Calculation Analysis of the Impact Melting and Resolidification Process for the Bismuth Using the Ti-Cu-W Pillow Flyer
-
摘要: 采用数值计算设计了Ti-Cu-W材料体系Pillow飞片,实现金属铋样品的冲击加载和准等熵加载,并通过实验研究铋的冲击熔化再凝固这一复杂的物理过程,实验获得的速度波剖面结果与数值模拟结果基本一致。还建立了金属铋的包含5个固相和1个液相的完全物态方程,计算相图的三相点以及高压区的Hugoniot线与实验数据吻合较好,计算还获得了冲击加载再凝固实验中的温度信息和相变信息。通过计算分析和对实验数据的解读,认为Ti-Cu-W材料体系Pillow飞片加载可以用于铋的冲击熔化再凝固复杂物理过程研究,为实验探索研究建立了适用的研究方法和有效的技术手段。Abstract: Numerical simulations are carried out to design the Pillow flyer of Ti-Cu-W system, and the impact loading and quasi-isentropic loading of the bismuth sample are also carried out.We experimentally investigate the intricate physical process of impact melting and resolidification.Experiment results of wave profiles are similar with numerical ones.The complete equation of state of bismuth including five solid phases and one liquid phase is established.Triple points in phase diagram and the Hugoniot curve in high pressure area agree well with the experiment data.The temperature and phase transition information in impact loading and resolidification experiment are also obtained.According to the calculation analysis and interpretation of the experiment data, the loading experiment based on Ti-Cu-W flyer is available to study the physical process of impact melting and resolidification of bismuth, and an appropriate research method and effective technique means for experiment exploration is established.
-
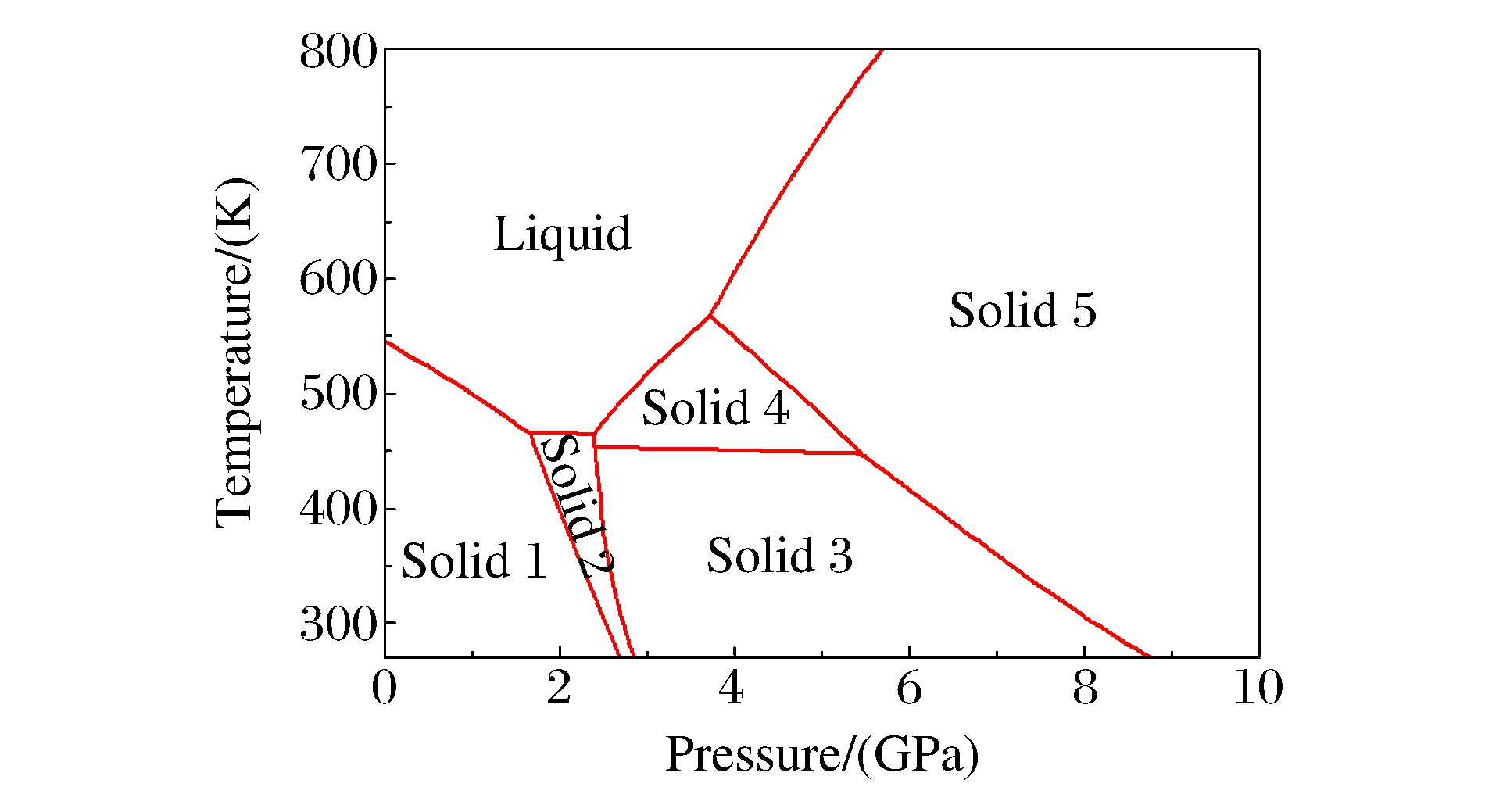
表 1 相图三相点对比
Table 1. Comparisons of triple point in phase diagram
Phase Ref.[13] This work T/(K) p/(GPa) T/(K) p/(GPa) Melting point 544 Zero 545 Zero Ⅰ-Ⅱ-L 465 1.65 466 1.66 Ⅱ-Ⅳ-L 464 2.10 464 2.38 Ⅱ-Ⅲ-Ⅳ 455 2.15 454 2.40 Ⅳ-Ⅴ-L 569 3.80 568 3.72 Ⅲ-Ⅳ-Ⅴ 448 5.40 448 5.45 表 2 状态方程参数表
Table 2. Parameters for equation of state
Phase F0
/(Pa·m3/g)S0
/[Pa·m3/(g·K)]T0
/(K)p0
/(GPa)v0
/(cm3/g)Cv
/[Pa·m3/(g·K)]b
/(g/cm3)K0
/(GPa)a1 a2 n Ⅰ 0 0 300 0 0.102 0 0.122 6 10.3 32.17 3.5 8.5 Ⅱ 7.47 0.698 4 456 1.7 0.093 2 0.120 0 20.0 60.20 Ⅲ 19.29 0.725 3 456 1.7 0.088 2 0.084 0 36.0 75.25 Ⅳ 19.30 0.773 0 456 1.7 0.088 2 0.084 0 36.0 75.25 Ⅴ 41.02 0.800 3 447 5.3 0.082 9 0.108 0 23.0 78.26 3.9 Liquid -9.93 1.630 0 544 0 0.099 6 0.133 0 19.2 25.00 5.8 表 3 设计和实验研制的14层Ti-Cu-W体系飞片的各层组成成分
Table 3. Components of each layer for designed and fabricated Ti-Cu-W flyer
Material
systemTape Ti/Cu (%) ρ/(g/cm3) Z g/(cm2·μs) Design Exp. Design Exp. Design Exp. Cu-W 1 Cu/20.0 Cu/21.08 15.606 15.450 5.800 5.733 2 Cu/40.0 Cu/38.25 13.145 13.329 4.832 4.898 3 Cu/58.0 Cu/56.47 11.512 11.635 4.279 4.319 4 Cu/80.0 Cu/78.74 9.994 10.070 3.806 3.829 5 Cu/100.0 Cu/98.90 8.924 8.977 3.489 3.505 Ti-Cu 6 Ti/3.0 Ti/2.67 8.659 8.688 3.413 3.421 7 Ti/10.0 Ti/10.20 8.099 8.084 3.253 3.249 8 Ti/18.0 Ti/18.82 7.541 7.488 3.096 3.081 9 Ti/25.0 Ti/26.36 7.112 7.034 2.975 2.953 10 Ti/30.0 Ti/31.74 6.835 6.743 2.897 2.871 11 Ti/33.0 Ti/34.98 6.678 6.579 2.853 2.825 12 Ti/36.0 Ti/38.20 6.529 6.424 2.811 2.781 13 Ti/39.0 Ti/41.44 6.386 6.274 2.771 2.739 14 Ti/42.0 Ti/44.67 6.249 6.133 2.732 2.699 -
[1] Nguyen J H, Orlikowski D, Streitz F H, et al. High-pressure tailored compression: Controlled thermodynamic paths[J]. J Appl Phys, 2006, 100(2): 023508. doi: 10.1063/1.2214209 [2] Nguyen J H, Orlikowski D, Streitz F H, et al. Specifically prescribed dynamic thermodynamic paths and resolidification experiments[C]//Furnish M D, Gupta Y M, Forbes J W. Shock Compression of Condensed Matter-2003. New York: AIP, 2004: 1225-1230. [3] Martin L P, Nguyen J H. Fabrication and characterization of graded impedance gas gun impactors from tape cast metal powders, UCRL-JRNL-217359[R]. Livermore, CA: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, 2005. [4] Martin L P, Orlikowski D, Nguyen J H. Fabrication and characterization of graded impedance impactors for gas gun experiments from tape cast metal powders[J]. Mat Sci Eng A, 2006, 427(1): 83-91. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921509306004709 [5] Martin L P, Patterson J R, Orlikowski D, et al. Application of tape-cast graded impedance impactors for light-gas gun experiments[J]. J Appl Phys, 2007, 102(2): 023507. doi: 10.1063/1.2756058 [6] 华劲松, 经福谦, 龚自正, 等.准等熵压缩的数值模拟[J].高压物理学报, 2000, 14(3): 195-202.Hua J S, Jing F Q, Gong Z Z, et al. Study of numerical simulation for quasi-isentropic compression[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2000, 14(3): 195-202. (in Chinese) [7] 沈强, 王传彬, 张联盟, 等.为实现准等熵压缩的波阻抗梯度飞片的实验研究[J].物理学报, 2002, 51(8): 1759-1762.Shen Q, Wang C B, Zhang L M, et al. A study on generating quasi-isentropic compression via graded impedance flyer[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2002, 51(8): 1759-1762. (in Chinese) [8] 柏劲松, 罗国强, 黄娇凤, 等. Pillow飞片气炮加载实验的数值模拟研究[J].高压物理学报, 2011, 25(5): 390-394.Bai J S, Luo G Q, Huang J F, et al. Numerical simulation of the gas gun experiment with Pillow impactor loading[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2011, 25(5): 390-394. (in Chinese) [9] 柏劲松, 罗国强, 王翔, 等. Mg-W体系密度梯度飞片复杂加载实验的计算分析[J].力学学报, 2010, 42(6): 1068-1073.Bai J S, Luo G Q, Wang X, et al. Calculation and analysis of the Mg-W GDI complex loading experiment[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2010, 42(6): 1068-1073. (in Chinese) [10] 柏劲松, 沈强, 唐蜜, 等. W-Mo-Ti-Mg体系阻抗梯度飞片无冲击驱动过程数值计算[J].振动与冲击, 2010, 29(6): 72-75.Bai J S, Shen Q, Tang M, et al. Numerical analysis on complex loadings and shockless compressions of the W-Mo-Ti-Mg graded impedance impactor[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2010, 29(6): 72-75. (in Chinese) [11] Luo G Q, Bai J S, Tan H, et al. Characterizations of Mg-W system graded-density materials for complex loading-unloading light-gas gun experiments[J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2010, 41(9): 2389-2395. doi: 10.1007/s11661-010-0309-0 [12] 柏劲松, 罗国强, 唐蜜, 等.冲击加载-准等熵加载过程的密度梯度飞片计算设计[J].高压物理学报, 2009, 23(3): 173-180.Bai J S, Luo G Q, Tang M, et al. Computational design of graded impactors for shock loading and quasi-isentropic compression[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2009, 23(3): 173-180. (in Chinese) [13] Tonkov E Y, Pomyatovsky E G. Phase Transformations of Elements under High Pressure[M]. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2005: 148-157. [14] Pélissier J L, Wetta N. A model potential approach for bismuth(Ⅰ). Densification and melting curve calculation[J]. Physica A, 2001, 289(3): 459-478. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378437100005148 [15] Pélissier J L, Partouche-Sebban D. Pyrometry measurements on shock-heated bismuth using PMMA and sapphire windows[J]. Physica B, 2005, 364(1): 14-28. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921452605006332 [16] Partouche S D, Pélissier J L, Anderson W W, et al. Investigation of shock-induced light from sapphire for use in pyrometry studies[J]. Physica B, 2005, 364(1): 1-13. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921452605005557 [17] Johnson J N, Hayes D B, Asay J R. Equations of state and shock-induced transformations in solid Ⅰ-solid Ⅱ-liquid bismuth[J]. J Phys Chem Solids, 1974, 35(4): 501-515. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3697(74)80004-1 [18] Kane J O, Smith R F. Modeling non-equilibrium phase transitions in isentropically compressed Bi[C]//Furnish M D, Elert M L, Russell Th P, et al. Shock Compression of Condensed Matter-2005. New York: AIP, 2006: 244. [19] Marsh S P. LASL Shock Hugoniot Data[Z]. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1980: 23. [20] Walsh J M, Rice M H, McQeen R G, et al. Shock-wave compressions of twenty-seven metals. Equations of state of metals[J]. Phys Rev, 1957, 108(2): 196. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.108.196 [21] Hayes D B. Wave propagation in a condensed medium with N transforming phases: Application to solidⅠ-solid Ⅱ-liquid bismuth[J]. J Appl Phys, 1975, 46(8): 3438-3443. doi: 10.1063/1.322065 -







 下载:
下载: