High Precision Targets Fabrication for Sound Velocity Measurements in Terapascal Pressure
-
摘要: 声速反映小应力扰动在介质中的传播特征,是材料在一定热力学状态下的重要属性,是研究材料状态方程、相变(包括固-固相变)以及物质构成等的重要手段。超高压声速测量对于地球和行星物理、惯性约束聚变以及第一性原理的建模等多个物理研究领域具有重要意义。基于侧向稀疏方法连续测量冲击绝热线上的体声速是获取超高压声速的全新方法。该方法对靶的制备要求很高。为此,详细介绍了基于该方法的靶的制备要求,探讨了制备工艺、测量技术以及影响实验精度的主要因素,并根据“神光Ⅲ”原型装置的实验结果进行相应的分析。Abstract: Sound velocity is an intrinsic property of material, which is equal to the spread velocity of weak perturbation. Measurements of sound velocity are very important for the research of equation of state, phase transition and component of matter at extreme conditions. A continuous side-release method which can work to terapascal pressure was newly developed. In this paper, we described details of high precision targets fabrication of this method, including requirements, methodology and detection. Also, key factors which lead to fatal issues are analyzed for better signals and reliability. Experimental results on SGIII prototype laser facility are shown to validate the technology of targets fabrication.
-
Key words:
- sound velocity /
- high pressure /
- Hugoniot curve /
- target physics
-
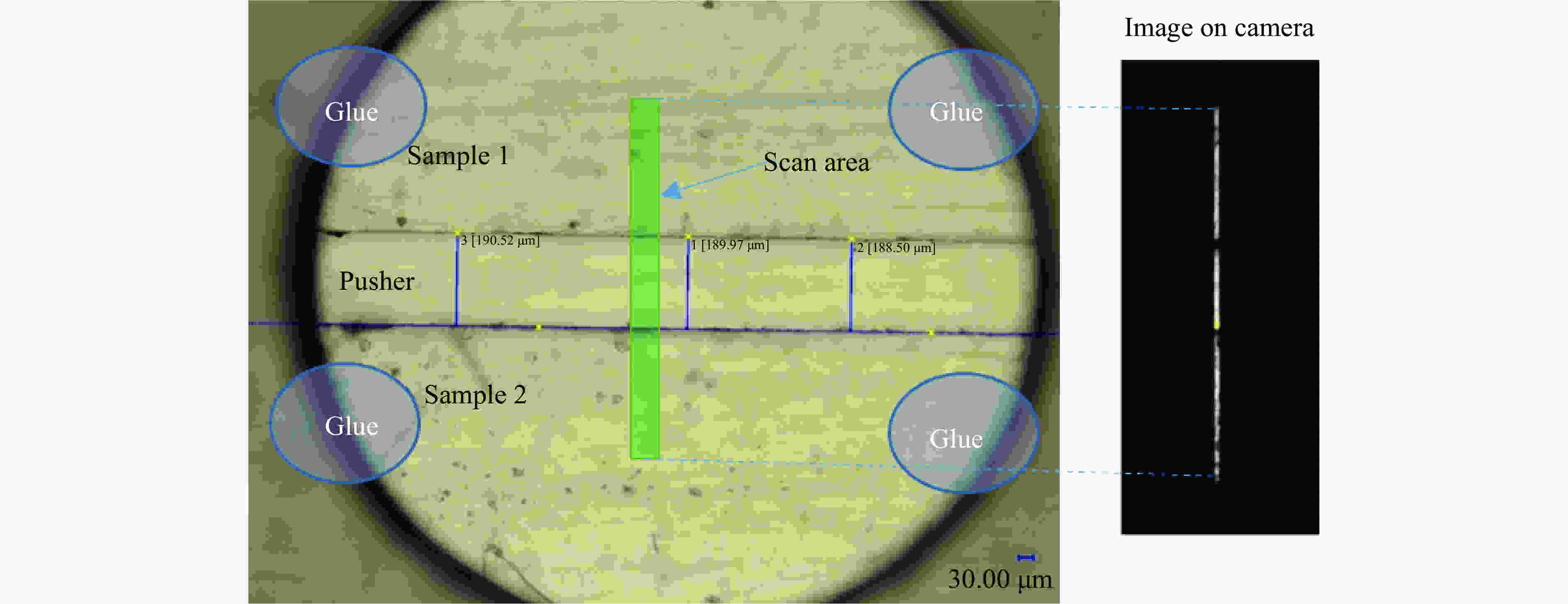
表 1 基于“神光Ⅲ”原型装置的驱动方式和靶参数对致盲及预热的影响
Table 1. Effects of drive modes and target parameters on sample preheating and reflection of probe beam in SGⅢ prototype laser experiments
Drive
modeLaser inject Ablator/pusher Sample Flatness of shock Preheating and blindness Indirect
drive$\varnothing$2.0 mm × 1.7 mm
gold hohlraum, one
end, 8 beams of laser,
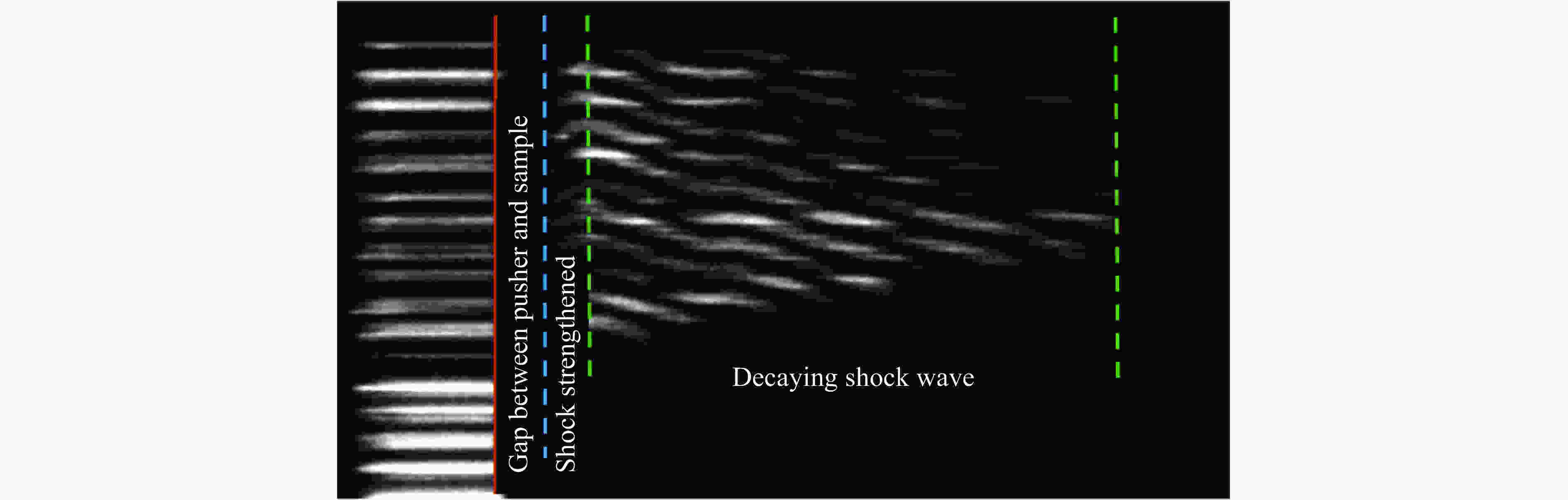
3ω, 4.8 kJ40 μm Al Polystyrene Excellent Very serious at both blindness and preheating, > 1 500 ℃ 15 μm Al (ablator) +
10 μm Au + 15 μm AlPolystyrene Acceptable No blindness, no observable preheating Indirect
drive$\varnothing$1.5 mm × 1.4 mm
gold hohlraum, one
end, 8 beams of laser,
3ω, 2.8 kJ15 μm Al (ablator) +
10 μm Au + 15 μm AlPolystyrene High uniformity at incident, follows with chaos Observable blindness, no observable preheating 15 μm Al (ablator) +
10 μm Au + 15 μm Al$ \alpha $-quartz High uniformity at incident, follows with chaos No blindness, no observable preheating Direct
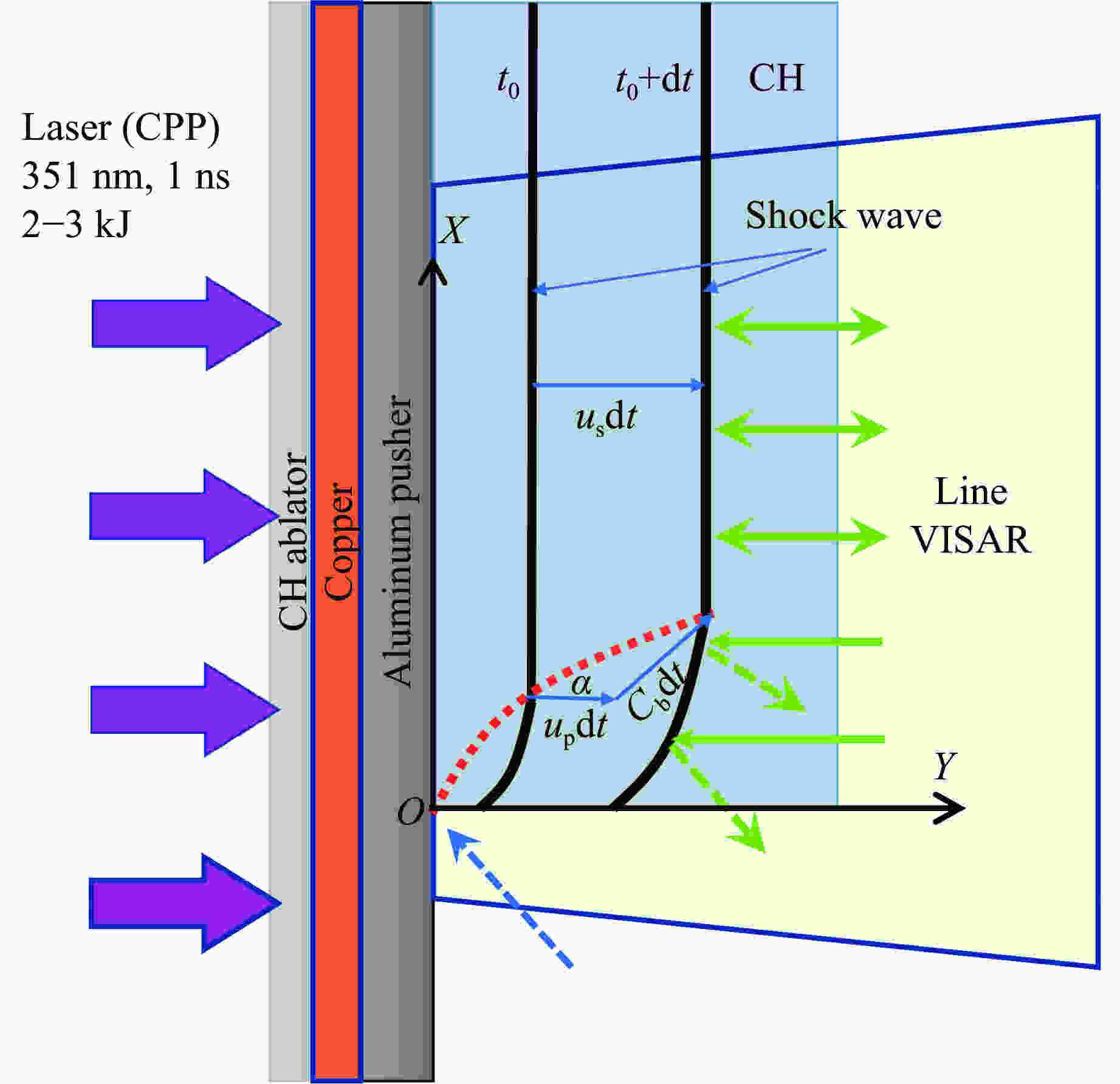
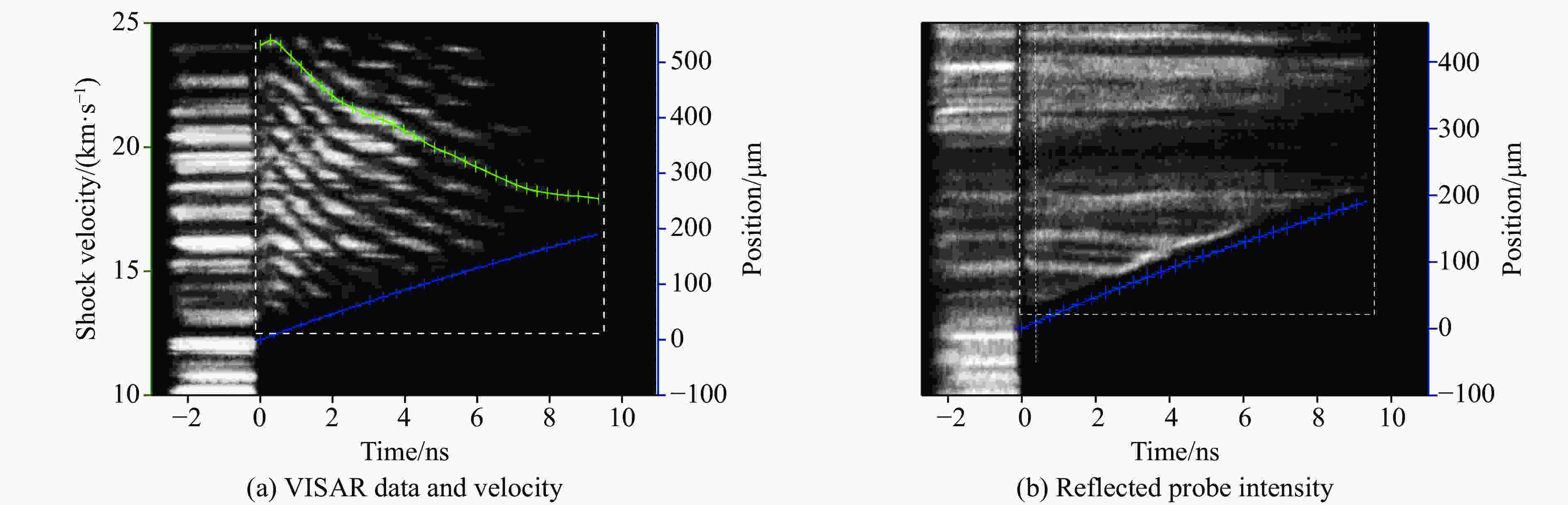
driveOverlap of 4 beams of laser with $\varnothing$2 mm CPP, incidence angle 45°,
3ω, 2–3 kJ25 μm PI + 40 μm Al Polystyrene Acceptable Slightly dim VISAR, no observable preheating 25 μm PI + 40 μm Al $ \alpha $-quartz Acceptable Unobservable 25 μm PI + 70 μm Al Polystyrene Acceptable Unobservable 25 μm PI + 12 μm Cu +
40 μm AlPolystyrene Acceptable Unobservable -
[1] FORBES J W. Shock wave compression of condensed matter [M]//PRIMER A. Shock Wave and High Pressure Phenomena. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2012. [2] DUFFY T, MADHUSUDHAN N, LEE K KM. Mineralogy of super earth planets [M]//Treatise on Geophysics. Elsevier, 2015: 149–178. [3] DUFFY T S, AHRENS T J. Sound velocities at high pressure and temperature and their geophysical implications [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 1992, 97(B4): 4503–4520. doi: 10.1029/91JB02650 [4] DUFFY T S, VOS W L, ZHA C, et al. Sound velocities in dense hydrogen and the interior of Jupiter [J]. Science, 1994, 263(5153): 1590–1593. doi: 10.1126/science.263.5153.1590 [5] HU J B, ZHOU X M, DAI C D, et al. Shock inducedbct bcc transition and melting of tin identified by sound velocity measurements [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 104(8): 083520. doi: 10.1063/1.3003325 [6] NISSIM N, ELIEZER S, WERDIGER M. The sound velocity throughout the P-ρ phase space with application to laser induced shock wave in matter precompressed by a diamond anvil cell [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 115(21): 213503. doi: 10.1063/1.4879855 [7] OHTANI E, MIBE K, SAKAMAKI T, et al. Sound velocity measurement by inelastic X ray scattering at high pressure and temperature by resistive heating diamond anvil cell [J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2015, 56(1/2): 190–195. [8] MCCOY C A, KNUDSON M D, ROOT S. Absolute measurement of the Hugoniot and sound velocity of liquid copper at multimegabar pressures [J]. Physical Review B, 2017, 96(17): 174109. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.96.174109 [9] LI M, ZHANG S, ZHANG H P, et al. Continuous sound velocity measurements along the shock Hugoniot curve of quartz [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(21): 215703. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.215703 [10] BRADLEY D K, EGGERT J H, HICKS D G, et al. Shock compressing diamond to a conducting fluid [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 93(19): 195506. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.195506 [11] MCCOY C A, GREGOR M C, POLSIN D N, et al. Measurements of the sound velocity of shockcompressed liquid silica to 1100 GPa [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2016, 120(23): 235901. doi: 10.1063/1.4972338 -






 下载:
下载: