A Numerical Study on the Effect of Ignition Pattern on Wavelet Features in Rotating Detonation Waves
doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20220593
-
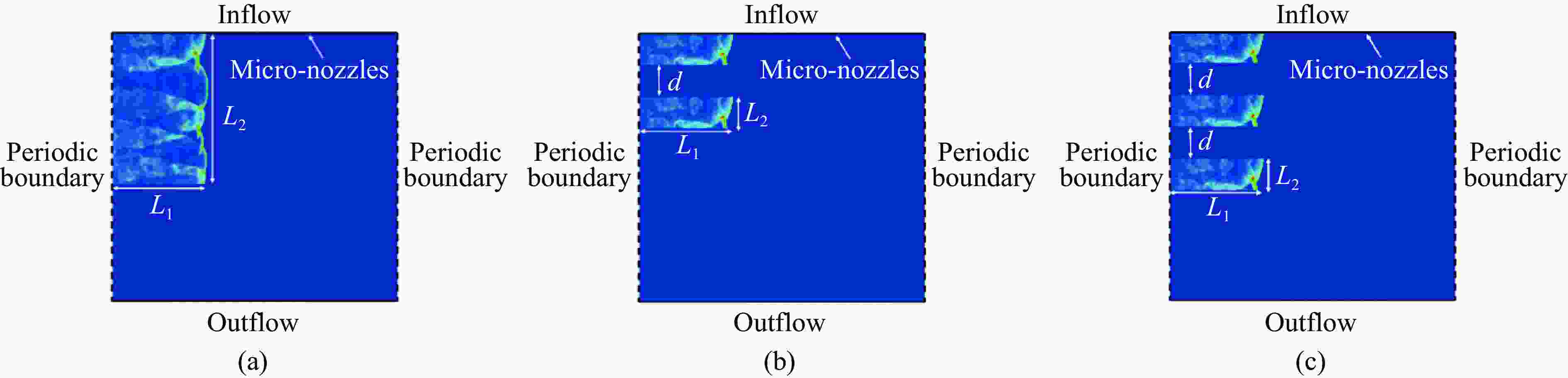
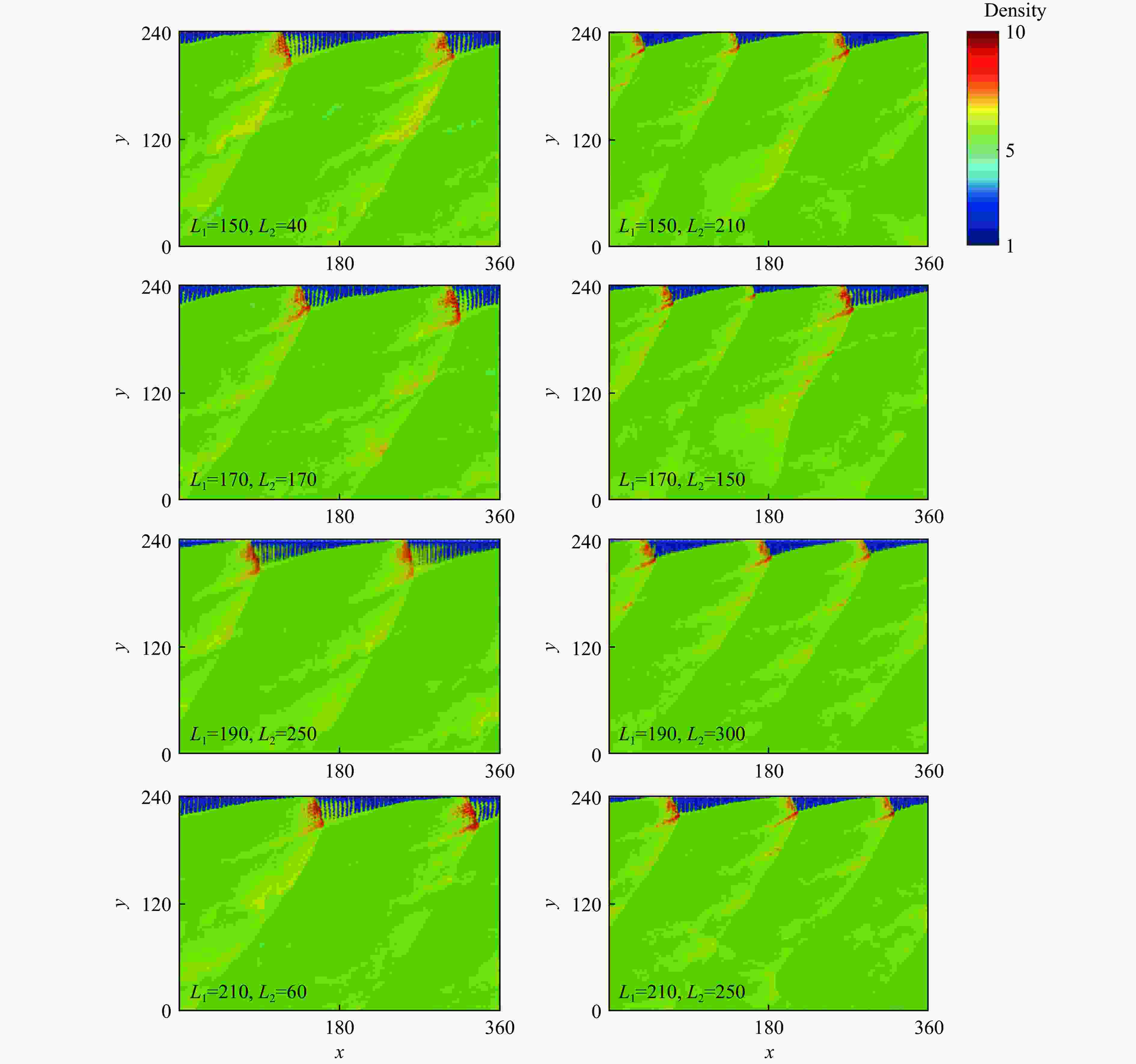
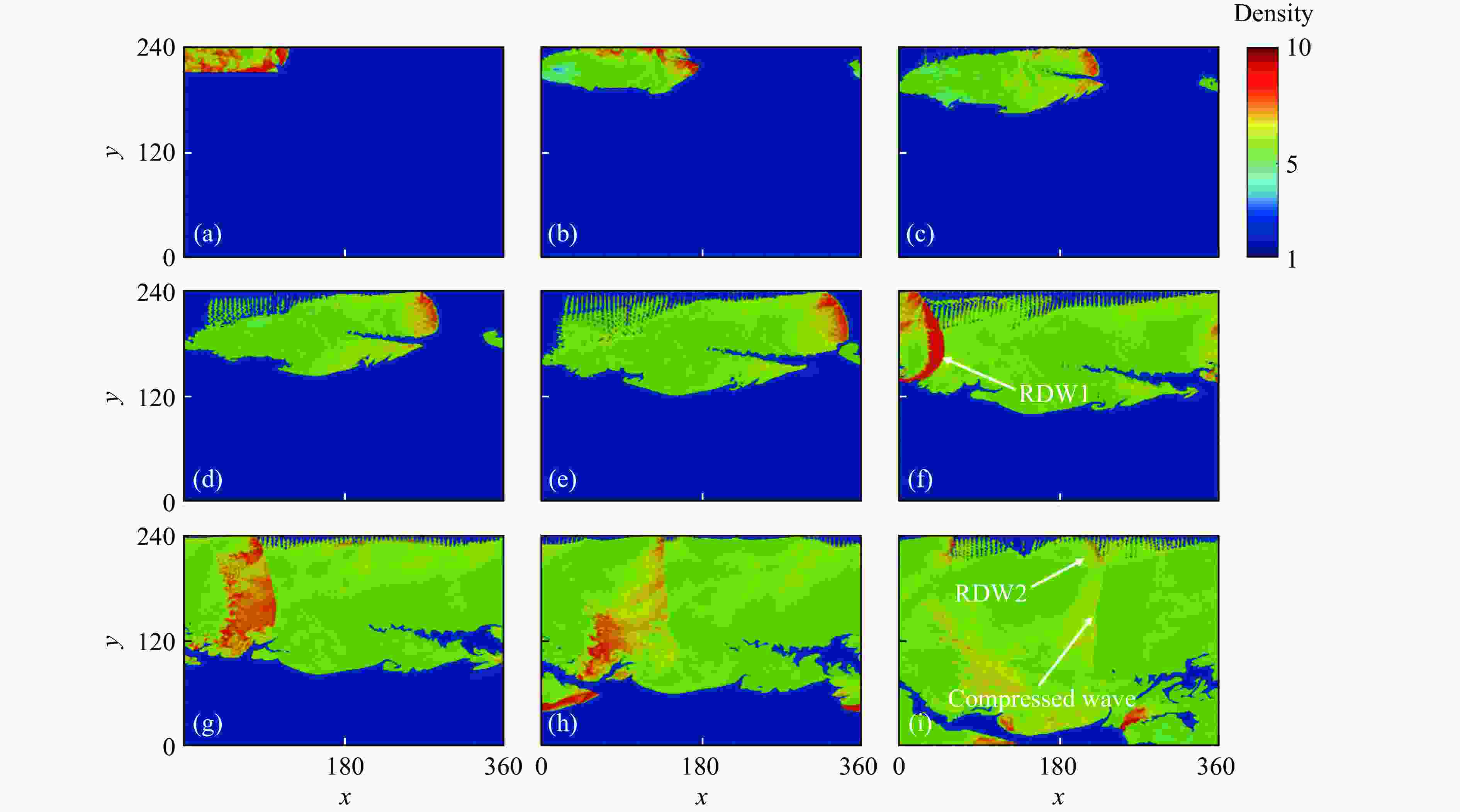
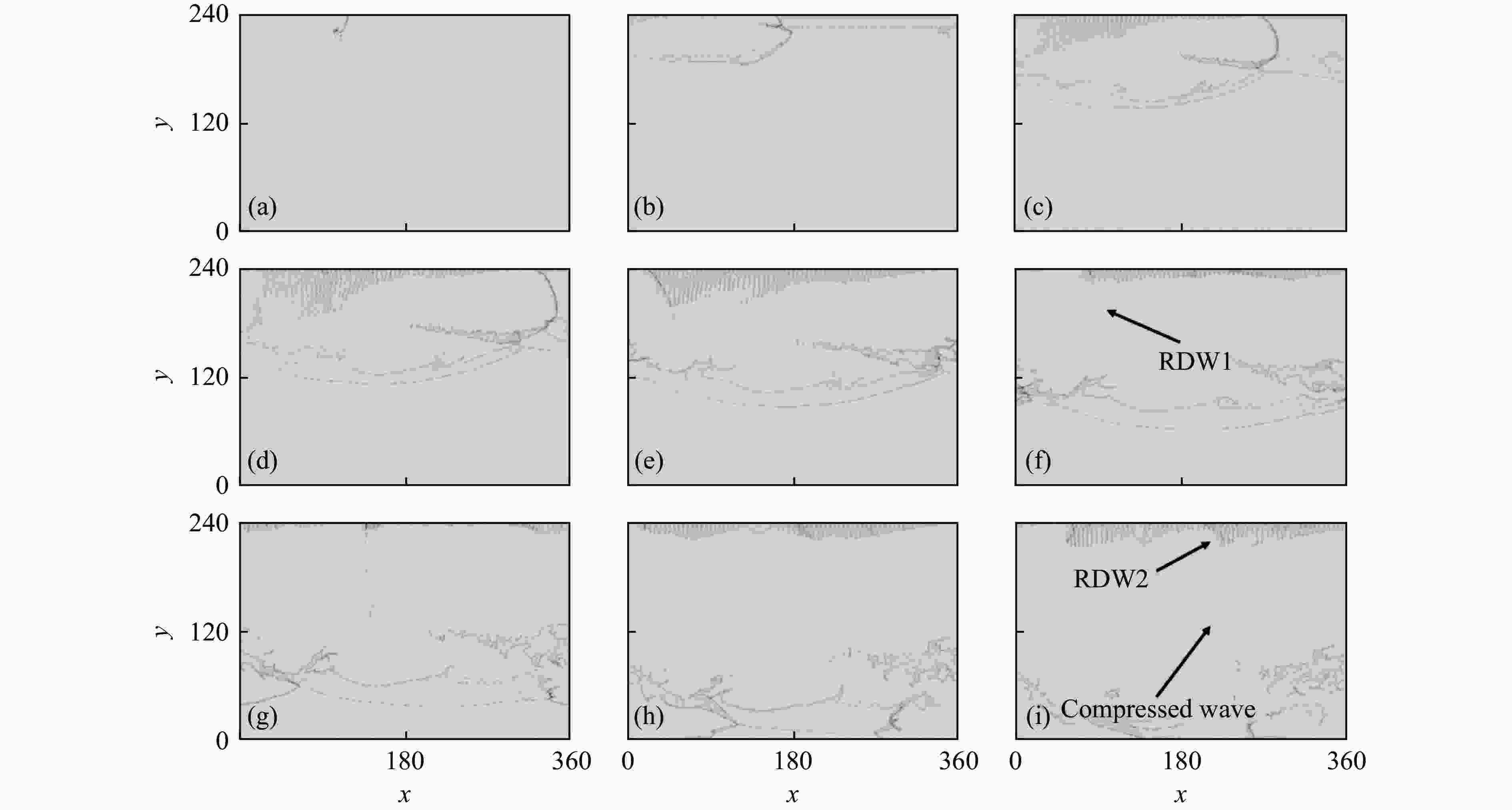
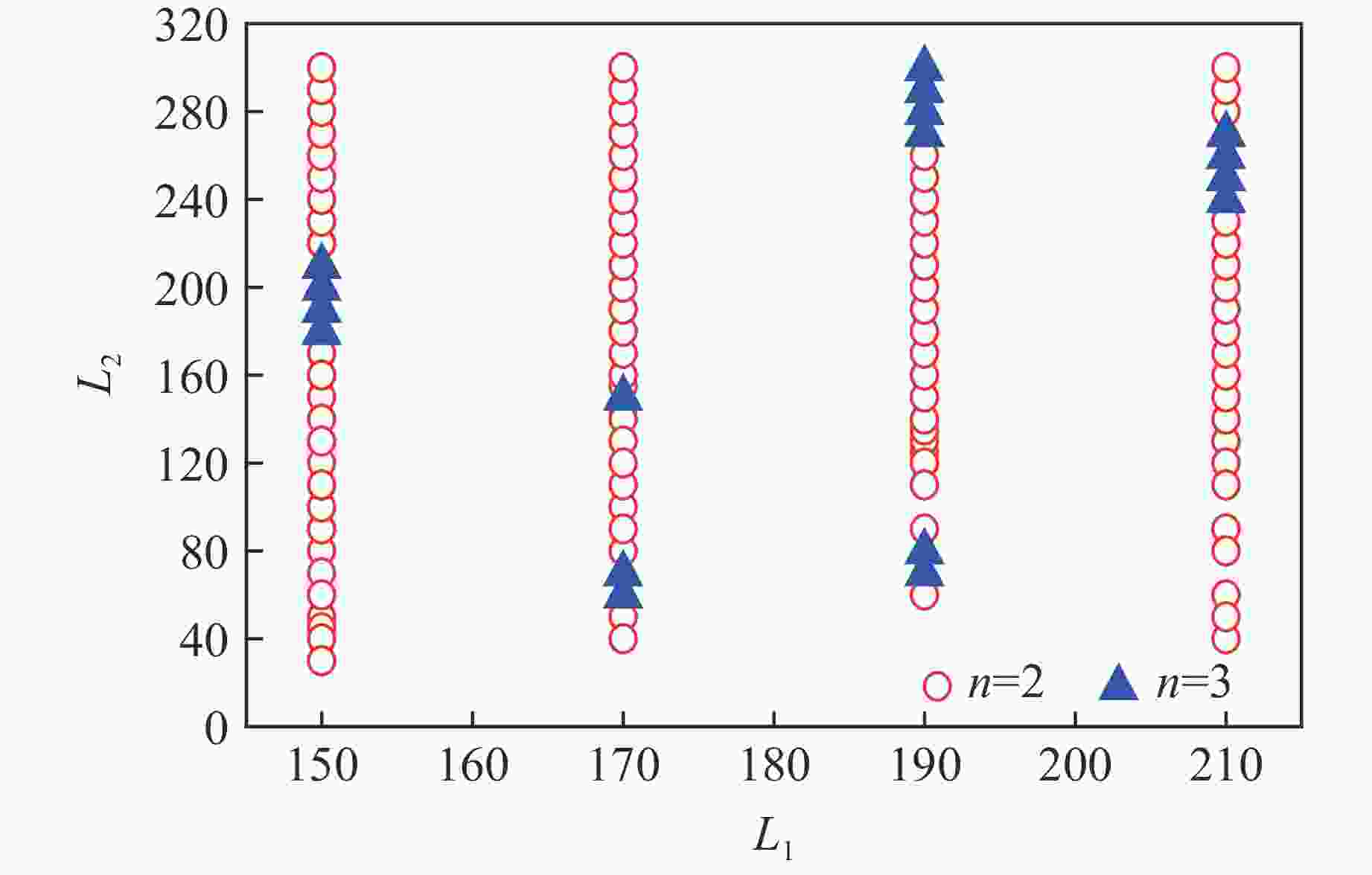
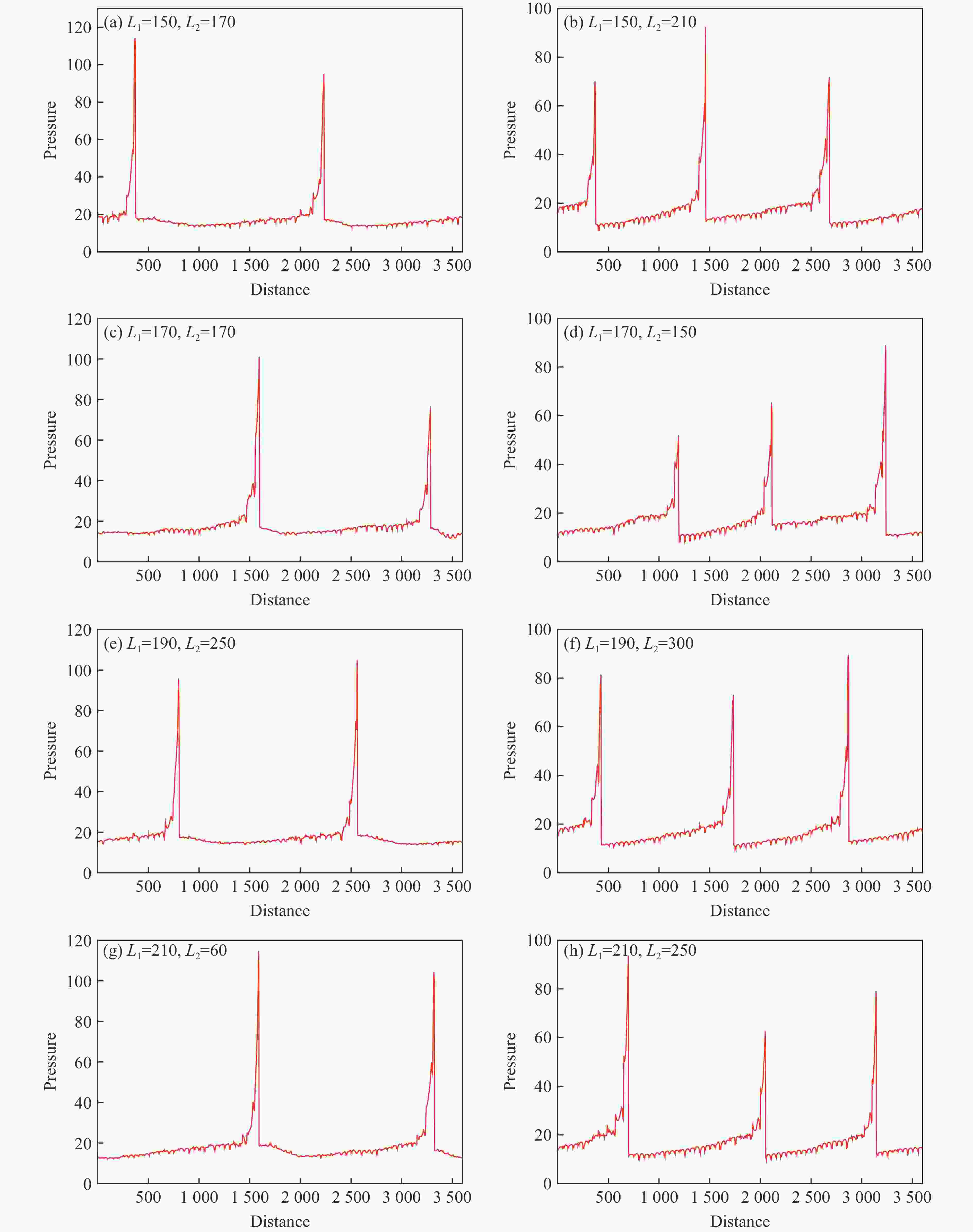
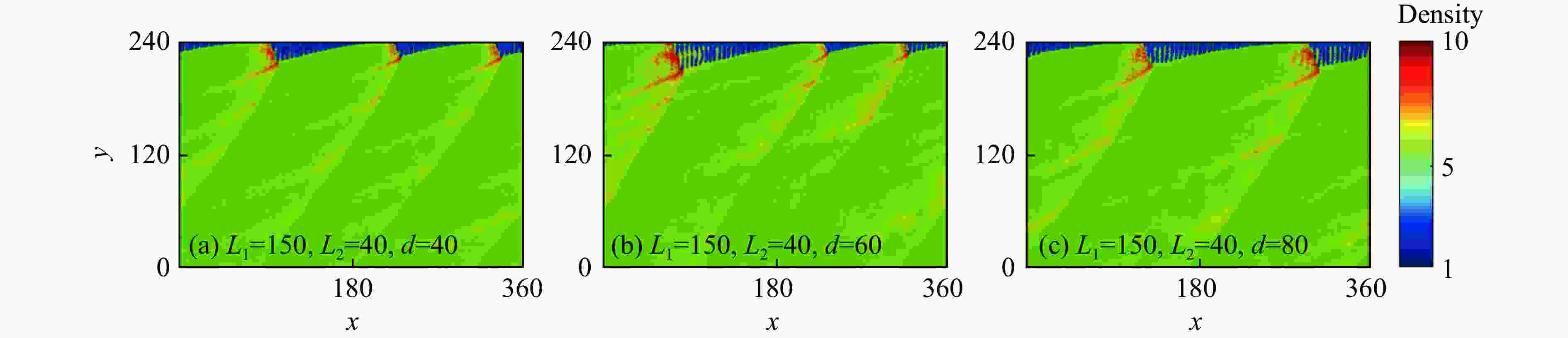
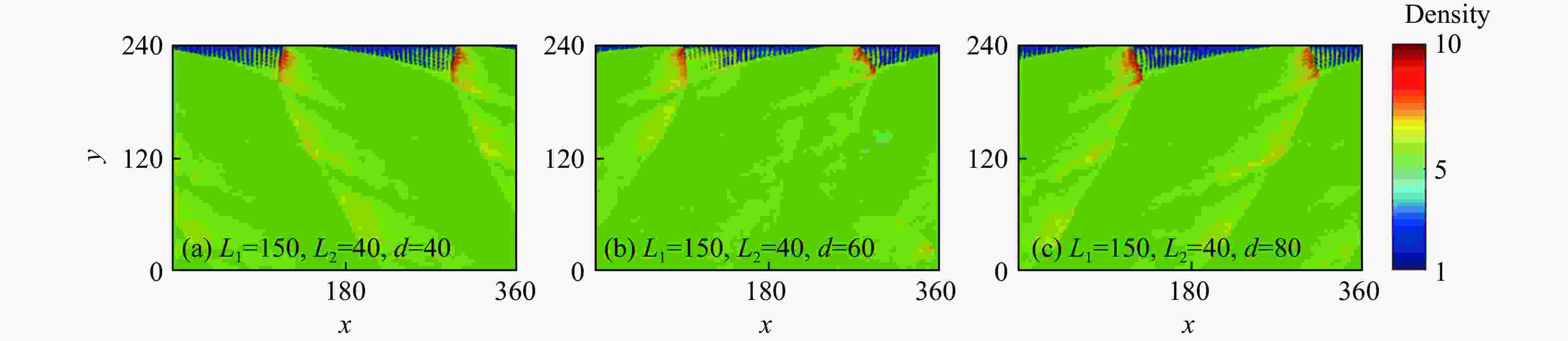
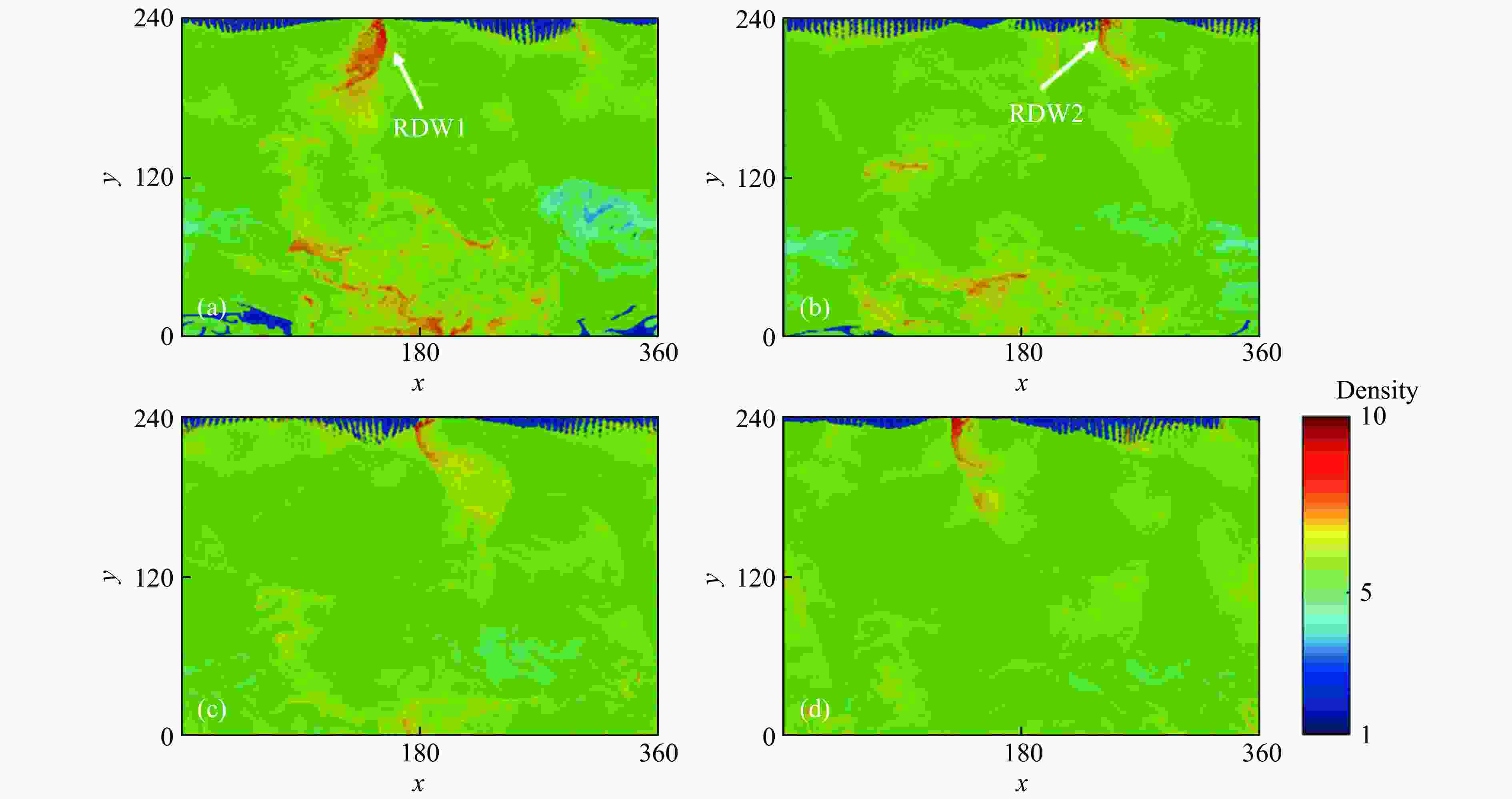
摘要: 采用欧拉方程和两步诱导反应模型,详细研究了点火源参数对旋转爆轰波特征的影响规律,详细考虑了点火源尺寸、数量和间距的影响。利用提前计算得到的C-J爆轰波作为点火源,改变C-J爆轰波的大小便可得到不同尺寸的点火源。数值模拟结果表明:旋转爆轰波特征与点火源参数密切相关;仅可观察到双波和三波模式;旋转爆轰波数量与点火源尺寸之间呈现非线性关系。对于一个点火源,在相同的点火源宽度下,双波模式出现的概率超过80%,而三波模式的出现是一个随机现象。旋转爆轰波的形成机理可总结如下:第一个旋转爆轰波来源于入射C-J爆轰波的直接起爆,后续的旋转爆轰波则起源于压缩波与可燃气体射流之间的相互作用。旋转爆轰波特征与点火源数量及间距密切相关,它们之间的关系也都呈现非线性。Abstract: In this study, the effect of ignition pattern on the wavelet features of rotating detonation waves (RDWs) is numerically investigated with Euler equations and two-step induction-reaction model. The influences of the size, the number and the spacing of the ignition zone were considered. The theoretical Chapman-Jouguet (C-J) detonation wave was used as the ignition zone, and different ignition patterns were obtained by changing the size of the C-J detonation wave. The numerical results indicate that the wavelet features of rotating detonation waves closely depend on the ignition zone size. Only the two-wave and the three-wave modes are observed for the single ignition zone with various sizes, and the relation between the quantity of RDWs and the ignition size is non-linear. For the single ignition zone with the same width, the occurrence probability of the two-wave mode is approximately greater than 80%, while the three-wave mode is a completely random phenomenon. The formation mechanisms of the multiple-wave modes can be summarized as follows: (1) the first RDW is directly produced from the initial C-J detonation wave near the top of the combustor; (2) the subsequent RDW is induced by the interaction between the compressed wave produced by the initial C-J detonation and the jet flow from the micro-nozzles. The quantity of RDWs increases with the quantity or the spacing of ignition zone, but their relations are both non-linear.
-
Key words:
- ignition patterns /
- rotating detonation waves /
- wavelet features /
- compressed wave /
- jet flow
-
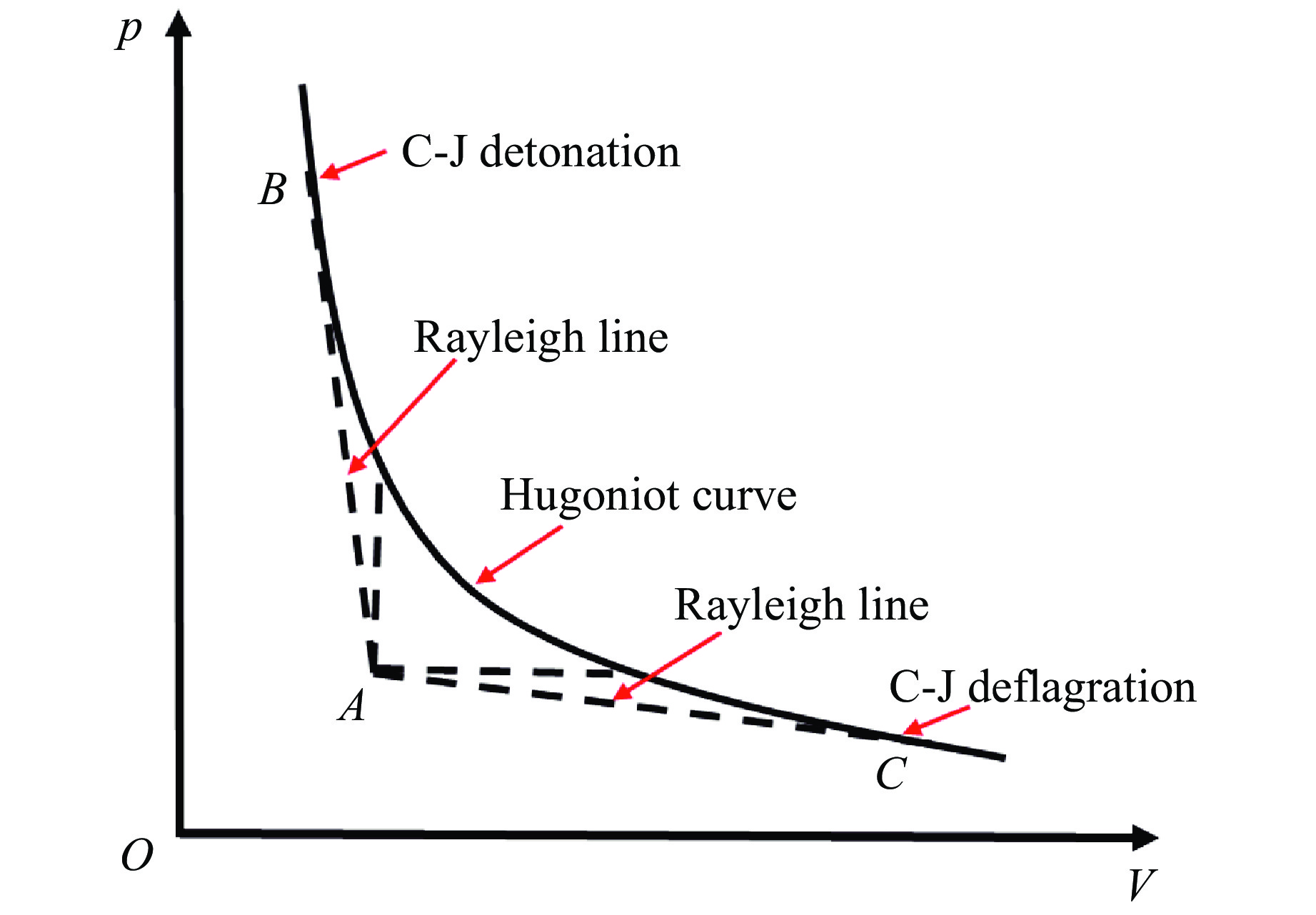
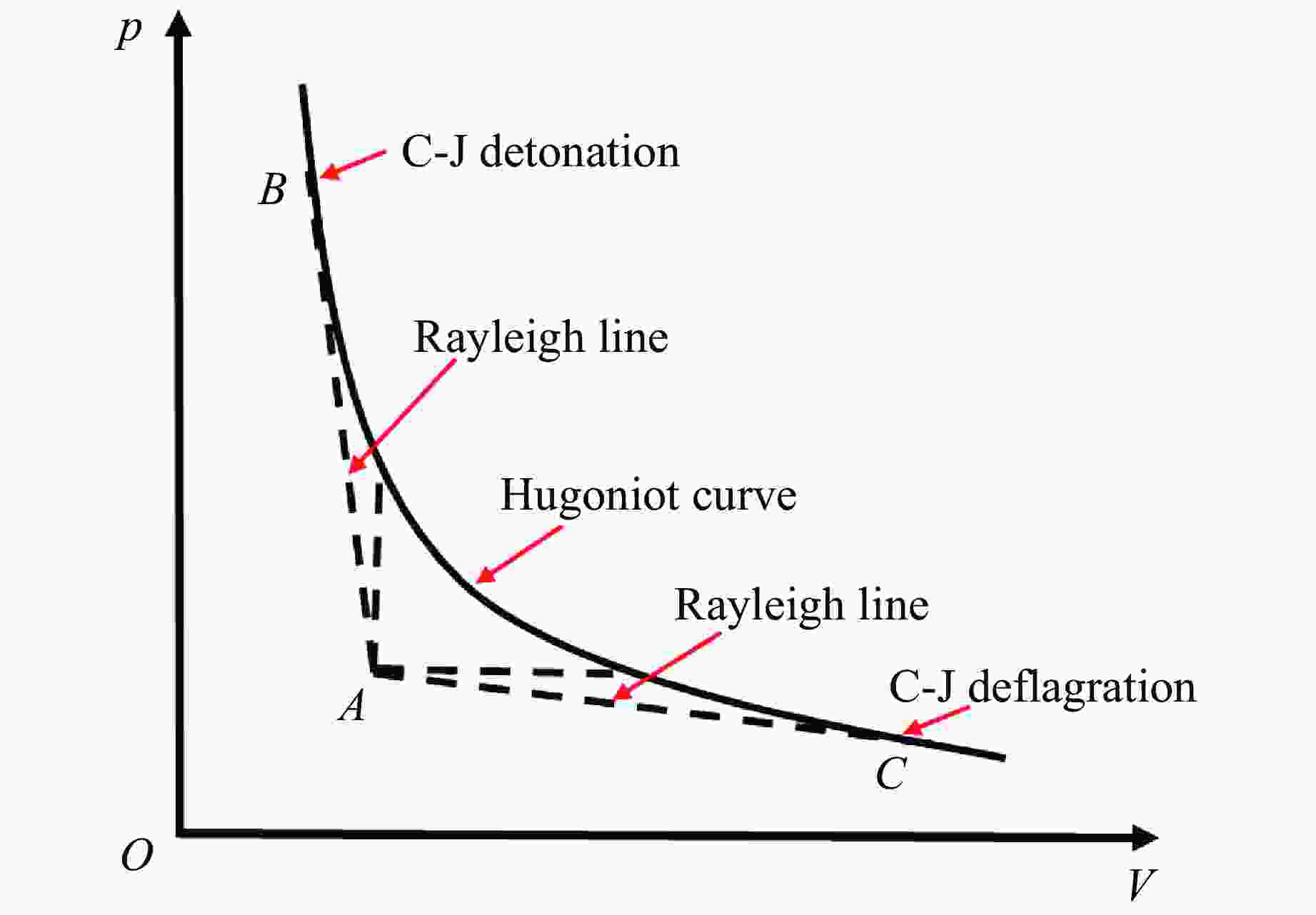
Figure 1. Rayleigh lines and Hugoniot curve in p-V diagram[1]
Table 1. Stoichiometric hydrogen-air mixture parameters and corresponding ZND C-J detonation properties
Q TS EI ER KI KR $ \gamma $ 25.3100 5.7353 6.5200 TS 1.0000 TS 1.0538 3.7400 1.3200 -
[1] ZHOU R, WU D, WANG J P. Progress of continuously rotating detonation engines [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2016, 29(1): 15–29. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2015.12.006 [2] WOLAŃSKI P. Application of the continuous rotating detonation to gas turbine [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2015, 782: 3–12. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.782.3 [3] ANAND V, GUTMARK E. Rotating detonation combustors and their similarities to rocket instabilities [J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2019, 73: 182–234. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2019.04.001 [4] WOLAŃSKI P. Detonative propulsion [J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2013, 34(1): 125–158. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2012.10.005 [5] YI T H, LOU J, TURANGAN C, et al. Propulsive performance of a continuously rotating detonation engine [J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2011, 27(1): 171–181. doi: 10.2514/1.46686 [6] HISHIDA M, FUJIWARA T, WOLANSKI P. Fundamentals of rotating detonations [J]. Shock Waves, 2009, 19(1): 1–10. doi: 10.1007/s00193-008-0178-2 [7] SCHWER D A, KAILASANATH K. Numerical study of the effects of engine size on rotating detonation engines [C]//Proceedings of the 49th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. Orlando: AIAA, 2011: 581. [8] ZHOU R, WANG J P. Numerical investigation of shock wave reflections near the head ends of rotating detonation engines [J]. Shock Waves, 2013, 23(5): 461–472. doi: 10.1007/s00193-013-0440-0 [9] KATTA V R, CHO K Y, HOKE J L, et al. Effect of increasing channel width on the structure of rotating detonation wave [J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2019, 37(3): 3575–3583. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2018.05.072 [10] ANAND V, ST GEORGE A, DRISCOLL R, et al. Characterization of instabilities in a rotating detonation combustor [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(46): 16649–16659. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.09.046 [11] YANG C L, WU X S, MA H, et al. Experimental research on initiation characteristics of a rotating detonation engine [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2016, 71: 154–163. doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2015.10.019 [12] ZHOU S B, MA H, LIU D K, et al. Experimental study of a hydrogen-air rotating detonation combustor [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(21): 14741–14749. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.04.214 [13] TENG H H, ZHOU L, YANG P F, et al. Numerical investigation of wavelet features in rotating detonations with a two-step induction-reaction model [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(7): 4991–5001. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.12.063 [14] YAMADA T, HAYASHI K, TSUBOI N, et al. Numerical analysis of threshold of limit detonation in rotating detonation engine [C]//Proceedings of the 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. Orlando: AIAA, 2010: 153. [15] TSUBOI N, WATANABE Y, KOJIMA T, et al. Numerical estimation of the thrust performance on a rotating detonation engine for a hydrogen-oxygen mixture [J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2015, 35(2): 2005–2013. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2014.09.010 [16] SHAO Y T, LIU M, WANG J P. Numerical investigation of rotating detonation engine propulsive performance [J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2010, 182(11/12): 1586–1597. [17] SHAO Y T, WANG J P. Change in continuous detonation wave propagation mode from rotating detonation to standing detonation [J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2010, 27(3): 034705. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/27/3/034705 [18] SHAO Y T, LIU M, WANG J P. Continuous detonation engine and effects of different types of nozzle on its propulsion performance [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2010, 23(6): 647–652. doi: 10.1016/S1000-9361(09)60266-1 [19] ZHOU R, WANG J P. Numerical investigation of flow particle paths and thermodynamic performance of continuously rotating detonation engines [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2012, 159(12): 3632–3645. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2012.07.007 [20] SCHWER D, KAILASANATH K. Numerical investigation of the physics of rotating-detonation-engines [J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2011, 33(2): 2195–2202. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2010.07.050 [21] SCHWER D, KAILASANATH K. Fluid dynamics of rotating detonation engines with hydrogen and hydrocarbon fuels [J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2013, 34(2): 1991–1998. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2012.05.046 [22] UEMURA Y, HAYASHI A K, ASAHARA M, et al. Transverse wave generation mechanism in rotating detonation [J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2013, 34(2): 1981–1989. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2012.06.184 [23] LIU Y, ZHOU W J, YANG Y J, et al. Numerical study on the instabilities in H2-air rotating detonation engines [J]. Physics of Fluids, 2018, 30(4): 046106. doi: 10.1063/1.5024867 [24] TORO E F. Riemann solvers and numerical methods for fluid dynamics [M]. 3rd edtion. Berlin: Springer, 2009. [25] KAILASANATH K. Recent developments in the research on rotating-detonation-wave engines [C]//Proceedings of the 55th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting. Grapevine: AIAA, 2017: 784. [26] ZHAO M J, CLEARY M J, ZHANG H W. Combustion mode and wave multiplicity in rotating detonative combustion with separate reactant injection [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2021, 225: 291–304. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2020.11.001 -






 下载:
下载: