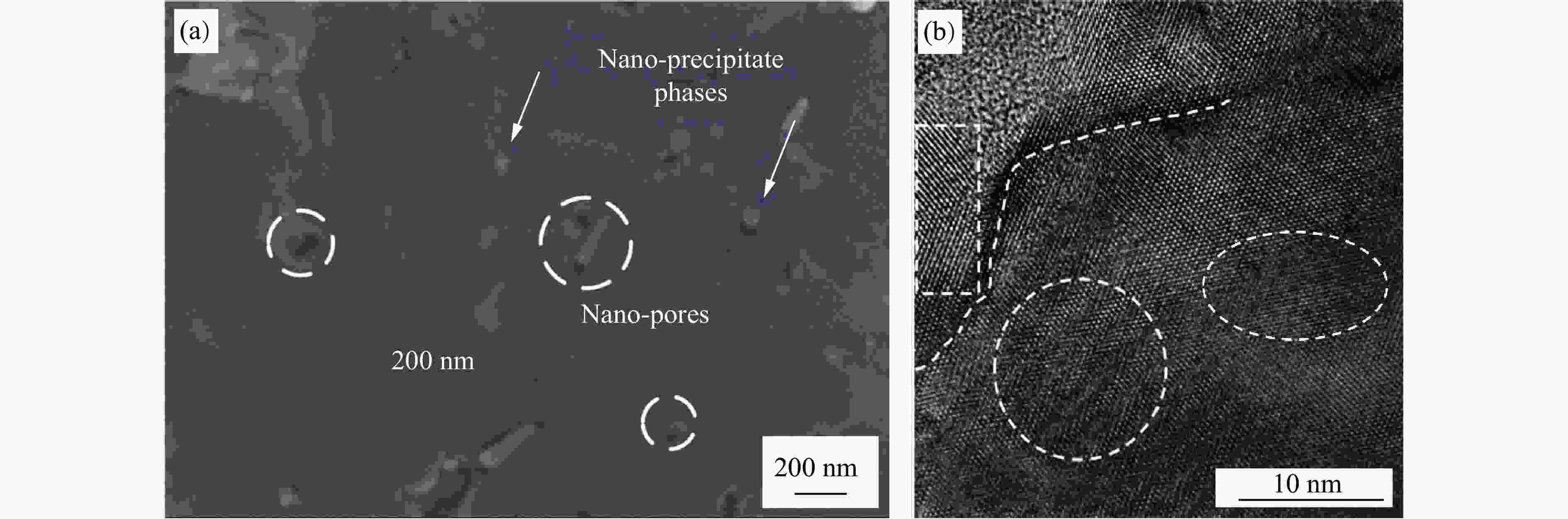
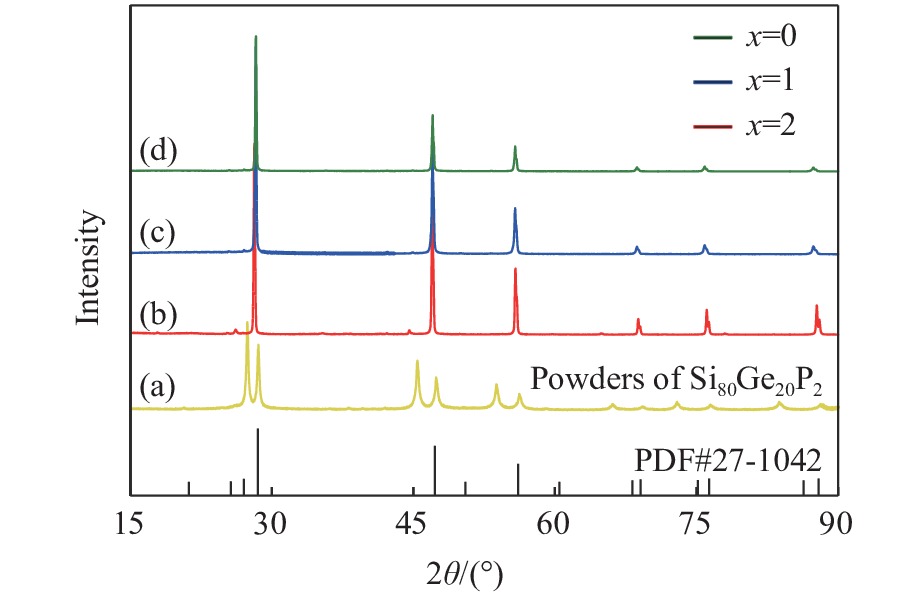
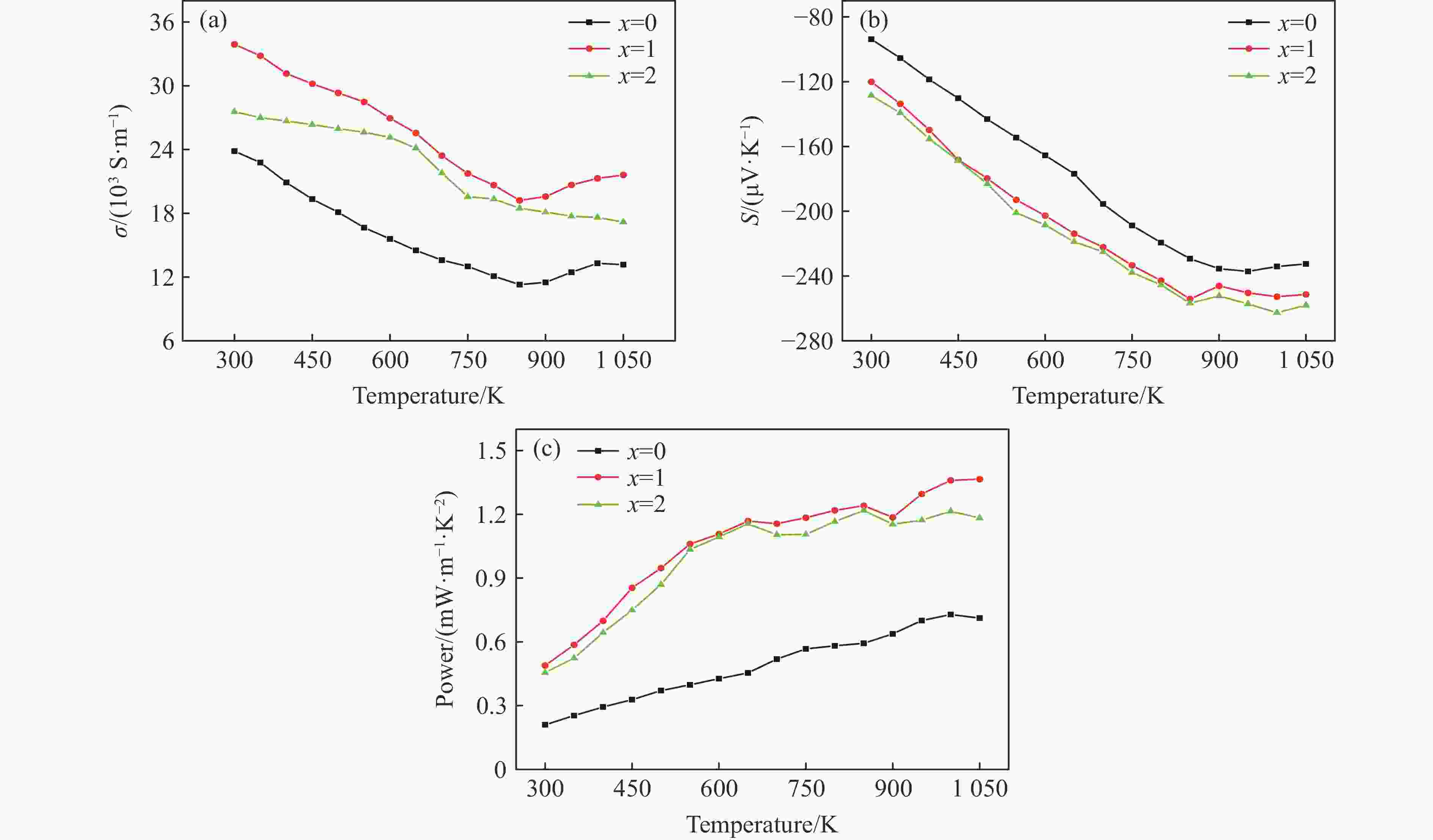
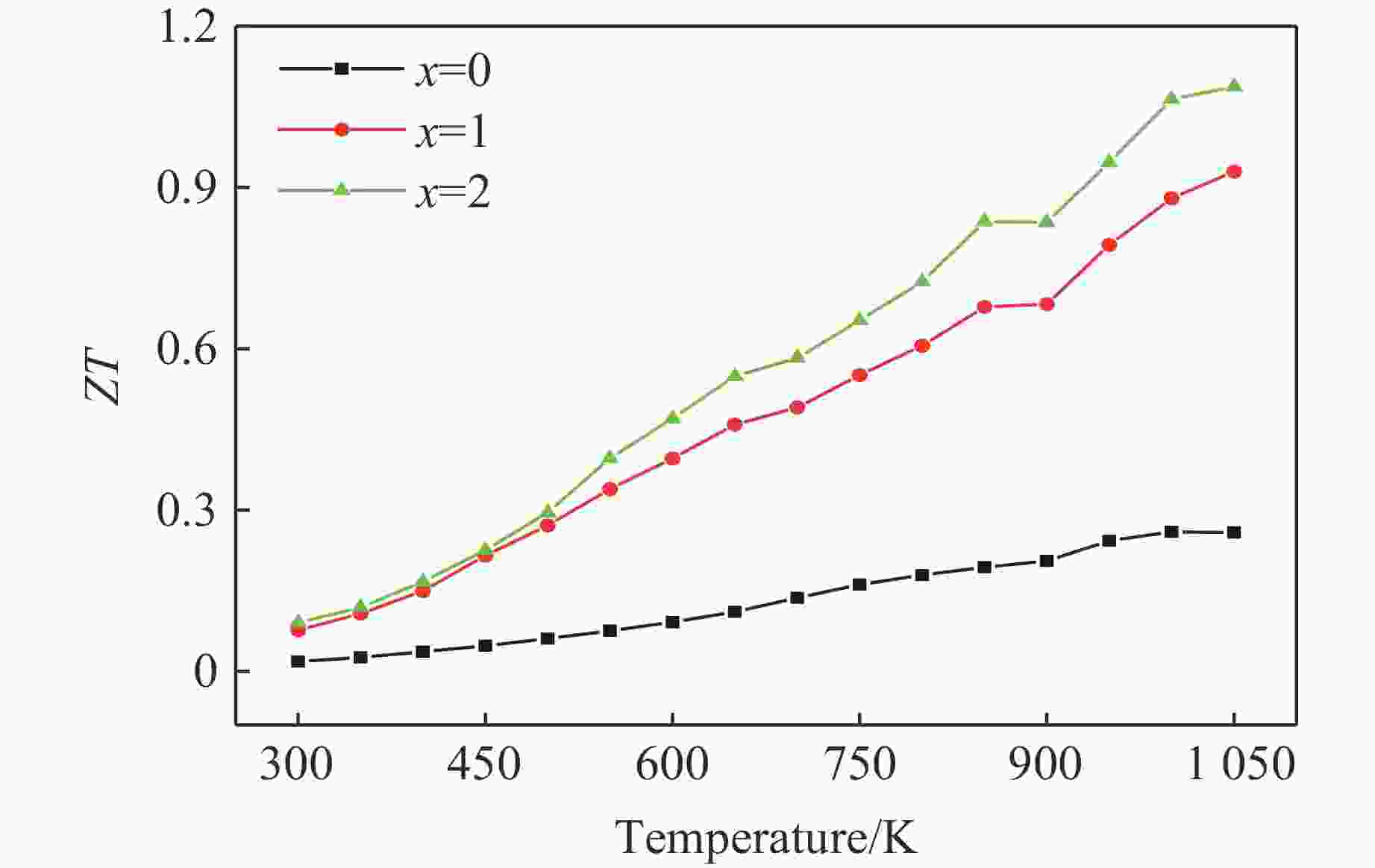
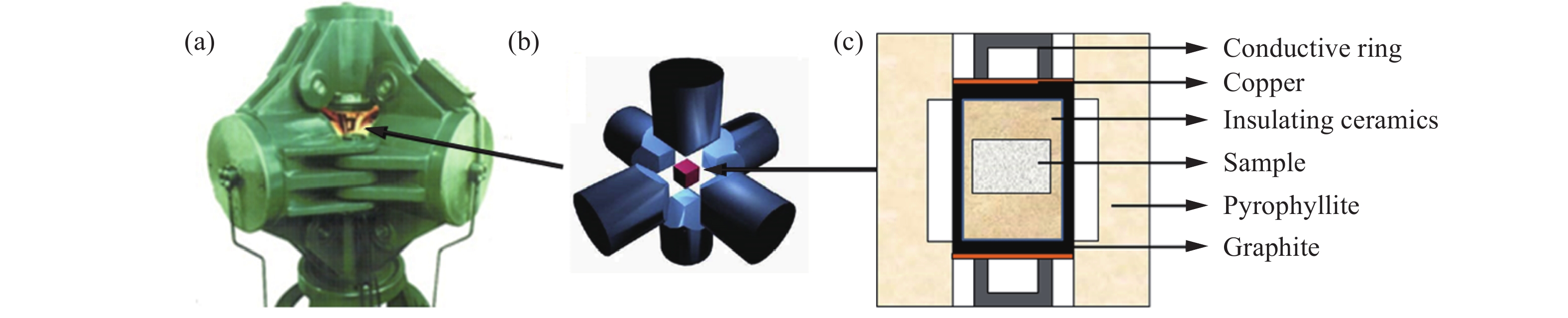
| [1] |
SHI X L, ZOU J, CHEN Z G. Advanced thermoelectric design: from materials and structures to devices [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(15): 7399–7515. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00026
|
| [2] |
BELL L E. Cooling, heating, generating power, and recovering waste heat with thermoelectric systems [J]. Science, 2008, 321(5895): 1457–1461. doi: 10.1126/science.1158899
|
| [3] |
CHAMPIER D. Thermoelectric generators: a review of applications [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 140: 167–181. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2017.02.070
|
| [4] |
DISALVO F J. Thermoelectric cooling and power generation [J]. Science, 1999, 285(5428): 703−706.
|
| [5] |
LIU W, XIAO Y, GANG C, et al. Recent advances in thermoelectric nanocomposites [J]. Nano Energy, 2012, 1(1): 42–56. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2011.10.001
|
| [6] |
BASU R, SINGH A. High temperature Si-Ge alloy towards thermoelectric applications: a comprehensive review [J]. Materials Today Physics, 2021, 21: 100468. doi: doi.org/10.1016/j.mtphys.2021.100468
|
| [7] |
DISMUKES J P, EKSTROM L, STEIGMEIER E F, et al. Thermal and electrical properties of heavily doped Ge-Si alloys up to 1300 °K [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1964, 35(10): 2899–2907. doi: 10.1063/1.1713126
|
| [8] |
JOSHI G, LEE H, WANG X, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric figure-of-merit in nanostructured p-type silicon germanium bulk alloys [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(19): 459–259.
|
| [9] |
OKUTANI T, KABEYA Y, NAGAI H. Thermoelectric n-type silicon germanium synthesized by unidirectional solidification in microgravity [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 551: 607–615. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.11.022
|
| [10] |
VISHWAKARMA A, CHAUHAN N S, BHARDWAJ R, et al. Melt-spun SiGe nano-alloys: microstructural engineering towards high thermoelectric efficiency [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2021, 50(1): 364–374. doi: 10.1007/s11664-020-08560-6
|
| [11] |
MURUGASAMI R, VIVEKANANDHAN P, KUMARAN S, et al. Synergetic enhancement of thermoelectric and mechanical properties of n-type SiGe-P alloy through solid state synthesis and spark plasma sintering [J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2019, 118: 110483. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.05.008
|
| [12] |
MURUGASAMI R, VIVEKANANDHAN P, KUMARAN S, et al. Thermoelectric power factor performance of silicon-germanium alloy doped with phosphorus prepared by spark plasma assisted transient liquid phase sintering [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2018, 143: 35–39. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.08.048
|
| [13] |
周绪彪, 李尚升, 李洪涛, 等. Sn1− xGexTe的高温高压合成及热电性能 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2022, 36(1): 011102.ZHOU X B, LI S S, LI H T, et al. Synthesis and thermoelectric properties of Sn 1−xGexTe by high temperature and high pressure [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2022, 36(1): 011102.
|
| [14] |
KALLEL A C, ROUX G, MARTIN C L. Thermoelectric and mechanical properties of a hot pressed nanostructured n-type Si80Ge20 alloy [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2013, 564: 65–70.
|
| [15] |
BATHULA S, JAYASIMHADRI M, SINGH N, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric figure-of-merit in spark plasma sintered nanostructured n-type SiGe alloys [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 101(21): 213902.
|
| [16] |
SURYANARAYANA C. Mechanical alloying and milling [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2001, 46: 1–184. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6425(99)00010-9
|
| [17] |
YANG M, SU T, ZHOU D, et al. High-pressure synthesis and thermoelectric performance of tellurium doped with bismuth [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52(17): 10526–10532. doi: 10.1007/s10853-017-1180-9
|
| [18] |
ZHU H, SU T, LI H, et al. High pressure synthesis, structure and thermoelectric properties of BiCuChO (Ch = S, Se, Te) [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(4): 1541–1546. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.10.021
|
| [19] |
YANG M, ZHU H, LI H, et al. Electrical transport and thermoelectric properties of PbTe1− xIx synthesized by high pressure and high temperature [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 696: 161–165. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.11.253
|
| [20] |
宿太超, 朱品文, 马红安, 等. 高温高压下掺杂N型PbTe的热电性能 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2007, 21(1): 55–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5773.2007.01.009SU T C, ZHU P W, MA H A, et al. Thermoelectric properties of N-PbTe doped with Sb2Te3 prepared by high-pressure and high-temperature [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2007, 21(1): 55–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5773.2007.01.009
|
| [21] |
BUX S K, BLAIR R G, GOGNA P K, et al. Nanostructured bulk silicon as an effective thermoelectric material [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 19(15): 2445–2452.
|
| [22] |
ZHU G H, LEE H, LAN Y C, et al. Increased phonon scattering by nanograins and point defects in nanostructured silicon with a low concentration of germanium [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102(19): 196803.
|
| [23] |
MINGO N, HAUSER D, KOBAYASHI N P, et al. “Nanoparticle-in-alloy” approach to efficient thermoelectrics: silicides in SiGe [J]. Nano Letters, 2009, 9(2): 711–715. doi: 10.1021/nl8031982
|
| [24] |
ROWE D M, SHUKLA V S. The effect of phonon-grain boundary scattering on the lattice thermal conductivity and thermoelectric conversion efficiency of heavily doped fine-grained, hot-pressed silicon germanium alloy [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1981, 52(12): 7421–7426. doi: 10.1063/1.328733
|
| [25] |
BATHULA S, JAYASIMHADRI M, GAHTORI B, et al. The role of nanoscale defect features in enhancing the thermoelectric performance of p-type nanostructured SiGe alloys [J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(29): 12474–12483. doi: 10.1039/C5NR01786F
|
| [26] |
SON J H, OH M W, KIM B S, et al. Effect of ball milling time on the thermoelectric properties of p-type (Bi, Sb)2Te3 [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 566: 168–174. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.03.062
|
| [27] |
BERA C, MINGO N, VOLZ S. Marked effects of alloying on the thermal conductivity of nanoporous materials [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104(11): 115502.
|
| [28] |
VINEIS C J, SHAKOURI A, MAJUMDAR A, et al. Nanostructured thermoelectrics: big efficiency gains from small features [J]. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(36): 3970–3980. doi: 10.1002/adma.201000839
|
| [29] |
WALKER C T, POHL R O. Phonon scattering by point defects [J]. Physical Review, 1963, 131(4): 1433–1442. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.131.1433
|
| [30] |
ZOU J, KOTCHETKOV D, BALANDIN A A, et al. Thermal conductivity of GaN films: effects of impurities and dislocations [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 92(5): 2534–2539. doi: 10.1063/1.1497704
|
| [31] |
CARRUTHERS P. Theory of thermal conductivity of solids at low temperatures [J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1961, 33(1): 92−138.
|
| [32] |
MORELLI D T, HEREMANS J P, SLACK G A. Estimation of the isotope effect on the lattice thermal conductivity of group Ⅳ and group Ⅲ-Ⅴ semiconductors [J]. Physical Review B, 2002, 66(19): 195304.
|
| [33] |
VINING C B. Thermoelectric properties of pressure-sintered Si0.8Ge0.2 thermoelectric alloys [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1991, 69(8): 4333–4340. doi: 10.1063/1.348408
|
| [34] |
REGEL A R, SMIRNOV I A, SHADRICHEV E V. Investigation of thermal conductivity of semiconducting melts [J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1972, 8: 266–271.
|
| [35] |
KIM H S, GIBBS Z M, TANG Y, et al. Characterization of Lorenz number with Seebeck coefficient measurement [J]. APL Materials, 2015, 3(4): 041506.
|
| [36] |
ZHAO L J, YANG J, ZOU Y H, et al. Tuning Ag content to achieve high thermoelectric properties of Bi-doped p-type Cu3SbSe4-based materials [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 872: 159659.
|
| [37] |
SLACK G A, HUSSAIN M A. The maximum possible conversion efficiency of silicon-germanium thermoelectric generators [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1991, 70(5): 2694–2718. doi: 10.1063/1.349385
|






 下载:
下载: