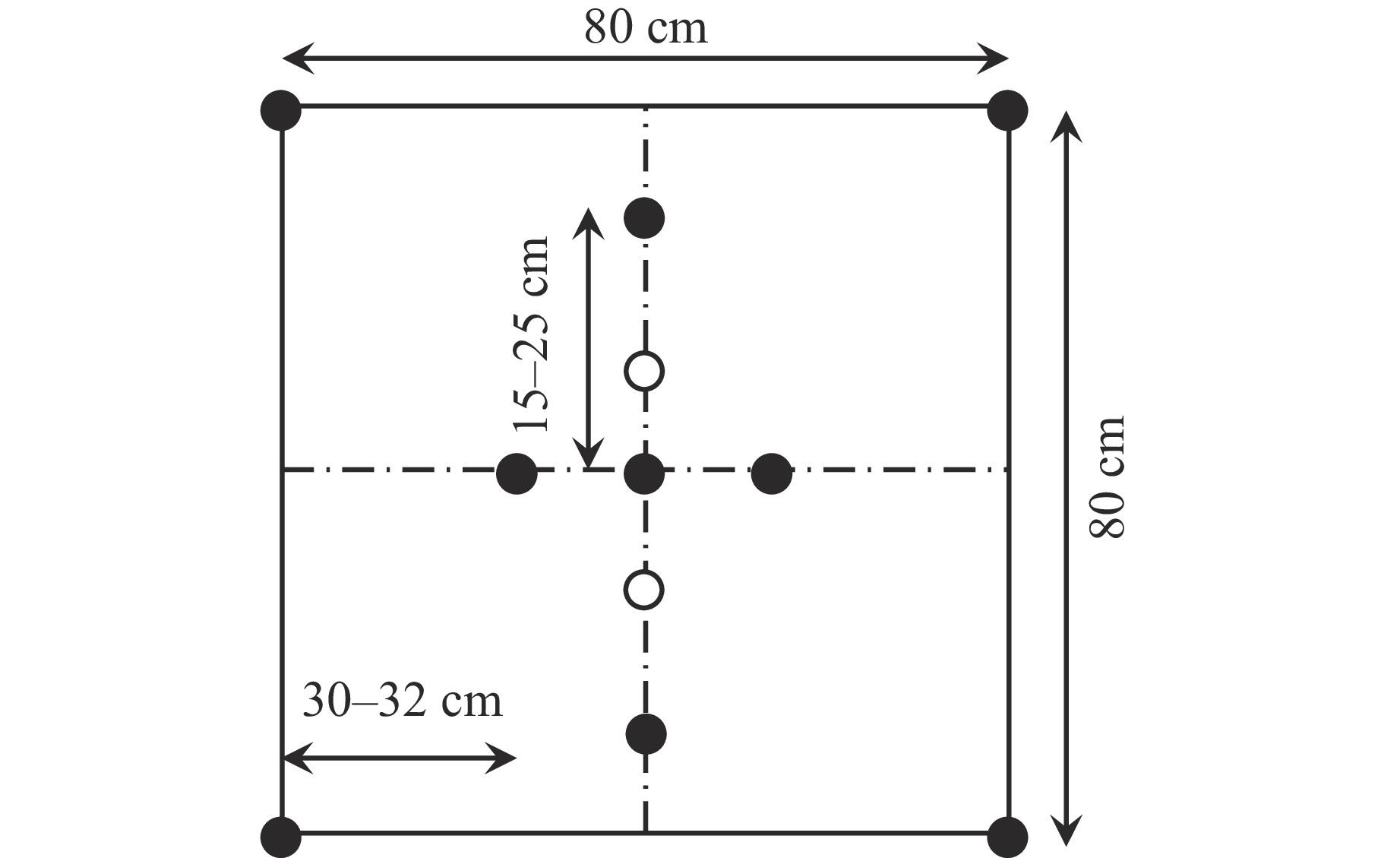
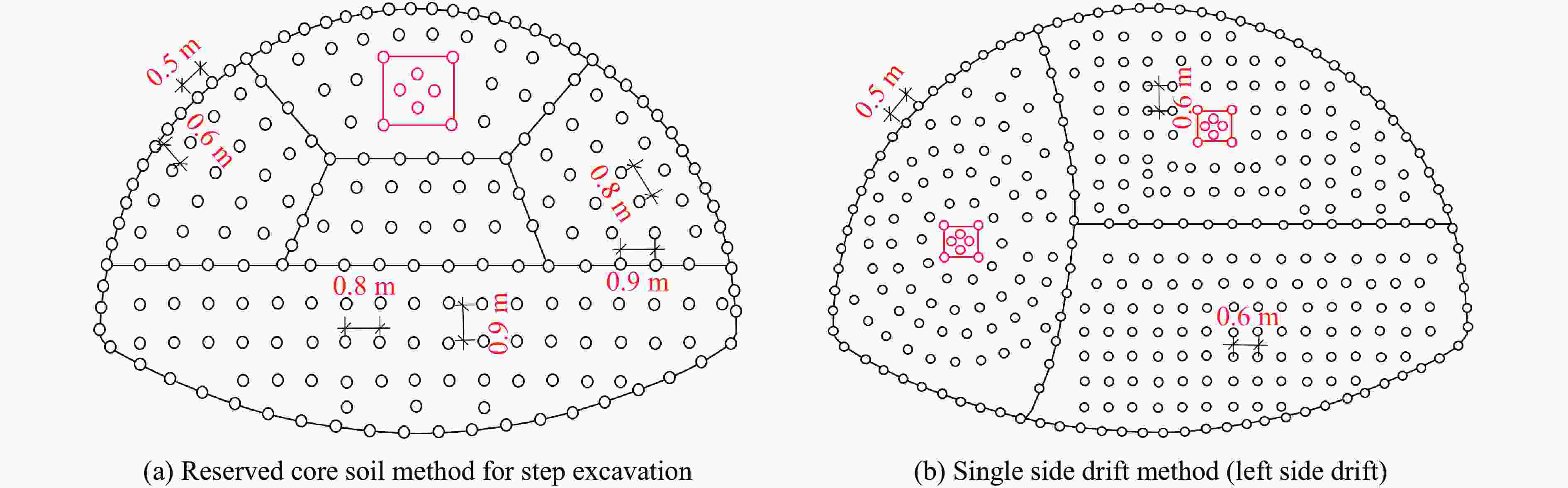
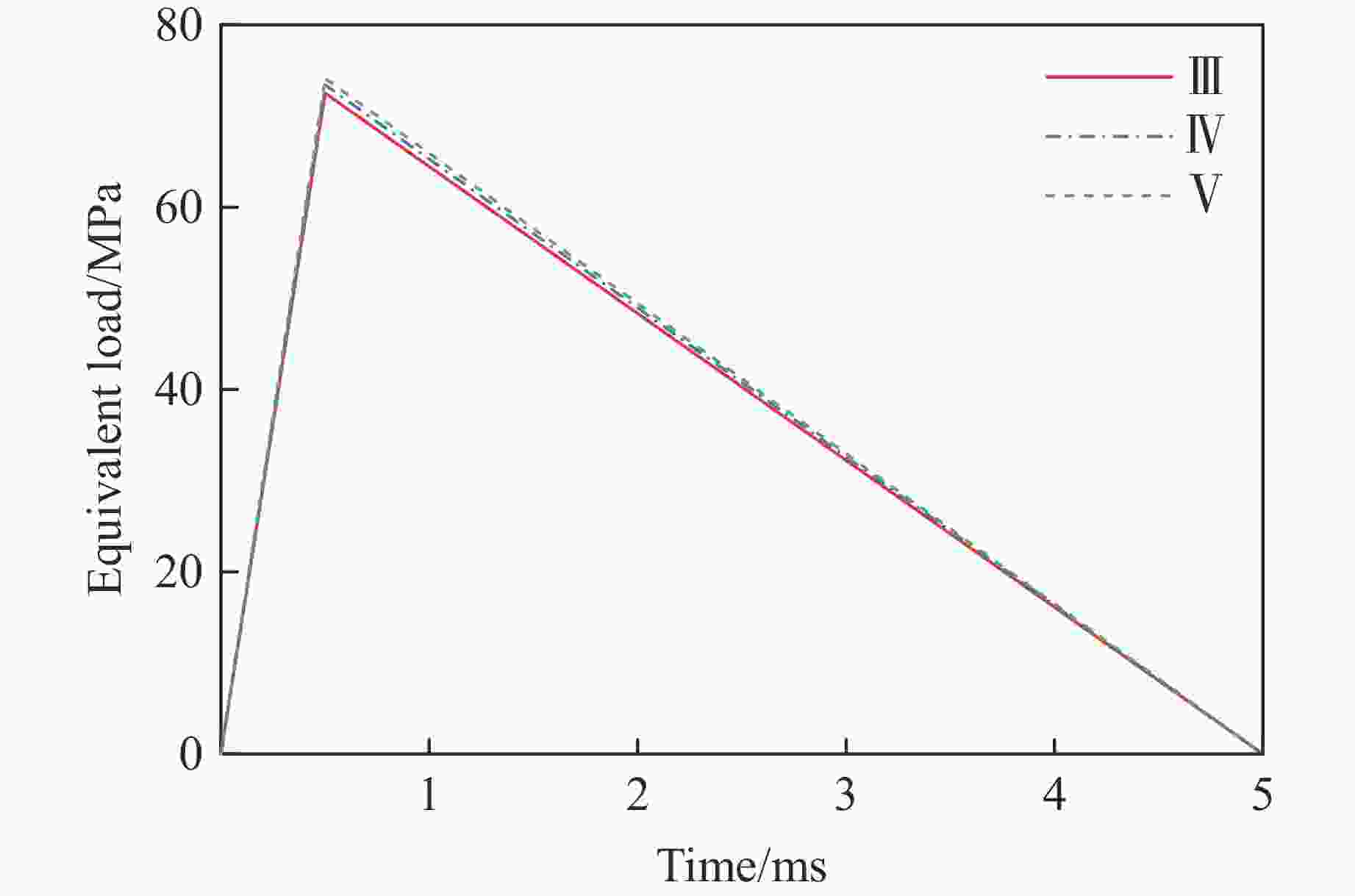
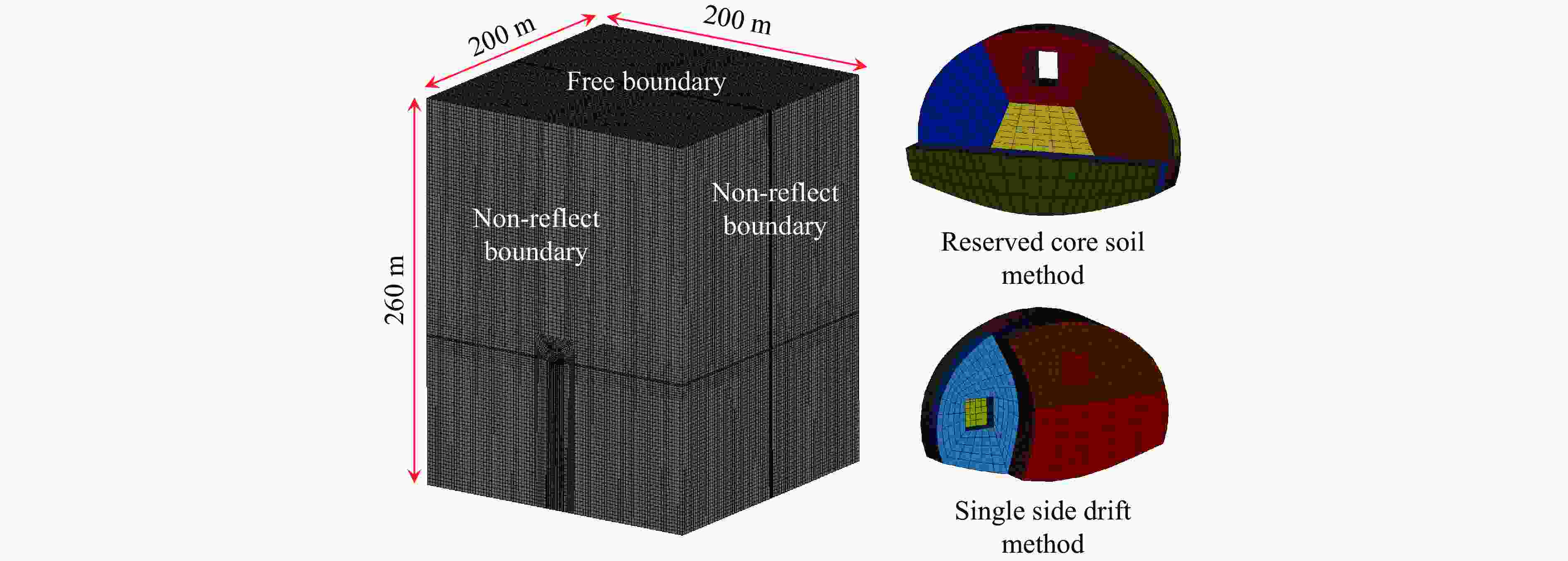
Propagation Laws and Prediction of Blasting Vibration in Mountain Highway Tunnels with Multi-Level Surrounding Rock
-
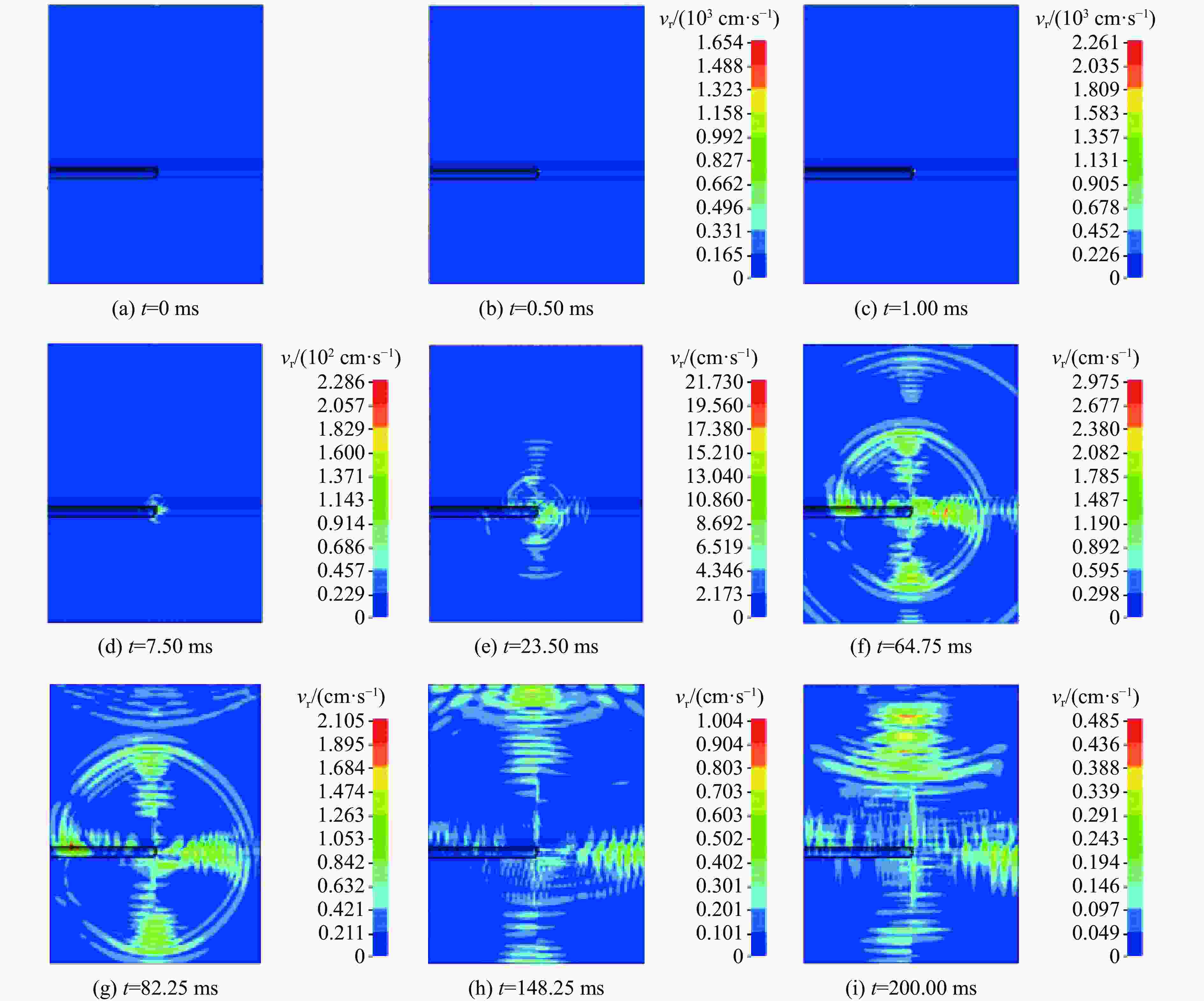
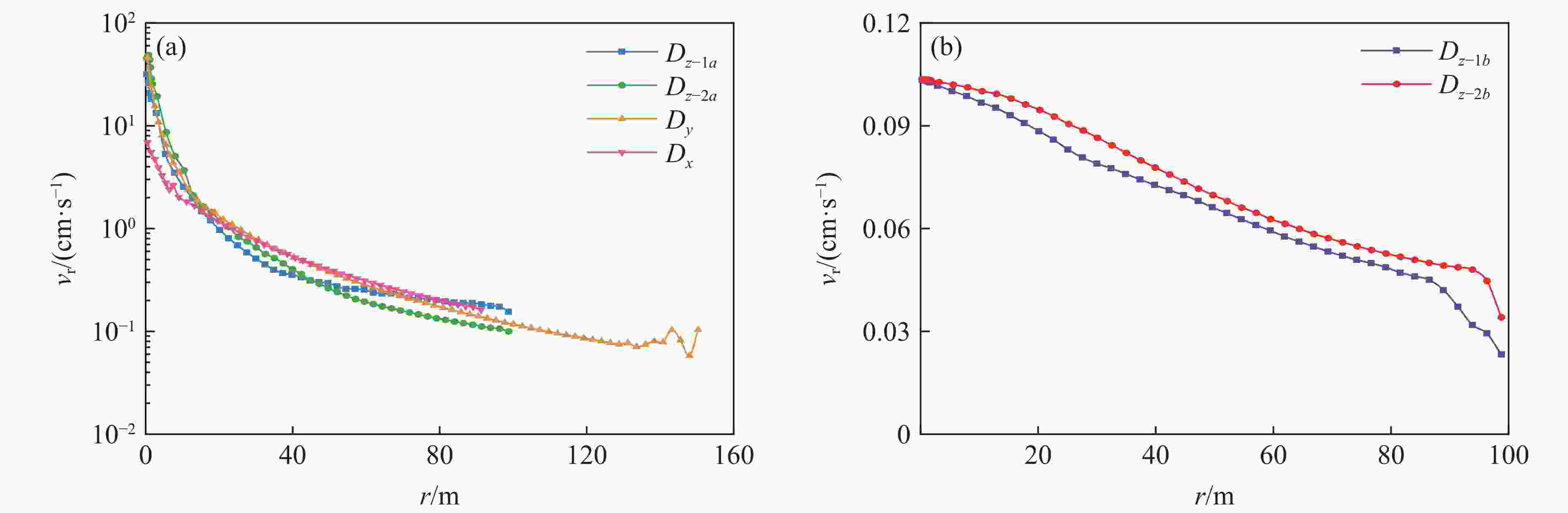
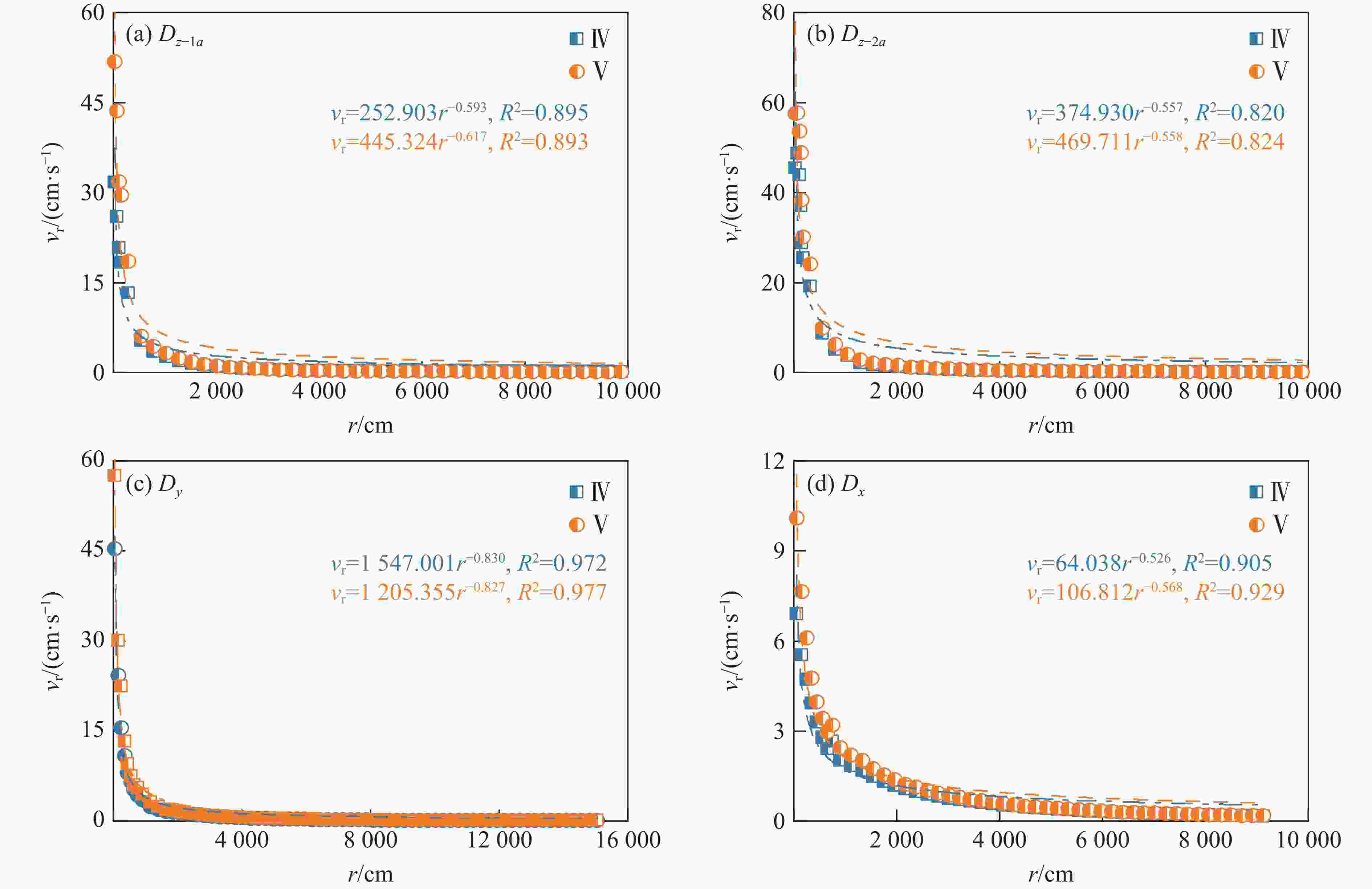
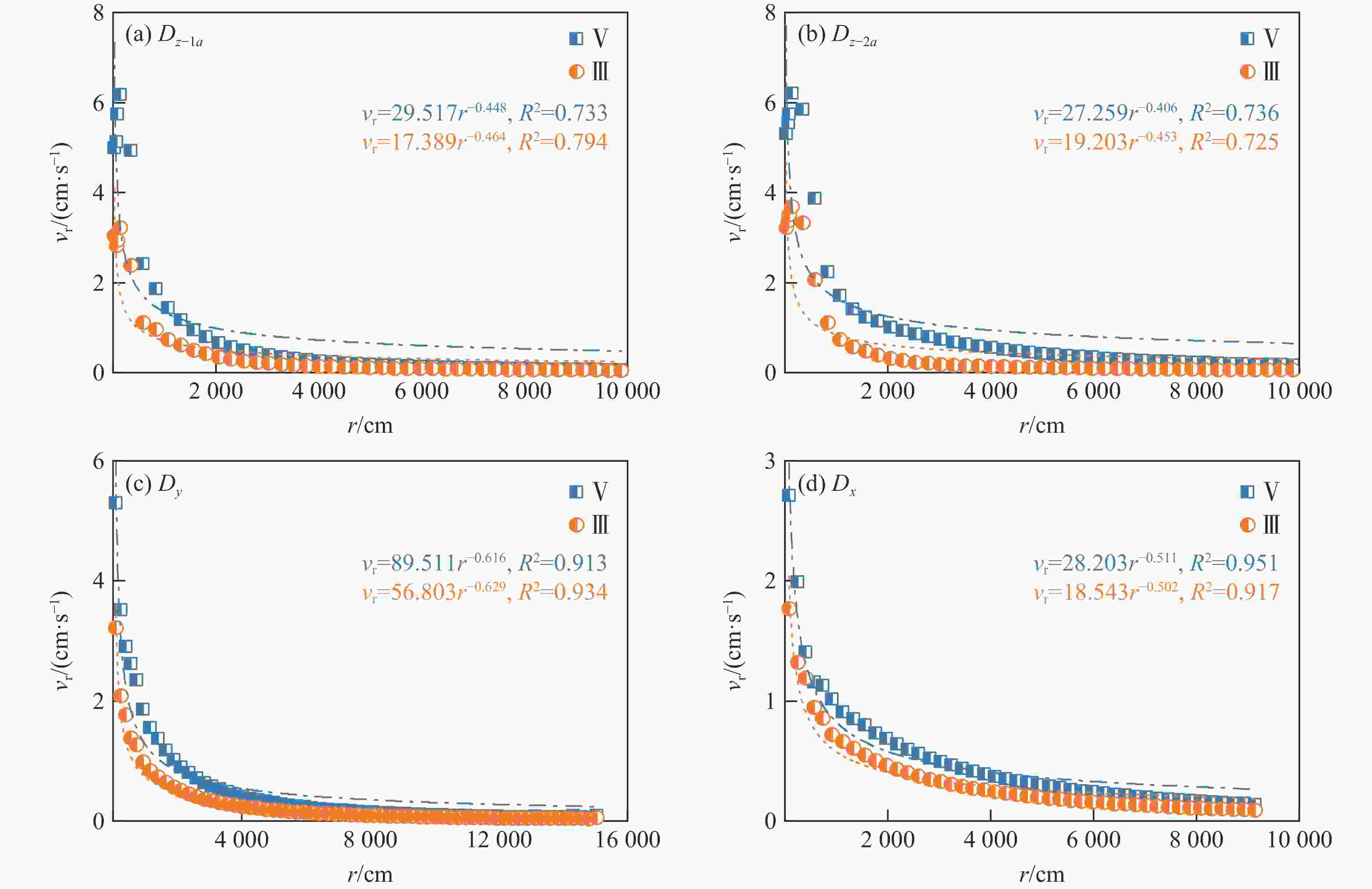
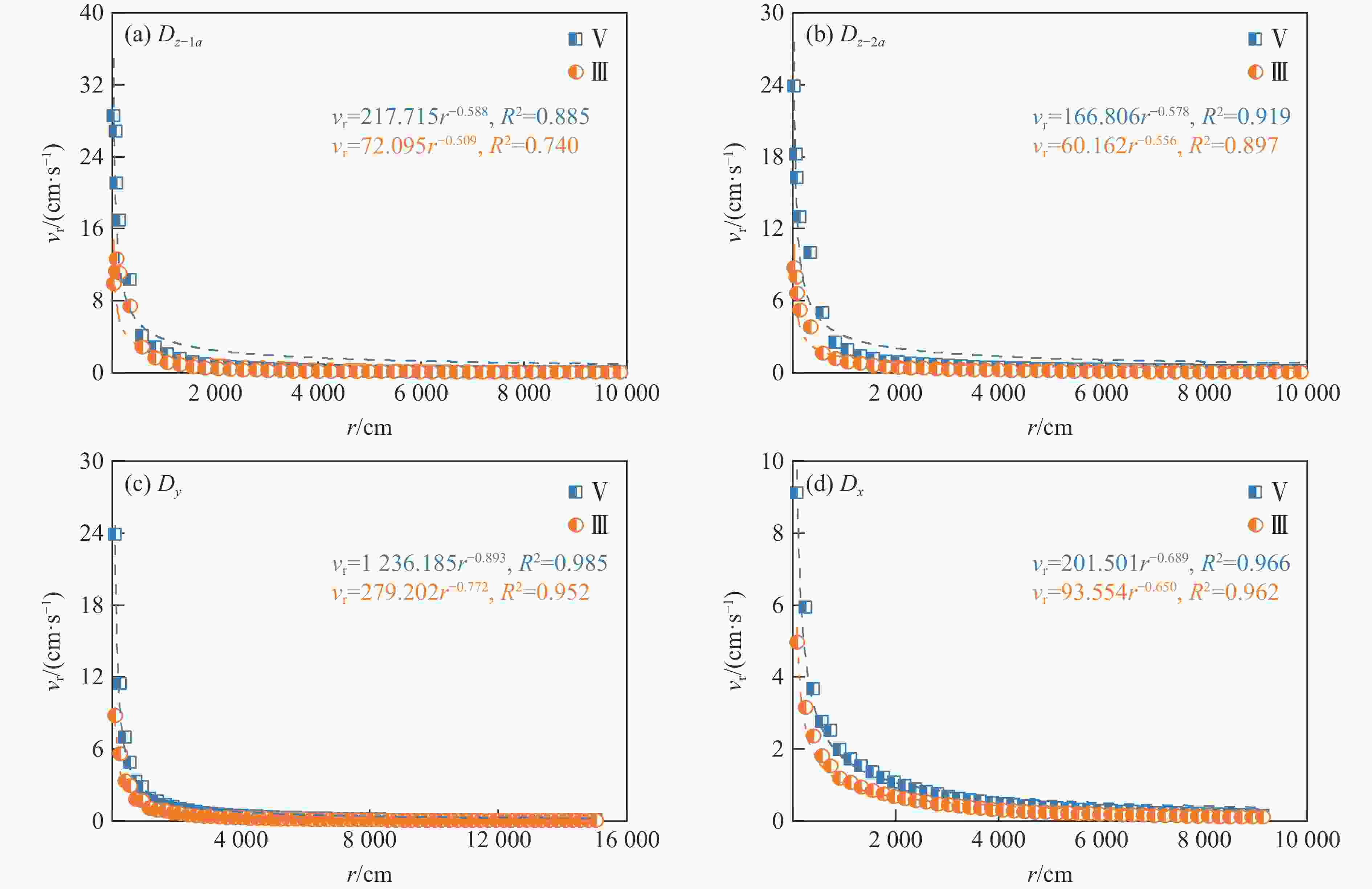
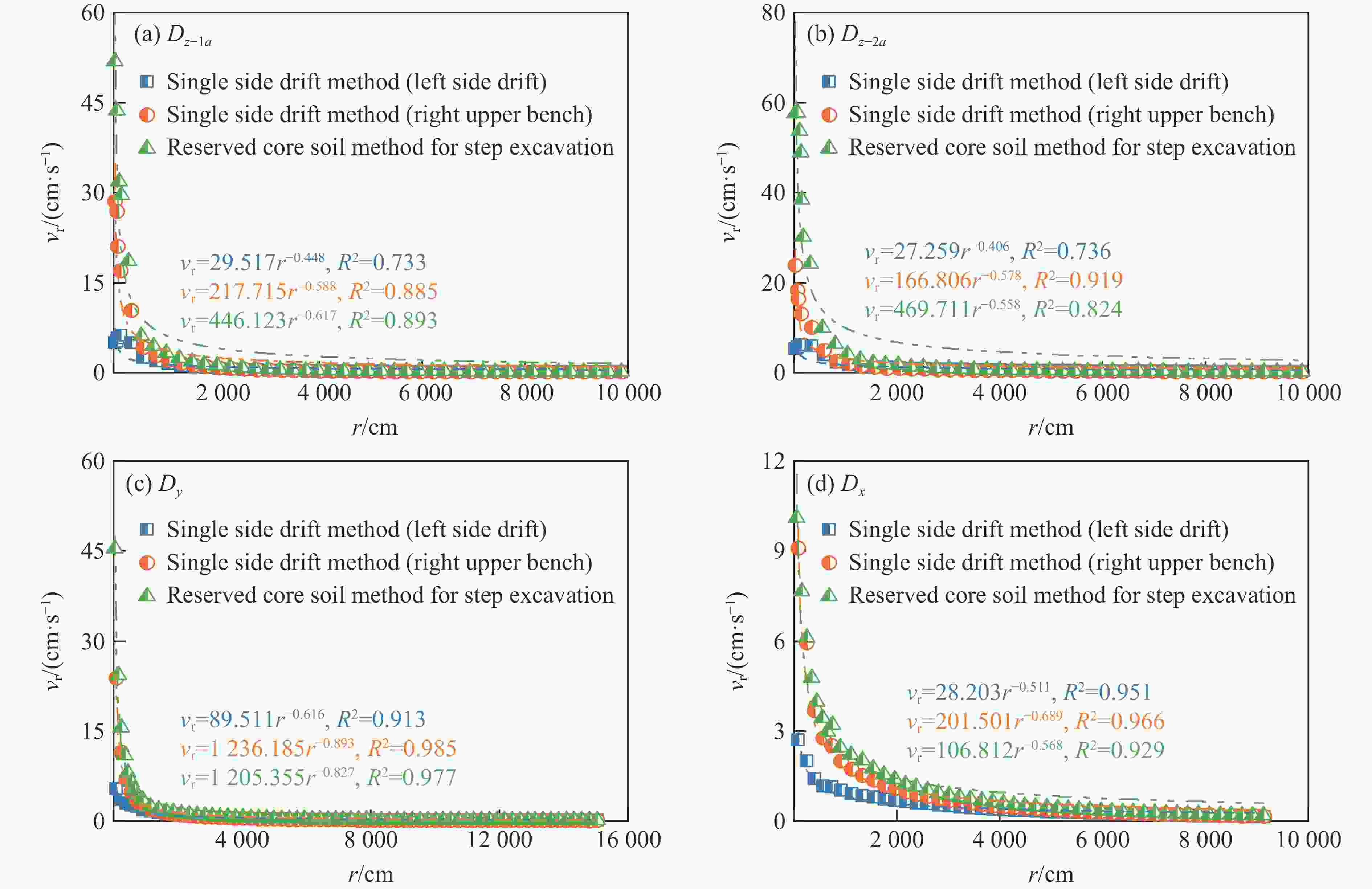
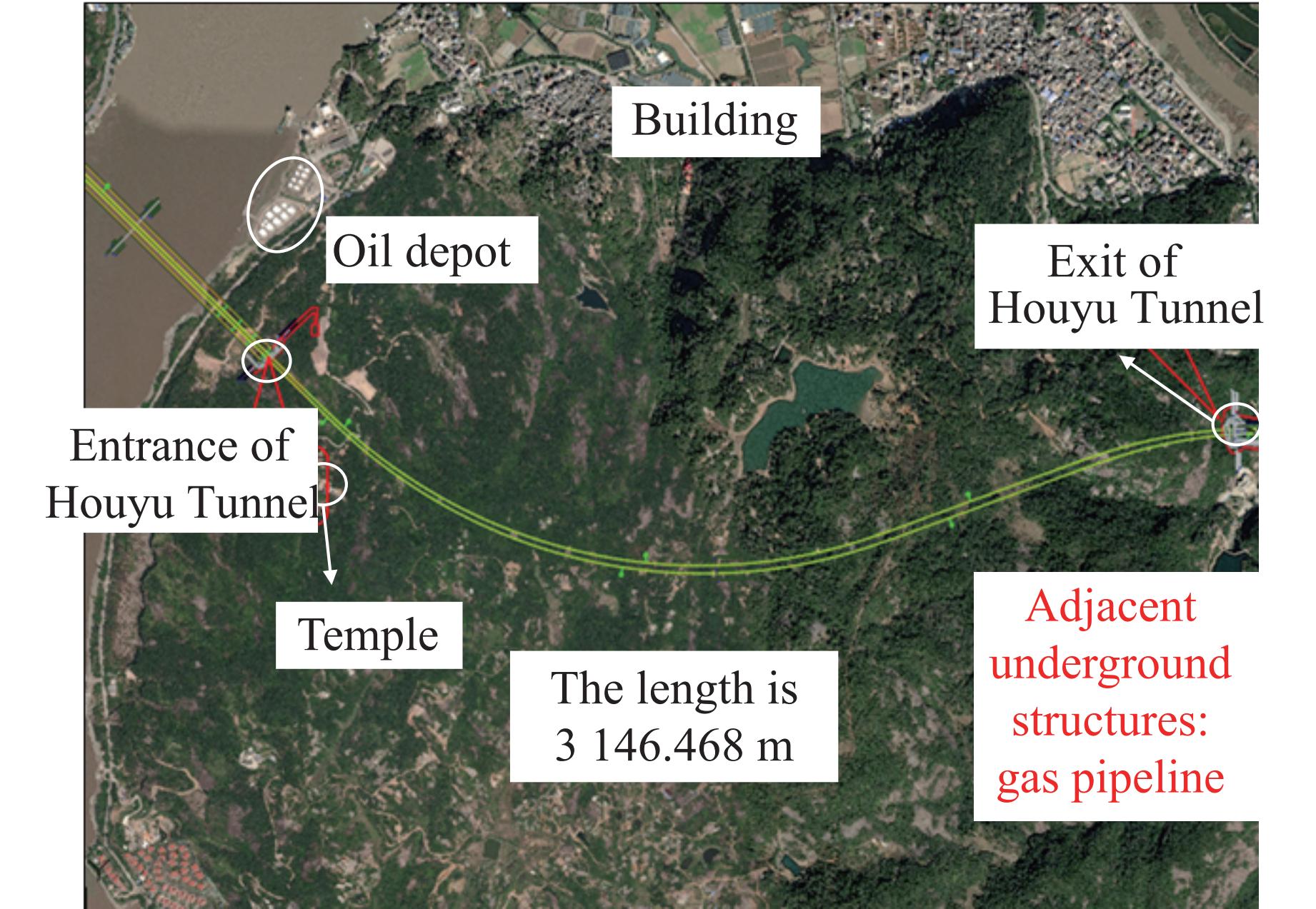
摘要: 为实现复杂地质环境下隧道爆破振动的有效控制,明晰爆破振动传播规律、准确预测爆破振动速度是爆破安全施工中的重要关注内容。依托高速公路猴屿隧道多级别围岩多方案爆破实际工程,通过LS-DYNA分析了不同爆破方式下不同级别围岩的振动衰减特征,并利用现场试验验证了数值模拟的合理性,最后采用量纲分析理论建立了考虑地表高程差影响的振速预测模型。结果表明:随着爆源距增加,合振速先迅速衰减后缓慢衰减,其中已开挖区隧道上部围岩振速大于未开挖区,围岩强度等级和围岩振动速度整体上呈负相关关系。对于围岩合振速,采用上下台阶留核心土法时最大,单侧壁导坑法-右侧上台阶爆破次之,单侧壁导坑法-左侧壁导坑爆破最小;而对于围岩合振速衰减速率,单侧壁导坑法-右侧上台阶爆破时最大,上下台阶留核心土法次之,单侧壁导坑法-左侧壁导坑爆破时最小。采用上下台阶留核心土法时,埋地管道、建筑群、寺庙、油库的最小安全距离分别为95、81、447和73 m;采用单侧壁导坑法时,埋地管道、建筑群、寺庙、油库的最小安全距离分别为56、72、327和71 m。Abstract: To achieve vibration control in tunnel blasting under complex geological conditions, clarifying the propagation laws of blasting velocities and accurately predicting blasting velocities are crucial aspects of safe blasting construction. Based on the multi-level surrounding rock and multi-scheme blasting engineering of the Houyu tunnel on the expressway, LS-DYNA was used to analyze the vibration attenuation characteristics of multi-level surrounding rock under various blasting methods. Field tests were conducted to validate the rationality of the numerical simulations. Finally, a velocity prediction model considering the influence of elevation differences was established by dimensional theory. The results show that as the blast center distance increases, the resultant velocity decays rapidly at first and then more slowly. The velocity of the surrounding rock above the tunnel in the excavated area is greater than that in the unexcavated area. There is a negative correlation between the strength grade of rock and the vibration velocity. The resultant velocities of the surrounding rock, from largest to smallest, are as follows: the reserved core soil method for step excavation, the single side drift method with right upper bench, and the single side drift method with left side drift. The attenuation rates of the resultant velocities, from largest to smallest, are as follows: the single side drift method with right upper bench, the reserved core soil method for step excavation, and the single side drift method with left side drift. When using the reserved core soil method for step excavation, the minimum safety distances for buried pipelines, building clusters, temples, and oil depots are 95, 81, 447 and 73 m, respectively. When using the single side drift method, the minimum safety distances for buried pipelines, building clusters, temples, and oil depots are 56, 72, 327 and 71 m, respectively.
-
表 1 围岩的物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of surrounding rock
Rock grade Density/(g·cm−3) Elastic modulus/GPa Poisson’s ratio Yield strength/MPa Shear modulus/GPa Ⅲ 2.40 27.72 0.26 60 11.00 Ⅳ 2.20 9.50 0.32 45 3.60 Ⅴ 2.10 4.08 0.36 36 1.50 表 2 数值模拟工况
Table 2. Numerical simulation conditions
Case Excavation method Rock grade 1 Reserved core soil method for step excavation Ⅳ 2 Reserved core soil method for step excavation Ⅴ 3 Single side drift method (left side drift) Ⅲ 4 Single side drift method (left side drift) Ⅴ 5 Single side drift method (right upper bench) Ⅲ 6 Single side drift method (right upper bench) Ⅴ 表 3 数值模拟与现场试验得到的振速结果的对比
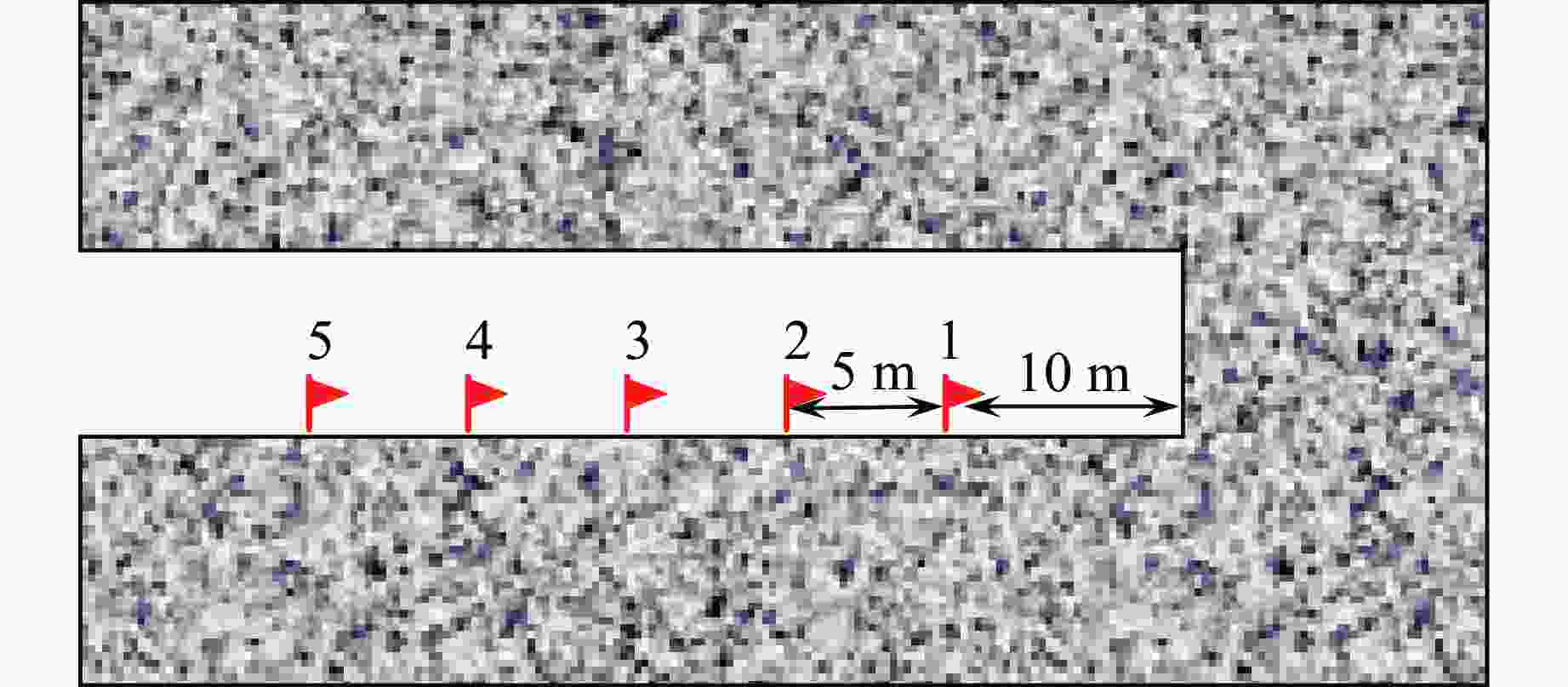
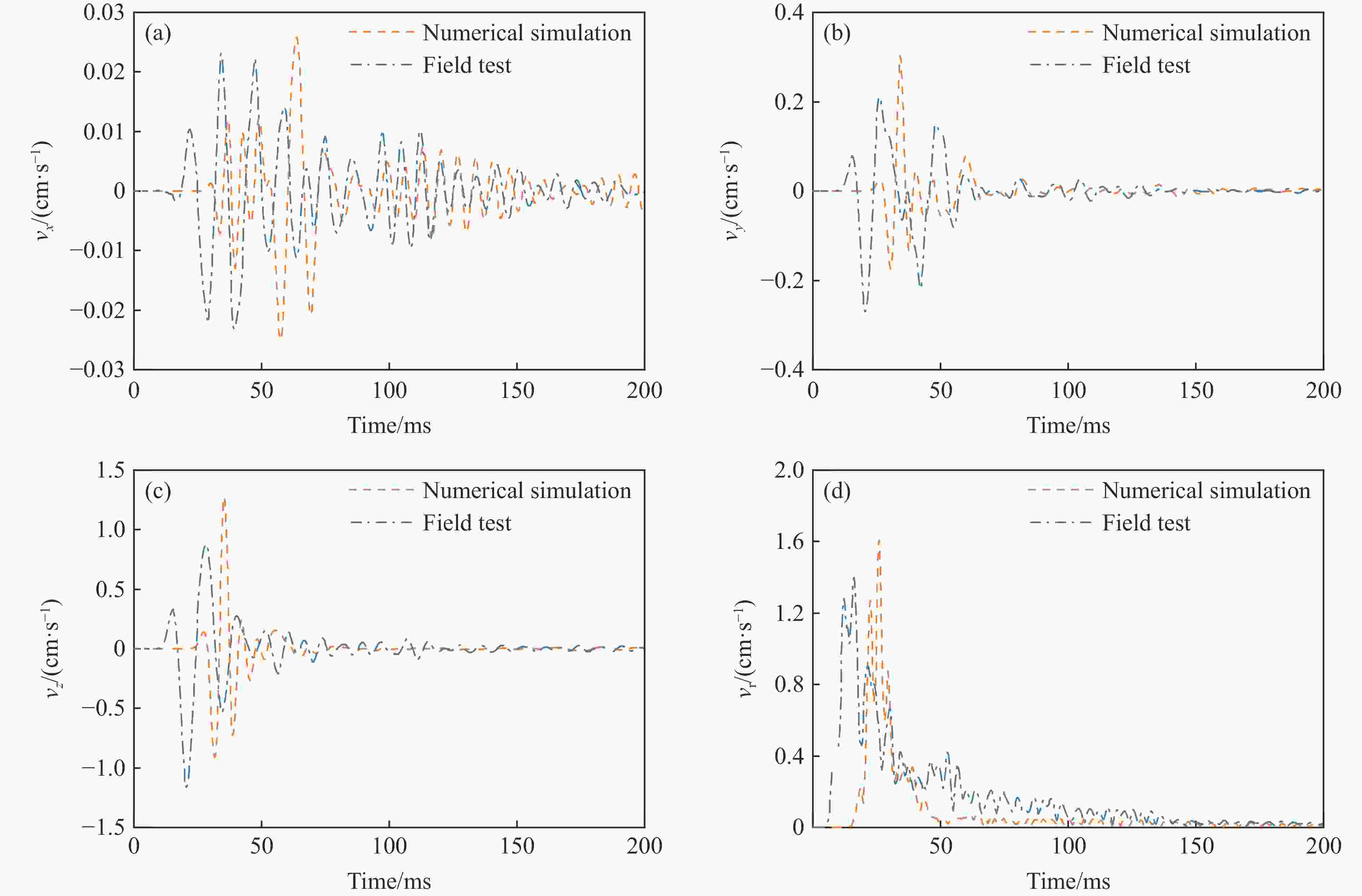
Table 3. Comparison of vibration velocity results between numerical simulation and field tests
Monitoring
pointvx vy Num./(cm·s−1) Test/(cm·s−1) Error/% Num./(cm·s−1) Test/(cm·s−1) Error/% 1 0.025 0.023 8.343 0.302 0.270 10.566 2 0.022 0.020 7.356 0.278 0.252 9.345 3 0.017 0.015 9.763 0.241 0.215 10.864 4 0.014 0.013 6.535 0.218 0.201 7.934 5 0.012 0.011 7.745 0.193 0.176 8.935 Monitoring
pointvz vr Num./(cm·s−1) Test/(cm·s−1) Error/% Num./(cm·s−1) Test/(cm·s−1) Error/% 1 1.279 1.155 9.687 1.605 1.399 12.854 2 1.057 0.933 11.742 1.236 1.103 10.745 3 0.887 0.809 8.738 0.974 0.879 9.734 4 0.796 0.723 9.176 0.867 0.786 9.246 5 0.709 0.634 10.646 0.777 0.694 10.745 表 4 爆破振动速度的影响因素及其量纲
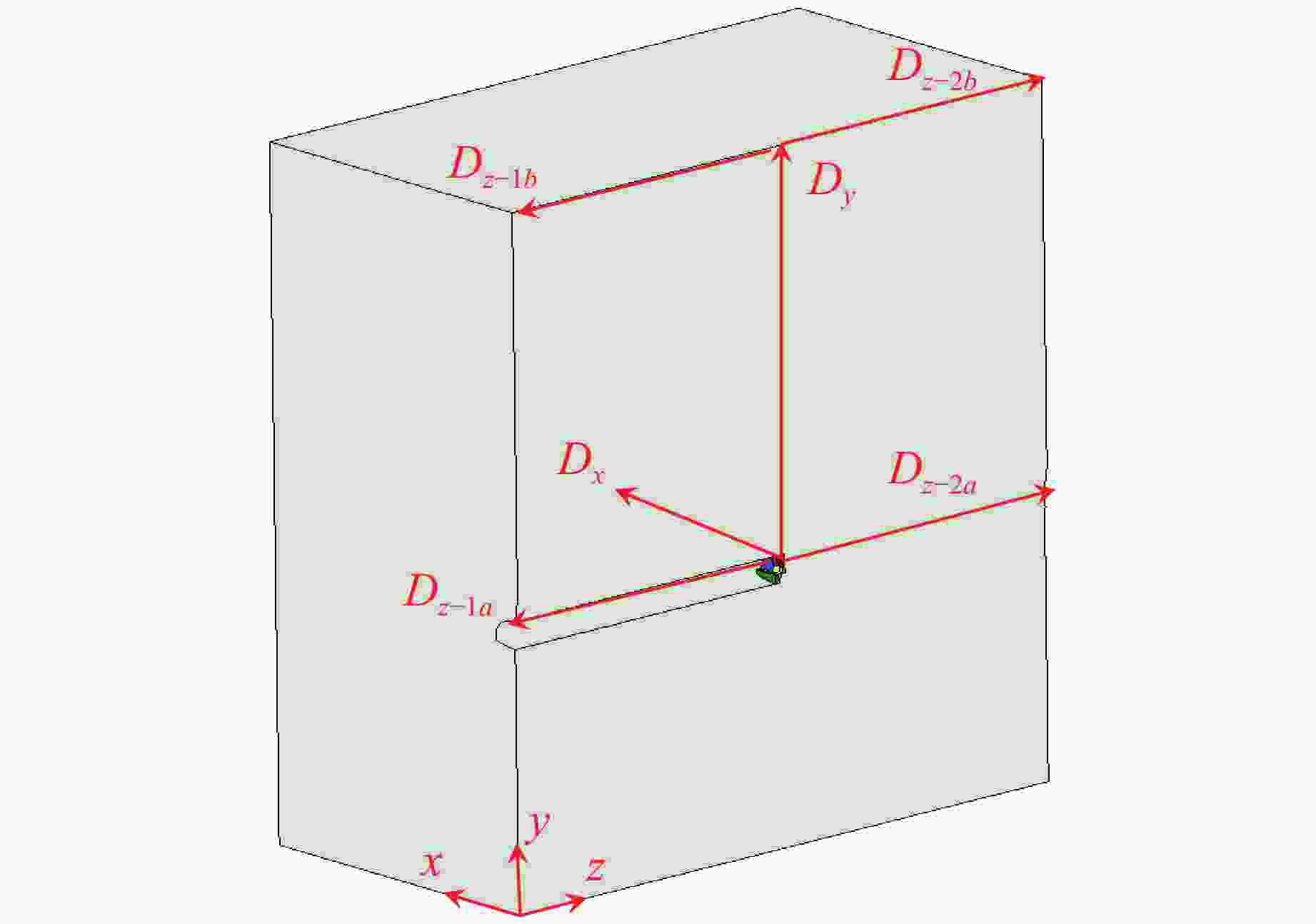
Table 4. Influence factors of blasting vibration velocity and their dimensions
Influence factor Dimension Influence factor Dimension Q M r L H L ρ ML−3 vr LT−1 c LT−1 表 5 不同保护对象的安全控制距离
Table 5. Safety distance for different protection objects
Excavation method Rock grade Safety distance/m Gas pipeline Building Temple Oil depot Reserved core soil method
for step excavationⅣ 58 74 224 71 Ⅴ 95 81 447 73 Single side drift method
(left side drift)Ⅲ 40 71 70 71 Ⅴ 56 72 327 71 Single side drift method
(right upper bench)Ⅲ 41 71 153 71 Ⅴ 42 71 133 71 -
[1] 王子一, 吴桂义, 罗畅, 等. 多次爆破振动下陡边坡振动响应及稳定性研究 [J]. 爆破, 2023, 40(3): 158–169, 176. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.03.022WANG Z Y, WU G Y, LUO C, et al. Study on vibration response and stability of steep slope under multiple blasting vibrations [J]. Blasting, 2023, 40(3): 158–169, 176. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.03.022 [2] 闵鹏, 谢俊, 申玉生, 等. 考虑自由面参数影响的地铁隧道爆破振速预测公式优化研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2023, 42(21): 245–253, 283. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.21.029MIN P, XIE J, SHEN Y S, et al. Optimization of prediction formula for blasting vibration velocity of subway tunnels considering effects of free surface parameters [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2023, 42(21): 245–253, 283. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.21.029 [3] 何丽平, 汪晓俊, 郭剑雄, 等. 砂泥岩互层岩质边坡爆破振动衰减规律现场试验研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2023, 37(5): 055301. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230666HE L P, WANG X J, GUO J X, et al. Field experimental research on blasting vibration attenuation law of sand-mudstone interbedded rock slope [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2023, 37(5): 055301. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230666 [4] 赵茉溪, 杨玉民, 周传波, 等. 基于MD-PCA-BP模型的露天矿山爆破振动速度预测 [J]. 爆破, 2024, 41(2): 203–211. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2024.02.025ZHAO M X, YANG Y M, ZHOU C B, et al. Prediction of blasting vibration velocity in open-pit mine based on MD-PCA-BP model [J]. Blasting, 2024, 41(2): 203–211. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2024.02.025 [5] 汪艮忠, 胡宇, 周汉红, 等. 浅埋偏压隧道掘进爆破地表振动效应研究 [J]. 工程爆破, 2023, 29(6): 147–152, 166. doi: 10.19931/j.EB.20230134WANG G Z, HU Y, ZHOU H H, et al. Study on surface vibration effect of shallow-buried bias tunnel [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2023, 29(6): 147–152, 166. doi: 10.19931/j.EB.20230134 [6] 高军伟, 赵岩, 王奔. 立体交叉铁路隧道爆破振动效应的研究 [J]. 爆破器材, 2023, 52(6): 39–47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2023.06.007GAO J W, ZHAO Y, WANG B. Vibration law in the blasting of railway tunnels with interchange [J]. Explosive Materials, 2023, 52(6): 39–47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2023.06.007 [7] 李小帅, 高文学, 宿利平, 等. 小净距隧道掘进爆破及其振动响应规律研究 [J]. 爆破, 2024, 41(2): 194–202. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2024.02.024LI X S, GAO W X, SU L P, et al. Study on attenuation law of blasting vibration in a small clear distance highway tunnel [J]. Blasting, 2024, 41(2): 194–202. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2024.02.024 [8] 王亚琼, 杨御博, 高启栋, 等. 无中墙连拱隧道爆破振动响应特性及安全控制措施 [J]. 中国公路学报, 2023, 36(11): 266–277. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2023.11.008WANG Y Q, YANG Y B, GAO Q D, et al. Study on blast vibration characteristics and safety control measures in the excavation of multi-arch tunnel without a middle wall [J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2023, 36(11): 266–277. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2023.11.008 [9] 柳之森. 地铁隧道下穿黄鹤楼景区爆破振动效应分析 [J]. 爆破, 2023, 40(2): 190–198. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.02.027LIU Z S. Blasting vibration effect of subway tunnel underpassing scenic spot of Yellow Crane Tower [J]. Blasting, 2023, 40(2): 190–198. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.02.027 [10] 吉凌, 周传波, 张波, 等. 大断面隧道爆破作用下围岩动力响应特性与损伤效应研究 [J]. 铁道学报, 2021, 43(7): 161–168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2021.07.021JI L, ZHOU C B, ZHANG B, et al. Study on dynamic response and damage effect of surrounding rock in large tunnel under blasting excavation [J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2021, 43(7): 161–168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2021.07.021 [11] 马晨阳, 吴立, 孙苗. 自由面数量对水下钻孔爆破振动信号能量分布及衰减规律的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(1): 015201. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0436MA C Y, WU L, SUN M. Influence of free surface numbers on the energy distribution and attenuation of vibration signals of underwater drilling blasting [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(1): 015201. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0436 [12] 陈祥, 刘明学, 祁小博. 爆破振动作用下大型地下洞室群围岩动力响应及合理间距分析 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(1): 277–285. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.01.036CHEN X, LIU M X, QI X B. Dynamic response of surrounding rock of large underground caverns under blast vibration and reasonable spacing between adjacent caverns [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(1): 277–285. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.01.036 [13] 王林台, 高文学, 张发财, 等. 爆破地震作用下建筑物振动响应研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(Suppl 1): 121–134.WANG L T, GAO W X, ZHANG F C, et al. Research on blasting vibration response of high-rise building based on model simplification [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2018, 39(Suppl 1): 121–134. [14] 公伟增, 段宝福, 张雪伟, 等. 隧道爆破地震波作用下砌体建筑物振动响应分析 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(33): 377–383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.33.056GONG W Z, DUAN B F, ZHANG X W, et al. Analysis of vibration response of surface masonry buildings under tunnel blasting seismic wave [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(33): 377–383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.33.056 [15] 傅鹤林, 姜智博, 邱琼. 浅埋暗挖隧道爆破对敏感建筑物的影响及优化 [J]. 铁道工程学报, 2023, 40(3): 71–78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2023.03.012FU H L, JIANG Z B, QIU Q. Influence and optimization of blasting of shallow-buried tunnel on sensitive buildings [J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2023, 40(3): 71–78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2023.03.012 -






 下载:
下载: