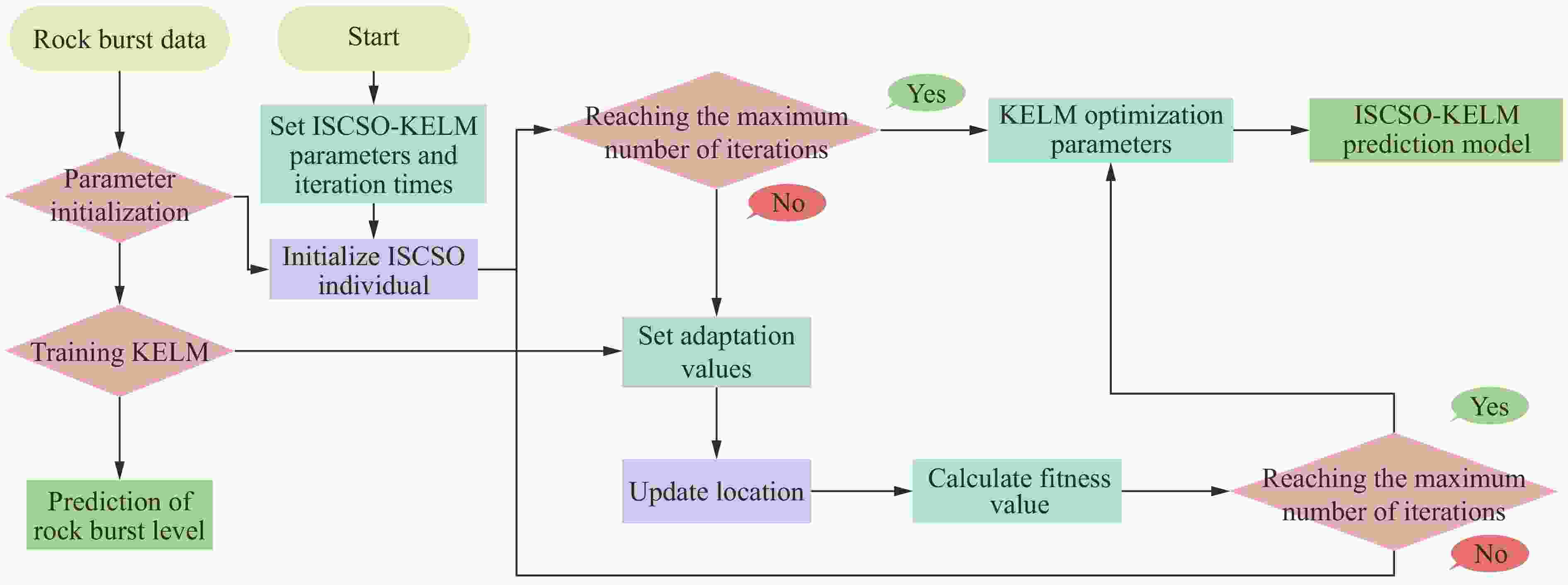
Prediction of Rock Burst Intensity Based on the ISCSO-KELM Model
-
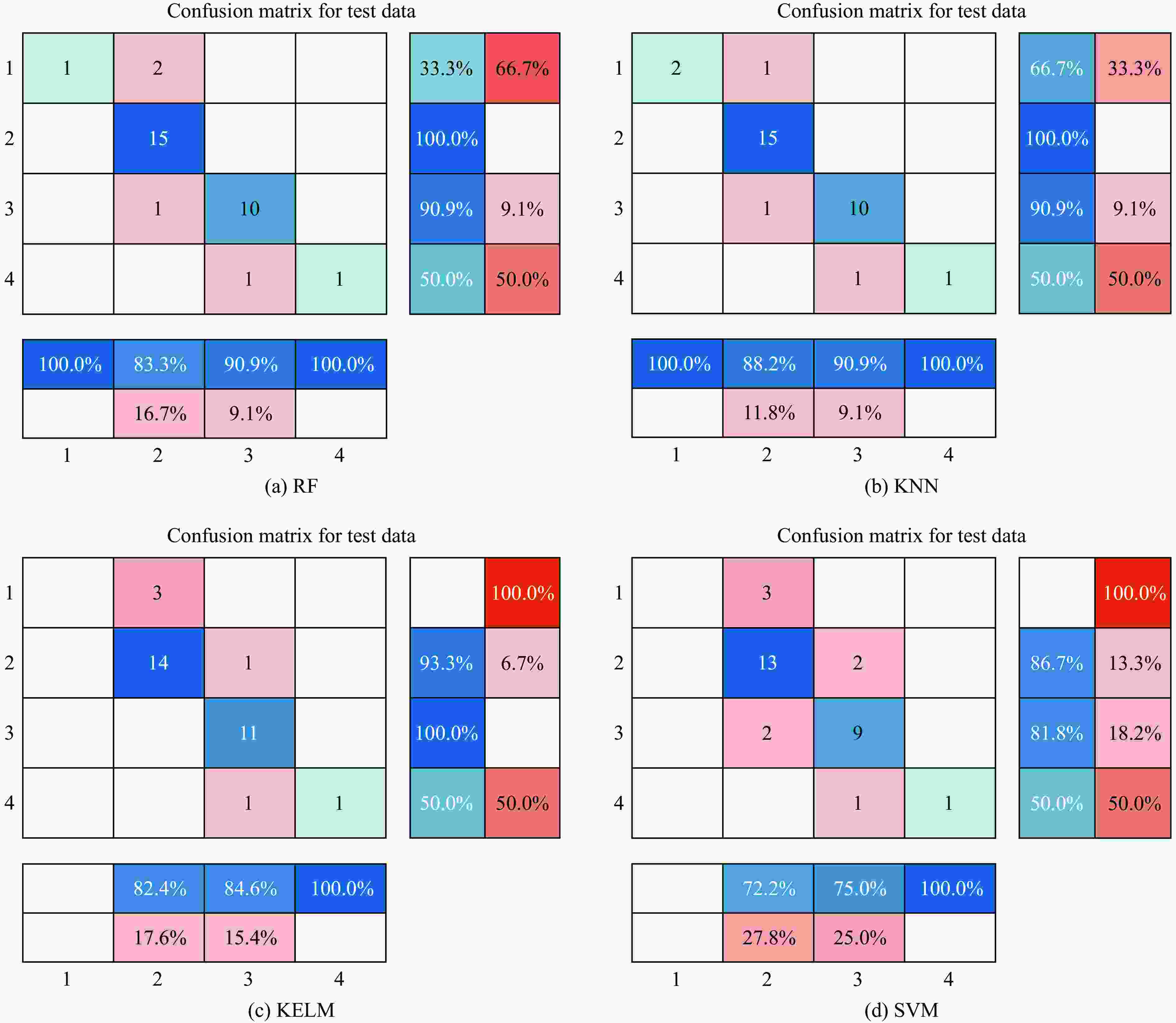
摘要: 针对施工过程中的岩爆事故防控需求,提出了一种基于改进沙猫群-核极限学习机(improved sand cat swam optimization-kernel based extreme learning machine,ISCSO-KELM)算法的新型岩爆预测模型。在指标选取方面,采用围岩最大切向应力、单轴抗压强度、单轴抗拉强度和岩石弹性能量指数作为岩爆的评价指标。选取国内外105组岩爆实例作为机器学习样本,通过对比随机森林、K最近邻、支持向量机、核极限学习机等模型所预测的混淆矩阵,验证了ISCSO-KELM模型在评估精确率(96.774 2%)和召回率方面的优越性。最后,以相关工程实例作为验证集对岩爆等级进行验证。结果表明,ISCSO-KELM模型在处理岩爆问题上可以更好地捕捉岩爆等级与评价指标间的内在关联,具有良好的适用性,为岩爆预测提供了一种新的技术途径。Abstract: In order to reduce the occurrence of rock burst accidents during construction, the rock burst intensity should be assessed. In this paper, we propose a new rock burst prediction model based on the improved sandcat swam optimization-kernel based extreme learning machhine (ISCSO-KELM) algorithm. The maximum tangential stress, uniaxial compressive strength, uniaxial tensile strength and rock elastic energy index were selected as the evaluation indexes of rock burst. 105 domestic and international examples of rock burst were selected as samples for machine learning. Comparison of the relative ratios of the model presented herein with confusion matrix predicted by models including random forest (RF), K-nearest neighbor (KNN), support vector machine (SVM) and kernel based extreme learning machhine (KELM) models shows that, the ISCSO-KELM model is superior at assessing both evaluation accuracy and recall. The evaluation accuracy of the model reached 96.774 2%, indicating the superiority of ISCSO-KELM. Relevant engineering cases were used to verify the rock burst intensity. The results show that ISCSO-KELM model is more effective in capturing the connection between rock burst intensity and the indexes, thus providing a new highly applicable method for rock burst prediction.
-
表 1 岩爆等级及分类依据
Table 1. Rock burst intensity and classification basis
Intensity prediction Classification Classification basis Sound size Rock explosion performance Fragments size Impact on construction Ⅰ No rock burst Ⅱ Slight rock
burstNo sound or
weak soundRock fall freely or
after relaxationThe rock is small in size
and small in quantityIt has little impact
on constructionⅢ Medium rock
burstThere was a
crisp burstLings or blocks pop up
to the face surfaceThe rock size is large and
number is numerousIt has a certain impact
on the constructionⅣ Severe rock
burstThere is a
loud noiseSharp-edged fragments
of rock flew outThe rock size is large and
number is numerousIt has a great impact
on the construction表 2 岩爆分级标准
Table 2. Rock burst classification criteria
Intensity prediction σθ/MPa σc/MPa σt/MPa Wet Ⅰ 0−24 0−80 0−5 0−2.0 Ⅱ 24−60 80−120 5−7 2.0−3.5 Ⅲ 60−126 120−180 7−9 3.5−5.0 Ⅳ 126−200 180−320 9−30 5.0−20 表 3 ISCSO-KELM的Matlab参数
Table 3. Matlab parameters for ISCSO-KELM
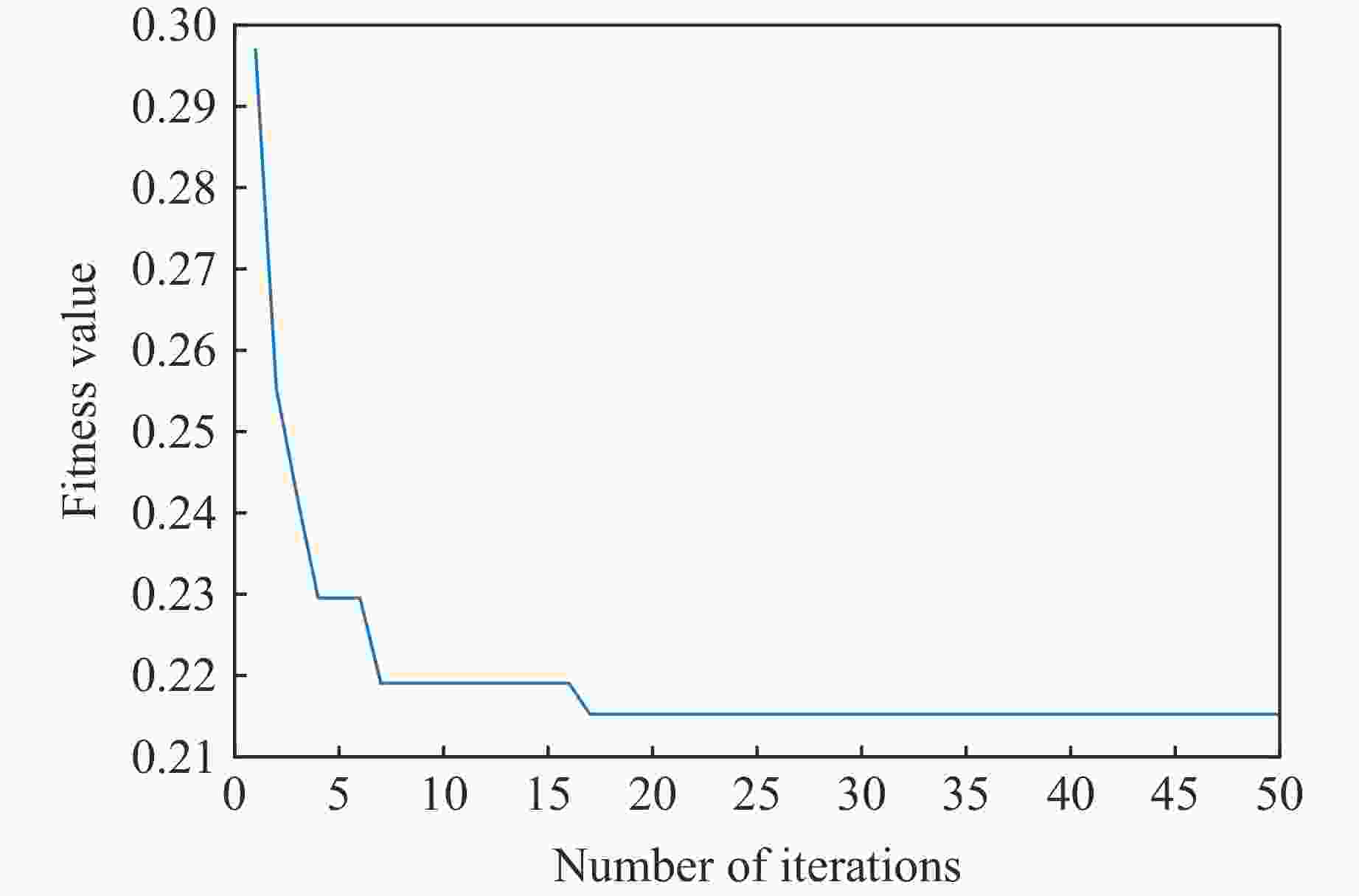
Parameters Value Population quantity 10 Iterations 50 Regularized coefficient upper and lower boundaries [100,1] Kernel function parameters upper and lower boundaries [100,1] Dimension 2 Best_pos [97.363 4,1] Best_score 0.187 6 表 4 部分岩爆案例实测数据
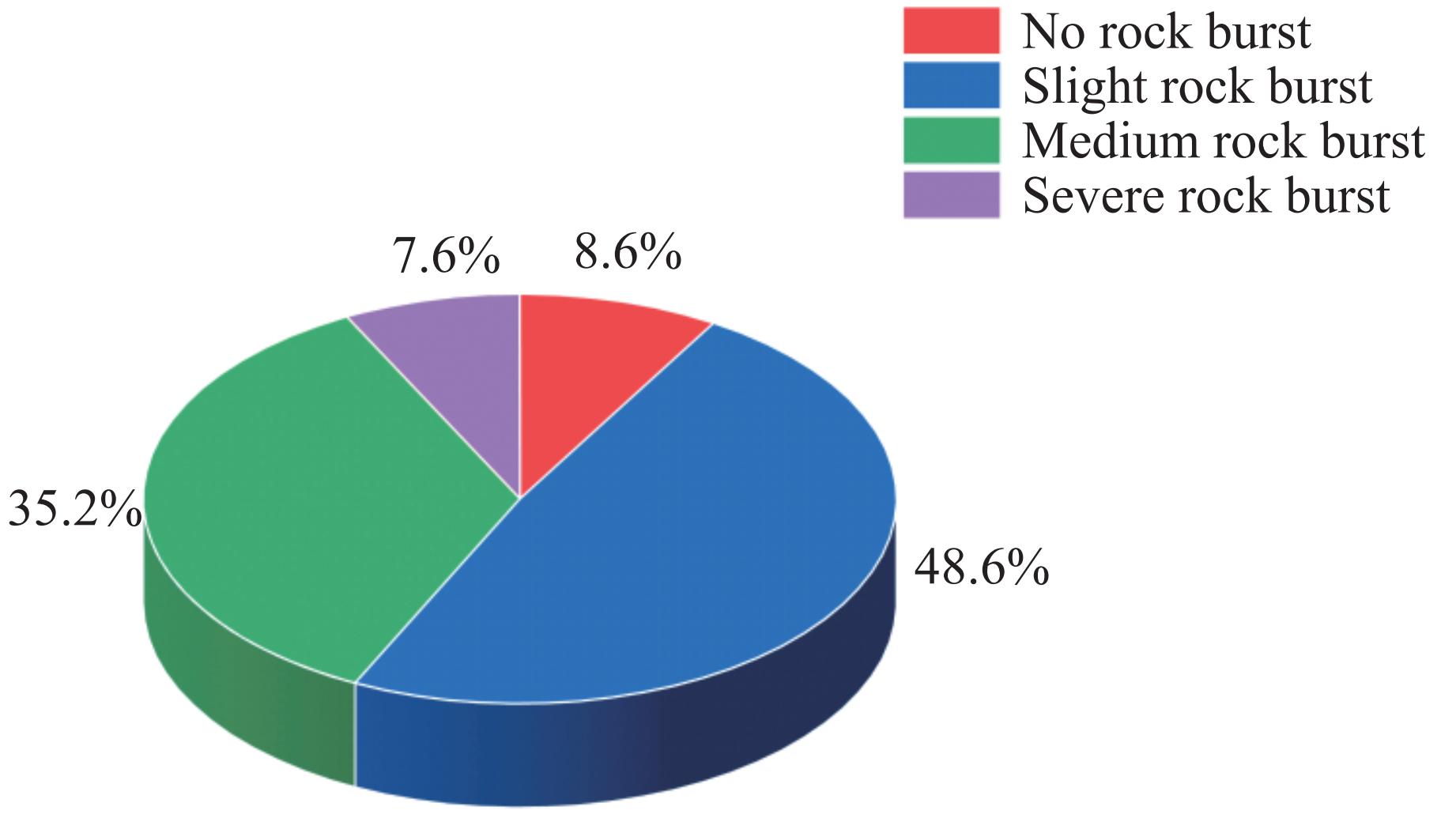
Table 4. Actual measured data of some rock burst cases
Sample No. σθ /MPa σc/MPa σt/MPa Wet Grade 1 43.08 114.08 12.29 6.12 Ⅲ 2 42.15 83.24 8.52 5.60 Ⅱ 3 40.87 139.00 6.00 0.81 Ⅰ 4 50.09 124.00 5.00 6.53 Ⅱ 5 59.09 88.25 3.60 6.14 Ⅱ 6 62.13 124.00 5.00 4.62 Ⅱ … … … … … … 98 68.85 48.96 13.66 1.35 Ⅲ 99 45.94 78.48 14.25 2.45 Ⅱ 100 80.06 67.65 8.28 3.98 Ⅲ 101 119.69 119.77 9.35 10.19 Ⅳ 102 83.63 112.30 10.13 3.21 Ⅲ 103 103.82 206.28 12.10 6.33 Ⅲ 104 112.38 178.81 12.07 7.68 Ⅳ 105 120.37 72.21 9.53 4.15 Ⅲ Estimated value True value xT xP xT xTP xFP xF xFN xTN 表 6 模型评估指标结果
Table 6. Results of the model evaluation indicators
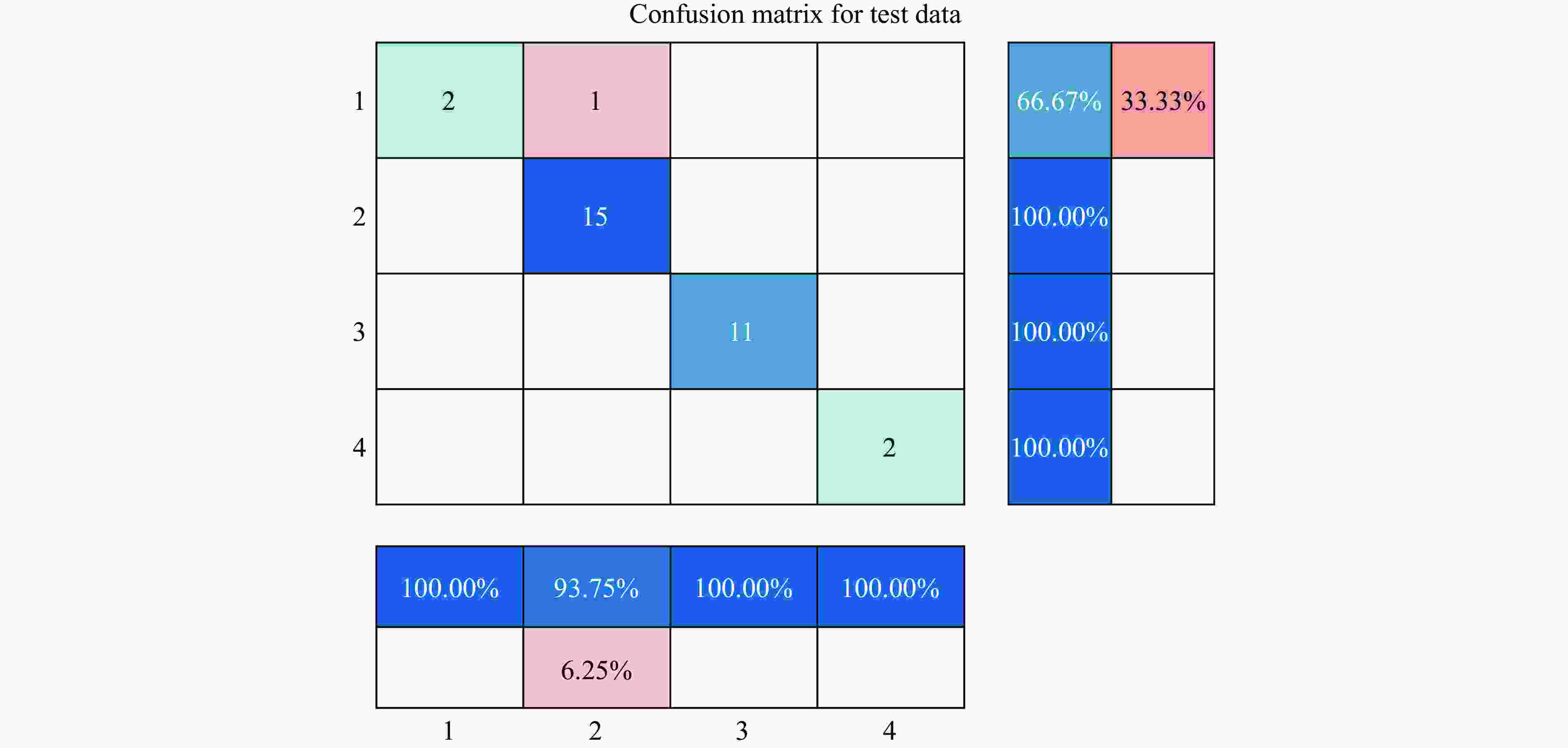
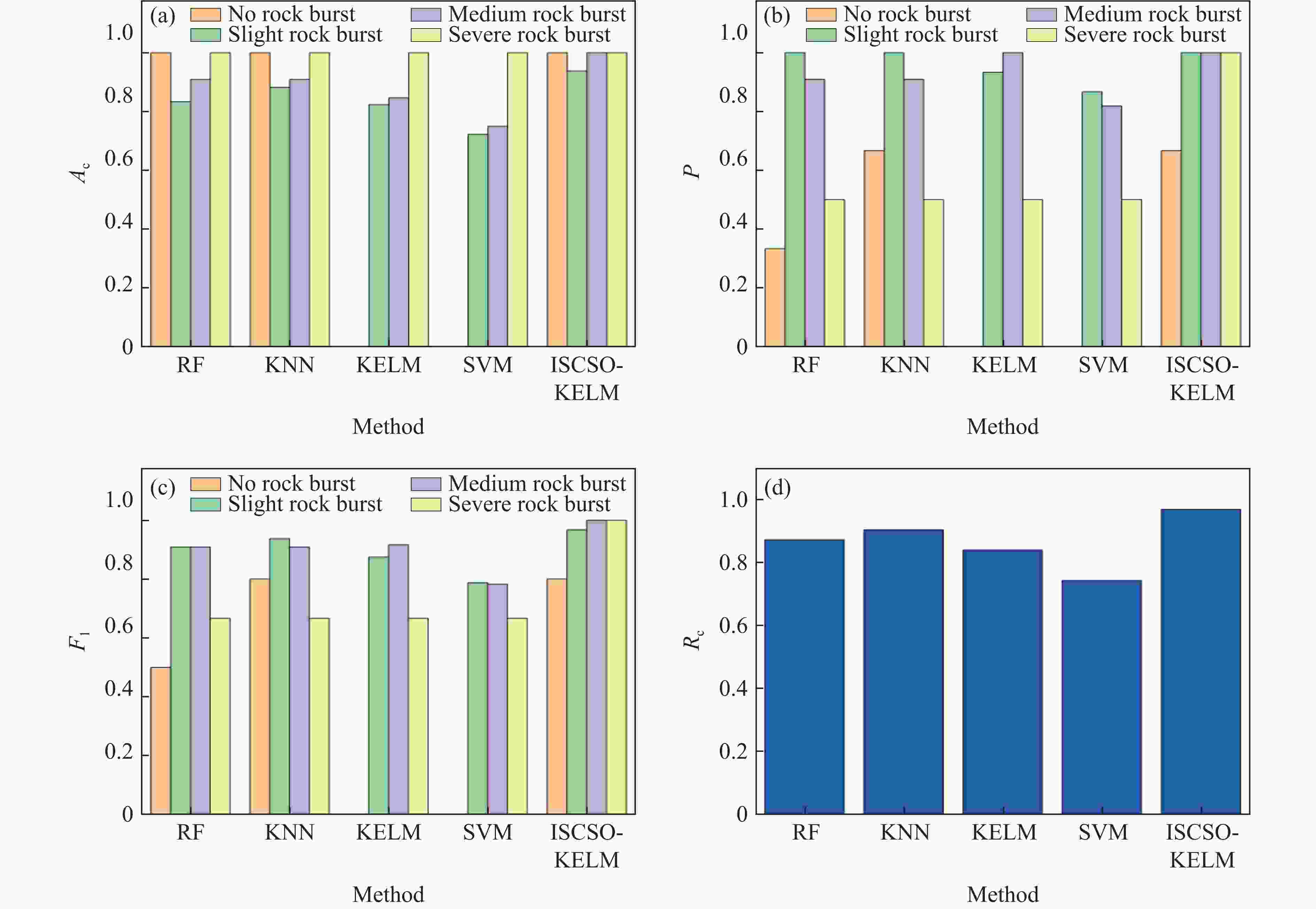
Rock burst intensity Ac/% P/% F1 Rc/% No rock burst 100.00 66.67 0.800 2 Slight rock burst 93.75 100.00 0.967 7 Medium rock burst 100.00 100.00 1.000 0 Severe rock burst 100.00 100.00 1.000 0 All intensities 96.774 2 表 7 样本数据
Table 7. Sample data
Sample No. σθ/MPa σc/MPa σt/MPa Wet Grade Project case 1 63.80 110.00 4.50 6.31 Ⅲ Maluping mine 750 m K1 2 2.60 20.00 3.00 1.39 Ⅰ Maluping mine 750 m K2 3 46.20 105.00 5.30 2.30 Ⅱ Jinping Ⅱ Hydropower Station 1+640 4 46.40 100.00 4.90 2.00 Ⅱ Jinping Ⅱ Hydropower Station 1+731 5 90.52 107.00 3.92 3.10 Ⅲ Jinping Ⅱ Hydropower Station 3+000 6 88.41 105.00 5.33 2.30 Ⅲ Jinping Ⅱ Hydropower Station 3+390 表 8 模型结果对比表
Table 8. Comparison of the model results
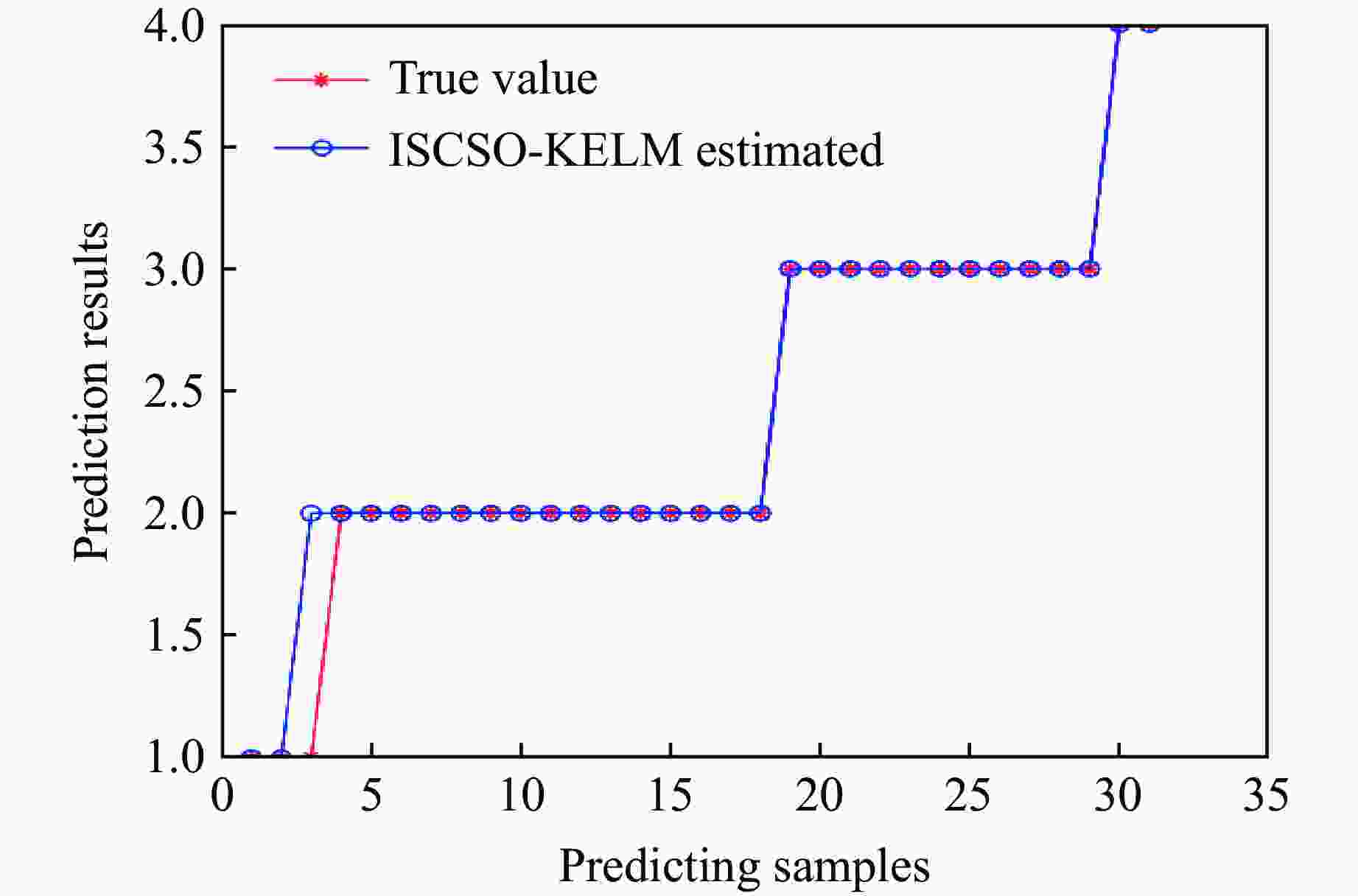
Sample No. Predicted rock burst grade Actual rock burst grade RF SVM KELM ISCSO-KELM 1 Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ 2 Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ 3 Ⅱ Ⅲ* Ⅲ* Ⅱ Ⅱ 4 Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅱ 5 Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ 6 Ⅲ Ⅱ* Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Note: “*” indicate a discrepancy from the actual grade. -
[1] 李鲒, 傅鹤林, 李国良, 等. 基于能量考虑危害性与可能性的岩爆评价指标 [J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51(10): 126–133. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.230687LI J, FU H L, LI G L, et al. Rockburst evaluation index considering degree of hazard and possibility of rockburst occurrence based on energy analysis [J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(10): 126–133. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.230687 [2] 刘德军, 戴庆庆, 左建平, 等. 基于Stacking集成算法的岩爆等级预测研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(Suppl 1): 2915–2926. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0831LIU D J, DAI Q Q, ZUO J P, et al. Research on rockburst grade prediction based on stacking integrated algorithm [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(Suppl 1): 2915–2926. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0831 [3] 靳春玲, 姬照泰, 贡力, 等. 基于WOA-SVM的引水隧洞岩爆烈度评估模型 [J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(9): 41–48. doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.09.1143JIN C L, JI Z T, GONG L, et al. Evaluation model of rockburst intensity of diversion tunnel based on WOA-SVM [J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(9): 41–48. doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.09.1143 [4] 詹术霖, 黄明清, 陈霖, 等. 基于3种机器学习模型的岩爆类型预测 [J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51(6): 879–886. doi: 10.7631/issn.1000-2243.22570ZHAN S L, HUANG M Q, CHEN L, et al. Rockburst type prediction based on three machine learning models [J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(6): 879–886. doi: 10.7631/issn.1000-2243.22570 [5] 侯克鹏, 包广拓, 孙华芬. 改进的MVO-GRNN神经网络岩爆预测模型研究 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2024, 24(3): 923–932. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2023.0341HOU K P, BAO G T, SUN H F. Research on improved MVO-GRNN neural network rockburst prediction model [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2024, 24(3): 923–932. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2023.0341 [6] 李宁, 王李管, 贾明涛. 基于粗糙集理论和支持向量机的岩爆预测 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 48(5): 1268–1275.LI N, WANG L G, JIA M T. Rockburst prediction based on rough set theory and support vector machine [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2017, 48(5): 1268–1275. [7] 刘剑, 周宗红. 基于修正散点图矩阵与随机森林的岩爆等级预测 [J]. 有色金属工程, 2022, 12(3): 120–128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.03.016LIU J, ZHOU Z H. Rockburst grade prediction based on modified scatter graph matrix and random forest [J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2022, 12(3): 120–128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.03.016 [8] 白云飞, 邓建, 董陇军, 等. 深部硬岩岩爆预测的FDA模型及其应用 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 40(5): 1417–1422.BAI Y F, DENG J, DONG L J, et al. Fisher discriminant analysis model of rock burst prediction and its application in deep hard rock engineering [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2009, 40(5): 1417–1422. [9] 张晓君, 刘啸, 王宇晨. 基于扰动和层间作用的硬岩层爆演化及预测 [J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2024, 41(3): 504–510. doi: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2022.0326ZHANG X J, LIU X, WANG Y C. Study on the evolution and prediction of stratified burst in hard rocks based on disturbance and interlayer interaction [J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2024, 41(3): 504–510. doi: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2022.0326 [10] 刘春, 易俊, 姜德义, 等. 基于灰色关联分析理论的岩爆烈度预测研究 [J]. 中国矿业, 2007, 16(12): 100–103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2007.12.031LIU C, YI J, JIANG D Y, et al. Study on rockburst intensity prediction method based on gray relational analysis theory [J]. China Mining Magazine, 2007, 16(12): 100–103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2007.12.031 [11] 温廷新, 王泽锋. 基于K-means SMOTE和IDBO-RF岩爆烈度等级预测模型 [J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2024, 20(6): 140–146. doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2024.06.019WEN T X, WANG Z F. Prediction model of rockburst intensity levels based on K-means SMOTE and IDBO-RF [J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2024, 20(6): 140–146. doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2024.06.019 [12] 周航, 陈仕阔, 张广泽, 等. 基于功效系数法和地应力场反演的深埋长大隧道岩爆预测研究 [J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(6): 1386–1396. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-340ZHOU H, CHEN S K, ZHANG G Z, et al. Efficiency coefficient method and ground stress field inversion for rockburst predicition in deep and long tunnel [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(6): 1386–1396. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-340 [13] 吴菡, 郭永刚, 郝守宁, 等. 数据缺失的SOA-KELM岩爆倾向性预测 [J]. 有色金属(矿山部分), 2023, 75(6): 148–155, 170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4172.2023.06.021WU H, GUO Y G, HAO S N, et al. SOA-KELM rockburst risk prediction with missing data [J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mining Section), 2023, 75(6): 148–155, 170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4172.2023.06.021 [14] 郭延华, 赵帅. 基于KPCA-WOA-KELM的岩爆烈度预测 [J]. 河北工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 38(2): 1–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9469.2021.02.001GUO Y H, ZHAO S. Classified prediction model of rockburst using KPCA-WOA-KELM [J]. Journal of Hebei University of Engineering (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 38(2): 1–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9469.2021.02.001 [15] 刘志祥, 郑斌, 刘进, 等. 金属矿深部开采岩爆危险预测的GA-ELM模型研究 [J]. 矿冶工程, 2019, 39(3): 1–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2019.03.001LIU Z X, ZHENG B, LIU J, et al. Rockburst prediction with GA-ELM model for deep mining of metal mines [J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2019, 39(3): 1–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2019.03.001 [16] 兰明, 刘志祥, 冯凡. 在线极限学习机在岩爆预测中的应用 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2014, 14(2): 90–93. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2014.02.020LAN M, LIU Z X, FENG F. Attempt to study the applicability of the online sequential extreme learning machine to the rock burst forecast [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2014, 14(2): 90–93. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2014.02.020 [17] ZHOU J, LI X B, SHI X Z. Long-term prediction model of rockburst in underground openings using heuristic algorithms and support vector machines [J]. Safety Science, 2012, 50(4): 629–644. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2011.08.065 [18] PU Y Y, APEL D B, XU H W. Rockburst prediction in kimberlite with unsupervised learning method and support vector classifier [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2019, 90: 12–18. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2019.04.019 [19] 回立川, 于千皓. 多策略混合的改进沙猫群优化算法及其应用 [J]. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(10): 3216–3224. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2023.1095HUI L C, YU Q H. Improved sand cat swarm optimization algorithm based on multi-strategy mixing and its application [J]. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(10): 3216–3224. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2023.1095 [20] SEYYEDABBASI A, KIANI F. Sand cat swarm optimization: a nature-inspired algorithm to solve global optimization problems [J]. Engineering with Computers, 2023, 39(4): 2627–2651. doi: 10.1007/s00366-022-01604-x [21] 熊自然. 基于解路径的核方法模型选择研究 [D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2022: 13−16.XIONG Z R. Research on kernel method model selection based on solution path [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2022: 13−16. [22] 汤志立. 深埋隧道岩爆预警与围岩动力破坏机理研究 [D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2019: 31−37.TANG Z L. Study on rockburst precursors and dynamic failure mechanism of deep-buried tunnels [D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2019: 31−37. [23] 谭文侃, 叶义成, 胡南燕, 等. LOF与改进SMOTE算法组合的强烈岩爆预测 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(6): 1186–1194. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.1035TAN W K, YE Y C, HU N Y, et al. Severe rock burst prediction based on the combination of LOF and improved SMOTE algorithm [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(6): 1186–1194. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.1035 -






 下载:
下载: