression
ignitionOver-
grindingMild
grindingPartial
ruptureNo obvious
damage0.03 221.89 A 10 10 0 0 0 0 B 10 0 10 0 0 0 C 10 0 0 10 0 0 0.04 156.27 A 10 0 10 0 0 0 B 10 0 0 0 6 4 C 10 0 0 0 0 10 0.05 117.12 A 10 0 0 0 8 2 B 10 C 10 0.06 98.22 A 10 0 0 0 0 10 B 10 C 10 表 4 冲击后各药头的发火时间
Table 4. Ignition time of each charge head after impact
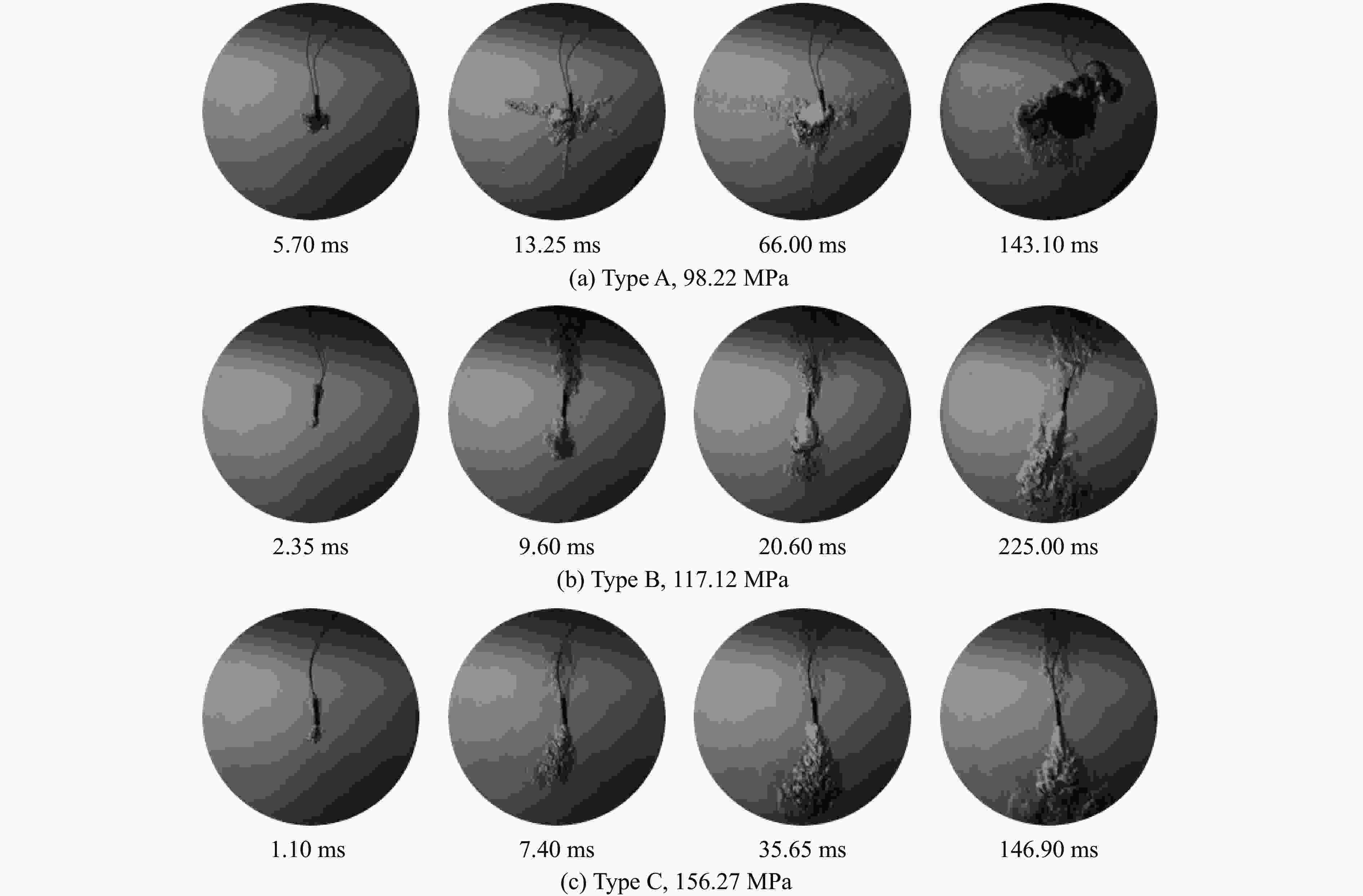
Test No. Ignition time/ms Type A,98.22 MPa Type B,117.12 MPa Type C,156.27 MPa 1 143.10 225.00 146.90 2 147.40 223.40 146.20 3 145.60 225.50 148.30 4 148.30 227.20 147.50 5 140.50 221.80 146.10 Mean value 144.98 224.58 147.00 Rate of change/% 41.10 8.30 0.89 -
[1] 王勉, 王建国, 马军, 等. 小断面巷道精确延时逐孔起爆技术研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(3): 245–256. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.0418WANG M, WANG J G, MA J, et al. Research on precise delay hole-by-hole detonation technology in small section roadway [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(3): 245–256. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.0418 [2] 杨文, 岳彩新, 宋家良, 等. 工业电子雷管抗冲击性能试验研究 [J]. 火工品, 2022(2): 16–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2022.02.004YANG W, YUE C X, SONG J L, et al. Experimental research on the impact resistance of industrial electronic detonators [J]. Initiators & Pyrotechnics, 2022(2): 16–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1480.2022.02.004 [3] 王家乐, 李洪伟, 王小兵, 等. 冲击载荷作用下钽电容的电压瞬变特性及微观机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(4): 043101. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0232WANG J L, LI H W, WANG X B, et al. Voltage transient characteristics and microscopic mechanism of tantalum capacitors under impact load [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(4): 043101. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0232 [4] 李洪伟, 王家乐, 梁昊, 等. 爆炸冲击对电子雷管发火电容释能特性的影响 [J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(3): 227–235.LI H W, W J L, LIANG H, et al. Effect of explosion shock on the energy release characteristics of ignition capacitance of electronic detonator [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(3): 227–235. [5] 杨文. 工业电子雷管抗冲击性能研究 [D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2022.YANG W. Research on impact resistance performance of industrial electronic detonator [D]. Beijing: China Coal Research Institute, 2022. [6] 韩体飞, 钟帅, 张涵, 等. 药头质量分布对电引火药头发火时间精度的影响 [J]. 爆破器材, 2015, 44(1): 37–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2015.01.009HAN T F, ZHONG S, ZHANG H, et al. Effect of the fusehead mass distribution on ignition delay precision of the electric fusehead [J]. Explosive Materials, 2015, 44(1): 37–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2015.01.009 [7] 成一, 陈守文. 电点火头发火过程的时间结构的研究 [J]. 爆破器材, 2001, 30(5): 22–24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2001.05.006CHENG Y, CHEN S W. Study on the time structure of electric ignition process in fuse head [J]. Explosive Materials, 2001, 30(5): 22–24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2001.05.006 [8] 张文洲, 孙磊. 钛粉对电子雷管电引火药头性能的影响 [J]. 爆破器材, 2019, 48(2): 43–46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2019.02.008ZHANG W Z, SUN L. Effect of titanium powder on performances of electric fusehead of electric detonator [J]. Explosive Materials, 2019, 48(2): 43–46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2019.02.008 [9] 欧仙荣. 硝酸肼镍-铅丹-硅系电引火药头性能研究 [C]//爆破器材——2013年民爆技术论坛论文集. 南京: 中国兵工学会民用爆破器材专业委员会, 2013: 172–178.OU X R. Study on the performance of hydrazine nitrate-nickel-lead-silicon electric ignition head [C]//Proceedings of the 2013 Civil Explosive Technology Forum. Nanjing: Civil Explosives Committee of China Ordnance Society, 2013: 172–178. [10] MATSUI K, MATSUURA Y, TOKUDOME S, et al. Function test of experimental system to obtain laser ignition characteristics of low-temperature boron/potassium nitrate [J]. Journal of Evolving Space Activities, 2023, 1: 17. doi: 10.57350/jesa.17 [11] LI Y F, WANG J, LIU H Y, et al. Combustion properties of mg-based ignition charge using Mg-Gd alloy powder as the fuel [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 441: 135633. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.135633 [12] ZHANG X H, SHANG W, LIU Q L. Study on the improvement design and ignition performance of B/KNO3 nitrate delay ignition charge under high overload [J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 804: 042042. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/804/4/042042 [13] 林尚剑, 王金相, 马腾, 等. 水下多点爆炸冲击波叠加效应研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(Suppl 1): 39–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.S1.006LIN S J, WANG J X, MA T, et al. Superimposed effect of shock waves of underwater explosion [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(Suppl 1): 39–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.S1.006 [14] 张轶凡, 刘亮涛, 王金相, 等. 水下爆炸冲击波和气泡载荷对典型圆柱壳结构的毁伤特性 [J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(2): 345–359. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0598ZHANG Y F, LIU L T, WANG J X, et al. Damage characteristics of underwater explosion shock wave and bubble load on typical cylindrical shell structure [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(2): 345–359. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0598 [15] HU H W, SONG P, GUO S F, et al. Shock wave and bubble characteristics of underwater array explosion of charges [J]. Defence Technology, 2022, 18(8): 1445–1453. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2021.05.020 [16] RAJASEKAR J, KIM T H, KIM H D. Visualization of shock wave propagation due to underwater explosion [J]. Journal of Visualization, 2020, 23(5): 825–837. doi: 10.1007/s12650-020-00664-9 [17] 郑星, 黄海莹, 毛勇建, 等. 基于高速纹影技术的爆炸冲击波图像测量研究 [J]. 光学 精密工程, 2022, 30(18): 2187–2194. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223018.2187ZHENG X, HUANG H Y, MAO Y J, et al. Research on image measurement of explosion shock wave based on high speed schlieren technology [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(18): 2187–2194. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223018.2187 [18] 宫翔飞, 刘文韬, 张树道, 等. 水下爆炸近场峰值压力的数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(4): 041409. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0262GONG X F, LIU W T, ZHANG S D, et al. Numerical simulation of peak pressure in near-field underwater explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(4): 041409. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0262 [19] 周恩, 李洪伟, 孙翼, 等. 电子雷管储能电容和点火药头的抗冲击性能研究 [J]. 工程爆破, 2024: 1–11.ZHOU E, LI H W, SUN Y, et al. Study on impact resistance of energy storage capacitor and ignition head in electronic detonator [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2024: 1–11. [20] 欧仙荣. 数码电子雷管中影响点火头性能因素分析 [J]. 四川兵工学报, 2014, 35(5): 128–131. doi: 10.11809/scbgxb2014.05.036OU X R. Influencing factors of digital detonator matchhead performance [J]. Journal of Sichuan Ordnance, 2014, 35(5): 128–131. doi: 10.11809/scbgxb2014.05.036 [21] 黄孝楠, 马志钢, 邵子豪, 等. 药头内部空孔对电药头发火时间精度的影响 [J]. 淮南职业技术学院学报, 2016, 16(5): 4–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4733.2016.05.002HUANG X N, MA Z G, SHAO Z H, et al. Effect of empty hole in the head on fire time accuracy of fuse head [J]. Journal of Huainan Vocational Technical College, 2016, 16(5): 4–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4733.2016.05.002 -






 下载:
下载: