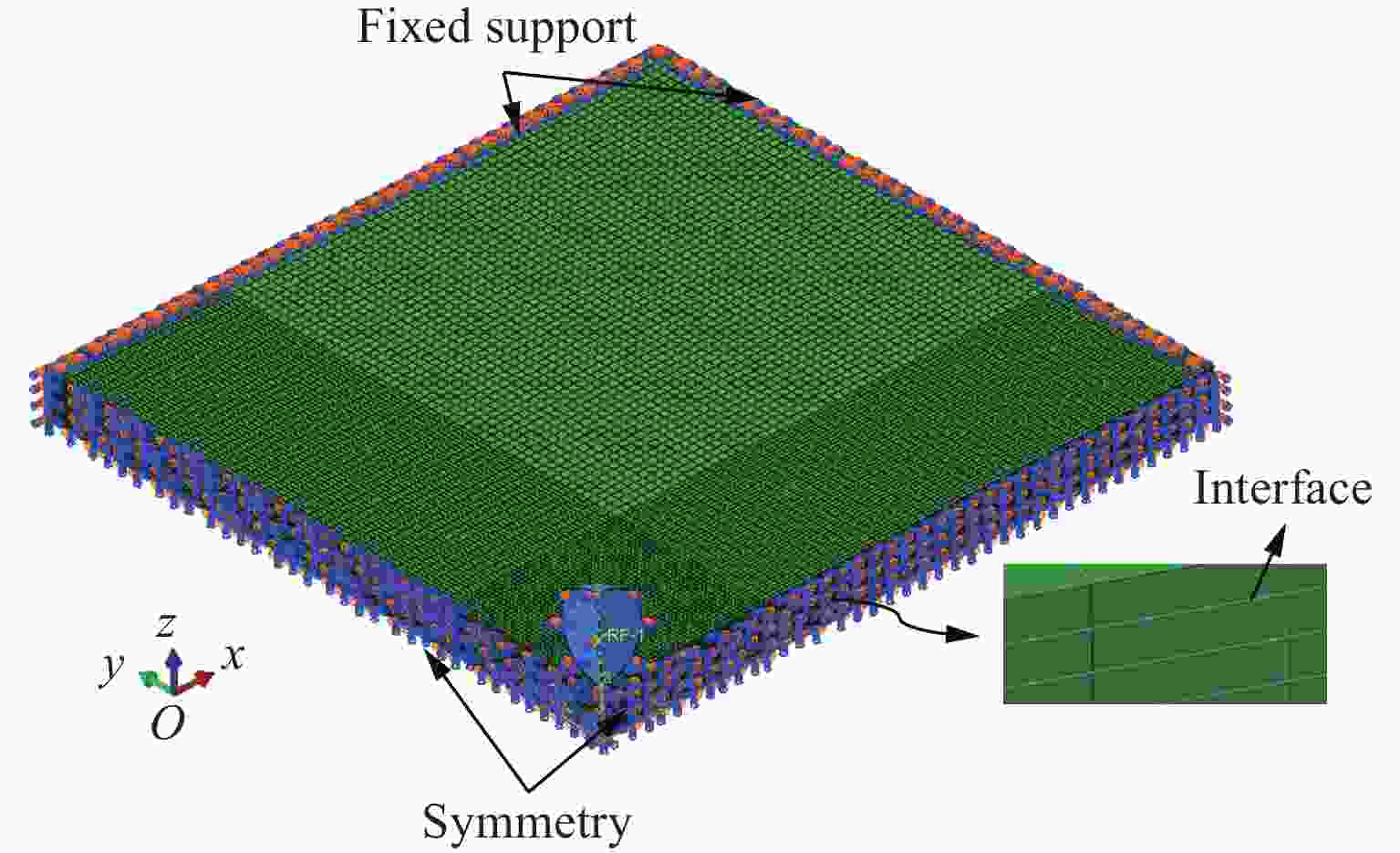
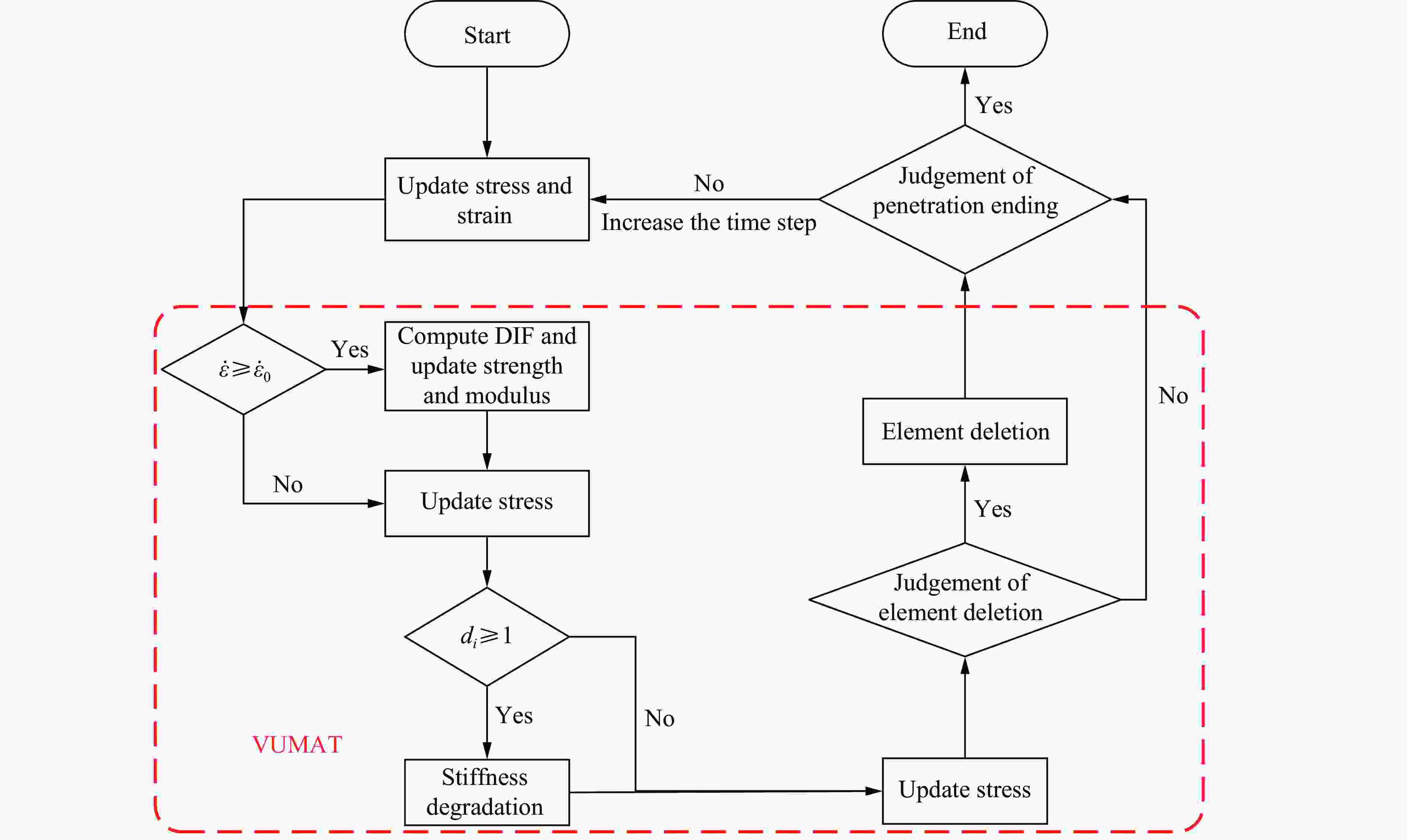
Multiscale Simulation Method for Anti-Penetration of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Laminates
-
摘要: 针对纤维增强复合材料层合板结构设计和抗侵彻数值仿真需要大量材料参数和动态试验数据的问题,以碳纤维增强复合材料层合板为研究对象,采用多尺度模拟方法,实现了纤维丝-纤维束-层合板的微观-介观-宏观力学性能和抗侵彻能力的全流程数值仿真预测。首先,建立微观代表性体积单元(representative volume elements,RVE),基于最大应力准则,预测出纤维束的力学性能;然后,根据编织结构的空间特征建立介观RVE模型,采用Hashin和Hou的失效准则,预测出宏观等效力学性能;最后,根据已发表的试验数据,建立了宏观弹道侵彻数值模型,提出了一种考虑材料应变率效应的改进Hashin失效准则,进而研究了弹道侵彻作用下纤维增强复合材料层合板的剩余速度和损伤特征。结果表明:试验与仿真得到的剩余速度的相对误差在5%以内,宏观数值模型准确捕捉到了纤维断裂、层间分层等损伤模式,验证了多尺度模拟方法的合理性和准确性;拟合得到了弹道极限速度随板厚变化的关系式,两者呈线性关系,且相关系数达0.97以上。研究结果有助于实现纤维增强复合材料层合板抗侵彻的低成本、短周期结构设计,对纤维增强复合材料层合板的正向性能预测和逆向结构设计均具有重要的科学和工程应用价值。Abstract: Aiming at the problem that a large number of material parameters and required for the structural design and numerical simulation of penetration resistance of fiber reinforced composite laminates, this article takes carbon fiber reinforced composite laminates as the research object, and adopts multi-scale simulation method to realize the whole process numerical simulation prediction of micro-, meso-, and macro-scale mechanical properties and penetration resistance of fiber-bundle-laminates. Firstly, microscopic representative volume elements (RVE) were established to predict the mechanical properties of fiber bundles based on the maximum stress criterion. Then, based on Hashin and Hou’s failure criteria, the macroscopic equivalent mechanical properties were predicted by the mesoscopic RVE models established according to the spatial characteristics of braided structures. Finally, an improved Hashin failure criterion considering the strain rate effect was proposed, and the numerical model of ballistic penetration was established based on the literature tests to study the residual velocities and damage characteristics. The results show that the errors of residual velocity results are less than 5%, and the macroscopic numerical models can accurately simulate the damage modes such as fiber fracture as well as interlayer delamination, which verifies the rationality and accuracy of multi-scale simulation method in this article. The relationship between the ballistic limit velocity and the thickness of the plate is linear and the correlation coefficient is above 0.97. The findings of this paper can help to realize the design of low-cost and short-period fiber reinforced composite laminates, which has important scientific and engineering application values for property prediction and inverse structural design of fiber reinforced composite laminates.
-
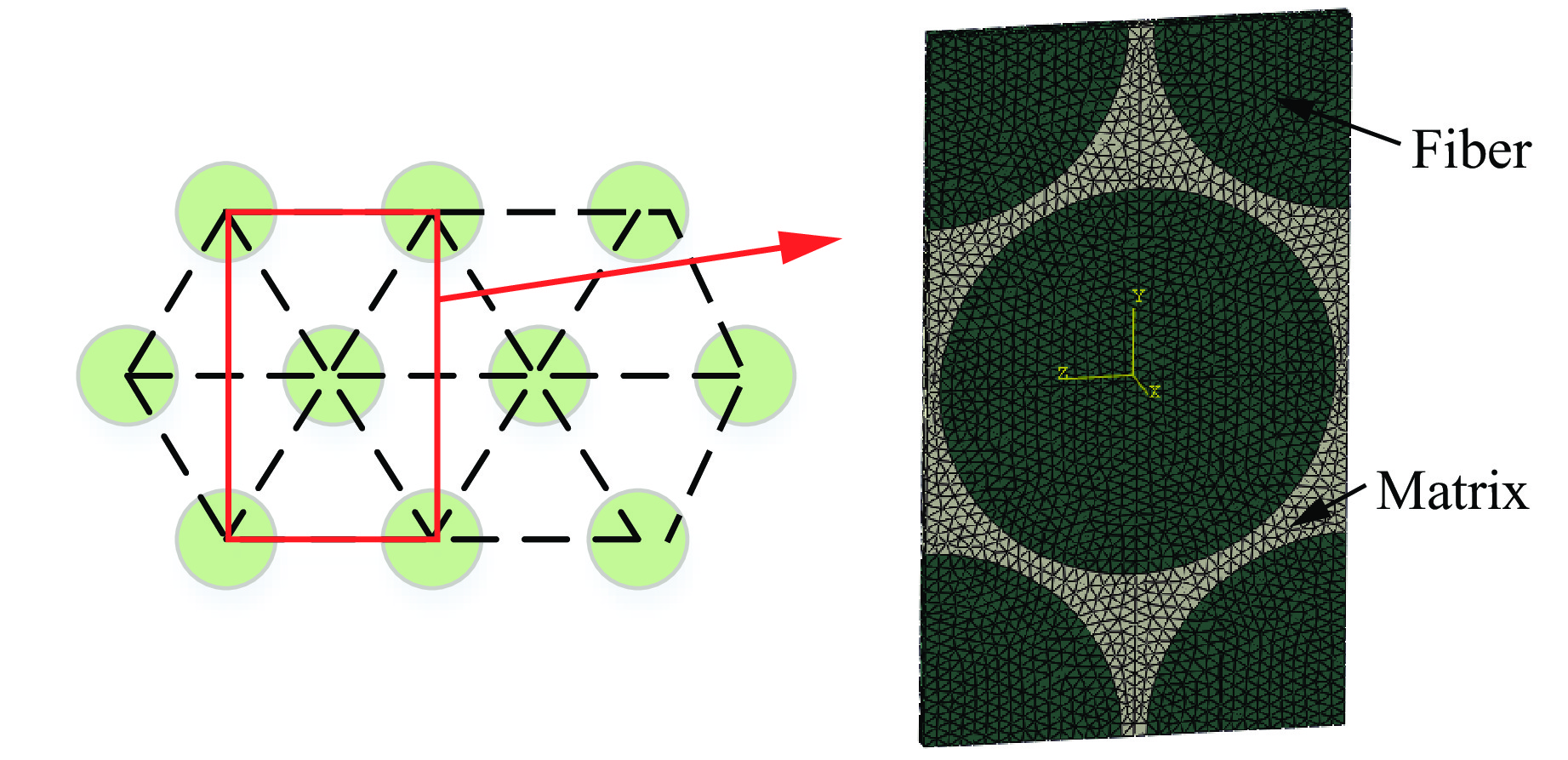
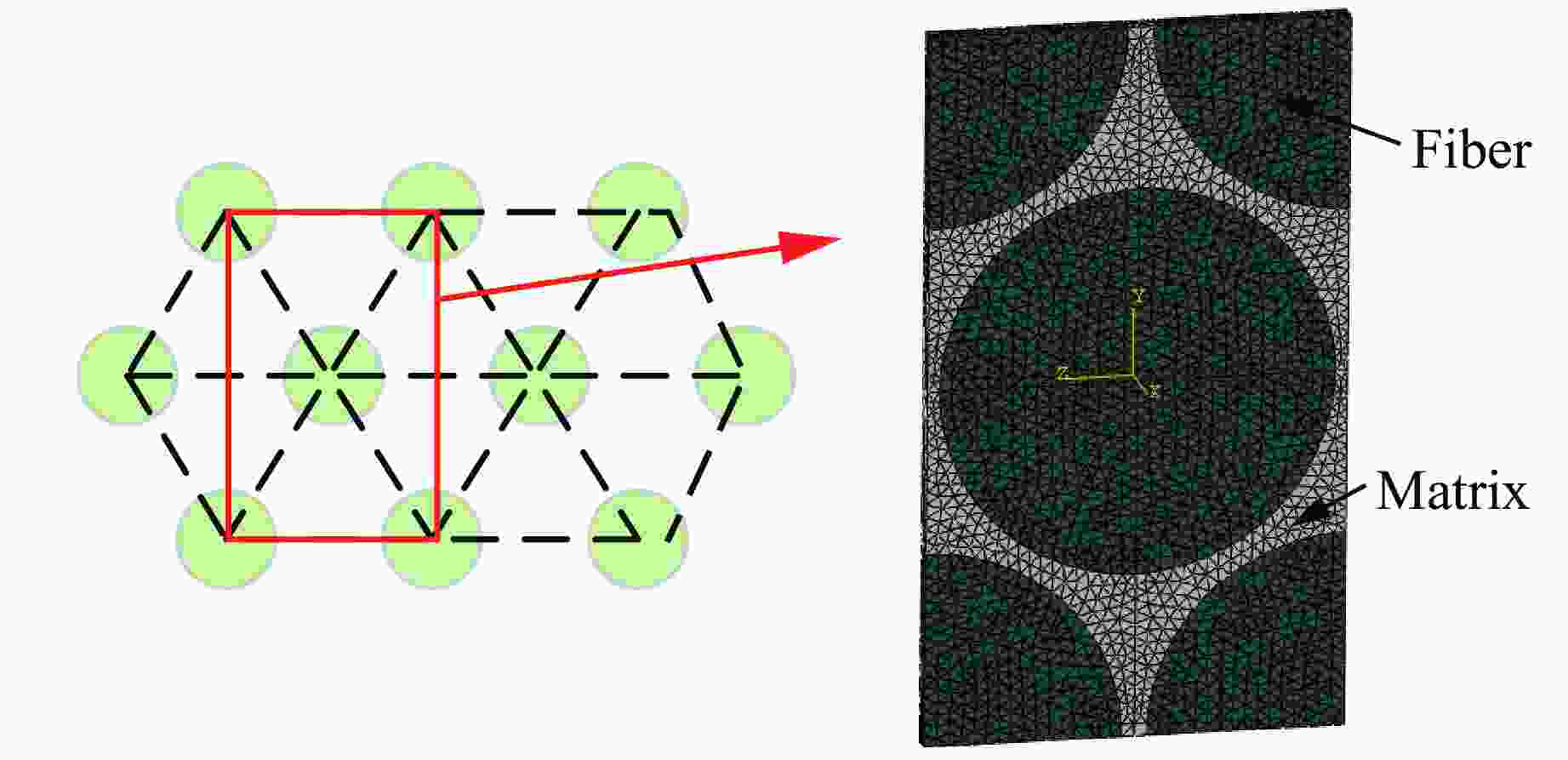
Ef1/GPa Ef2/GPa Ef3/GPa Gf12/GPa μf12 μf13 μf23 Xft/MPa Xfc/MPa 221 13.81 13.81 9 0.27 0.27 0.30 3530 2470 Em/GPa μm Smt/MPa Smc/MPa Sms/MPa 3.55 0.33 80 241 60 表 3 介观RVE模型参数
Table 3. Parameters of mesoscopic RVE model
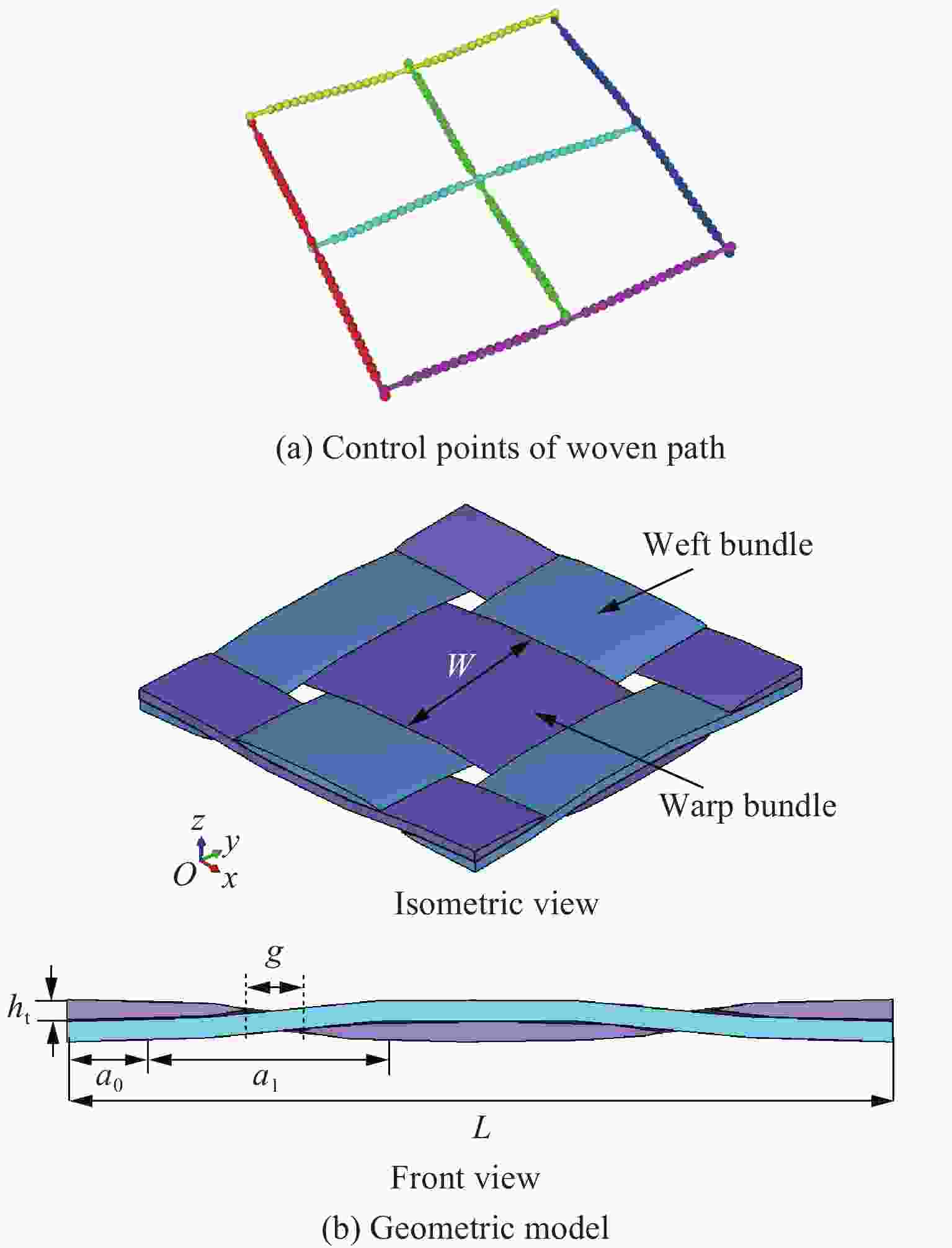
L/mm W/mm ht/mm a0/mm a1/mm 4.00 1.75 0.10 0.25 1.50 表 4 纤维束刚度参数计算结果
Table 4. Results of fiber bundle stiffness parameters
Method Elastic modulus/GPa Shear modulus/GPa Poisson’s ratio E1 E2 E3 G12 G13 G23 $ {\mu }_{12} $ $ {\mu }_{13} $ $ {\mu }_{23} $ Simulation 177.69 10.14 10.14 5.36 5.36 3.51 0.280 0.280 0.350 Equation 177.51 10.58 10.58 5.60 5.60 3.77 0.282 0.282 0.369 Error/% 0.10 −4.17 −4.17 −4.33 −4.33 −6.83 −0.71 −0.71 −5.06 表 5 纤维束强度参数计算结果
Table 5. Results of fiber bundle strength parameters
Method Tension strength/MPa Compressive strength/MPa Shear strength/MPa Xt Yt Zt Xc Yc Zc S12 S13 S23 Simulation 2865.11 72.72 72.72 1938.67 208.44 208.44 64.50 64.50 52.26 Equation 2835.34 74.39 74.39 1983.94 224.09 224.09 Error/% 1.05 −2.24 −2.24 −2.28 −6.99 −6.99 表 6 宏观等效力学参数对比
Table 6. Comparison of macroscopic equivalent mechanical parameters
Method E1/GPa E2/GPa E3/GPa G12/GPa G13/GPa G23/GPa Xt/MPa Simulation 56.50 56.50 7.90 3.59 2.51 2.51 740.37 Test[15] 57.94 57.94 3.59 726 Error/% −2.49 −2.49 0 1.98 Method Yt/MPa Xc/MPa Yc/MPa S12/MPa S13 /MPa S23/MPa Simulation 740.37 630.34 630.34 64.95 62.88 62.88 Test[15] 726 113.29 65.82 65.82 Error/% 1.98 −42.67 −4.47 −4.47 $ {t}_{\mathrm{n}}^{0} $/MPa $ {t}_{\mathrm{s}}^{0} $/MPa $ {t}_{\mathrm{t}}^{0} $/MPa $ {G}_{\mathrm{c}}^{{Ⅰ}} $/(kJ·m−2) $ {G}_{\mathrm{c}}^{{Ⅱ}} $/(kJ·m−2) $ {G}_{\mathrm{c}}^{{Ⅲ}} $/(kJ·m−2) 50 90 90 0.52 0.92 0.92 表 8 仿真与试验得到的剩余速度和单位面密度吸能的对比
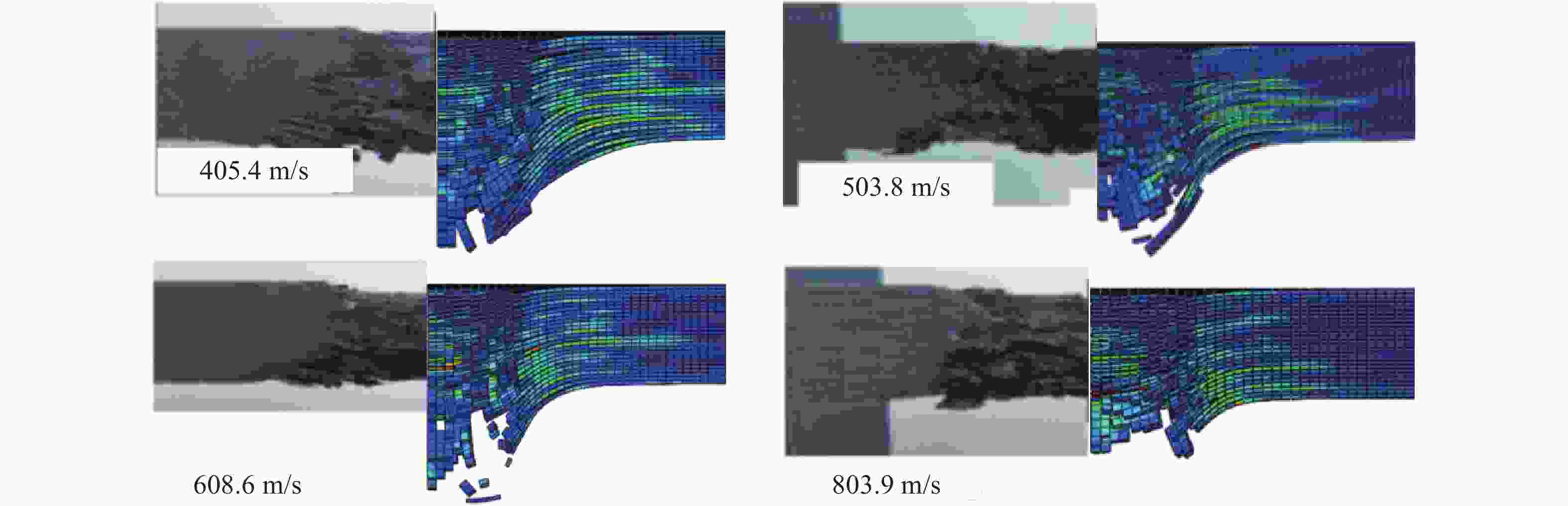
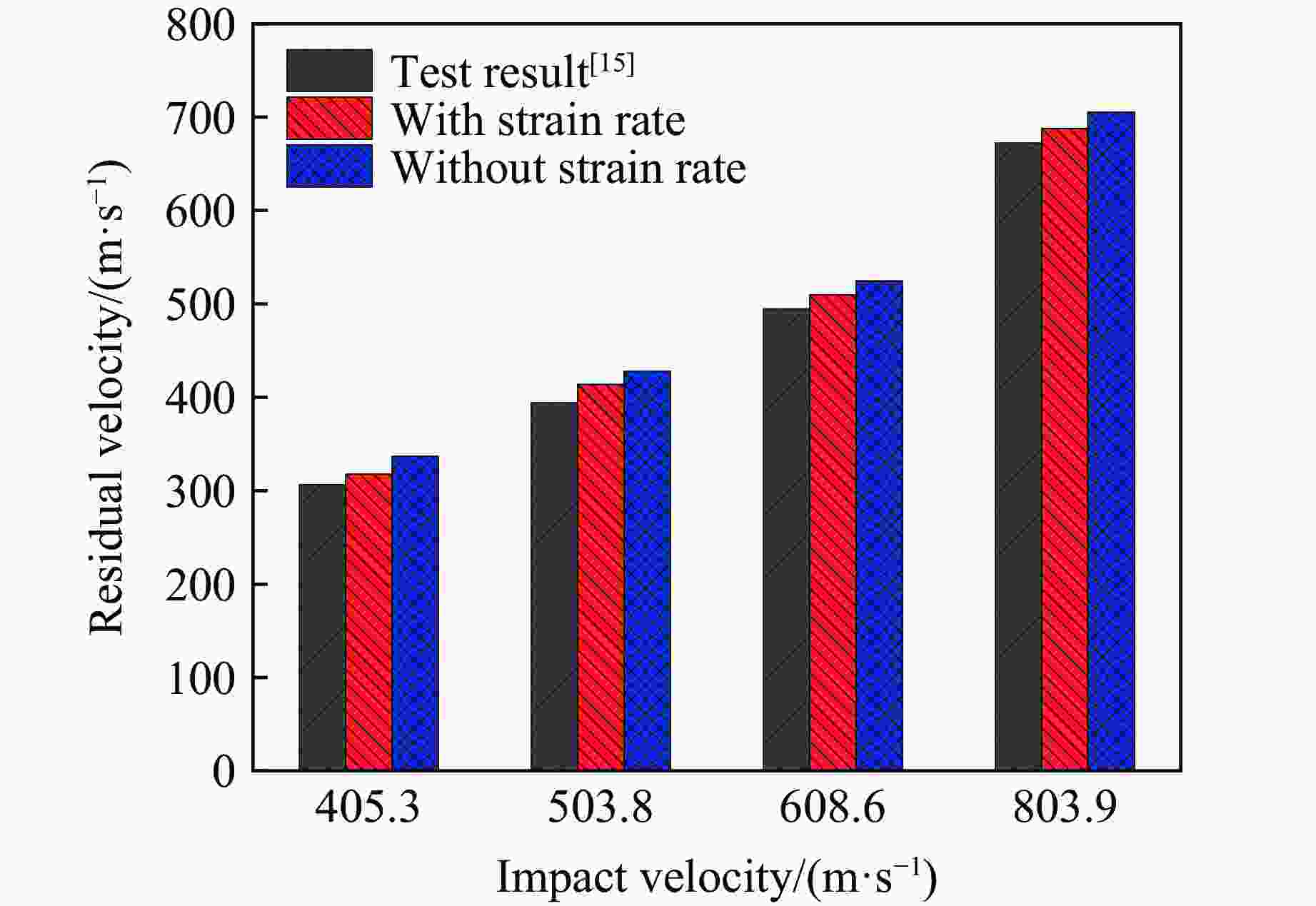
Table 8. Comparison of residual velocity and energy absorption per unit surface density between simulation and test
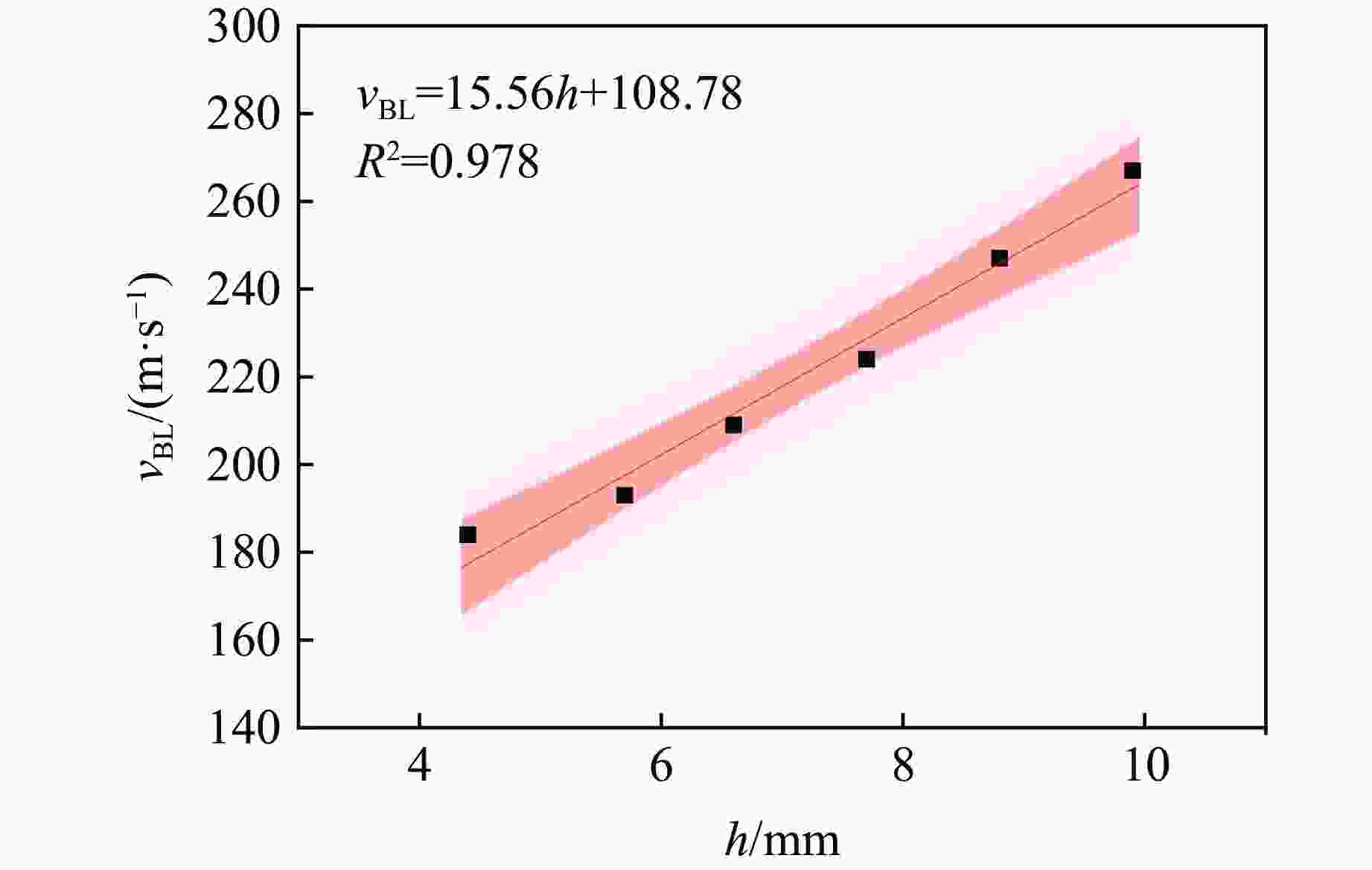
表 9 不同板厚下的拟合参数
Table 9. Fitting parameters under different plate thicknesses
h/mm a p 4.4 0.897 2.089 5.7 0.884 2.051 6.6 0.856 2.104 7.7 0.837 2.030 8.8 0.800 2.164 9.9 0.805 2.032 -
[1] 罗锡林, 魏建辉, 李飘, 等. 碳纤维编织复合材料层合板抗侵彻性能研究 [J]. 材料开发与应用, 2023, 38(4): 61–68. doi: 10.19515/j.cnki.1003-1545.2023.04.004LUO X L, WEI J H, LI P, et al. Study on penetration resistance of carbon fiber braided composite laminates [J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2023, 38(4): 61–68. doi: 10.19515/j.cnki.1003-1545.2023.04.004 [2] DU C L, XIA R Z, LIU P, et al. On the impact damage characteristics of spread-tow woven composites: from high velocity to hyper velocity [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2023, 146: 107109. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2023.107109 [3] PENG Y, WANG X, CHEN X Z, et al. Numerical simulation of the effect of projectile shape and size on the high-velocity impact of carbon fiber reinforced composite laminates [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2024, 30: 5109–5120. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.04.218 [4] ALONSO L, MARTÍNEZ-HERGUETA F, GARCIA-GONZALEZ D, et al. A finite element approach to model high-velocity impact on thin woven GFRP plates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 142: 103593. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103593 [5] MEYER C S, O'BRIEN D J, HAQUE B Z, et al. Mesoscale modeling of ballistic impact experiments on a single layer of plain weave composite [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2022, 235: 109753. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109753 [6] 牟浩蕾, 李仪, 宋东方, 等. 芳纶平纹编织复合材料平板弹道冲击特性及损伤分析 [J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2024(1): 89–97, 104. doi: 10.19936/j.cnki.2096-8000.20240128.012MOU H L, LI Y, SONG D F, et al. Ballistic impact characteristics and damage analysis of aramid plain woven composite plates [J]. Composites Science and Engineering, 2024(1): 89–97, 104. doi: 10.19936/j.cnki.2096-8000.20240128.012 [7] 陈玉丽, 马勇, 潘飞, 等. 多尺度复合材料力学研究进展 [J]. 固体力学学报, 2018, 39(1): 1–68. doi: 10.19636/j.cnki.cjsm42-1250/o3.2017.030CHEN Y L, MA Y, PAN F, et al. Research progress in multi-scale mechanics of composite materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2018, 39(1): 1–68. doi: 10.19636/j.cnki.cjsm42-1250/o3.2017.030 [8] 王新峰. 机织复合材料多尺度渐进损伤研究 [D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2007.WANG X F. Multi-scale analyses of damage evolution in woven composite materials [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2007. [9] MADKE R R, CHOWDHURY R. A multiscale continuum model for inelastic behavior of woven composite [J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 226: 111267. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111267 [10] ZHU Y X, HE C W, ZHAO T, et al. Towards accurate prediction of the dynamic behavior and failure mechanisms of three-dimensional braided composites: a multiscale analysis scheme [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2024, 203: 112188. doi: 10.1016/J.TWS.2024.112188 [11] 张洁皓. 开孔平纹机织复合材料低速冲击性能研究 [D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2020.ZHANG J H. Study on low-velocity impact performance of plain weave composites with holes [D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2020. [12] 王涛, 侯玉亮, 铁瑛, 等. 基于ECPL模型的平纹机织复合材料低速冲击多尺度模拟 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(20): 295–304. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2020.20.038WANG T, HOU Y L, TIE Y, et al. Multi-scale simulation of low-velocity impact on plain woven composites based on an ECPL model [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(20): 295–304. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2020.20.038 [13] 赵巧莉, 侯玉亮, 刘泽仪, 等. 碳纤维平纹机织复合材料低速冲击及冲击后压缩性能多尺度分析 [J]. 中国机械工程, 2021, 32(14): 1732–1742. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2021.14.012ZHAO Q L, HOU Y L, LIU Z Y, et al. Multi-scale analysis of LVI and CAI behaviors of plain woven carbon-fiber-reinforced composites [J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 32(14): 1732–1742. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2021.14.012 [14] SMOJVER I, BREZETIĆ D, IVANČEVIĆ D. Explicit multi-scale modelling of intrinsic self-healing after low-velocity impact in GFRP composites [J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 302: 116213. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116213 [15] BAO J W, WANG Y W, AN R, et al. Investigation of the mechanical and ballistic properties of hybrid carbon/aramid woven laminates [J]. Defence Technology, 2022, 18(10): 1822–1833. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2021.09.009 [16] ZHENG T, GUO L C, HUANG J Z, et al. A novel mesoscopic progressive damage model for 3D angle-interlock woven composites [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2020, 185: 107894. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107894 [17] 陈占光. 基于多尺度方法的含孔机织复合材料强度分析研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021.CHEN Z G. Strength analysis of woven composites with holes based on multi-scale method [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021. [18] GAROZ D, GILABERT F A, SEVENOIS R D B, et al. Consistent application of periodic boundary conditions in implicit and explicit finite element simulations of damage in composites [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 168: 254–266. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.12.023 [19] CHAMIS C C. Mechanics of composite materials: past, present, and future [J]. Journal of Composites Technology and Research, 1989, 11(1): 3–14. doi: 10.1520/CTR10143J [20] 葛辛辛. 斜纹编织碳纤维层合厚板低速冲击损伤及剩余压缩强度研究 [D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2022.GE X X. Research on low-velocity impact damage and residual compressive strength of twill woven carbon fiber reinforced thick composite laminates [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2022. [21] TIE Y, HOU Y L, LI C, et al. Optimization for maximizing the impact-resistance of patch repaired CFRP laminates using a surrogate-based model [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2020, 172: 105407. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105407 [22] 陈战辉. 碳纤维平纹织物层合板高速冲击损伤研究 [D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2019.CHEN Z H. Investigation on damage in carbon woven composite laminates caused by high velocity impact [D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2019. [23] 方盈盈. 高应变率下碳纤维复合材料动态力学性能研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2018.FANG Y Y. Study on dynamic mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced composite materials under high strain rate [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2018. [24] LI J T, LIU M B. An analytical model to predict the impact of a bullet on ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composite laminates [J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 282: 115064. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.115064 -






 下载:
下载: