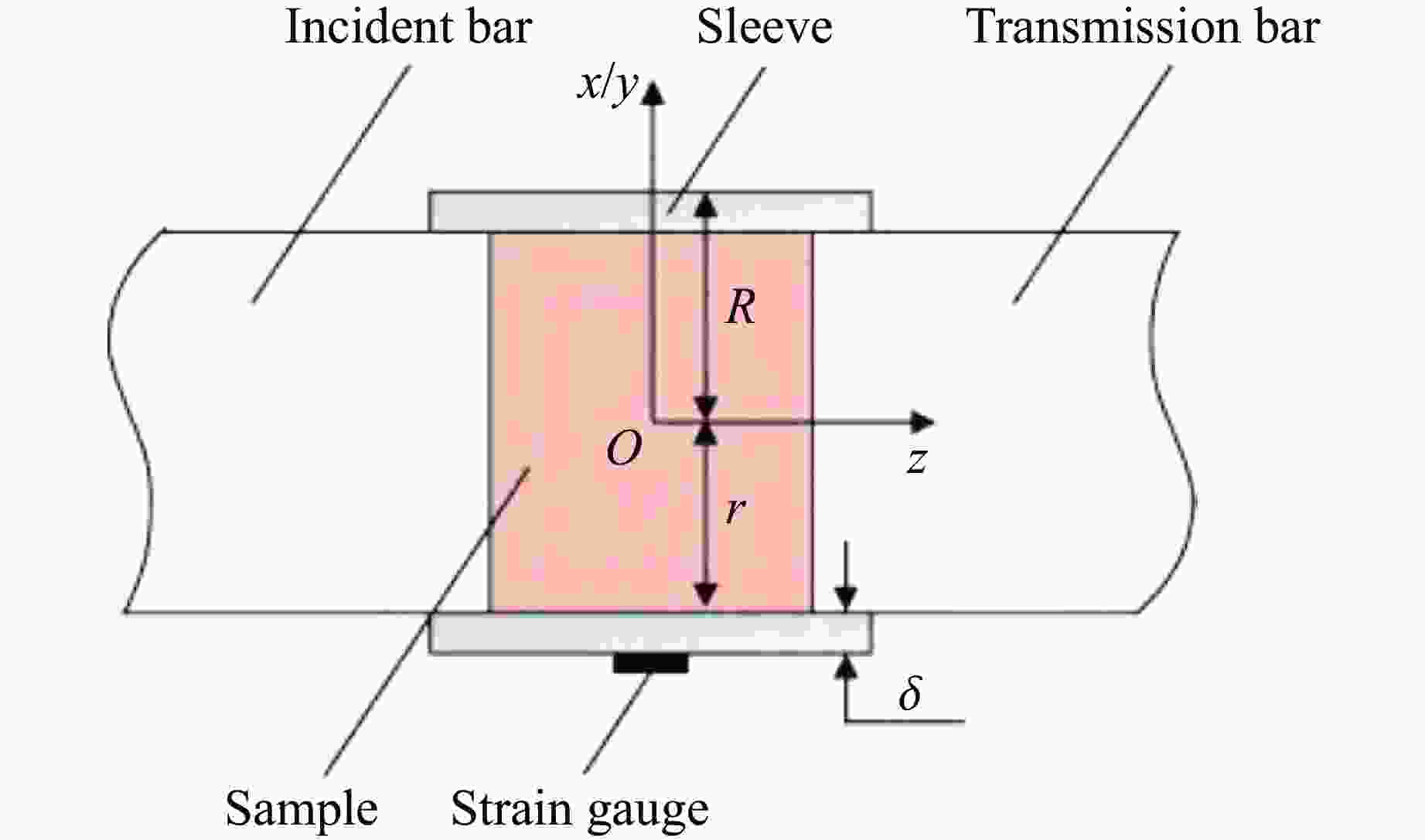
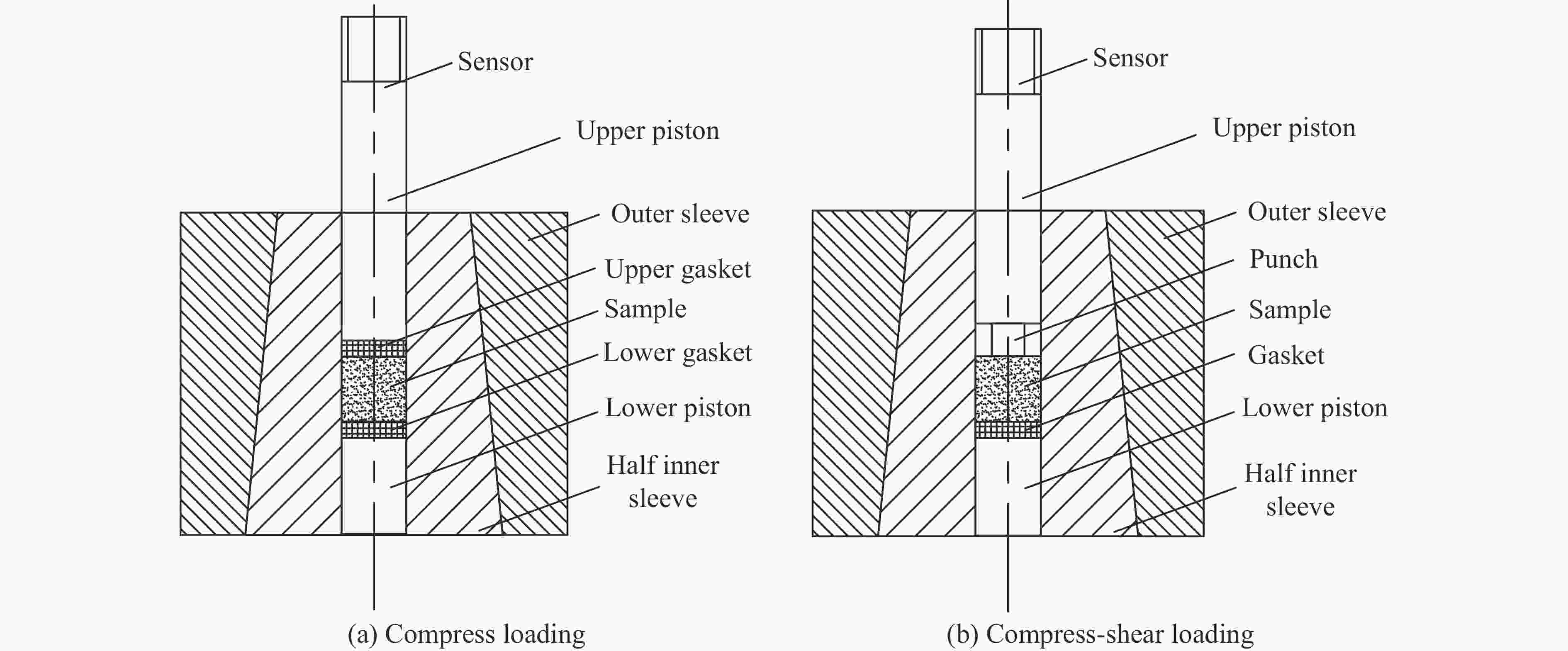
Dynamic Mechanical Behavior and Ignition Characteristics of DNAN-Based Melt-Cast Explosives
-
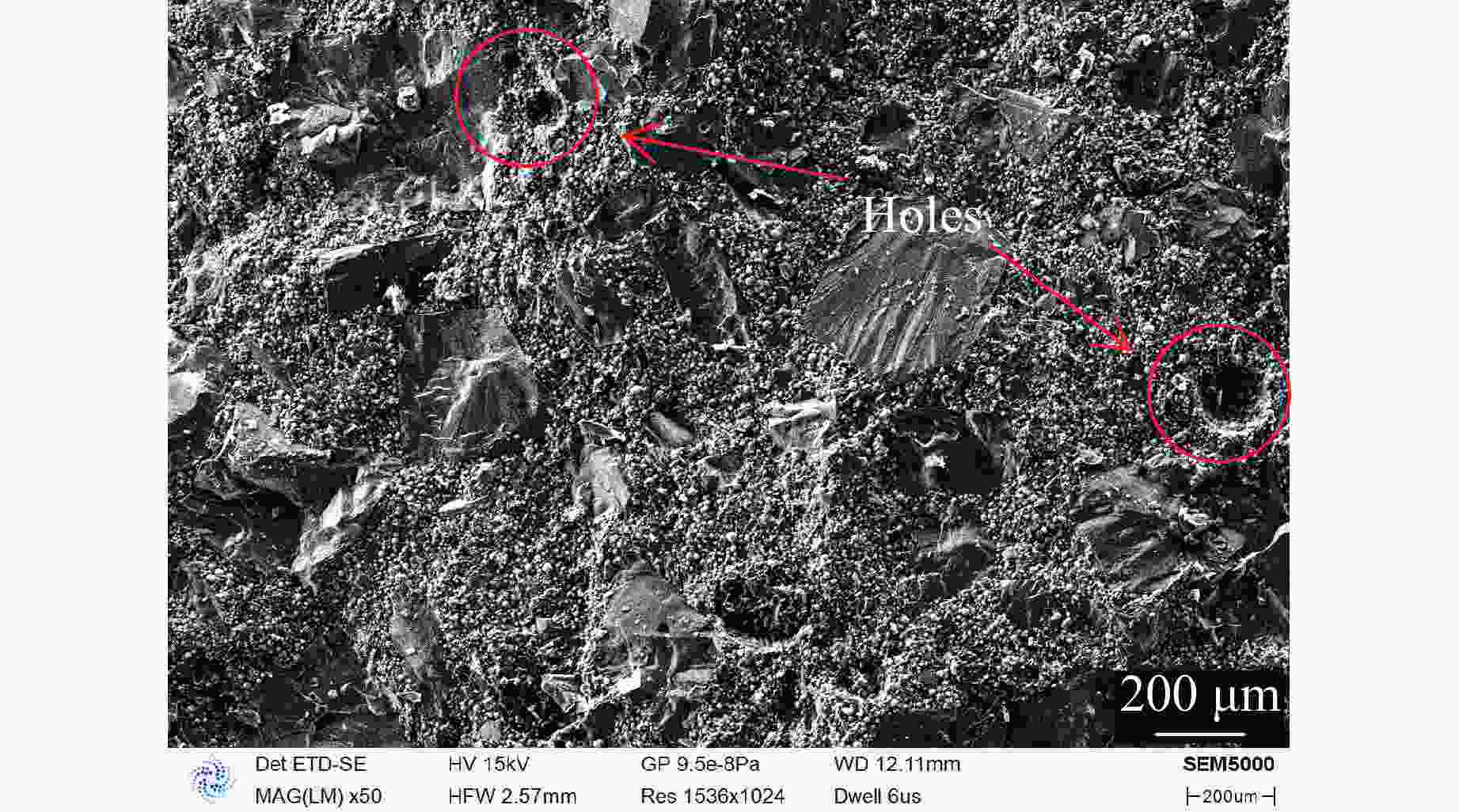
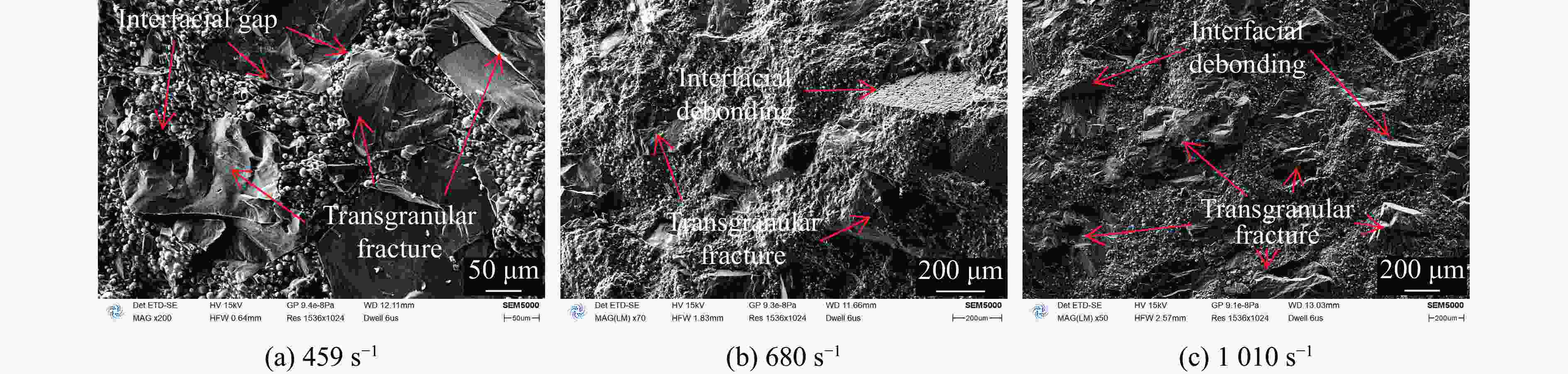
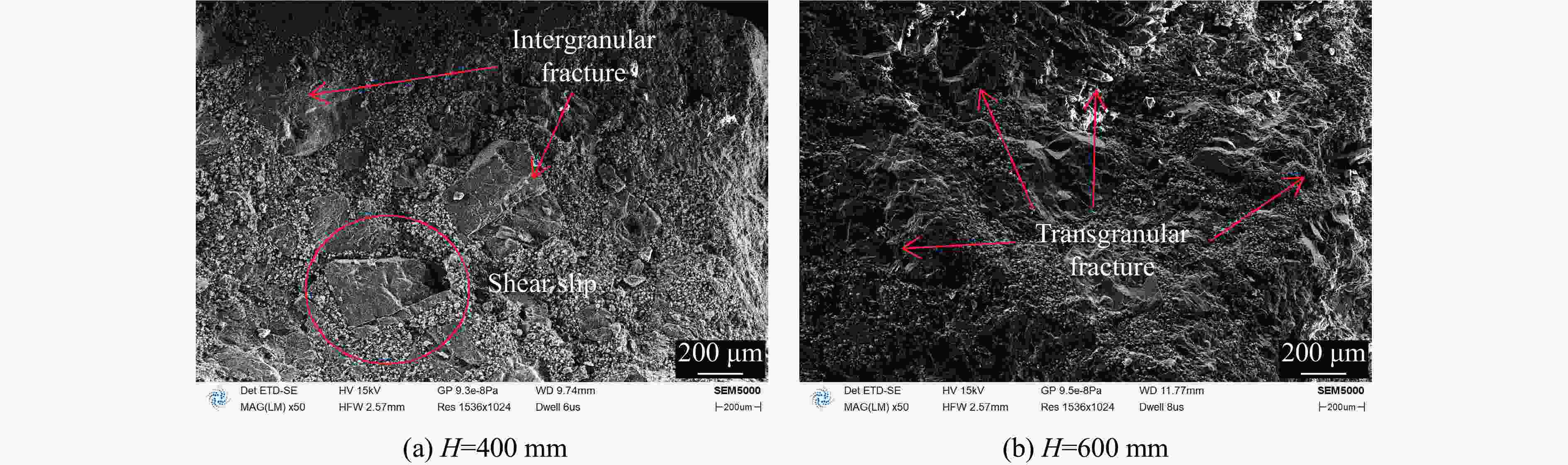
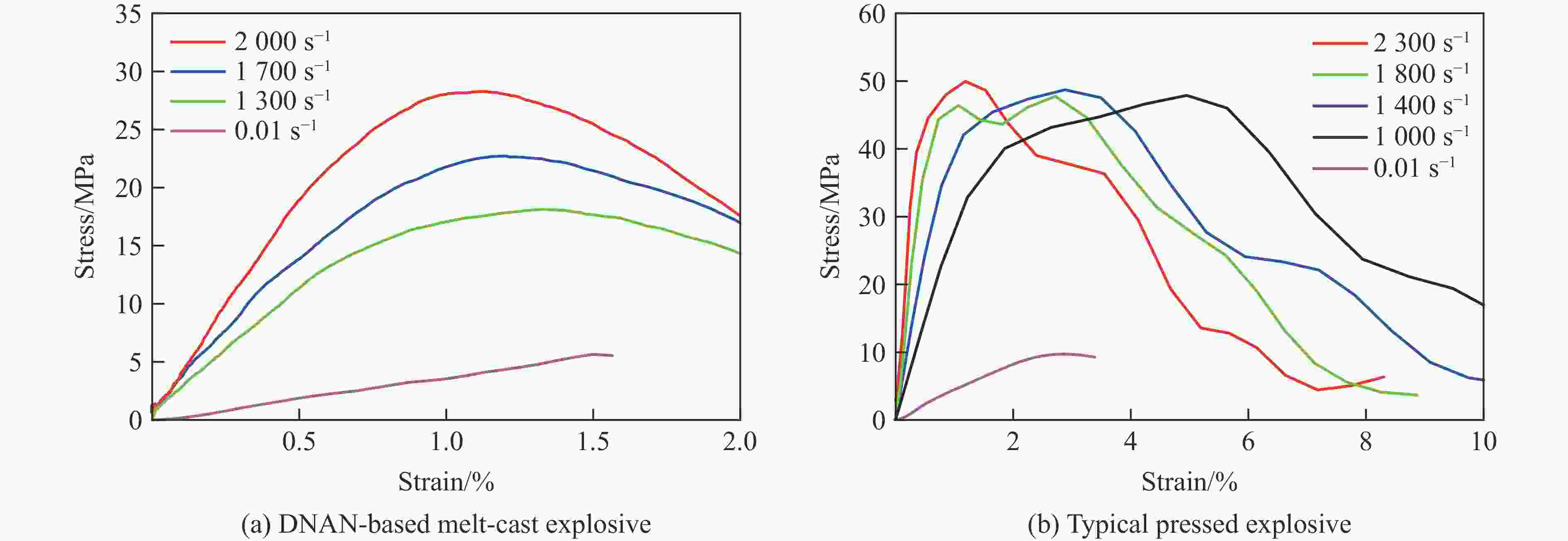
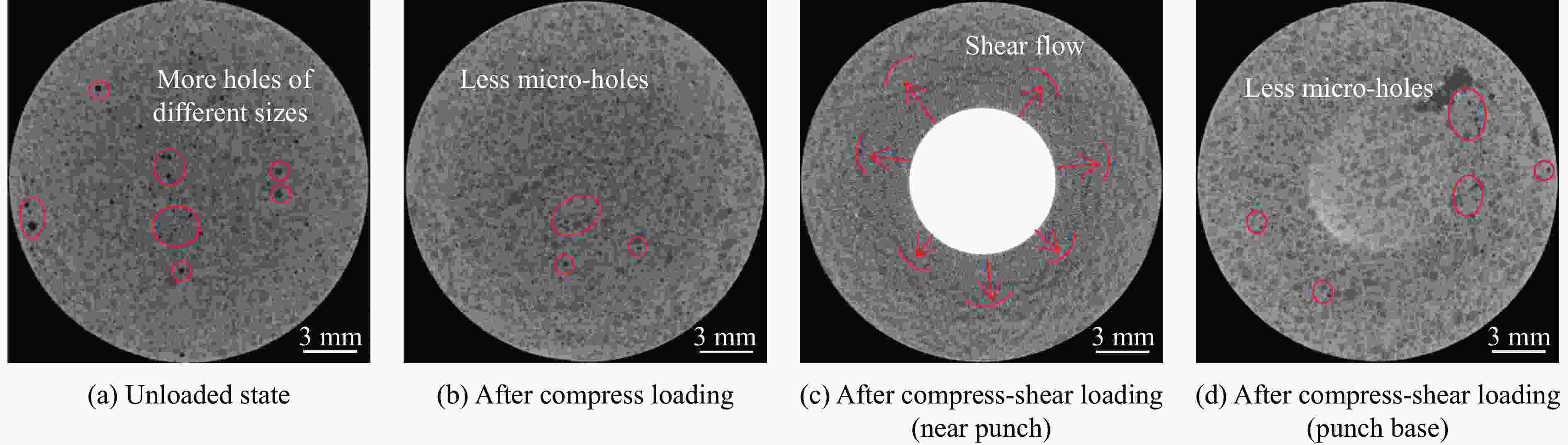
摘要: 为研究某2,4-二硝基苯甲醚(2,4-dinitroanisole,DNAN)基熔铸炸药的动态力学行为和点火特性,基于万能材料试验机和分离式霍普金森压杆(split Hopkinson pressure bar,SHPB)分别开展准静态/动态压缩试验和被动围压试验,并开展落锤冲击点火试验,结合扫描电镜和工业计算机断层扫描观察加载前、后试样的形貌特征,获得了不同加载条件下DNAN基熔铸炸药的应力-应变曲线、点火阈值和损伤特征,揭示了炸药在不同条件下的动态力学行为、点火特性和损伤机制。结果表明:DNAN基熔铸炸药的动态力学行为具有应变率相关性,相较于典型压装炸药,脆性特征更明显,在单轴压缩状态下强度更低,多轴压缩状态下峰值应力接近;孔洞为该炸药的主要初始损伤形式,压缩加载下孔洞被填充压实,主要损伤机制为穿晶断裂、界面脱粘,压剪耦合加载下装药内发生剪切流动,颗粒重新排布,随着加载强度的增大,主要损伤机制由沿晶断裂转向穿晶断裂;落锤冲击点火试验中DNAN基熔铸炸药对压缩加载更敏感,压缩和压剪加载下的最大未反应落高和峰值应力分别为500 mm、556 MPa和600 mm、622 MPa,主要点火机制可能是由孔洞损伤受压缩引起的气泡绝热压缩或孔洞冲击塌缩生热。Abstract: In order to study the dynamic mechanical behavior and ignition characteristics of a DNAN-based melt-cast explosive, quasi-static and dynamic compression tests, as well as passive confining pressure tests were carried out using a universal material testing machine and a split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB). Impact ignition test was carried out using a drop hammer. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and industrial computed tomography (CT) were used to examine the morphology changes in the samples before and after loading. The stress-strain curves, ignition thresholds and damage characteristics of DNAN-based melt-cast explosive under different loading conditions were obtained. The dynamic mechanical behavior, ignition characteristics and damage mechanism of the explosive under different loading conditions were obtained. The results show that the dynamic mechanical behavior of the DNAN-based melt-cast explosive exhibits a strain-rate dependence, demonstrating more pronounced brittleness compared to typical press-loaded explosives, lower strength under uniaxial compression, and peak stresses comparable to those observed in multi-axial compression. The holes are the main initial damage form of the explosive. The holes are filled and compacted under compressive loading. The main damage mechanisms are transgranular fracture and interfacial debonding. Under coupled compress-shear loading, shear flow occurs in the charge and the particles are rearranged. With the increase of loading strength, the main damage mechanism changes from intergranular fracture to transgranular fracture. In the drop-weight impact ignition test, DNAN-based melt-cast explosives are more sensitive to compression loading. The maximum unreacted drop heights and peak stresses under compress and compress-shear loading are 500 mm, 556 MPa and 600 mm, 622 MPa, respectively. The primary ignition mechanism is likely attributable to either the adiabatic compression of bubbles or the thermal energy generated by the impact collapse of voids resulting from compressive damage.
-
表 1 不同应变率单轴压缩加载下的力学参量
Table 1. Mechanical parameters under different strain rates of uniaxial compression loading
Explosives Strain rate/s−1 E/GPa σm/MPa Strain at σm/% DNAN-based melt-cast explosive 0.01 0.37 5.64 1.50 1300 2.12 18.12 1.32 1700 2.62 22.71 1.19 2000 3.77 28.26 1.12 Typical pressed explosive 0.01 0.38 9.72 2.88 1000 2.94 47.89 4.95 1400 4.41 48.71 2.88 1800 8.02 47.76 2.71 2300 11.36 49.95 1.18 表 2 被动围压状态不同应变率下的力学参量
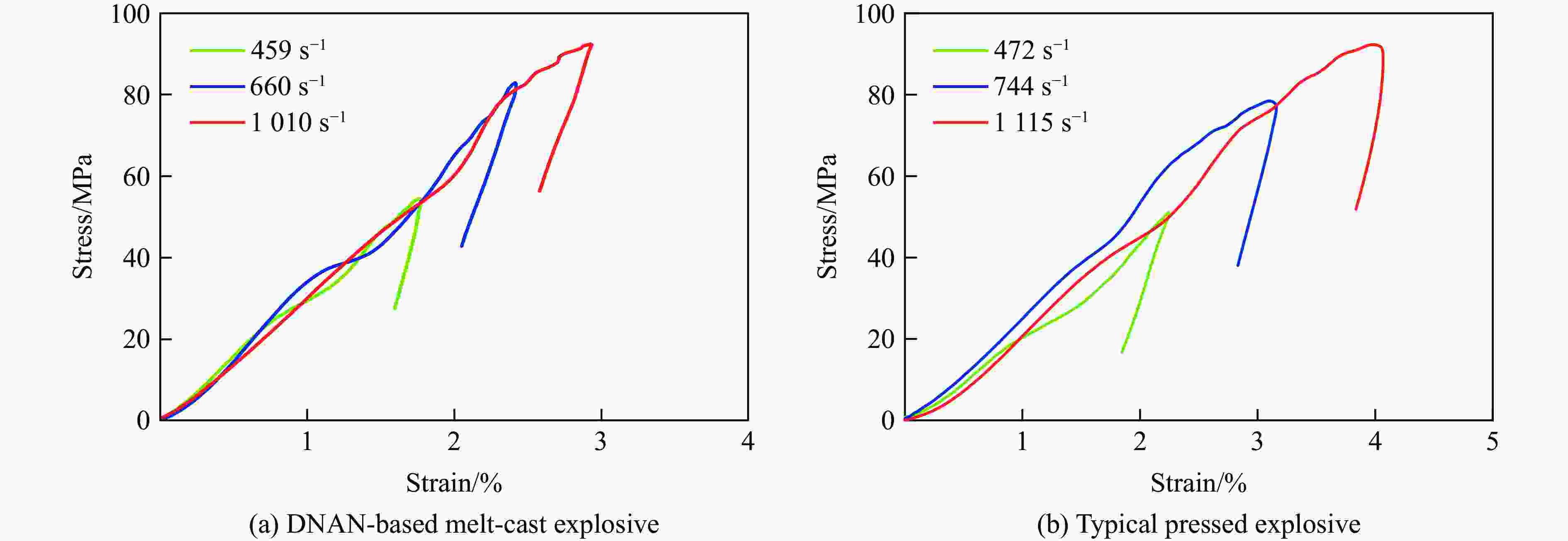
Table 2. Mechanical parameters under different strain rates of passive confinement loading
Explosives Strain rate/s−1 σm/MPa Strain at σm/% DNAN-based melt-cast explosive 459 54.46 1.76 660 82.88 2.40 1010 92.38 2.93 Typical pressed explosive 472 51.05 2.24 744 78.46 3.10 1115 92.28 3.98 表 3 落锤冲击加载试验结果
Table 3. Test results of the drop-weight impact loading
Explosives Impact mode H/mm σm/MPa Result DNAN-based melt-cast explosive Compress 500 556 No-ignition 600 537* Ignition 800 509* Ignition Compress-shear 400 487 No-ignition 600 622 No-ignition 800 546* Ignition Typical pressed explosive Compress 600 668 No-ignition 800 715 No-ignition 1000 771 No-ignition 1200 460* Ignition 1500 411* Ignition Compress-shear 800 726 No-ignition 1000 668* Ignition Note: The superscript “*” indicates the stress at which the explosive begins to ignition at this height. -
[1] DIENES J K. Frictional hot-spots and propellant sensitivity [J]. MRS Online Proceedings Library, 1983, 24(1): 373–381. doi: 10.1557/PROC-24-373 [2] 李尚昆, 黄西成, 王鹏飞. 高聚物黏结炸药的力学性能研究进展 [J]. 火炸药学报, 2016, 39(4): 1–11. doi: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.2016.04.001LI S K, HUANG X C, WANG P F. Recent advances in the investigation on mechanical properties of PBX [J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2016, 39(4): 1–11. doi: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.2016.04.001 [3] 屈可朋, 陈鹏, 李亮亮, 等. 含能装药损伤研究进展 [J]. 飞航导弹, 2018(11): 92–96. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.20180153QU K P, CHEN P, LI L L, et al. Research progress on damage of energetic charge [J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2018(11): 92–96. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.20180153 [4] 朱道理, 周霖, 张向荣, 等. DNAN及TNT基熔铸炸药综合性能比较 [J]. 含能材料, 2019, 27(11): 923–930. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2019170ZHU D L, ZHOU L, ZHANG X R, et al. Comparison of comprehensive properties for DNAN and TNT-based melt-cast explosives [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2019, 27(11): 923–930. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2019170 [5] LI S R, DUAN Z P, GAO T Y, et al. Size effect of explosive particle on shock initiation of aluminized 2, 4-dinitroanisole (DNAN)-based melt-cast explosive [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 128(12): 125903. doi: 10.1063/5.0016310 [6] 蒙君煚, 周霖, 曹同堂, 等. 2, 4-二硝基苯甲醚(DNAN)基熔铸炸药研究进展 [J]. 含能材料, 2020, 28(1): 13–24. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2018359MENG J J, ZHOU L, CAO T T, et al. Research progress of 2, 4-dinitroanisole-based melt-cast explosives [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2020, 28(1): 13–24. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2018359 [7] RAVI P, BADGUJAR D M, GORE G M, et al. Review on melt cast explosives [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2011, 36(5): 393–403. doi: 10.1002/prep.201100047 [8] TAYLOR S, PARK E, BULLION K, et al. Dissolution of three insensitive munitions formulations [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 119: 342–348. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.06.050 [9] 李东伟, 姜振明, 张向荣, 等. 2, 4-二硝基苯甲醚基高爆速熔铸炸药爆轰性能表征 [J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(4): 656–660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.04.012LI D W, JIANG Z M, ZHANG X R, et al. Characterization of new 2, 4-dinitroanisole-based melt-cast high detonation velocity explosives [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(4): 656–660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.04.012 [10] 蒙君煚, 周霖, 金大勇, 等. 成型工艺对2, 4-二硝基苯甲醚基熔铸炸药装药质量的影响 [J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(9): 1719–1726. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.09.007MENG J J, ZHOU L, JIN D Y, et al. Effect of forming process on casting quality of 2, 4-dinitroanisole-based casting explosive [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2018, 39(9): 1719–1726. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.09.007 [11] 李全俊, 杨治林, 岳显, 等. 战斗部熔铸装药精密成型工艺参数优化方法 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2023, 44(5): 125–132. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2023.05.019LI Q J, YANG Z L, YUE X, et al. Optimization method of precision forming process parameters of warhead fusion casting charge [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2023, 44(5): 125–132. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2023.05.019 [12] 蒙君煚, 姜振明, 张向荣, 等. 功能助剂对2, 4-二硝基苯甲醚基熔铸炸药性能的影响 [J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(3): 424–430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.03.006MENG J J, JIANG Z M, ZHANG X R, et al. Effect of functional agents on the performance of 2, 4-dinitroanisole-based melt-cast explosives [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(3): 424–430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.03.006 [13] QIAN W, CHEN X Z, LUO G. Polymer reinforced DNAN/RDX energetic composites: interfacial interactions and mechanical properties [J]. Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 2017, 14(3): 726–741. doi: 10.22211/cejem/75609 [14] 蒙君煚, 周霖, 金大勇, 等. 功能助剂对DNAN/RDX熔铸炸药界面黏结强度的影响 [J]. 含能材料, 2018, 26(9): 765–771. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2018061MENG J J, ZHOU L, JIN D Y, et al. Effect of functional additives on interface bonding strength of DNAN/RDX melt-cast explosives [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2018, 26(9): 765–771. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2018061 [15] SUN S H, ZHANG H B, XU J J, et al. Two novel melt-cast cocrystal explosives based on 2, 4-dinitroanisole with significantly decreased melting point [J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2019, 19(12): 6826–6830. doi: 10.1021/acs.cgd.9b00680 [16] YANG Y, DUAN Z P, LI S R, et al. Detonation characteristics of an aluminized DNAN-based melt-cast explosive [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2023, 48(1): e202200088. doi: 10.1002/prep.202200088 [17] 李淑睿, 段卓平, 高天雨, 等. 2, 4-二硝基苯甲醚基钝感熔铸含铝炸药的冲击起爆特性 [J]. 含能材料, 2021, 29(2): 88–95. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2020238LI S R, DUAN Z P, GAO T Y, et al. Shock initiation characteristic of insensitive DNAN-based aluminized melt-cast explosive [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2021, 29(2): 88–95. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2020238 [18] 张思危, 崔庆忠. DNAN基高固含量熔铸炸药力学性能研究 [J]. 兵工自动化, 2022, 41(12): 100–105, 113. doi: 10.7690/bgzdh.2022.12.022ZHANG S W, CUI Q Z. Study on mechanical properties of DNAN-based high solid content melt-cast explosive [J]. Ordnance Industry Automation, 2022, 41(12): 100–105, 113. doi: 10.7690/bgzdh.2022.12.022 [19] 李东伟, 苗飞超, 张向荣, 等. 2, 4-二硝基苯甲醚基不敏感熔注炸药动态力学性能 [J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(11): 2344–2349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.11.007LI D W, MIAO F C, ZHANG X R, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties of an insensitive DNAN-based melt-cast explosive [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(11): 2344–2349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.11.007 [20] ZHU D L, ZHOU L, ZHANG X R, et al. Simultaneous determination of multiple mechanical parameters for a DNAN/HMX melt-cast explosive by Brazilian disc test combined with digital image correlation method [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2017, 42(8): 864–872. doi: 10.1002/prep.201700010 [21] 马腾, 董小丽, 杨年, 等. 约束对DNAN基熔铸炸药点火反应特性的影响 [J]. 火炸药学报, 2023, 46(12): 1086–1092. doi: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.202302007MA T, DONG X L, YANG N, et al. Effect of constraints on the ignition reaction characteristics of DNAN-based melt-cast explosives [J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2023, 46(12): 1086–1092. doi: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.202302007 [22] 杨年, 马腾, 黄寅生, 等. 损伤对DNAN基熔铸炸药点火后反应增长的影响 [J]. 火炸药学报, 2023, 46(11): 990–998. doi: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.202302006YANG N, MA T, HUANG Y S, et al. Effect of damage on reaction growth of DNAN based melt-cast explosive after ignition [J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2023, 46(11): 990–998. doi: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.202302006 [23] 赵东, 屈可朋, 董泽霖. 凝聚相炸药损伤-点火特性的研究进展 [J]. 爆破器材, 2024, 53(3): 1–9, 16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2024.03.001ZHAO D, QU K P, DONG Z L. Research progress on damage and ignition characteristics of condensed phase explosives [J]. Explosive Materials, 2024, 53(3): 1–9, 16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2024.03.001 -






 下载:
下载: