Research of Damage Indexes of KE-Rod Penetration on Target
-
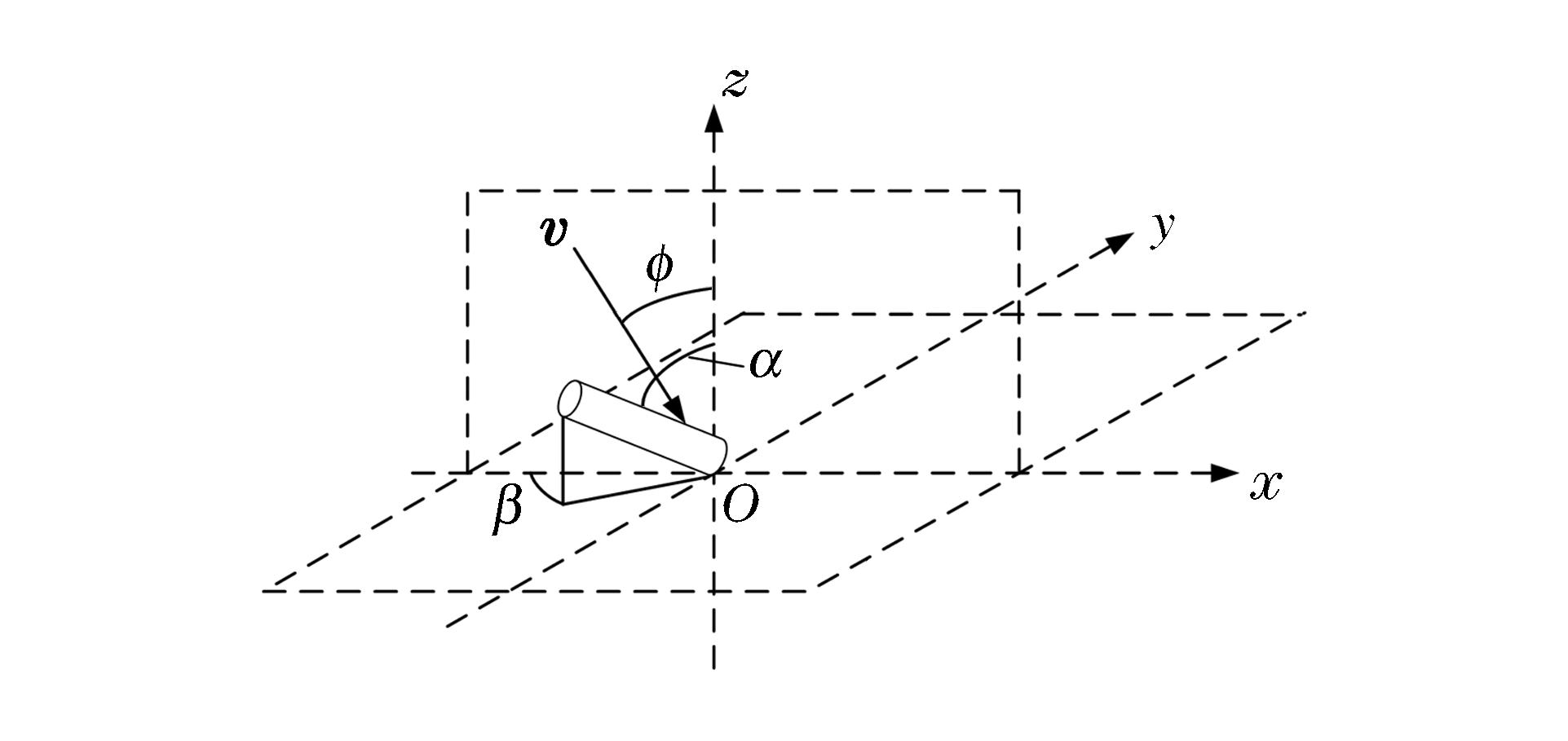
摘要: 针对动能杆侵彻目标靶的毁伤评估问题,从有限元角度出发,在数值模拟的基础上,提出了单根动能杆的毁伤指数计算模型; 以不同杆体角(从-60°到90°以30°递增)和速度角(从0°到75°以15°递增)对靶板进行侵彻仿真,得到了多种情况下动能杆的毁伤指数和分布规律。一般情况下,毁伤指数随速度角的增加而增大,但当速度角为30°或60°时,速度角和杆体角一致时毁伤指数最大,并针对此种情况进行了分析。将动能杆垂直侵彻靶板的仿真结果与经验公式的计算结果进行了对比,二者相差4.06%,证实该仿真方法是可行的。Abstract: In allusion to the question of damage assessment for KE-Rod penetration on target, a single-impact damage index model was proposed based on numerical results of KE-Rod penetration on target with different rod-angles(varying from -60° to 90° by step of 30°) and velocity-angles (varying from 0° to 75° by step of 15°) using finite element method.Results show that the damage index increases with velocity-angle in general, but when the velocity-angel is 60° or 30°, the damage index reaches maximum while the rod-angel is the same.The result of simulation for vertical penetration is in good agreement with the experimental data, and the error is 4.06%, which validates the feasibility of the scheme.
-
Key words:
- kinetic energy rod /
- target /
- penetration /
- damage index
-
Material ρ/(g/cm3) A/(GPa) B/(GPa) n C m D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 93 W 17.6 1.506 0.177 0.12 0.016 1.00 0.16 3.13 -2.04 0.007 0.37 4340 steel 7.83 1.189 0.765 0.26 0.014 1.03 0.05 3.44 -212 0.002 0.61 -
[1] Anderson C E Jr, Walker J D, Bless S J, et al. On the L/D effect for long-rod penetrators[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 1996, 18(3): 247-264. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)00028-9 [2] Chocron S, Anderson C E Jr, Walker J D, et al. A unified model for long-rod penetration in multiple metallic plates[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2003, 28(4): 391-411. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00069-6 [3] Johnson G R, Cook W H. Lagrangian EPIC code computations for oblique, yawed-rod impacts onto thin-plate and spaced-plate targets at various velocities[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 1993, 14(1): 373-383. [4] Gee D J, Littlefield D L. Yaw impact of rod projectiles[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2001, 26(1): 211-220. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/222983774_Yaw_impact_of_rod_projectiles_Int_J_Impact_Eng [5] Chen X W, Li Q M. Transition from nondeformable projectile penetration to semihydrodynamic penetration[J]. J Eng Mech, 2004, 130(1): 123-127. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2004)130:1(123) [6] Johnson G R, Cook W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures[C]//Proceedings of 7th International Symposium on Ballistics. Hague, Netherlands, 1983, 21: 541-547. [7] 高光发, 李永池, 刘卫国, 等.长杆弹截面形状对垂直侵彻深度的影响[J].兵器材料科学与工程, 2011, 34(3): 5-8.Gao G F, Li Y C, Liu W G, et al. Influence of the cross-section shapes of long rod projectile on the vertical penetration depth[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2011, 34(3): 5-8. [8] Partom Y, Yaziv D. Penetration of L/D=10 and 20 tungsten alloy projectiles into RHA targets[J]. High Pressure Science and Technology-1993, 1994, 309(1): 1801-1804. [9] Johnson G R, Cook W H. Fracture characteristics of three metals subjected to various strains, strain rates, temperatures and pressures[J]. Eng Fract Mech, 1985, 21(1): 31-48. doi: 10.1016/0013-7944(85)90052-9 [10] Anderson C E Jr, Hohler V, Walker J D, et al. Time-resolved penetration of long rods into steel targets[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 1995, 16(1): 1-18. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(94)E0030-Y -







 下载:
下载: