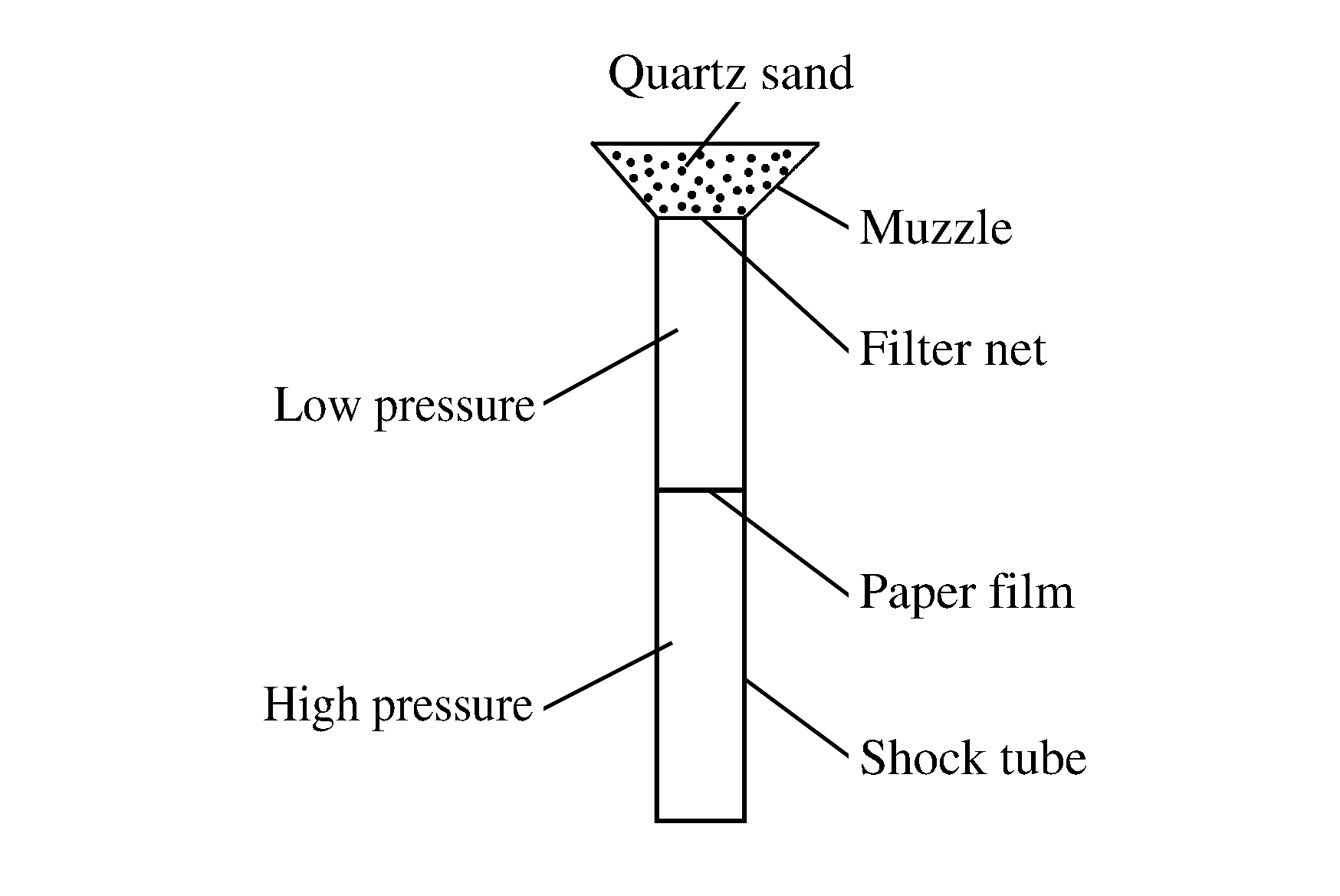
Numerical Simulation of Quartz Sand Dispersion under Shock Tube Loading
-
摘要: 为了研究激波驱动下固体颗粒的抛洒问题,采用FLUENT的离散相模型,对不同直径(2.00~3.00 mm、0.80~1.10 mm和0.42 mm)、质量均为5 g的石英砂颗粒在激波管加载下抛洒的气-固两相流动过程进行了数值模拟,得到了石英砂颗粒云团的中心颗粒在抛洒过程中不同时刻沿激波加载方向的平均速度和平均位移,并与实验结果进行了对比。结果表明,两者的吻合度较好,只是由于计算模型中未考虑滤网,并且假定激波管纸膜为瞬间破裂,因此导致数值模拟得到的平均速度和平均位移略高于实验值。Abstract: In order to study the dispersion of solid particle under the loading of shock tube, a numerical simulation of the dispersion of quartz sand with a mass of 5 g and different diameters of 2.00-3.00 mm, 0.80-1.10 mm and 0.42 mm respectively was carried out by means of DPM (dispersion phase model) of FLUENT.For the particles in the center of the quartz sand cloud during the dispersion, the average velocity and the average displacement along the loading direction were obtained.The numerical simulation results have a good agreement with the experimental results.Compared with the experimental results, the simulation result is slightly larger, probably because the dissipation energy on the sieve is ignored in the numerical simulation and the paper film of shock tube is considered to be ruptured instantaneously in the assumption.
-
Key words:
- shock tube /
- quartz sand /
- disperse /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 激波管驱动石英砂颗粒抛洒的实验参数
Table 1. Experimental parameters of the quartz sand dispersion under shock tube loading
Shot No. Ma D/(mm) m/(g) v/(m/s) 1 1.47 2.00-3.00 5 21.52 2 1.47 0.80-1.10 5 24.24 3 1.47 0.42 5 27.40 -
[1] Zhang F, Frost D L, Thibault P A, et al. Explosive dispersal of solid particles[J]. Shock Waves, 2001, 10(6): 431-443. doi: 10.1007/PL00004050 [2] 范宝春, 雷勇, 赵振平.激波与堆积粉尘相互作用的实验和理论研究[J].实验力学, 2002, 17(1): 77-81. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sylx200201012Fan B C, Lei Y, Zhao Z P. A measurement for the constitutive equations of granular materials and its analysis[J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2002, 17(1): 77-81. (in Chinese) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sylx200201012 [3] Boiko V M, Kiselev V P, Kiselev S P, et al. Shock wave interaction with a cloud of particles[J]. Shock Waves, 1997, 7(5): 275-285. doi: 10.1007/s001930050082 [4] Zhang F, Murray S B, Gerrard K B. Aluminum particles-air detonation at elevated pressures[J]. Shock Waves, 2006, 15(5): 313-324. doi: 10.1007/s00193-006-0027-0 [5] Rogue X, Rodriguez G, Haas J F, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of the shock-induced fluidization of a particles bed[J]. Shock Waves, 1998, 8(1): 29-45. doi: 10.1007/s001930050096 [6] 施红辉.用激波管研究超音速气固两相流[J].应用力学学报, 2003, 20(4): 41-45. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91535X/20034/8887718.htmlShi H H. Using shock tube to investigate supersonic gas-solid two-phase flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2003, 20(4): 41-45. (in Chinese) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91535X/20034/8887718.html [7] 张博, 李斌, 沈正祥, 等.激波与固体颗粒群相互作用实验研究[J].实验流体力学, 2009, 23(3): 16-19. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90272B/20093/31621540.htmlZhang B, Li B, Shen Z X, et al. Experimental investigation on the interaction between shock wave and solid particles[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2009, 23(3): 16-19. (in Chinese) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90272B/20093/31621540.html [8] 于勇, 张俊明, 姜连田. FLUENT入门与进阶教程[M].北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2008: 145.Yu Y, Zhang J M, Jiang L T. FLUENT Introduction and Advanced Tutorial[M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2008: 145. (in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: