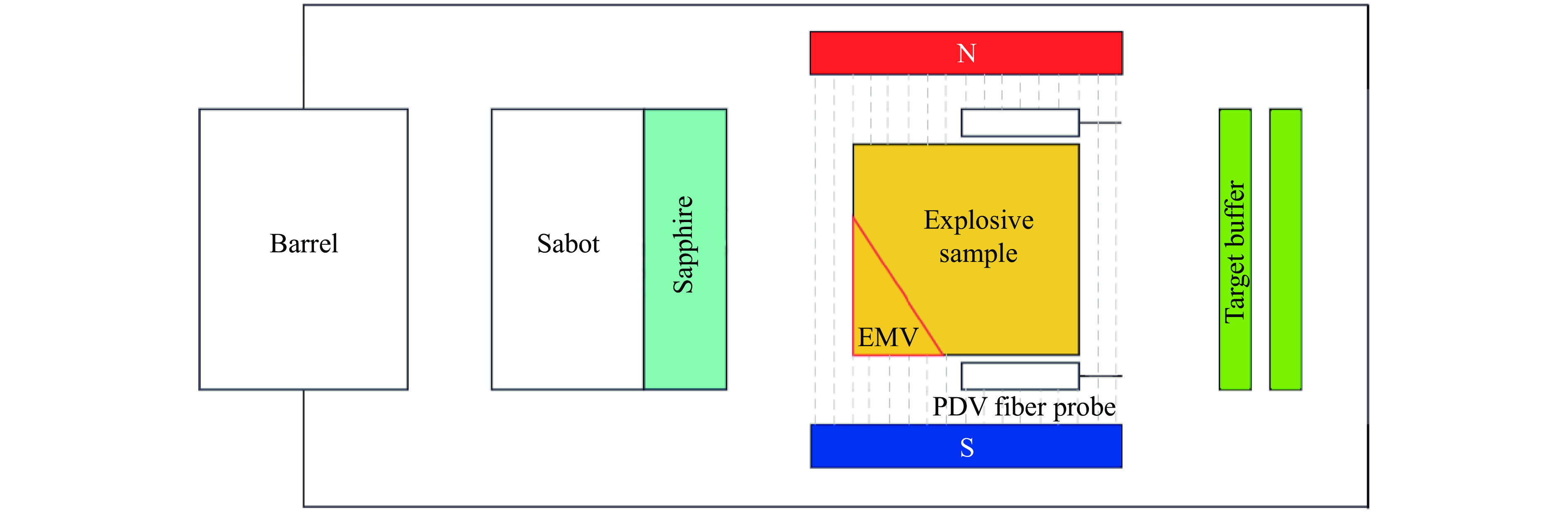
The Influence of Pulse Width on the Shock Initiation Process of TATB-Based Insensitive Explosives
-
摘要: 冲击波脉宽是冲击起爆过程中影响炸药冲击转爆轰的重要因素之一。为此,利用火炮平台,对1,3,5-三氨基-2,4,6-三硝基苯(1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene,TATB)-2钝感炸药进行了冲击起爆实验。通过改变冲击飞片厚度控制冲击波脉宽,采用电磁粒子速度计和示踪计记录冲击波速度、炸药的波后粒子速度等实验数据。通过数据分析,得到了TATB-2炸药的冲击波脉宽与爆轰距离等参数之间的关系。结果表明,脉宽效应对TATB-2炸药的冲击起爆过程有显著影响。研究结果可为理解钝感炸药的冲击起爆特性提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 脉宽效应 /
- 1,3,5-三氨基-2,4,6-三硝基苯基炸药 /
- 冲击起爆 /
- 波后粒子速度 /
- 冲击波速度
Abstract: The shock wave pulse width is one of the essential factors influencing the shock-to-detonation transition in explosives. This study experimentally investigates the pulse width effect on the shock initiation process of the insensitive explosive 1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene (TATB). Shock initiation experiments were conducted on TATB-2 explosives on the gun platform. The pulse width was controlled by varying the thickness of shock flyers. Experimental data including shock wave velocity and particle velocity after wave were recorded using the electromagnetic particle velocity meter and tracer meter. The relationships between pulse width effect, the distance to detonation, and other parameters of TATB-2 explosives were calculated and analyzed. The results demonstrate that pulse width effect significantly affects the detonation build-up process, providing essential references for understanding the shock initiation characteristics of insensitive explosives. -
表 1 未反应炸药材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters of unreacted explosive
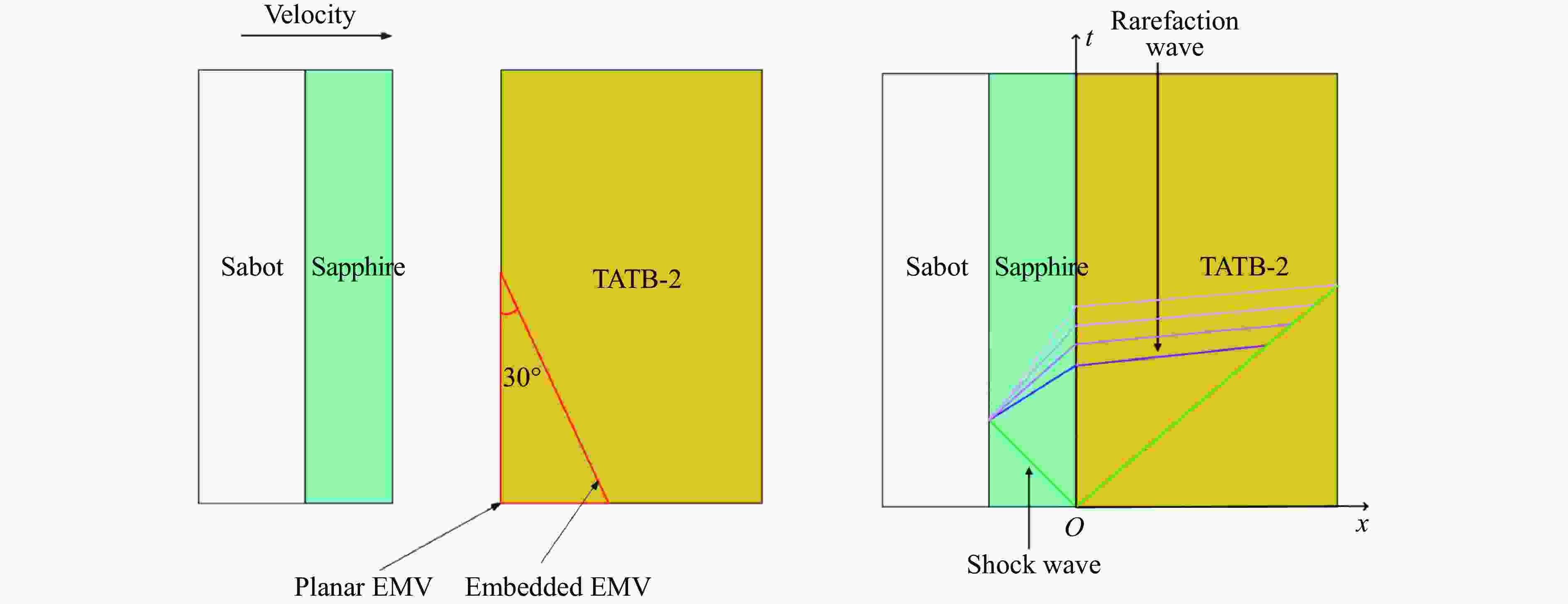
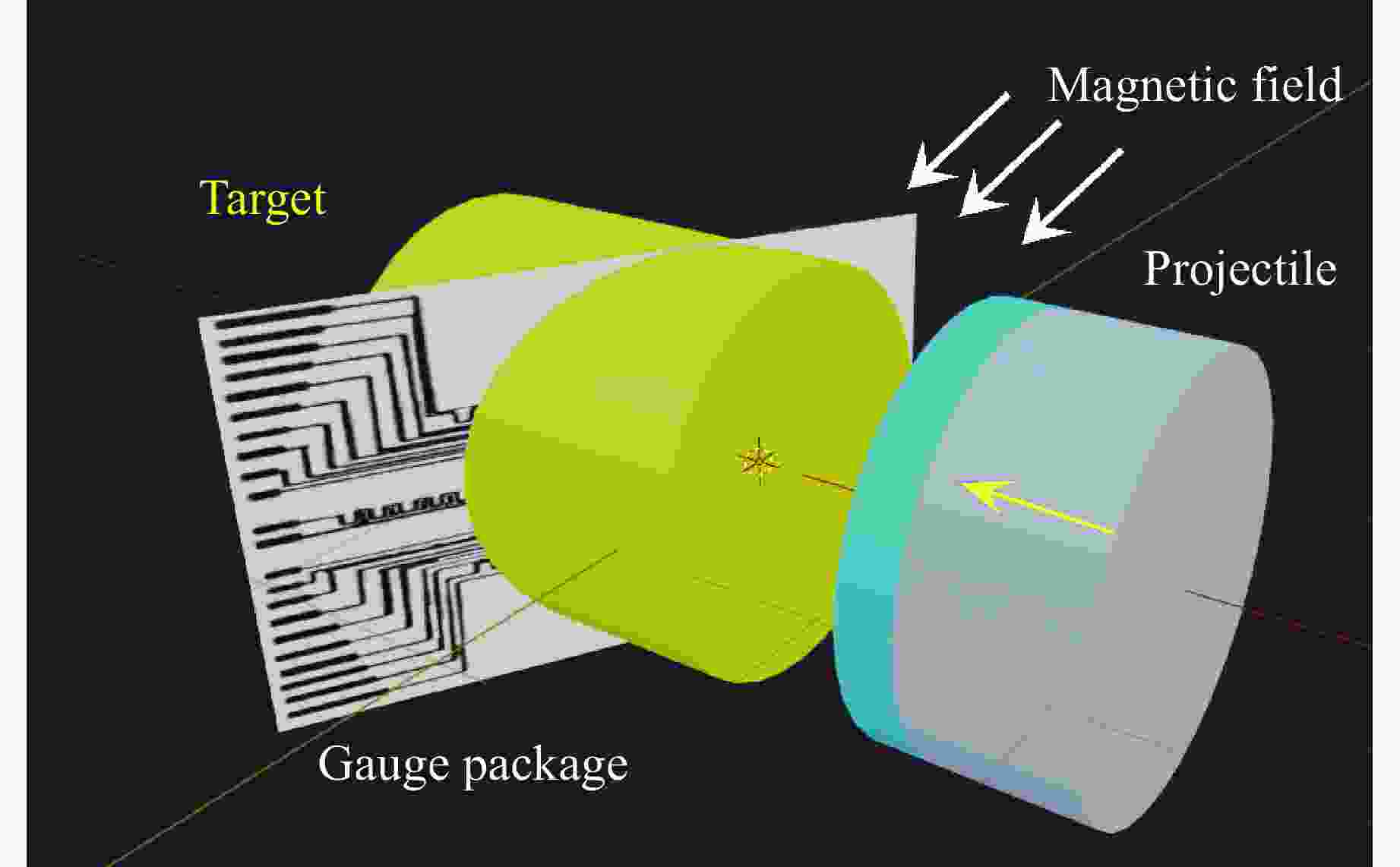
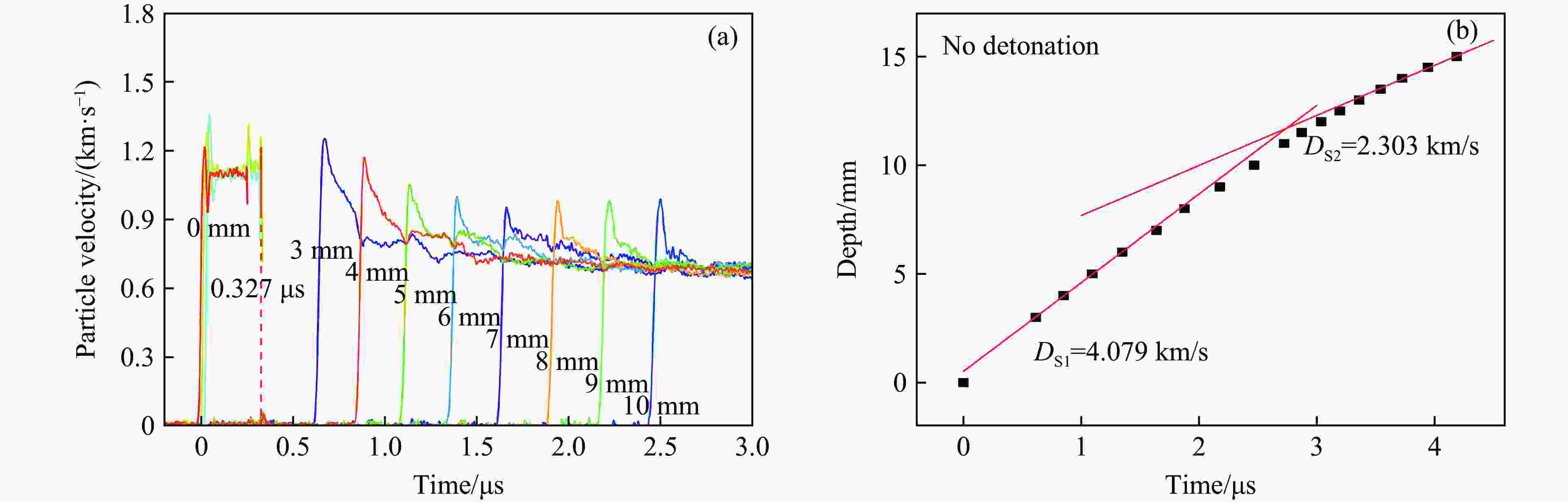
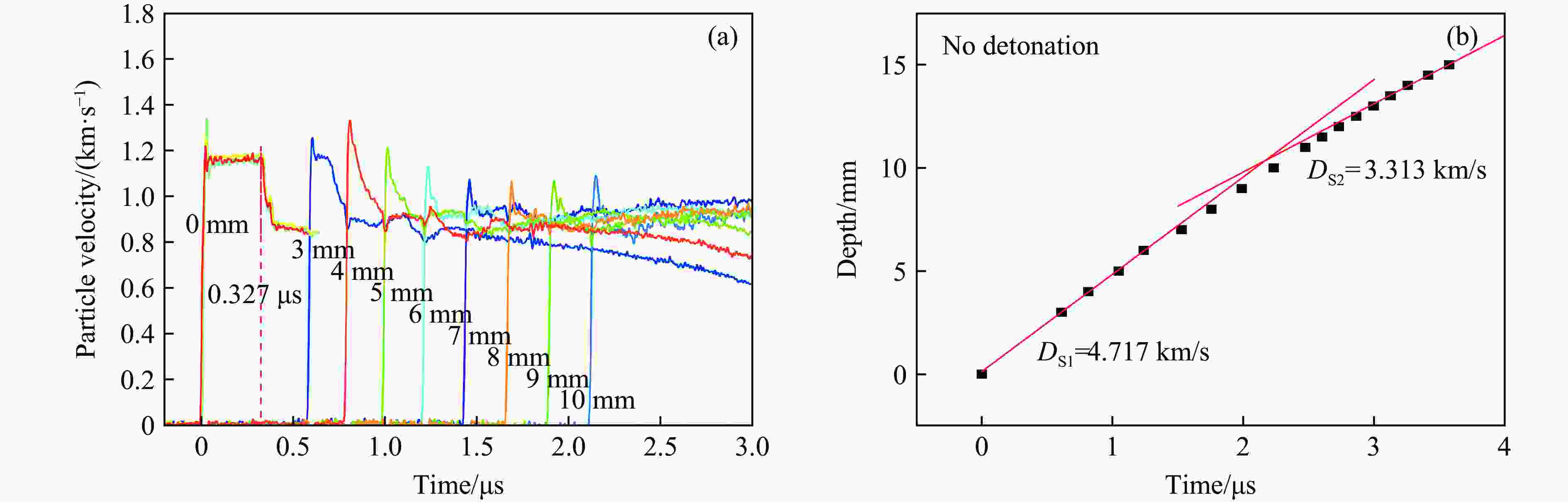
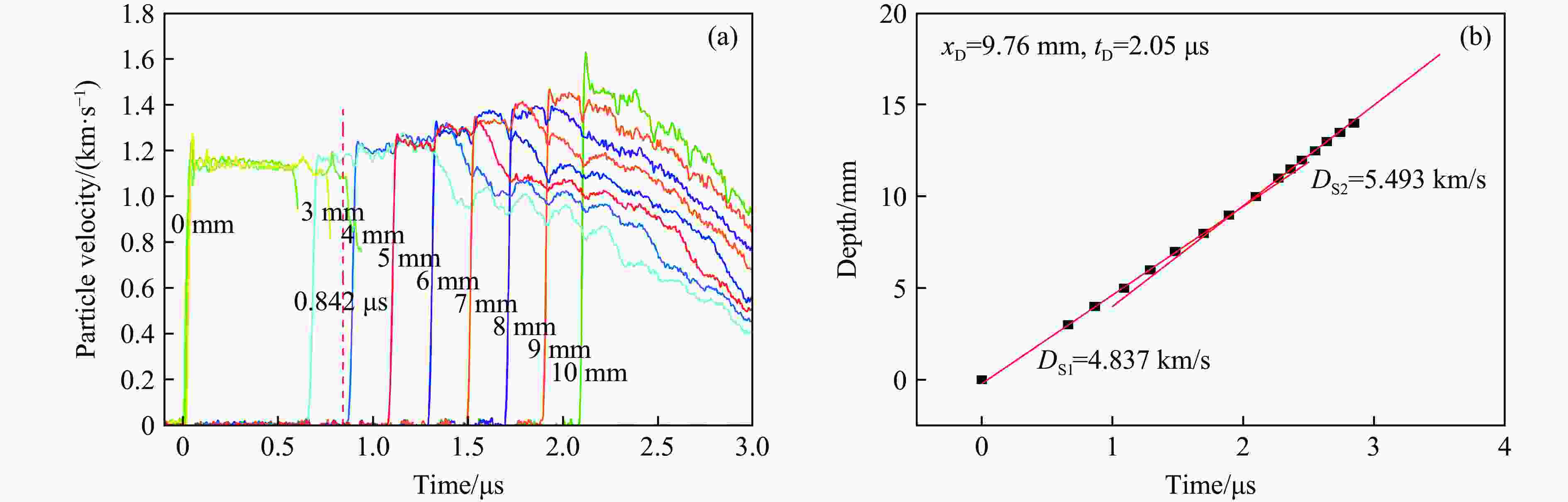
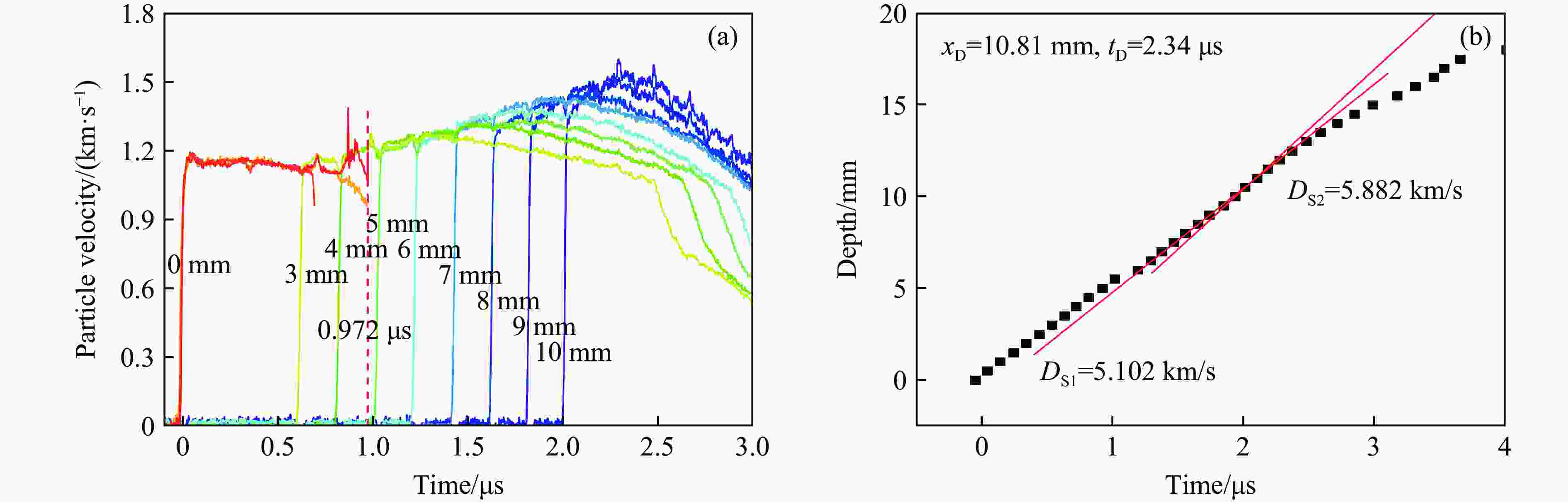
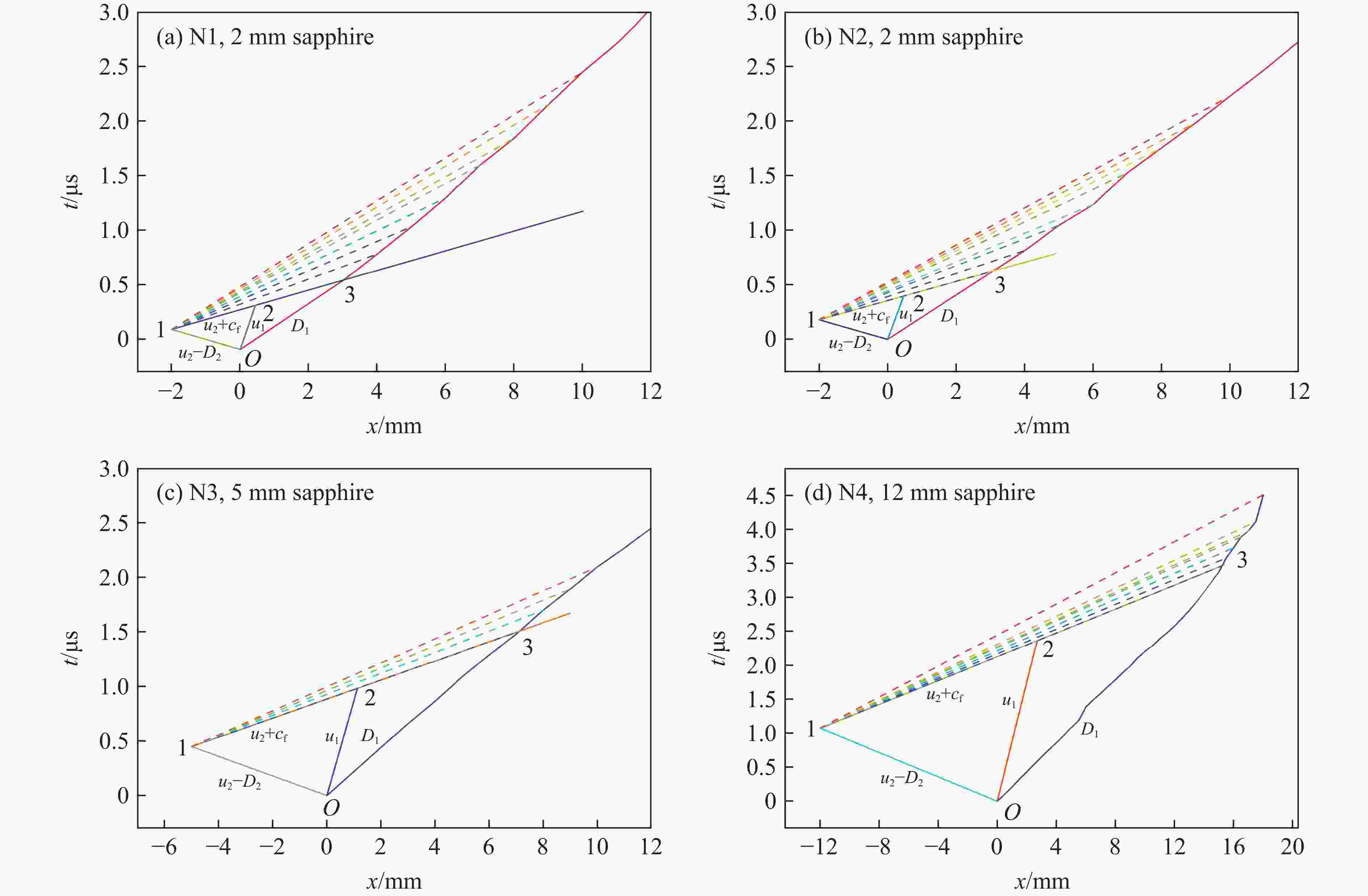
Exp. No. H/mm $ {\rho }_{0,\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p}} $ (up/down)/(g·cm−3) m/g uimp/(km·s−1) p0/GPa T0/℃ N1 2 1.894 491.99 1.37 10.03 12.5 N2 2 1.894 491.02 1.39 10.83 16.2 N3 5 1.894 490.94 1.40 11.07 15.0 N4 12 1.898/1.893 492.45 1.33 10.42 16.0 表 2 TATB-2实验中脉宽效应及相关参数
Table 2. TATB-2 experimental pulse width effect and other related parameters
Exp. No. H/mm $ {\rho }_{0,\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p}} $(up/down)/
(g·cm−3)uimp/(km·s−1) p0/GPa Pulse-width/μs xD/mm tD/μs N1 2 1.894 1.37 10.03 0.327 N2 2 1.894 1.39 10.83 0.327 N3 5 1.894 1.40 11.07 0.842 9.76 2.05 N4 12 1.898/1.893 1.33 10.42 0.972 10.81 2.34 表 3 TATB-2实验中稀疏波的相关参数
Table 3. Parameters about rarefaction wave of TATB-2 experiment
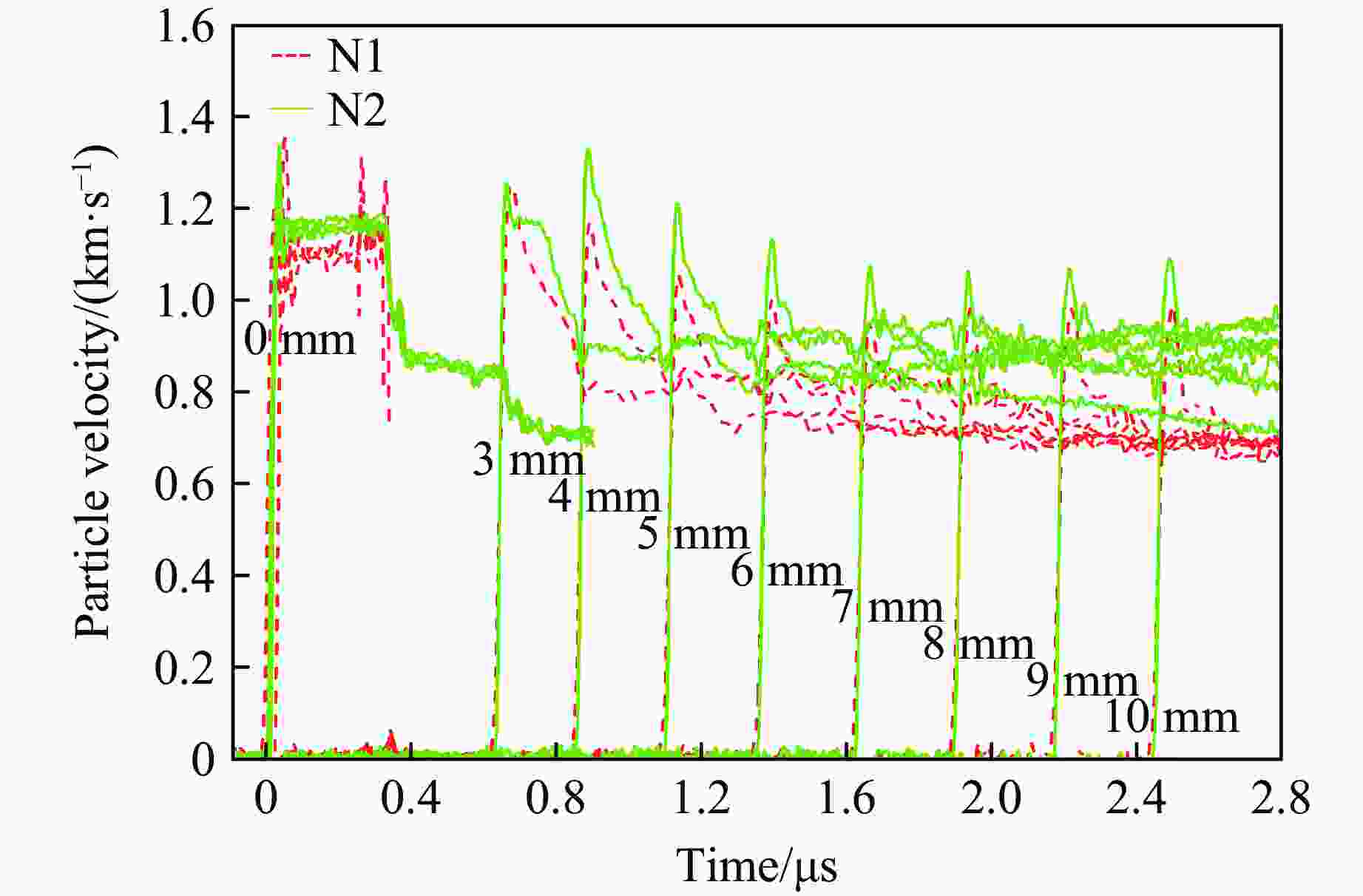
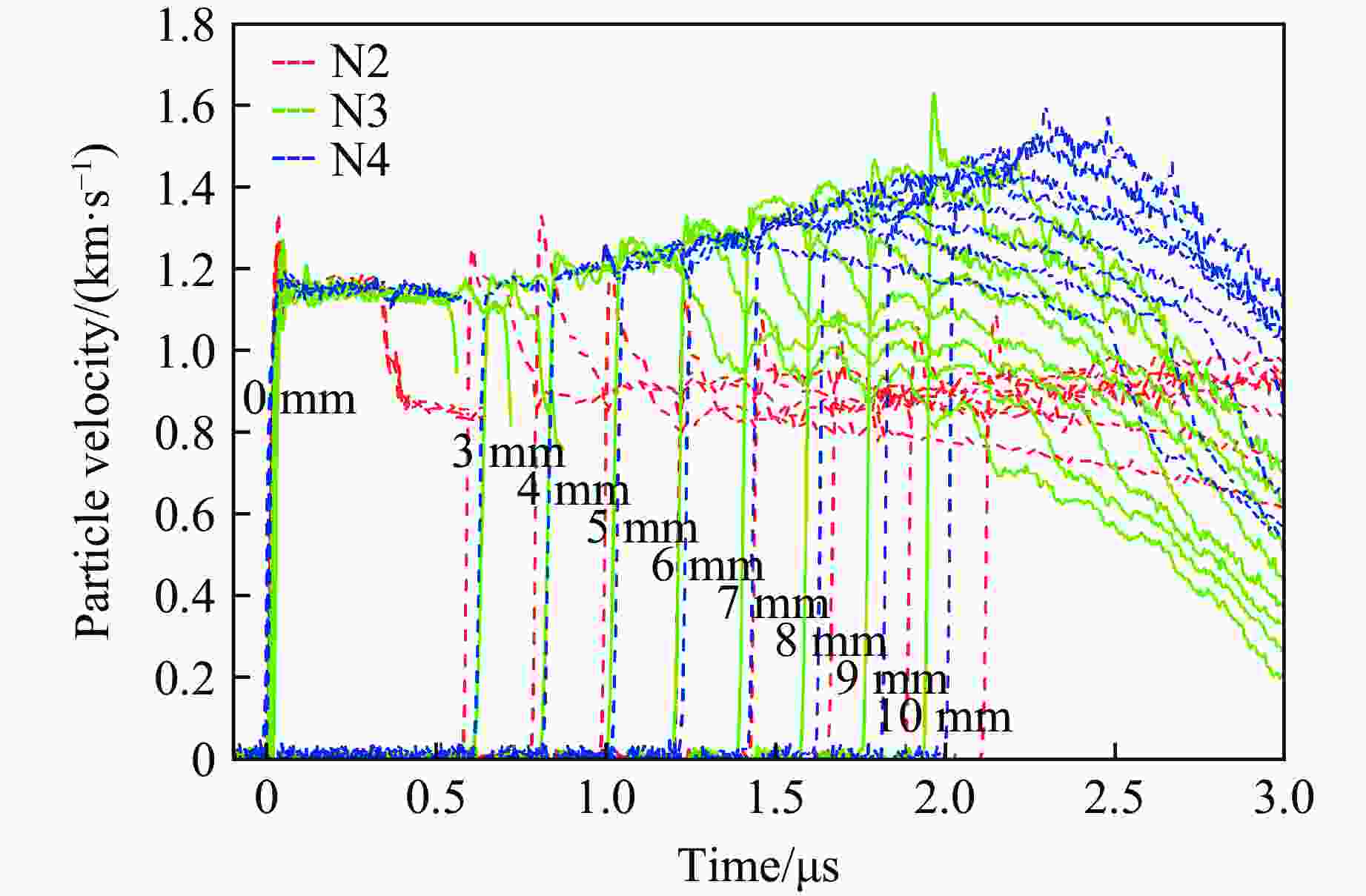
Exp. No. Position u1/(km·s−1) u2/(km·s−1) D1/(km·s−1) D2/(km·s−1) Point 1 Point 2 Point 3 N1 (−2.00, 0.18) (0.44, 0.39) (3.02, 0.62) 1.12 0.25 4.82 11.44 N2 (−2.00, 0.18) (0.46, 0.39) (3.07, 0.62) 1.17 0.22 4.81 11.41 N3 (−5.00, 0.45) (1.13, 0.98) (7.13, 1.51) 1.15 0.25 4.88 11.44 N4 (−12.00, 1.07) (2.69, 2.36) (15.22, 3.46) 1.27 0.18 5.14 11.37 -
[1] BURNS M J, GUSTAVSEN R L, BARTRAM B D. One-dimensional plate impact experiments on the cyclotetramethylene tetranitramine (HMX) based explosive EDC32 [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 112(6): 064910. doi: 10.1063/1.4752865 [2] WANG C, LIU X Q, NING J G. High resolution numerical simulation of shock-to-detonation transition of condensed-phase explosives [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2013, 767: 40–45. doi: 10.4028/WWW.SCIENTIFIC.NET/MSF.767.40 [3] 莫建军, 王桂吉, 吴刚, 等. 炸药TATB/粘结剂的短脉冲冲击起爆阈值测量 [J]. 实验力学, 2010, 25(1): 41–46.MO J J, WANG G J, WU G, et al. Measurement of the short-duration pulse shock initiation thresholds for TATB explosive/adhesive [J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2010, 25(1): 41–46. [4] 王桂吉, 赵同虎, 莫建军, 等. 一种以TATB/HMX为基的高聚物粘结炸药的短脉冲冲击起爆特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2007, 27(3): 230–235. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2007)03-0230-06WANG G J, ZHAO T H, MO J J, et al. Short-duration pulse shock initiation characteristics of a TATB/HMX-based polymer bonded explosive [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2007, 27(3): 230–235. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2007)03-0230-06 [5] 杨舒棋, 张旭, 彭文杨, 等. 利用电磁法研究HMX与TATB混合钝感炸药的冲击起爆特性 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2020, 34(3): 033403. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190852YANG S Q, ZHANG X, PENG W Y, et al. Impact initiation characteristics of TATB based insensitive explosives mixed with HMX by electromagnetic velocity gauges [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2020, 34(3): 033403. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190852 [6] 张琪敏, 张旭, 赵康, 等. TATB基钝感炸药JB-9014的冲击起爆反应增长规律 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(4): 041405. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0050ZHANG Q M, ZHANG X, ZHAO K, et al. Law of reaction growth of shock initiation on the TATB based insensitive explosive JB-9014 [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(4): 041405. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0050 [7] 张旭, 池家春, 冯民贤. JB9014钝感炸药冲击绝热线测量 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2001, 15(4): 304–308. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2001.04.011ZHANG X, CHI J C, FENG M X. Hugoniot relation of JB9014 insensitive high explosive [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2001, 15(4): 304–308. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2001.04.011 [8] 裴红波, 刘俊明, 张旭, 等. 基于反向撞击法的JB-9014炸药Hugoniot关系测量 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(5): 052301. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0395PEI H B, LIU J M, ZHANG X, et al. Measurement of Hugoniot relation for unreacted JB-9014 explosive with reverse-impact method [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(5): 052301. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0395 [9] 刘俊明, 张旭, 裴红波, 等. JB-9014钝感炸药冲击Hugoniot关系测量 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2018, 32(3): 033202. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20170669LIU J M, ZHANG X, PEI H B, et al. Measurement of Hugoniot relation for JB-9014 insensitive explosive [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2018, 32(3): 033202. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20170669 [10] 刘俊明, 张旭, 赵康, 等. 用PVDF压力计研究未反应JB-9014钝感炸药的Grüneisen参数 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2018, 32(5): 051301. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20180524LIU J M, ZHANG X, ZHAO K, et al. Using PVDF gauge to study Grüneisen parameter of unreacted JB-9014 insensitive explosive [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2018, 32(5): 051301. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20180524 -






 下载:
下载: