Experimental Studies on Failure Mode of Low Speed Projectilesby Local Modification on Steel Plates
-
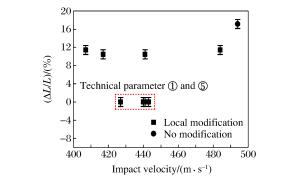
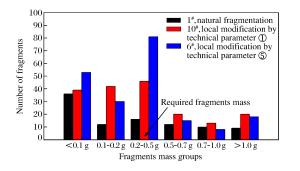
摘要: 为研究局部改性弹体结构的破坏和质量损失规律,设计了不同改性特征的侵彻弹体,在380~500 m/s速度范围内进行了侵彻装甲靶板的实验研究,并对弹体的破坏形式、质量损失等问题进行了探讨。结果表明:随着初始速度的增加,实验弹体的弹长侵蚀率及相对质量损失率相应增加,而弹径磨损率变化较小;穿靶后实验弹体以头部剪切断裂为主要破坏形式,但主体部分仍然保持稳定。改性工艺①和工艺⑤既与弹体强度有较好的匹配性,又可保持良好的破碎性能。Abstract: In this work different modification features were designed for the study of the fracture characteristic and mass abrasion of projectiles with local modification, normal impact experiments were performed on typical RHA targets at velocities ranging from 380 to 500 m/s, and the failure mode and mass loss of the penetrating projectile were examined.The results show that the length eroding and mass loss of the projectile increase as the impact velocity increases, yet the variation of the diameter eroding is small.The failure mode of the projectiles is mainly shear fracture, and the macroscopic damage degree of the projectiles by local modification processes is comparable to that of the unmodified projectiles, of which the main structure and modification parts remain stable.The local modification ① and ⑤ with better fragmentation performance can prevent the damage from occurring during ballistic impacts.
-
Key words:
- penetration /
- local modification /
- failure mode /
- mass loss /
- fragmentation
-
表 1 局部改性工艺
Table 1. Processes of local modification
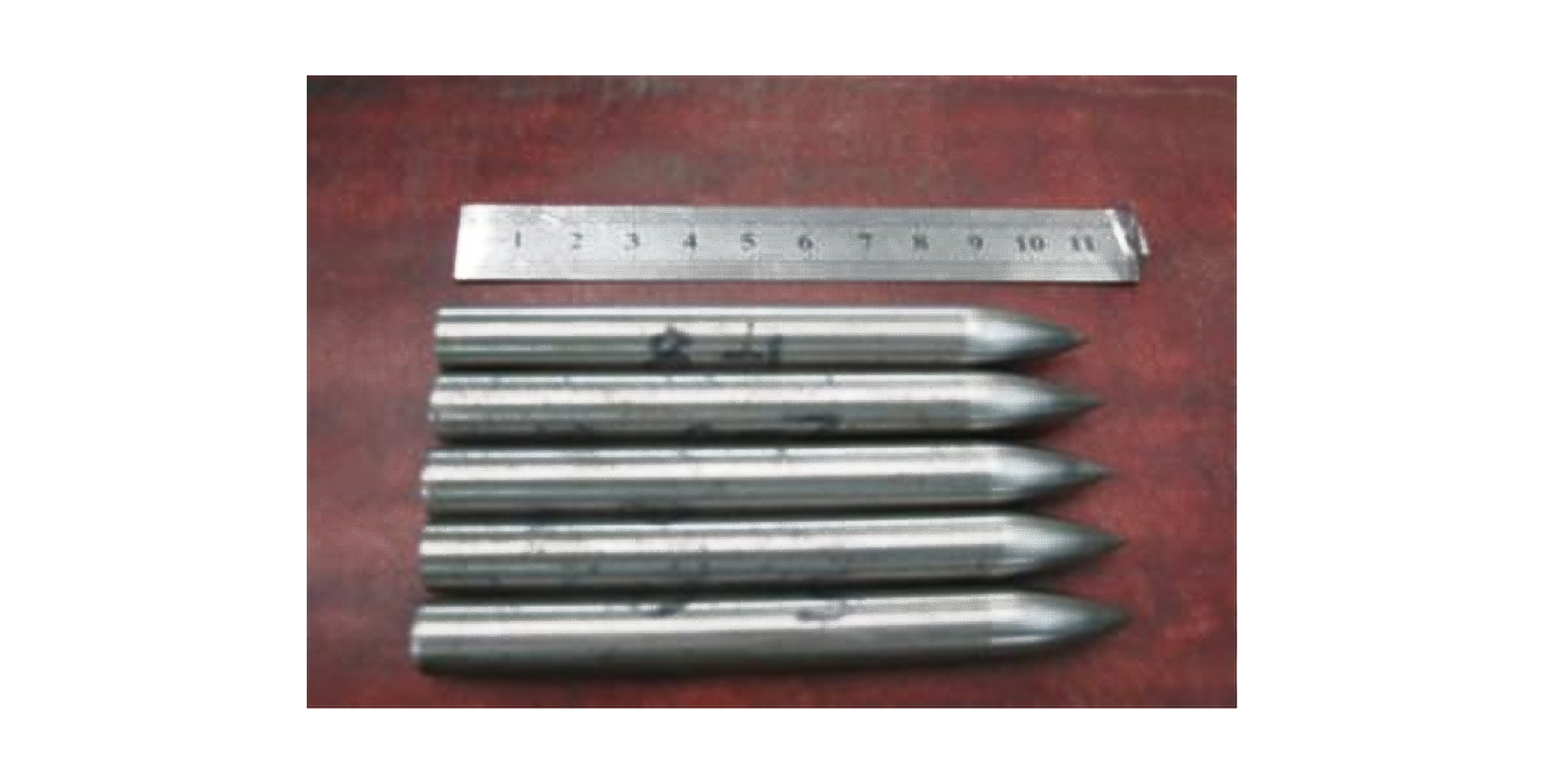
Technical parameter Voltage/(kV) Focus current/(mA) Scan speed/(mm/s) Projectile No. ① 60 520 90 8#, 10# ② 60 515 70 2#, 3# ③ 50 405 75 4#, 5# ④ 60 400 70 9# ⑤ 50 410 90 6#, 7# None 1# 表 2 弹体侵彻装甲靶板实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results of penetration into RHA target
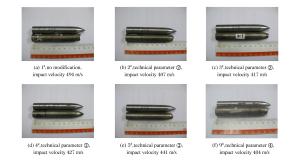
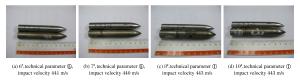
Projectile No. Target thickness/(mm) Mass of projectile/(g) Technical parameter Impact velocity/(m/s) Results 1# 4 107.0 None 494 Perforation with projectile nose destroyed 2# 4 107.2 ② 407 Perforation with projectile nose destroyed 3# 4 105.5 ② 417 Perforation with projectile nose destroyed 4# 4 106.6 ③ 427 Perforation with projectile nose destroyed 5# 4 106.1 ③ 441 Perforation with projectile nose destroyed 6# 4 105.6 ⑤ 441 Perforation with projectile integrity 7# 4 105.8 ⑤ 440 Perforation with projectile integrity 8# 4 107.1 ① 443 Perforation with projectile integrity 9# 4 107.5 ④ 484 Perforation with projectile nose destroyed 10# 4 105.1 ① 443 Perforation with projectile integrity 表 3 穿靶后弹体的质量损失
Table 3. Variation of the projectiles mass after impacting
Projectile No. m0/(g) mf/(g) $ \frac{{\Delta m}}{{{m_0}}}/\left( \% \right) $ 1# 107.0 100.3 6.20 2# 107.2 104.9 2.10 3# 105.5 104.3 1.10 4# 106.6 106.5 0.09 5# 106.1 103.7 2.26 6# 105.6 105.5 0.09 7# 105.8 105.4 3.70 8# 107.1 107.0 0.09 9# 107.5 103.6 3.62 10# 105.1 105.0 0.09 -
[1] 徐文铮, 王晶禹, 陆震, 等.弹性弹体侵彻混凝土靶板的过载特性研究[J].振动与冲击, 2010, 29(5):91-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2010.05.020XU W Z, WANG J Y, LU Z, et al.Drag acceleration characteristic of penetration of elastic projectiles into a concrete target[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2010, 29(5):91-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2010.05.020 [2] WOODWARD R L.Penetration of semi-infinite metal targets by deforming projectiles[J].Int J Mech Sci, 1982, 24(2):73-87. doi: 10.1016/0020-7403(82)90039-X [3] MEYERS M A.Effects of metallurgical parameters on shear band formation in low-carbon steels[J].Metall Trans A, 1990, 21:3153-3164. doi: 10.1007/BF02647311 [4] FORRESTAL M J, PIEKUTOWSKI A J.Penetration experiments with 6061-T6511 aluminum targets and spherical nose steel projectiles at striking velocities between 0.5 and 3.0 km/s[J].Int J Impact Eng, 2000, 24(1):57-67. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(99)00033-0 [5] MISHRA B, RAMAKRISHNA B, JENA P K, et al.Experimental studies on the effect of size and shape of holes on damage and microstructure of high hardness armour steel plates under ballistic impact[J].Mater Des, 2013, 43:17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2012.06.037 [6] 皮爱国, 黄风雷.大长细比结构弹体侵彻2024-O铝靶的弹塑性动力响应[J].爆炸与冲击, 2008, 28(3):252-260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2008.03.010PI A G, HUANG F L.Elastic-plastic dynamic response of slender projectiles penetrating into 2024-O aluminum targets[J].Explosion and Shock Waves, 2008, 28(3):252-260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2008.03.010 [7] 王可慧, 耿宝刚, 初哲, 等.弹体高速侵彻钢筋混凝土靶的结构变形及质量损失的实验研究[J].高压物理学报, 2014, 28(1):61-68. http://www.gywlxb.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1671.shtmlWANG K H, GENG B G, CHU Z, et al.Experimental studies on structural response and mass loss of high velocity projectiles penetrating into reinforced concrete targets[J].Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2014, 28(1):61-68. http://www.gywlxb.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1671.shtml [8] 陈小伟, 张方举, 梁斌, 等.A3钢钝头弹撞击45钢板破坏模式的试验研究[J].爆炸与冲击, 2006, 26(3):199-207. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2006.03.002CHEN X W, ZHANG F J, LIANG B, et al.Three modes of penetration mechanics of A3 steel cylindrical projectiles impact onto 45 steel plates[J].Explosion and Shock Waves, 2006, 26(3):199-207. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2006.03.002 [9] 王富耻, 王琳, 李树奎, 等.空心侵彻弹侵彻金属靶板的细观损伤行为研究[J].兵工学报, 2004, 25(3):359-362. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2004.03.025WANG F C, WANG L, LI S K, et al.Micro-damage study of hollow steel projectiles impacting steel plates[J].Acta Armamentarii, 2004, 25(3):359-362. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2004.03.025 [10] 刘峰涛, 袁书强, 陈炯, 等.高能束控制破碎弹体威力对比研究[J].兵器材料科学与工程, 2008, 31(1):67-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2008.01.018LIU F T, YUAN S Q, CHEN J, et al.Comparative study on the shell power after high-energy-beam controlled fragmentation[J].Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2008, 31(1):67-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2008.01.018 [11] 陈炯, 袁书强, 周春华, 等.高能束控制破碎钨合金壳体破碎效果研究[J].兵器材料科学与工程, 2010, 33(6):62-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2010.06.019CHEN J, YUAN S Q, ZHOU C H, et al.Fragmentation effect of tungsten alloy shells controlled by high-erengy-beam[J].Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2010, 33(6):62-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2010.06.019 [12] SILLING S A, FORRESTAL M J.Mass loss from abrasion on ogive-nose steel projectiles that penetrate concrete tergets[J].Int J Impact Eng, 2007, 34:1814-1820. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.10.008 [13] 武海军, 黄风雷, 王一楠, 等.高速侵彻混凝土弹体头部侵蚀终点效应实验研究[J].兵工学报, 2012, 33(1):48-55. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bgxb201201009WU H J, HUANG F L, WANG Y N, et al.Experimental investigation on projectile nose eroding effect of high-velocity penetration into concrete[J].Acta Armamentarii, 2012, 33(1):48-55. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bgxb201201009 [14] ZHONG W Z, SONG S C, CHEN G, et al.Stress field of orthotropic cylinder subjected to axial compression[J].Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2010, 31(3):305-316. doi: 10.1007/s10483-010-0304-z -







 下载:
下载: