Numerical Study on Ballistic Resistance of Metal Perforated Armor to Projectile Impact
-
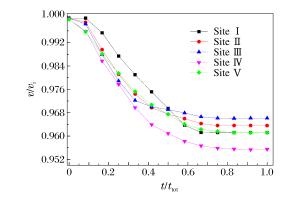
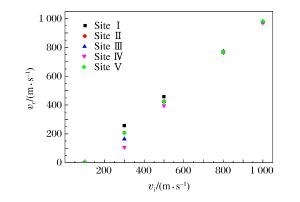
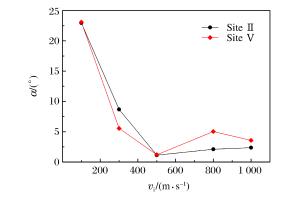
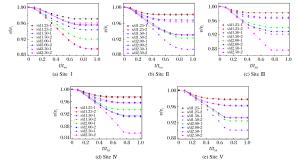
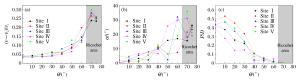
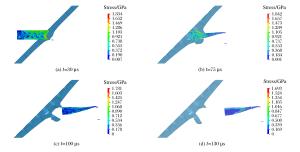
摘要: 采用数值模拟方法研究了高速弹体冲击下孔结构金属装甲的抗弹能力,系统讨论了弹体冲击速度、入射角、弹着点、孔径、孔间距等因素对抗弹能力的影响。结果表明,在弹道极限速度附近,随着弹体冲击速度的增加,弹着点效应逐渐变得不明显;弹体垂直入射不对称弹着点时会出现明显偏转,而倾斜入射时即使在对称弹着点上也会出现明显的偏转现象;当弹体入射角度大于45°时,弹体剩余速度和侵彻深度出现较明显的下降,当入射角度大于65°时,出现弹跳现象。Abstract: In this paper, we numerically studied the ballistic resistance of the metal perforated armor to the high-velocity projectile, and analyzed in detail the effects of various factors on its ballistic resistance, including the impact velocity, the oblique angle, the hitting location and the size of holes.The results showed that the effect of hitting position decreases with the increase of the impact velocity near the ballistic limit.Both the normal impact at the asymmetric hitting position and the oblique impact at the symmetric hitting position result in the projectile yaw.The residual velocity of the projectile and the penetration depth decrease dramatically as the oblique angle is larger than 45°, and furthermore, the ricochet appears as the oblique angle is larger than 65°.
-
Key words:
- metallic perforated armor /
- high-velocity impact /
- penetration /
- perforation /
- ballistic limit
-
表 1 钨合金和Secure 500高强钢的模型参数[6, 12]
Table 1. Material model parameters for tungsten alloy and Secure 500 high hardness steel (HHS)[6, 12]
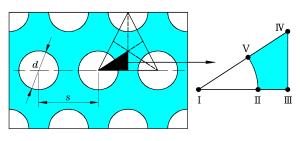
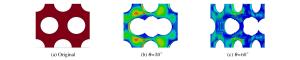
Material ρ/(g·cm-3) G/GPa A/MPa B/MPa n C m cp/(J·g-1·K-1) Tm/K T0/K ${{\dot \varepsilon }_0}$/s-1 D1 D2 D3 c/(m·s-1) D4 D5 S1 S2 S3 γ0 Tungsten alloy 17.70 160 631 1 258 0.092 0.014 0.94 0.134 1 723 293 1.0 0.0 0.04 0.63 4 029 0.0 0.0 1.237 0.0 0.0 1.54 Secure 500 HHS 7.85 80 1 200 1 580 0.175 0.004 1.00 0.450 1 800 300 0.000 1 0.1 0.4 -1.3 4 570 0.05 0.0 1.730 0.0 0.0 1.67 表 2 不同孔洞尺寸的孔结构装甲板
Table 2. Perforated plates with different hole sizes
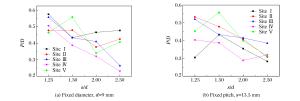
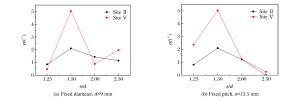
Target Hole size d/mm s/mm s/d s/d1.25-1 10.80 13.50 1.25 s/d1.25-2 9.00 11.25 1.25 s/d1.50-1 9.00 13.50 1.50 s/d1.50-2 7.00 10.50 1.50 s/d2.00-1 6.75 13.50 2.00 s/d2.00-2 9.00 18.00 2.00 s/d2.50-1 5.40 13.50 2.50 s/d2.50-2 9.00 22.50 2.50 -
[1] BEN-MOSHE D, TARSI Y, ROSENBERG G. An armor assembly for armored vehicles: EP 0209221. 1986. [2] CHOCRON S, ANDERSON C E JR, GROSCH D J, et al.Impact of the 7.62 mm APM2 projectile against the edge of a metallic target[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2001, 25(5):423-437. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(00)00063-4 [3] BALOS S, GRABULOV V, SIDJANIN L, et al.Geometry, mechanical properties and mounting of perforated plates for ballistic application[J].Materials & Design, 2010, 31(6):2916-2924. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0218815196 [4] MISHRA B, RAMAKRISHNA B, JENA P K, et al.Experimental studies on the effect of size and shape of holes on damage and microstructure of high hardness armour steel plates under ballistic impact[J].Materials & Design, 2013, 43:17-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0228757162 [5] RADISAVLJEVIC I, BALOS S, NIKACEVIC M, et al.Optimization of geometrical characteristics of perforated plates[J].Materials & Design, 2013, 49:81-89. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0231243838 [6] KILIC N, BEDIR S, ERDIK A, et al.Ballistic behavior of high hardness perforated armor plates against 7.62 mm armor piercing projectile[J].Materials & Design, 2014, 63:427-438. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0261306914004798 [7] 胡丽萍, 王智慧, 满红, 等.孔结构间隙复合装甲位置效应研究[J].兵器材料科学与工程, 2010, 33(1):89-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2010.01.025HU L P, WANG Z H, MAN H, et al.Study on the spot effect of spaced composite armor with multi-holes[J].Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2010, 33(1):89-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2010.01.025 [8] 肖红亮, 李晓源, 时捷, 等.倾角效应对高强度钢板抗弹性能的影响[J].兵器材料科学与工程, 2011, 34(6):36-40. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bqclkxygc201106010XIAO H L, LI X Y, SHI J, et al.Influence of obliquity effect on the ballistic performance of high strength steel plate[J].Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2011, 34(6):36-40. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bqclkxygc201106010 [9] 李换芝.倾角穿孔装甲对14.5 mm穿燃弹防护性能的影响[J].科技创新与生产力, 2016(2):90-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9146.2016.02.090LI H Z.Influence of oblique perforated armor on the protective performance of the 14.5 mm armor-piercing incendiary[J].Technology Innovation and Productivity, 2016(2):90-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9146.2016.02.090 [10] 王建波, 闫慧敏, 范秉源, 等.弹着点对多孔钢板抗弹性能影响的数值模拟[J].兵器材料科学与工程, 2011, 33(6):73-75. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bqclkxygc201006022WANG J B, YAN H M, FAN B Y, et al.Numerical simulation analysis about the influence of the hitting position on the ballistic performance of the multi-hole steel plate[J].Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2011, 33(6):73-75. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bqclkxygc201006022 [11] BØRVIK T, HOPPERSTAD O S, BERSTAD T, et al.A computational model of viscoplasticity and ductile damage for impact and penetration[J].European Journal of Mechanics-A/Solids, 2001, 20(5):685-712. doi: 10.1016/S0997-7538(01)01157-3 [12] LIDÉN E, MOUSAVI S, HELTE A, et al.Deformation and fracture of a long-rod projectile induced by an oblique moving plate:numerical simulations[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2012, 40:35-45. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0734743X11001436 [13] WARREN T L, POORMON K L.Penetration of 6061-T6511 aluminum targets by ogive-nosed VAR 4340 steel projectiles at oblique angles:experiments and simulations[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2001, 25(10):993-1022. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(01)00024-0 -






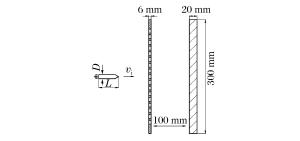
 下载:
下载: